Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents in the Synthesis of Inorganic Nanoparticles
Abstract
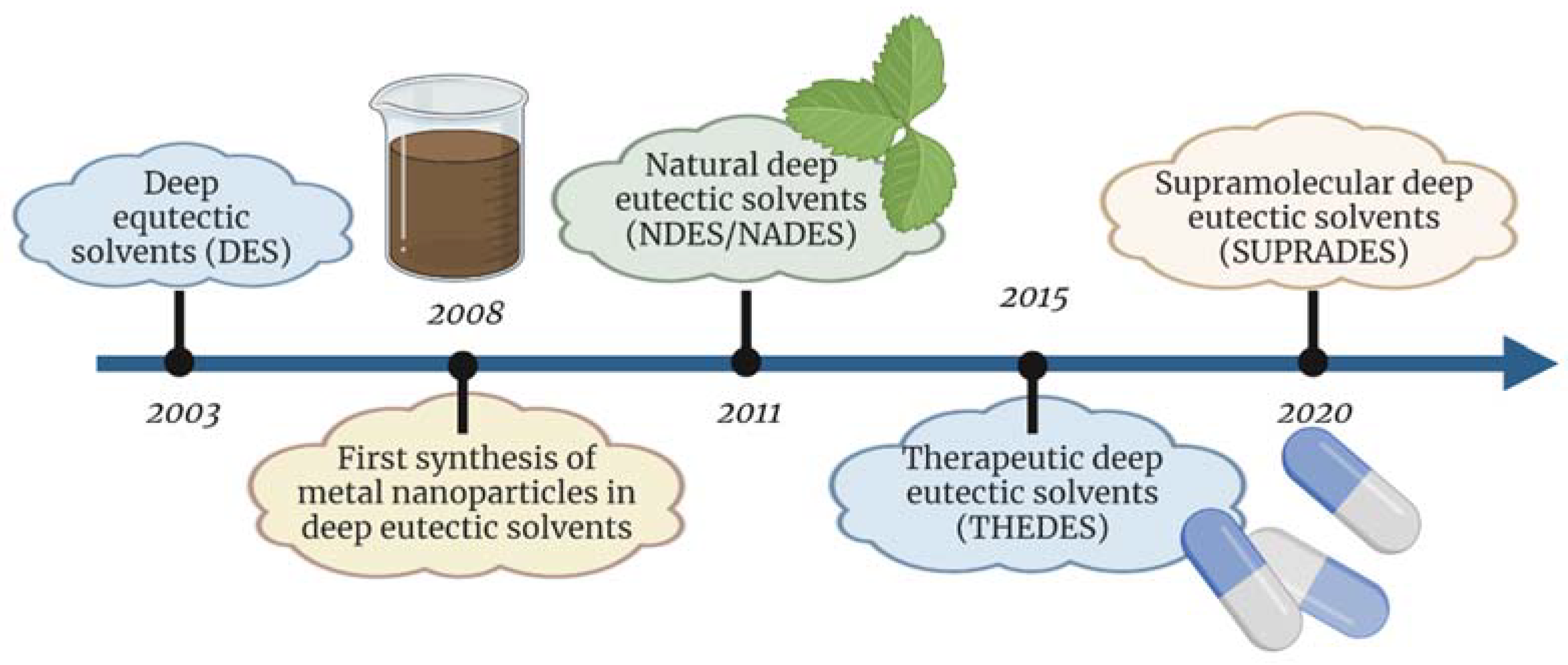
1. Introduction
2. Definition of NDES and Their Classification
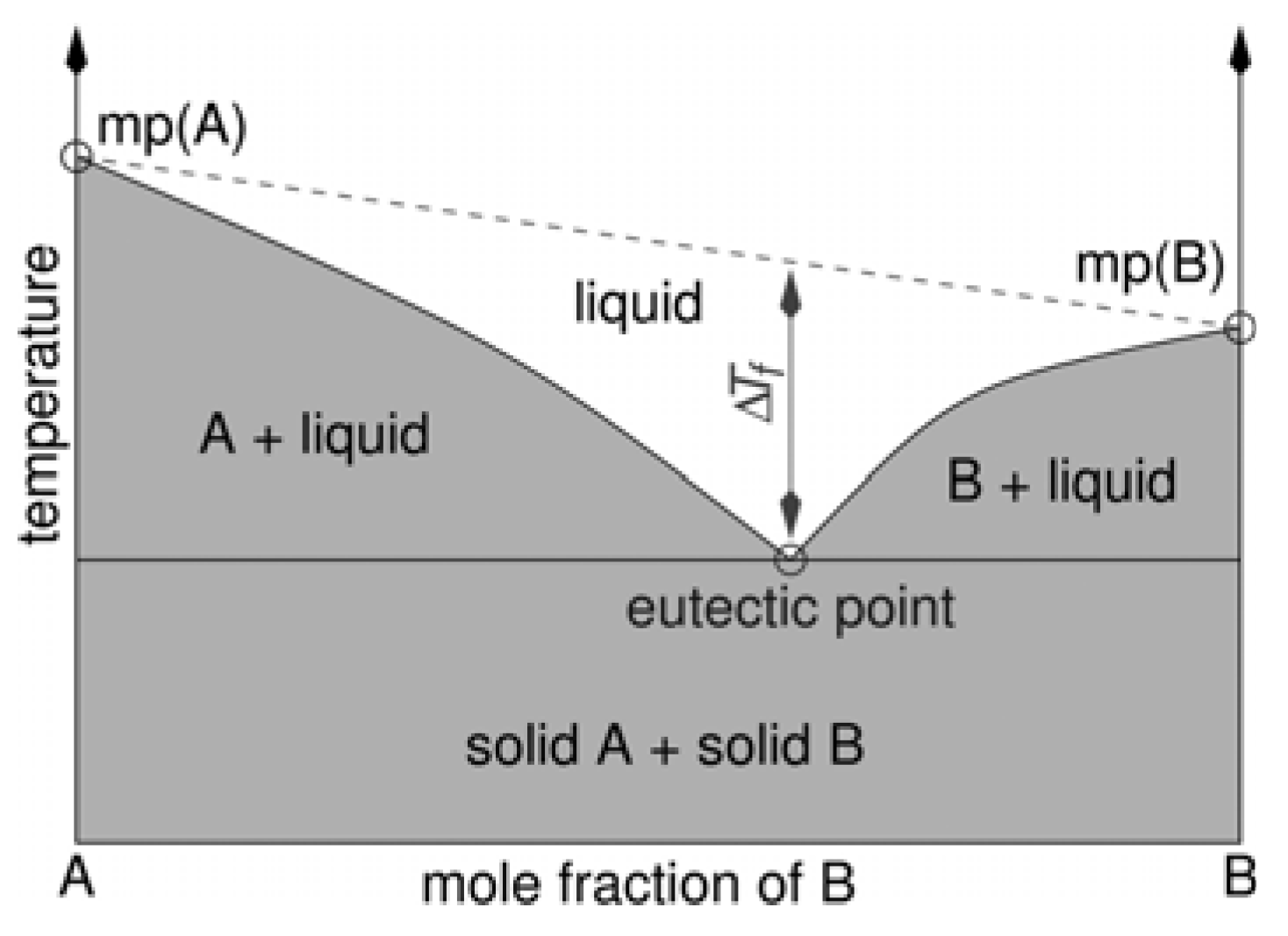
2.1. Eutectic Mixtures
2.2. Comparison of Deep Eutectic and Ionic Liquid Mixtures
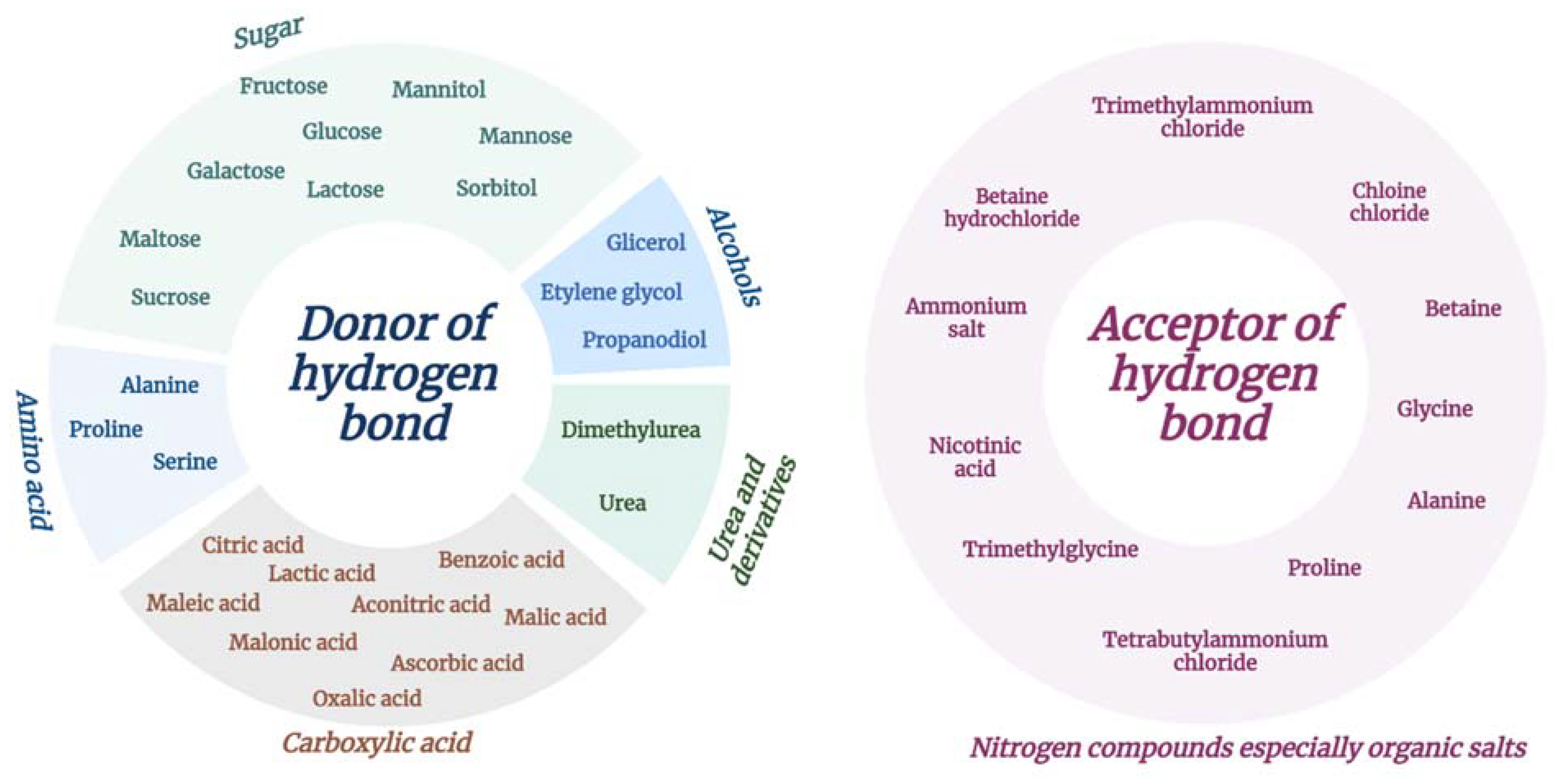
2.3. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents
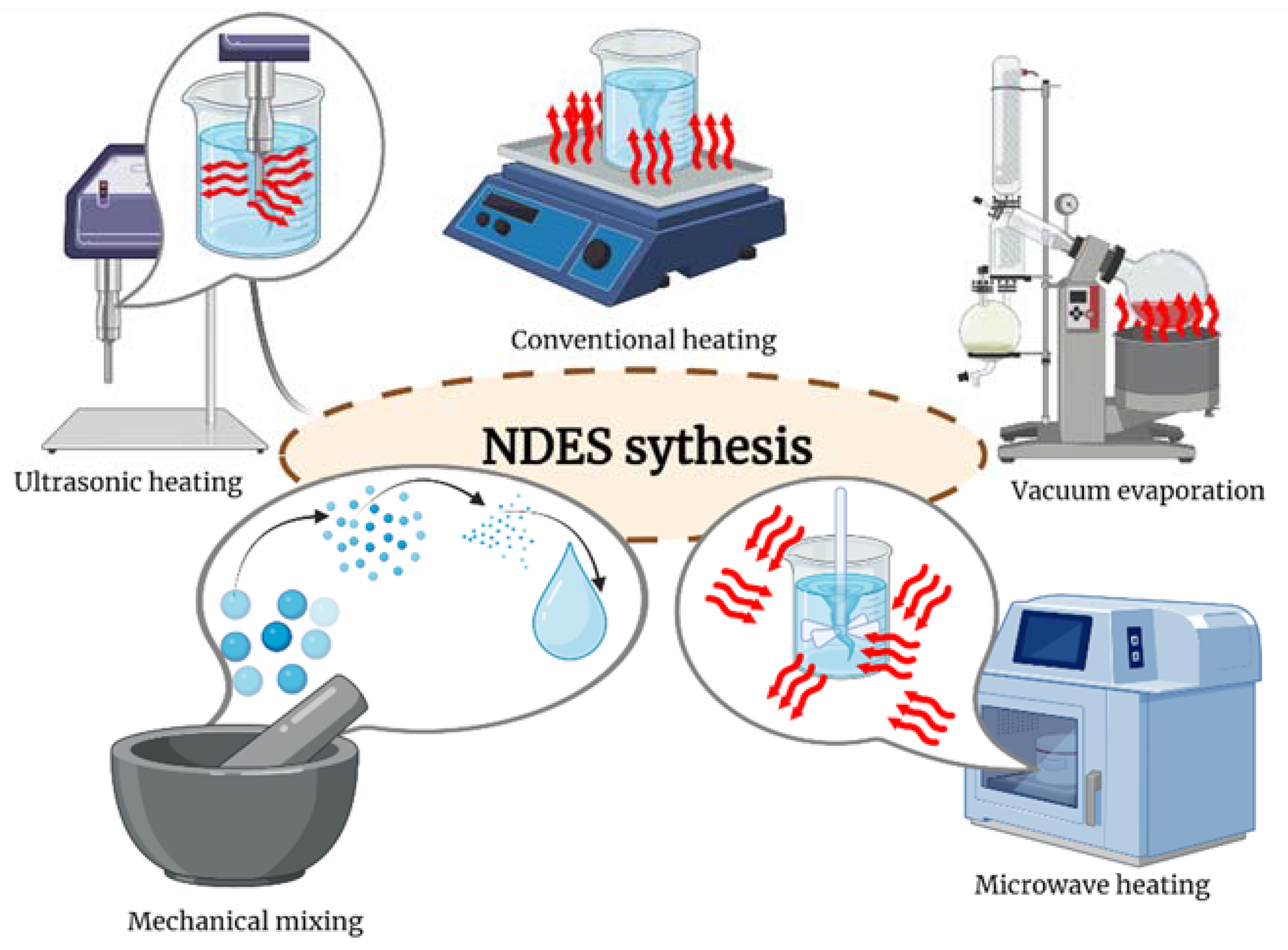
3. Synthesis of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents
3.1. Mechanical Methods
3.2. Vacuum Evaporation and Lyophilisation
3.3. Thermal Methods
3.3.1. Conventional Heating
3.3.2. Ultrasound
3.3.3. Microwave Radiation
4. Properties and Characterisation of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents
4.1. Viscosity and Density
4.2. pH of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents
4.3. Refractive Index
4.4. Reducing Properties
4.5. Complexing and Stabilising Properties
4.6. Thermal Properties
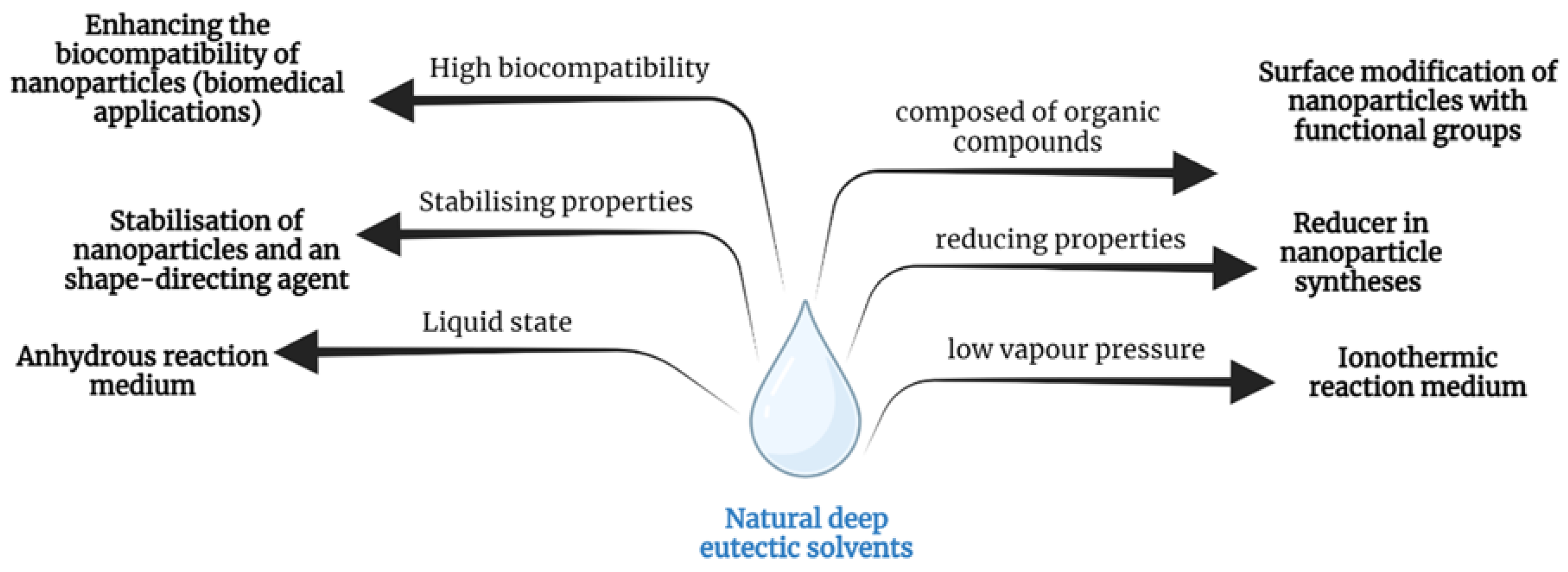
5. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents Applications in Nanotechnology
5.1. Reaction Media for the Synthesis of Nanomaterials
5.2. Reducers and Stabilisers for Nanomaterials
5.3. Biocompatibility of NDESs—Applications in Medicine
5.4. Examples of Preparation of Nanoparticles Using NDESs
5.4.1. Examples of Obtaining Metal Nanoparticles
| Material | Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents | Process Parameters of NDES Synthesis | Size of Nanoparticles | NDES Function | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | Choline chloride–urea (1:2) | Conventional heating in 100 °C | 300 nm | Reaction medium, stabiliser | [7] |
| Au | Choline chloride–urea (1:2) | Conventional heating in 80 °C | 5 nm | Growth media | [74] |
| Au | Choline chloride–urea (1:2) Choline chloride–ethylene glycol (1:2) | Conventional heating in 80 °C | 17.74–23.54 nm | Reaction medium, stabiliser | [75] |
| Au | Choline chloride–gallic acid–glycerol (1:0.25:0.25) | Conventional heating in 100 °C | 30–100 nm | Reaction medium, stabiliser, reducer | [76] |
| Au | trimethylglycine–glycolic acid Trimethylglycine–phenylacetic acid, trimethylglycine–glycerol | Conventional heating in 90 °C | 4–7 nm | Reaction medium, stabiliser | [71] |
| Ag | Choline chloride–ethylene glycol (1:2) | Conventional heating in 50 °C | Ag coatings 35 nm thick | Material used to disperse the silver layer on the nickel substrate | [72] |
| Au | Choline chloride–urea (1:2) | Conventional heating in 100 °C | 35.1–46.7 nm | Reaction medium | [77] |
| Ag | Choline nitrate–glycerol (1:2) Choline chloride–glycerol (1:2) Choline acetate–glycerol (1:2) | Conventional heating in 60–70 °C | 7.6–11.5 nm | Reaction medium | [73] |
| Ag | Silver triflate–acetamide (1:4) | Conventional heating in 70 °C | 9–16 nm | Reaction media, source of silver nanoparticles | [78] |
| Pt | Choline chloride–urea (1:2) | Conventional heating in 80 °C | Approx. 200 nm | Reaction medium, growth media | [79] |
5.4.2. Examples of Obtaining Metal Oxide Nanoparticles
| Material | Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents | Process Parameters of NDES Synthesis | Size of Nanoparticles | NDES Function | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag2O | Malonic acid–glucose (1:1) Malonic acid–fructose (1:1) | Evaporation in a vacuum at 50 °C | 95.42–185.99 nm | Reaction medium, stabiliser | [94] |
| CeO2 | Choline chloride–urea (1:2) Choline chloride–glycol ethylene (1:2) | Conventional heating at 80 °C | 10–30 nm | Ionothermal reaction medium | [92] |
| Cu2O | Choline chloride-ethylene glycol (1:2) | Conventional heating at 100 °C | 116.2–148.2 nm | Reaction medium, stabiliser | [95] |
| Cu2O on TiO2 | Choline chloride and urea (1:2) | Conventional heating at 60 °C | 1.2–2.0 nm | Reaction medium | [96] |
| Fe2O3 | Choline chloride–urea (1:2) | Conventional heating at 80 °C | 180 nm | Ionothermal reaction medium | [63] |
| Fe3O4 | Choline chloride–urea (1:2) | Conventional heating at 80 °C | 11 nm | Reaction medium, stabiliser | [83] |
| Mg, Co, Ni ferrite | Choline chloride–maleic acid (1:1) Choline chloride–oxalic acid (1:1) n,n’-Dimethylurea–citric acid (7:2) | Heated up to 80 °C in an aluminium heating block | 120–480 nm | Reaction medium, stabiliser | [89] |
| MnxOy | Choline chloride-glucose (1:2) Choline chloride–ethylene glycol–glucose (1:1:1) | Conventional heating at 58–60 °C | 1300 nm | Reaction medium, stabiliser | [97] |
| Mn3O4 | Choline chloride–ethylene glycol (1:2) | Conventional heating at 90 °C | 18 nm | Reaction medium, stabiliser | [84] |
| NiO | Choline chloride–urea (1:2) | Conventional, 80 °C | 100 nm | Reaction medium | [98] |
| SnO2 | Choline chloride–urea (1:2) | Conventional, 80 °C | 4–10 nm | Reaction medium | [85] |
| TiO2 | Choline chloride–succinic acid (1:1) | Conventional heating at 80–100 °C | 40–65 nm | Reaction medium, stabiliser | [87] |
| ZnO | Choline chloride–urea (1:2) | Mixing in a glovebox with an argon atmosphere | 60–650 nm | Reaction medium, stabiliser, solvent of ZnO | [86] |
| ZnO | Choline chloride–ethylene glycol (1:2) | Conventional heating at 80 °C | 30 nm | Ionothermal reaction medium | [81] |
| ZnO | Betaine and phenol (1:2) | Conventional heating at 30–40 °C, 30 min | 100 nm | Reaction medium | [13] |
| ZrOx MnOx CuO | Choline chloride–urea (1:2) | Conventional heating at 60 °C, 1 h | 19.16 nm 49.46 nm 44.22 nm | Reaction medium | [93] |
5.4.3. Examples of Obtaining Salt Nanoparticles and Other Inorganic Nanoparticles
| Material | Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents | Process Parameters of Synthesis of NDES | Size of Nanoparticles | NDES Function | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amorphous Ca3(PO4)2 | Choline chloride–urea (1:2) Choline chloride–ethylene glycol (1:2) Choline chloride–glycerol (1:2) | Conventional heating at 100 °C | 24–39 nm | Reaction medium, stabiliser | [62] |
| MgFe2O4 | Choline chloride–malonic acid (1:1) Choline chloride–oxalic acid (1:1) Choline chloride–urea (1:2) Choline chloride–ethylene glycol (1:2) Choline chloride–fructose (2:1) | Conventional heating at 25–80 °C | <100 nm | Reaction medium, stabiliser | [55] |
| (Mg, Sr, Zn)3(PO4)2 | Choline chloride–fructose-H2O (5:2:5) Choline chloride–glucose-H2O (5:2:5) Choline chloride–sucrose-H2O (4:1:4) | Heated at 80 °C with continuous sonication | <500 nm | Reaction medium | [107] |
| CuCo2O4 | Choline chloride–urea 1:2 | Conventional heating at 60 °C | 10–45 nm | Reaction medium | [108] |
| FeMnO3 | Thymol–menthol (1:1) | Conventional heating at Tpok, 30 min | <100 nm | Reaction medium | [109] |
| HgS | Choline chloride–urea (1:2) | Conventional heating at 60 °C, 1 h | 23.51 nm | Reaction medium | [93] |
| CuCl | Choline chloride–urea (1:2) | Conventional heating at 74 °C | 50 nm | Reaction medium | [110] |
| (Ni(NH3)6Cl2, NiCl2, α-Ni(OH)2 and NiO | Choline chloride–urea (1:2) | Conventional heating at 80 °C | Approx. 100 nm | Ionothermal reaction medium, nucleation and growth control | [111] |
6. Current Limitations of Application of NDESs in Nanotechnology
- (a)
- Experiments that explore potential interrelationships between the properties of NDES components;
- (b)
- Carefully collecting, cataloguing and publishing all possible/practical physicochemical properties, especially for commonly studied compounds and constituents of DES (using reproducible synthesis protocols, carefully controlled storage of samples, detailed treatment, and pretreatment methods, etc.);
- (c)
- Processing such aggregated data and applying advanced computational techniques to find new correlations or empirical fits;
- (d)
- Undertaking much more in-depth studies on the coupling of liquid-phase dynamics to physical properties;
- (e)
- Taking a more detailed approach to understanding the nature and behaviour of esoteric hydrogen bond types/networks, particularly regarding the unusual behaviour of DES.
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santana, A.P.R.; Mora-Vargas, J.A.; Guimarães, T.G.S.; Amaral, C.D.B.; Oliveira, A.; Gonzalez, M.H. Sustainable Synthesis of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADES) by Different Methods. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 293, 111452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Achkar, T.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Fourmentin, S. Basics and Properties of Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, L.; Larm, N.E.; Baker, G.A. Batch and Flow Nanomanufacturing of Large Quantities of Colloidal Silver and Gold Nanocrystals Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 14679–14689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.; Ruck, M. Synthesis and Dissolution of Metal Oxides in Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2019, 25, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaji, R.; Ilangeswaran, D. Synthesis of Some Metal Nanoparticles Using the Effective Media of Choline Chloride Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 56, 3366–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel Solvent Properties of Choline Chloride/Urea Mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.G.; Jiang, Y.X.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Chen, S.P.; Sun, S.G. Shape-Controlled Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles in Deep Eutectic Solvents for Studies of Structure–Functionality Relationships in Electrocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 9100–9103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Mar Contreras-Gámez, M.; Galán-Martín, A.; Seixas, N.; da Costa Lopes, A.M.; Silvestre, A.; Castro, E. Deep Eutectic Solvents for Improved Biomass Pretreatment: Current Status and Future Prospective towards Sustainable Processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 369, 128396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Achkar, T.; Moura, L.; Moufawad, T.; Ruellan, S.; Panda, S.; Longuemart, S.; Legrand, F.X.; Costa Gomes, M.; Landy, D.; Greige-Gerges, H.; et al. New Generation of Supramolecular Mixtures: Characterization and Solubilization Studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 584, 119443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Álvarez, M.J.; García-Garrido, S.E.; Perrone, S.; García-Álvarez, J.; Capriati, V. Deep Eutectic Solvents and Heterogeneous Catalysis with Metallic Nanoparticles: A Powerful Partnership in Sustainable Synthesis. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 39, 100723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Kumar, A.; Rayavarapu, R.G. The Role of Deep Eutectic Solvents and Carrageenan in Synthesizing Biocompatible Anisotropic Metal Nanoparticles. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 924–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagle, D.V.; Zhao, H.; Baker, G.A. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Sustainable Media for Nanoscale and Functional Materials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2299–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, S.M.; Barzinjy, A.A.; Hamad, A.H.; Hamad, S.M. Betaine-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents Mediated Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles at Low Temperature. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 28951–28960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontrani, L.; Donia, D.T.; Maria Bauer, E.; Tagliatesta, P.; Carbone, M. Novel Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Type IV Deep Eutectic Solvents. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2023, 545, 121268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Lankin, D.C.; Chen, S.N.; Pauli, G.F. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents: Properties, Applications, and Perspectives. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.B.; Spittle, S.; Chen, B.; Poe, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klein, J.M.; Horton, A.; Adhikari, L.; Zelovich, T.; Doherty, B.W.; et al. Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1232–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; de la Guardia, M.; Andruch, V.; Vilková, M. Deep Eutectic Solvents vs Ionic Liquids: Similarities and Differences. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünlü, A.E.; Arlkaya, A.; Takaç, S. Use of Deep Eutectic Solvents as Catalyst: A Mini-Review. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, L.I.N.; Baião, V.; da Silva, W.; Brett, C.M.A. Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Production and Application of New Materials. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 10, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; van Spronsen, J.; Dai, Y.; Verberne, M.; Hollmann, F.; Arends, I.W.C.E.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R. Are Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents the Missing Link in Understanding Cellular Metabolism and Physiology? Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents as a New Extraction Media for Phenolic Metabolites in Carthamus Tinctorius, L. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6272–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, J.K.U.; Hadinoto, K. Deep Eutectic Solvent as Green Solvent in Extraction of Biological Macromolecules: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; He, H.; Zhang, S.; Fan, M. Hydrogen-Bonding Interactions in Pyridinium-Based Ionic Liquids and Dimethyl Sulfoxide Binary Systems: A Combined Experimental and Computational Study. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voroshylova, I.V.; Ferreira, E.S.C.; Koverga, V.A.; Pereira, C.M.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S. Structure and Noncovalent Interactions in Ionic Liquids Mixtures and Deep Eutectic Solvents. In Theoretical and Computational Approaches to Predicting Ionic Liquid Properties; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 105–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wang, C.; Yi, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Tan, Z. Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent Systems as a Pretreatment for Nanofibrillation of Ramie Fibers. Cellulose 2019, 26, 3069–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, S.; Lv, J.; Li, S.; Shi, Y.; Hu, D.; Ma, W. Large-Scale and Green Production of Multi-Layer Graphene in Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 4615–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, D.E.; Wright, L.A.; James, S.L.; Abbott, A.P. Efficient Continuous Synthesis of High Purity Deep Eutectic Solvents by Twin Screw Extrusion. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 4215–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Gu, C.D.; Wang, X.L.; Tu, J.P. Ionothermal Synthesis of Cobalt Iron Layered Double Hydroxides (LDHs) with Expanded Interlayer Spacing as Advanced Electrochemical Materials. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2014, 2, 17066–17076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, G.; Vian, M.; Cavalluzzi, M.M.; Franchini, C.; Corbo, F.; Lentini, G.; Chemat, F. Ultrasound and Deep Eutectic Solvents: An Efficient Combination to Tune the Mechanism of Steviol Glycosides Extraction. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 69, 105255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, A.P.R.; Andrade, D.F.; Guimarães, T.G.S.; Amaral, C.D.B.; Oliveira, A.; Gonzalez, M.H. Synthesis of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents Using a Mixture Design for Extraction of Animal and Plant Samples Prior to ICP-MS Analysis. Talanta 2020, 216, 120956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; He, H.; Dong, Q.; Wang, Y.; An, F.; Song, H. Structural and Rheological Properties of Nanocellulose with Different Polymorphs, Nanocelluloses I and II, Prepared by Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents from Sugarcane Bagasse. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 220, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Tsai, M.L.; Chen, C.W.; Sun, P.P.; Patel, A.K.; Singhania, R.R.; Nargotra, P.; Dong, C. Di Deep Eutectic Solvents as Promising Pretreatment Agents for Sustainable Lignocellulosic Biorefineries: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Gray, S. Design of Improved Deep Eutectic Solvents Using Hole Theory. ChemPhysChem 2006, 7, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho-Silva, V.H.; Coutinho, N.D.; Aquilanti, V. Temperature Dependence of Rate Processes beyond Arrhenius and Eyring: Activation and Transitivity. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigmatullin, R.R.; Osokin, S.I.; Smith, G. New Approach in the Description of Dielectric Relaxation Phenomenon: Correct and Interpretation of the Vogel–Fulcher–Tamman Equation. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2003, 15, 3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroso, I.M.; Paiva, A.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents from Choline Chloride and Betaine—Physicochemical Properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 241, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Xue, Z.; Mu, T. Eutectics: Formation, Properties, and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8596–8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietro, M.E.; Goloviznina, K.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; de Araujo Lima E Souza, G.; Costa Gomes, M.; Padua, A.A.H.; Mele, A. Lithium Salt Effects on the Liquid Structure of Choline Chloride-Urea Deep Eutectic Solvent. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 11835–11845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, D.; Münzner, P.; Gainaru, C.; Lunkenheimer, P.; Loidl, A.; Böhmer, R. Translational and Reorientational Dynamics in Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 154, 154501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, H.; Sharma, V.K.; Mitra, S. Can the Microscopic and Macroscopic Transport Phenomena in Deep Eutectic Solvents Be Reconciled? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 22854–22873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, S.; Eiden, P.; Beichel, W.; Slattery, J.M.; Beyersdorff, T.F.; Schubert, T.J.S.; Krossing, I. Temperature Dependence of the Viscosity and Conductivity of Mildly Functionalized and Non-Functionalized [Tf2N]−Ionic Liquids. ChemPhysChem 2011, 12, 2296–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basaiahgari, A.; Panda, S.; Gardas, R.L. Effect of Ethylene, Diethylene, and Triethylene Glycols and Glycerol on the Physicochemical Properties and Phase Behavior of Benzyltrimethyl and Benzyltributylammonium Chloride Based Deep Eutectic Solvents at 283.15-343.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2018, 63, 2613–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafie, M.H.; Yusof, R.; Gan, C.Y. Synthesis of Citric Acid Monohydrate-Choline Chloride Based Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) and Characterization of Their Physicochemical Properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 288, 111081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Peng, X.; Bi, Z.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, B.; Mu, T. Factors Affecting the Refractive Index of Amino Acid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Chem. Thermodyn. Therm. Anal. 2021, 3–4, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, K.; Bagh, F.S.G.; Mjalli, F.S.; AlNashef, I.M.; Hashim, M.A. Prediction of Refractive Index and Density of Deep Eutectic Solvents Using Atomic Contributions. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2013, 354, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leron, R.B.; Soriano, A.N.; Li, M.H. Densities and Refractive Indices of the Deep Eutectic Solvents (Choline Chloride + ethylene Glycol or Glycerol) and Their Aqueous Mixtures at the Temperature Ranging from 298.15 to 333.15 K. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2012, 43, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, F.; Percevault, L.; Paquin, L.; Limanton, E.; Lagrost, C.; Hapiot, P. Electron Transfer Kinetics in a Deep Eutectic Solvent. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, E.M.; Clark, J.A.; Soliman, J.; Derr, J.B.; Morales, M.; Vullev, V.I. Practical Aspects of Cyclic Voltammetry: How to Estimate Reduction Potentials when Irreversibility Prevails. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, H3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateli, I.M.; Abbott, A.P.; Jenkin, G.R.T.; Hartley, J.M. Electrochemical Oxidation as Alternative for Dissolution of Metal Oxides in Deep Eutectic Solvents. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 8360–8368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, J.; Li, G.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, X.; Mu, T. The Electrochemical Stability of Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents. Sci. China Chem. 2016, 59, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, O.J.; Walker, K.A.D. Graphene Functionalization for Biosensor Applications. In Silicon Carbide Biotechnology (Second Edition): A Biocompatible Semiconductor for Advanced Biomedical Devices and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 85–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnashef, I.; Manan, N.; Mjali, F. Cyclic Voltammetry of Metallic Acetylacetonate Salts in Quaternary Ammonium and Phosphonium Based Deep Eutectic. J. Solut. Chem. 2013, 42, 2329–2341. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Ma, Q.; Su, H.; Qiao, F.; Leung, P.; Shah, A.; Xu, Q. Redox Characteristics of Iron Ions in Different Deep Eutectic Solvents. Ionics 2020, 26, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baby, J.N.; Sriram, B.; Wang, S.-F.; George, M. Effect of Various Deep Eutectic Solvents on the Sustainable Synthesis of MgFe2O4 Nanoparticles for Simultaneous Electrochemical Determination of Nitrofurantoin and 4-Nitrophenol. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajardo-Parra, N.F.; Lubben, M.J.; Winnert, J.M.; Leiva, Á.; Brennecke, J.F.; Canales, R.I. Physicochemical Properties of Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents and Excess Properties of Their Pseudo-Binary Mixtures with 1-Butanol. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 133, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guender, A.V. A Comparative Analysis of the Stabilizing Properties of Nominal Income Growth Targeting. Econ. Lett. 2007, 95, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Hamad, A.; Hayyan, M.; AlSaadi, M.A.H.; Hashim, M.A. Potential Applications of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Nanotechnology. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 273, 551–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, S.; Shayanfar, A. Deep Eutectic Solvents for Pharmaceutical Formulation and Drug Delivery Applications. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2020, 25, 779–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bai, T.; Sun, Y.; Xin, B.; Zhang, S. Ionic Liquid/Deep Eutectic Solvent-Mediated Ni-Based Catalysts and Their Application in Water Splitting Electrocatalysis. Catalysts 2022, 12, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontrani, L.; Tagliatesta, P.; Donia, D.T.; Bauer, E.M.; Bonomo, M.; Carbone, M. Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Inorganic Materials Using Environmentally Friendly Media. Molecules 2022, 27, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Hesaraki, S.; Alizadeh, M.; Kazemzadeh, A. A Facile and Sustainable Method Based on Deep Eutectic Solvents toward Synthesis of Amorphous Calcium Phosphate Nanoparticles: The Effect of Using Various Solvents and Precursors on Physical Characteristics. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2016, 443, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.Q.; Tu, J.P.; Ge, X.; Wang, X.L.; Gu, C.D. One-Step Synthesis of Hematite Nanospindles from Choline Chloride/Urea Deep Eutectic Solvent with Highly Powerful Storage versus Lithium. J. Power Sources 2015, 274, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Hammond, O.S.; Mudring, A.-V. Chemical Communications Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectics as a Transformative Platform for the Synthesis of Nanomaterials. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.H.; Lee, J.S. Synthesis of Gold Microstructures with Surface Nanoroughness Using a Deep Eutectic Solvent for Catalytic and Diagnostic Applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 3753–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, Y.J.; Wang, L.; Han, J.; Wu, J.C.; Li, C.M.; Wang, Y. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents as Green and Biocompatible Reaction Medium for Carbonic Anhydrase Catalysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 190, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroso, I.M.; Craveiro, R.; Rocha, Â.; Dionísio, M.; Barreiros, S.; Reis, R.L.; Paiva, A.; Duarte, A.R.C. Design of Controlled Release Systems for THEDES—Therapeutic Deep Eutectic Solvents, Using Supercritical Fluid Technology. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 492, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkliang, F.; Siriwarin, B.; Yusakul, G.; Phaisan, S.; Sakdamas, A.; Chuphol, N.; Putalun, W.; Sakamoto, S. Biocompatible Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Extraction and Cellulolytic Enzyme-Mediated Transformation of Pueraria Mirifica Isoflavones: A Sustainable Approach for Increasing Health-Bioactive Constituents. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, H.; Huang, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Isolation of Transferrin by Imprinted Nanoparticles with Magnetic Deep Eutectic Solvents as Monomer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 6237–6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Vigier, K.D.O.; Royer, S.; Jerome, F. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Syntheses, Properties and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Crescenzo, A.; Tiecco, M.; Zappacosta, R.; Boncompagni, S.; di Profio, P.; Ettorre, V.; Fontana, A.; Germani, R.; Siani, G. Novel Zwitterionic Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents as Environmentally Friendly Media for Spontaneous Self-Assembly of Gold Nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 268, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; el Ttaib, K.; Frisch, G.; Ryder, K.S.; Weston, D. The Electrodeposition of Silver Composites Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 2443–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, L.; Larm, N.E.; Bhawawet, N.; Baker, G.A. Rapid Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles in a Halide-Free Deep Eutectic Solvent. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5725–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuwanshi, V.S.; Ochmann, M.; Hoell, A.; Polzer, F.; Rademann, K. Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Self-Assembly of Gold Nanoparticles: A SAXS, UV-Vis, and TEM Investigation. Langmuir 2014, 30, 6038–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirea, M.; Freitas, A.; Vasile, B.S.; Ghitulica, C.; Pereira, C.M.; Silva, F. Gold Nanowire Networks: Synthesis, Characterization, and Catalytic Activity. Langmuir 2011, 27, 3906–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahyari, F.A.; Tohidi, M.; Safavi, A. Synthesis of Gold Nanoflowers Using Deep Eutectic Solvent with High Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering Properties. Mater. Res. Express 2016, 3, 095006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stassi, S.; Cauda, V.; Canavese, G.; Manfredi, D.; Pirri, C.F. Synthesis and Characterization of Gold Nanostars as Filler of Tunneling Conductive Polymer Composites. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 2012, 2669–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, L.; Larm, N.E.; Baker, G.A. Argentous Deep Eutectic Solvent Approach for Scaling up the Production of Colloidal Silver Nanocrystals. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 11036–11043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Fan, Y.J.; Wang, H.H.; Tian, N.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Sun, S.G. Electrochemically Shape-Controlled Synthesis in Deep Eutectic Solvents of Pt Nanoflowers with Enhanced Activity for Ethanol Oxidation. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 76, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, S.K.; Sandhu, S.; Kaur, N.; Shahi, J.S.; Kaur, M.; Singh, V.; Singh, V. DES-Mediated Synthesis of ZnO Nanostructures with Exposed {0001} Facets: Photoluminescence and Photocatalytic Properties. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 18865–18873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cun, T.; Dong, C.; Huang, Q. Ionothermal Precipitation of Highly Dispersive ZnO Nanoparticles with Improved Photocatalytic Performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 384, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Row, K.H. Exploration of Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Mesoporous Silica Spheres as High-Performance Size Exclusion Chromatography Packing Materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xie, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, R. Synthesis of Spherical Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles by Co-Precipitation in Choline Chloride/Urea Deep Eutectic Solvent. Mater. Lett. 2013, 112, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Eshraghi, M.J. One-Pot and Green Synthesis of Mn3O4 Nanoparticles Using an All-in-One System (Solvent, Reactant and Template) Based on Ethaline Deep Eutectic Solvent. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 696, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.D.; Zheng, H.; Wang, X.L.; Tu, J.P. Superior Ethanol-Sensing Behavior Based on SnO2 Mesocrystals Incorporating Orthorhombic and Tetragonal Phases. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 9143–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.Y.; Hsu, Y.J.; Wong, D.S.H.; Lu, S.Y. Growth of ZnO Nanostructures with Controllable Morphology Using a Facile Green Antisolvent Method. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 8867–8872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Ozasa, K.; Kitamura, F.; Katsumata, K.I.; Maeda, M.; Okada, K.; Matsushita, N. Self-Organization of TiO2 Nanobamboos by Anodization with Deep Eutectic Solvent. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 153, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winiarski, J.; Niciejewska, A.; Ornik, M.G.; Jakubowski, J.; Tylus, W.; Szczygieł, B. Titanium Anodizing in a Choline Dihydrogencitrate Salt-Oxalic Acid Deep Eutectic Solvent: A Step towards Green Chemistry in Surface Finishing of Titanium and Its Alloys. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 21104–21115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sçldner, A.; Ach, J.; Iwanow, M.; Gärtner, T.; Schlosser, M.; Pfitzner, A.; Çnig, B. Preparation of Magnesium, Cobalt and Nickel Ferrite Nanoparticles from Metal Oxides Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Chem. European J. 2016, 22, 13108–13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Gu, C.D.; Wang, X.L.; Tu, J.P. Endowing Manganese Oxide with Fast Adsorption Ability through Controlling the Manganese Carbonate Precursor Assembled in Ionic Liquid. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 438, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xie, S.; Huang, X.; Qiu, X. Ionothermal Synthesis of Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles as Efficient Heterogeneous Fenton-like Catalysts for Degradation of Organic Pollutants with H2O2. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, O.S.; Edler, K.J.; Bowron, D.T.; Torrente-Murciano, L. Deep Eutectic-Solvothermal Synthesis of Nanostructured Ceria. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, R.; Ilangeswaran, D. Choline Chloride—Urea Deep Eutectic Solvent an Efficient Media for the Preparation of Metal Nanoparticles. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 100446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarjuna, K.; Ilangeswaran, D. Preparation and Physico-Chemical Studies of Ag2O Nanoparticles Using Newly Formed Malonic Acid and ZnCl2-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Mater Today Proc. 2021, 49, 2943–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yan, Y.; Sun, W.; Shi, X.; Shi, N.; Huo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Said, Z.; Sharifpur, M. Preparation and Thermophysical Study on a Super Stable Copper Oxide/Deep Eutectic Solvent Nanofluid. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 356, 119020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohite, S.v.; Kim, S.; Lee, C.; Bae, J.; Kim, Y. Z-Scheme Heterojunction Photocatalyst: Deep Eutectic Solvents-Assisted Synthesis of Cu2O Nanocluster Improved Hydrogen Production of TiO2. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 928, 167168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruchamy, K.; Maalige, R.; Halanur, M.M.; Mahto, A.; Nagaraj, R.; Kalpana, D.; Ghosh, D.; Mondal, D.; Nataraj, S.K. Ultrafast Synthesis of Exfoliated Manganese Oxides in Deep Eutectic Solvents for Water Purification and Energy Storage. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorat, G.M.; Jadhav, A.H.; Jadhav, H.S.; Lee, K.; Seo, J.G. Template-Free Synthesis and Characterization of Nickel Oxide Nanocrystal with High-Energy Facets in Deep Eutectic Solvent. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 11009–11013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wei, X.; Tang, H.; Munyemana, J.C.; Guan, M.; Zhang, S.; Qiu, H. Deep Eutectic Solvents-Assisted Synthesis of ZnCo2O4 Nanosheets as Peroxidase-like Nanozyme and Its Application in Colorimetric Logic Gate. Talanta 2021, 222, 121680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, S.H.; Ruddy, D.A.; Pylypenko, S.; Richards, R.M. Deep Eutectic Solvent Approach towards Nickel/Nickel Nitride Nanocomposites. Catal. Today 2018, 306, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yu, Y.; Cao, L.; Su, G.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y. Synthesis of Monoclinic Structured BiVO4 Spindly Microtubes in Deep Eutectic Solvent and Their Application for Dye Degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, Z.; Abdollahi, S.H.; Safavi, A. Sugar-Based Natural Deep Eutectic Mixtures as Green Intercalating Solvents for High-Yield Preparation of Stable MoS2 Nanosheets: Application to Electrocatalysis of Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018, 1, 5896–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Doert, T.; Ruck, M. Synthesis of Metal Sulfides from a Deep Eutectic Solvent Precursor (DESP). Z Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2017, 643, 1913–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Kong, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, J.P.; Dong, J.X.; Lin, Z. Ionothermal Synthesis of a Three-Dimensional Zinc Phosphate with DFT Topology Using Unstable Deep-Eutectic Solvent as Template-Delivery Agent. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 115, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Wei, H.; Dong, M.; Wang, J.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Li, J.; Dong, J.; Morris, R.E. Ionothermal Synthesis of Zirconium Phosphates and Their Catalytic Behavior in the Selective Oxidation of Cyclohexane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 2206–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, M.; Hesaraki, S.; Alizadeh, M.; Kazemzadeh, A. One-Pot and Sustainable Synthesis of Nanocrystalline Hydroxyapatite Powders Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Mater. Lett. 2016, 175, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraj, D.; Pradeepkumar, P.; Rajan, M. Synthesis of Morphology Tuning Multi Mineral Substituted Apatite Nanocrystals by Novel Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents. Mater. Discov. 2017, 9, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.K.; Karade, S.S.; Maile, N.C.; Yadav, H.M.; Ghodake, G.S.; Jagadale, A.D.; Kim, D.Y. Green Synthesis of Novel CuCo2O4 Nanocomposite for Stable Hybrid Supercapacitors by Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 116390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherlin, V.A.; Joseph, X.B.; Wang, S.-F.; Baby, J.N.; George, M. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent Assisted Synthesis of FeMnO3 Entrapped Functionalized Carbon Nanofiber Composite: An Electrochemical Detection of Nimesulide. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 367, 120421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Shen, F.; La, J.; Luo, G.; Lai, J.; Liu, C.; Chu, G. Synthesis and Characterization of CuCl Nanoparticles in Deep Eutectic Solvents. Part. Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Gu, C.D.; Lu, Y.; Wanga, X.L.; Tua, J.P. A Versatile Protocol for the Ionothermal Synthesis of Nanostructured Nickel Compounds as Energy Storage Materials from a Choline Chloride-Based Ionic Liquid. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2013, 1, 13454–14461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolmachev, D.; Lukasheva, N.; Ramazanov, R.; Nazarychev, V.; Borzdun, N.; Volgin, I.; Andreeva, M.; Glova, A.; Melnikova, S.; Dobrovskiy, A.; et al. Computer Simulations of Deep Eutectic Solvents: Challenges, Solutions, and Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, X.-T.; Ma, E.-Q.; Mo, L.-P.; Zhang, Z.-H. Superparamagnetic CuFeO2 Nanoparticles in Deep Eutectic Solvent: An Efficient and Recyclable Catalytic System for the Synthesis of Imidazo[1,2-a]Pyridines. ChemCatChem 2014, 6, 2854–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukesh, C.; Mondal, D.; Sharma, M.; Prasad, K. Choline Chloride–Thiourea, a Deep Eutectic Solvent for the Production of Chitin Nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Y.; Yao, X. Recycling of Deep Eutectic Solvent for Sustainable and Efficient Pretreatment of Corncob. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 183, 115005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type | Composition |
|---|---|
| Type I | Organic salt + metal chloride (e.g., choline chloride–) |
| Type II | Organic salt + metal chloride hydrate (e.g., choline chloride–) |
| Type III | Organic salt + hydrogen bond donor (e.g., choline chloride–urea) |
| Type IV | Hydrogen bond donor + metal chloride hydrate (e.g., urea–) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Długosz, O. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents in the Synthesis of Inorganic Nanoparticles. Materials 2023, 16, 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020627
Długosz O. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents in the Synthesis of Inorganic Nanoparticles. Materials. 2023; 16(2):627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020627
Chicago/Turabian StyleDługosz, Olga. 2023. "Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents in the Synthesis of Inorganic Nanoparticles" Materials 16, no. 2: 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020627
APA StyleDługosz, O. (2023). Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents in the Synthesis of Inorganic Nanoparticles. Materials, 16(2), 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020627





