Effect of Different Initial CaO/SiO2 Molar Ratios and Curing Times on the Preparation and Formation Mechanism of Calcium Silicate Hydrate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Raw Materials
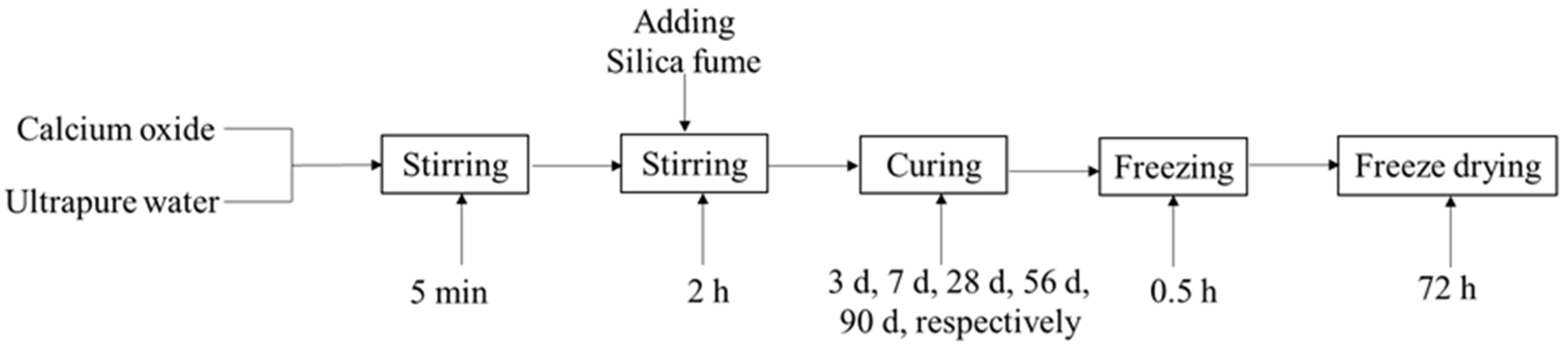
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
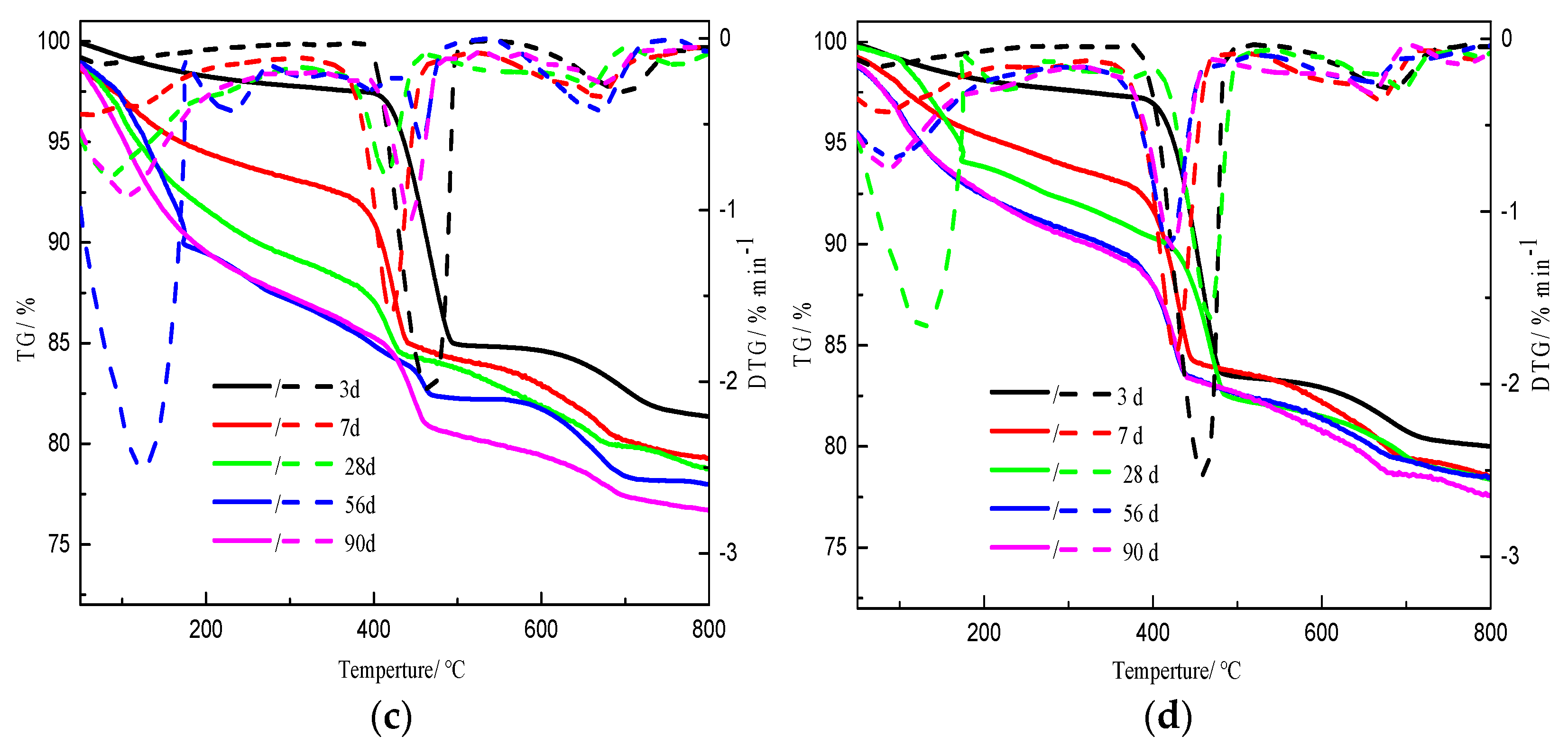
3.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis
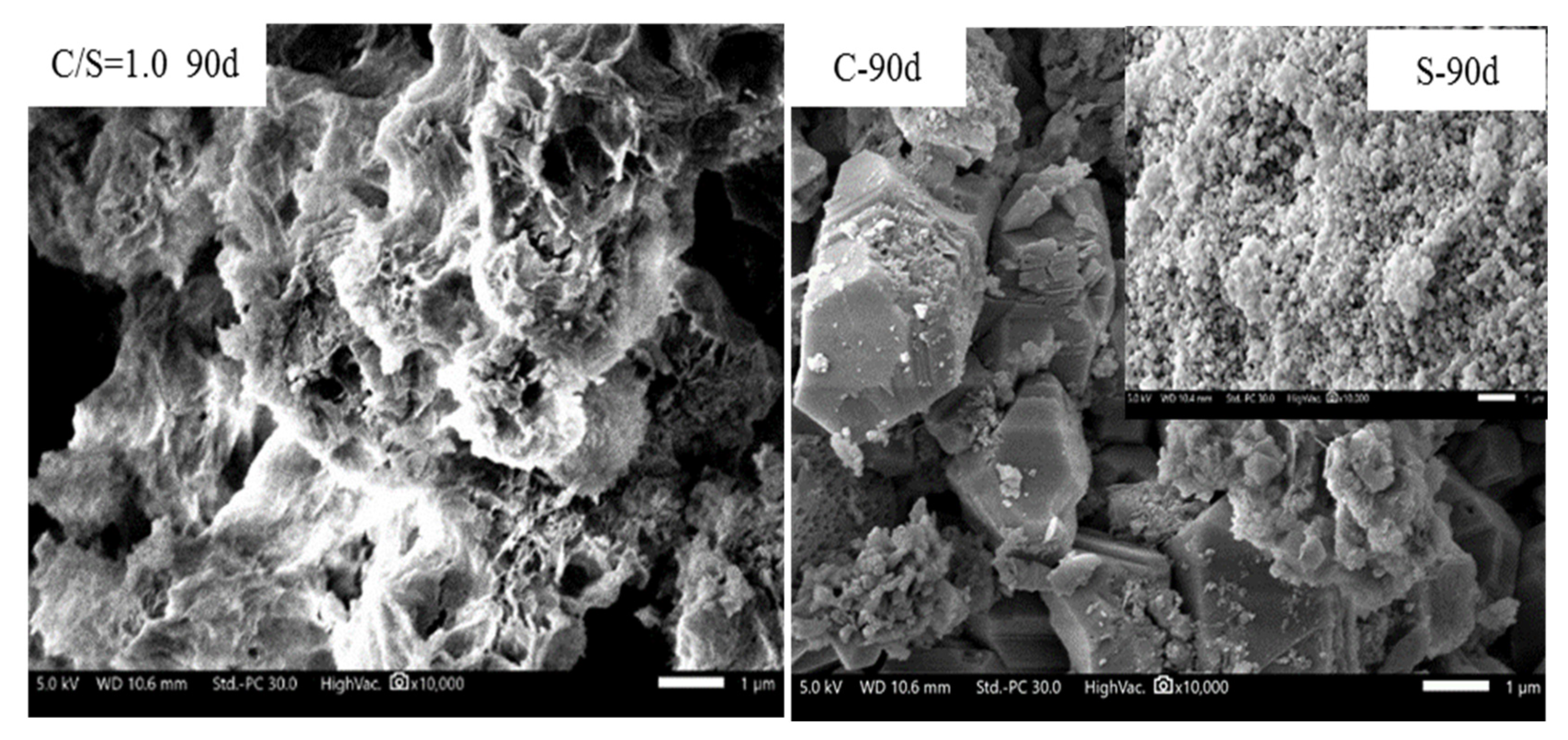
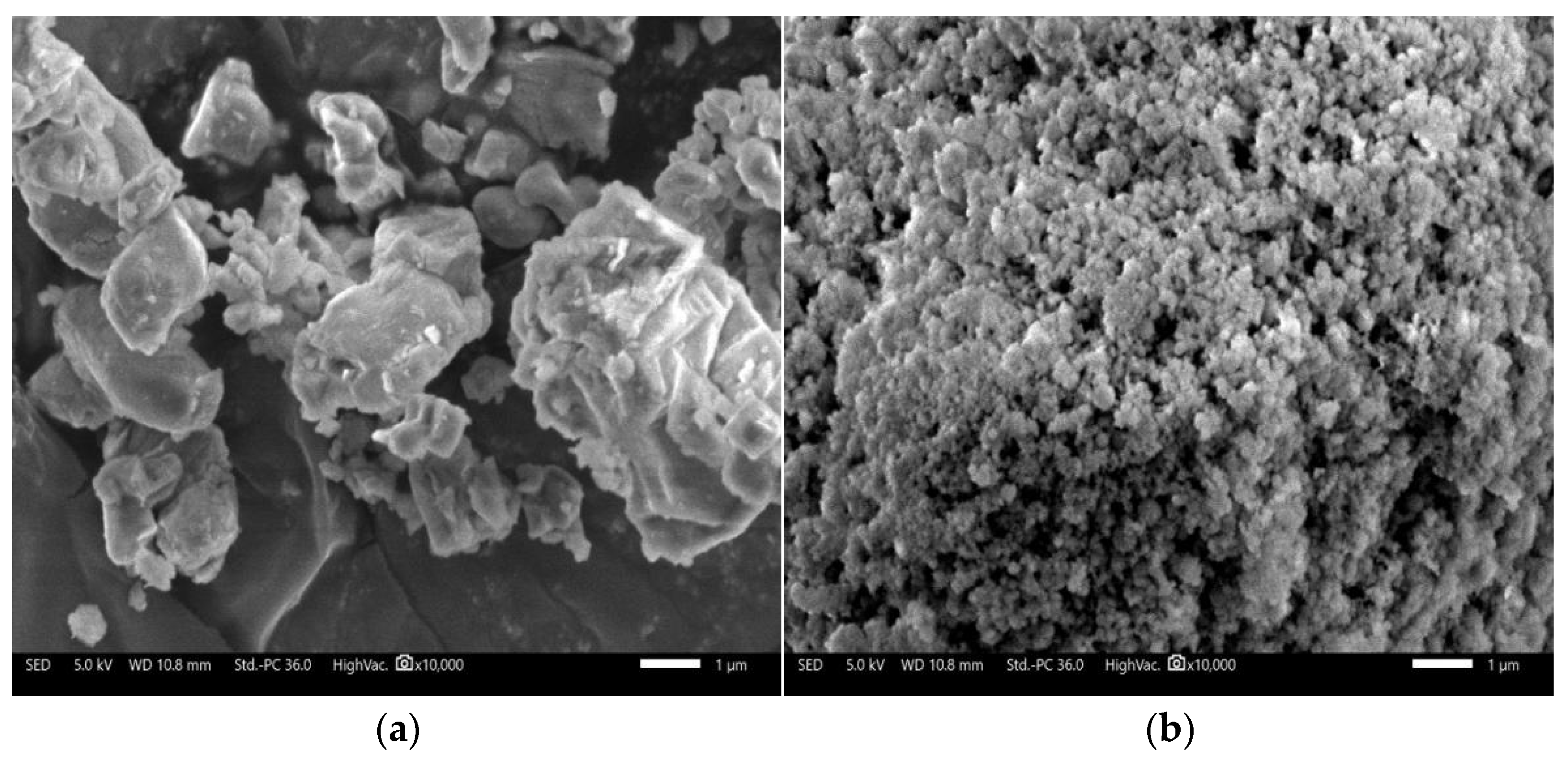
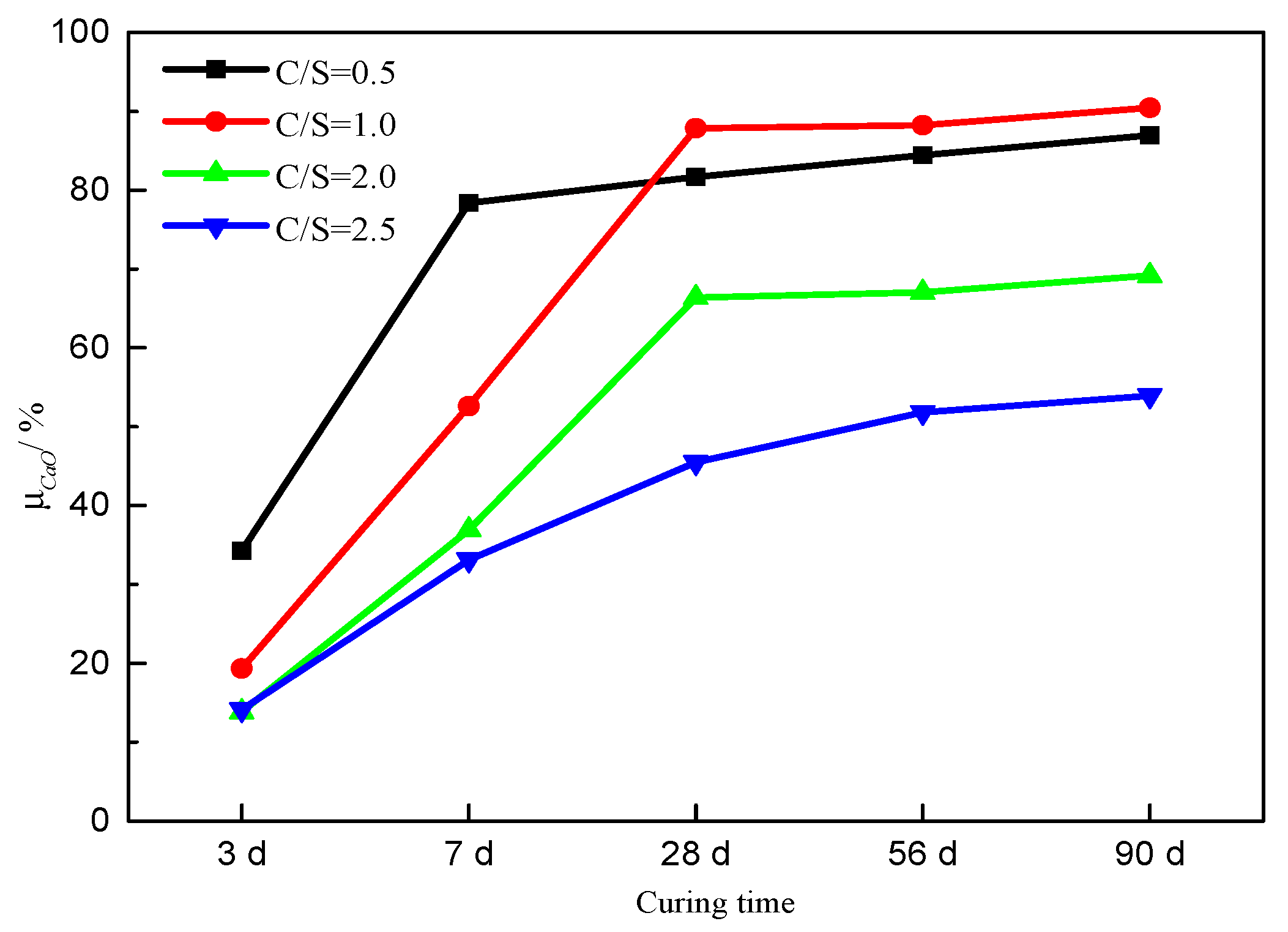
3.2. Formation of C-S-H
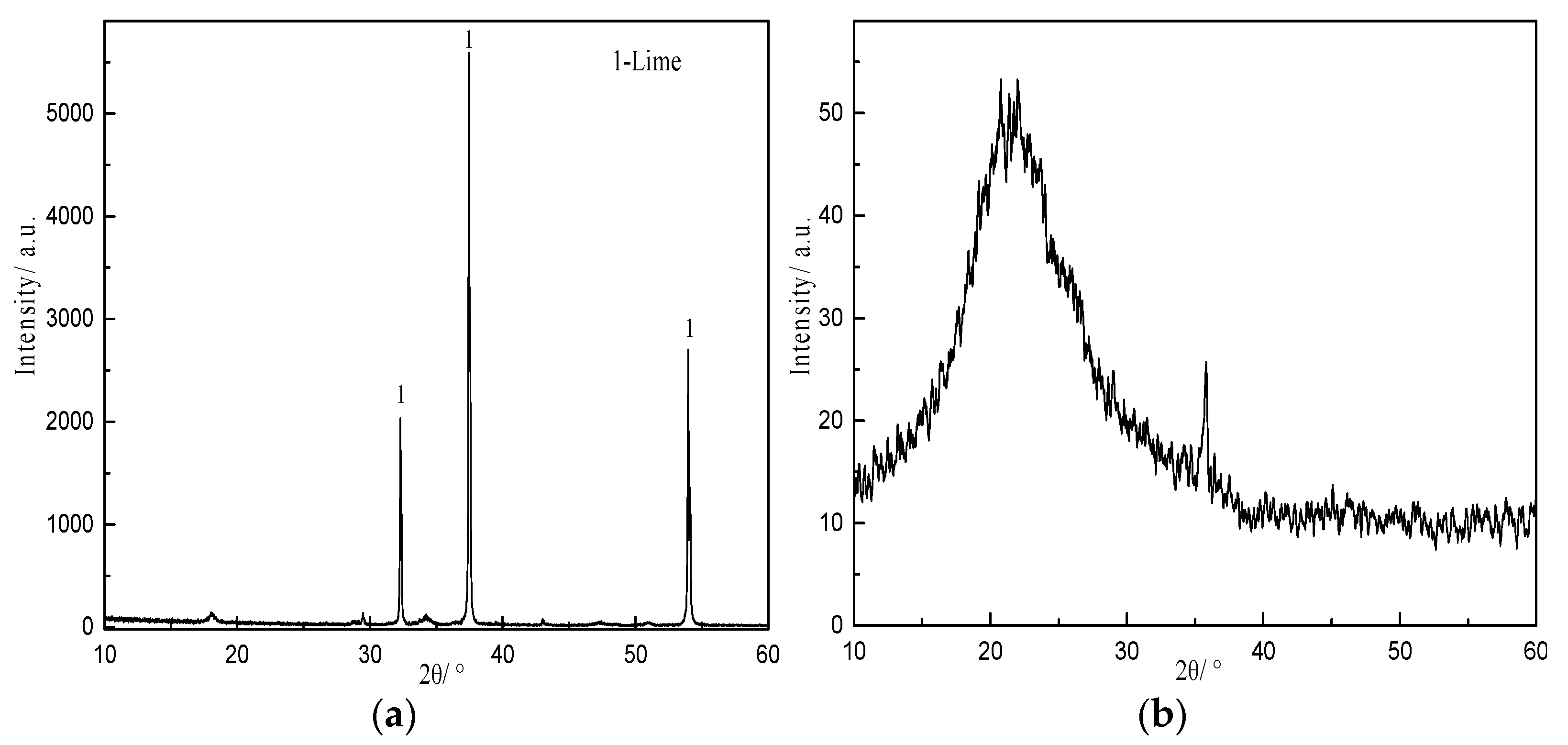
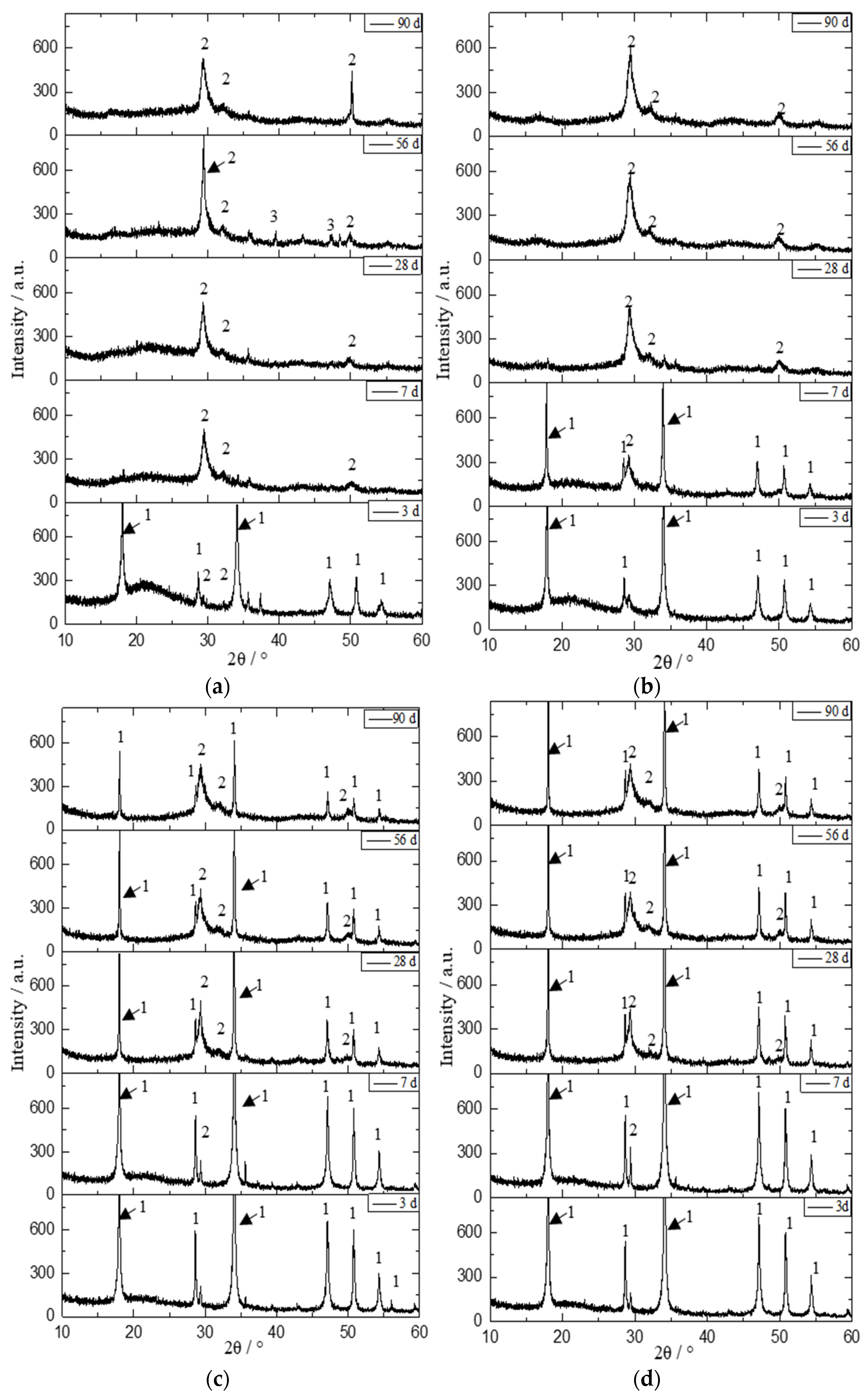
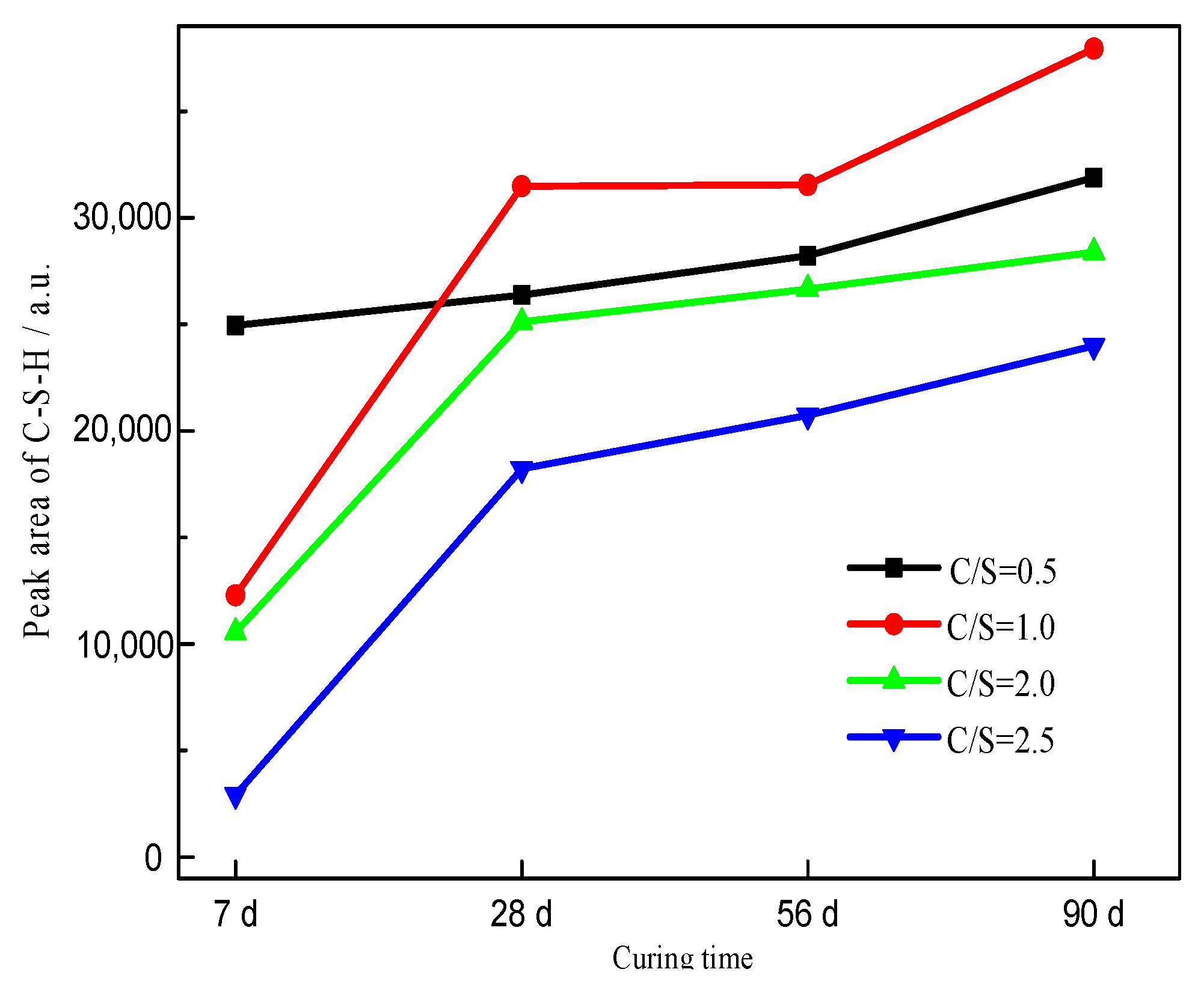
3.3. XRD Analysis
3.4. 29Si MAS-NMR Analysis
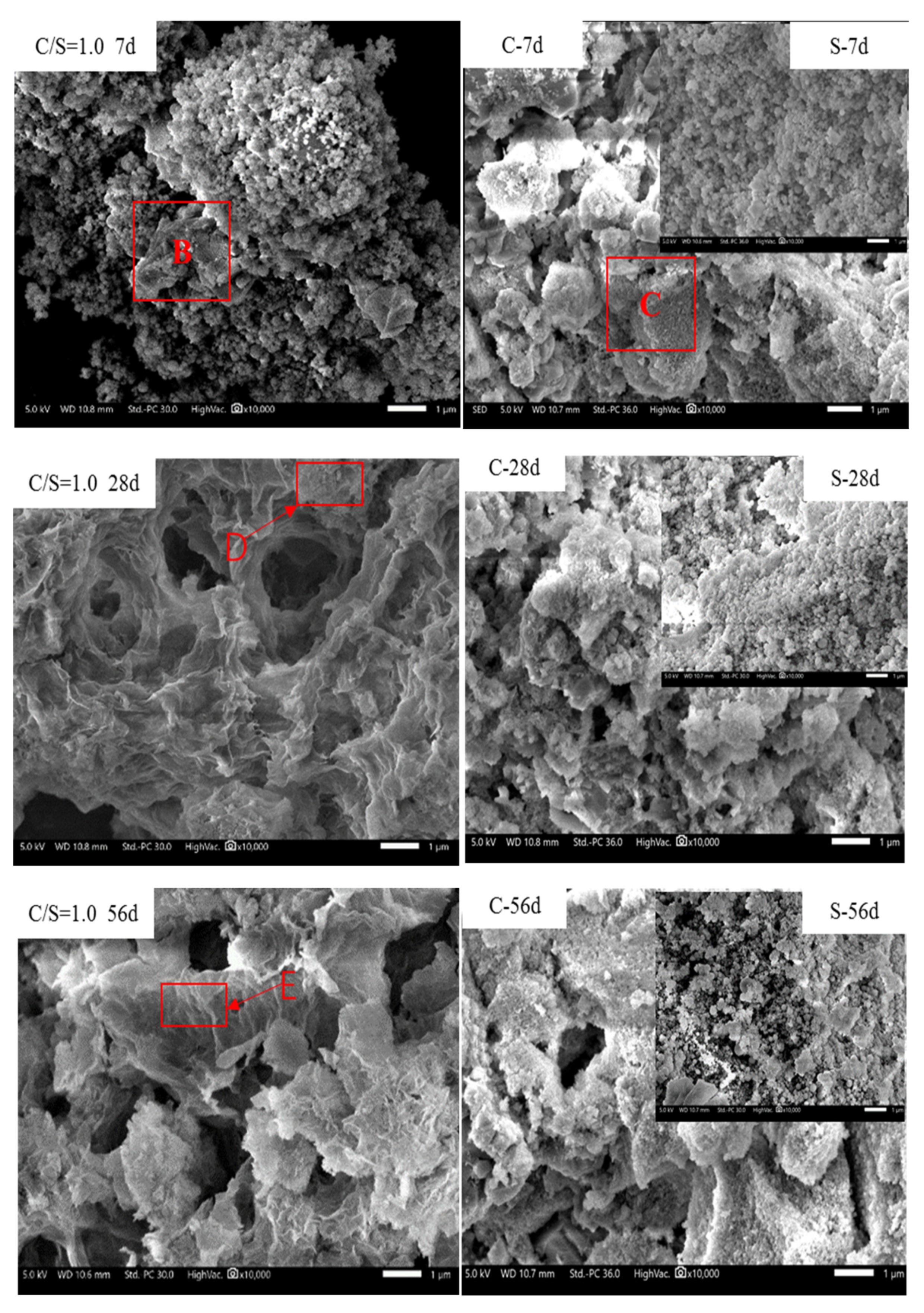
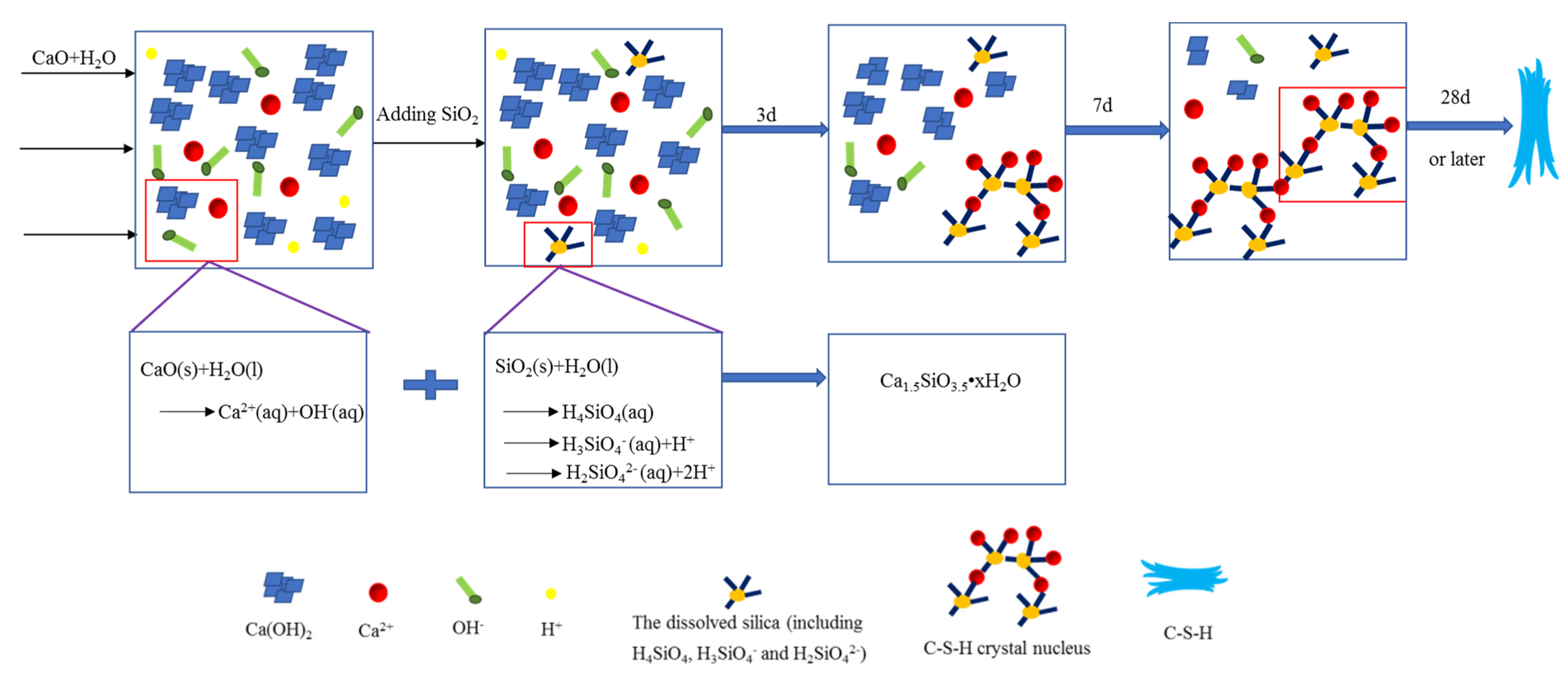
3.5. Analysis of the Formation Mechanism of C-S-H
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- L’Hôpital, E.; Lothenbach, B.; Kulik, D.; Scrivener, K. Influence of calcium to silica ratio on aluminium uptake in calcium silicate hydrate. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 85, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lu, L.; Struble, L.J.; Rapp, J.L.; Mondal, P.; Hu, S. Effect of calcium–silicon ratio on microstructure and nanostructure of calcium silicate hydrate synthesized by reaction of fumed silica and calcium oxide at room temperature. Mater. Struct. 2013, 47, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddalena, R.; Hall, C.; Hamilton, A. Effect of silica particle size on the formation of calcium silicate hydrate [C-S-H] using thermal analysis. Thermochim. Acta 2019, 672, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Liao, H.; Ma, Z.; Cheng, F.; Fang, L.; Gao, H.; Yang, H. The relevance of ultrafine fly ash properties and mechanical properties in its fly ash-cement gelation blocks via static pressure forming. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cui, L.; Bi, C.; Wu, A. Insight into the isothermal multiphysics processes in cemented paste backfill: Effect of curing time and cement-to-tailings ratio. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 325, 126739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Meng, H.; Pan, G.; Mi, R. Influence of CSH grown in situ on steel slag powder on the performance of fresh and hardened cement pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 344, 128269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golewski, G.L.; Szostak, B. Strengthening the very early-age structure of cementitious composites with coal fly ash via incorporating a novel nanoadmixture based on C-S-H phase activators. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 312, 125426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Huo, Z.; Xu, Q.; Hou, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Hu, X. Characteristics of CSH under carbonation and its effects on the hydration and microstructure of cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 364, 129952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossen, J.E.; Lothenbach, B.; Scrivener, K.L. Composition of C–S–H in pastes with increasing levels of silica fume addition. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 75, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H. Cement Chemistry; Academic Press: London, UK, 1990; pp. 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- García-Lodeiro, I.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Blanco, M.T.; Palomo, A. FTIR study of the sol–gel synthesis of cementitious gels: C–S–H and N–A–S–H. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2008, 45, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Sinn, E. Observation of calcium silicate hydrate by the precipitation method. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1994, 13, 1058–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Schulenberg, D.; Buhl, J.-C. Synthesis and Structural Characterization of CSH-Phases in the Range of C/S = 0.41–1.66 at Temperatures of the Tobermorite Xonotlite Crossover. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2015, 11, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, I. Tobermorite/jennite- and tobermorite/calcium hydroxide-based models for the structure of C-S-H: Applicability to hardened pastes of tricalcium silicate, β-dicalcium silicate, Portland cement, and blends of Portland cement with blast-furnace slag, metakaolin, or silica fume. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1733–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Zhao, T.; Ma, H.; Li, Z. Reactive Molecular Simulation on Water Confined in the Nanopores of the Calcium Silicate Hydrate Gel: Structure, Reactivity, and Mechanical Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadifar, M.; Königer, F.; Gerdes, A.; Wöll, C.; Thissen, P. Correlation between Composition and Mechanical Properties of Calcium Silicate Hydrates Identified by Infrared Spectroscopy and Density Functional Theory. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 10868–10873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadifar, M.; Natzeck, C.; Emmerich, K.; Weidler, P.G.; Gohari, S.; Burvill, C.; Thissen, P. Unexpected Chemical Activity of a Mineral Surface: The Role of Crystal Water in Tobermorite. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 12405–12412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolhosseini Qomi, M.J.; Krakowiak, K.J.; Bauchy, M.; Stewart, K.L.; Shahsavari, R.; Jagannathan, D.; Brommer, D.B.; Baronnet, A.; Buehler, M.J.; Yip, S.; et al. Combinatorial molecular optimization of cement hydrates. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, S.V.; Vassileva, C.G. Geochemistry of coals, coal ashes and combustion wastes from coal-fired power stations. Fuel Process. Technol. 1997, 51, 19–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, S.V.; Vassileva, C.G. Methods for Characterization of Composition of Fly Ashes from Coal-Fired Power Stations: A Critical Overview. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 1084–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Brown, P.W. Hydrothermal reactions of fly ash with Ca(OH)2 and CaSO4·2H2O. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, E.; Matschei, T.; Stephan, D. Nucleation seeding with calcium silicate hydrate—A review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 113, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, N.; Nuruddin, M.F.; Kamaruddin, I. Comparison of engineering and durability properties of fly ash blended cement concrete made in UK and Malaysia. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2007, 106, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, S.V.; Menendez, R.; Alvarez, D.; Diaz-Somoano, M.; Martinez-Tarazona, M. Phase-mineral and chemical composition of coal fly ashes as a basis for their multicomponent utilization. 1. Characterization of feed coals and fly ashes☆. Fuel 2003, 82, 1793–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.-B.; Shih, S.-M.; Liu, C.-F. Characteristics and reactivities of Ca(OH)2/silica fume sorbents for low-temperature flue gas desulfurization. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 58, 3659–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.; Snellings, R.; Lothenbach, B. A Practical Guide to Microstructural Analysis of Cementitious Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ivan, K.; Benoît, P.; Joseph, V.; André, N. C-S-H Structure Evolution with Calcium Content by Multinuclear NMR. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of Cemen-Based Materials; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998; pp. 119–141. [Google Scholar]
- Bullard, J.W.; Jennings, H.M.; Livingston, R.A.; Nonat, A.; Scherer, G.W.; Schweitzer, J.S.; Scrivener, K.L.; Thomas, J.J. Mechanisms of cement hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 1208–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothenbach, B.; Nied, D.; L’Hôpital, E.; Achiedo, G.; Dauzères, A. Magnesium and calcium silicate hydrates. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 77, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajuelo Rodriguez, E.; Garbev, K.; Merz, D.; Black, L.; Richardson, I.G. Thermal stability of C-S-H phases and applicability of Richardson and Groves’ and Richardson C-(A)-S-H(I) models to synthetic C-S-H. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 93, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbev, K.; Bornefeld, M.; Beuchle, G.; Stemmermann, P. Cell Dimensions and Composition of Nanocrystalline Calcium Silicate Hydrate Solid Solutions. Part 2: X-Ray and Thermogravimetry Study. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 3015–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteagudo, S.; Moragues, A.; Gálvez, J.; Casati, M.; Reyes, E. The degree of hydration assessment of blended cement pastes by differential thermal and thermogravimetric analysis. Morphological evolution of the solid phases. Thermochim. Acta 2014, 592, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.J.; L’Hôpital, E.; Provis, J.L.; Lothenbach, B. Effect of temperature and aluminium on calcium (alumino)silicate hydrate chemistry under equilibrium conditions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 68, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, G.B.; Heston, W.M.; Iler, R.K. The Solubility of Amorphous Silica in Water. J. Phys. Chem. 1954, 58, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, S.A. Reaction between silica and calcium hydroxide solutions. I. kinetics in the temperature range 30 to 85°. J. Phys. Chem. 1961, 65, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunematsu, S.; Inoue, K.; Kimura, K.; Yamada, H. Improvement of acid resistance of calcium silicate hydrate by thermal treatment. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunematsu, S.; Inoue, K.; Yamada, H. Characteristics of carbonated tobermorites and its immobilization property to Cd2+ iron. Inorg. Mater. 1996, 3, 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Lothenbach, B.; Nonat, A. Calcium silicate hydrates: Solid and liquid phase composition. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yao, W.; Stephan, D. Preparation of calcium silicate hydrate seeds by means of mechanochemical method and its effect on the early hydration of cement. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni Tan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Qing, Z.; Birdi, G.; Grover, L.M. Synthesis of Pure Dicalcium Silicate Powder by the Pechini Method and Characterization of Hydrated Cement. Mater. Sci. Forum 2014, 787, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z. A novel carbonate binder from waste hydrated cement paste for utilization of CO2. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 32, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y. Uniaxial tension study of calcium silicate hydrate (C–S–H): Structure, dynamics and mechanical properties. Mater. Struct. 2014, 48, 3811–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapote-Barreira, A.; Porcar, L.; Cama, J.; Soler, J.M.; Allen, A.J. Structural changes in C–S–H gel during dissolution: Small-angle neutron scattering and Si-NMR characterization. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 72, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapote-Barreira, A.; Cama, J.; Soler, J.M. Dissolution kinetics of C–S–H gel: Flow-through experiments. Phys. Chem. Earth 2014, 70–71, 17–31. [Google Scholar]
- Sugita, S.; Yu, Q.; Isojima, Y. Hydrothermal and mechanochemical reactions of rice husk ash with calcium hydroxide. Inorg. Mater. 1998, 5, 208–214. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.A. Use of Diatomaceous Earth as a Siliceous Material in the Formation of Alkali Activated Fine-Aggregate Limestone Concrete. Master’s Thesis, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, J.; Wicht, B. Zement unt Kalk: Der Baustoff als Werkstoff; Birkhäuser Verla: Basel, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg, S.A.; Chang, T.N.; Anderson, E. Investigation of colloidal hydrated calcium silicates. I. solubility products. J. Phys. Chem. 1960, 64, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Component | SiO2 | Al2O3 | K2O | CaO | Fe2O3 | MgO | Na2O | Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 92.82 | 0.49 | 0. 53 | 0.59 | 0.29 | 0.49 | 0.42 | 4.37 |
| Initial C/S Molar Ratio | Weight Loss Due to C-S-H/% | Weight Loss Due to C−H/% | Weight Loss Due to CaCO3/% | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 d | 7 d | 28 d | 56 d | 90 d | 3 d | 7 d | 28 d | 56 d | 90 d | 3 d | 7 d | 28 d | 56 d | 90 d | |
| 0.5 | 3.1 | 7.9 | 8.1 | 11.6 | 12.5 | 4.8 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.5 |
| 1.0 | 2.8 | 6.7 | 12.2 | 13.0 | 13.5 | 9.3 | 5.1 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.8 |
| 2.0 | 2.1 | 5.4 | 9.6 | 11.4 | 11.7 | 12.7 | 8.7 | 4.2 | 3.5 | 2.3 | 3.1 | 3.3 | 2.8 | 4.1 | 6.0 |
| 2.5 | 2.2 | 5.0 | 7.6 | 8.1 | 8.5 | 13.9 | 9.8 | 8.0 | 6.8 | 6.4 | 3.0 | 3.7 | 3.0 | 3.3 | 3.4 |
| Initial C/S Molar Ratio | Mineral Composition | 2θ/° | Area | Height | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 d | 28 d | 56 d | 90 d | 7 d | 28 d | 56 d | 90 d | |||
| 0.5 | Ca1.5SiO3.5·xH2O | 29.4 | 20,254 | 19,548 | 25,382 | 20,727 | 278 | 285 | 616 | 276 |
| 32.1 | 1520 | 2963 | 1542 | 3161 | 31 | 48 | 47 | 50 | ||
| 50.1 | 3183 | 3854 | 1297 | 9449 | 35 | 53 | 22 | 338 | ||
| Total | 24,957 | 26,365 | 28,221 | 31,894 | 344 | 386 | 685 | 664 | ||
| 1.0 | Ca1.5SiO3.5·xH2O | 29.4 | 12,283 | 22,292 | 23,702 | 29,711 | 172 | 289 | 212 | 390 |
| 32.1 | — | 3756 | 3009 | 2999 | — | 47 | 154 | 43 | ||
| 50.1 | — | 5435 | 4835 | 5222 | — | 54 | 90 | 58 | ||
| Total | 12,283 | 31,483 | 31,546 | 37,932 | 172 | 390 | 456 | 491 | ||
| 2.0 | Ca1.5SiO3.5·xH2O | 29.4 | 10,559 | 20,048 | 18,915 | 21,723 | 123 | 319 | 233 | 248 |
| 32.1 | — | 2192 | 2847 | 2440 | — | 32 | 40 | 37 | ||
| 50.1 | — | 2880 | 4898 | 4231 | — | 23 | 40 | 46 | ||
| Total | 10,559 | 25,120 | 26,660 | 28,394 | 123 | 374 | 313 | 331 | ||
| 2.5 | Ca1.5SiO3.5·xH2O | 29.4 | 2923 | 15,238 | 17,315 | 17,566 | 219 | 209 | 238 | 228 |
| 32.1 | — | 2964 | 2585 | 2608 | — | 31 | 37 | 36 | ||
| 50.1 | — | 20 | 831 | 3820 | — | 10 | 16 | 83 | ||
| Total | 2923 | 18,222 | 20,731 | 23,994 | 219 | 250 | 291 | 347 | ||
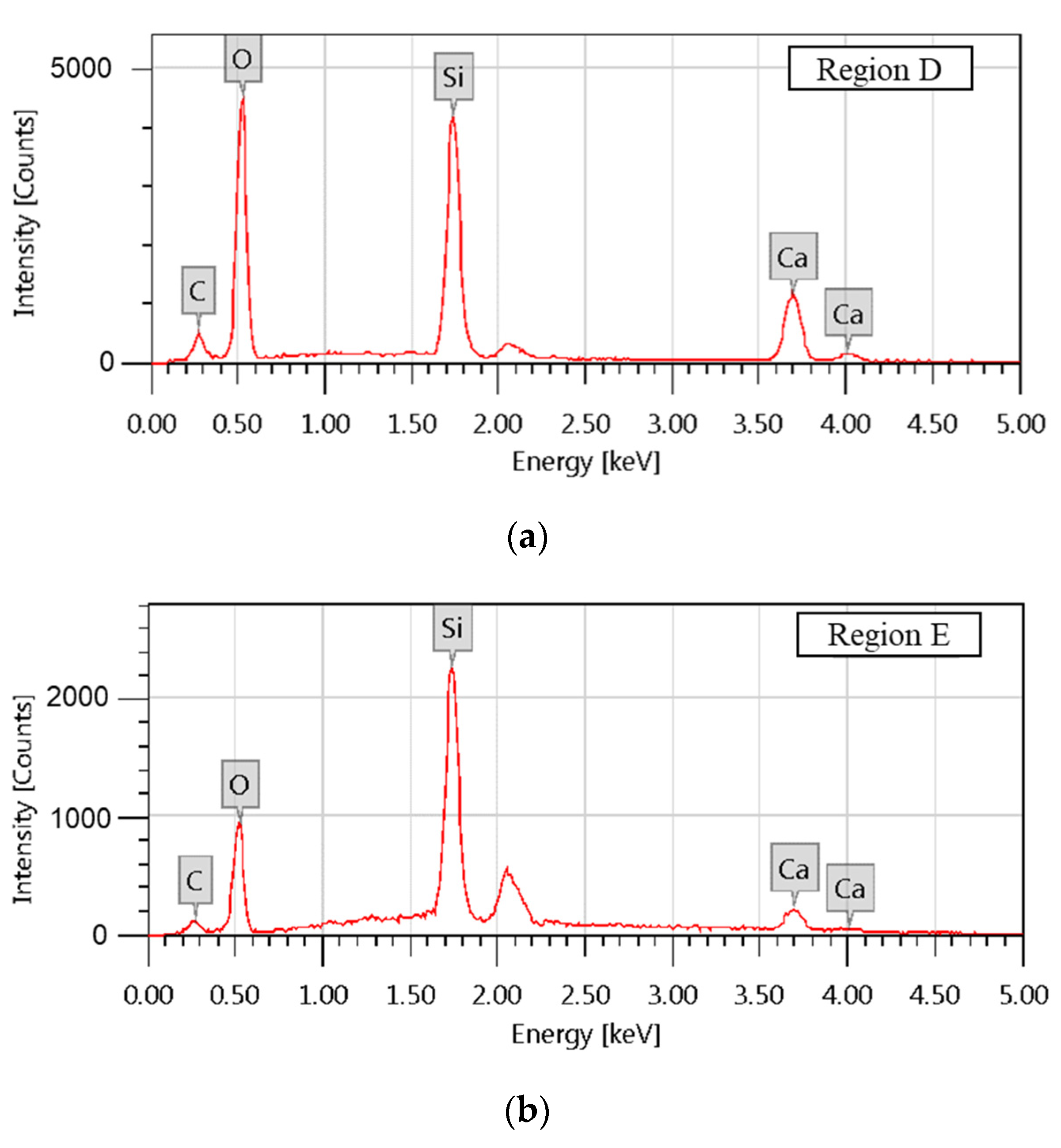
| Region | Atomic Composition /% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Si | Ca | |
| D | 8.86 ± 0.08 | 59.80 ± 0.28 | 17.95 ± 0.12 | 13.39 ± 0.13 |
| E | 1.77 ± 0.33 | 18.65 ± 0.20 | 33.45 ± 0.32 | 46.13 ± 1.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Liao, H.; Ma, Z.; Song, H.; Cheng, F. Effect of Different Initial CaO/SiO2 Molar Ratios and Curing Times on the Preparation and Formation Mechanism of Calcium Silicate Hydrate. Materials 2023, 16, 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020717
Wu J, Liao H, Ma Z, Song H, Cheng F. Effect of Different Initial CaO/SiO2 Molar Ratios and Curing Times on the Preparation and Formation Mechanism of Calcium Silicate Hydrate. Materials. 2023; 16(2):717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020717
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jianfang, Hongqiang Liao, Zhuohui Ma, Huiping Song, and Fangqin Cheng. 2023. "Effect of Different Initial CaO/SiO2 Molar Ratios and Curing Times on the Preparation and Formation Mechanism of Calcium Silicate Hydrate" Materials 16, no. 2: 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020717
APA StyleWu, J., Liao, H., Ma, Z., Song, H., & Cheng, F. (2023). Effect of Different Initial CaO/SiO2 Molar Ratios and Curing Times on the Preparation and Formation Mechanism of Calcium Silicate Hydrate. Materials, 16(2), 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020717





