Modification of Bulk Density, Flow Property and Crystallinity of Microcrystalline Cellulose Prepared from Waste Cotton
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Modification of Prepared MCC
2.3. Identification of Microcrystalline Cellulose by Chemical Test
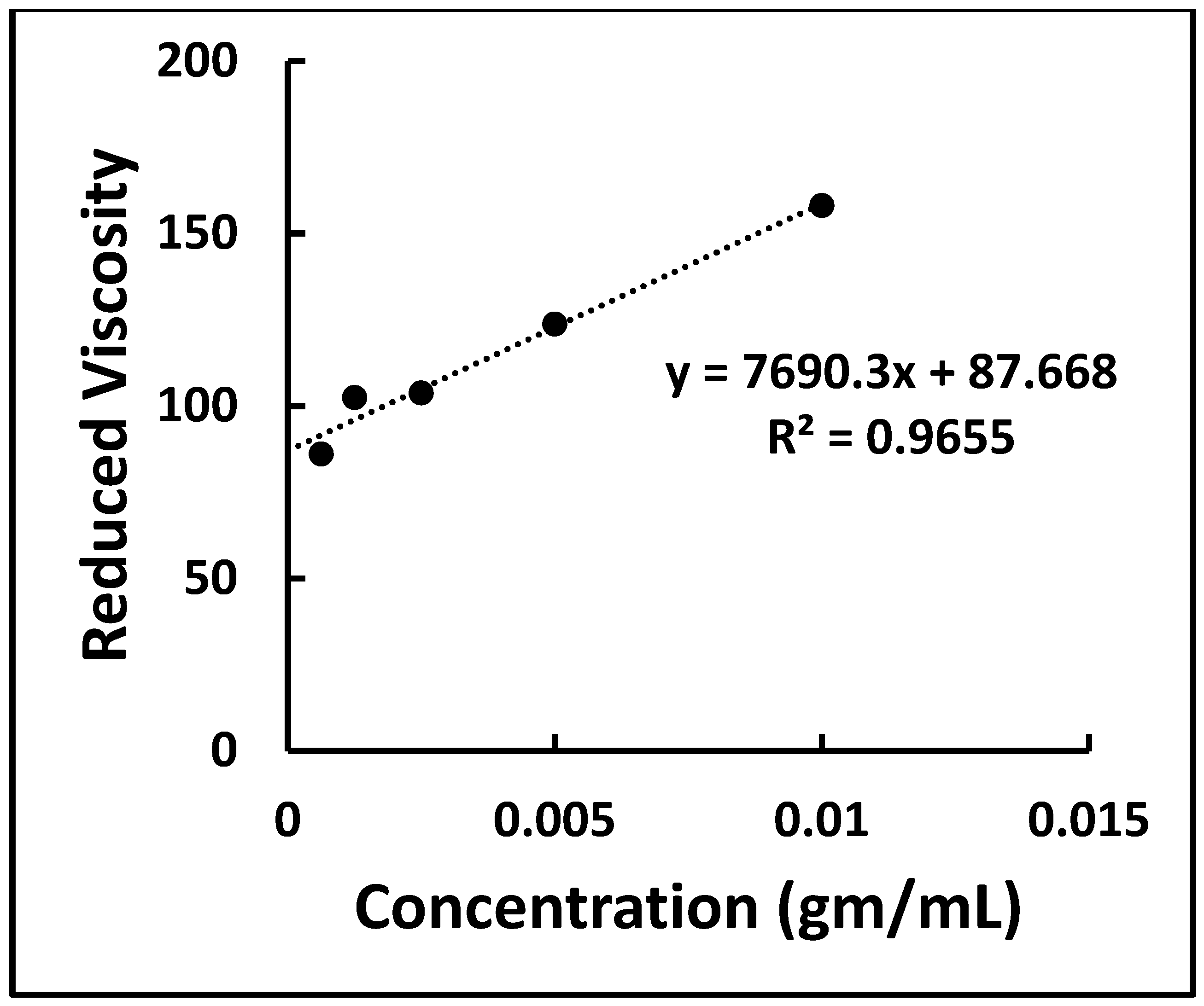
2.4. Identification of MCC by Determining Degree of Polymerization
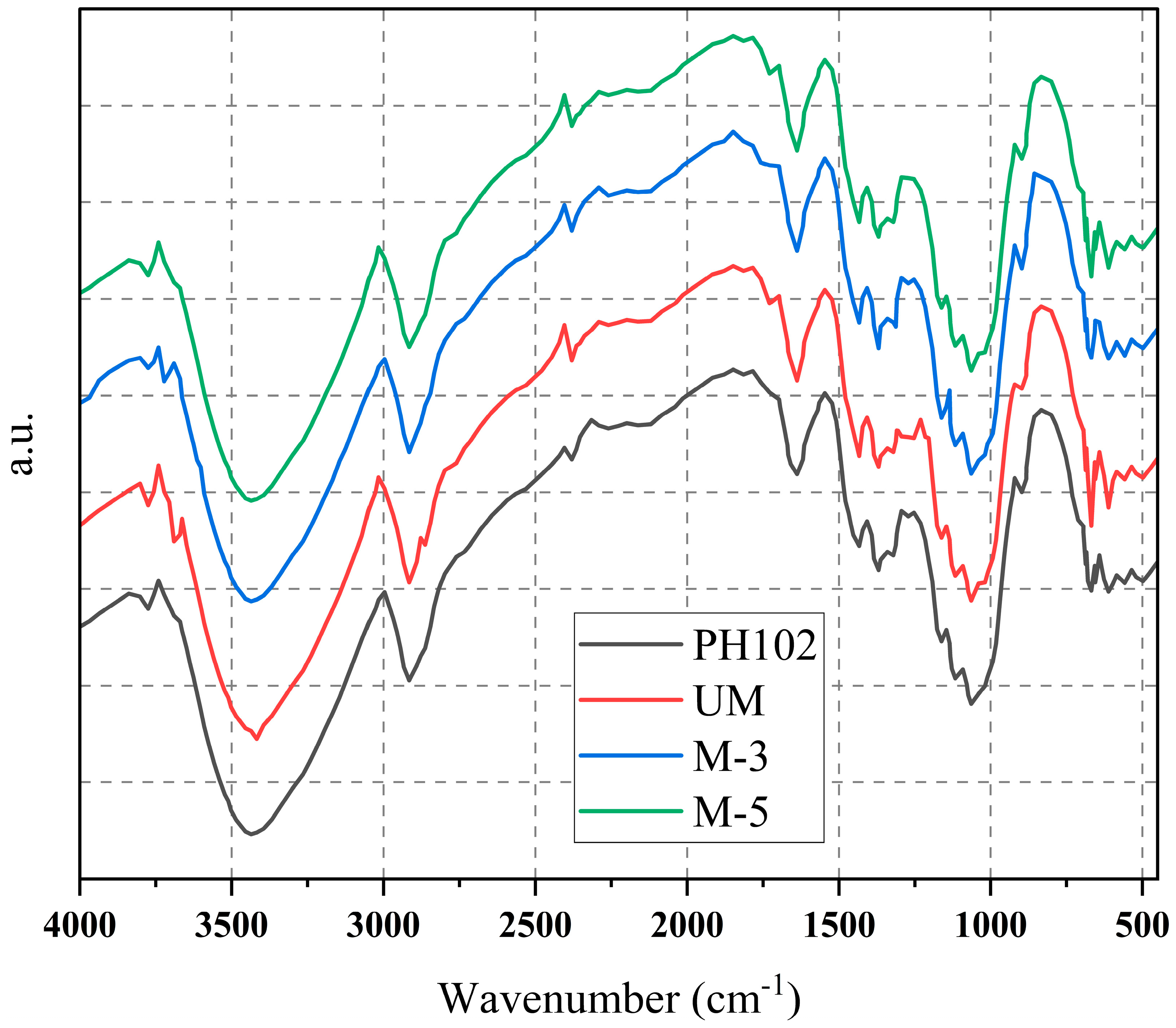
2.5. Identification of MCC by FT-IR
2.6. Evaluation of Bulk Density and Tapped Density of the Unmodified and Modified MCC
2.7. Analysis of Flow Property by Measuring Hausner Index and Compressibility Index (Carr’s Index)
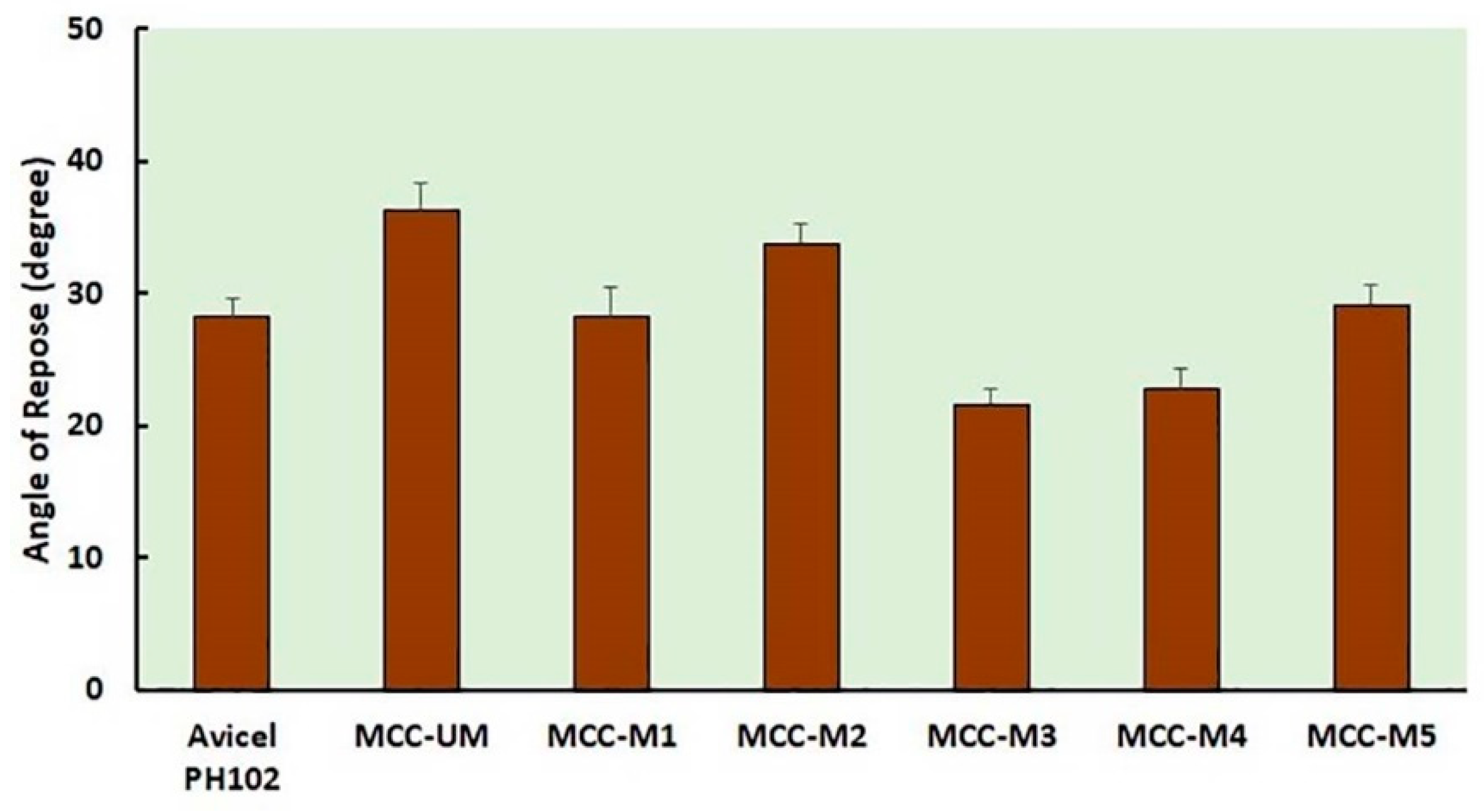
2.8. Analysis of Flow Property by Measuring the Angle of Repose
2.9. Morphology Analysis by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
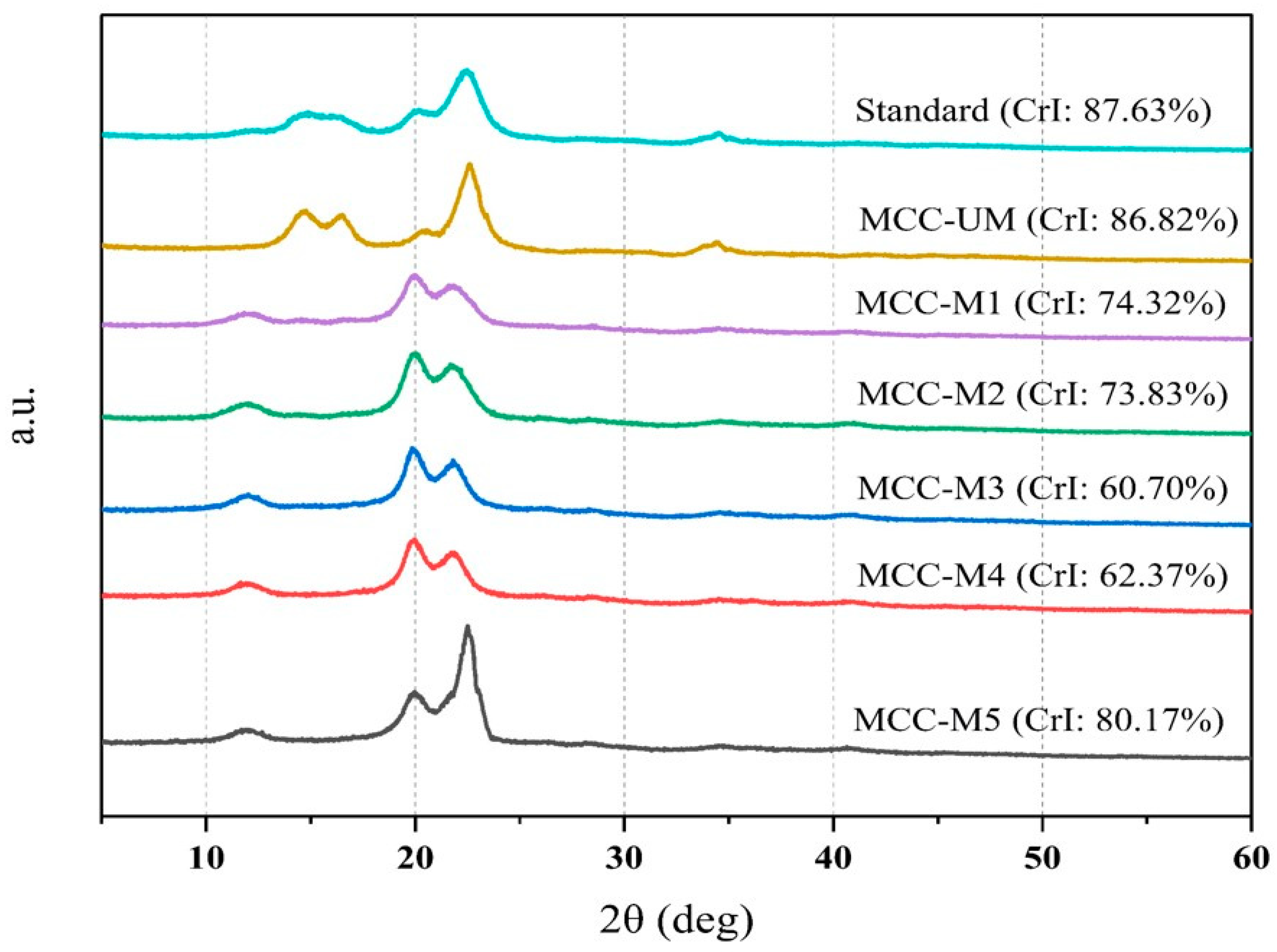
2.10. Evaluation of Crystallinity of the MCC by X-ray Diffraction
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Chemical Identification of the MCC
3.2. Identification of the MCC by Degree of Polymerization of the MCC
3.3. Identification of the MCC by FT-IR of MCC
3.4. Evaluation of Flow Property (CI, Hausner Index, Angle of Repose) of the Unmodified and Modified MCC
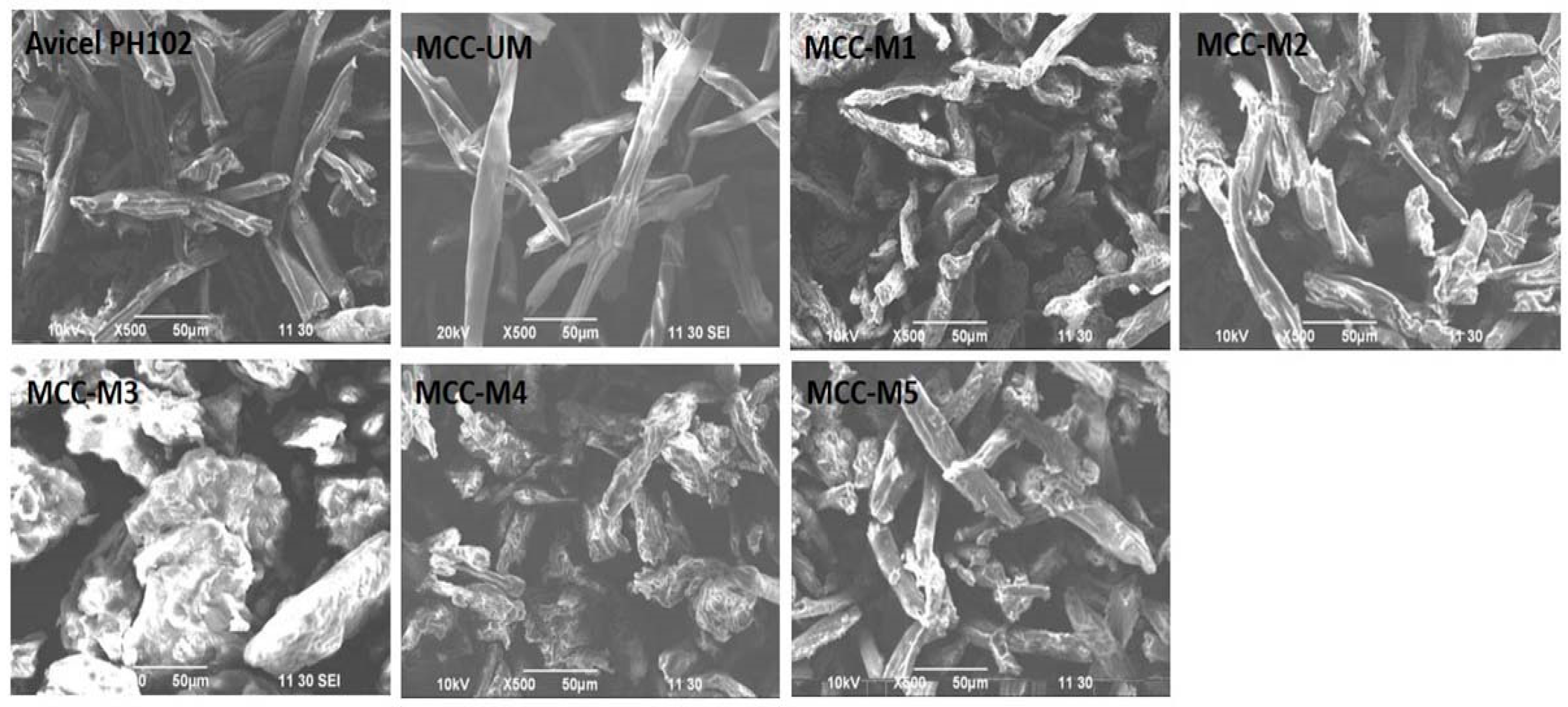
3.5. Evaluation of MCC by SEM
3.6. Evaluation of Crystallinity of the MCC by X-ray Diffraction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- USP 29-NF 24; Microcrystalline Cellulose. United States Pharmacopeia and Formulary. United States Pharmacopeia Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2006.
- Kushnir, E.Y.; Autlov, S.A.; Bazarnova, N.G. Preparation of microcrystalline cellulose directly from wood under microwave radiation. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2015, 41, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setu, M.N.I.; Mian, M.Y.; Lubna, N.J.; Chowdhury, A.A. Preparation of microcrystalline cellulose from cotton and its evaluation as direct compressible excipient in the formulation of naproxen tablets. Dhaka Univ. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 13, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo-Zhi, F.; Wang, Y.; Song, G.; Yan, J.; Li, J. Preparation of microcrystalline cellulose from rice straw under microwave irradiation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44901. [Google Scholar]
- Krivokapić, J.; Ivanović, J.; Djuriš, J.; Medarević, D.; Potpara, Z.; Maksimović, Z.; Ibrić, S. Tableting properties of microcrystalline cellulose obtained from wheat straw measured with a single punch bench top tablet press. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 287, 10–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owolabia, A.; Haafiza, M.; Hossain, M.; Hussin, H.; Fazita, N. Influence of alkaline hydrogen peroxide pre-hydrolysis on the isolation of microcrystalline cellulose from oil palm fronds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 95, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahan, M.S.; Saeed, A.; He, Z.; Ni, Y. Jute as raw material for the preparation of microcrystalline cellulose Synthetic process of MCC. Cellulose 2011, 18, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katakojwala, R.; Mohan, S.V. Microcrystalline cellulose production from sugarcane bagasse: Sustainable process development and life cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249, 119342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Hu, N.; Liu, M.; Xu, Y. Preparation and Characterization of Porous Microcrystalline Cellulose from Corncob. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 151, 112457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhimte, N.A.; Tayade, P.T. Evaluation of microcrystalline cellulose prepared from sisal fibers as a tablet excipient: A technical note. Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists (AAPS). Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2007, 8, E56–E62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Ding, L.; Zhang, K.; Han, J.; Jiang, S. Micro- and nano-fibrils of manau rattan and solvent-exchange-induced high-haze transparent holocellulose nanofibril film. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 298, 120075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Han, X.; Wu, W.; Wang, X.; Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, C.; et al. Oxidation of cellulose molecules toward delignified oxidated hot-pressed wood with improved mechanical properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 15, 123343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miinea, L.A.; Merci, A.; Urbano, A.; Victória, E.M.; Tischer, C.A.; Mali, S. Properties of microcrystalline cellulose extracted from soybean hulls by reactive extrusion. Food Res. Int. 2015, 73, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Monschein, M.; Reisinger, C.; Nidetzky, B. Enzymatic hydrolysis of microcrystalline cellulose and pretreated wheat straw: A detailed comparison using convenient kinetic analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbach, D.; Kruse, A.; Sauer, J.; Storz, J. Is Steam Explosion a Promising Pretreatment for Acid Hydrolysis of Lignocellulosic Biomass? Processes 2020, 8, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, B.; Haldar, D.; Purkait, M.K. A critical review on the techniques used for the synthesis and applications of crystalline cellulose derived from agricultural wastes and forest residues. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoorens, G.; Krier, F.; Leclercq, B.; Carlin, B.; Evrard, B. Microcrystalline cellulose, a direct compression binder in a quality by design environment—A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Changquan Calvin Sun, C.C. A microcrystalline cellulose based drug-composite formulation strategy for developing low dose drug tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 585, 119517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Tanaka, C.; Yuasa, H.; Sakamoto, T. Utility of Microcrystalline Cellulose for Improving Drug Content Uniformity in Tablet Manufacturing Using Direct Powder Compression. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2019, 20, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diarsa, M.; Gupte, A. Preparation, characterization and its potential applications in Isoniazid drug delivery of porous microcrystalline cellulose from banana pseudostem fibers. 3Biotech 2021, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandevivere, L.; Denduyver, P.; Portier, C.; Häusler, O.; De Beer, T.; Vervaet, C.; Vanhoorne, V. Influence of binder attributes on binder effectiveness in a continuous twin screw wet granulation process via wet and dry binder addition. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 585, 119466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, S.; Goodwin, D.J.; Anderson, A.; Sibik, J.; Wilson, D.I.; Gladden, L.F.; Zeitler, J.A. The disintegration process in microcrystalline cellulose based tablets: Influence of temperature, porosity and superdisintegrants. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 3440–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Sugiyama, H.; Kano, M.; Shimono, R.; Shimada, G.; Furukawa, R.; Mano, E.; Motoyama, K.; Koide, T.; Matsui, Y.; et al. Control strategy and methods for continuous direct compression processes. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhao, L.; Lin, X.; Shen, L. An update on microcrystalline cellulose in direct compression: Functionality, critical material attributes, and co-processed excipients. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 278, 118968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amidon, G.E.; Meyer, P.J.; Mudie, D.M. Chapter 10—Particle, Powder, and Compact Characterization. In Developing Solid Oral Dosage Forms Pharmaceutical Theory and Practice, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 271–293. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A. Prediction of quality attributes (mechanical strength, disintegration behavior and drug release) of tablets on the basis of characteristics of granules prepared by high shear wet granulation. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0261051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thielemans, K.; De Bondt, Y.D.; Bosch, S.V.D.; Bautil, A.; Roye, C.; Deneyer, A.; Courtin, C.M.; Sels, B.F. Decreasing the degree of polymerization of microcrystalline cellulose by mechanical impact and acid hydrolysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 294, 119764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Pharmacopeia. Bulk Density and Tapped Density of Powders. Stage 6 Harmonization Official USP; United States Pharmacopeia Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Clayton, J. An introduction to powder characterization. In Handbook of Pharmaceutical Wet Granulation: Theory and Practice in a Quality by Design Paradigm, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 569–613. [Google Scholar]
- Moravkar, K.K.; Shah, D.S.; Magar, A.G.; Bhairav, B.A.; Korde, S.D.; Ranch, K.M.; Chalikwar, S.S. Assessment of pharmaceutical powders flowability and comparative evaluation of lubricants on development of gastro retentive tablets: An application of powder flow tester. J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol. 2022, 71, 103265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, M.; Jawaid, M.; Karim, Z.; Abdullah, L.C. Morphological, physiochemical and thermal properties of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) extracted from bamboo fiber. Molecules 2020, 25, 2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Takabe, K.; Xu, F. Unraveling variations of crystalline cellulose induced by ionic liquid and their effects on enzymatic hydrolysis. Sci. Rep.-Nat. 2017, 7, 10230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kim, H.J. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and simple algorithm analysis for rapid and non-destructive assessment of developmental cotton bers. Sensors 2017, 17, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, R.D.; Bansal, P.S.; Gorade, V.G. Extraction of microcrystalline cellulose from cotton sliver and its comparison with commercial microcrystalline cellulose. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, R.H.; Rana, M.S.; Tasnim, S.; Haque, M.R.; Kabir, S.; Amran, M.S.; Chowdhury, A.A. Characterization and tableting properties of microcrystalline cellulose derived from waste paper via hydrothermal method. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 12, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swensson, B.; Larsson, A.; Hasani, M. Dissolution of cellulose using a combination of hydroxide bases in aqueous solution. Cellulose 2020, 27, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Bertelsen, B.; Andersson, E.; Köhnke, T.; Hedlund, A.; Stigsson, L.; Olsson, U. Revisiting the dissolution of cellulose in NaOH as “Seen” by X-rays. Polymers 2020, 12, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagman, J.; Gentile, L.; Jessen, C.M.; Behrens, M.; Bergqvist, K.E.; Olsson, U. On the Dissolution state of cellulose in cold alkali solutions. Cellulose 2017, 24, 2003–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.; Mallick, S.S.; Garcia-Trinanes, P.; Berry, R.J. An investigation into the flowability of fine powders used in pharmaceutical industries. Powder Technol. 2018, 336, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulton, M.E.; Taylor, K. Pharmaceutics: The Science of Dosage Form Design, 5th ed.Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 2017; p. 247. [Google Scholar]
- Castellanos, A. The relationship between attractive interparticle forces and bulk behaviour in dry and uncharged fine powders. Adv. Phys. 2005, 54, 263–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Muteki, K.; Zhang, L.; Kim, G. Prediction of bulk powder flow performance using comprehensive particle size and particle shape distributions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.S.; Rahim, M.A.; Mosharraf, M.P.; Tipu, M.F.K.; Chowdhury, J.A.; Haque, M.R.; Kabir, S.; Amran, M.S.; Chowdhury, A.A. Morphological, spectroscopic and thermal analysis of cellulose nanocrystals extracted from waste jute fiber by acid hydrolysis. Polymers 2023, 15, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahvenainen, P.; Kontro, I.; Svedström, K. Comparison of sample crystallinity determination methods by X-ray diffraction for challenging cellulose I materials. Cellulose 2016, 23, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Alexandridis, P.; Tsianou, M. Cellulose Dissolution: Insights on the Contributions of Solvent-Induced Decrystallization and Chain Disentanglement. Cellulose 2017, 24, 571–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Bulk Density | Tapped Density | Hausner Ratio | Compressibility Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard (Avicel PH102) | 0.327 ± 0.006 | 0.447 ± 0.006 | 1.368 ± 0.056 | 26.801 ± 3.087 |
| MCC-UM | 0.210 ± 0.010 | 0.300 ± 0.017 | 1.428 ± 0.041 | 29.957 ± 2.056 |
| MCC-M1 | 0.303 ± 0.012 | 0.417 ± 0.012 | 1.374 ± 0.047 | 27.188 ± 2.517 |
| MCC-M2 | 0.253 ± 0.006 | 0.343 ± 0.006 | 1.355 ± 0.008 | 26.218 ± 0.437 |
| MCC-M3 | 0.593 ± 0.015 | 0.693 ± 0.015 | 1.167 ± 0.004 | 14.428 ± 0.316 |
| MCC-M4 | 0.473 ± 0.012 | 0.583 ± 0.021 | 1.232 ± 0.017 | 18.834 ± 1.084 |
| MCC-M5 | 0.433 ± 0.015 | 0.553 ± 0.015 | 1.277 ± 0.010 | 21.698 ± 0.594 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tasnim, S.; Tipu, M.F.K.; Rana, M.S.; Rahim, M.A.; Haque, M.; Amran, M.S.; Chowdhury, A.A.; Chowdhury, J.A. Modification of Bulk Density, Flow Property and Crystallinity of Microcrystalline Cellulose Prepared from Waste Cotton. Materials 2023, 16, 5664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165664
Tasnim S, Tipu MFK, Rana MS, Rahim MA, Haque M, Amran MS, Chowdhury AA, Chowdhury JA. Modification of Bulk Density, Flow Property and Crystallinity of Microcrystalline Cellulose Prepared from Waste Cotton. Materials. 2023; 16(16):5664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165664
Chicago/Turabian StyleTasnim, Sabiha, Md. Fazlul Karim Tipu, Md. Sohel Rana, Md. Abdur Rahim, Mithila Haque, Md. Shah Amran, Abu Asad Chowdhury, and Jakir Ahmed Chowdhury. 2023. "Modification of Bulk Density, Flow Property and Crystallinity of Microcrystalline Cellulose Prepared from Waste Cotton" Materials 16, no. 16: 5664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165664
APA StyleTasnim, S., Tipu, M. F. K., Rana, M. S., Rahim, M. A., Haque, M., Amran, M. S., Chowdhury, A. A., & Chowdhury, J. A. (2023). Modification of Bulk Density, Flow Property and Crystallinity of Microcrystalline Cellulose Prepared from Waste Cotton. Materials, 16(16), 5664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165664








