Leaching Stability and Redox Activity of Copper-MFI Zeolites Prepared by Solid-State Transformations: Comparison with Ion-Exchanged and Impregnated Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Catalyst Preparation
2.3. Catalyst Characterization
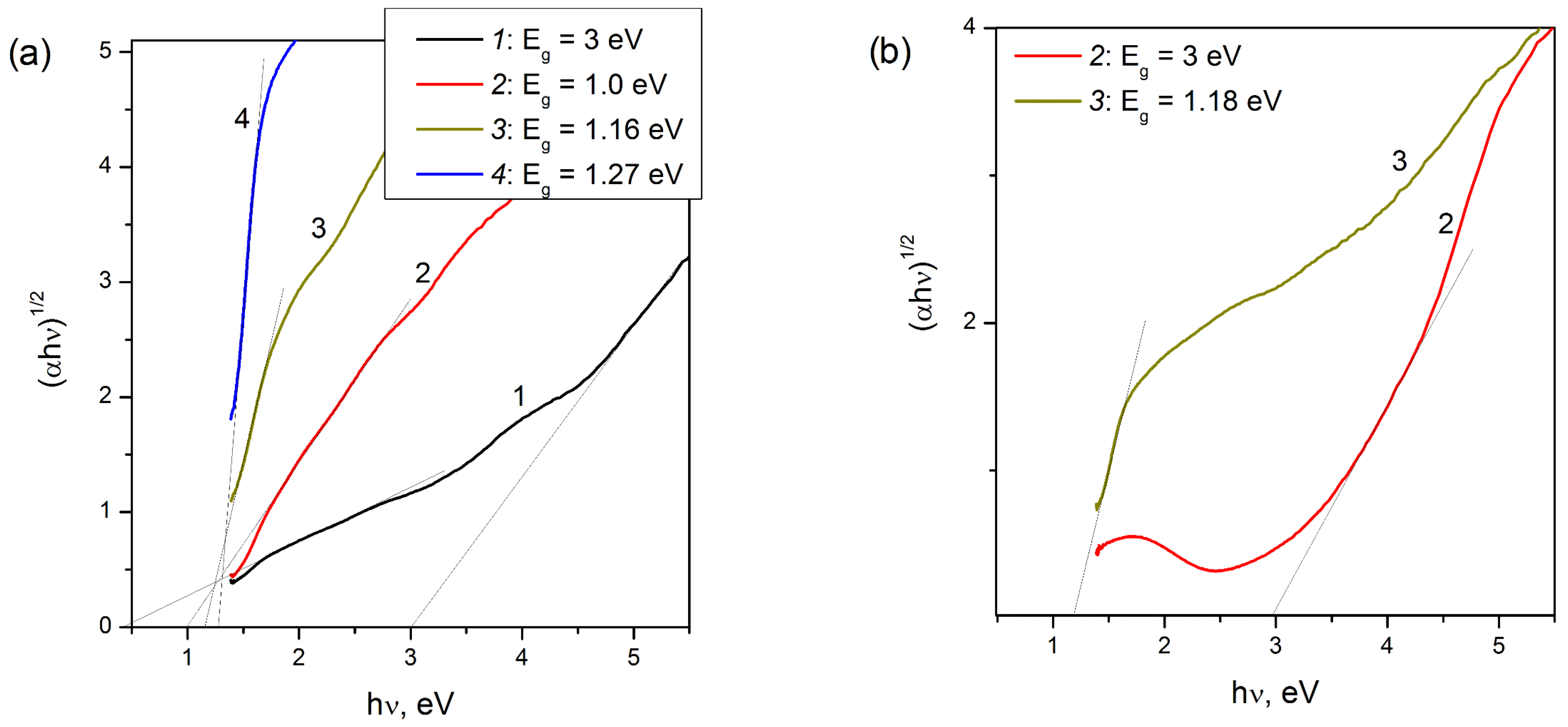
3. Results and Discussion
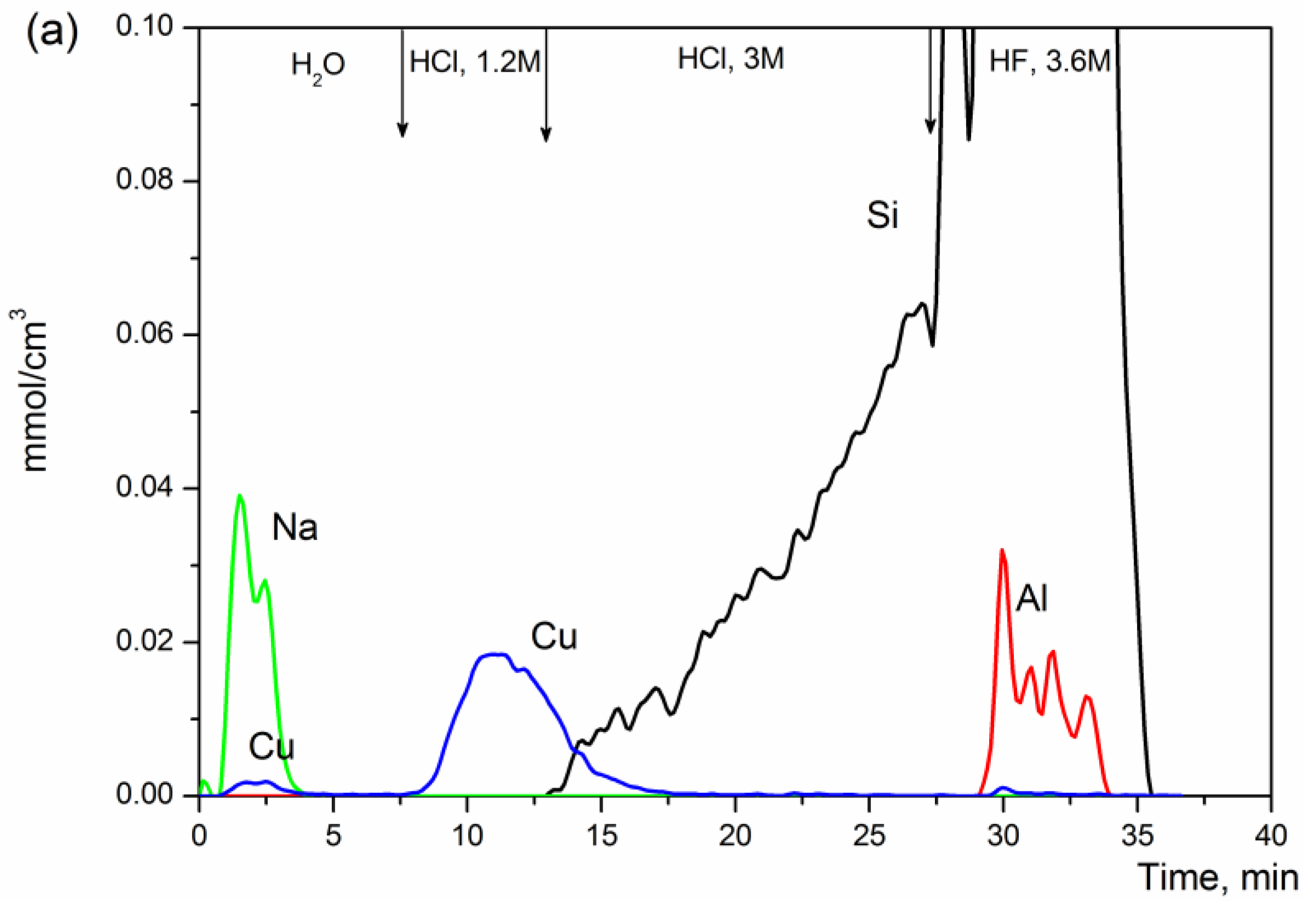
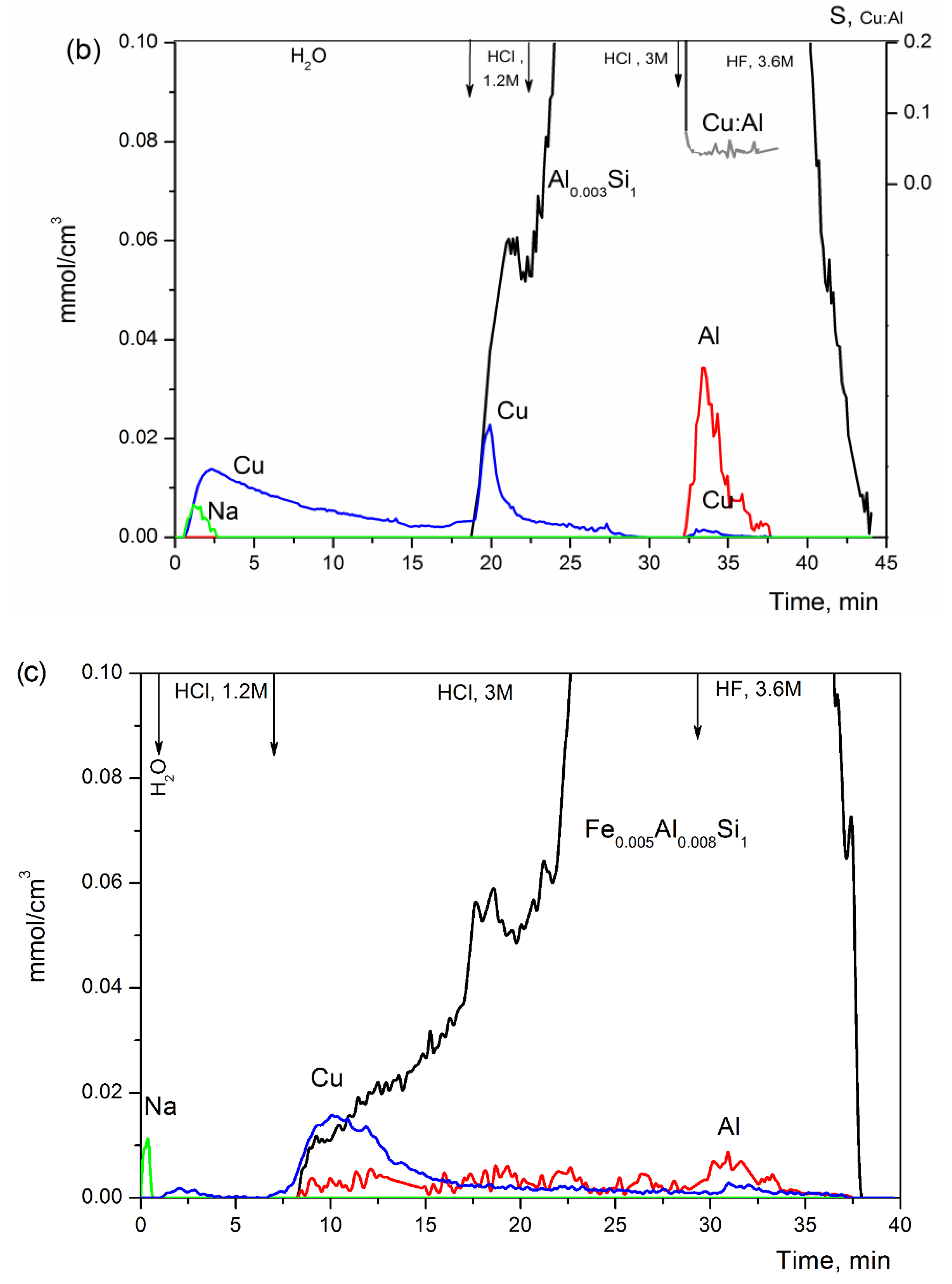
3.1. Leaching Stability
3.2. XRD Study of Cu-Containing Silicalites and Alumosilicalites with MFI Topology
3.3. EPR and UV-Vis DR Study of Cu-Containing MFI-Silicalites and Zeolites with Low Copper Loading
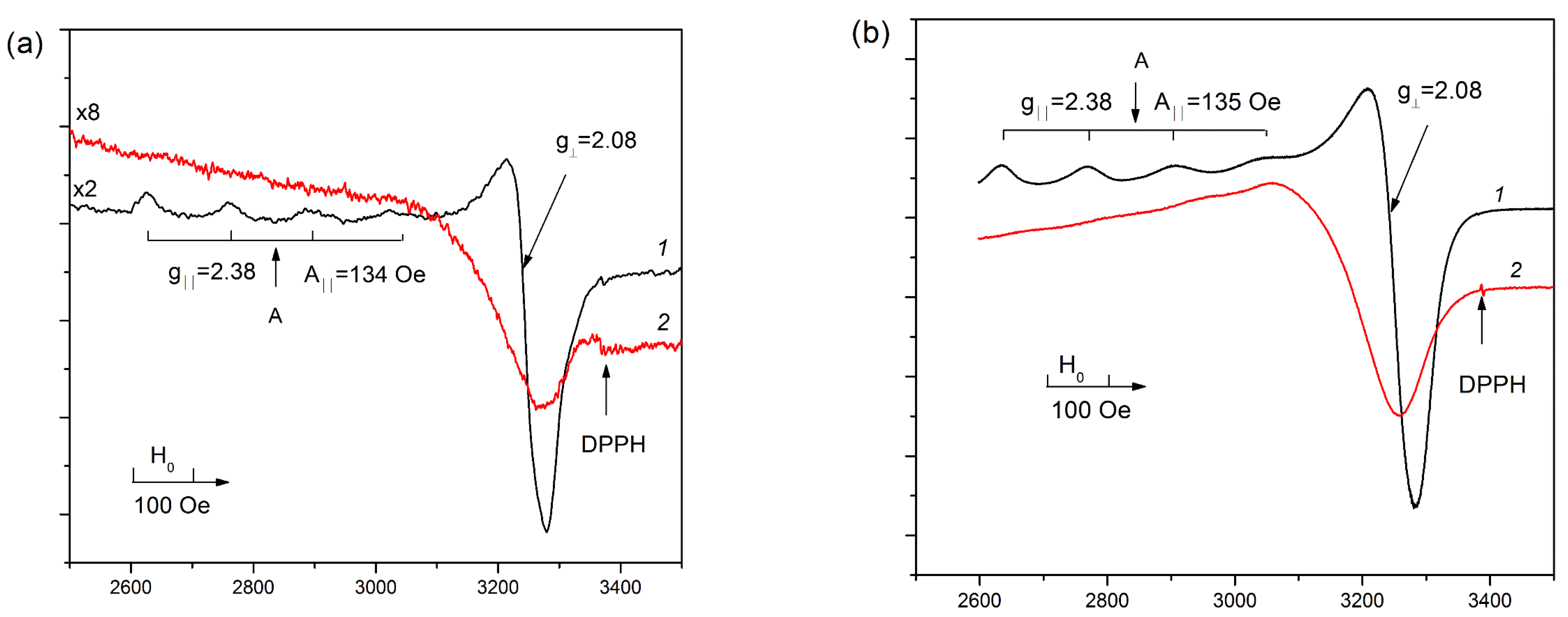
3.3.1. EPR Data
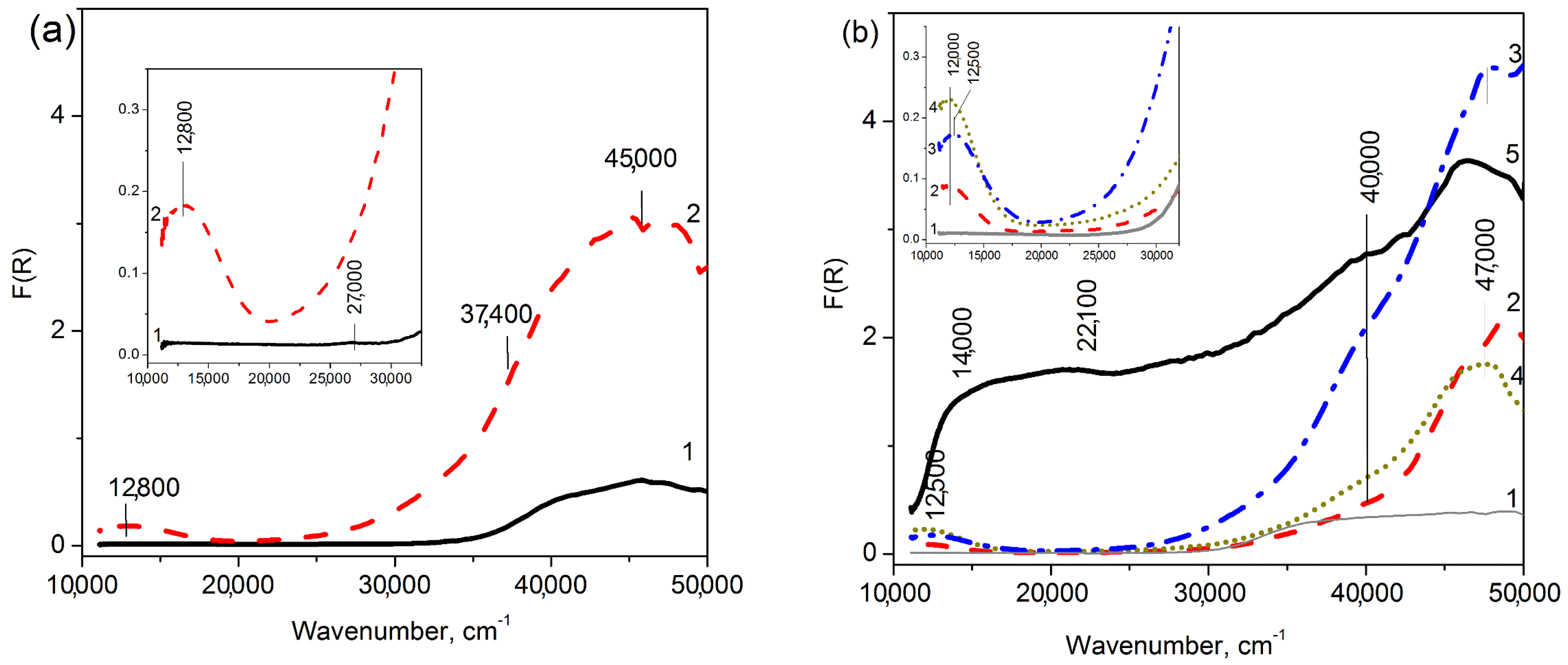
3.3.2. UV-Vis DR Data
3.4. EPR and UV-Vis DR Study of Cu-Containing MFI-Silicalites and Zeolite with High Copper Loading
3.4.1. EPR Data
3.4.2. UV-Vis DR Data
3.5. Redox Performance of Cu-Containing Zeolites
3.6. Leaching Stability of Cu-Containing Zeolites Vrs Copper State
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iwamoto, M.; Yahiro, H.; Mine, Y.; Kagawa, S. Excessively Copper Ion-exchanged ZSM-5 Zeolite as Highly Active Catalysts for Direct Decomposition of Nitrogen Monoxide. Chem. Lett. 1989, 2, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, P.J.; Sels, B.F.; van Teeffelen, R.M.; Leeman, H.; Hensen, E.J.M.; Schoonheydt, R.A. The catalytic performance of Cu-containing zeolites in N2O decomposition and the influence of O2, NO and H2O on recombination of oxygen. J. Catal. 2008, 256, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, W.; Konig, A.; Richter, T.; Puppe, L. Catalytic NOx Reduction in Net Oxidizing Exhaust Gas. SAE Tech. Pap. Ser. 1990, 900496, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto, M.; Hamada, H. Removal of nitrogen monoxide from exhaust gases through novel catalytic processes. Catal. Today 1991, 10, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjovall, H.; Olsson, L.; Fridell, E.; Blint, R.J. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over Cu-ZSM-5 The effect of changing the gas composition. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 64, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.A.; Verma, A.A.; Paolucci, C.; Parekh, A.A.; Anggara, T.; Yezerets, A.; Schneider, W.F.; Miller, J.T.; Delgass, W.N.; Ribeiro, F.H. Methods for NH3 titration of Brønsted acid sites in Cu-zeolites that catalyze the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. J. Catal. 2014, 312, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotta, L.F.; Gruttadauria, M.; Di Carlo, G.; Perrini, G.; Librando, V. Heterogeneous catalytic degradation of phenolic substrates: Catalysts activity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dukkanci, M.; Gunduz, G.; Yilmaz, S.; Prihod’ko, R.V. Heterogeneous Fenton-like degradation of Rhodamine 6G in water using CuFeZSM-5 zeolite catalyst prepared by hydrothermal synthesis. J. Hazard. Mat. 2010, 181, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkaj, K.M.; Katovic, A.; Zrncevic, S. Investigation of the catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of phenol over different types of Cu/ZSM-5 catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 144, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taran, O.P.; Yashnik, S.A.; Ayusheev, A.B.; Piskun, A.S.; Prihod’ko, R.V.; Ismagilov, Z.R.; Goncharuk, V.V.; Parmon, V.N. Cu-containing MFI zeolites as catalysts for wet peroxide oxidation of formic acid as model organic contaminant. Appl. Catal. B 2013, 140–141, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taran, O.P.; Zagoruiko, A.N.; Ayusheev, A.B.; Yashnik, S.A.; Prihod’ko, R.V.; Ismagilov, Z.R.; Goncharuk, V.V.; Parmon, V.N. Cu and Fe-containing ZSM-5 zeolites as catalysts for wet peroxide oxidation of organic contaminants: Reaction kinetics. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2015, 41, 9521–9537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taran, O.P.; Zagoruiko, A.N.; Ayusheev, A.B.; Yashnik, S.A.; Prihod’ko, R.V.; Ismagilov, Z.R.; Goncharuk, V.V.; Parmon, V.N. Wet peroxide oxidation of phenol over Cu-ZSM-5 catalyst in a flow reactor. Kinetics and diffusion study. Chem. Engin. J. 2015, 282, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashnik, S.A.; Taran, O.P.; Surovtsova, T.A.; Ayusheev, A.B.; Parmon, V.N. Cu- and Fe-substituted ZSM-5 zeolite as an effective catalyst for wet peroxide oxidation of Rhodamine 6G Dye. J. Envir. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, C.; Forde, M.M.; Ab Rahim, M.H.; Thetford, A.; He, Q.; Jenkins, R.L.; Dimitratos, N.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.A.; Dummer, N.F.; Murphy, D.M.; et al. Direct Catalytic Conversion of Methane to Methanol in an Aqueous Medium by using Copper-Promoted Fe-ZSM-5. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5129–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Armstrong, R.D.; Shaw, G.; Dummer, N.F.; Freakley, S.J.; Taylor, S.H.; Hutchings, G.J. Continuous selective oxidation of methane to methanol over Cu- and Fe-modified ZSM-5 catalysts in a flow reactor. Catal. Today 2016, 270, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashnik, S.A.; Boltenkov, V.V.; Babushkin, D.E.; Taran, O.P.; Parmon, V.N. Methane Oxidation by H2O2 over Different Cu-Species of Cu-ZSM-5 Catalysts. Top. Catal. 2020, 63, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulfers, M.J.; Teketel, S.; Ipek, B.; Lobo, R.F. Conversion of methane to methanol on copper-containing small-pore zeolites and zeotypes. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 4447–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, M.A.; Knorpp, A.J.; Sushkevich, V.L.; Palagin, D.; van Bokhoven, J.A. Active Sites and Mechanisms in the Direct Conversion of Methane to Methanol Using Cu in Zeolitic Hosts: A Critical Examination. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1449–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrienko, A.A.; Kolganov, A.A.; Arzumanov, S.S.; Yashnik, S.A.; Kriventsov, V.V.; Freude, D.; Stepanov, A.G. Effect of Copper State in Cu/H-ZSM-5 on Methane Activation by Brønsted Acid Sites, Studied by 1H MAS NMR In Situ Monitoring the H/D Hydrogen Exchange of the Alkane with Brønsted Acid Sites. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2021, 125, 2182–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashnik, S.A.; Ismagilov, Z.R.; Anufrienko, V.F. Catalytic Properties and Electronic Structure of Copper Ions in Cu-ZSM-5. Catal. Today 2005, 110, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashnik, S.; Ismagilov, Z. Cu-Substituted ZSM-5 Catalyst: Controlling of DeNOx Reactivity via Ion-Exchange Mode with Copper–Ammonia Solution. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 170–171, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashnik, S.A.; Salnikov, A.V.; Vasenin, N.T.; Anufrienko, V.F.; Ismagilov, Z.R. Regulation of the copper-oxide cluster structure and DeNOx activity of Cu-ZSM-5 catalysts by variation of OH/Cu2+. Catal. Today 2012, 197, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karge, H.G.; Wichterlova, B.; Beyer, H.K. High-temperature Interaction of Solid Cu Chlorides and Cu Oxides in Mixtures with H-forms of ZSM-5 and Y Zeolites. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1992, 88, 345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, G.L.; Kanazirev, V.; Church, D.F. Formation of Cu-MFI NO Decomposition Catalyst via Reductive Solid-state Ion Exchange. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucherov, A.V.; Slinkin, A.A. Introduction of transition metal ions in cationic positions of high-silica zeolites by a solid state reaction, Interaction of copper compounds with H-mordenite or H-ZSM-5. Zeolites 1986, 6, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, C.; Bordiga, S.; Salvalaggio, M.; Spoto, G.; Zecchina, A.; Geobaldo, F.; Vlaic, G.; Bellatreccia, M. XAFS, IR, and UV−Vis Study of the CuI Environment in CuI-ZSM-5. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 344–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Drake, I.J.; Bell, A.T. Characterization of Cu-ZSM-5 Prepared by Solid-State Ion Exchange of H-ZSM-5 with CuCl. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 2347–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, M.; Yahiro, H.; Tanda, K.; Mizuno, N.; Mine, Y.; Kagawa, S. Removal of Nitrogen Monoxide through a Novel Catalytic Process. 1. Decomposition on Excessively Copper Ion Exchanged ZSM-5 Zeolites. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 3727–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedecek, J.; Sobalik, Z.; Tvaruzkova, Z.; Kaucky, D.; Wichterlova, B. Coordination of Cu ions in High-Silica Zeolite Matrices. Cu+ photoluminescence, IR of NO adsorbed on Cu2+, and Cu2+ ESR Study. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 16327–16337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucherov, A.V.; Slinkin, A.A.; Kondrat’ev, D.A.; Bondarenko, T.N.; Rubinstein, A.M.; Minachev, K.M. Cu(2+)-cation location and reactivity in mordenite and ZSM-5: ESR-study. Zeolite 1985, 5, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handreck, G.P.; Smith, T.D. A physicochemical study of the alumination of silicalite and the dealumination of zeolite ZSM-5. Zeolites 1990, 10, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiivanov, K.; Knozinger, H.; Milushev, A. FTIR study of low-temperature CO adsorption on Cu/silicalite-1. Catal. Commun. 2002, 3, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossi, C.; Fusi, A.; Recchia, S.; Psaro, R.; Moretti, G. Cu–ZSM-5 (Si/Al = 66), Cu–Fe–S-1 (Si/Fe = 66) and Cu–S-1 catalysts for NO decomposition: Preparation, analytical characterization and catalytic activity. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 30, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, G.; Moretti, G.; Fierro, G. Copper exchanged Silicalite-1: Evidence of the location of copper oxide nanoclusters in the supermicropores of S-1. Stud. Sur. Sci. Catal. 2008, 174, 925–928. [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda, Y.; Kotani, A.; Maeda, H.; Moriwaki, H.; Morimato, T. The state of excessively ion-exchanged copper in mordenite: Formation of tetragonal hydroxy-bridged copper ion. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1992, 88, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groothaert, M.H.; van Bokhoven, J.A.; Battiston, A.A.; Weckhuysen, B.M.; Schoonheydt, R.A. Bis(μ-oxo)dicopper in Cu-ZSM-5 and Its Role in the Decomposition of NO: A Combined in Situ XAFS, UV-Vis-Near-IR, and Kinetic Study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 7629–7640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ione, K.G.; Vostrikova, L.A.; Petrova, A.V.; Mastikhin, V.M. Synthesis and Study of Properties of ZSM-II Type Silicalites of I-VIII Group Elements. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1984, 18, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Anufrienko, V.F.; Poluboyarov, V.A.; Vostrikova, L.A.; Ione, K.G. Specificity of states of Cu2+ ions in ZSM-5 Zeolites due to the cooperative Janh-Teller Effect. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 1984, 25, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkaj, K.M.; Tomasic, V.; Katovic, A.; Bielanska, E. Synthesis and characterization of Cu-MFI catalyst for the direct medium temperature range NO decomposition. Mater. Sci.-Pol. 2016, 34, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, T.; Inayat, A.; Schwieger, W. Reactivity and applications of layered silicates and layered double hydroxides. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 10365–10387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salou, M.; Kooli, F.; Kiyozumi, Y.; Mikamizu, F. Effect of aluminium source and content on the synthesis of zeolite ZSM-5 from kanemite via solid-state transformation. J. Mater. Chem. 2001, 11, 1476–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocılteu, S.M.; Salou, M.; Kiyozumi, Y.; Niwa, S.; Mizukami, F.; Haneda, M. Uniform distribution of copper and cobalt during the synthesis of SiMFI-5 from kanemite through solid-state transformation. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, H.; Yan, Y. Cu-MFI zeolite supported on paper-like sintered stainless fiber for catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of phenol in a batch reactor. Sep. Pur. Techn. 2018, 190, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivoruchko, O.P.; Larina, T.V.; Shutilov, R.A.; Gavrilov, V.Y.; Yashnik, S.A.; Sazonov, V.A.; Molina, I.; Ismagilov, Z.R. Effect of the Electronic State and Copper Localization in ZSM-5 Pores on Performance in NO Selective Catalytic Reduction by Propane. Appl. Catal. B 2011, 103, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, T.; Katovic, A.; Valkaj, K.; Tagarelli, A.; Giordano, G. Cu-silicalite-1 catalyst for the wet hydrogen peroxide oxidation of phenol. J. Porous Mater. 2009, 16, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakhov, V.V.; Boldyreva, N.N.; Vlasov, A.A.; Dovlitova, L.S. Methodology and Procedure of the Stoichiographic Analysis of Solid Inorganic Substances and Materials. J. Anal. Chem. 2011, 66, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prihod’ko, R.; Stolyarova, I.; Gündüz, G.; Taran, O.; Yashnik, S.; Parmon, V.; Goncharuk, V. Fe-exchanged zeolites as materials for catalytic wet peroxide oxidation. Degradation of Rodamine G dye. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 104, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sass, C.E.; Kevan, L. Electron Spin Echo Modulation of the Interaction of Cu+2 with framework Al in ZSM-5 zeolite. J. Phys. Chem. 1989, 93, 7856–7859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-K.; Kurshev, V.; Luan, Z.; Lee, C.W.; Kevan, L. Reaction of NO with copper ions in Cu(II)-exchanged ZSM-5 zeolite: Electron spin resonance, electron spin echo modulation and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2000, 38, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, S.C.; Aylor, A.; Bell, A.T.; Reimer, J.A. Electron Paramagnetic resonance studies of Copper Ion-Exchanged ZSM-5. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 11533–11540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomino, G.T.; Fisicaro, P.; Bordiga, S.; Zecchina, A.; Giamello, E.; Lamberti, C. Oxidation States of Copper Ions in ZSM-5 Zeolites. A Multitechnique Investigation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 4064–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.X.; Thurston, T.R.; Tranquada, J.M.; Shirane, G. Magnetic neutron scattering study of single-crystal cupric oxide. Phys. Rev. B 1989, 39, 4343–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierro, G.; Ferraris, G.; Moretti, G. CuO nanoparticles entrapped in MFI framework: Investigation of textural, magnetic and catalytic properties of Cu-ZSM-5 and Cu-S-1 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 91, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lever, A.B.P. Inorganic Electronic Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; p. 863. ISBN 0444423893. [Google Scholar]
- Yashnik, S.A.; Anufrienko, V.F.; Sazonov, V.A.; Ismagilov, Z.R.; Parmon, V.N. Low-Temperature Activation of Nitrogen Oxide on Cu–ZSM-5 Catalysts. Kin. Catal. 2012, 53, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centi, G.; Perathoner, S.; Biglino, D.; Giambello, E. Adsorption and reactivity of NO on Copper-on-Alumina Catalysts. J. Catal. 1995, 152, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, M.C.; Garboeski, E.; Primet, M. Physicochemical properties of copper oxide loaded alumina in methane combustion. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1990, 86, 3027–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Dong, L.; Shen, M.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Ding, W.; Chen, Y. Influence of supports on the activities of copper oxide species in the low-temperature NO-CO reaction. Appl. Catal. B 2001, 31, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimokawabe, M.; Asakawa, H.; Takezawa, H. Characterization of copper-zirconia catalysts prepared by an impregnation method. Appl. Catal. 1990, 59, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Amiridis, M.D.; Chen, Y. Characterization of CuO Supported on Tetragonal ZrO2 Catalysts for N2O Decomposition to N2. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altshuler, S.A.; Kozirev, B.M. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance in Compounds of Transition Elements, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1974; p. 672. ISBN 9781483225562. [Google Scholar]
- Carl, P.J.; Larsen, S.C. EPR Study of Copper-Exchanged Zeolites: Effects of Correlated g- and A-Strain, Si/Al Ratio, and Parent Zeolite. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 6568–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carl, P.J.; Larsen, S.C. Variable-Temperature Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Studies of Copper-Exchanged Zeolites. J. Catal. 1999, 182, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimov, N.G.; Anufrienko, V.F.; Ione, K.G. EPR study of the interaction of Cu2+ ions with ammonia in Cu-Y zeolites. Doklady AN SSSR 1973, 212, 142–145. [Google Scholar]
- Sukhorukov, Y.; Loshkareva, N.N.; Samokhvalov, A.A.; Moskvin, A.S. Absorption spectra of CuO single crystals near the absorption edge and the nature of the optical gap in copper oxides. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 1995, 81, 998–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Gizhevskii, B.A.; Sukhorukov, Y.P.; Moskvin, A.S.; Loshkareva, N.N.; Mostovshchikova, E.V.; Ermakov, A.E.; Kozlov, E.A.; Uimin, M.A.; Gaviko, V.S. Anomalies in the optical properties of nanocrystalline copper oxides CuO and Cu2O near the fundamental absorption edge. JETP 2006, 102, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, N.F.; Davies, E.A. Electronic Processes in Non-Crystalline Materials, 2nd ed.; Oxford Clarendon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979; p. 590. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, S.; Mumtaz, A.; Hasanain, S.K. Size effects on the magnetic and optical properties of CuO nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 2497–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, J.M.; Geron, C.; Kribii, A.; Barbier, J. Preparation of supported copper catalysts. II. Reduction of copper/alumina catalyst. Appl. Catal. 1989, 47, L9–L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow, W.-P.; Wang, Y.-P.; Huang, T.-J. Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia supported copper oxide catalyst. I. Effect of oxygen vacancy of support on copper oxide reduction. J. Catal. 1996, 160, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow, W.-P.; Wang, Y.-P.; Huang, T.-J. TPR and XRD studies of yttria-doped ceria/g-alumina-supported copper oxide catalyst. Appl. Catal. A 2000, 190, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Grift, C.J.G.; Mulder, A.; Geus, J.W. Characterizatuion of silica-supported copper catalysts by means of temperature-programmed reduction. Appl. Catal. 1990, 60, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praliaud, H.; Mikhailenko, S.; Chajar, Z.; Primet, M. Surface and bulk properties of Cu-ZSM-5 and Cu/Al2O3 solid during redox treatment. Correlation with the selective reduction of nitric oxide by hydrocarbons. Appl. Catal. B 1998, 16, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkany, J.; d’Itri, J.L.; Sachtler, W.M.H. Redox chemistry in excessively ion-exchanged Cu/Na-ZSM-5. Catal. Lett. 1992, 16, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashnik, S.A.; Ismagilov, Z.R. Zeolite ZSM-5 Containing Copper Ions: The Effect of the Copper Salt Anion and NH4OH/Cu2+ Ratio on the State of the Copper Ions and on the Reactivity of the Zeolite in DeNOx. Kin. Catal. 2016, 57, 776–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample | Method of Cu Introduction | Chemical Composition, wt.% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Na | Fe | Al | Si | |||
| 1. | 0.5%Cu-MFI-SST | SST | 0.49 | 2.94 | 0.08 | 0.19 | 44.8 |
| 2. | 1.0%Cu-MFI-SST | SST | 1.18 | 2.73 | 0.13 | 0.21 | 45.1 |
| 3. | 2.0%Cu-MFI-SST | SST | 2.72 | 1.92 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 43.7 |
| 4. | 16.0%Cu-MFI-SST | SST | 16.1 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 37.3 |
| 5. | 1.0%Cu-MFI-IEX | IEX | 0.95 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.30 | 43.4 |
| 6. | 2.0%Cu-MFI-IEX | IEX | 2.03 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.27 | 42.7 |
| 7. | 0.5%Cu-ZSM-5-IEX | IEX | 0.47 | 0.06 | 0.65 | 1.43 | 42.9 |
| 8. | 1.0%Cu-ZSM-5-IEX | IEX | 1.05 | 0.05 | 0.65 | 1.40 | 42.9 |
| 9. | 2.0%Cu-ZSM-5-IEX | IEX | 1.97 | 0.05 | 0.65 | 1.41 | 42.9 |
| 10. | 2.0%Cu-ZSM-5-IMP | IMP | 2.01 | 0.06 | 0.65 | 1.43 | 42.8 |
| 11. | 16.0%Cu-ZSM-5-IMP | IMP | 16.0 | 0.05 | 0.65 | 1.43 | 42.8 |
| N | Sample | Fragmentary Chemical Composition of Dissolved Species and Phases | Phase Contents, wt.% | Hypothesized Structural Compound |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5%Cu-MFI-SST | Cu(II), soluble in H2O | <0.05 (3% Cu) | CuO on external surface of silicalite |
| Cu(II), soluble in 1.2 M HCl, part of them dissolved with SiO2 | 2 (67% Cu) | CuO with strong interaction with external surface of silicalite | ||
| Al0.001Si1 containing Cu(II) with Cu0.0015Si1 and Cu0.30Al1, it is soluble in 3.6 M HF | 98 (30% Cu) | Cu2+ ions, in cation-exchange sites of MFI, bulk of Al-silicalite | ||
| 2 | 2.0%Cu-MFI-SST | Cu(II), soluble in H2O | 0.14 (7% Cu) | CuO on external surface of silicalite |
| Cu(II), soluble in 1.2 M HCl, part of them dissolved with Si-matrix | 1.8 (91% Cu) | CuO with strong interaction with external surface of silicalite | ||
| Al0.0008Si1 containing Cu(II) with Cu0.0001Si1 and Cu0.01Al1, it is total soluble in 3.6 M HF | 97 (2% Cu) | Cu2+ ions, in cation-exchange sites of MFI, bulk of Al-silicalite | ||
| Al soluble in 3.6 M HF | 0.2 | (AlO)x-like, extralattice Al3+ ions | ||
| 3 | 16%Cu-MFI-SST | Cu(II), soluble in H2O | 0.8 (5.4% Cu) | CuO on external surface of silicalite |
| Cu(II), soluble in 1.2 M HCl, part of them dissolved with SiO2 | 14.9 (93% Cu) | CuO with strong interaction with external surface of silicalite | ||
| Al0.001Si1 containing Cu(II) with Cu0.0001Si1 and Cu0.013Al1, it is total soluble in 3.6 M HF | 84 (2.7% Cu) | Cu2+ ions, in cation-exchange sites of MFI, bulk of Al-silicalite | ||
| 4 | 2.0%Cu-MFI-IEX | Cu(II), soluble in H2O | 1.3 (65% Cu) | CuO on external zeolite surface |
| SiO2 containing Cu(II), both are soluble in 1.2 M HCl | 9.0 (33% Cu) | CuO (decorated by SiO2) in near-surface layers of zeolite crystal | ||
| Al0.003Si1 containing Cu(II) with Cu0.04Al1, both are soluble in 3.6 M HF | 91 (2% Cu) | Cu2+ ions, in cation-exchange sites, bulk of silicalite | ||
| Al soluble in 3.6 M HF | 0.2 | (AlO)x-like, extralattice Al3+ ions | ||
| 5 | 2.0%Cu-ZSM-5-IEX | Cu(II), soluble in 1.2 M HCl | 0.5 (2.7% Cu) | CuO-like clusters |
| Al0.008Fe0.003Si1 containing Cu(II) with Cu0.0004Si1, both are soluble in 3.6 M HF | 98 (97.3%Cu) | Cu2+ ions, in cation-exchange sites, bulk of zeolite | ||
| Al3+, soluble in 1.2 M HCl and 3.6 M HF | 0.1% | (AlO)x-like, extralattice Al3+ ions |
| Sample | Ab. Band in UV-Vis DR, cm−1 | EPR Parameters at −196 °C | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d-d Cu2+isol | CTB L → M | g|| | A‖ | G⊥ | Spin/g | %Cu a | |||
| 1. | 0.5%Cu-MFI-SST | Cu2+, D4h | 14,100 b | 32,000 c | 2.38 | 138 | 2.08 | 3.8 × 1019 | 80 |
| 2. | 1.0%Cu-MFI-SST | Cu2+, D4h | 14,100 b | 32,000 c | 2.38 | 138 | 2.08 | 8.4 × 1019 | 90 |
| 3. | 2.0%Cu-MFI-SST | Cu2+, D4h CuO-like | - 16,500 b | 32,000 c 22,100 d | 2.38 | 138 | 2.08 | 5.6 × 1019 | 30 |
| 4. | 16.0%Cu-MFI-SST | Cu2+, D4h CuO-like | - 16,500 b | 32,000 c 22,100 d | 2.38 2.42 | 138 114 | 2.08 | 1.4 × 1019 | 1 |
| 5. | 1.0%Cu-MFI-IEX | Cu2+, Oh | 12,800 | 32,000 c 45,000 | 2.38 | 134 | 2.08 | 5.7 × 1019 | 45 |
| 6. | 2.0%Cu-MFI-IEX | Cu2+, Oh | 13,000 | 32,000 c 45,000 | 2.38 | 134 | 2.08 | 3.1 × 1019 | 25 |
| 7. | 0.5%Cu-ZSM-5-IEX | Cu2+, Oh | 12,000 | 47,500 | 2.38 | 135 | 2.07 | 6.0 × 1019 | 95 |
| 8. | 1.0%Cu-ZSM-5-IEX | Cu2+, Oh | 12,000 | 47,500 | 2.38 | 135 | 2.07 | 1.2 × 1020 | 95 |
| 9. | 2.0%Cu-ZSM-5-IEX | Cu2+, Oh | 12,700 | 47,500 | 2.38 | 135 | 2.07 | 9.6 × 1020 | 80 |
| 10. | 2.0%Cu-ZSM-5-IMP | Cu2+, Oh | 12,500 | - | 2.38 | 138 | 2.08 | 1.4 × 1020 | 70 |
| 11. | 16.0%Cu-ZSM-5-IMP | Cu2+, Oh | 13,300 | - | 2.38 | 138 | 2.08 | 1.3 × 1020 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yashnik, S.A.; Surovtsova, T.A.; Salnikov, A.V.; Parmon, V.N. Leaching Stability and Redox Activity of Copper-MFI Zeolites Prepared by Solid-State Transformations: Comparison with Ion-Exchanged and Impregnated Samples. Materials 2023, 16, 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020671
Yashnik SA, Surovtsova TA, Salnikov AV, Parmon VN. Leaching Stability and Redox Activity of Copper-MFI Zeolites Prepared by Solid-State Transformations: Comparison with Ion-Exchanged and Impregnated Samples. Materials. 2023; 16(2):671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020671
Chicago/Turabian StyleYashnik, Svetlana A., Tatjana A. Surovtsova, Anton V. Salnikov, and Valentin N. Parmon. 2023. "Leaching Stability and Redox Activity of Copper-MFI Zeolites Prepared by Solid-State Transformations: Comparison with Ion-Exchanged and Impregnated Samples" Materials 16, no. 2: 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020671
APA StyleYashnik, S. A., Surovtsova, T. A., Salnikov, A. V., & Parmon, V. N. (2023). Leaching Stability and Redox Activity of Copper-MFI Zeolites Prepared by Solid-State Transformations: Comparison with Ion-Exchanged and Impregnated Samples. Materials, 16(2), 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020671






