Experimental Study of Amphibolite–Basalt (SiO2-AlO3-CaO-Fe2O3) Glasses for Glass-Ceramic Materials Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
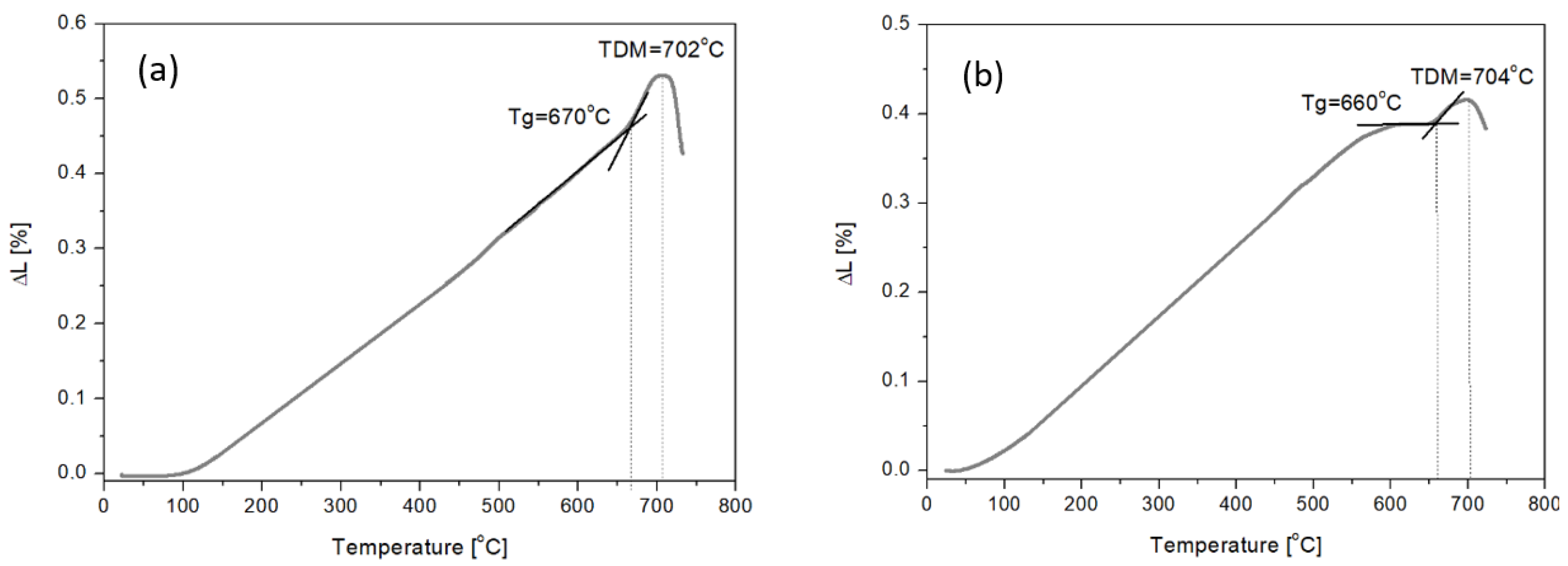
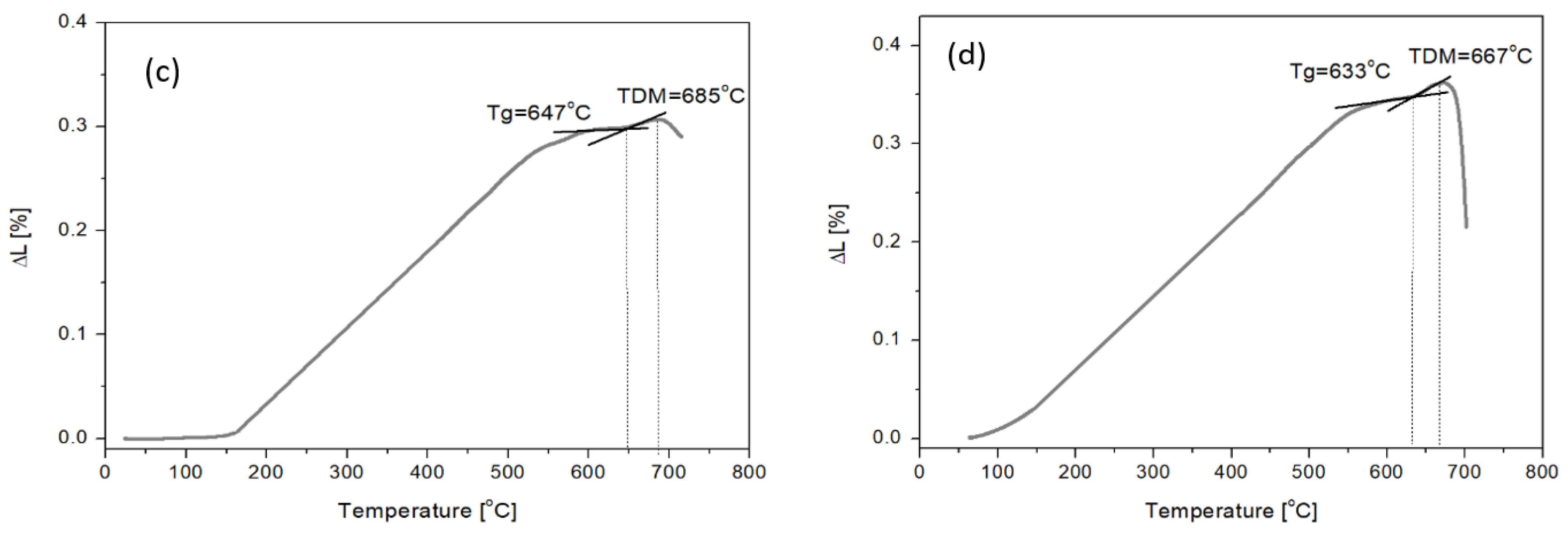
Study of Amphibolite Glasses after the Melting Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miao, Z.; Xingna, L.; Zhen, C.; Ji, W.; Wenhua, S. Experimental study of the heat flux effect on combustion characteristics of commonly exterior thermal insulation materials. Procedia Eng. 2014, 84, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chin, D.D.; Yahya, M.N.; Din, N.B.; Ong, P. Acoustic properties of biodegradable composite micro-perforated panel (BC-MPP) made from kenaf fibre and polyactic acid (PLA). Appl. Acoust. 2018, 138, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yu, J.; Wu, H.; Jaworska, B.; Ellias, B.; Li, V. Discontinuous micro-fibers as intrinsic reinforcement for ductile Engineered Cementitious Composites (ECC). Compos. Part B 2020, 184, 107741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanitskii, S.G.; Gorbachev, G.F. Continuous basalt fibers: Production aspects and simulation of forming processes. I. State of the art in continuous basalt fiber technologies. Sov. Powder Met. Met. Ceram. 2011, 50, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perevozchikova, V.; Pisciotta, A.; Osovetsky, B.M.; Menshikov, E.A.; Kazymov, K.P. Quality evaluation of the Kuluevskaya basalt outcrop for the production of mineral fiber, Southern Urals, Russia. Energy Procedia 2014, 59, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffler, C.; Förster, T.; Mäder, E.; Heinrich, G.; Hempel, S.; Mechtcherine, V. Aging of alkali-resistant glass and basalt fibers in alkaline solutions: Evaluation of the failure stress by Weibull distribution function. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2009, 355, 2588–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigonis, M.; Lipinskas, D.; Maciulaitis, R.; Jocius, V. Fire resistance and reaction to fire tests of buildings construction. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference, Vilnius, Lithuania, 19–21 May 2010; pp. 1218–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, X. 13—Mineral fibres: Basalt. In Handbook of Natural Fibres, 2nd ed.; Volume 1: Types, Properties and Factors Affecting Breeding and Cultivation; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2020; pp. 433–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbakian, A.; Sentyakov, B.; Božek, P.; Kuric, I.; Sentyakov, K. Automated separation of basalt fiber and other earth resources by the means of acoustic vibrations. Acta Montan. Slovaca 2018, 23, 271–281. [Google Scholar]
- Buratti, C.; Moretti, E.; Belloni, E.; Agosti, F. Thermal and acoustic performance evaluation of new basalt fiber insulation panels for buildings. Energy Procedia 2015, 78, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouk, M.; Soltan, A.; Schlüter, S.; Hamzawy, E.; Farrag, A.; El-Kammar, A.; Yahya, A.; Pollmann, H. Optimization of microstructure of basalt-based fibers intended for improved thermal and acoustic insulations. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 34, 101904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.W.; Zhang, Z.T.; Tang, X.L.; Liu, L.L.; Wang, X.D. Preparation of slag wool byintegrated waste-heat recovery and resource recycling of molten blast furnace slags: From fundamental to industrial application. Energies 2014, 7, 3121–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Du, P.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, H.; Wei, G.; Wang, H. Influence of polyvinyl alcohol–glutaraldehyde on properties of thermal insulation pipe from blast furnace slag fiber. High Temp. Mater. Process. 2020, 39, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, W.X.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Yang, A.M.; Zhao, K. Research on modifying blast furnace slag as a raw material of slag fiber. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2014, 30, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.-L.; Zhang, Z.-T.; Guo, M.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.-D. Viscosities Behavior of CaO-SiO2-MgO-Al2O3 Slag with Low Mass Ratio of CaO to SiO2 and Wide Range of A12O3 Content. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2011, 18, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, W.; Beall, G. Glass-Ceramic Technology; The American Ceramic Society: Westerville, OH, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blissett, R.S.; Rowson, R.A. A Review of the Multicomponent Utilization of Coal Fly Ash. Fuel 2012, 97, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquini, L.; Furlani, E.; Bruckner, S.; Maschio, S. Production and characterization of sintered ceramics from paper mill sludge and glass cullet. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.T.; Liu, X.H.; Chen, J.Q.; Qi, J.L.; Wang, Y.B.; Ai, Z.R. Preparation of glass-ceramics with low density and high strength using blast furnace slag, glass fiber and water glass. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 6044–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Zhang, X.; Cang, D.; Zhao, L.; Wei, W. Synthesis of steel slag ceramics: Chemical composition and crystalline phases of raw materials. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2015, 22, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, M.; Küçükbayrak, S.; Ersoy-Meriçboyu, A. Production of glass-ceramics obtained from industrial wastes by means of controlled nucleation and crystallization. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 132, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, M.; Eftekhari-Yekta, B.; Solati-Hashjin, M.; Marghussian, V. Effect of Cr2O3, Fe2O3 and TiO2 nucleants on the crystallization behaviour of SiO2-Al2O3-CaO-MgO(R2O) glass-ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2005, 31, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnam, R.K.; Francis, A.A.; Will, J.; Bernardo, E.; Boccaccini, A.R. Functional glasses and glass-ceramics derived from iron rich waste and combination of industrial residues. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2013, 365, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala Valderrama, D.M.; Gómez Cuaspud, J.A.; Roether, J.A.; Boccaccini, A.R. Development and Characterization of Glass-Ceramics from Combinations of Slag, Fly Ash, and Glass Cullet without Adding Nucleating Agents. Materials 2019, 12, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toya, T.; Kameshima, Y.; Yasumori, A.; Okada, K. Preparation and properties of glass-ceramics from wastes (Kira) of silica sand and kaolin clay refining. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 24, 2367–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Moon, S.O.; Heo, J. Crystalline phase control of glass ceramics obtained from sewage sludge fly ash. Ceram. Int. 2003, 29, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C28 (2015); Standard Specification for Gypsum Plasters. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- Snellings, R.; Mertens, G.; Elsen, J. Supplementary Cementitious Materials. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2014, 74, 211–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunlong, L.; Fu, W.; Hanzhen, Z.; Qilong, L.; Laibao, L. Preparation and characterization of glass-ceramics with granite tailings and titanium-bearing blast furnace slags. J. Non-Cryst. Solids Vol. 2022, 582, 121463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.L.; Wang, F.; Liao, Q.L.; Liu LBWang, Y.L.; Zhou, J.J.; Xu, Y.L.; Zhu, H.Z.; Gu, Y.X. Effect of TiO2 on crystallization kinetics, microstructure and properties of building glass-ceramics based on granite tailings. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2021, 572, 121092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaella, L.E.; Correa, R.S. Comportamiento de concreto con bajos porcentajes de ceniza volante (termo paipa IV) y agua constante. Cienc. E Ing. Neogranadina 2004, 14, 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Vianchá, G.; Roldan, P.R. Propuesta Para la Utilización de Cenizas Volantes Como Adición en la Fabricación de Cemento Tipo I en la Planta Cementera de Holcim Colombia S.A; Universidad de la Sabana: Chía, Colombia, 2007; Available online: https://studylib.es/doc/5118574/propuesta-para-la-utilizaci%C3%B3n-de-cenizas-volantes (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Rawlings, R.D.; Wu, J.P.; Boccaccini, A.R. Glass-ceramics: Their production from wastes—A Review. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 733–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojovan, W.; Juoi, J.M.; Boccaccini, A.R. Glass Composite Materials for Nuclear and Hazardous Waste Immobilisation. MRS Online Proc. Libr. Arch. 2008, 245, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savvilotidou, V.; Kritikaki, A.; Stratakis, A.; Komnitsas, K.; Gidarakos, E. Energy efficient production of glass-ceramics using photovoltaic (P/V) glass and lignite fly ash. Waste Manag. 2019, 90, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Test Method for Assignment of the Glass Transition Temperature by Thermomechanical Analysis. Available online: https://www.astm.org/e1545-22.html (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Sitarz, M. The structure of simple silicate glasses in the light of Middle Infrared spectroscopy studies. J. Non-Crystalline Solids 2011, 357, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharczyk, S.; Sitarz, M.; Zajac, M.; Deja, J. The effect of CaO/SiO2 molar ratio of CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 glasses on their structure and reactivity in alkali activated system. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 194, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayazit, M.; Isik, I.; Cereci, S.; Issi, A.; Genc, E. FT-IR spectroscopic analysis of potsherds excavated from the first settlement layer of kuriki mound, turkey. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Ceramics, International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series, Bikaner, India, 12–13 December 2013; Volume 22, pp. 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grelowska, I.; Kosmal, M.; Reben, M.; Pichniarczyk, P.; Sitarz, M.; Olejniczak, Z. Structural and thermal studies of modified silica-strontium-barium glass from CRT. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1126, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RRUFF. Available online: https://rruff.info/Wollastonite/R040131 (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Öveçoğlu, M.; Kuban, B.; Özer, H. Characterization and crystallization kinetics of a diopside-based glass-ceramic developed from glass industry raw materials. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 1997, 17, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, P.; Singh, K. Effect of Field Strength and Electronegativity of CaO and MgO on Structural and Optical Properties of SiO2–K2O-CaO-MgO Glasses. Silicon 2015, 8, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldsen, J.; Smedskjaer, M.M.; Potuzak, M.; Yue, Y. Role of elastic deformation in determining the mixed alkaline earth effect of hardness in silicate glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 034903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenev, V.A.; Kondakov, D.F.; Pechenkina, E.N.; Fomichev, S.V. Modification of the Composition of Gabbro-Basalt Raw Materials during melting in an oxidizing, Inert, or rediusing atmosphere. Glass Ceram. 2020, 76, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomichev, S.V.; Babievskava, I.Z.; Noskova, N.P.; Krenev, V.A. Evaluation and modification of the initial composition of gabro-basalt rocks for mineral-fiber fabrication and stone casting. Inorg. Mater. 2010, 46, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Zhang, Y.; Long, Y.; Xing, L. Effect of the Acidity Coefficient on the Properties of Molten Modified Blast Furnace Slag and Those of the Produced Slag Fibers. Materials 2022, 15, 3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




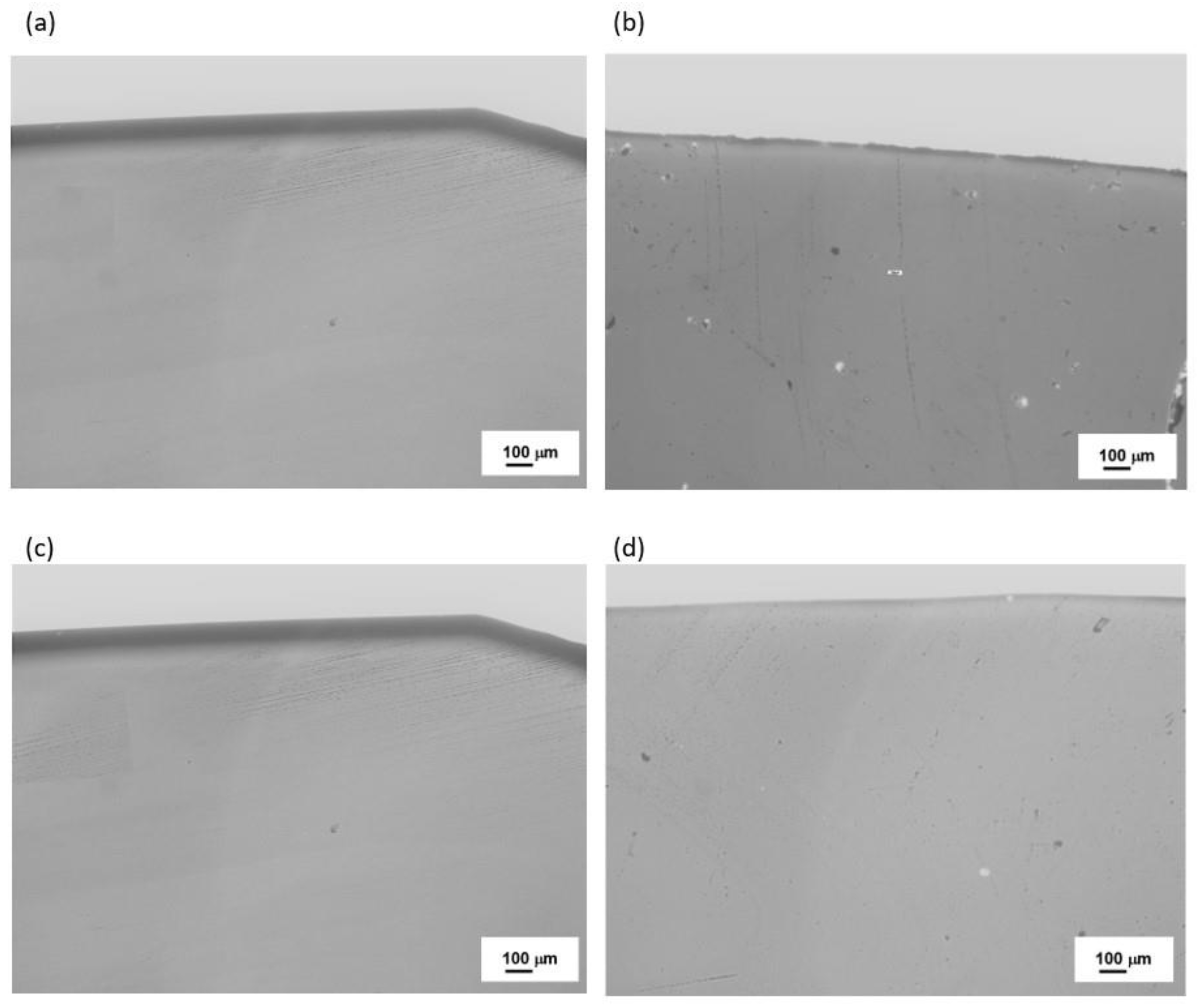
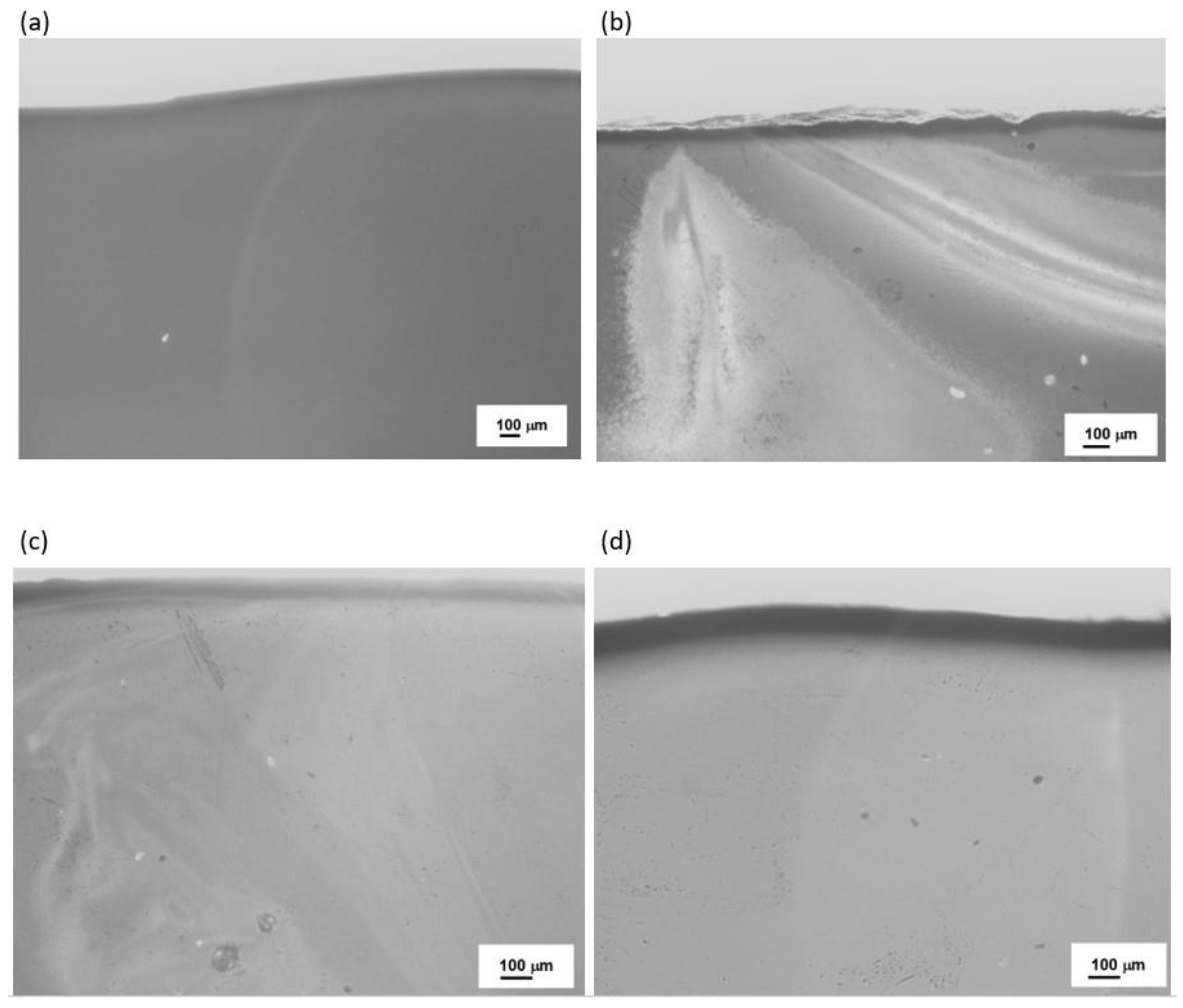
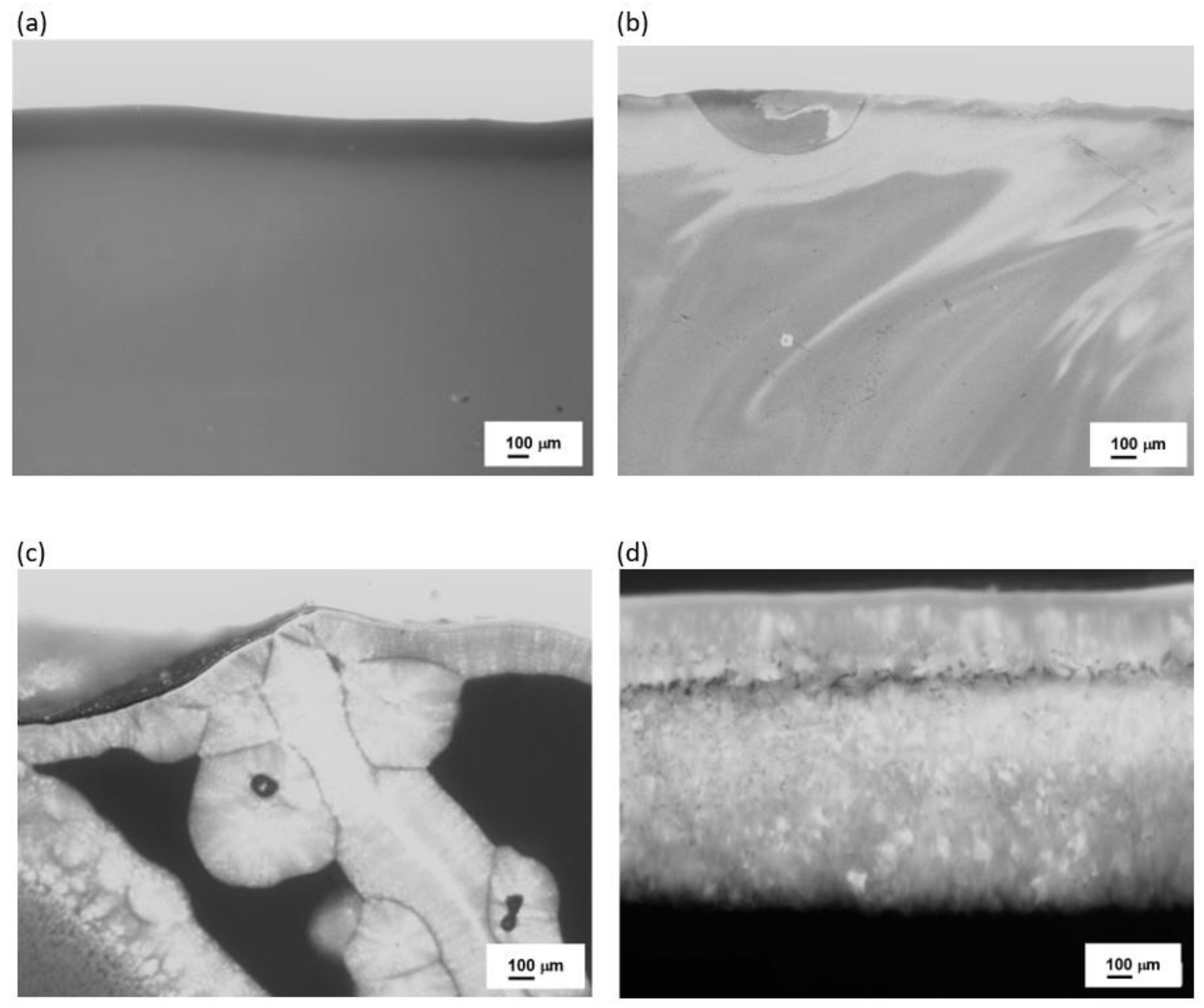

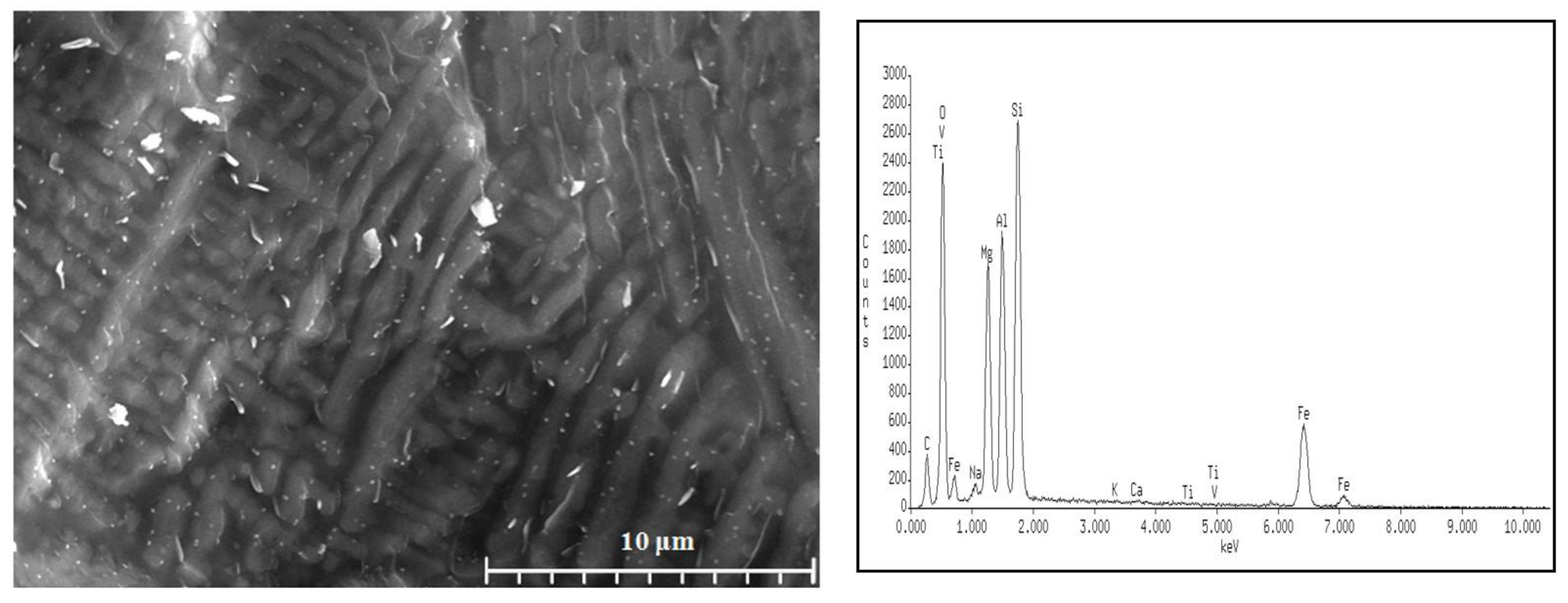
| Sets | Raw Material (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Basalt | Amphibolite | Glass Cullet | |
| Set 1 | 100 | - | - |
| Set 2 | 50 | 40 | 10 |
| Set 3 | 50 | 30 | 20 |
| Set 4 | 50 | 20 | 30 |
| Glass | The Chemical Composition of the Glasses | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | Fe2O3 | Na2O | K2O | TiO2 | MnO | |
| 1 | 40.23 | 13.07 | 9.39 | 10.66 | 10.69 | 5.04 | 0.98 | 2.68 | 0.16 |
| 2 | 46.80 | 13.16 | 9.28 | 8.12 | 9.60 | 6.33 | 0.85 | 2.06 | 0.15 |
| 3 | 48.42 | 11.80 | 9.27 | 7.67 | 8.29 | 7.76 | 0.82 | 1.89 | 0.13 |
| 4 | 50.04 | 10.43 | 9.26 | 7.22 | 7.31 | 9.20 | 0.79 | 1.71 | 0.11 |
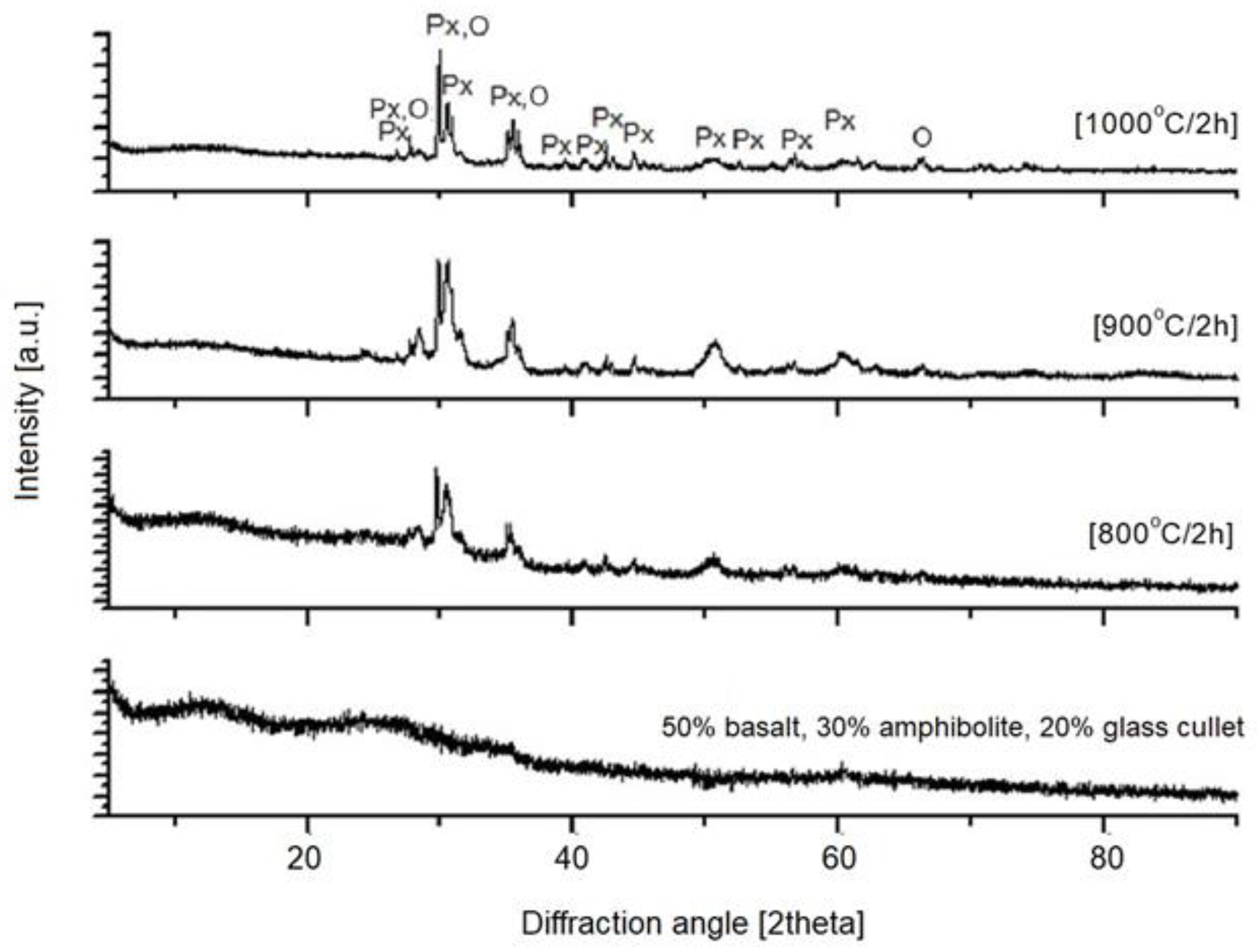
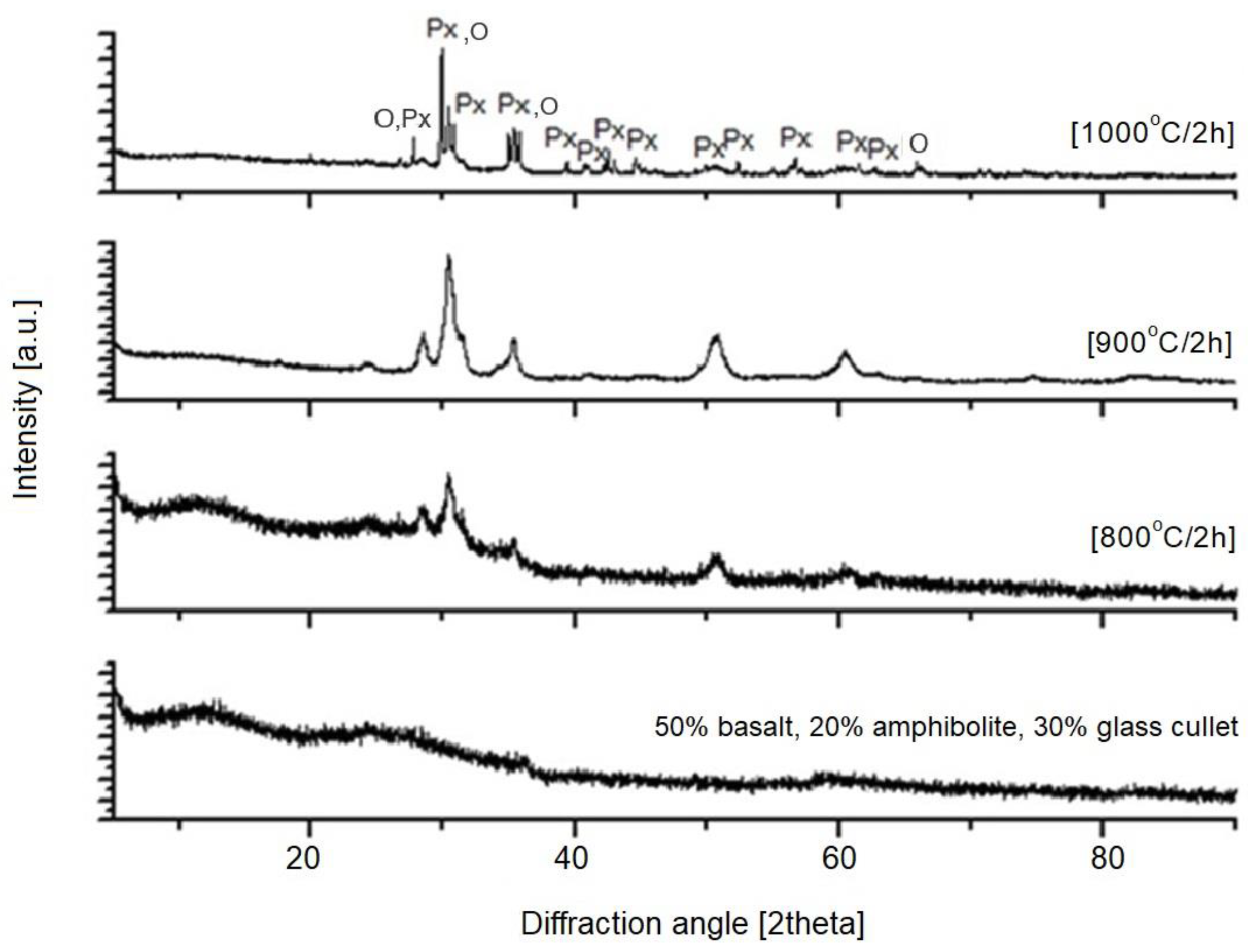
| Glass | Degree of Crystallization (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 800 °C/2 h | 900 °C/2 h | 1000 °C/2 h | |
| 1—100% basalt | 2.6 | 7.2 | 14.8 |
| 2—50% basalt, 40% amphibolite, 10% glass cullet | 3.5 | 16.3 | 21.1 |
| 3—50% basalt, 30% amphibolite, 20% glass cullet | 4.3 | 17.2 | 21.2 |
| 4—50% basalt, 20% amphibolite, 30% glass cullet | 14.8 | 21.5 | 27.3 |
| Mk Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Melted Glass | Glass 1 | Glass 2 | Glass 3 | Glass 4 |
| 1.52 | 1.83 | 1.84 | 1.84 | |
| Microhardness HV0.05 | ||||
| 753 | 670 | 625 | 631 | |
| Annealed Glass | Microhardness HV0.05 | |||
| 800 °C/2 h | 835 | 751 | 659 | 638 |
| 900 °C/2 h | 913 | 823 | 736 | 767 |
| 1000 °C/2 h | 946 | 856 | 896 | 859 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lubas, M.; Zawada, A.; Jasinski, J.J.; Nowak, A. Experimental Study of Amphibolite–Basalt (SiO2-AlO3-CaO-Fe2O3) Glasses for Glass-Ceramic Materials Production. Materials 2023, 16, 6887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16216887
Lubas M, Zawada A, Jasinski JJ, Nowak A. Experimental Study of Amphibolite–Basalt (SiO2-AlO3-CaO-Fe2O3) Glasses for Glass-Ceramic Materials Production. Materials. 2023; 16(21):6887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16216887
Chicago/Turabian StyleLubas, Malgorzata, Anna Zawada, Jaroslaw Jan Jasinski, and Adrian Nowak. 2023. "Experimental Study of Amphibolite–Basalt (SiO2-AlO3-CaO-Fe2O3) Glasses for Glass-Ceramic Materials Production" Materials 16, no. 21: 6887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16216887
APA StyleLubas, M., Zawada, A., Jasinski, J. J., & Nowak, A. (2023). Experimental Study of Amphibolite–Basalt (SiO2-AlO3-CaO-Fe2O3) Glasses for Glass-Ceramic Materials Production. Materials, 16(21), 6887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16216887





