Waste Polyurethane Foams as Biomass Carriers in the Treatment Process of Domestic Sewage with Increased Ammonium Nitrogen Content
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Materials
2.1.1. Biological Material
2.1.2. Selection of the Type of Biomass Carriers
2.1.3. Batch Culture of Microorganisms
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Microbial Growth Rate Determination
2.2.2. Selection of the Type of Biomass Carriers
2.2.3. Ammonium Nitrogen Removal in Continuous Cultures
2.3. Determinations
2.3.1. Optical Density Determination
2.3.2. Biomass Content in the Tested Carriers
2.3.3. Microscopic Observations of Biomass
2.3.4. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Observations
2.3.5. Illumina Sequencing of 16S rRNA Gene
2.3.6. 16S rRNA Gene Sequence Analysis
2.3.7. The Efficiency of the Nitrogen Removal Process
2.4. Statistical Analyzes
3. Results and Discussion
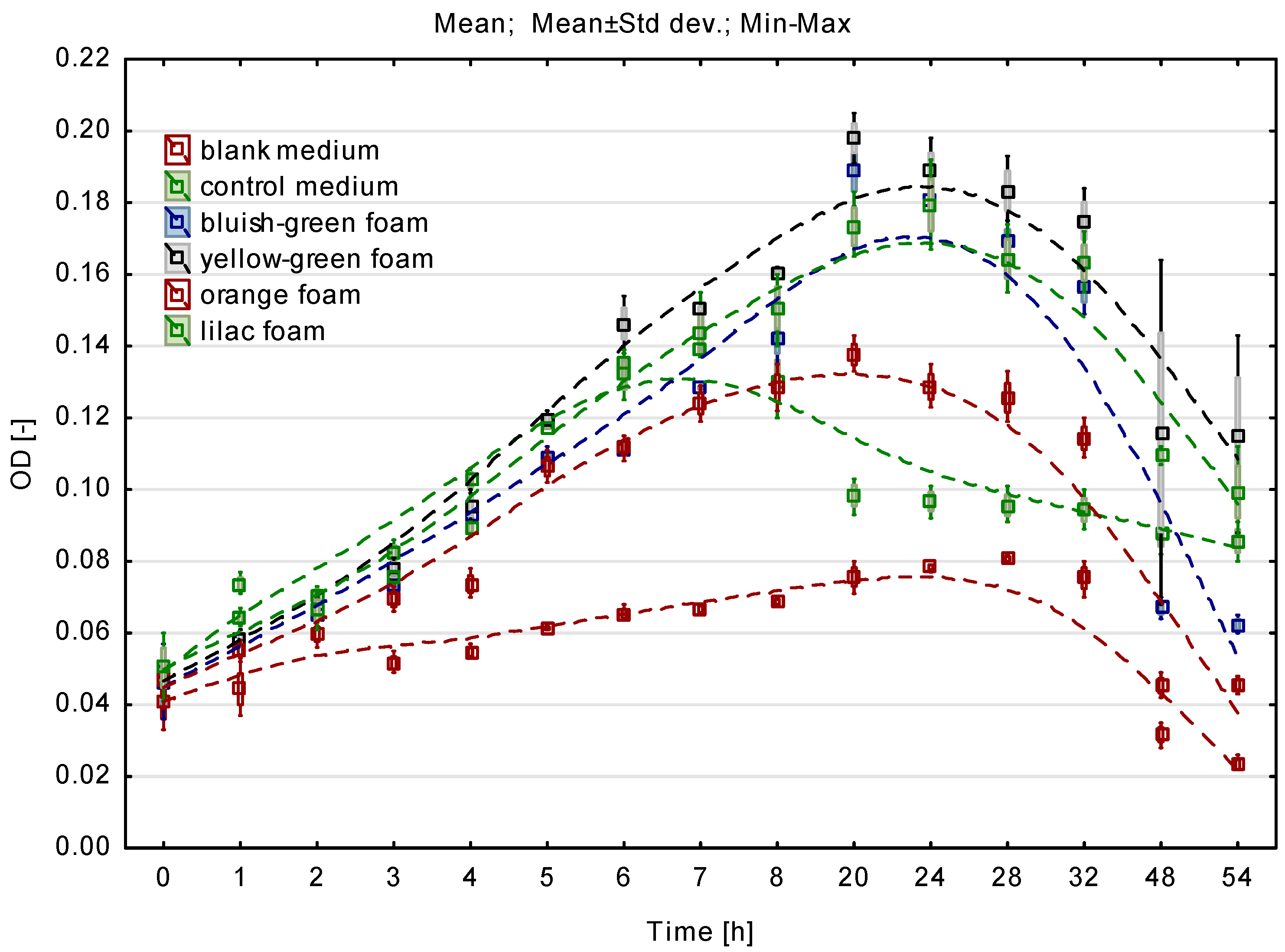
3.1. Microbial Growth Rate Determination
3.2. Selection of the Type of Biomass Carriers
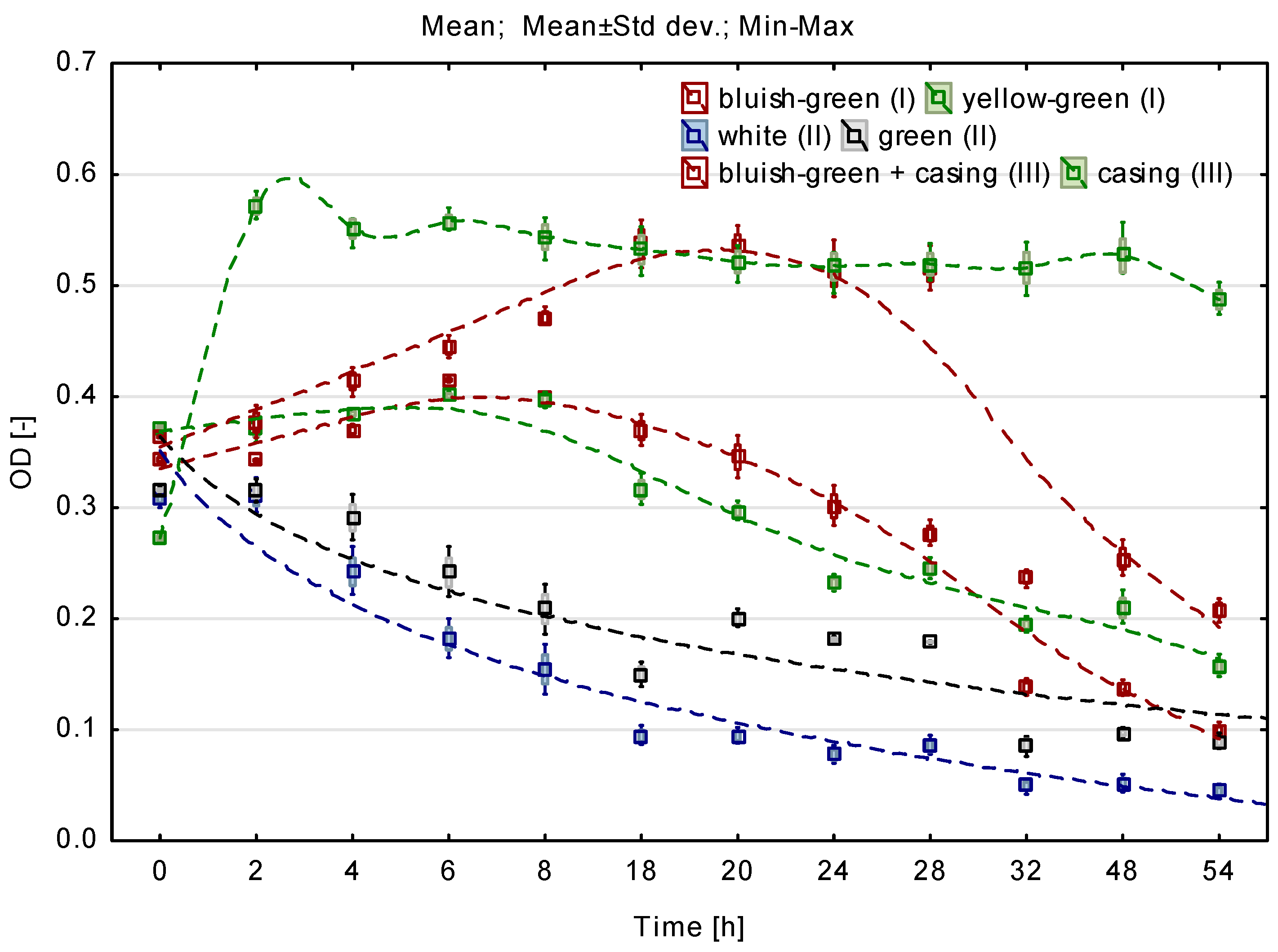
3.3. Ammonium Nitrogen Removal in Continuous Cultures
3.4. Microscopic Observations of Biomass
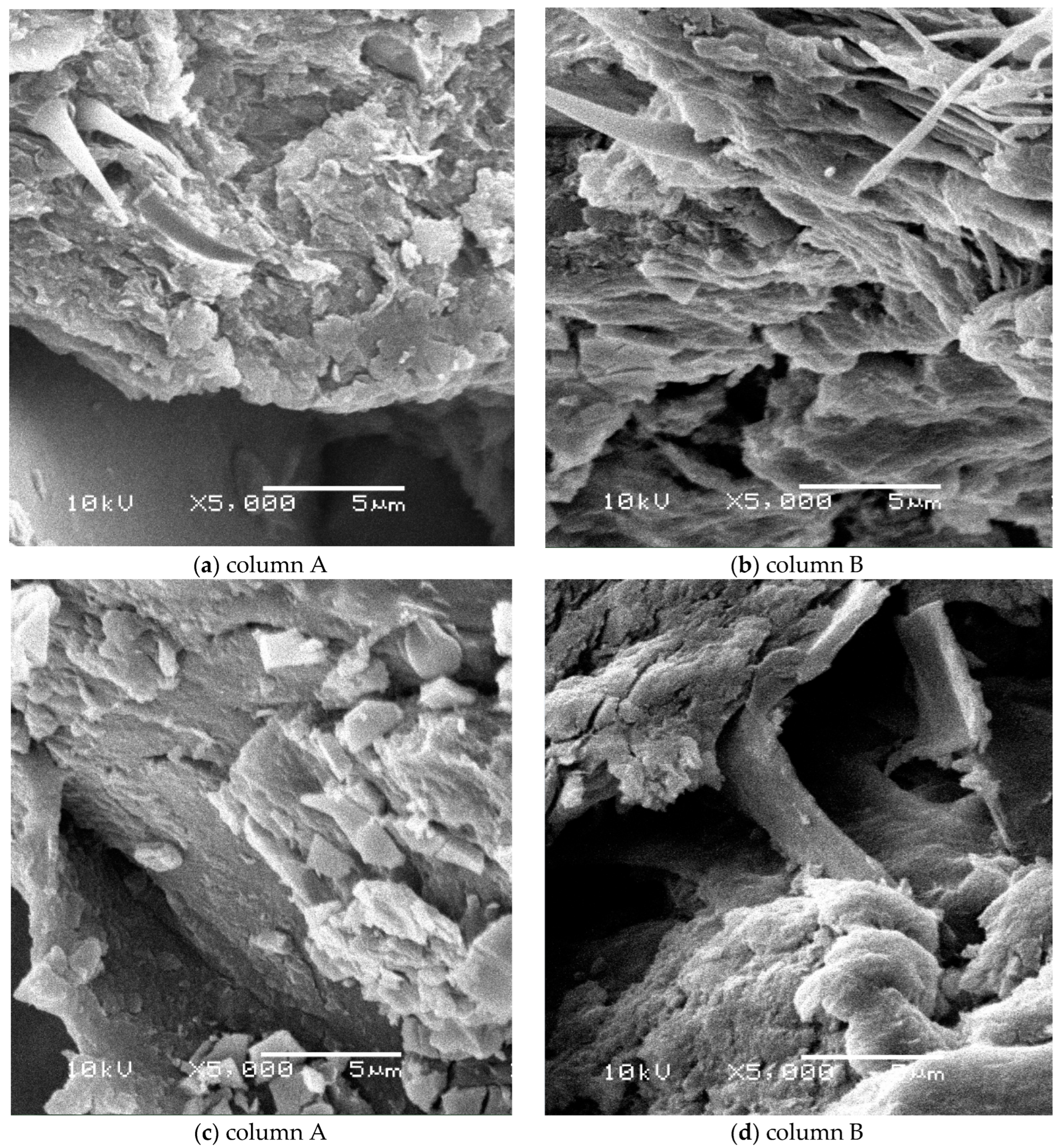
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Observations
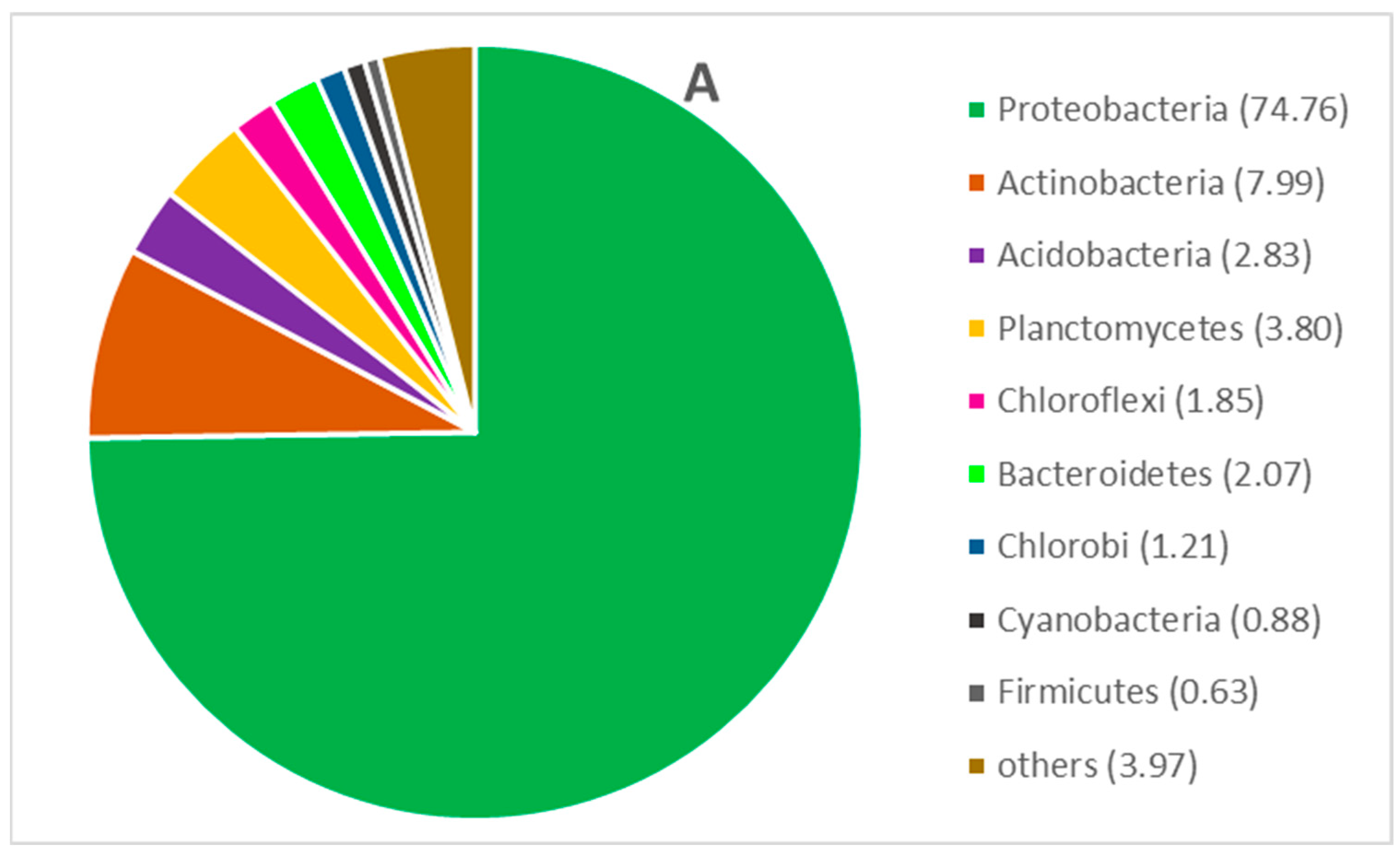
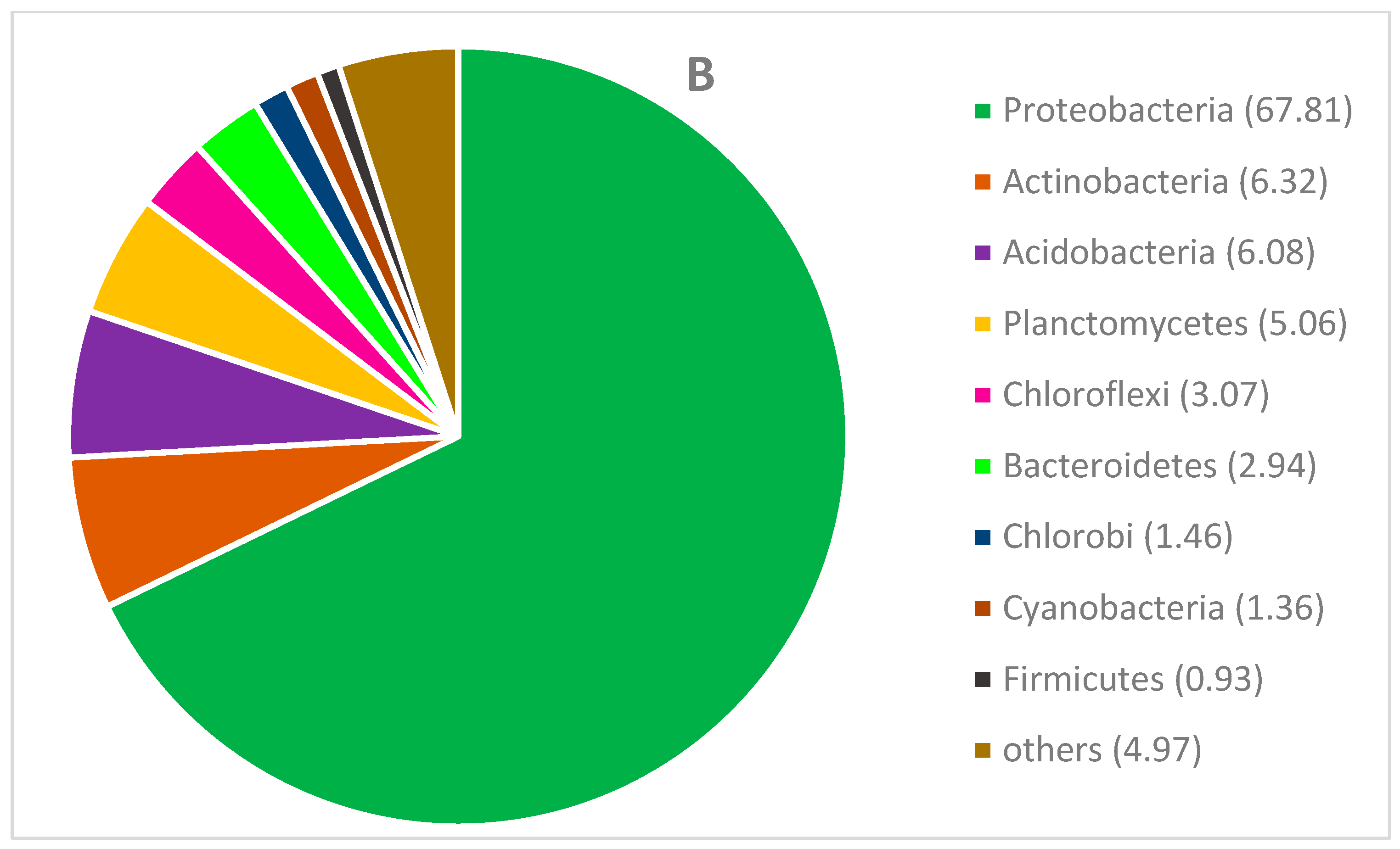
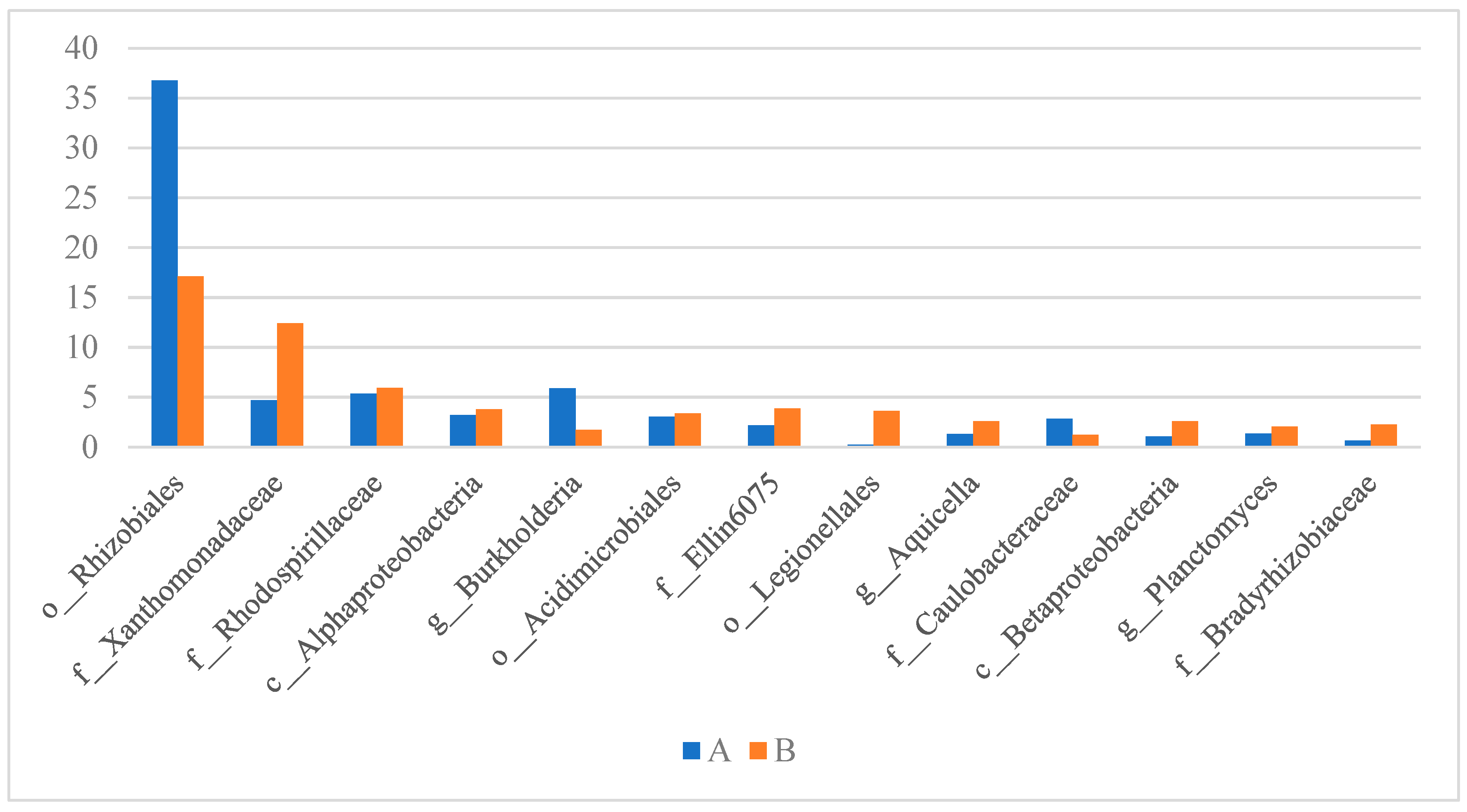
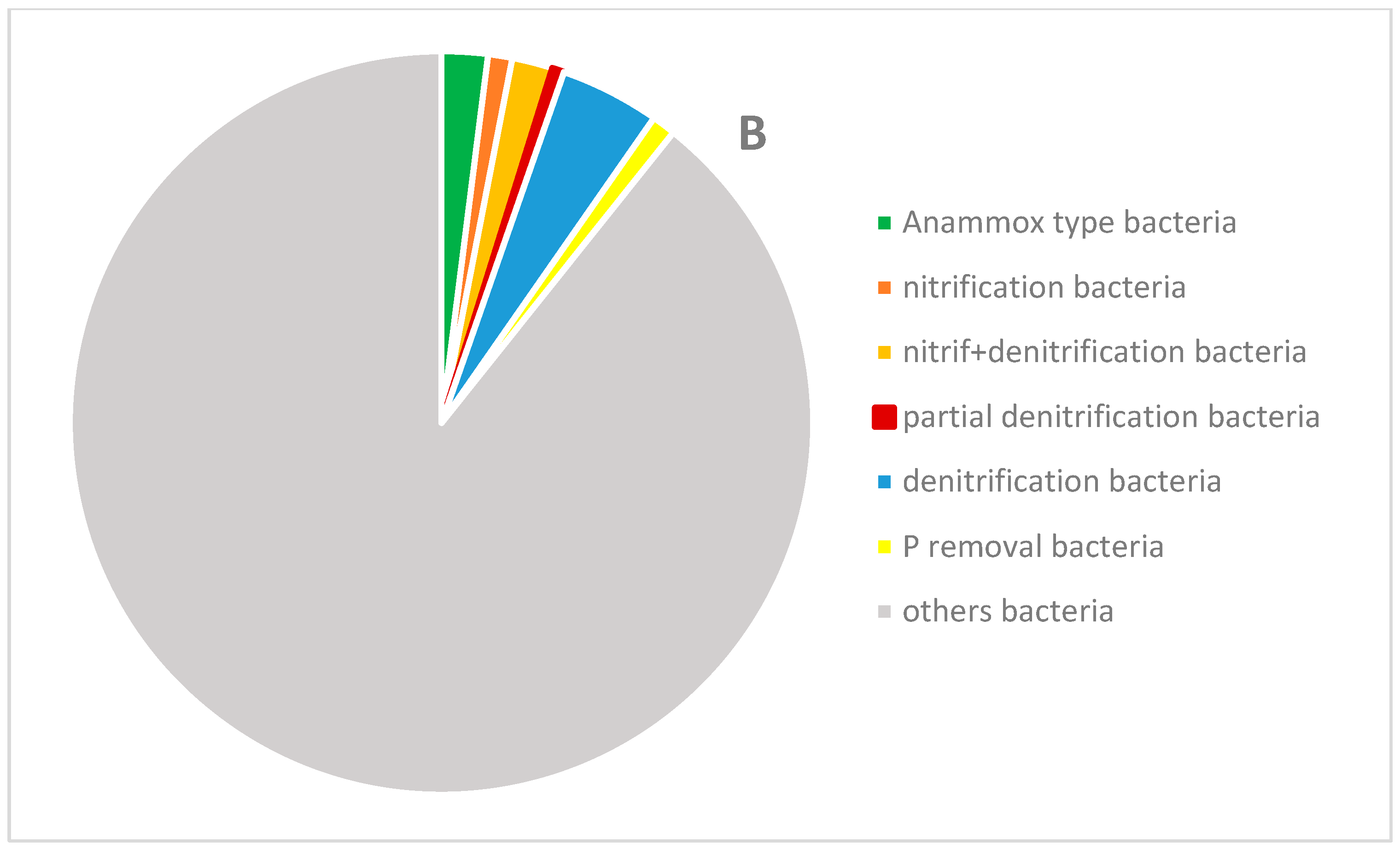
3.6. Microbial Community Analysis
3.7. Efficiency of Ammonium Nitrogen Removal Process
4. Possible Future Prospects Associated with the Use of Waste PUF as Biomass Carriers
5. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lou, W.Y.; Fernández-Lucas, J.; Ge, J.; Wu, C. Enzyme or whole cell immobilization for efficient biocatalysis: Focusing on novel supporting platforms and immobilization techniques. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 620292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Amshawee, S.; Yunus, M.Y.B.M.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Tran, N.H. Biocarriers for biofilm immobilization in wastewater treatments: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1925–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracconi, M.; Ambrosetti, M.; Maestri, M.; Groppi, G.; Tronconi, E. A systematic procedure for the virtual reconstruction of open-cell foams. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 315, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, S.C.S.; Martins, C.M.; Fiúza, L.M.C.G.; Santaella, S.T. Immobilization of microbial cells: A promising tool for treatment of toxic pollutants in industrial wastewater. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 4412–4418. [Google Scholar]
- Varesche, M.; Zaiat, M.; Vieira, L.; Vazoller, R.; Foresti, E. Characterization of Anaerobic Biomass Immobilized in Polyurethane Foam Matrices from HAIS Reactor by Scanning Electron Microscopy; Universidade de São Paulo: Ribeirão Preto, Brazil, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Lu, H.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, C. Aerobic biodegradation of nitrobenzene by a defined microbial consortium immobilized in polyurethane foam. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, S.; Okubo, T.; Maeno, K.; Takahashi, M.; Kubota, K.; Harada, H. Evaluation of water distribution and oxygen mass transfer in sponge support media for a down-flow hanging sponge reactor. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2016, 10, 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Dacewicz, E.; Grzybowska-Pietras, J. Polyurethane foams for domestic sewage treatment. Materials 2021, 14, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandrello, M.J.; Tomás, M.S.J.; Raimondo, E.E.; Vullo, D.L.; Ferrero, M.A. Petroleum oil removal by immobilized bacterial cells on polyurethane foam under different temperature conditions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setty, Y.P. Multistage fluidized bed bioreactor for dye decolorization using immobilized polyurethane foam: A novel approach. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 152, 107368. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, R.; Prabhavathi, P.; Karthiksundaram, S.; Pattabi, S.; Kumar, S.D.; Santhanam, P. Biodecolorization and bioremediation of denim industrial wastewater by adapted bacterial consortium immobilized on inert polyurethane foam (PUF) matrix: A first approach with biobarrier model. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qin, J.; Zhao, Q.; Ye, Z. Treatment of dairy wastewater by immobilized microbial technology using polyurethane foam as carrier. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharjan, N.; Hewawasam, C.; Hatamoto, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Harada, H.; Araki, N. Downflow hanging sponge system: A self-sustaining option for wastewater treatment. In Promising Techniques for Wastewater Treatment and Water Quality Assessment; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Akindoyo, J.O.; Beg, M.D.; Ghazali, S.; Islam, M.R.; Jeyaratnam, N.; Yuvaraj, A.R. Polyurethane types, synthesis and applications—A review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 114453–114482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Gracida-Alvarez, U.R.; Gallant, E.T.; Gillis, P.A.; Marques, Y.A.; Abramo, G.P.; Dunn, J.B. Material flows of polyurethane in the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 14215–14224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markets. 2022. Available online: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=151784541 (accessed on 22 April 2022).
- Dacewicz, E.; Jurik, Ľ. Application of a double layer sand filter with a PUR foams layer in the treatment of domestic sewage with an increased content of ammonia nitrogen. Acta Sci. Pol. Form. Circumiectus 2019, 2, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacewicz, E. Waste assessment decision support systems used for domestic sewage treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 31, 100885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacewicz, E. Application of selective and porous materials for the removal of biogenic compounds and indicator bacteria from domestic wastewater. Acta Sci. Pol. Form. Circumiectus 2018, 17, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, J.; Tummala, A.; Kapadia, C.; Dandamudi, M.; Belovich, J.M. Procedure to quantify biofilm activity in carriers used in wastewater treatment systems. J. Environ. Eng. 2006, 132, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacewicz, E.; Chmielowski, K. Application of multidimensional clustering for an assessment of pollutants removal from domestic wastewater using a filter with a plastic waste filling. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 29, 100794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, M.J.; Muyzer, G.; Ward, D.M. Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis profiles of 16S rRNA-defined populations inhabiting a hot spring microbial mat community. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illumina Technology. 2022. Available online: https://www.illumina.com/science/technology/next-generation-sequencing/beginners/ngs-workflow.html (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Illumina Products. 2022. Available online: https://www.illumina.com/documents/products/techspotlights/techspotlight_sequencing.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Chernov, T.I.; Tkhakakhova, A.K.; Kutovaya, O.V. Assessment of diversity indices for the characterization of the soil prokaryotic community by metagenomic analysis. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2015, 48, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacewicz, E. Impact of the sponge structure of a multilayer sand filter on the treatment of domestic sewage with an increased content of ammonia nitrogen. Acta Sci. Polonorum. Form. Circumiectus 2020, 19, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, S.; Suzuki, S.; Abe, K.; Kubota, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ohashi, A.; Harada, H. Removal of organic substances and oxidation of ammonium nitrogen by a down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) reactor under high salinity conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5180–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dacewicz, E. Application of the filtration bed with a foamsand filling for treatment of sewage with an elevated concentration of ammonia nitrogen. Infrastruct. Ecol. Rural Areas 2019, 1, 165–180. [Google Scholar]
- Onodera, T.; Matsunaga, K.; Kubota, K.; Taniguchi, R.; Harada, H.; Syutsubo, K.; Yamaguchi, T. Characterization of the retained sludge in a down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) reactor with emphasis on its low excess sludge production. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamoto, M.; Okubo, T.; Kubota, K.; Yamaguchi, T. Characterization of downflow hanging sponge reactors with regard to structure, process function, and microbial community compositions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 10345–10352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaoka, Y.; Hatamoto, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Syutsubo, K. Eukaryotic community shift in response to organic loading rate of an aerobic trickling filter (down-flow hanging sponge reactor) treating domestic sewage. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 73, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, T.; Takemura, Y.; Kubota, K.; Kato, R.; Okubo, T.; Kanaya, G.; Uemura, S. Evaluation of microbial community succession and trophic transfer using microscopic, molecular and stable isotope ratio analysis in a sponge-based sewage treatment system. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 171, 108002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.; Varesche, M.B.A.; Foresti, E.; Zaiat, M. Influence of the carbon source on the anaerobic biomass adhesion on polyurethane foam matrices. J. Environ. Manag. 2005, 74, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Wang, J. Comparison of polyurethane foam and biodegradable polymer as carriers in moving bed biofilm reactor for treating wastewater with a low C/N ratio. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machdar, I.; Onodera, T.; Syutsubo, K.; Ohashi, A. Effects of sponge pore-size on the performance of a down-flow hanging sponge reactor in post-treatment of effluent from an anaerobic reactor treating domestic wastewater. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2018, 28, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorado, A.D.; Lafuente, F.J.; Gabriel, D.; Gamisans, X. A comparative study based on physical characteristics of suitable packing materials in biofiltration. Environ. Technol. 2010, 31, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shade, A.; Peter, H.; Allison, S.D.; Baho, D.L.; Berga, M.; Bürgmann, H.; Huber, D.H.; Langenheder, S.; Lennon, J.T.; Martiny, J.B.; et al. Fundamentals of microbial community resistance and resilience. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, N.; Kuroda, K.; Dehama, K.; Hatamoto, M.; Yamaguchi, T. Development of slow sponge sand filter (SpSF) as a post-treatment of UASB-DHS reactor effluent treating municipal wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watari, T.; Mai, T.C.; Tanikawa, D.; Hirakata, Y.; Hatamoto, M.; Syutsubo, K.; Fukuda, M.; Nguyen, N.B.; Yamaguchi, T. Development of downflow hanging sponge (DHS) reactor as post treatment of existing combined anaerobic tank treating natural rubber processing wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watari, T.; Mai, T.C.; Tanikawa, D.; Hirakata, Y.; Hatamoto, M.; Syutsubo, K.; Fukuda, M.; Nguyen, N.B.; Yamaguchi, T. Performance of the pilot scale upflow anaerobic sludge blanket—Downflow hanging sponge system for natural rubber processing wastewater treatment in South Vietnam. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 237, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida Fernandes, L.; Pereira, A.D.; Leal, C.D.; Davenport, R.; Werner, D.; Filho, C.R.M.; Bressani-Ribeiro, T.; de Lemos Chernicharo, C.A.; de Araujo, J.C. Effect of temperature on microbial diversity and nitrogen removal performance of an anammox reactor treating anaerobically pretreated municipal wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 258, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, C.D.; Pereira, A.D.; Nunes, F.T.; Ferreira, L.O.; Coelho, A.C.; Bicalho, S.K.; Mac Conell, E.F.; Ribeiro, T.B.; de Lemos Chernicharo, C.A.; de Araujo, J.C. Anammox for nitrogen removal from anaerobically pre-treated municipal wastewater: Effect of COD/N ratios on process performance and bacterial community structure. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Yu, G.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, H.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.Y. Key factors governing the performance and microbial community of one-stage partial nitritation and anammox system with bio-carriers and airlift circulation. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 324, 124668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strous, M.; Heijnen, J.J.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M.S.M. The sequencing batch reactor as a powerful tool for the study of slowly growing anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing microorganisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 50, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.D.; Cabezas, A.; Etchebehere, C.; Chernicharo, C.A.; Araújo, J.C. Microbial communities in anammox reactors: A review. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2017, 6, 74–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, G. Chapter 10—The Rhizobium-Legume Nitrogen-Fixing Symbiosis. In Biology of the Nitrogen Cycle; Bothe, H., Ferguson, S.J., Newton, W.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 147–163. ISBN 9780444528575. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Li, J.; Wei-Xie, L.; Shao, L. Oligotrophic Nitrification and Denitrification Bacterial Communities in a Constructed Sewage Treatment Ecosystem and Nitrogen Removal of Delftia tsuruhatensis NF4. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Pang, Q.; Peng, F.; Zhang, A.; Zhou, Y.; Lian, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, C.; et al. Response Characteristics of Nitrifying Bacteria and Archaea Community Involved in Nitrogen Removal and Bioelectricity Generation in Integrated Tidal Flow Constructed Wetland-Microbial Fuel Cell. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhla, G.; Farooq, S. Simultaneous nitrification-denitrification in slow sand filters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 96, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac Conell, E.F.; Almeida, P.G.S.; Martins, K.E.L.; Araújo, J.C.; Chernicharo, C.A.L. Bacterial community involved in the nitrogen cycle in a down-flow sponge-based trickling filter treating UASB effluent. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riahi, H.S.; Heidarieh, P.; Fatahi-Bafghi, M. Genus Pseudonocardia: What we know about its biological properties, abilities and current application in biotechnology. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 890–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, N.; He, J.; Ma, X.; Peng, Y.; Li, X. Phosphorus removal performance and population structure of phosphorus-accumulating organisms in HA-A/A-MCO sludge reduction process. Bioengineered 2016, 7, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthonisen, A.C.; Loehr, R.C.; Prakasam, T.B.S.; Srinath, E.G. Inhibition of nitrification by ammonia and nitrous acid. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1976, 48, 835–852. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wei, W.; Sun, Y. Comparative study of wastewater treatment and nutrient recycle via activated sludge, microalgae and combination systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Zheng, L.; Gu, X. Partial nitrification performance and mechanism of zeolite biological aerated filter for ammonium wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarelli, D.; Rott, M.; Schlaeppi, K.; Ver Loren van Themaat, E.; Ahmadinejad, N.; Assenza, F.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Revealing structure and assembly cues for Arabidopsis root-inhabiting bacterial microbiota. Nature 2012, 488, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Zuo, J.; Zhao, D.; Zou, X.; Zhu, Z.; An, S. A hardy plant facilitates nitrogen removal via microbial communities in subsurface flow constructed wetlands in winter. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, K.; Hayashi, M.; Matsunaga, K.; Iguchi, A.; Ohashi, A.; Li, Y.Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Harada, H. Microbial community composition of a down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) reactor combined with an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor for the treatment of municipal sewage. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 151, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watari, T.; Vazquez, C.L.; Hatamoto, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; van Lier, J.B. Development of a single-stage mainstream anammox process using a sponge-bed trickling filter. Environ. Technol. 2021, 42, 3036–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strous, M.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M.S. Key physiology of anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 3248–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Ma, F.; Wei, L.; Chua, H.; Chang, C.C.; Zhang, X.J. Electricity generation from cattle dung using microbial fuel cell technology during anaerobic acidogenesis and the development of microbial populations. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, T.H.; Souza, T.S.; Varesche, M.B.A. Feeding strategies for enrichment and characterization of anammox biomass in a sequencing batch reactor. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 5, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Su, Y. Analysis of rapid culture of high-efficiency nitrifying bacteria and immobilized filler application for the treatment of municipal wastewater. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 19240–19246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Yang, Y.L.; Li, X.; Zhou, Z.W.; Liu, C.J.; Liu, Y.W.; Fan, X.Y. Intensified nitrogen removal by heterotrophic nitrification aerobic denitrification bacteria in two pilot-scale tidal flow constructed wetlands: Influence of influent C/N ratios and tidal strategies. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tu, Z.; Wu, S.; Yu, G.; Du, C.; Wang, H.; Li, H. Recent advances in partial denitrification-anaerobic ammonium oxidation process for mainstream municipal wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yang, L.; Liang, X. The characteristics of a novel heterotrophic nitrifying and aerobic denitrifying bacterium, Acinetobacter junii YB. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, Z.; Peng, Y.; Yang, A.; Zhang, S.; Li, B.; Wang, B.; Wang, S. Rapid nitrite production via partial denitrification: Pilot-scale operation and microbial community analysis. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirishima, Y.; Choeisai, P.; Khotwieng, W.; Hatamoto, M.; Watari, T.; Choeisai, K.; Panchaban, P.; Wong-asa, T.; Yamaguchi, T. Efficiency of high rate treatment of low-strength municipality sewage by a pilot-scale combination system of a sedimentation tank and a down-flow hanging sponge reactor. Environ. Technol. 2022, 43, 2457–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomoto, N.; Hatamoto, M.; Hirakata, Y.; Ali, M.; Jayaswal, K.; Iguchi, A.; Harada, H. Defining microbial community composition and seasonal variation in a sewage treatment plant in India using a down-flow hanging sponge reactor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 4381–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
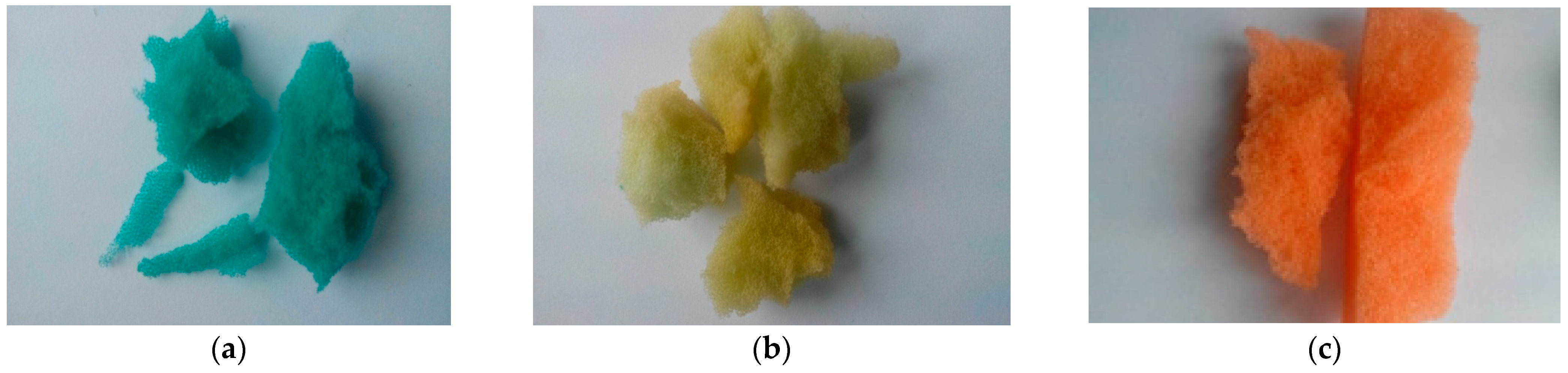

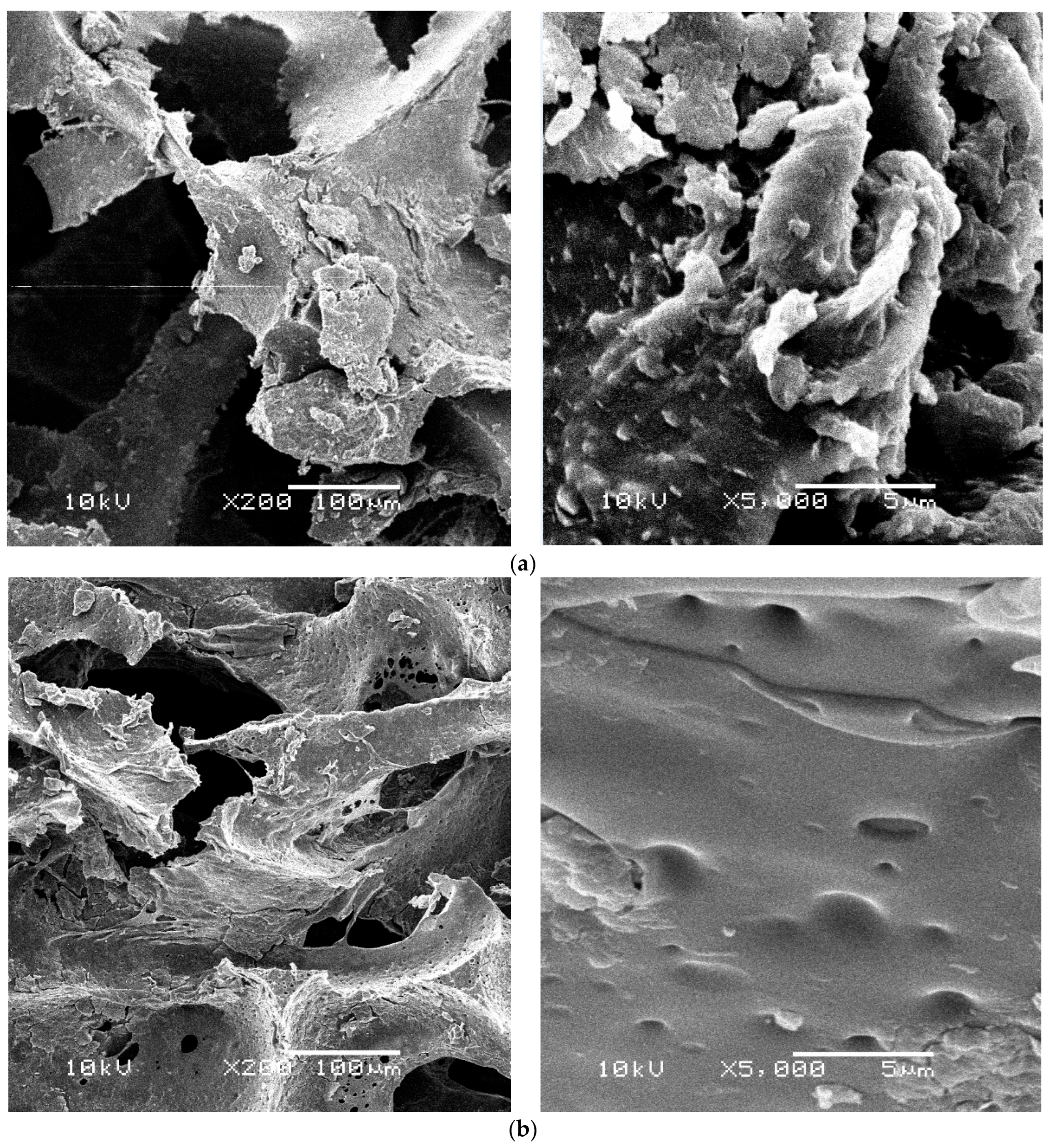
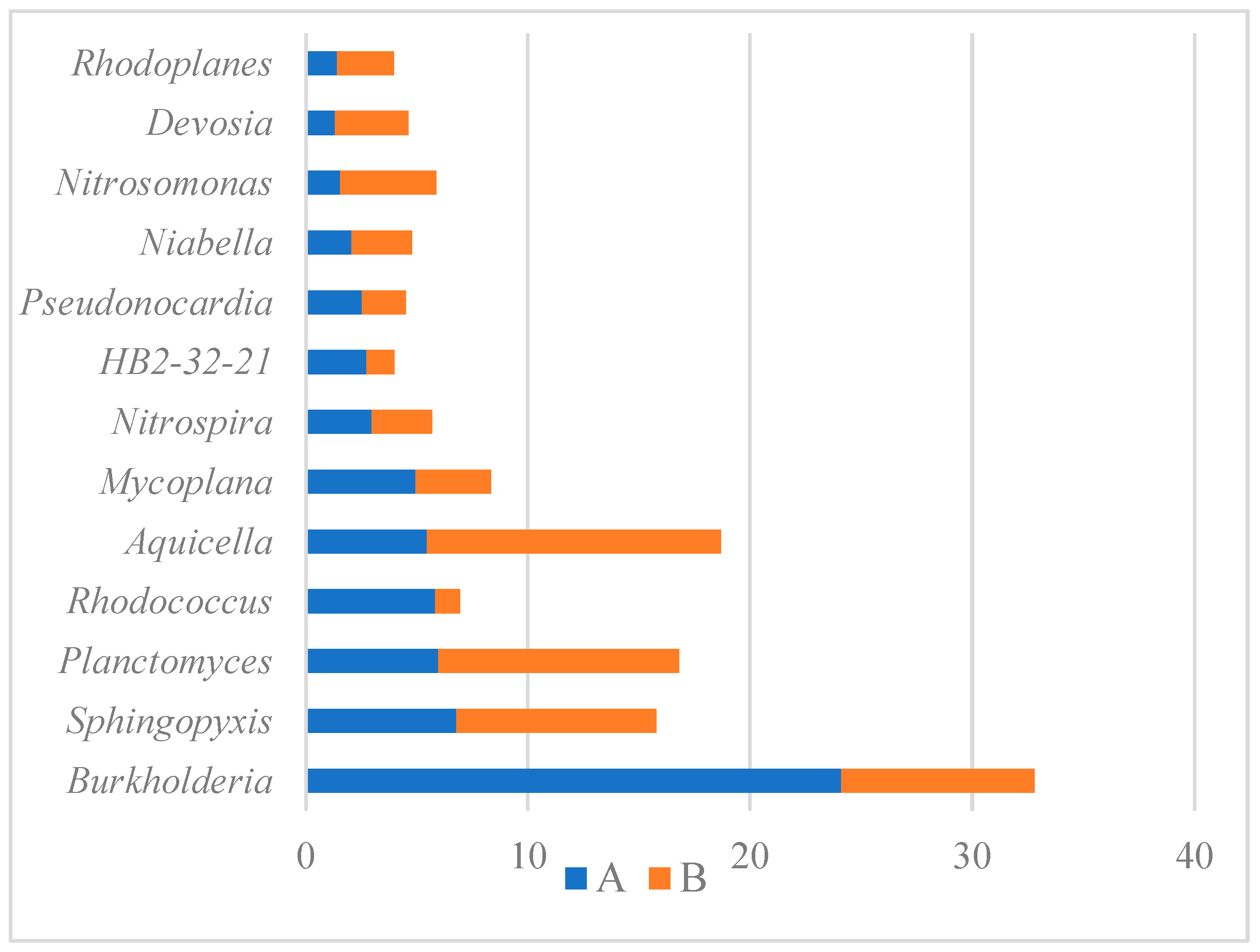
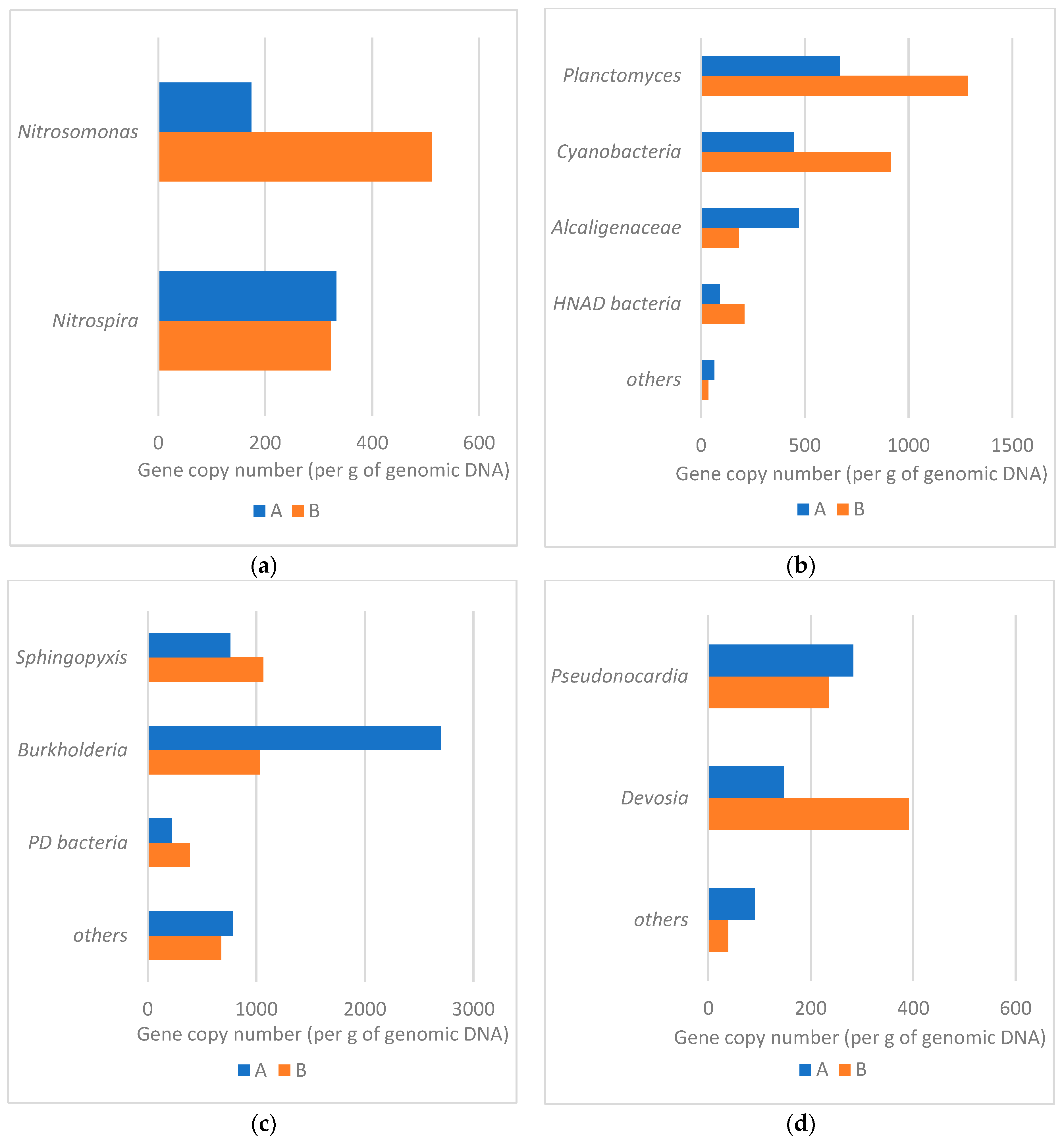
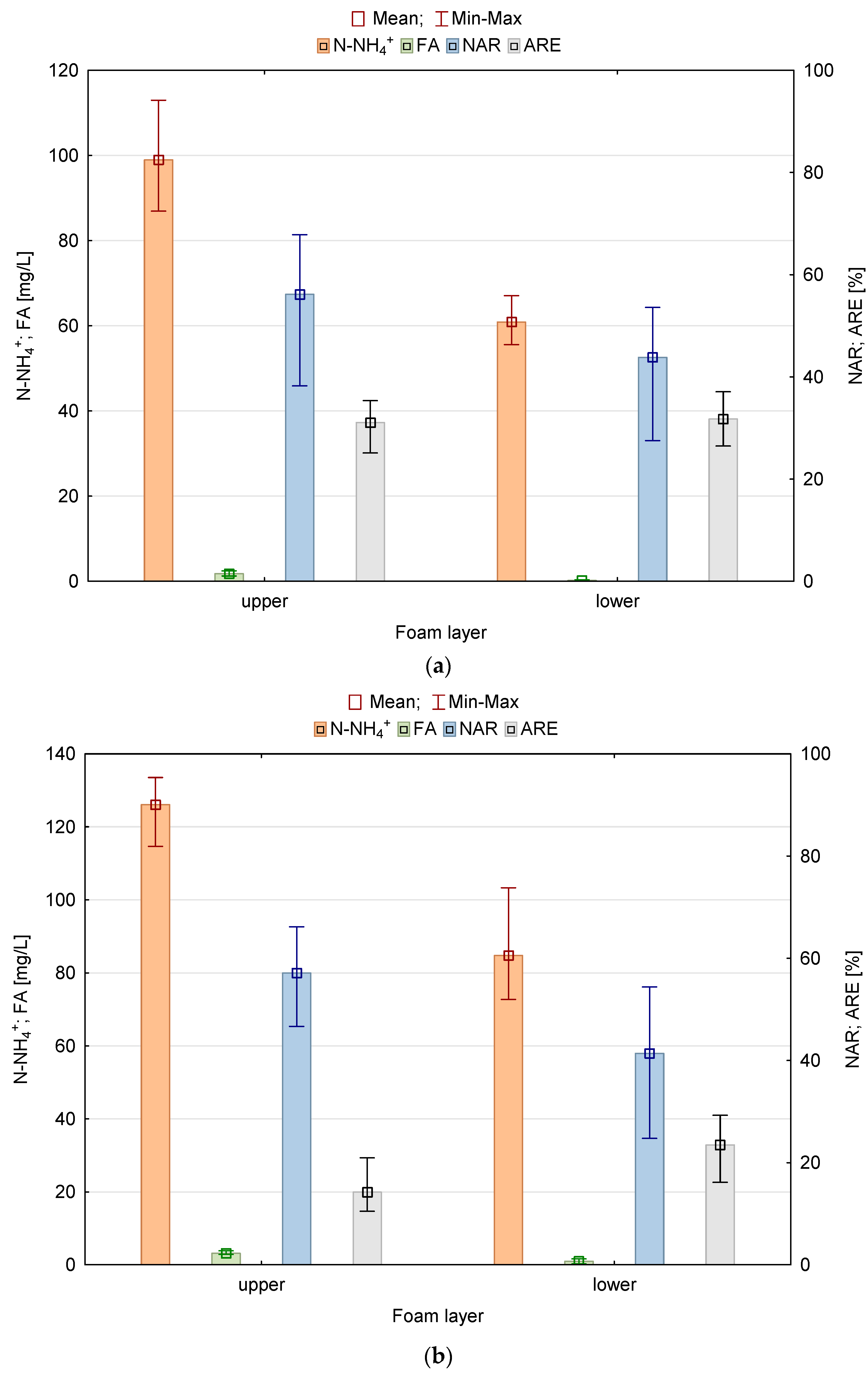
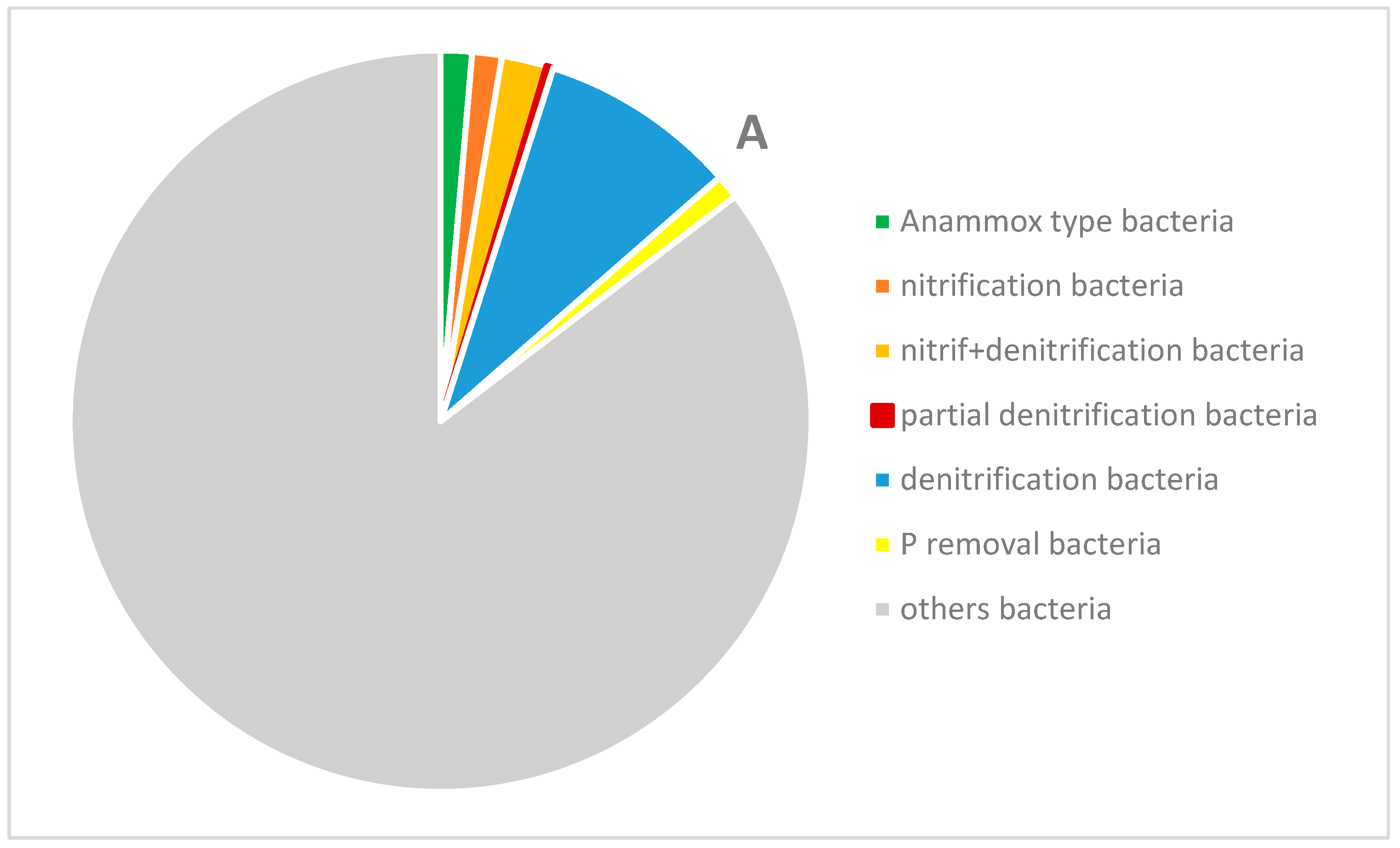
| Amount of Biomass [g/1 g of Weighed Amount] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Yellow-Green Foam | Bluish-Green Foam | Orange Foam | Lilac Foam |
| 0.193 | 0.224 | 0.060 | 0.071 |
| Groups | Type of Filling | Biomass [g/1 g of Weighed Sample] |
|---|---|---|
| I | soft bluish-green foam | 0.2120 |
| soft yellow-green foam | 0.1820 | |
| II | rigid white foam | 0.0678 |
| rigid green foam | 0.0636 | |
| III | pieces of conduit | 0.0025 |
| conduit + soft bluish-green foam | 0.7182 |
| Groups | Samples | |
|---|---|---|
| A | B | |
| Total sequence reads | 51,056 | 67,264 |
| OTUs | 828 | 872 |
| Shannon diversity index | 3.97 | 4.73 |
| Simpson index | 0.12 | 0.03 |
| Margalef richness | 46.12 | 45.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dacewicz, E.; Lenart-Boroń, A. Waste Polyurethane Foams as Biomass Carriers in the Treatment Process of Domestic Sewage with Increased Ammonium Nitrogen Content. Materials 2023, 16, 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020619
Dacewicz E, Lenart-Boroń A. Waste Polyurethane Foams as Biomass Carriers in the Treatment Process of Domestic Sewage with Increased Ammonium Nitrogen Content. Materials. 2023; 16(2):619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020619
Chicago/Turabian StyleDacewicz, Ewa, and Anna Lenart-Boroń. 2023. "Waste Polyurethane Foams as Biomass Carriers in the Treatment Process of Domestic Sewage with Increased Ammonium Nitrogen Content" Materials 16, no. 2: 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020619
APA StyleDacewicz, E., & Lenart-Boroń, A. (2023). Waste Polyurethane Foams as Biomass Carriers in the Treatment Process of Domestic Sewage with Increased Ammonium Nitrogen Content. Materials, 16(2), 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020619







