Study on the Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Nd-Fe-B/Fe-Co Composite Nanowires
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
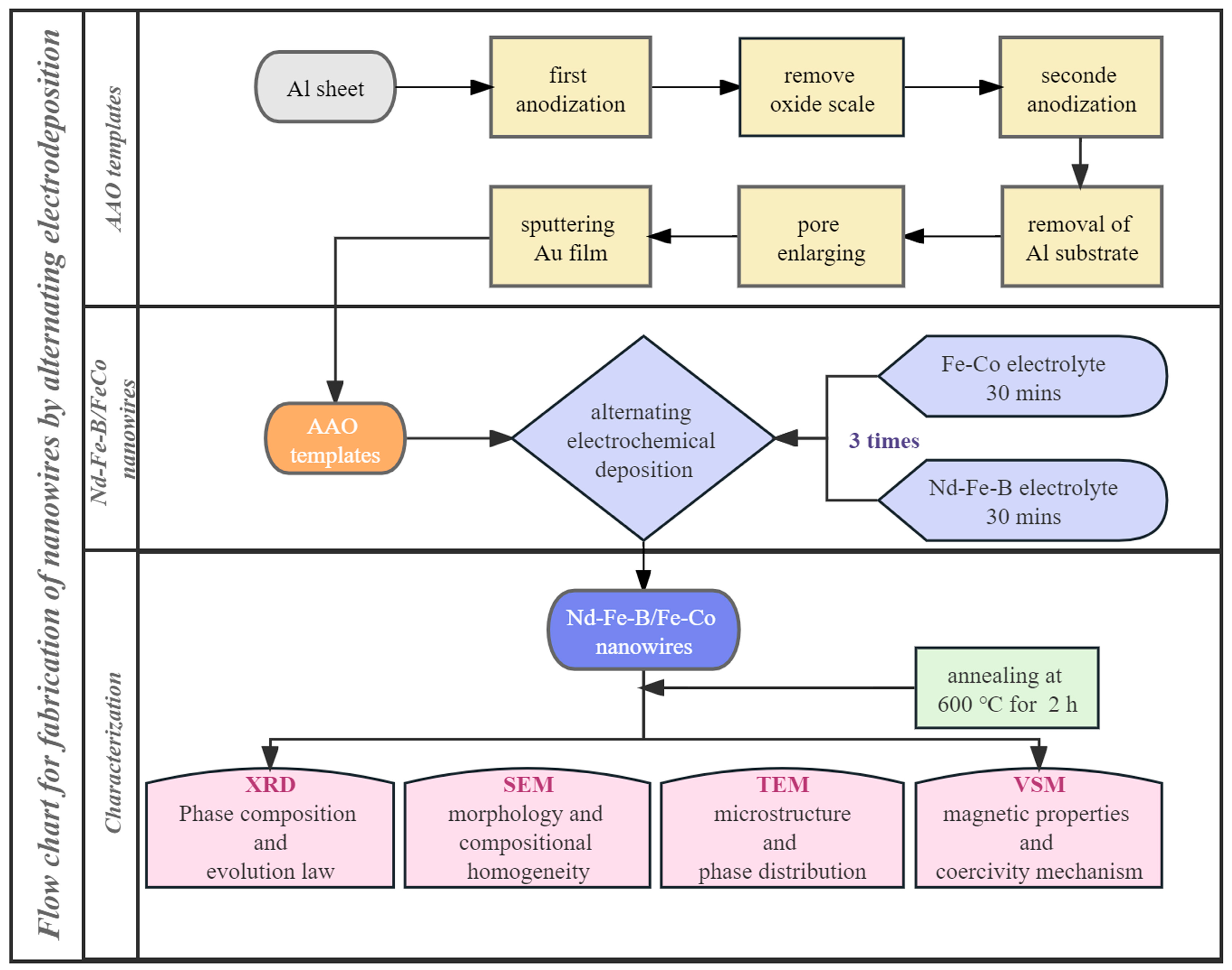
2.1. Synthesizing Process of AAO Template
2.2. Electrochemical Deposition of Nd-Fe-B/Fe-Co Composite Nanowires
2.3. Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Phase Analysis
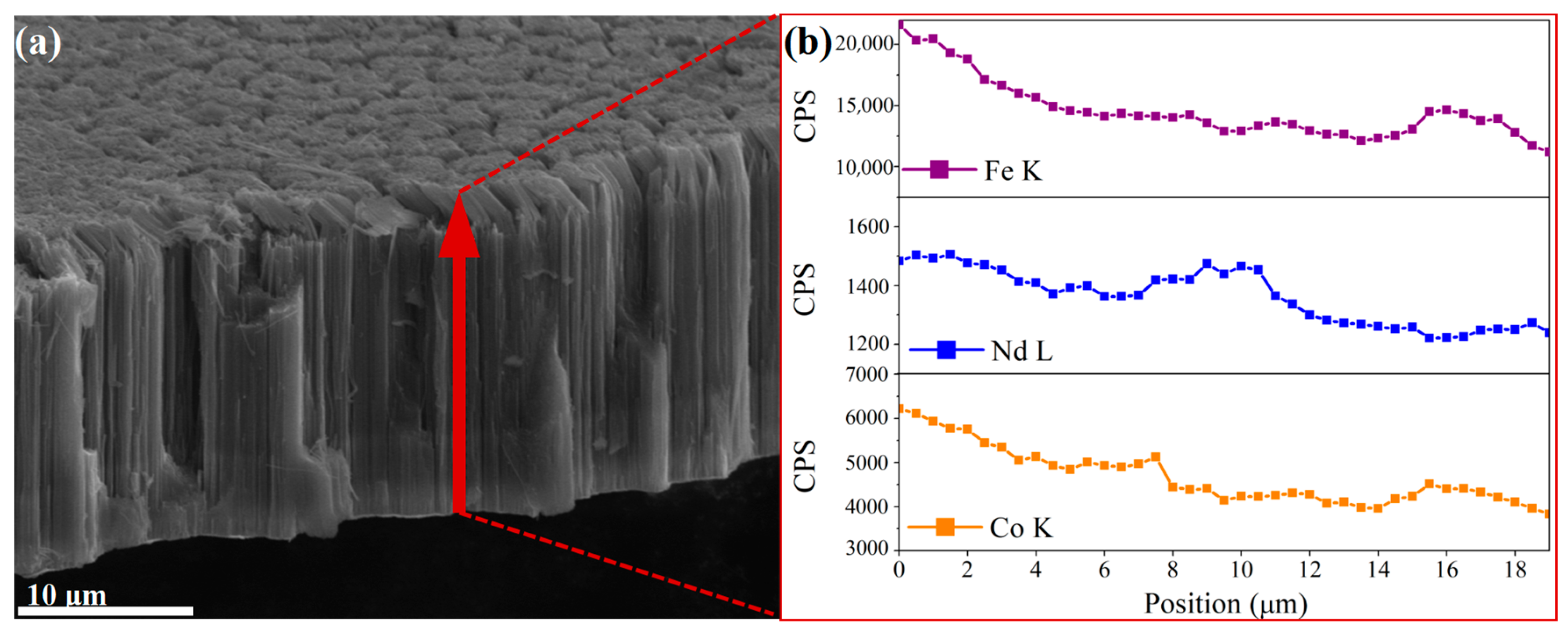
3.2. Morphology and Microstructure
3.3. Magnetic Properties Analysis
- (1)
- The as-deposited Nd-Fe-B/Fe-Co nanowires are soft magnetic Fe7Co3 and amorphous phases with low Hc. After annealing, the amorphous phase crystallizes into a polycrystalline structure containing Nd2(Fe, Co)14B, NdB4, NdB6, and Fe7Nd, while the soft magnetic Fe7Co3 phase still exists in the nanowires. The generation of the hard magnetic phase Nd2(Fe, Co)14B with a high anisotropy field hinders the nucleation of the magnetization reversal domain nucleus and the rotation of the magnetic domain, thereby enhancing the coercivity. At the same time, according to the XRD results and Formula (8) [31,32]:The content of the hard magnetic Nd2(Fe, Co)14B phase in Nd-Fe-B/Fe-Co composite nanowires prepared via alternating electrodeposition can be calculated as a volume fraction of 0.81, which is significantly higher than that of the hard magnetic phase Nd2Fe14B (volume fraction of 0.73) in Nd-Fe-B nanowires. This is due to the presence of Co ions in the alternating deposition process, which promotes more Nd ions in the electrolyte to be pulled into the AAO template and induces co-deposition, increasing the deposition quantity of Nd atoms and providing favorable conditions for the subsequent generation of a greater amount of hard magnetic phases. In the subsequent heat treatment process, some Co atoms enter the 2:14:1-type main phase to replace the Fe atoms, reducing the crystallization formation energy of the 2:14:1-type hard magnetic phase and contributing to precipitating more hard magnetic phases in nanowires. The coercivity is further enhanced by the increased content of the hard magnetic 2:14:1-type phase.
- (2)
- After annealing, the soft and hard magnetic phases intersect with each other in composite nanowires, existing with a large number of edge dislocations at phase interfaces. This causes the domain wall motion in nanowires to be hindered, enhancing the pinning effect between the soft and hard magnetic phases and increasing the pinning resistance, thus increasing the coercivity.
- (3)
- The exchange coupling between the hard magnetic Nd2(Fe, Co)14B phase and soft magnetic phase of Fe7Co3 will prevent the magnetic moments from orienting along the respective easy magnetization directions and promote the improvement of Mr. According to the exchange spring model proposed by Kneller and Hawig, the exchange-correlation length of the soft magnetic phase can be written as [33]:wherein As is the exchange energy for the soft magnetic phase, and Kh is the magnetic crystal anisotropy constant of the hard magnetic phase [34]. In order to achieve sufficiently strong exchange coupling, the grain size for the soft magnetic phase must be less than 2bcm. According to Formula (8), where A(Fe7Co3) = 1.67 × 10−11 J/m [35], K(Nd2Fe14B) = 4.3 × 106 J/m3, it can be calculated that the soft magnetic phase size in the Nd-Fe-B/Fe-Co composite magnet is less than 13.8 nm, which in line with the results observed in the TEM image. Therefore, there is a strong exchange coupling effect in soft–hard magnetic phases in annealed nanowires, facilitating to increase Ms. Based on the Stoner Wohlfarth theory, the phenomenon of remanence enhancement will occur in the magnet under the coupling of soft and hard magnetic exchange when Mr/Ms is much higher than 0.5. As the data listed in Table 3, the Mr/Ms of annealed Nd-Fe-B/Fe-Co composite nanowires is as high as 0.89, therefore exhibiting the magnetic characteristics of high remanence and a high magnetic energy product of 28 MGOe under strong exchange coupling.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, D.Q.; Fu, J.L.; Xu, Y.; Xue, D.S. Preparation and magnetic properties of Nd5Fe95-xBx nanowire arrays. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3070–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Pal, U.; Kang, Y.S. Facile synthesis and magnetic phase transformation of Nd-Fe-B nanoclusters by oxygen bridging. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Z.; Cao, J.W.; Yan, D.M.; Liu, F.F.; Zhang, C.; Guo, J.B.; Fu, Y.D. The influences of annealing on surface morphology and microstructure of Nd-Fe-B thin film. J. Phys. Conf. 2020, 1507, 102013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Urushibata, K.; Matsushita, T.; Sakamoto, S.; Suzuki, S. Magnetic properties and domain structures in NdFeB sintered magnets with Tb additive reacted and diffused from the sample surface. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 615, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.B.; Zhang, Z.X.; Wang, D.S.; Xu, Z.Y.; Li, Y.F.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.F. Magnetic properties, microstructure and magnetization reversal in sintered Nd12.2Fe81.8B6 magnets with the addition of Tb17Fe75B8. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 483, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Parmar, H.; Zhong, Y.; Chaudhary, V.; Ramanujan, R.V. Effect of Dy substitution on the microstructure and magnetic properties of high (BH)max Nd-Dy-Fe-Co-B nanoparticles prepared by microwave processing. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 471, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.Y.; Wang, J.W.; Lu, Z.X. Coercivity enhancement of Nd-Fe-B thin film magnets by Dy buffer and capping layers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 370–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Sasaki, T.T.; Ohkubo, T.; Takada, Y.; Kato, A.; Kaneko, Y.; Hono, K. Microstructure and coercivity of grain boundary diffusion processed Dy-free and Dy-containing Nd-Fe-B sintered magnets. Acta Mater. 2019, 172, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.B.; Altounian, Z. The partitioning of Dy and Tb in Nd-Fe-B magnets: A first-principles study. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 07A701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.B.; Tang, X.; Chen, R.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Zong, J.W.; Aru, Y.; Xu, Y.H. Effect of Tb-Fe diffusion on magnetic properties and thermal stability of hot-deformed magnets. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 773, 1108–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, H.; Ghasemi, A.; Mozaffarinia, R. Coercivity enhancement mechanism in Dy-substituted Nd-Fe-B nanoparticles synthesized by sol-gel base method followed by a reduction-diffusion process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 429, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C.; Zhao, G.P.; Xia, J.; Yue, M.; Yuan, X.H.; Xie, L.H. Micromagnetic simulation of Sm-Co/α-Fe/Sm-Co trilayers with various angles between easy axes and the film plane. Chin. Phys. B 2014, 23, 097504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawatzki, S.; Heller, R.; Mickel, C. Largely enhanced energy density in epitaxial SmCo5/Fe/SmCo5 exchange spring trilayers. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 123922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.P.; Liang, R.Y.; Bai, Y.H.; Yang, Y.; Sun, J.; Jiang, Y.N.; Wang, F.; Xu, X.H. Magnetic properties and magnetic reversal process of exchange-coupled Nd2Fe14B/α-Fe16N2 bilayer. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 233902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Takahashi, Y.K.; Gopalan, R.; Hono, K. Sm(Co,Cu)5/Fe exchange spring multilayer films with high energy product. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 122509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finger, R.T.; Kozloweski, G. Microstructure and magnetic properties of Fe-Co alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81, 4110–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclaren, J.M.; Schulthess, T.C.; Bulter, W.H.; Mchenry, M. Electronic structure, exchange interaction and curie temperature of Fe-Co. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 4833–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourmail, T. Near equiatomic FeCo alloys: Constitution, mechanical and magnetic properties. Prog. Mater Sci. 2005, 50, 816–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushboo, B.; Prasanta, K.; Pallavi, P.; Ajay, G. Study of magnetic nanowires of amorphous Co20Fe60B20 prepared by oblique angle deposition on nanorippled substrate. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 529, 167842. [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri, N.; Benbrahim-Cherief, N.; Chainet, E.; Charlot, F.; Encinas, T.; Boudinar, S.; Benfedda, B.; Hamadou, L.; Kadri, A. Electrodeposition of equiatomic FeNi and FeCo nanowires: Structural and magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 493, 165746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Lu, J.D.; Gao, Y.H. FeCo nanowires deposited in a magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 393, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniukov, E.Y.; Shumskaya, A.E.; Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Zdorovets, M.V.; Trukhanov, A.V.; Zubar, T.I.; Tishkevich, D.I.; Vinnik, D.A.; Khairetdinova, D.R.; Evstigneeva, S.A.; et al. Structure and magnetic properties of FeCo nanotubes obtained in pores of ion track templates. Nano Struct. Nano Object 2021, 26, 100691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuanto, M. Magnetic properties of exchange coupled SmCo5/FeCo composite particles synthesized by magnetic self-assembly. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2018, 696, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, C.X.; Chen, F.H.; Yang, W.; Li, H.F.; Liu, Q.Z.; Sun, J.B. Electrochemical fabrication, microstructure and magnetic properties of Sm2Co17/Fe7Co3 dual phase nanocomposite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 160, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; Zha, L.; Lie, M.N.; Yang, W.Y.; Yang, J.B. Micromagnetic simulation for optimizing nanocomposite Nd2Fe14B/α-Fe permanent magnets by changing grain size and volume fraction. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 523, 167622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryo, H.S.; Kim, K.G.; Kim, Y.J. An analytic study on coercivity mechanism of exchange coupled Nd2Fe14B/α-Fe nanocomposite magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 469, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choong, J.Y.; Eon, B.P. The effect of magnetic field treatment on the enhanced exchange coupling of a Nd2Fel4B/Fe3B magnet. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 475, 554–562. [Google Scholar]
- Vorobjova, A.I.; Shimanovich, D.L.; Sycheva, O.A.; Ezovitova, T.I.; Tishkevich, D.I.; Trykhanov, A.V. Studying the thermodynamic properties of composite magnetic material based on anodic alumina. Russ. Microelectron. 2019, 48, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, R.X.; Cui, C.X.; Yang, W.; Kang, L.C. The microstructure and magnetic behaviors of Pr-Fe-B/Fe7Co3 dual phase nanowires: As a perpendicular magnetic recording candidate. Mater. Charact. 2021, 180, 111410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, A.; Makino, A.; Inoue, A. Effect of Co addition on the magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Fe-rich Fe-Nb-(Nd,Pr)-B alloys produced by crystallization of an amorphous phase. Scripta Mater. 2001, 44, 1383–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, R.X.; Cui, C.X.; Yang, W.; Guo, M.F. Fabrication and magnetic properties of Tb-doped multiphase Pr-Tb-Fe-B magnetic nanowire arrays. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 262, 124299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.W.; Cui, C.X.; Yang, W.; Sun, J.B. Effects of cobalt addition on microstructure and magnetic properties of PrNdFeB/Fe7Co3 nanocomposite. J. Rare Earth. 2017, 35, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gao, R.W.; Liu, L.M.; Zhu, M.G.; Han, G.B.; Liu, H.Q.; Li, W. Effective anisotropy, exchange-coupling length and coercivity in Nd8−xRxFe87.5B4.5 (R = Dy, Sm, x = 0–0.6) nanocomposite. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2004, 110, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Xiao, Q.F.; Zhang, Z.D. Effect of magnetocrystalline anisotropy on the magnetic properties of Fe-rich R-Fe-B nanocomposite magnets. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 75, 2298–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skomski, R.; Coey, J.M.D. Giant energy product in nanostructured two-phase magnets. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 48, 812–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











| Electrolyte | Concentration/(mol/L) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NdCl3 | FeCl2 | CoCl2 | C6H8O7 | C6H8O6 | H3BO3 | C2H5NO2 | NH4Cl | |
| Fe-Co | 0 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.073 | 0.007 | 0.485 | 0 | 0 |
| Nd-Fe-B | 0.03 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0.007 | 0.485 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| Specimen | Phase | Imax | ∆G = ∆H/(J/mol) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 600 °C | 570 °C | |||
| Nd-Fe-B/Fe-Co | Nd2(Fe, Co)14B | 347 | 300 | 29,188.6 |
| Fe7Nd | 138 | 91 | 82,220.4 | |
| Fe7Co3 | 83 | 104 | −46,742.8 | |
| NdB4 | 68 | 44 | 90,461.4 | |
| NdB6 | 78 | 53 | 84,392.5 | |
| Nd-Fe-B | Nd2Fe14B | 271 | 230 | 33,264.0 |
| NdB4 | 108 | 58 | 125,723.9 | |
| Fe3.5B | 72 | 59 | 43,845.8 | |
| Sample | State | Hc/Oe | Mr/(emu/g) | Ms/(emu/g) | Mr/Ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-Co | as-deposited | 413.52 | 15.26 | 101.29 | 0.15 |
| annealed | 648.56 | 10.28 | 66.28 | 0.16 | |
| Nd-Fe-B | as-deposited | 366.70 | 6.55 | 77.10 | 0.09 |
| annealed | 1404.32 | 15.97 | 39.74 | 0.40 | |
| Nd-Fe-B/Fe-Co | as-deposited | 399.75 | 6.31 | 64.01 | 0.10 |
| annealed | 4203.25 | 68.51 | 76.45 | 0.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, L.; Yang, W.; Zhao, L.; Cui, C.; Cao, F. Study on the Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Nd-Fe-B/Fe-Co Composite Nanowires. Materials 2023, 16, 5541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165541
Kang L, Yang W, Zhao L, Cui C, Cao F. Study on the Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Nd-Fe-B/Fe-Co Composite Nanowires. Materials. 2023; 16(16):5541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165541
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Licong, Wei Yang, Lichen Zhao, Chunxiang Cui, and Feng Cao. 2023. "Study on the Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Nd-Fe-B/Fe-Co Composite Nanowires" Materials 16, no. 16: 5541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165541
APA StyleKang, L., Yang, W., Zhao, L., Cui, C., & Cao, F. (2023). Study on the Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Nd-Fe-B/Fe-Co Composite Nanowires. Materials, 16(16), 5541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165541






