Manipulating the Cathodic Modification Effect on Corrosion Resistance of High Corrosion-Resistant Titanium Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimens Preparation
2.2. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructural Characterization with Cooling Rate
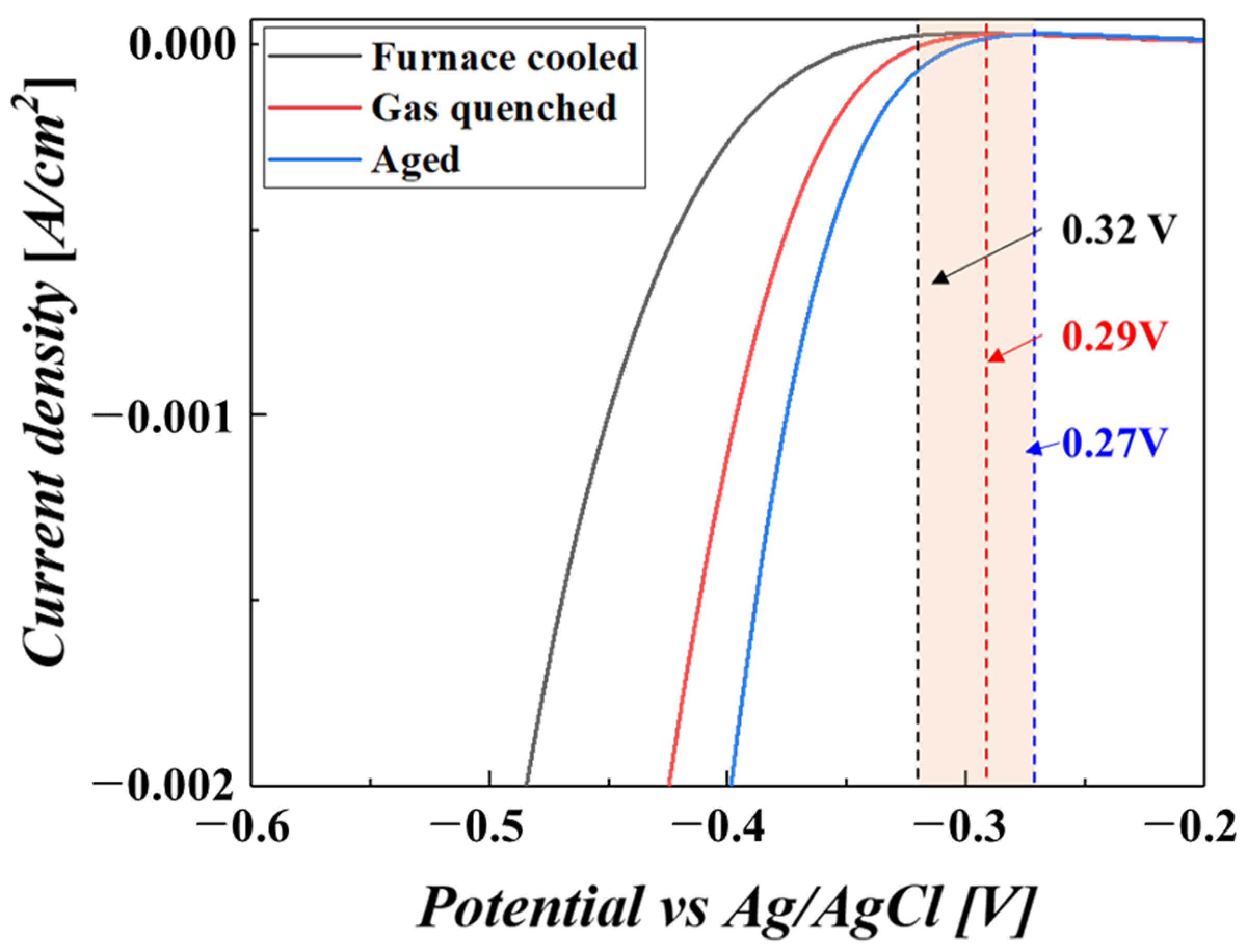
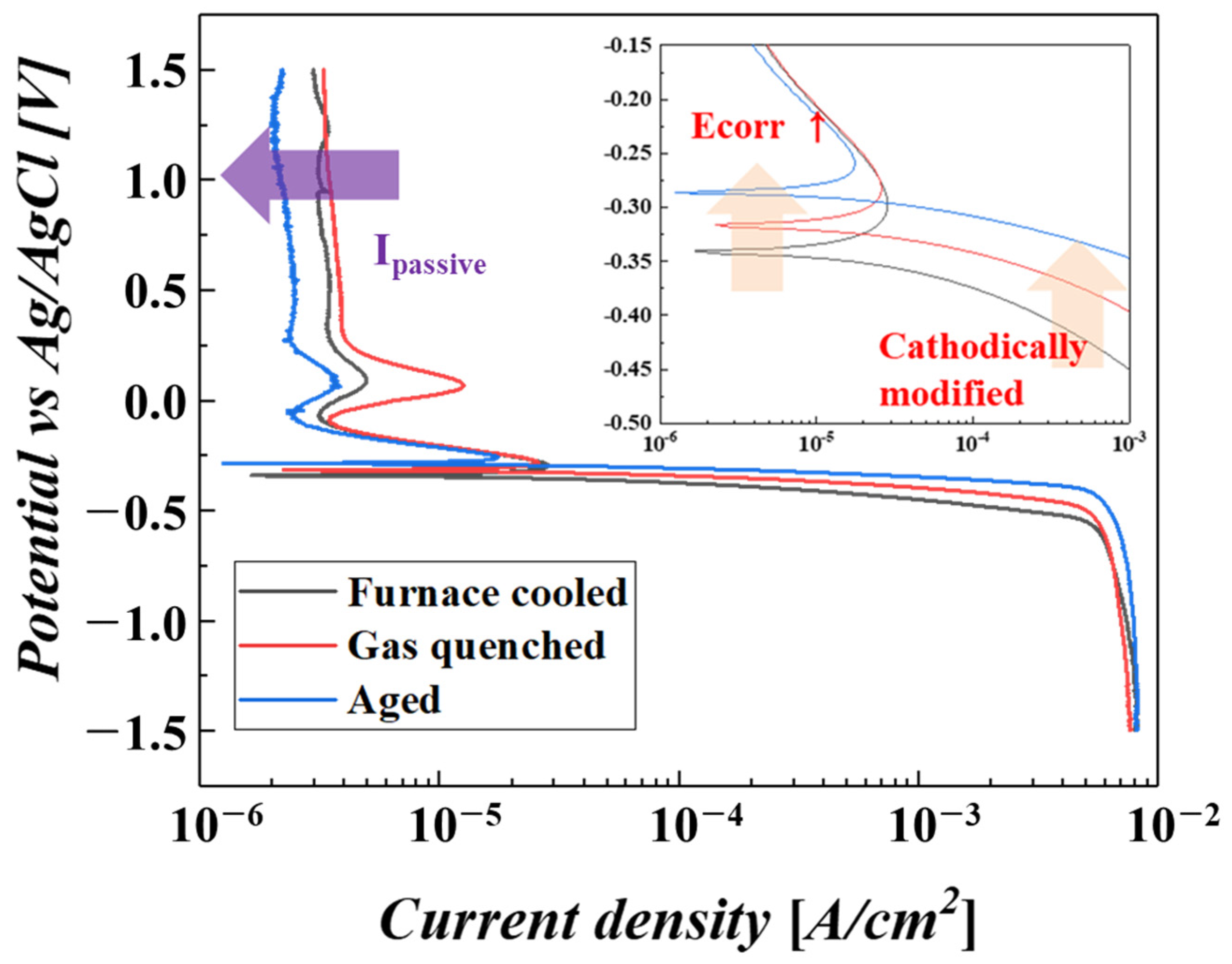
3.2. Corrosion Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Revie, R.W. Corrosion and Corrosion Control: An Introduction to Corrosion Science and Engineering; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Marcus, P. Corrosion Mechanisms in Theory and Practice; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- McCafferty, E. Introduction to Corrosion Science; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gorynin, I. Titanium alloys for marine application. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 263, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.; Bomberger, H.; Froes, F. Corrosion behavior and use of titanium and its alloys. JOM 1984, 36, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurrappa, I. Characterization of titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V for chemical, marine and industrial applications. Mater. Charact. 2003, 51, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutz, R. 2003 FN speller Award Lecture: Platinum group metal additions to titanium: A highly effective strategy for enhancing corrosion resistance. Corrosion 2003, 59, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potgieter, J. Alloys cathodically modified with noble metals. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1991, 21, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, M.; Wissenberg, H. The influence of noble metal alloy additions on the electrochemical and corrosion behavior of titanium. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1959, 106, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Lingen, E.; Sandenbergh, R. The cathodic modification behaviour of ruthenium additions to titanium in hydrochloric acid. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potgieter, J.; Skinner, W.; Heyns, A. The nature of the passive film on cathodically modified stainless steels. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1993, 23, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olubambi, P.A.; Potgieter, J.H.; Cornish, L. Corrosion behaviour of superferritic stainless steels cathodically modified with minor additions of ruthenium in sulphuric and hydrochloric acids. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ju, P.; Tang, Y.; Zuo, Y. Corrosion resistance mechanism of palladium film-plated stainless steel in boiling H2SO4 solution. Corros. Sci. 2018, 135, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutz, R. Ruthenium enhanced titanium alloys. Platin. Met. Rev. 1996, 40, 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Lingen, E.; de Villiers Steyn, H. The potential of ruthenium as an alloying element in titanium. In Titanium 1994: Products and Applications; Titanium Development Association, 1994; pp. 450–461. [Google Scholar]
- Sedriks, A. Corrosion resistance of titanium-ruthenium alloys. Corrosion 1975, 31, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Feng, C.; Liu, H.; Yi, D.; Jiang, L.; Feng, Y. Revealing the role of Ru in improving corrosion resistance of titanium alloys in HCl solution. Heat Treat. Surf. Eng. 2019, 1, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminaka, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Kamio, H. Characteristics and applications of high corrosion resistant titanium alloys. Nippon Steel Tech. Rep. 2014, 106, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Gao, D.; Zhuo, J.; Zhu, Z. Size-dependent enhancement of electrocatalytic oxygen-reduction and hydrogen-evolution performance of MoS2 particles. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 11939–11948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Encinas, A.; Scheifers, J.P.; Zhang, Y.; Fokwa, B.P.T. Boron-dependency of molybdenum boride electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 5575–5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddeler, S.; Hagemann, U.; Schulz, S. Effect of the Size and Shape on the Electrocatalytic Activity of Co3O4 Nanoparticles in the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 10013–10024. [Google Scholar]
- Morinaga, M. The molecular orbital approach and its application to biomedical titanium alloy design. In Titanium in Medical and Dental Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 39–64. [Google Scholar]
- Dobromyslov, A.; Elkin, V. Martensitic transformation and metastable β-phase in binary titanium alloys with d-metals of 4–6 periods. Scr. Mater. 2001, 44, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, B.; Park, H.-K.; Park, C.-S.; Park, K. Effect of alloying elements on corrosion properties of high corrosion resistant titanium alloys in high concentrated sulfuric acid. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, B.; Park, H.-K.; Park, C.-S.; Park, K. Role of Ta in improving corrosion resistance of titanium alloys under highly reducing condition. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 4955–4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G31-72; Standard Practice for Laboratory Immersion Corrosion Testing of Metals. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004.
- Andijani, I.N.; Ahmad, S.; Malik, A.U. Corrosion behavior of titanium metal in the presence of inhibited sulfuric acid at 50 °C. Desalination 2000, 129, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, N.D.; Kim, M.J.; Jang, Y.W.; Kim, J.G. Effect of tin on the corrosion behavior of low-alloy steel in an acid chloride solution. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, L.; Liu, H.; Huang, G.; Jiang, B.; Atrens, A.; Pan, F. Microstructure and corrosion behavior of Mg-Sc binary alloys in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 2020, 174, 108831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüce, A.O.; Döner, A.; Kardaş, G. NiMn composite electrodes as cathode material for hydrogen evolution reaction in alkaline solution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 4466–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darband, G.B.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Rouhaghdam, A.S. Three-dimensional porous Ni-CNT composite nanocones as high performance electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 829, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.M.; Huang, L.; Zaman, S.; Guo, W.; Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Xia, B.Y. Corrosion chemistry of electrocatalysts. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2200840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higginson, A. Passivation of cathodically modified alloys. Br. Corros. J. 1989, 24, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potgieter, J.; Heyns, A.; Skinner, W. Cathodic modification as a means of improving the corrosion resistance of alloys. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1990, 20, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.B.; Hu, H.X.; Zheng, Y.G.; Ke, W.; Qiao, Y.X. Comparison of the corrosion behavior of pure titanium and its alloys in fluoride-containing sulfuric acid. Corros. Sci. 2016, 103, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomashov, N.; Chernova, G.; Ruscol, Y.; Ayuyan, G. The passivation of alloys on titanium bases. Electrochim. Acta 1974, 19, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwood, D.; Peter, L.; Williams, D. Stability and open circuit breakdown of the passive oxide film on titanium. Electrochim. Acta 1988, 33, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krýsa, J.; Mraz, R.; Roušar, I. Corrosion rate of titanium in H2SO4. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1997, 48, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacs, H.S. The localized breakdown and repair of passive surfaces during pitting. Corros. Sci. 1989, 29, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchetta, P.; Chen, L.-Y.; Tardelli, J.D.C.; Reis, A.C.d.; Almeraya-Calderón, F.; Leo, P. Passive layers and corrosion resistance of biomedical Ti-6Al-4V and β-Ti alloys. Coatings 2021, 11, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaquez-Munoz, J.M.; Gaona-Tiburcio, C.; Cabral-Miramontes, J.; Nieves-Mendoza, D.; Maldonado-Bandala, E.; Olguin-Coca, J.; Almeraya-Calderon, F. Electrochemical noise analysis of the corrosion of titanium alloys in NaCl and H2SO4 solutions. Metals 2021, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
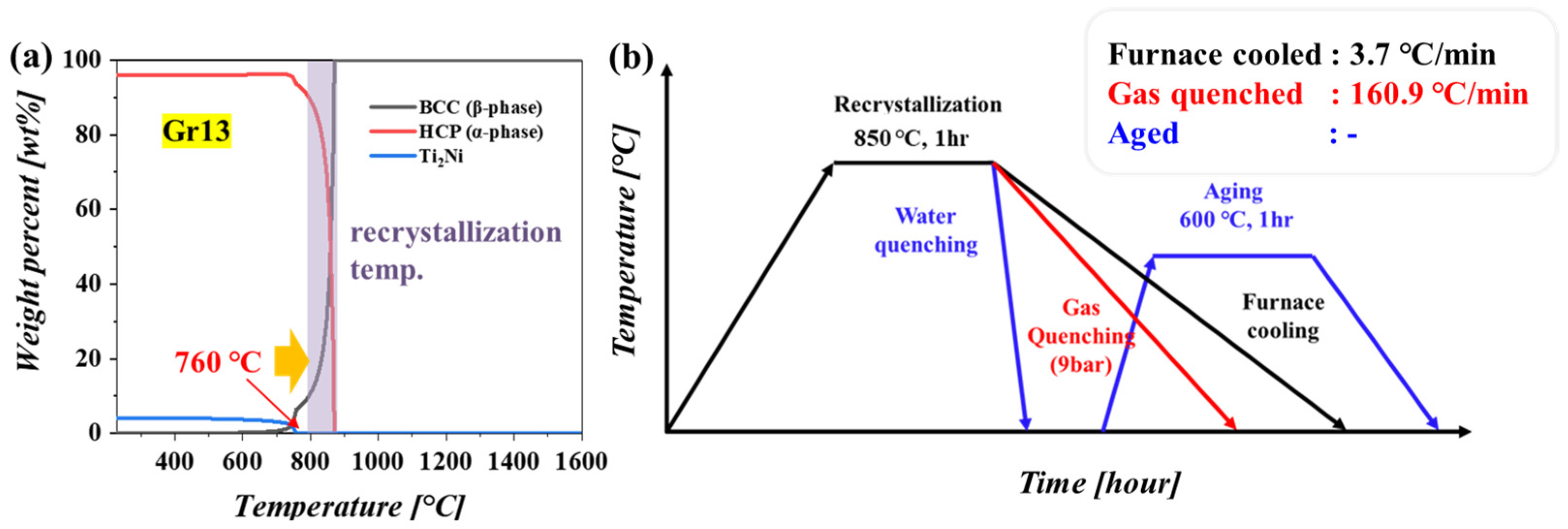
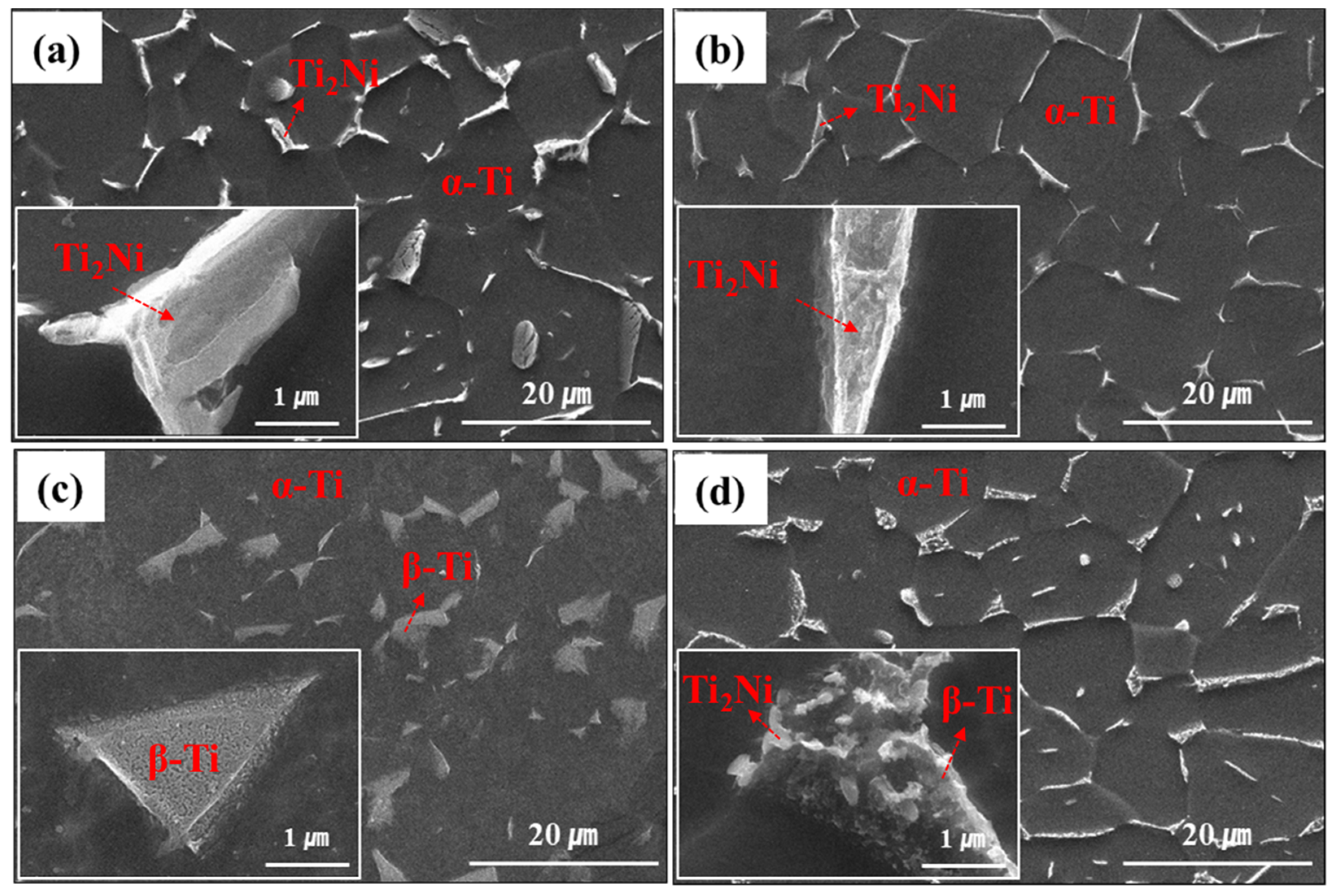
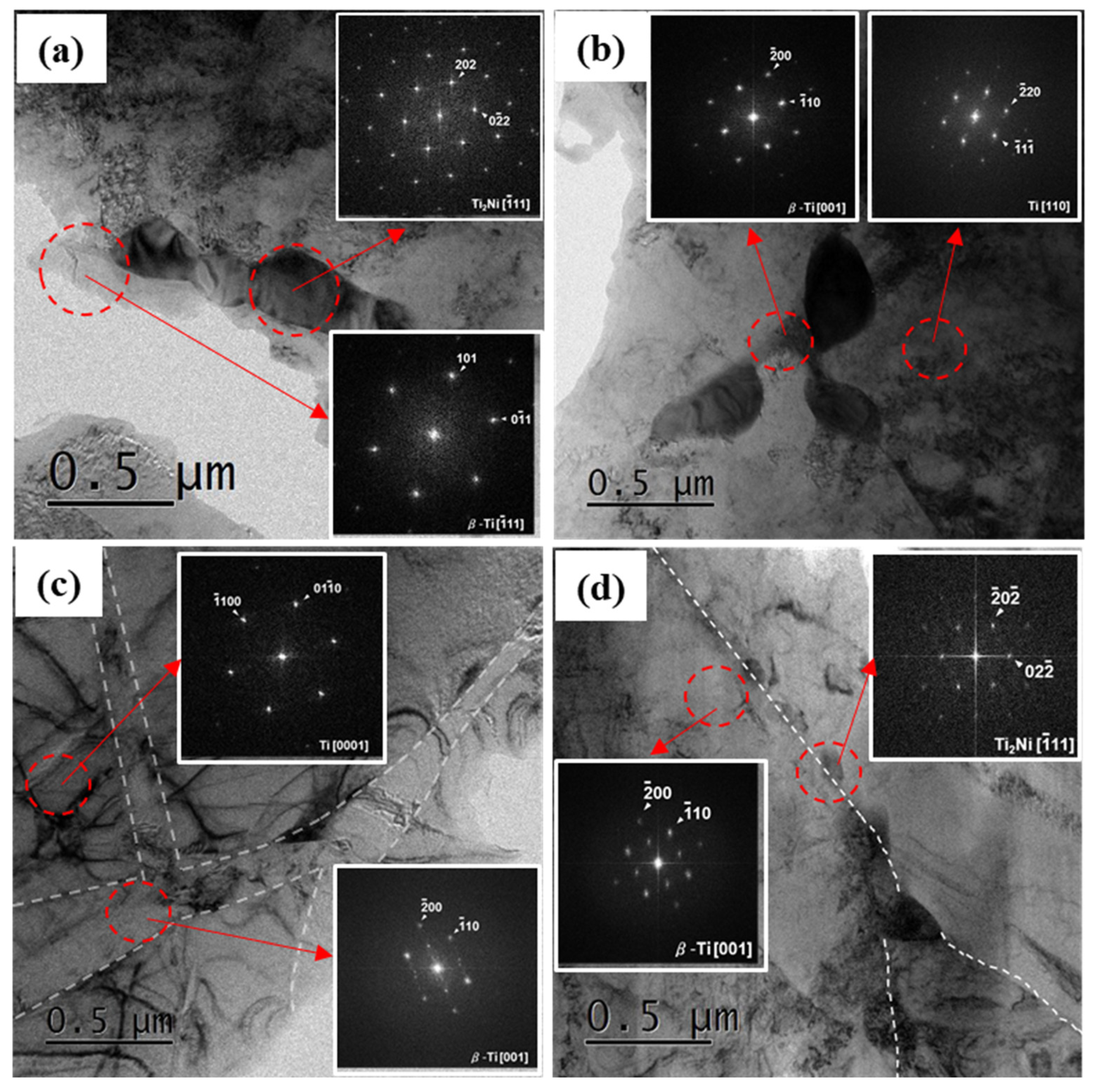

| Furnace Cooling | Gas Quenching | Water Quenching | Water Quenching + Aging | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti2Ni | Ti 65.6 wt% Ni 34.2 wt% Ru 0.2 wt% | Ti 64.7 wt% Ni 35.3 wt% | - | Ti 70.1 wt% Ni 29.9 wt% |
| β-Ti | Ti 78.5 wt% Ni 3.0 wt% Ru 18.5 wt% | Ti 82.8 wt% Ru 17.2 wt% | Ti 86.0 wt% Ni 8.6 wt% Ru 5.4 wt% | Ti 95.6 wt% Ru 4.4 wt% |
| α-Ti | Ti 100 wt% | Ti 100 wt% | Ti 100 wt% | Ti 100 wt% |
| Sample | Corrosion Rate [mm/yr] | Average Corrosion Rate [mm/yr] | Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Furnace cooling | 1 | 3.83 | 4.42 | 0.54 |
| 2 | 5.14 | |||
| 3 | 4.29 | |||
| Gas quenching | 1 | 2.04 | 1.82 | 0.24 |
| 2 | 1.93 | |||
| 3 | 1.49 | |||
| Water quenching + aging | 1 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.13 |
| 2 | 0.25 | |||
| 3 | 0.57 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, B.; Park, H.-K.; Park, C.-S.; Kim, S.; Park, K. Manipulating the Cathodic Modification Effect on Corrosion Resistance of High Corrosion-Resistant Titanium Alloy. Materials 2023, 16, 6217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16186217
Seo B, Park H-K, Park C-S, Kim S, Park K. Manipulating the Cathodic Modification Effect on Corrosion Resistance of High Corrosion-Resistant Titanium Alloy. Materials. 2023; 16(18):6217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16186217
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Bosung, Hyung-Ki Park, Chang-Soo Park, Seongtak Kim, and Kwangsuk Park. 2023. "Manipulating the Cathodic Modification Effect on Corrosion Resistance of High Corrosion-Resistant Titanium Alloy" Materials 16, no. 18: 6217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16186217
APA StyleSeo, B., Park, H.-K., Park, C.-S., Kim, S., & Park, K. (2023). Manipulating the Cathodic Modification Effect on Corrosion Resistance of High Corrosion-Resistant Titanium Alloy. Materials, 16(18), 6217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16186217






