Perspectives on Developing Burn Resistant Titanium Based Coatings—An Opportunity for Cold Spraying
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Burn Resistant Ti Alloys
3. Burn Resistant Surface Technologies of Ti Alloys
4. Cold Spray Technology
5. The Opportunity of Cold Spray for Fabricating Burn-Resistant Ti-Based Coating
6. Post-Treatment of Cold Sprayed Ti-Based Coatings
7. Conclusions and Outlook
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peters, M.; Kumpfert, J.; Ward, C.H.; Leyens, C. Titanium Alloys for Aerospace Applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2003, 5, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zeng, W.; Zhou, D.; Lai, Y. Hot Workability of Burn Resistant Ti-35V-15Cr-0.3Si-0.1C Alloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Li, W.; Li, D.; Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Huang, J. A Review on Combustion Behavior and Mechanism of Ti Alloys for Advanced Aero-Engine. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 960, 170584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Deng, J. Effects of the Alloying Element Cr on the Burning Behavior of Titanium Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 1999, 284, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, K.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Feng, L.; Wu, H. One Kind β Type a Low Cost Titanium Alloy. CN106507830B, 27 February 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, L.; Xie, G.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Yu, J.; Hao, Z.; Lu, W.; Liu, X. Combustion Behaviour and Mechanism of TC4 and TC11 Alloys. Corros. Sci. 2020, 168, 108564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.N.; Huo, Y.Z.; Song, X.D.; Bi, Z.Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, Y.Q. Burn-Resistant Behavior and Mechanism of Ti14 Alloy. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2016, 23, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Xie, G.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Yu, J.; Feng, K.; Xue, W. The Effect of Cu Content and Ti2Cu Precipitation on the Combustion Behaviour and Mechanism of Ti-XCu Alloys. Corros. Sci. 2021, 190, 109641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Wen, D.; Wang, Q.; Che, J.; Dong, C.; Liaw, P.K.; Xu, F.; Sun, L. Design of Near-α Ti Alloys via a Cluster Formula Approach and Their High-Temperature Oxidation Resistance. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, W.; Bo, A.; Zhan, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wan, M.; Gu, Y. Underlying Burning Resistant Mechanisms for Titanium Alloy. Mater. Des. 2018, 156, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Wu, H.; Feng, L. One Kind α Type a Low Cost Titanium Alloy. CN106507831B, 27 February 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhan, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, Y. Multiscale Exploit the Role of Copper on the Burn Resistant Behavior of Ti-Cu Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 863, 158639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, L.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Y.-J.; Li, Y.; Tian, H.-F.; Cai, Y.; Lin, C.-X. High Speed Laser Cladded Ti-Cu-NiCoCrAlTaY Burn Resistant Coating and Its Oxidation Behavior. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 392, 125697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Qiu, Y.; Hu, T.; Clare, A.T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.C. Microstructures and Mechanical Behavior of Beta-Type Ti-25V-15Cr-0.2Si Titanium Alloy Coating by Laser Cladding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 796, 140063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Hu, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, T.; Fan, W.; Zhang, L.C. Solidification Effect on the Microstructure and Mechanism of Laser-Solid-Forming-Produced Flame-Resistant Ti–35V–15Cr Alloy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22, 2000102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, T.; Zhao, H.; Tan, H.; Hu, G.; Zhang, Z. Influence of Processing Parameters on Beta Grain Morphology of Laser Solid Forming of Ti-25V-15Cr Burn-Resistant Titanium Alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 91, 1461–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Qiu, Y.; Mei, M.; Yang, X.; Hu, T. Burn-Resistant Property of Laser Solid Forming Ti-25V-15Cr Alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2018, 47, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F. Direct Laser Fabrication of Ti-25V-15Cr-2Al-0.2C (Wt Pct) Burn-Resistant Titanium Alloy. Met. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Met. Mater. Sci. 2012, 43, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Sharman, R.; Mei, J.; Voice, W. Direct Laser Fabrication and Microstructure of a Burn-Resistant Ti Alloy. Mater. Des. 2002, 23, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Sharman, R.; Mei, J.; Voice, W. Microstructure and Properties of a Laser Fabricated Burn-Resistant Ti Alloy. Mater. Des. 2004, 25, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Mei, J.; Wu, X. Microstructure Study of Direct Laser Fabricated Ti Alloys Using Powder and Wire. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 1424–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, F.; Fan, W.; Feng, Z.; Lin, X. Investigation on Microstructure and Properties of Laser Solid Formed Low Expansion Invar 36 Alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 5827–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, Z.; Gong, Y.; Liang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, X. Analysis of the Sequentially Coupled Thermal–Mechanical and Cladding Geometry of a Ni60A-25%WC Laser Cladding Composite Coating. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 167, 109595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bai, P.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Guo, Z. Effect of Ni Contents on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TiC-Ni Cermets Obtained by Direct Laser Fabrication. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2009, 27, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.X.; Yao, Z.J.; Zhang, P.Z.; Miao, Q.; Liang, W.P.; Wei, D.B.; Chen, Y. A Study on High Temperature Oxidation Behavior of Double Glow Plasma Surface Metallurgy Fe-Al-Cr Alloyed Layer on Q235 Steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 305, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, H.E.; Taylor, M.P. Diffusion Cells and Chemical Failure of MCrAlY Bond Coats in Thermal-Barrier Coating Systems. Oxid. Met. 2001, 55, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.B.; Li, M.F.; Zhou, X.; Li, F.K.; Li, S.Q.; Zhang, P.Z. Preparation of NiCr/YSZ two-layered burn-resistant coating on γ-TiAl alloys based on plasma surface metallurgy and ion plating methods. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B Metall. 2021, 57, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, W.; Ji, S.; Zhong, X.; Lian, Z. Research Progress and Trend of Plasma Metallurgy on Titanium Metallic Surface. MATEC Web Conf. 2020, 321, 06007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, G.H.; He, Z.Y. Preparation of Double Glow Pl as Ma Surface Metall Urgy Treated Ti-Cu Burn-Resistant Alloy. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2005, 15, 110–115. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, P.; Huang, G.; Peng, X.; Zheng, S. Study on the Burn-Resistant Properties of Titanium Alloy Ti6Al4V Surface by Diffusing Copper. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2011, 40, 286–289. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, G.H.; He, Z.Y.; Li, Z.Y. Study of Surface Burn-Resistant Ti-Cu Titanium Alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2005, 34, 162–165. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, G.H.; He, Z.Y.; Yao, Z.J. Plasma Surface Alloying of Titanium Alloy for Enhancing Burn-Resistant Property. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2006, 16, S2100–S2103. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.Z.; Li, Z.Y.; He, Z.Y.; Zhong, G.H. Surface Chromizing of Ti-6Al-4V by Double Glow Plasma Surface Alloying Technology. Ordnance Mater. Sci. Eng. 2005, 28, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, G.; He, Z. Surface Plasma Chromized Burn-Resistant Titanium Alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 4884–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, G.H.; He, Z.Y.; Wu, H.Y.; Yao, Z.J. Surface Plasma Molybdenized Burn-Resistant Titanium Alloy. Key Eng. Mater. 2007, 353–358, 1837–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, P.Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, G.H.; Zhang, Y.M.; Wu, H.Y.; Yao, Z.J. Double Glow Plasma Surface Molybdenizing of Pure Ti and Ti-6Al-4V. J. Nanjing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 2005, 37, 582–586. [Google Scholar]
- Endres, S.; Wilke, M.; Knöll, P.; Frank, H.; Kratz, M.; Wilke, A. Correlation of in Vitro and in Vivo Results of Vacuum Plasma Sprayed Titanium Implants with Different Surface Topography. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chu, P.K.; Ding, C. Surface Modification of Titanium, Titanium Alloys, and Related Materials for Biomedical Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2004, 47, 49–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ma, X.; Yu, B. A Study on Mechanical Properties of Combustion-Resistant and Thermal Barrier Functional Coating Prepared on Titanium Alloy Surface. J. Xiangtan Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2019, 41, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, Y.; Cui, M.; Han, A.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J. Multi-Criteria Optimization of Automatic Electro-Spark Deposition TiCrNiVSi0.1 Multi-Principal Element Alloy Coating on TC4 Alloy. Coatings 2023, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, C.; Liu, F.; Liu, F.; Song, M.; Ke, L. Nanocrystallization of a Ti40 Cladding Layer by Ultrasonic Impact to Improve Burn Resistance. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 11, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ding, R.; Shen, Y.; Hu, Y.; Guo, Y. Preparation of Ti-Cr and Ti-Cu Flame-Retardant Coatings on Ti-6Al-4V Using a High-Energy Mechanical Alloying Method: A Preliminary Research. Mater. Des. 2012, 35, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Fu, S. Ti-Cu Flame-Retardant Modified Layer Prepared by Friction Stir Processing on Surface of TC4 Ti Alloy. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2018, 28, 435–445. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Huang, J.; Xie, G.; Yu, J.; Zhang, C.; Shao, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; He, G. Effect of Electroplating Cr Coating on Combustion Characteristics of TC4 Titanium Alloy. Chin. J. Eng. 2020, 42, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Chen, G.; Du, L.; Lan, H.; Huang, C.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W. Preparation and Characterization of Titanium Alloy Protective Coating. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2018, 47, 647–651. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.J.; Wang, Y.Y. Effect of Particle State on the Adhesive Strength of HVOF Sprayed Metallic Coating. J. Therm. Spray. Technol. 2002, 11, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Han, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, X. HVOF Spray Performance Optimization Analysis and Experimental Research of WC–12Co Coating on Ti Alloy. Met. Mater. Int. 2023, 29, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Gärtner, F.; Assadi, H.; Kreye, H. Development of a Generalized Parameter Window for Cold Spray Deposition. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardan, A.; Berndt, C.C.; Ahmed, R. Numerical Modelling of Particle Impact and Residual Stresses in Cold Sprayed Coatings: A Review. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 409, 126835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadi, H.; Gärtner, F.; Stoltenhoff, T.; Kreye, H. Bonding Mechanism in Cold Gas Spraying. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 4379–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani-Gangaraj, M.; Veysset, D.; Champagne, V.K.; Nelson, K.A.; Schuh, C.A. Adiabatic Shear Instability Is Not Necessary for Adhesion in Cold Spray. Acta Mater. 2018, 158, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moridi, A.; Hassani-Gangaraj, S.M.; Guagliano, M.; Dao, M. Cold Spray Coating: Review of Material Systems and Future Perspectives. Surf. Eng. 2014, 30, 369–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadi, H.; Kreye, H.; Gärtner, F.; Klassen, T. Cold Spraying—A Materials Perspective. Acta Mater. 2016, 116, 382–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.T.; Guo, X.P.; Liao, H.L.; Li, C.J.; Coddet, C. Significant Influences of Metal Reactivity and Oxide Films at Particle Surfaces on Coating Microstructure in Cold Spraying. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 3557–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khun, N.W.; Tan, A.W.Y.; Sun, W.; Liu, E. Wear and Corrosion Resistance of Thick Ti-6Al-4V Coating Deposited on Ti-6Al-4V Substrate via High-Pressure Cold Spray. J. Therm. Spray. Technol. 2017, 26, 1393–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; He, P.; Liao, H.; Wang, X. Deposition Features of Ti Coating Using Irregular Powders in Cold Spray. J. Therm. Spray. Technol. 2014, 23, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Li, W.Y. Deposition Characteristics of Titanium Coating in Cold Spraying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 167, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, P.; Silvello, A. Mechanical and Microstructural Behavior of Cold-Sprayed Titanium- and Nickel-Based Coatings. J. Therm. Spray. Technol. 2015, 24, 1506–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.T.; Wei, Y.K.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.J. Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Ti and Ti6Al4V Prepared by an In-Situ Shot Peening Assisted Cold Spraying. Mater. Des. 2015, 85, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cizek, J.; Kovarik, O.; Siegl, J.; Khor, K.A.; Dlouhy, I. Influence of Plasma and Cold Spray Deposited Ti Layers on High-Cycle Fatigue Properties of Ti6Al4V Substrates. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 217, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Fan, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Lupoi, R.; Yin, S. Microstructure Evolution and Composition Redistribution of FeCoNiCrMn High Entropy Alloy under Extreme Plastic Deformation. Mater. Res. Lett. 2022, 10, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koricherla, M.V.; Torgerson, T.B.; Alidokht, S.A.; Munagala, V.N.V.; Chromik, R.R.; Scharf, T.W. High Temperature Sliding Wear Behavior and Mechanisms of Cold-Sprayed Ti and Ti–TiC Composite Coatings. Wear 2021, 476, 203746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munagala, V.N.V.; Chromik, R.R. The Role of Metal Powder Properties on the Tribology of Cold Sprayed Ti6Al4V-TiC Metal Matrix Composites. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 411, 126974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.W.Y.; Lek, J.Y.; Sun, W.; Bhowmik, A.; Marinescu, I.; Buenconsejo, P.J.; Dong, Z.; Liu, E. Microstructure, Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Cold Sprayed Ti6Al4V–CoCr Composite Coatings. Compos. B Eng. 2020, 202, 108280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Sone, M.; Ma, W.; Fukanuma, H. The Effects of Heat Treatment on the Mechanical Properties of Cold-Sprayed Coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 261, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blose, R.E.; Walker, B.H.; Walker, R.M.; Froes, S.H. New Opportunities to Use Cold Spray Process for Applying Additive Features to Titanium Alloys. Met. Powder Rep. 2006, 61, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselova, T.; Celotto, S.; Morgan, R.; Fox, P.; O’Neill, W. Formation of TiAl Intermetallics by Heat Treatment of Cold-Sprayed Precursor Deposits. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 436, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.Y.; Shen, L.; Lu, B.; Yang, R.; Cui, X.Y.; Li, T.F.; Xiong, T.Y. Preparation of TiAl 3-Al Composite Coating by Cold Spray and Its High Temperature Oxidation Behavior. J. Therm. Spray. Technol. 2010, 19, 1206–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselova, T.; Fox, P.; Morgan, R.; O’Neill, W. Experimental Study of Titanium/Aluminium Deposits Produced by Cold Gas Dynamic Spray. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 2775–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnicki, M.; Jasiorski, M.; Baszczuk, A.; Korzeniowski, M. Heat-Treatment of Aluminium-Nickel Composite Cold Sprayed Coating. Coatings 2020, 10, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Jung, S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Ko, K.H. Alloying of Cold-Sprayed Al-Ni Composite Coatings by Post-Annealing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 3496–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikbakht, R.; Assadi, H.; Jodoin, B. Intermetallic Phase Evolution of Cold-Sprayed Ni-Ti Composite Coatings: Influence of As-Sprayed Chemical Composition. J. Therm. Spray. Technol. 2021, 30, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.T.; Li, C.J.; Yang, G.J.; Li, C.X. Cold Spraying of Fe/Al Powder Mixture: Coating Characteristics and Influence of Heat Treatment on the Phase Structure. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 2538–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; McCartney, D.G.; Shipway, P.H.; Marrocco, T. Corrosion Behavior of Cold Sprayed Titanium Coatings and Free Standing Deposits. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2011, 20, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrocco, T.; Hussain, T.; McCartney, D.G.; Shipway, P.H. Corrosion Performance of Laser Posttreated Cold Sprayed Titanium Coatings. J. Therm. Spray. Technol. 2011, 20, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Bell, T. Enhanced Wear Resistance of Titanium Surfaces by a New Thermal Oxidation Treatment. Wear 2000, 238, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidyuk, T.M.; Dudina, D.V.; Korchagin, M.A.; Gavrilov, A.I.; Bokhonov, B.B.; Ukhina, A.V.; Esikov, M.A.; Shikalov, V.S.; Kosarev, V.F. Spark Plasma Sintering Treatment of Cold Sprayed Materials for Synthesis and Structural Modification: A Case Study Using TiC-Cu Composites. Mater. Lett. X 2022, 14, 100140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, A.; Wei-Yee Tan, A.; Sun, W.; Wei, Z.; Marinescu, I.; Liu, E. On the Heat-Treatment Induced Evolution of Residual Stress and Remarkable Enhancement of Adhesion Strength of Cold Sprayed Ti–6Al–4V Coatings. Results Mater. 2020, 7, 100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirvent, P.; Garrido, M.Á.; Sharp, J.; Rainforth, W.M.; Poza, P. Improving the Oscillating Wear Response of Cold Sprayed Ti-6Al-4V Coatings through a Heat Treatment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 399, 126128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, F.; Astarita, A.; Carlone, P.; Genna, S.; Leone, C.; Memola Capece Minutolo, F.; Squillace, A. Selective Laser Post-Treatment on Titanium Cold Spray Coatings. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 31, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrocco, T.; McCartney, D.G.; Shipway, P.H.; Sturgeon, A.J. Production of Titanium Deposits by Cold-Gas Dynamic Spray: Numerical Modeling and Experimental Characterization. J. Therm. Spray. Technol. 2006, 15, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.S.; Ma, Z.Y. Friction Stir Welding and Processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2005, 50, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Liu, H.; Yang, G.J.; Li, C.X.; Luo, X.T.; He, G.Y.; Zhou, L. Effect of Friction Stir Spot Processing on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Cold-Sprayed Al Coating on Ti Substrate. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 421, 127352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodabakhshi, F.; Marzbanrad, B.; Yazdanmehr, A.; Jahed, H.; Gerlich, A.P. Tailoring the Residual Stress during Two-Step Cold Gas Spraying and Friction-Stir Surface Integration of Titanium Coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 380, 125008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.J.; Yan, X.C.; Li, W.Y.; Wang, W.B.; Verdy, C.; Planche, M.P.; Liao, H.L.; Montavon, G. Post-Spray Modification of Cold-Sprayed Ni-Ti Coatings by High-Temperature Vacuum Annealing and Friction Stir Processing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 451, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
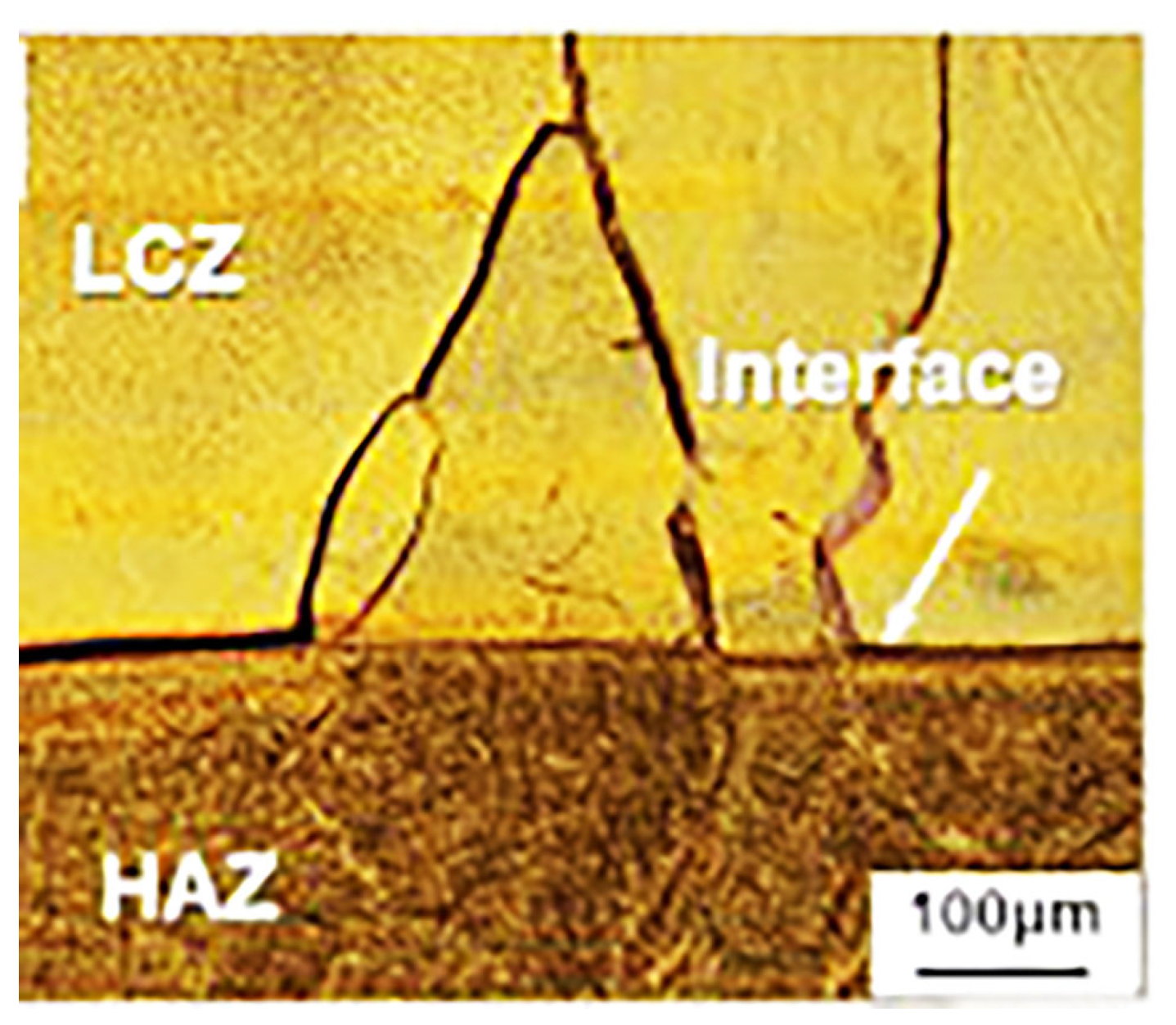





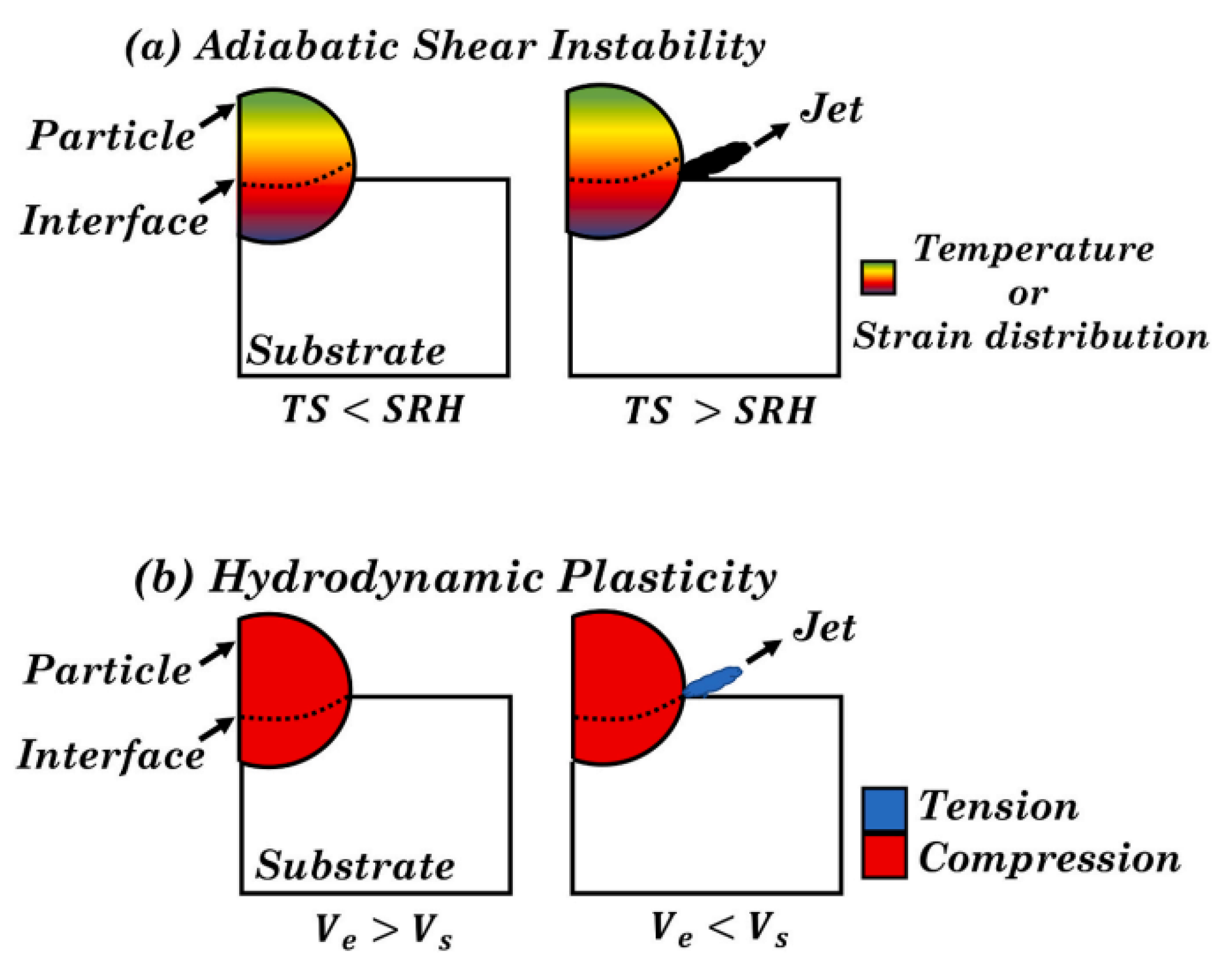
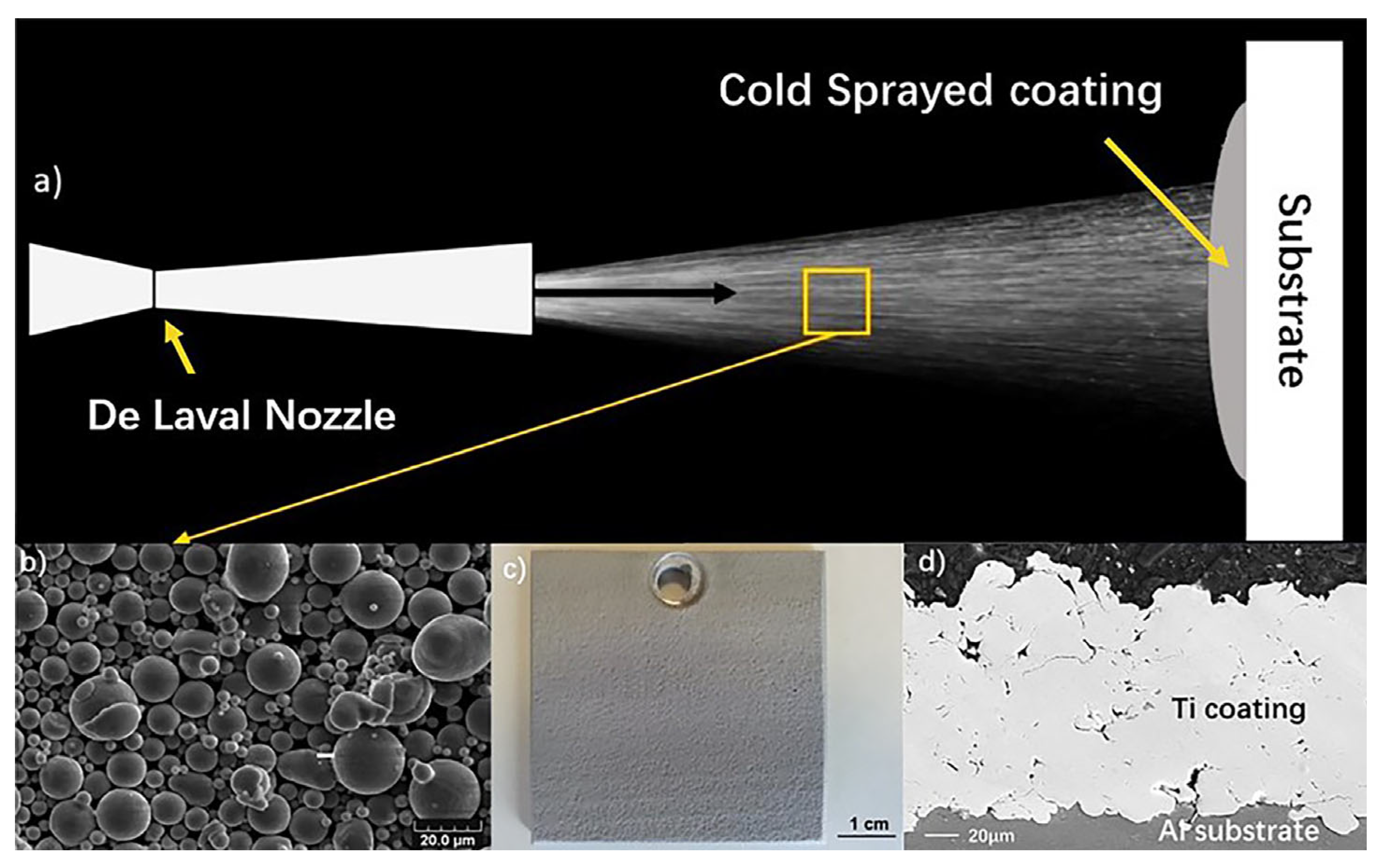



| Reference | Powder Flow Rate (g/min) | Linear Velocity (mm/s) | Gas Type | Working Distance (mm) | Laser Power (KW) | Material | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [13] | 19.8 | 132 | Ar | 15 | 1.5 | Cu | Laser Cladded (LC) |
| [13] | 21 | 250 | Ar | 15 | 2 | NiCoCrAlTaY | |
| [14] | 11 | 10 | Ar | 7.5 | 1.8 | Ti-6Al-4V | |
| [15] | 10 | 10 | CO2 | 12 | 2 | Ti–35V–15Cr | Laser Solid Forming (LSF) |
| [16] | 4.5 | 10 | CO2 | 12 | 1.5 | Ti-25V-15Cr | |
| 10 | 2.1 | Ti-25V-15Cr-2Al-0.2C | Direct Laser Fabrication (DLF) | ||||
| 10 | 2.4 | ||||||
| 7.5 | 2.1 | ||||||
| 5 | 2.1 | ||||||
| 2.5 | 2.1 | ||||||
| [17] | 4 | 10 | CO2 | 12 | 2.1 | ||
| [18] | 12 | 5.83 | CO2 | 10 | 0.75–1.14 | ||
| [19] | 8~10 | 2.5–7.5 | 0.25–0.7 | ||||
| [20] | 9~14 | 3.3–13.3 | 0.22–0.51 | ||||
| [21] | 2.64–18.21 | 1.66 | 0.755 |
| Double Glow Plasma Surface Metallurgy (DG) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate Material | Ti | Ti-6.5Al-0.3Mo-1.5Zr-0.25Si | Ti-6Al-4V | ||||||||
| Extreme Source Material | Mo | Ti-Mo | Cr | Cr | Mo | Ti-Mo | Cr | Cr | Cu | Cu | Cu |
| Polar source voltage (V) | 860–900 | 950 | 950 | 950 | 860–900 | 950 | 700 | 950 | 800 | 50,000 | 600–1000 |
| Working gas pressure (Pa) | 30 | 20–50 | 25 | 20–50 | 30 | 25 | 25 | 20–50 | 25 | 25 | 12–36 |
| Permeable layer thickness (um) | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 60 | 50 | 20–250 | 25–250 | 210–255 |
| Metal penetration time (h) | 3.5 | 1~6 | 4 | 1~6 | 3.5 | 4 | 2 | 1~6 | 3.5 | 0.25–1.41 | 3 |
| Reference | [36] | [32] | [34] | [32] | [36] | [35] | [33] | [32] | [31] | [30] | [29] |
| Other Process Titanium Based Refractory Coating Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|
| Plasma Spraying | ||
| Substrate material | TA32 | Ti40Zr25Ni3Cu12Be20 |
| Coating material | ZrO2.Y2O3 | |
| Frequency (Hz) | 2000 | |
| Deposition time per unit area (min/cm2) | 2 | |
| Ar flow (L/min) | 20 | 33 |
| Ar pressure (MPa) | 0.7 | |
| Electrode speed (r/min) | 2600 | |
| Coating thickness (um) | 20–40 | 200–250 |
| Voltage (V) | 60 | 140 |
| References | [34] | |
| Electron Beam Cladding | ||
| Substrate material | TC4 | |
| Wrapping material | Ti40 | |
| Current (mA) | 502 | |
| Welding speed (mm/min) | 960 | |
| Welding electron beams (mA) | 20 | |
| Frequency (kHz) | 20 | |
| References | [35] | |
| High-Energy Mechanical Alloying | ||
| Substrate material | Ti-6Al-4V | Ti-6Al-4V |
| Implant material | Cu | Cr, Cu, Ti |
| Mixing head material | WC-Co | Stainless steel |
| Stirring head speed (r/min) | 350 | 300–500 |
| Stirring head travel speed (mm/min) | 210 | |
| Mixing head shaft shoulder pressure (mm) | 0.05 | |
| Forward tilt angle of the mixing head (°) | 0 | 0 |
| References | [36] | [37] |
| Electrochemical Plating | ||
| Substrate material | TC4 | |
| CrO3 concentration (g/L) | 500 | |
| Concentrated H2SO4 concentration (g/L) | 2.5 | |
| temperature (°C) | 25–30 | |
| Current density (A/dm) | 30 | |
| Deposition rate (μm/h) | 30 | |
| Plating thickness (um) | 15–60 | |
| References | [38] | |
| Preparation Technology | Substrate Material | Coating | Coating Thickness (um) | Flame Retardant Performance (°C) | Anti-Oxidation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Cladded (LC) | Ti-6Al-4V | Ti-Cu-NiCoCrAlTaY | 170 | 900–1235 | better | [13] |
| Direct Laser Fabrication (DLF) | Ti-6Al-4V | Ti-25V-15Cr-2Al-0.2C | 250 | 500–800 | rather poor | [19] |
| Double glow plasma surface metallurgy (DG) | Ti-6Al-4V | Cu | 250 | 600 | [29] | |
| Cu | 250 | better | [30] | |||
| Cu | 250 | better | [31] | |||
| Cr | 100 | 600 | [33] | |||
| Cr | 100 | 600–800 | [34] | |||
| Ti-Mo | 50 | 800 | [35] | |||
| Ti-6.5Al-0.3Mo-1.5Zr-0.25Si | Mo | 50 | 600–800 | [36] | ||
| High energy mechanical alloying | Ti-6Al-4V | Cu | 955–990 | [43] | ||
| Plasma spraying | TA32 | Ti40Zr25Ni3Cu12Be20 | 750–900 | [39] |
| Preparation Technology | Substrate Material | Coating | Yield Strength (MPa) | Bond Strength (MPa) | Hardness (HV) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Laser Fabrication (DLF) | Ti-6Al-4V | Ti-25V-15Cr-2Al-0.2C | 800–900 | [18] | ||
| 800–1100 | [20] | |||||
| Double glow plasma surface metallurgy (DG) | Ti-6.5Al-0.3Mo-1.5Zr-0.25Si | Mo | 35–40 | Great | [36] | |
| Ti | Mo | 30–40 | Great | [36] | ||
| Ti-6Al-4V | Cu | 502 | [31] | |||
| Cr | 476 | [33] | ||||
| Ti-Mo | 568 | [35] | ||||
| Plasma spraying | TA32 | Ti40Zr25Ni3Cu12Be20 | 1064 | 37.6 | [39] | |
| HA | Ti | 8 | [38] | |||
| High-energy electron beam cladding | TC4 | Ti40 | Lower | 531 | [41] | |
| Preparation Technology | Substrate Material | Implant Materials | Porosity | Bond Strength (MPa) | HSL(GPa) | References |
| High-energy mechanical alloying | Ti-6Al-4V | Cu | High | High | 1.99 | [43] |
| Ti-6Al-4V | Cr | High | Higher | 1.39 |
| Preparation Technology | Coating | Defect | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Cladded(LC) | Ti-25V-15Cr-0.2Si | High residual stress | [13] |
| Laser Solid Forming(LSF) | Ti-35V-15Cr | High thermal stress | [14] |
| Ti-25V-15Cr | Dendrites, Voids, Thermal stress | [15] | |
| Direct Laser Fabrication (DLF) | Ti-25V-15Cr | Dendrites, Voids, Thermal stress | [16] |
| Ti-25V-15Cr-2Al-0.2C | Dendrites, Voids, cracks, High oxygen content, and Significant thermal impact | [17,18,19,20,21] | |
| Double glow plasma surface metallurgy (DG) | Ti-Cu, Ti-Cr, Ti-Mo | Small coating thickness | [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36] |
| Plasma spraying | Ti, TiZr-YSZ | High thermal impact, high porosity, cracks | [37,38,39] |
| Electron beam cladding | Ti-25V-15Cr-0.2Si | Coarse grains, high residual stress, cracks | [40,41] |
| High-energy mechanical alloying | Ti-Cr, Ti-Cu | Small scope of application | [42,43] |
| Plating | Ti-Cr, Ti-Ni | Low bonding strength | [44,45] |
| Coating Composition | Spray Pressure (MPa) | Spray Temperature (°C) | Porosity (%) | Hardness (HV) | Wear (mm3/N⋅m) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti–6Al–4V | 2.8 | 580 | 22.4 | [54] | ||
| Ti–6Al–4V | 5 | 1000 | 3.5 ± 0.9 | 458 ± 16 | 0.52 ± 0.01 | [55] |
| TiAl | 2.7 | 600 | 0.13 | [56] | ||
| Ti | 2/1 | 100, 300 | 2 MPa lower | [57] | ||
| Ti-TiAl3 | 0.5–4 | 25–600 | 1–10 | 850 | [58] | |
| Ti6Al4V, Ti | 2.8 | 550 | 1.3%, 2.7 | 192/363 | [59] | |
| Ti | 1.67 | 260 | 0.027 | [60] | ||
| Ti, TiC | 4 | 800 | 551 | 42 × 10−5 | [62] | |
| Ti6Al4V-TiC | 4 | 800 | 5.0 ± 0.7 (spherical powder) 1.1 ± 0.4 (irregular powder) | 218 ± 10 233 ± 8 | 20 × 10−5 | [63] |
| Ti6Al4V–CoCr | 4.5 | 1000 | 0.9–3.2 | 2~10 × 10−4 | [64] | |
| TiAl3-Al | 1.8 | 250 | 0.17 | [68] | ||
| Ti, Al | 1.5–2 | 200 | 5.8–22.8 | 50–163 | [69] |
| Material | Crystal Density (g/cm3) | The Density of the Mixture According to the Chemical Formula (g/cm3) | Density Change (%) | Solid-State Phase Transition Volume Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | 4.58 | - | - | |
| Al | 2.72 | - | - | |
| Cu | 8.89 | - | - | |
| TiAl | 3.83 | 3.65 | 4.7% | shrink |
| TiAl3 | 3.40 | 3.185 | 6.3% | shrink |
| TiCu | 6.44 | 6.735 | −4.6% | swell |
| Ti2Cu | 5.72 | 6.017 | −5.2% | swell |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, S.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Duan, T.; Normand, B.; Chen, T. Perspectives on Developing Burn Resistant Titanium Based Coatings—An Opportunity for Cold Spraying. Materials 2023, 16, 6495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196495
Liang S, Tang J, Wang Y, Duan T, Normand B, Chen T. Perspectives on Developing Burn Resistant Titanium Based Coatings—An Opportunity for Cold Spraying. Materials. 2023; 16(19):6495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196495
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Sihan, Junlei Tang, Yingying Wang, Tigang Duan, Bernard Normand, and Tongzhou Chen. 2023. "Perspectives on Developing Burn Resistant Titanium Based Coatings—An Opportunity for Cold Spraying" Materials 16, no. 19: 6495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196495
APA StyleLiang, S., Tang, J., Wang, Y., Duan, T., Normand, B., & Chen, T. (2023). Perspectives on Developing Burn Resistant Titanium Based Coatings—An Opportunity for Cold Spraying. Materials, 16(19), 6495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196495









