A Comprehensive Assessment of the Biocompatibility and Safety of Diamond Nanoparticles on Reconstructed Human Epidermis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
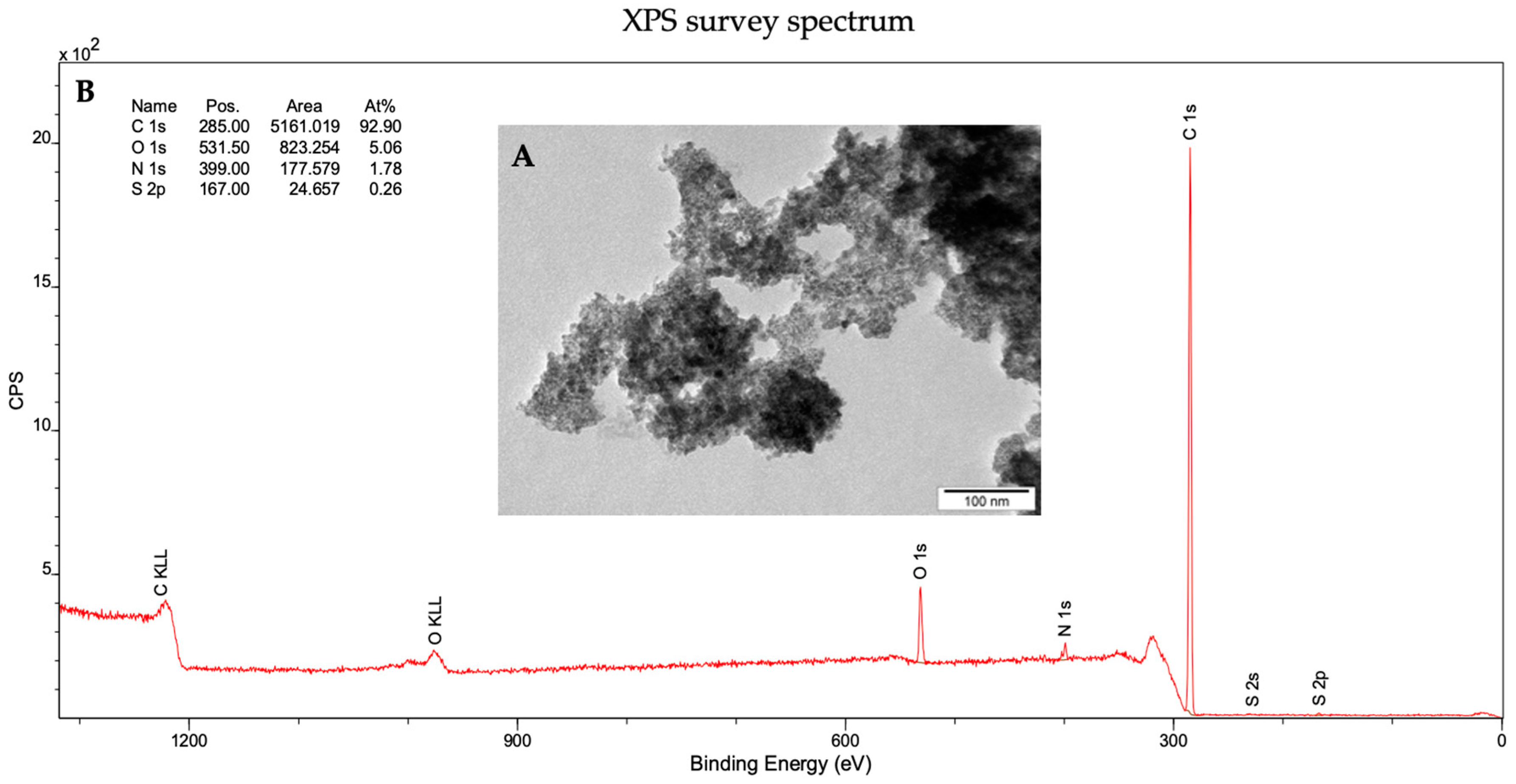
2.1. Characterization of Diamond Nanoparticles
2.2. EpiDermTM and ND Exposure
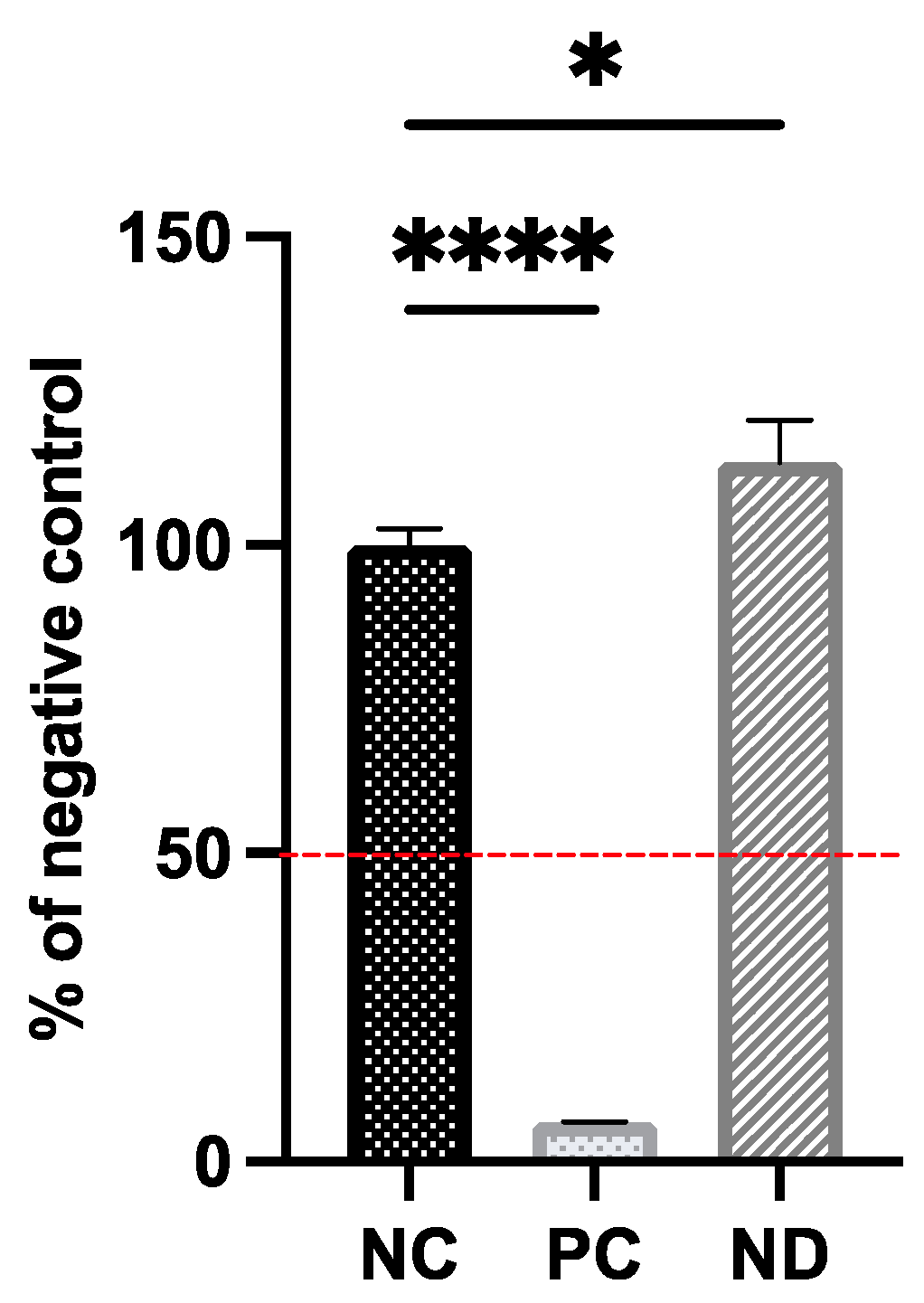
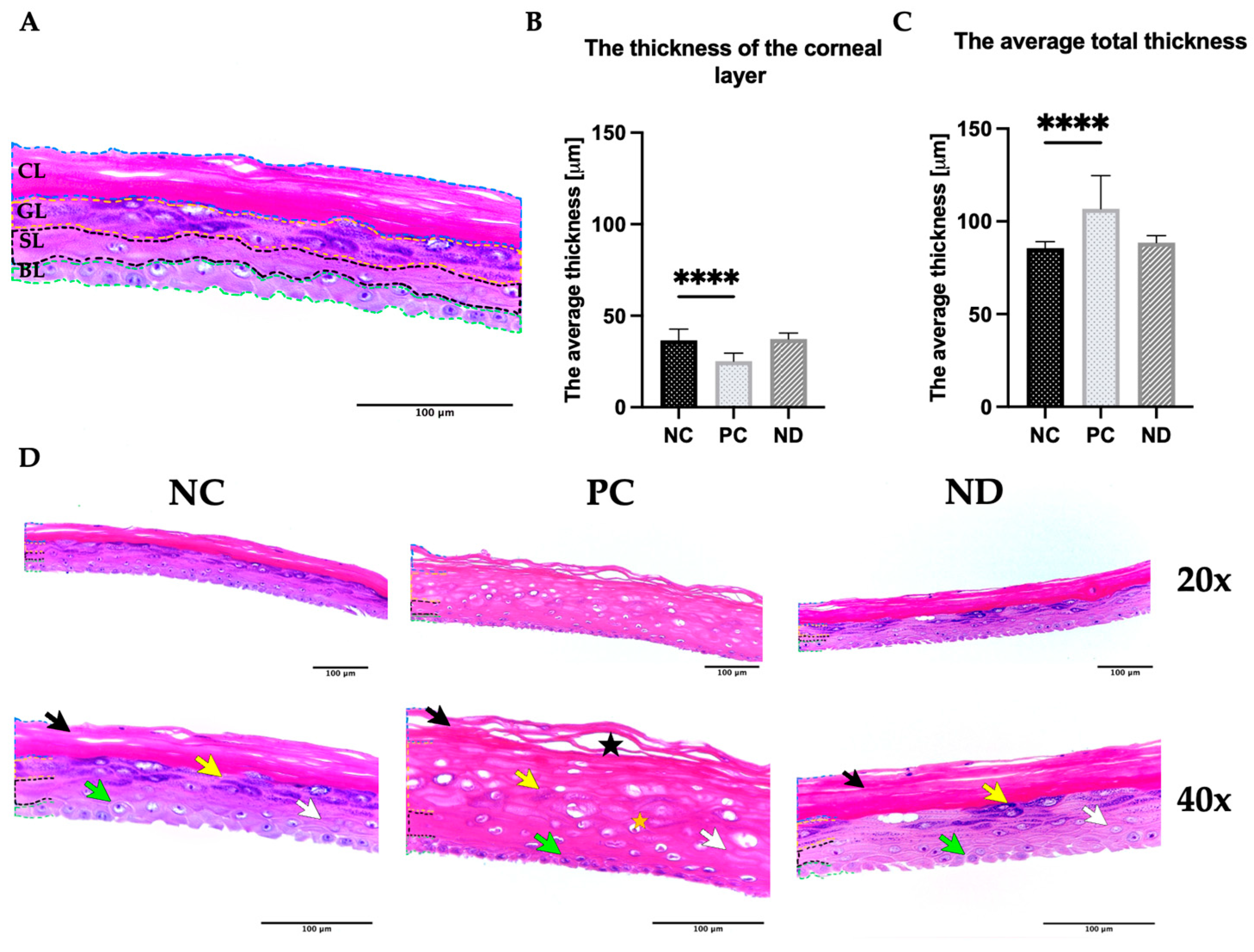
2.3. Tissues Viability Assay
2.4. Tissues Viability Assay
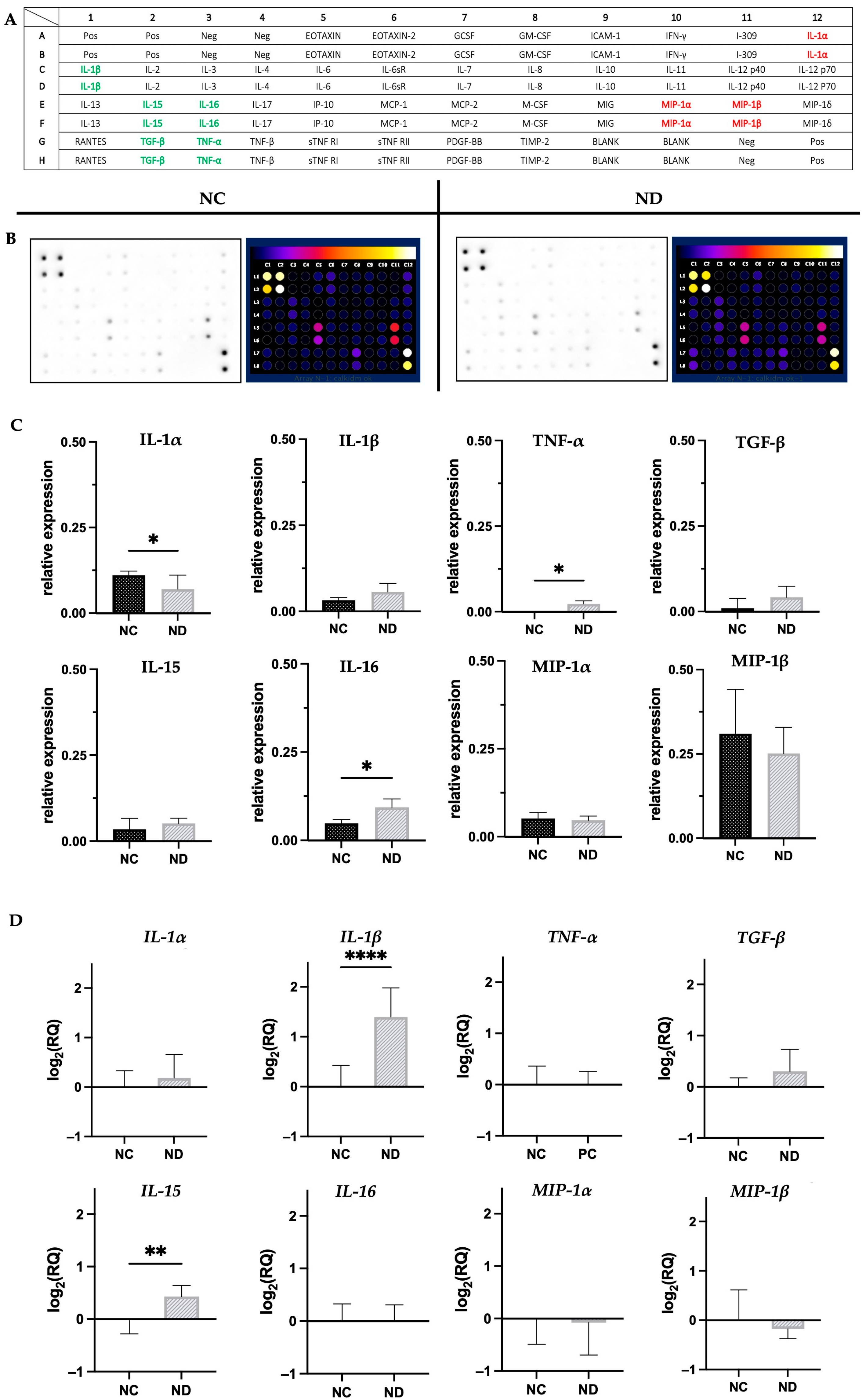
2.5. Inflammatory Cytokines Array
2.6. cDNA Synthesis and qPCR Analyses
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Diamond Nanoparticles
3.2. Biocompatibility of Diamond Nanoparticles
3.3. Evaluation of the Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pichot, V.; Muller, O.; Seve, A.; Yvon, A.; Merlat, L.; Spitzer, D. Optical Properties of Functionalized Nanodiamonds. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shenderova, O.; Koscheev, A.; Zaripov, N.; Petrov, I.; Skryabin, Y.; Detkov, P.; Turner, S.; Van Tendeloo, G. Surface Chemistry and Properties of Ozone-Purified Detonation Nanodiamonds. J. Phys. Chem. 2011, 115, 9827–9837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.; Punetha, V.D.; Bhatt, S.; Punetha, M. Carbon Nanotube-Based Biocompatible Polymer Nanocomposites as an Emerging Tool for Biomedical Applications. Eur. Pol. J. 2023, 16, 112257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprà, P.; Mino, L.; Battiato, A.; Olivero, P.; Sturari, S.; Valsania, M.C.; Varzi, V.; Picollo, F. Interaction of Nanodiamonds with Water: Impact of Surface Chemistry on Hydrophilicity, Aggregation and Electrical Properties. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namdar, R.; Nafisi, S. Nanodiamond Applications in Skin Preparations. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenderova, O.; Grichko, V.; Hens, S.; Walch, J. Detonation Nanodiamonds as UV Radiation Filter. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2007, 16, 2003–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.S.; Sun, D.S.; Lin, Y.C.; Cheng, C.L.; Hung, S.C.; Chen, P.K.; Yang, J.H.; Chang, H.H. Nanodiamonds Protect Skin from Ultraviolet B-Induced Damage in Mice. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batory, M.; Batory, D.; Grabarczyk, J.; Kaczorowski, W.; Kupcewicz, B.; Mitura, K.; Nasti, T.H.; Yusuf, N.; Niedzielski, P. Biological Properties of Carbon Powders Synthesized Using Chemical Vapour Deposition and Detonation Methods. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 9037–9046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adach, K.; Fijalkowski, M.; Skolimowski, J. Antioxidant Effect of Hydroxylated Diamond Nanoparticles Measured in Soybean Oil. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostructures 2015, 23, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 439; In Vitro Skin Irritation: Reconstructed Human Epidermis Test Method. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4; OECD: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS); United Nations: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; ISBN 9789211171990. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, S.A.; Abdelmalak, N.S.; Badawi, A.; Elbayoumy, T.; Sabry, N.; Ramly, A. El Formulation of Tretinoin-Loaded Topical Proniosomes for Treatment of Acne: In-Vitro Characterization, Skin Irritation Test and Comparative Clinical Study. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Draize, J.H.; Woodard, G.; Calvery, H.O. Methods For The Study Of Irritation And Toxicity Of Substances Applied Topically To The Skin And Mucous Membranes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. 1944, 82, 377–390. [Google Scholar]
- Kandarova, H.; Willoughby, J.A.; De Jong, W.H.; Letasiova, S.; Milasova, T.; Bachelor, M.A.; Breyfogle, B.; Handa, Y.; De la Fonteyne, L.; Coleman, K.P. Pre-Validation of an In Vitro Skin Irritation Test for Medical Devices Using the Reconstructed Human Tissue Model EpiDermTM. Toxicol. Vitr. 2018, 50, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, C.L.; Neal, P.J.; Southee, J.A.; Kubulus, J.; Klausner, M. New epidermal model for dermal irritancy testing. Toxicol Vitr. 1994, 8, 889–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosbaum, A.; Vocanson, M.; Rozieres, A.; Hennino, A.; Nicolas, J.F. Allergic and Irritant Contact Dermatitis. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2009, 19, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, J.N.; Griffiths, C.E.; Nickoloff, B.J.; Mitra, R.S.; Dixit, V.M. Keratinocytes as Initiators of Inflammation. Lancet 1991, 337, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bengalli, R.; Colantuoni, A.; Perelshtein, I.; Gedanken, A.; Collini, M.; Mantecca, P.; Fiandra, L. In Vitro Skin Toxicity of CuO and ZnO Nanoparticles: Application in the Safety Assessment of Antimicrobial Coated Textiles. NanoImpact 2021, 21, 100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzlaff, F.; Lehr, C.M.; Wertz, P.W.; Schaefer, U.F. The Human Epidermis Models EpiSkin®, SkinEthic® and EpiDerm®: An Evaluation of Morphology and Their Suitability for Testing Phototoxicity, Irritancy, Corrosivity, and Substance Transport. Eur J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2005, 60, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpentier, G.; Emilie, H. Protein Array Analyzer for ImageJ. In Proceedings of the ImageJ User and Developer Conference, Luxembourg, 27–29 October 2010; Centre de Recherche Public Henri Tudor: Luxembourg, 2010; pp. 238–240. [Google Scholar]
- Aithal, M.G.S.; Rajeswari, N. Validation of Housekeeping Genes for Gene Expression Analysis in Glioblastoma Using Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction. Brain Tumor. Res. Treat. 2015, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szliszka, E.; Czuba, Z.P.; Domino, M.; Mazur, B.; Zydowicz, G.; Krol, W. Ethanolic Extract of Propolis (EEP) Enhances the Apoptosis- Inducing Potential of TRAIL in Cancer Cells. Molecules 2009, 14, 738–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbuna, C.; Parmar, V.K.; Jeevanandam, J.; Ezzat, S.M.; Patrick-Iwuanyanwu, K.C.; Adetunji, C.O.; Khan, J.; Onyeike, E.N.; Uche, C.Z.; Akram, M.; et al. Toxicity of Nanoparticles in Biomedical Application: Nanotoxicology. J. Toxicol. 2021, 2021, 9954443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochalin, V.N.; Shenderova, O.; Ho, D.; Gogotsi, Y. The Properties and Applications of Nanodiamonds. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger, A.; Kataoka, F.; Ozawa, M.; Fujino, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Aleksenskii, A.E.; Vul’, A.Y.; Osawa, E. Unusually Tight Aggregation in Detonation Nanodiamond: Identification and Disintegration. Carbon N. Y. 2005, 43, 1722–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osswald, S.; Yushin, G.; Mochalin, V.; Kucheyev, S.O.; Gogotsi, Y. Control of Sp2/Sp3 Carbon Ratio and Surface Chemistry of Nanodiamond Powders by Selective Oxidation in Air. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 11635–11642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koinuma, M.; Tateishi, H.; Hatakeyama, K.; Miyamoto, S.; Ogata, C.; Funatsu, A.; Taniguchi, T.; Matsumoto, Y. Analysis of Reduced Graphene Oxides by X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy and Electrochemical Capacitance. Chem. Lett. 2013, 42, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, F.Y.; Xie, W.G.; Gong, L.; Zhang, W.H.; Chen, S.H.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Chen, J. Surface Characterization on Graphitization of Nanodiamond Powder Annealed in Nitrogen Ambient. Surf. Interface Anal. 2010, 42, 1514–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabchinskii, M.K.; Dideikin, A.T.; Kirilenko, D.A.; Baidakova, M.V.; Shnitov, V.V.; Roth, F.; Konyakhin, S.V.; Besedina, N.A.; Pavlov, S.I.; Kuricyn, R.A.; et al. Facile Reduction of Graphene Oxide Suspensions and Films Using Glass Wafers. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oh, Y.J.; Yoo, J.J.; Kim, Y.I.; Yoon, J.K.; Yoon, H.N.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S. Bin Oxygen Functional Groups and Electrochemical Capacitive Behavior of Incompletely Reduced Graphene Oxides as a Thin-Film Electrode of Supercapacitor. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 116, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mccafferty, E.; Wightman, J.P. Determination of the concentration of surface hydroxyl groups on metal oxide films by a quantitative XPS method. Surf. Interface Anal. 1998, 26, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stobinski, L.; Lesiak, B.; Malolepszy, A.; Mazurkiewicz, M.; Mierzwa, B.; Zemek, J.; Jiricek, P.; Bieloshapka, I. Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide Studied by the XRD, TEM and Electron Spectroscopy Methods. J. Electron. Spectros Relat. Phenom. 2014, 195, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larciprete, R.; Gardonio, S.; Petaccia, L.; Lizzit, S. Atomic Oxygen Functionalization of Double Walled C Nanotubes. Carbon N. Y. 2009, 47, 2579–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, B.P.; Biesinger, M.C.; McIntyre, N.S. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Studies of Reactions on Chromium Metal and Chromium Oxide Surfaces. J. Electron. Spectros Relat. Phenom. 2011, 184, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddi, C.; Bourquard, F.; Barnier, V.; Avila, J.; Asensio, M.C.; Tite, T.; Donnet, C.; Garrelie, F. Nano-Architecture of Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Films Synthesized from a Solid CN Source. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raicopol, M.; Andronescu, C.; Atasiei, R.; Hanganu, A.; Pilan, L. Post-Polymerization Electrochemical Functionalization of a Conducting Polymer: Diazonium Salt Electroreduction at Polypyrrole Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, G103–G113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.K.; Peng, B.; Haller, G.L.; Ember, E.E.; Lercher, J.A. Nitrogen Modified Carbon Nano-Materials as Stable Catalysts for Phosgene Synthesis. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 5843–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik, B.; Sawosz, E.; Szczepaniak, J.; Strojny, B.; Sosnowska, M.; Daniluk, K.; Zielińska-Górska, M.; Bałaban, J.; Chwalibog, A.; Wierzbicki, M. Effects of Metallic and Carbon-Based Nanomaterials on Human Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines Aspc-1 and Bxpc-3. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grodzik, M.; Szczepaniak, J.; Strojny-Cieslak, B.; Hotowy, A.; Wierzbicki, M.; Jaworski, S.; Kutwin, M.; Soltan, E.; Mandat, T.; Lewicka, A.; et al. Diamond Nanoparticles Downregulate Expression of CycD and Cyce in Glioma Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adach, K.; Fijalkowski, M.; Gajek, G.; Skolimowski, J.; Kontek, R.; Blaszczyk, A. Studies on the Cytotoxicity of Diamond Nanoparticles against Human Cancer Cells and Lymphocytes. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 254, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierzbicki, M.; Zawadzka, K.; Wójcik, B.; Jaworski, S.; Strojny, B.; Ostrowska, A.; Małolepszy, A.; Mazurkiewicz-Pawlicka, M.; Sawosz, E. Differences in the Cell Type-Specific Toxicity of Diamond Nanoparticles to Endothelial Cells Depending on the Exposure of the Cells to Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurantowicz, N.; Strojny, B.; Sawosz, E.; Jaworski, S.; Kutwin, M.; Grodzik, M.; Wierzbicki, M.; Lipińska, L.; Mitura, K.; Chwalibog, A. Biodistribution of a High Dose of Diamond, Graphite, and Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles After Multiple Intraperitoneal Injections in Rats. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices. Part 5: Tests for in Vitro Cytotoxicity. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Mitura, K.; Kornacka, J.; Niemiec-Cyganek, A.; Pawlus-łachecka, L.; Mydłowska, K.; Sobczyk-Guzenda, A.; Kaczorowski, W.; Ossowska, P.; Bałasz, B.; Wilczek, P. The Influence of Diamond Nanoparticles on Fibroblast Cell Line L929, Cytotoxicity and Bacteriostaticity of Selected Pathogens. Coatings 2022, 12, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majie, A. An Overview of Nano Diamond Formulation in Cancer Treatment. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2022, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, M.F.; desJardins-Park, H.E.; Mascharak, S.; Borrelli, M.R.; Longaker, M.T. Understanding the Impact of Fibroblast Heterogeneity on Skin Fibrosis. Dis. Model Mech. 2020, 13, dmm044164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burleson, T.; Yusuf, N.; Stanishevsky, A. Surface Modification of Nanodiamonds for Biomedical Application and Analysis by Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Achiev. Mater. 2009, 37, 258–263. [Google Scholar]
- Mytych, J.; Wnuk, M.; Rattan, S.I.S. Low Doses of Nanodiamonds and Silica Nanoparticles Have Beneficial Hormetic Effects in Normal Human Skin Fibroblasts in Culture. Chemosphere 2016, 148, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulskamp, K.; Diabaté, S.; Krug, H.F. Carbon Nanotubes Show No Sign of Acute Toxicity but Induce Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species in Dependence on Contaminants. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 168, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones-Vico, M.I.; Fernández-González, A.; Pérez-Castejón, E.; Montero-Vílchez, T.; Arias-Santiago, S. Cytotoxicity and Epidermal Barrier Function Evaluation of Common Antiseptics for Clinical Use in an Artificial Autologous Skin Model. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska-Górska, M.; Sawosz, E.; Sosnowska, M.; Hotowy, A.; Grodzik, M.; Górski, K.; Strojny-Cieślak, B.; Wierzbicki, M.; Chwalibog, A. Molecular Biocompatibility of a Silver Nanoparticle Complex with Graphene Oxide to Human Skin in a 3D Epidermis In Vitro Model. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perevedentseva, E.; Ali, N.; Karmenyan, A.; Skovorodkin, I.; Prunskaite-Hyyryläinen, R.; Vainio, S.; Cheng, C.L.; Kinnunen, M. Optical Studies of Nanodiamond-Tissue Interaction: Skin Penetration and Localization. Materials 2019, 12, 3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vasilyeva, E.Y.; Prokhorenkov, V.I.; Puzyr, A.P.; Bondar, V.S. The Effects of Nanodiamonds at the Action of Colored Metal Ions on the Skin of Guinea Pigs. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 07, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerber, P.A.; Buhren, B.A.; Schrumpf, H.; Homey, B.; Zlotnik, A.; Hevezi, P. The Top Skin-Associated Genes: A Comparative Analysis of Human and Mouse Skin Transcriptomes. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitura, K.; Niedzielski, P.; Bartosz, G.; Moll, J.; Walkowiak, B.; Pawłowska, Z.; Louda, P.; Kieć-Świerczyńska, M.; Mitura, S. Interactions between Carbon Coatings and Tissue. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 2117–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larese Filon, F.; Crosera, M.; Timeus, E.; Adami, G.; Bovenzi, M.; Ponti, J.; Maina, G. Human Skin Penetration of Cobalt Nanoparticles through Intact and Damaged Skin. Toxicol. Vitr. 2013, 27, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, P.M.; Friend, D.S. The Permeability Barrier In Mammalian Epidermis. J. Cell Biol. 1975, 65, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.G.; Choi, D.; Lim, K.M. Evaluation of Skin Irritation of Acids Commonly Used in Cleaners in 3D-Reconstructed Human Epidermis Model, KeraSkinTM. Toxics 2022, 10, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, J.P.; Hotchkiss, R.S.; Karl, I.E.; Buchman, T.G. Mechanisms of Cell Injury and Death. Br. J. Anaesth. 1996, 77, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novak-Bilić, G.; Vučić, M.; Japundžić, I.; Meštrović-Štefekov, J.; Stanić-Duktaj, S.; Lugović-Mihić, L. Irritant And Allergic Contact Dermatitis—Skin Lesion Characteristics. Acta Clin. Croat. 2018, 57, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jing, C.; Guo, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhai, L.; Liu, J.; Sun, G.; Wang, F.; Xu, Y.; et al. Screening and Research on Skin Barrier Damage Protective Efficacy of Different Mannosylerythritol Lipids. Molecules 2022, 27, 4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsabahy, M.; Wooley, K.L. Cytokines as Biomarkers of Nanoparticle Immunotoxicity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5552–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, C.; Wei, Q.; Zhu, J.; Qin, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, S. Clinical Value of Assessing Serum Levels of Inflammatory Cytokines in the Early Diagnosis of Patients with Primary Liver Carcinoma: A Retrospective Observational Study. J. BioX. Res. 2021, 4, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröne, A. Keratinocytes and Cytokines. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2002, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feghali, C.A.; Wright, T.M. Cytokines in acute and chronic inflammation. Front. Biosci. 1997, 2, d12–d26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magcwebeba, T.; Riedel, S.; Swanevelder, S.; Bouic, P.; Swart, P.; Gelderblom, W. Interleukin 1α, Induction in Human Keratinocytes (HaCaT): An In Vitro Model for Chemoprevention in Skin. J. Skin. Cancer 2012, 2012, 393681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bashir, M.M.; Sharma, M.R.; Werth, V.P. UVB and Proinflammatory Cytokines Synergistically Activate TNF-α Production in Keratinocytes through Enhanced Gene Transcription. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewis, R.W.; Mccall, J.C.; Botham, P.A.; Kimber, I. Investigation of TNF-alpha release as a measure of skin irritancy. Toxicol Vitr. 1993, 7, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Stieger, M.; Yawalkar, N.; Kakeda, M. Cytokines and Chemokines in Irritant Contact Dermatitis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 916497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dittmar, D.; Schuttelaar, M.L. Immunology and Genetics of Tumour Necrosis Factor in Allergic Contact Dermatitis. Contact Dermat. 2017, 76, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simó, R.; Barbosa-Desongles, A.; Lecube, A.; Hernandez, C.; Selva, D.M. Potential Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Downregulating Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin. Diabetes 2012, 61, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wullaert, A.; Van Loo, G.; Heyninck, K.; Beyaert, R. Hepatic Tumor Necrosis Factor Signaling and Nuclear Factor-ΚB: Effects on Liver Homeostasis and Beyond. Endocr. Rev. 2007, 28, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, D.; Lei, Q.; Pinget, G.; Cheong, D.A.; Gautam, A.; Yusoff, R.; Su, B.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kondyurin, A.; Knowles, J.C. The Protein Corona Determines the Cytotoxicity of Nanodiamonds: Implications of Corona Formation and Its Remodelling on Nanodiamond Applications in Biomedical Imaging and Drug Delivery. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 4798–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.Y.; Butler, A.P.; Locniskar, M.F.; Fischer, S.M. Signal Transduction Pathway(s) Involved in Phorbol Ester and Autocrine Induction of Interleukin-1α MRNA in Murine Keratinocytes. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 17971–17980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupper, T.S.; Chua, A.O.; Flood, P.; Mcguire, J.; Gubler, U. Interleukin 1 gene expression in cultured human keratinocytes is augmented by ultraviolet irradiation. J. Clin. Invest. 1987, 80, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, W.; Lee, W.; Kim, H.N.; Jeong, J.; Park, H.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Jung, D.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, S.W.; et al. Nanodiamond as a Cytokine Sponge in Infectious Diseases. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 862495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, K.; Katoh, N.; Soga, F.; Kishimoto, S. The Role of Interleukin-16 in Murine Contact Hypersensitivity. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2005, 140, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathy, N.L.; Scheuer, W.; Lanzendo, È.; Rfer, M.; Honold, K.; Ambrosius, D.; Norley, S.; Kurth, R. Interleukin-16 stimulates the expression and production of pro-inflammatory cytokines by human monocytes. Immunology 2000, 100, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.W.; Iwatsuki, K.; Inoue, M.; Matsui, T.; Nishibu, A.; Akiba, H.; Kaneko, F. Interleukin-15 is not a constitutive cytokine in the epidermis, but is inducible in culture or inflammatory conditions. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1999, 79, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blauvelt, A.; Asada, H.; Klaus-Kovtun, V.; Altman, D.J.; Lucey, D.R.; Katz, S.I. Interleukin-15 MRNA Is Expressed by Human Keratinocytes, Langerhans Cells, and Blood-Derived Dendritic Cells and Is Downregulated by Ultraviolet B Radiation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1996, 106, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rü, R.; Asadullah, K.; Seifert, M.; Budagian, V.M.; Arnold, R.; Trombotto, C.; Paus, R.; Bulfone-Paus, S. Inhibition of Keratinocyte Apoptosis by IL-15: A New Parameter in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis? J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 2240–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, A.M.; Griffiths, J.L.; Sanders, A.J.; Owen, S.; Ruge, F.; Harding, K.G.; Jiang, W.G. The Clinical Significance and Impact of Interleukin 15 on Keratinocyte Cell Growth and Migration. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blaber, S.P.; Hill, C.J.; Webster, R.A.; Say, J.M.; Brown, L.J.; Wang, S.C.; Vesey, G.; Herbert, B.R. Effect of Labeling with Iron Oxide Particles or Nanodiamonds on the Functionality of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e52997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolarsick, P.A.; Ann Kolarsick, M.; Goodwin, C. Anatomy and Physiology of the Skin. J. Dermatol. Nurses Assoc. 2006, 3, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raj, D.; Brash, D.E.; Grossman, D. Keratinocyte apoptosis in epidermal development and disease. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waldmann, T.A. Targeting the interleukin-15/interleukin-15 receptor system in inflammatory autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2004, 6, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mizutani, H.; Black, R.; Kupper, T.S. Human Keratinocytes Produce but Do Not Process Pro-Interleukin-1 (IL-1) Beta Different Strategies of IL-1 Production and Processing in Monocytes and Keratinocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 87, 1066–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- England, H.; Summersgill, H.R.; Edye, M.E.; Rothwell, N.J.; Brough, D. Release of Interleukin-1 α or Interleukin-1 β Depends on Mechanism of Cell Death. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 15942–15950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, L.O.; Lippiatt, S.; Biancanello, F.S.; Ridder, S.D.; Washburn, N.R. The Quantification of Cellular Viability and Inflammatory Response to Stainless Steel Alloys. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5296–5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, V.; Halloran, B.A.; Ambalavanan, N.; Catledge, S.A.; Vohra, Y.K. In Vitro Studies on the Effect of Particle Size on Macrophage Responses to Nanodiamond Wear Debris. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1939–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohammed, J.; Gunderson, A.J.; Khong, H.H.; Koubek, R.D.; Udey, M.C.; Glick, A.B. TGFβ1 Overexpression by Keratinocytes Alters Skin Dendritic Cell Homeostasis and Enhances Contact Hypersensitivity. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhavsar, I.; Miller, C.S.; Al-Sabbagh, M. Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-1 Alpha (MIP-1 Alpha)/CCL3: As a Biomarker. In General Methods in Biomarker Research and Their Applications; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 1–2, pp. 223–249. ISBN 9789400776968. [Google Scholar]
- Penn, J.W.; Grobbelaar, A.O.; Rolfe, K.J. The role of the TGF-β family in wound healing, burns and scarring: A review. Int. J. Burns Trauma. 2012, 2, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, R.W.D.; Vickaryous, M.K.; Viloria-Petit, A.M. Signalling by Transforming Growth Factor Beta Isoforms in Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration. J. Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, C.-K.; Tomic-Canic, M.; Lucas, D.J.; Simon, M.; Blumenberg, M. TGFP Promotes the Basal Phenotype of Epidermal Keratinocytes: Transcriptional Induction of K#5 and K# 14 Keratin Genes. Growth Factors 1995, 12, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauviel, A. Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Signaling in Skin: Stromal to Epithelial Cross-Talk. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Hu, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Fan, C.; Song, H. Reprogramming of Cancer Invasiveness and Macrophage Education: Via a Nanostructured Antagonist of the TGFβ Receptor. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laing, K.J.; Secombes, C.J. Chemokines. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2004, 28, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallud, A.; Delaval, M.; Kinaret, P.; Marwah, V.S.; Fortino, V.; Ytterberg, J.; Zubarev, R.; Skoog, T.; Kere, J.; Correia, M.; et al. Multiparametric Profiling of Engineered Nanomaterials: Unmasking the Surface Coating Effect. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2002221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, W.Y.; Chou, C.C.; Ho, C.C.; Yu, S.L.; Chen, H.Y.; Chou, H.Y.E.; Chen, J.J.W.; Chen, H.W.; Yang, P.C. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Induce Airway Hyperreactivity and Parenchymal Injury in Mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Sequence | Source |
|---|---|---|
| RPL13 | F: CATAGGAAGCTGGGAGCAAG R: GCCCTCCAATCAGTCTTCTG | [21] |
| IL-1α | F: TGTATGTGACTGCCCAAGATGAAG R: AGAGGAGGTTGGTCTCACTACC | sp |
| IL-1β | F: CCACAGACCTTCCAGGAGAATG R: GTGCAGTTCAGTGATCGTACAGG | sp |
| TNF-α | F: GGCTCCAGGCGGTGCTTGTTC R: AGAGGCGATGCGGCTGATG | [22] |
| TGF-β | F: TACCTGAACCCGTGTTGCTCTC R: GTTGCTGAGGTATCGCCAGGAA | sp |
| IL-15 | F: AACAGAAGCCAACTGGGTGAATG R: CTCCAAGAGAAAGCACTTCATTGC | sp |
| IL-16 | F: TTGGACACAGGGTTCTCGCTCA R: AGCAGGGAGATAACGGACTGAC | sp |
| MIP-1α | F: ACTTTGAGACGAGCAGCCAGTG R: TTTCTGGACCCACTCCTCACTG | sp |
| MIP-1β | F: GCTTCCTCGCAACTTTGTGGTAG R: GGTCATACACGTACTCCTGGAC | sp |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fraczek, W.; Kregielewski, K.; Wierzbicki, M.; Krzeminski, P.; Zawadzka, K.; Szczepaniak, J.; Grodzik, M. A Comprehensive Assessment of the Biocompatibility and Safety of Diamond Nanoparticles on Reconstructed Human Epidermis. Materials 2023, 16, 5600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165600
Fraczek W, Kregielewski K, Wierzbicki M, Krzeminski P, Zawadzka K, Szczepaniak J, Grodzik M. A Comprehensive Assessment of the Biocompatibility and Safety of Diamond Nanoparticles on Reconstructed Human Epidermis. Materials. 2023; 16(16):5600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165600
Chicago/Turabian StyleFraczek, Wiktoria, Kacper Kregielewski, Mateusz Wierzbicki, Patryk Krzeminski, Katarzyna Zawadzka, Jaroslaw Szczepaniak, and Marta Grodzik. 2023. "A Comprehensive Assessment of the Biocompatibility and Safety of Diamond Nanoparticles on Reconstructed Human Epidermis" Materials 16, no. 16: 5600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165600
APA StyleFraczek, W., Kregielewski, K., Wierzbicki, M., Krzeminski, P., Zawadzka, K., Szczepaniak, J., & Grodzik, M. (2023). A Comprehensive Assessment of the Biocompatibility and Safety of Diamond Nanoparticles on Reconstructed Human Epidermis. Materials, 16(16), 5600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165600









