Eco-Friendly Coal Gangue and/or Metakaolin-Based Lightweight Geopolymer with the Addition of Waste Glass
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Geopolymer Manufacturing Process
2.3. Methods
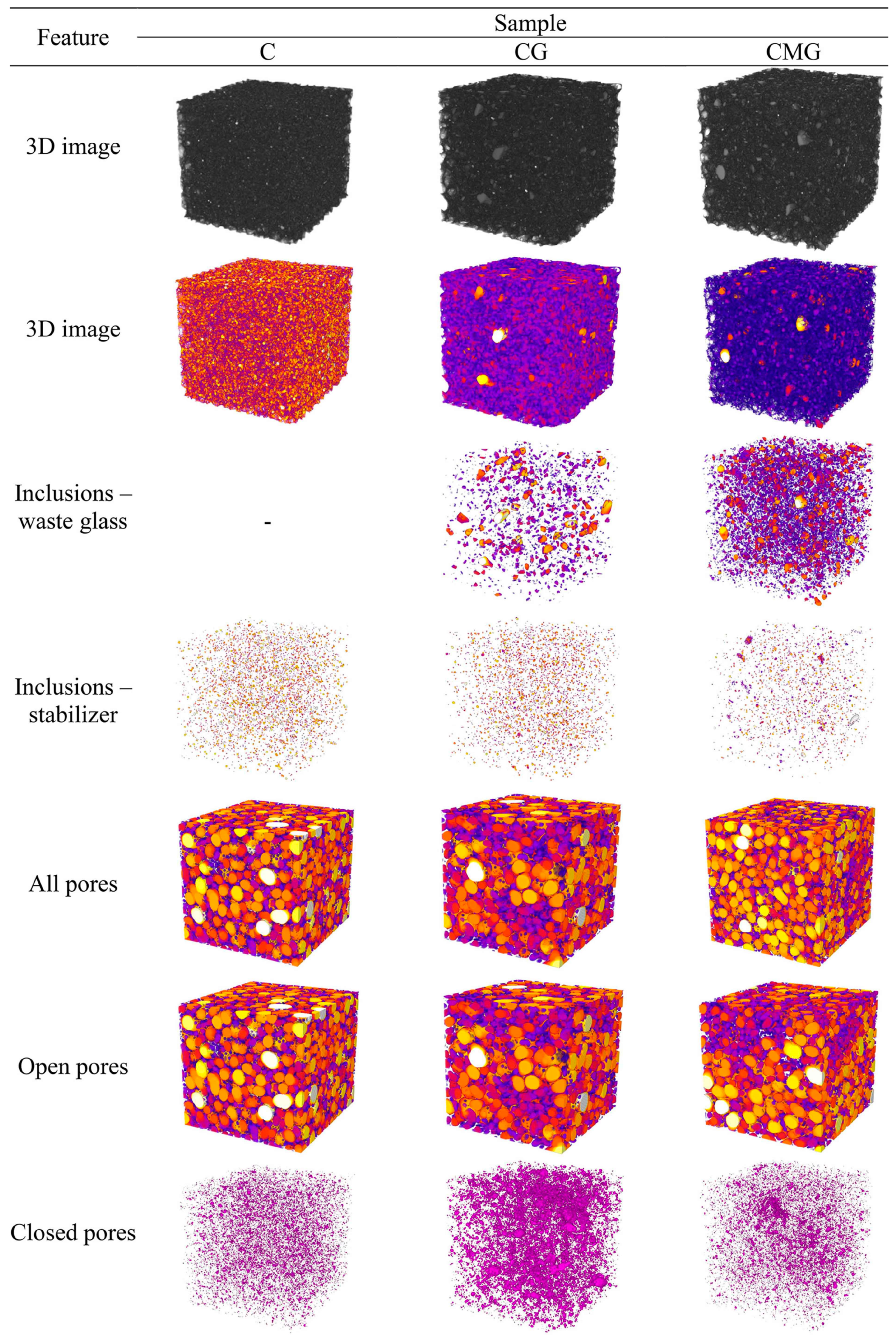
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Raw Materials
3.2. Geopolymers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sadigov, R. Rapid Growth of the World Population and Its Socioeconomic Results. Sci. World J. 2022, 2022, 8110229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marczyk, J.; Ziejewska, C.; Gądek, S.; Korniejenko, K.; Łach, M.; Góra, M.; Kurek, I.; Doğan-Sağlamtimur, N.; Hebda, M.; Szechyńska-Hebda, M. Hybrid Materials Based on Fly Ash, Metakaolin, and Cement for 3D Printing. Materials 2021, 14, 6874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Xuan, D.; Miao, Y.; Luo, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y. Accounting CO2 Emissions of the Cement Industry: Based on an Electricity–Carbon Coupling Analysis. Energies 2023, 16, 4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shao, X.; Ling, T.C. Life Cycle Assessment of Coal Gangue Composite Cements: From Sole OPC towards Low-Carbon Quaternary Binder. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glushkov, D.; Paushkina, K.; Shabardin, D.; Strizhak, P.; Gutareva, N. Municipal Solid Waste Recycling by Burning It as Part of Composite Fuel with Energy Generation. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Liu, F.; Zhao, H.; Ke, C.; Xu, Z. Mineral Phase Transformation in Coal Gangue by High Temperature Calcination and High-Efficiency Separation of Alumina and Silica Minerals. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 2281–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, B. Data-Driven Model SSD-BSP for Multi-Target Coal-Gangue Detection. Measurement 2023, 219, 113244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Edwards, D.J.; Hosseini, M.R.; Costin, G.P. A Review on Renewable Energy Transition in Australia: An Updated Depiction. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Shukla, P.R. Coal and Energy Security for India: Role of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Capture and Storage (CCS). Energy 2009, 34, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Kang, Y. Will Poland Fulfill Its Coal Commitment by 2030? An Answer Based on a Novel Time Series Prediction Method. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hupka, I.; Kotík, L. Dissolution Characteristics of Uranium and Lead in Simulated Lung Fluid Using Fly Ash Samples from Coal-Fired Power Plants in the Czech Republic. J. Environ. Radioact. 2023, 256, 107063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Liu, N.; Lu, X. Investigation of Un-Calcined Coal Gangue Together with Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag and Fly Ash to Ambient-Curing Production High-Strength Geopolymer. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 3985–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Xu, S.; Yang, J. Exploring Calcined Coal Gangue Fines as the Total Substitute of Fly Ash in the Production of Alkali-Activated Slag/Fly Ash Materials. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, Y.; Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Ni, W. Improvement on Pozzolanic Reactivity of Coal Gangue by Integrated Thermal and Chemical Activation. Fuel 2013, 109, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onifade, M.; Genc, B.; Wagner, N. Influence of Organic and Inorganic Properties of Coal-Shale on Spontaneous Combustion Liability. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2019, 29, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawer, M.E. Human Health and Environmental Impacts of Coal Combustion and Post-Combustion Wastes. J. Sustain. Min. 2018, 17, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Jämsä-Jounela, S.L.; Harjunkoski, I. Optimal Planning of Municipal Solid Waste Management Systems in an Integrated Supply Chain Network. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2019, 123, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbroek, C.D.; Bitting, J.; Craglia, M.; Azevedo, J.M.C.; Cullen, J.M. Global Material Flow Analysis of Glass: From Raw Materials to End of Life. J. Ind. Ecol. 2021, 25, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Liang, J.; Yang, G.; Dagestani, A.A.; Liu, W.; Luo, X.; Zeng, B.; Wu, H.; Huang, M.; Lin, L.; et al. Recycling of Waste Glass as Raw Materials for the Preparation of Self-Cleaning, Light-Weight and High-Strength Porous Ceramics. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 317, 128395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, H.; Alattar, A.; Tayeh, B.; Yahaya, F.; Thomas, B. Effect of Recycled Waste Glass on the Properties of High-Performance Concrete: A Critical Review. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, H.; Li, M.; Tan, J.; Dan, H.; Ma, Z.; Ma, S. Nano- and Microscale Characterization for Interfacial Transition Zone of Geopolymer Stabilized Recycled Aggregate of Asphalt Pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 397, 132368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziejewska, C.; Marczyk, J.; Korniejenko, K.; Bednarz, S.; Sroczyk, P.; Łach, M.; Mikuła, J.; Figiela, B.; Szechyńska-Hebda, M.; Hebda, M. 3D Printing of Concrete-Geopolymer Hybrids. Materials 2022, 15, 2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korniejenko, K.; Figiela, B.; Ziejewska, C.; Marczyk, J.; Bazan, P.; Hebda, M.; Choińska, M.; Lin, W.-T. Fracture Behavior of Long Fiber Reinforced Geopolymer Composites at Different Operating Temperatures. Materials 2022, 15, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shee-Ween, O.; Cheng-Yong, H.; Yun-Ming, L.; Mustafa Al Bakri Abdullah, M.; Li-Ngee, H.; Pakawanit, P.; Suhaimi Khalid, M.; Hazim Bin Wan Muhammad, W.; Wan-En, O.; Yong-Jie, H.; et al. Green Development of Fly Ash Geopolymer via Casting and Pressing Approaches: Strength, Morphology, Efflorescence and Ecological Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 398, 132446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilcan, H.; Sahin, O.; Unsal, Z.; Ozcelikci, E.; Kul, A.; Cağatay Demiral, N.; Ozkan Ekinci, M.; Sahmaran, M. Effect of Industrial Waste-Based Precursors on the Fresh, Hardened and Environmental Performance of Construction and Demolition Wastes-Based Geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 394, 132265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gier Della Rocca, D.; Santos e Sousa, F.A.; Domingos Ardisson, J.; Peralta, R.A.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Peralta Muniz Moreira, R.d.F. Magnetic Mining Waste Based-Geopolymers Applied to Catalytic Reactions with Ozone. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasupathy, K.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Sanjayan, J. 3D Concrete Printing of Eco-Friendly Geopolymer Containing Brick Waste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 138, 104943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeraj Varma, D.; Prasad Singh, S. Recycled Waste Glass as Precursor for Synthesis of Slag-Based Geopolymer. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, N.; Wu, D.; Chen, K.; Cao, K.; Huang, J. Combining Experiments and Molecular Dynamics Simulations to Investigate the Effects of Water on the Structure and Mechanical Properties of a Coal Gangue-Based Geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 389, 131556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Pullar, R.C.; Labrincha, J.A. Geopolymer Foams: An Overview of Recent Advancements. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 109, 100621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boros, A.; Korim, T. Development of Geopolymer Foams for Multifunctional Applications. Crystals 2022, 12, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsumi, T.; Terasawa, T.; Kudo, I.; Suzuki, T.; Nakayama, T.; Suematsu, H.; Ogawa, T. Preparation of Potassium and Metakaolin Based Geopolymer Foam with Millimeter Sized Open Pores for Hydrogen Recombining Catalyst Supports. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 128, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zheng, J.; Shao, J.; Loutou, M.; Bai, C.; Qiao, Y.; Miao, Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, T.; Colombo, P. Evaluation of Porosity, Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Self-Ignition Coal Gangue-Based Foams via Fast Microwave Foaming. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 68, 106062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traven, K.; Češnovar, M.; Škapin, S.D.; Ducman, V. High Temperature Resistant Fly-Ash and Metakaolin-Based Alkali-Activated Foams. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 25105–25120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, R.; Gombköto, I.; Svéda, M.; Mucsi, G. Effect of Grinding Fineness of Fly Ash on the Properties of Geopolymer Foam. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2017, 62, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Korat, L.; Ducman, V. The Influence of the Stabilizing Agent SDS on Porosity Development in Alkali-Activated Fly-Ash Based Foams. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 80, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Ren, X.; Wang, W.; He, C.; Xing, P. Preparation of Eco-Friendly Porous Ceramic with Low Thermal Conductivity by High-Temperature Treatment of Foamed Solid Waste Based Geopolymer with Cenospheres. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 398, 131190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhasindrakrishna, K.; Pasupathy, K.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Sanjayan, J. Progress, Current Thinking and Challenges in Geopolymer Foam Concrete Technology. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 116, 103886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, D.; Güden, M. Processing and Characterization of Geopolymer and Sintered Geopolymer Foams of Waste Glass Powders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 300, 124259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.; Shen, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S. A Novel Approach for Preparing Glass Ceramic Foams from MSWI Fly Ash: Foaming Characteristics and Hierarchical Pore Formation Mechanism. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, R.; Zhao, W.; Guo, H.; Yan, B.; Li, P. Sintered Glass-Ceramic Foams from Fluorite Tailings and Waste Glass with Calcium Phosphate Addition. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 359, 129528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, F.P.; Morais, C.R.d.S.; Pinto, H.C.; Rodrigues, A.M. Microstructure and Physico-Mechanical Properties of Al2O3-Doped Sustainable Glass-Ceramic Foams. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 256, 123612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisham, N.A.N.; Zaid, M.H.M.; Matori, K.A.; Shabdin, M.K. Effect of Ark Clam Shell on Crystal Growth and Mechanical Evaluation of Foam Glass-Ceramic Derived from Cullet Glass Waste. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2022, 281, 115730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, B.; Zhao, S.; Shen, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S. Preparation and Characterization of Glass Ceramic Foams Based on Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Ashes Using Secondary Aluminum Ash as Foaming Agent. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhu, H.; Wu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Feng, Z.; Jia, Z. Preparation and Properties of Foam Ceramic from Nickel Slag and Waste Glass Powder. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 23623–23628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddika, A.; Hajimohammadi, A.; Mamun, M.A.A.; Alyousef, R.; Ferdous, W. Waste Glass in Cement and Geopolymer Concretes: A Review on Durability and Challenges. Polymers 2021, 13, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulazeez, A.S.; Idi, M.A.; Kolawole, M.A.; Hamza, B. Effect of Waste Glass Powder as A Pozzolanic Material in Concrete Production. Int. J. Eng. Res. 2020, 9, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Sun, F.; Liu, T. Study on Preparation of Coal Gangue-Based Geopolymer Concrete and Mechanical Properties. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5117584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazzouk, A.; Douzane, O.; Mezreb, K.; Laidoudi, B.; Quéneudec, M. Thermal Conductivity of Cement Composites Containing Rubber Waste Particles: Experimental Study and Modelling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yang, W.; Ge, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, P. Thermal Conductivity of Cement Paste Containing Waste Glass Powder, Metakaolin and Limestone Filler as Supplementary Cementitious Material. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziejewska, C.; Grela, A.; Hebda, M. Influence of Waste Glass Particle Size on the Physico-Mechanical Properties and Porosity of Foamed Geopolymer Composites Based on Coal Fly Ash. Materials 2023, 16, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łach, M.; Grela, A.; Komar, N.; Mikuła, J.; Hebda, M. Calcined Post-Production Waste as Materials Suitable for the Hydrothermal Synthesis of Zeolites. Materials 2019, 12, 2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łach, M.; Pławecka, K.; Bąk, A.; Lichocka, K.; Korniejenko, K.; Cheng, A.; Lin, W.T. Determination of the Influence of Hydraulic Additives on the Foaming Process and Stability of the Produced Geopolymer Foams. Materials 2021, 14, 5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwek, S.Y.; Awang, H.; Cheah, C.B. Influence of Liquid-to-Solid and Alkaline Activator (Sodium Silicate to Sodium Hydroxide) Ratios on Fresh and Hardened Properties of Alkali-Activated Palm Oil Fuel Ash Geopolymer. Materials 2021, 14, 4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EN 12667:2001; Thermal Performance of Building Materials and Products—Determination of Thermal. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/f845e9a0-09c4-43ef-955c-6478a0497fb4/en-12667-2001 (accessed on 29 August 2023).
- EN 12390-2:2019; Testing Hardened Concrete—Part 2: Making and Curing Specimens for Strength Tests. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/ae7e6a86-1cbc-455e-8b2a-8964be9087f9/en-12390-2-2019 (accessed on 29 August 2023).
- Deng, J.; Li, B.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, C.P.; Lai-wang, B.; Shu, C.M. Combustion Properties of Coal Gangue Using Thermogravimetry–Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 116, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; et al. Dispersibility of Kaolinite-Rich Coal Gangue in Rubber Matrix and the Mechanical Properties and Thermal Stability of the Composites. Minerals 2021, 11, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Liu, Q.; Ai, B.; Ding, S.; Frost, R.L. Thermal Decomposition of Selected Coal Gangue. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 131, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Wang, C.; Lin, Q.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, C.; Bao, L. Combustion Behavior, Kinetics, Gas Emission Characteristics and Artificial Neural Network Modeling of Coal Gangue and Biomass via TG-FTIR. Energy 2020, 213, 118790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, R.; Saikia, J.; Saikia, B.K. Mineralogical and Ash Geochemical Studies of Coal-Mine Shale and Its Hydrocarbon Potential: A Case Study of Shale from Makum Coalfield, Northeast India. J. Geol. Soc. India 2017, 90, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzwiński, D.; Łach, M.; Hebda, M.; Walter, J.; Szechyńska-Hebda, M.; Mikuła, J. Thermal Phenomena of Alkali-Activated Metakaolin Studied with a Negative Temperature Coefficient System. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 4167–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J. Comprehensive Utilization and Environmental Risks of Coal Gangue: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 117946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Liu, C. Effect of Particle Size and Thermal Activation on the Coal Gangue Based Geopolymer. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 267, 124657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grela, A.; Hebda, M.; Łach, M.; Mikuła, J. Thermal Behavior and Physical Characteristics of Synthetic Zeolite from CFB-Coal Fly Ash. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 220, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Guo, H.; Deng, L.; Fan, W.; Yu, T.; Wang, Q. Undehydrated Kaolinite as Materials for the Preparation of Geopolymer through Phosphoric Acid-Activation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 199, 105887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragaw, T.A.; Kuraz, F. Physico-Chemical Characterizations of Ethiopian Kaolin for Industrial Applications: Case Study WDP Propoxur Formulations. In Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social-Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, LNICST; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 274, pp. 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.Q.; Do, Q.M.; Hoang, M.D.; Nguyen, H.T. The Role of Active Silica and Alumina in Geopolymerization. Vietnam J. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2018, 60, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chargui, F.; Hamidouche, M.; Belhouchet, H.; Jorand, Y.; Doufnoune, R.; Fantozzi, G. Mullite Fabrication from Natural Kaolin and Aluminium Slag. Bol. Soc. Esp. Cerám. Vidr. 2018, 57, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, Y.; Inagaki, M. Gas Adsorption/Desorption Isotherm for Pore Structure Characterization. In Materials Science and Engineering of Carbon: Characterization; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 227–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, J.; Ding, J.; Liu, T.; Shi, G.; Li, X.; Dang, W.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, R. Pore Structure and Fractal Characteristics of Different Shale Lithofacies in the Dalong Formation in the Western Area of the Lower Yangtze Platform. Minerals 2020, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, H.; Yliniemi, J.; Illikainen, M.; Rocha, F.; Ferreira, V.M. Mine Tailings Geopolymers as Awaste Management Solution for a More Sustainable Habitat. Sustainability 2019, 11, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valášková, M.; Klika, Z.; Vlček, J.; Matějová, L.; Topinková, M.; Pálková, H.; Madejová, J. Alkali-Activated Metakaolins: Mineral Chemistry and Quantitative Mineral Composition. Minerals 2022, 12, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Hongqiang, M.; Hongyu, C.; Jiaxin, W.; Jing, S.; Zonghui, L.; Mingkai, Y. Preparation and Characterization of Coal Gangue Geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 187, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, M.J.; Ajalloeian, R.; Hajiannia, A. Preparation and Application of Alkali-Activated Materials Based on Waste Glass and Coal Gangue: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 221, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, N.H.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Pa, F.C.; Mohamad, H.; Ibrahim, W.M.A.W.; Amonpattaratkit, P.; Gondro, J.; Sochacki, W.; Ibrahim, N. Self-Fluxing Mechanism in Geopolymerization for Low-Sintering Temperature of Ceramic. Materials 2021, 14, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsimbe, J.; Dinka, M.; Olukanni, D.; Musonda, I. Geopolymer: A Systematic Review of Methodologies. Materials 2022, 15, 6852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petlitckaia, S.; Poulesquen, A. Design of Lightweight Metakaolin Based Geopolymer Foamed with Hydrogen Peroxide. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szechyńska-Hebda, M.; Marczyk, J.; Ziejewska, C.; Hordyńska, N.; Mikuła, J.; Hebda, M. Optimal Design of PH-Neutral Geopolymer Foams for Their Use in Ecological Plant Cultivation Systems. Materials 2019, 12, 2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roviello, G.; Menna, C.; Tarallo, O.; Ricciotti, L.; Messina, F.; Ferone, C.; Asprone, D.; Cioffi, R. Lightweight Geopolymer-Based Hybrid Materials. Compos. B Eng. 2017, 128, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Heat-Insulating Materials and Sound-Absorbing Materials. In Building Materials in Civil Engineering; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 304–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Chantrenne, P.; Maruyama, S.; Dancette, S.; Maire, E. Thermal Conductivity of Highly Porous Metal Foams: Experimental and Image Based Finite Element Analysis. Int. J. Heat. Mass. Transf. 2018, 122, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiljanić, S.; Hribar, U.; Spreitzer, M.; König, J. Influence of Additives on the Crystallization and Thermal Conductivity of Container Glass Cullet for Foamed Glass Preparation. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 32867–32873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitarz, M.; Figiela, B.; Łach, M.; Korniejenko, K.; Mróz, K.; Castro-Gomes, J.; Hager, I. Mechanical Response of Geopolymer Foams to Heating—Managing Coal Gangue in Fire-Resistant Materials Technology. Energies 2022, 15, 3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinico, M.; Jadhav, S.D.; Witvrouw, A.; Vanmeensel, K.; Dewulf, W. A Micro-Computed Tomography Comparison of the Porosity in Additively Fabricated CuCr1 Alloy Parts Using Virgin and Surface-Modified Powders. Materials 2021, 14, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, K.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Ling, Y. Fabrication and Engineering Properties of Concretes Based on Geopolymers/Alkali-Activated Binders—A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, K.; Kunhanandan Nambiar, E.K.; Indu Siva Ranjani, G. A Classification of Studies on Properties of Foam Concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaya, N.A.; Yun-Ming, L.; Cheng-Yong, H.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Hussin, K. Correlation between Pore Structure, Compressive Strength and Thermal Conductivity of Porous Metakaolin Geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 247, 118641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACI 318M-11; Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete (ACI 318M-11). American Concrete Institute: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2011.
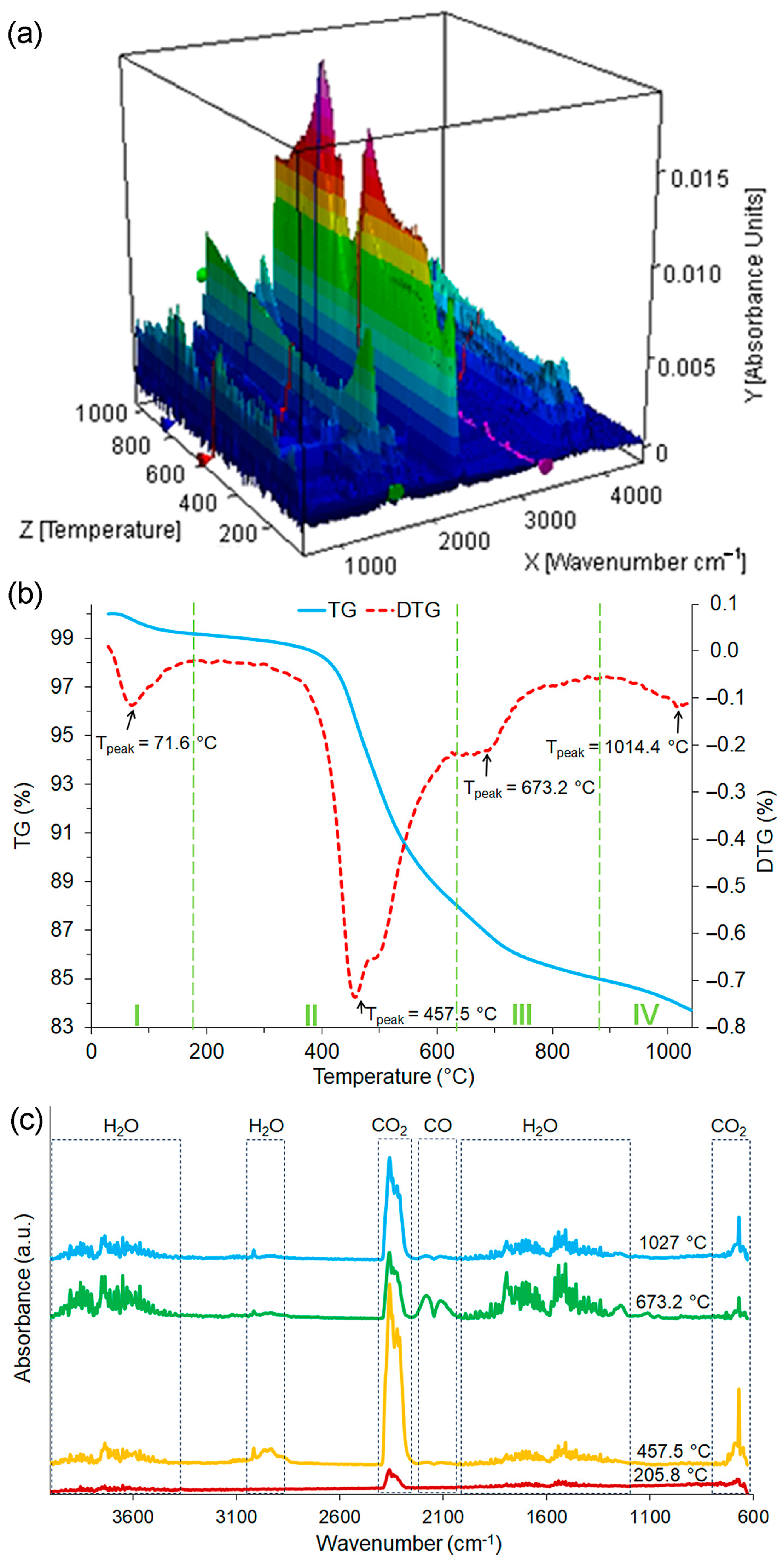
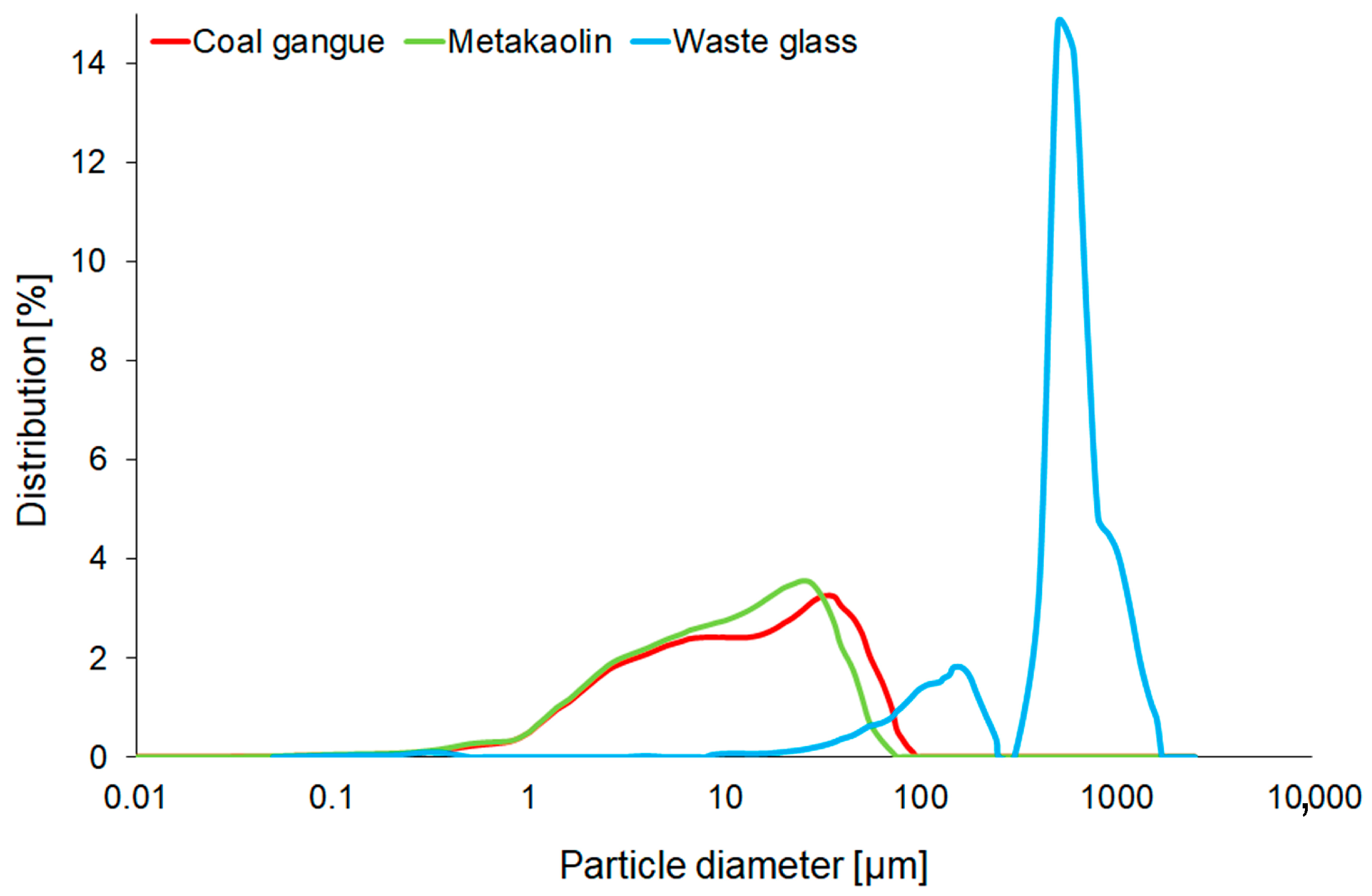
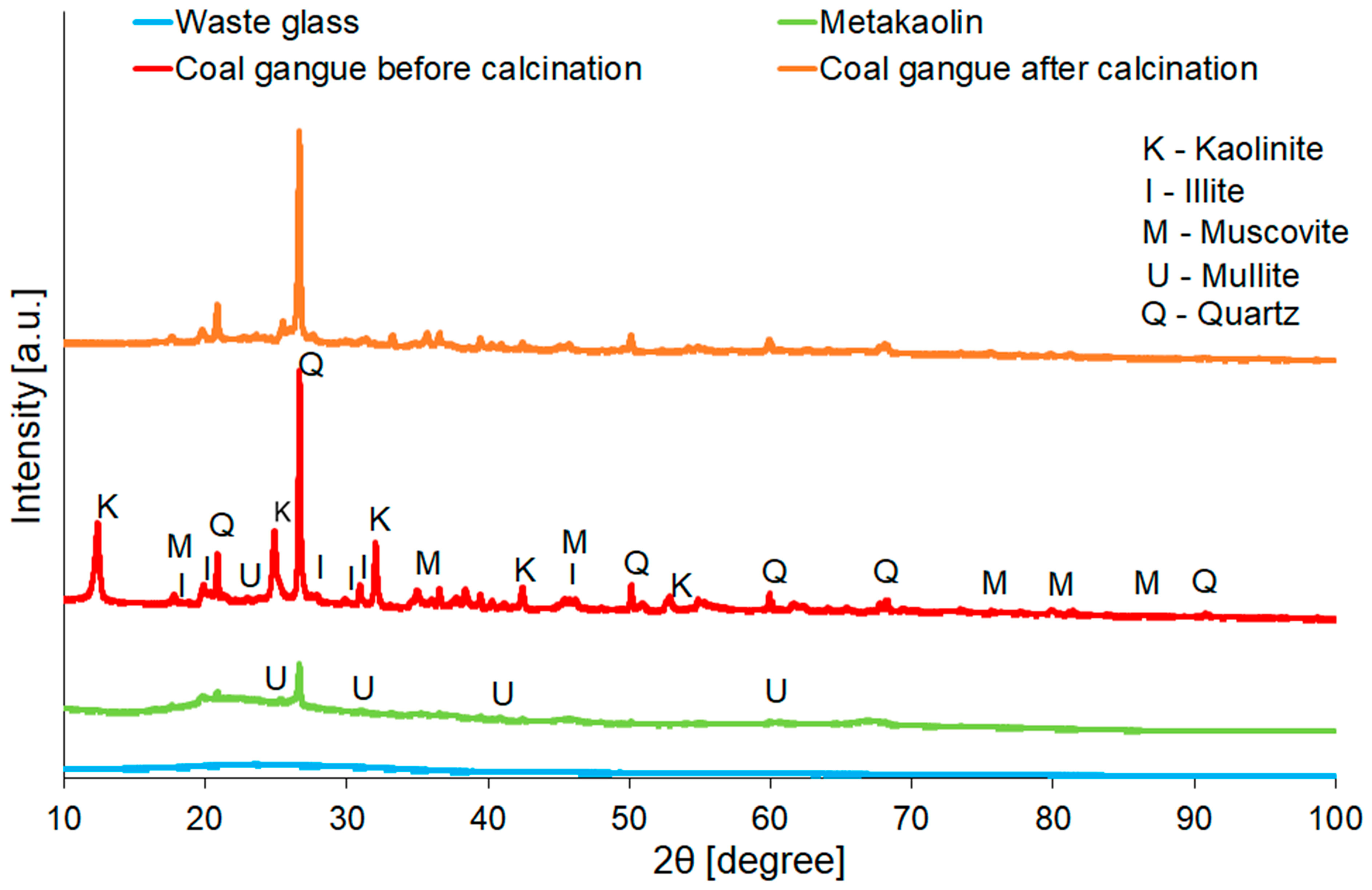
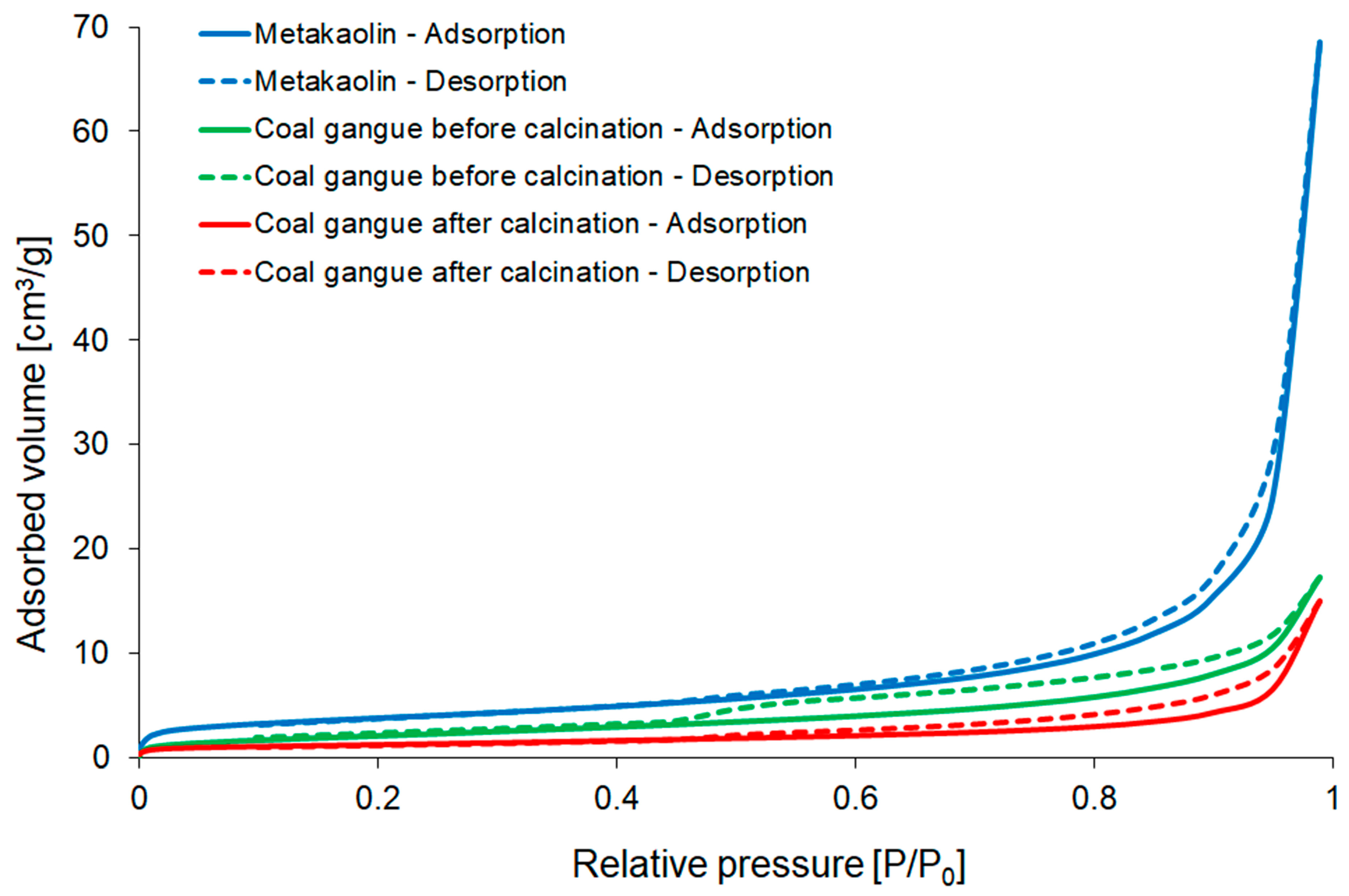
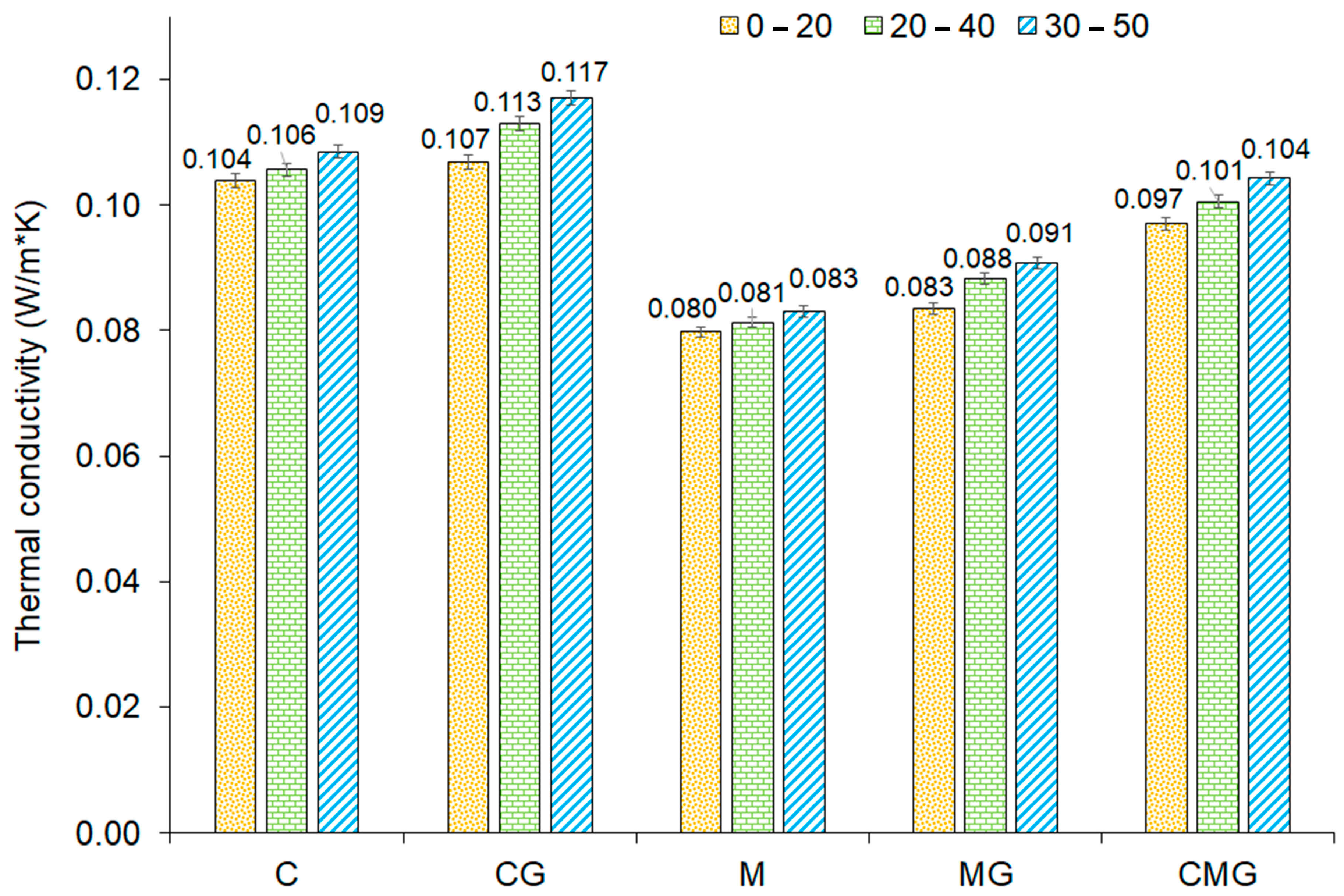
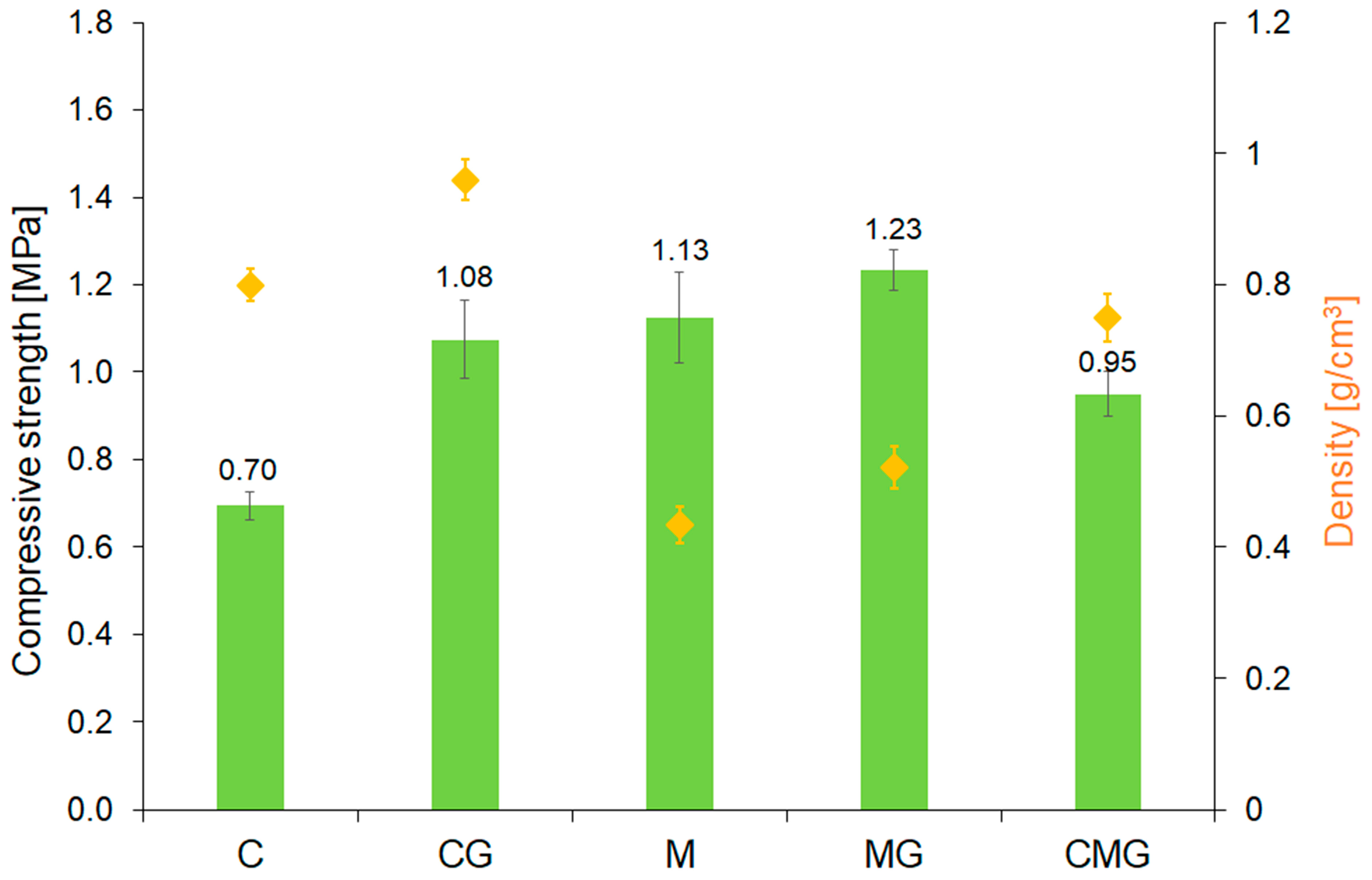

| Samples Designation | Coal Gangue (%) | Metakaolin (%) | Cement (%) | Waste Glass (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 90 | - | 10 | - |
| CG | 70 | - | 10 | 20 |
| M | - | 90 | 10 | - |
| MG | - | 70 | 10 | 20 |
| CMG | 35 | 35 | 10 | 20 |
| Compound Formula | Raw Material | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coal Gangue before Calcination | Coal Gangue after Calcination | Metakaolin | Cement | Waste Glass | |
| Content (%) | |||||
| SiO2 | 56.540 | 53.501 | 54.851 | 18.339 | 81.355 |
| Al2O3 | 26.180 | 26.683 | 41.841 | 3.673 | 1.587 |
| Fe2O3 | 7.448 | 12.496 | 1.068 | 4.524 | 1.030 |
| K2O | 3.898 | 3.092 | 1.163 | 0.745 | 0.703 |
| SO3 | 2.437 | 0.878 | 0.076 | 4.202 | 0.003 |
| CaO | 1.677 | 1.325 | 0.426 | 67.745 | 14.929 |
| TiO2 | 1.410 | 1.179 | 0.309 | 0.293 | 0.084 |
| MnO | 0.078 | 0.120 | - | 0.202 | 0.068 |
| V2O5 | 0.075 | 0.055 | 0.016 | 0.017 | |
| P2O5 | 0.062 | 0.515 | 0.097 | - | |
| SrO | 0.044 | 0.038 | 0.011 | 0.130 | 0.035 |
| Cr2O3 | 0.033 | 0.042 | - | 0.036 | 0.070 |
| ZrO2 | 0.030 | 0.025 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.028 |
| ZnO | 0.019 | 0.016 | 0.006 | 0.055 | 0.007 |
| SnO2 | 0.014 | 0.012 | - | - | |
| CuO | 0.011 | 0.010 | 0.004 | 0.024 | 0.007 |
| Y2O3 | 0.010 | 0.008 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| BaO | - | - | - | - | 0.079 |
| Material | D10 | D50 | D90 | Mean Size | Span (D90 − D10)/D50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [µm] | [µm] | [µm] | [µm] | [µm] | |
| Coal gangue | 1.82 ± 0.05 | 11.17 ± 0.36 | 44.32 ± 2.09 | 18.85 ± 0.81 | 3.80 ± 0.07 |
| Metakaolin | 1.63 ± 0.02 | 9.60 ± 0.12 | 32.50 ± 0.81 | 14.55 ± 0.29 | 3.21 ± 0.04 |
| Waste glass | 111.4 ± 11.7 | 474.9 ± 18.6 | 885.2 ± 66.5 | 541.1 ± 15.30 | 1.6 ± 0.2 |
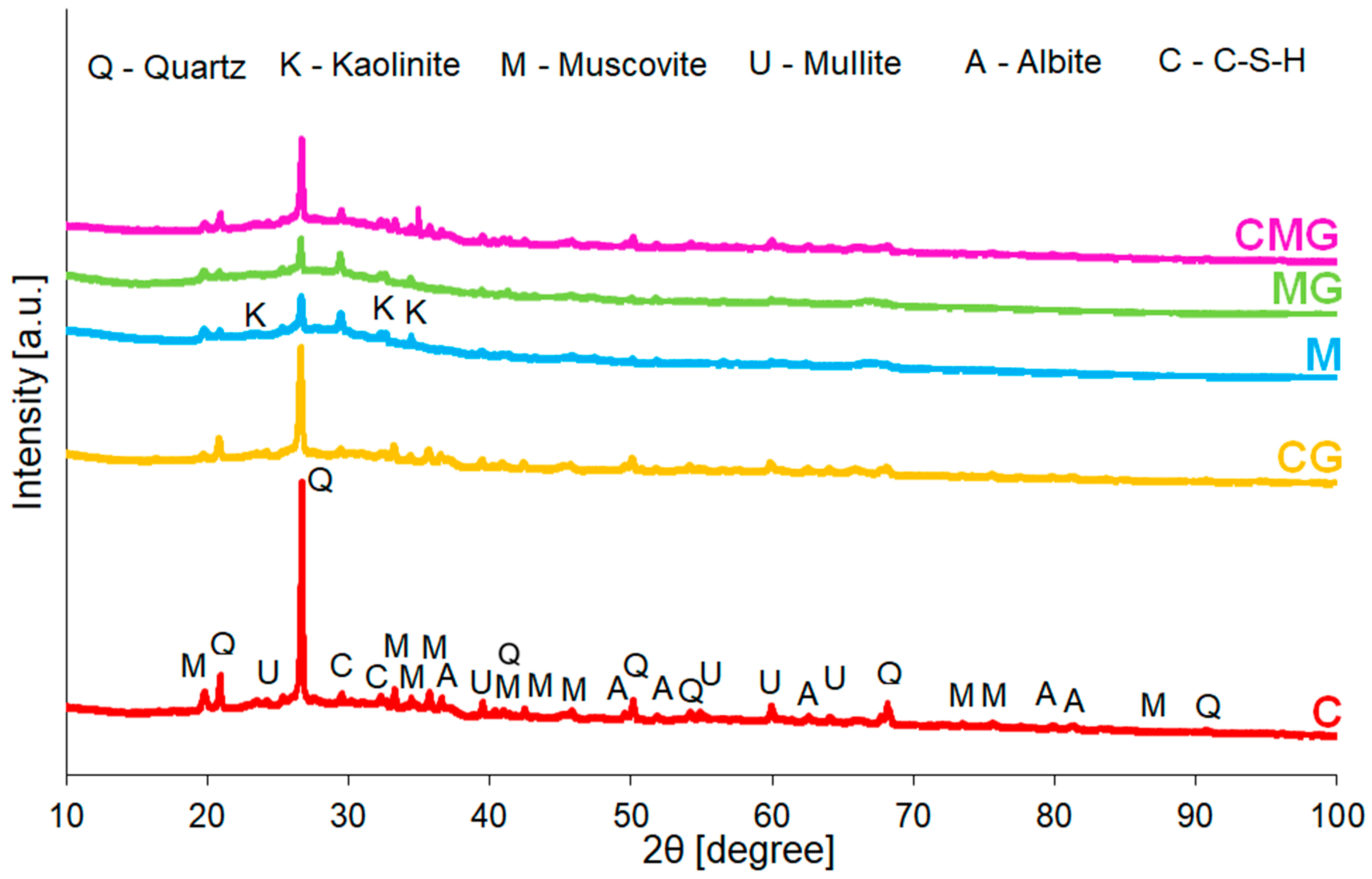
| Raw Material | Identified Mineralogical Compound (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | Kaolinite-1Ad | Illite-2M1 | Muscovite-2M1 | Mullite | |
| SiO2 | Al2Si2O5(OH)4 | (KH3O)Al2Si3AlO10(OH)2 | KAl2(Si3Al)O10(OH,F)2 | Al6O5(SiO4)2 | |
| Coal gangue before calcination | 27.4 | 49.5 | 11.5 | 11.5 | - |
| Coal gangue after calcination | 57.1 | 0.1 | 21.4 | 21.4 | - |
| Metakaolin | 6.3 | 48.0 | 20.6 | 20.6 | 4.6 |
| Material | Specific Surface Area (m2 g−1) | Pore Volume (cm3 g−1) | Pore Size (nm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Point BET | Multi-Point BET | BJH Pore Volume | Total Pore Volume at P/P0 = 0.99 | BJH Average Pore Diameter | |
| Coal gangue before calcination | 6.476 | 8.043 | 0.027 | 0.027 | 2.453 |
| Coal gangue after calcination | 3.819 | 4.150 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 3.056 |
| Metakaolin | 12.590 | 13.370 | 0.106 | 0.106 | 4.317 |
| Sample | Identified Mineralogical Compound | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | Kaolinite | Muscovite | Mullite | Albite | CSH | |
| SiO2 | Al2Si2O5(OH)4 | KAl2(Si3Al)O10(OH,F)2 | Al6O5(SiO4)2 | NaAlSi3O8 | Ca3Si3O9·H2O | |
| C | 27.9 | 0.0 | 35.4 | 10.1 | 0.2 | 26.4 |
| CG | 22.5 | 0.0 | 29.5 | 11.8 | 11.3 | 24.9 |
| M | 3.0 | 0.3 | 41.2 | 4.2 | 21.0 | 30.3 |
| MG | 2.6 | 0.6 | 58.9 | 3.0 | 16.8 | 18.0 |
| CMG | 9.7 | 1.0 | 21.7 | 9.7 | 25.0 | 32.9 |
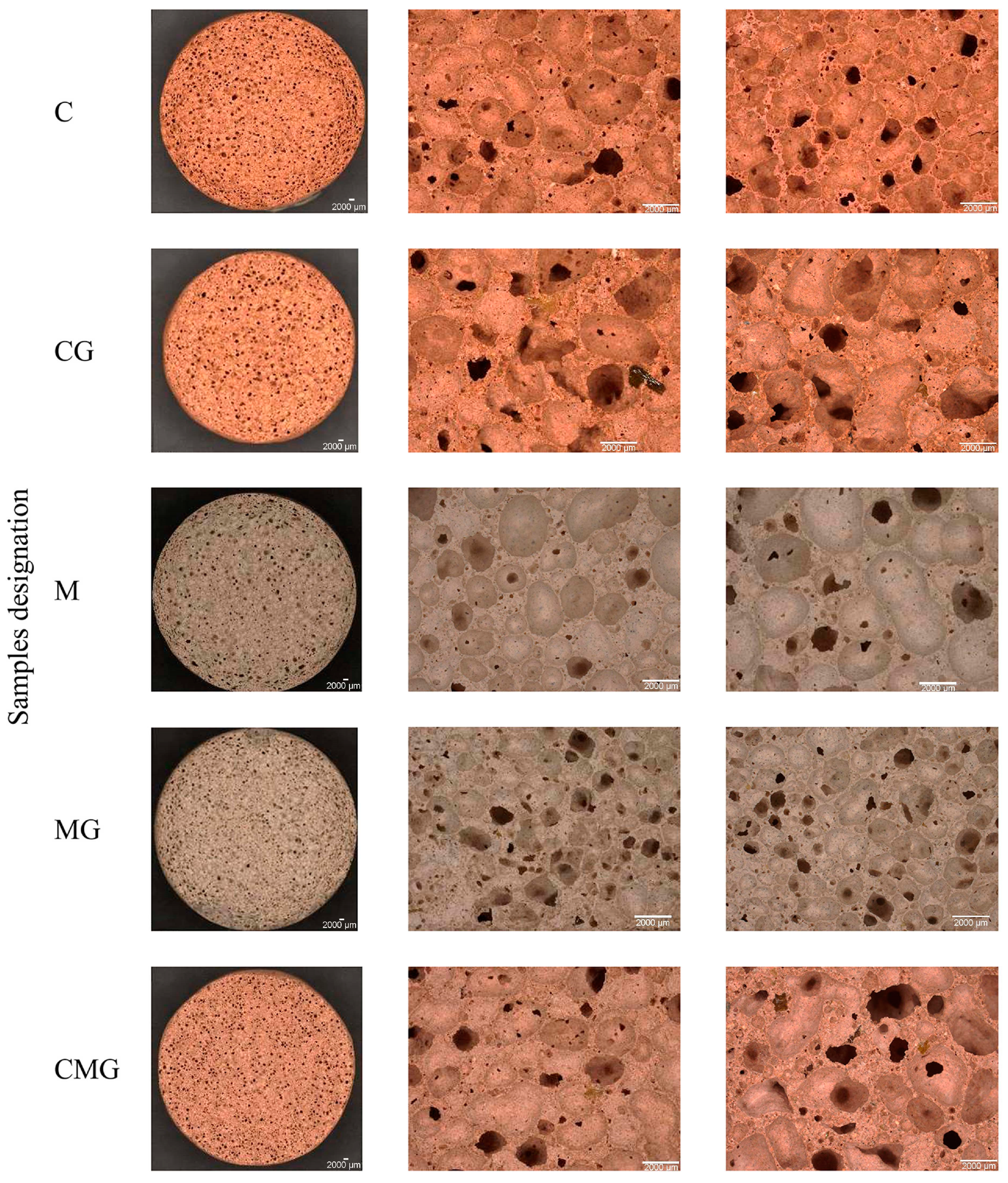
| Sample | Porosity | Inclusions | Structure Thickness | Pores Thickness | Degree of Anisotropy | Homogeneity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total [%] | Open [%] | Closed [%] | WG [%] | S [%] | [mm] | [mm] | - | XY [CTN] | XZ [CTN] | YZ [CTN] | Mean [CTN] | |
| C | 69.0 | 68.7 | 0.3 | - | 0.31 | 0.30 ± 0.08 | 1.62 ± 0.732 | 0.187 | 78.5 ± 15.4 | 78.5 ± 17.1 | 78.5 ± 16.3 | 78.5 ± 16.3 |
| CG | 58.7 | 56.8 | 1.8 | 1.08 | 0.26 | 0.62 ± 0.20 | 1.83 ± 0.658 | 0.156 | 104.9 ± 21.5 | 104.9 ± 21.3 | 104.9 ± 22.7 | 104.9 ± 21.8 |
| CMG | 67.3 | 66.9 | 0.4 | 3.74 | 0.21 | 0.33 ± 0.18 | 1.39 ± 0.569 | 0.126 | 82.9 ± 16.2 | 82.9 ± 17.1 | 82.9 ± 16.6 | 82.9 ± 16.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ziejewska, C.; Bąk, A.; Hodor, K.; Hebda, M. Eco-Friendly Coal Gangue and/or Metakaolin-Based Lightweight Geopolymer with the Addition of Waste Glass. Materials 2023, 16, 6054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16176054
Ziejewska C, Bąk A, Hodor K, Hebda M. Eco-Friendly Coal Gangue and/or Metakaolin-Based Lightweight Geopolymer with the Addition of Waste Glass. Materials. 2023; 16(17):6054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16176054
Chicago/Turabian StyleZiejewska, Celina, Agnieszka Bąk, Krzysztof Hodor, and Marek Hebda. 2023. "Eco-Friendly Coal Gangue and/or Metakaolin-Based Lightweight Geopolymer with the Addition of Waste Glass" Materials 16, no. 17: 6054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16176054
APA StyleZiejewska, C., Bąk, A., Hodor, K., & Hebda, M. (2023). Eco-Friendly Coal Gangue and/or Metakaolin-Based Lightweight Geopolymer with the Addition of Waste Glass. Materials, 16(17), 6054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16176054






