Structure of Complex Concentrated Alloys Derived from Iron Aluminide Fe3Al
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
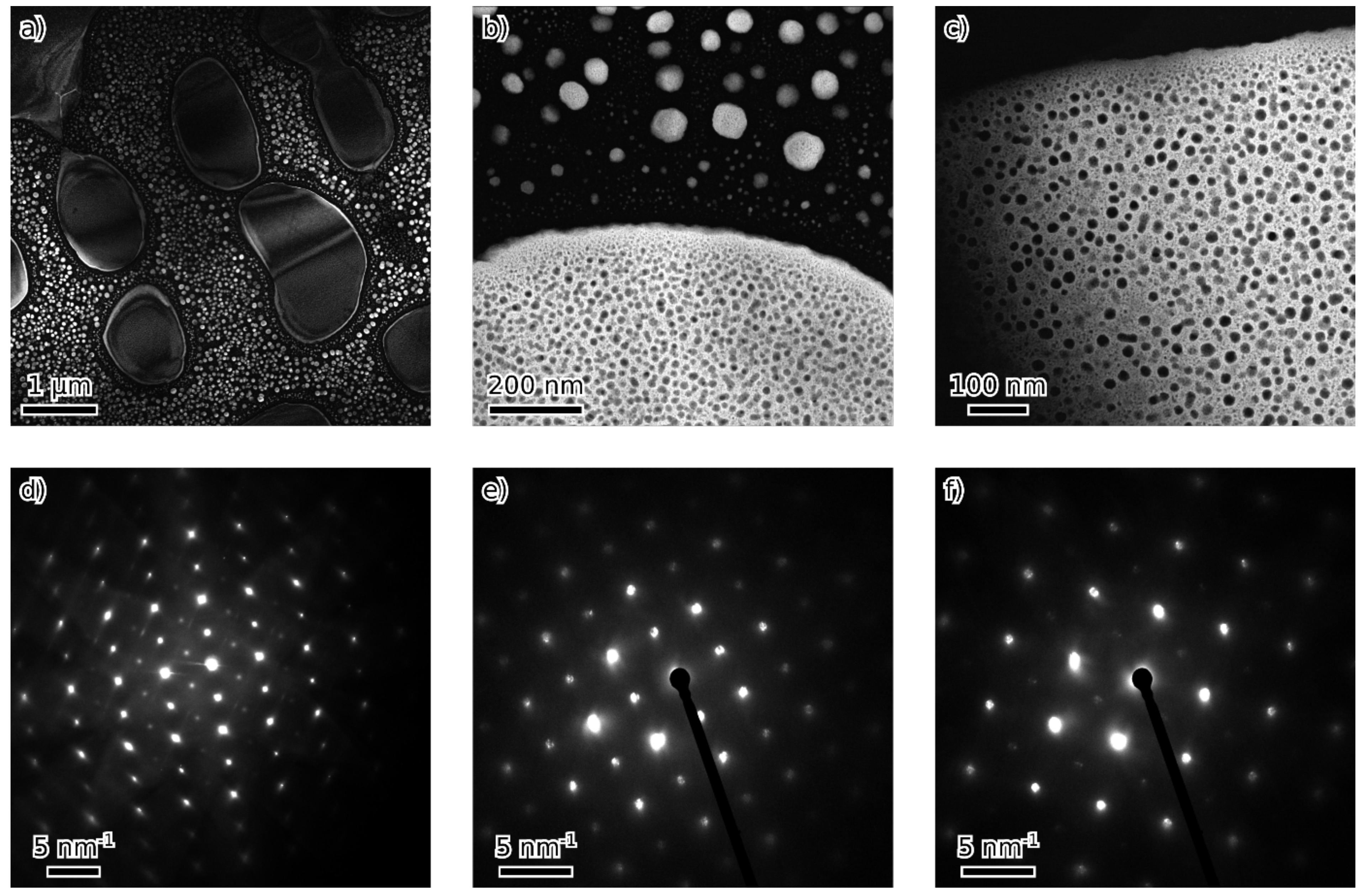
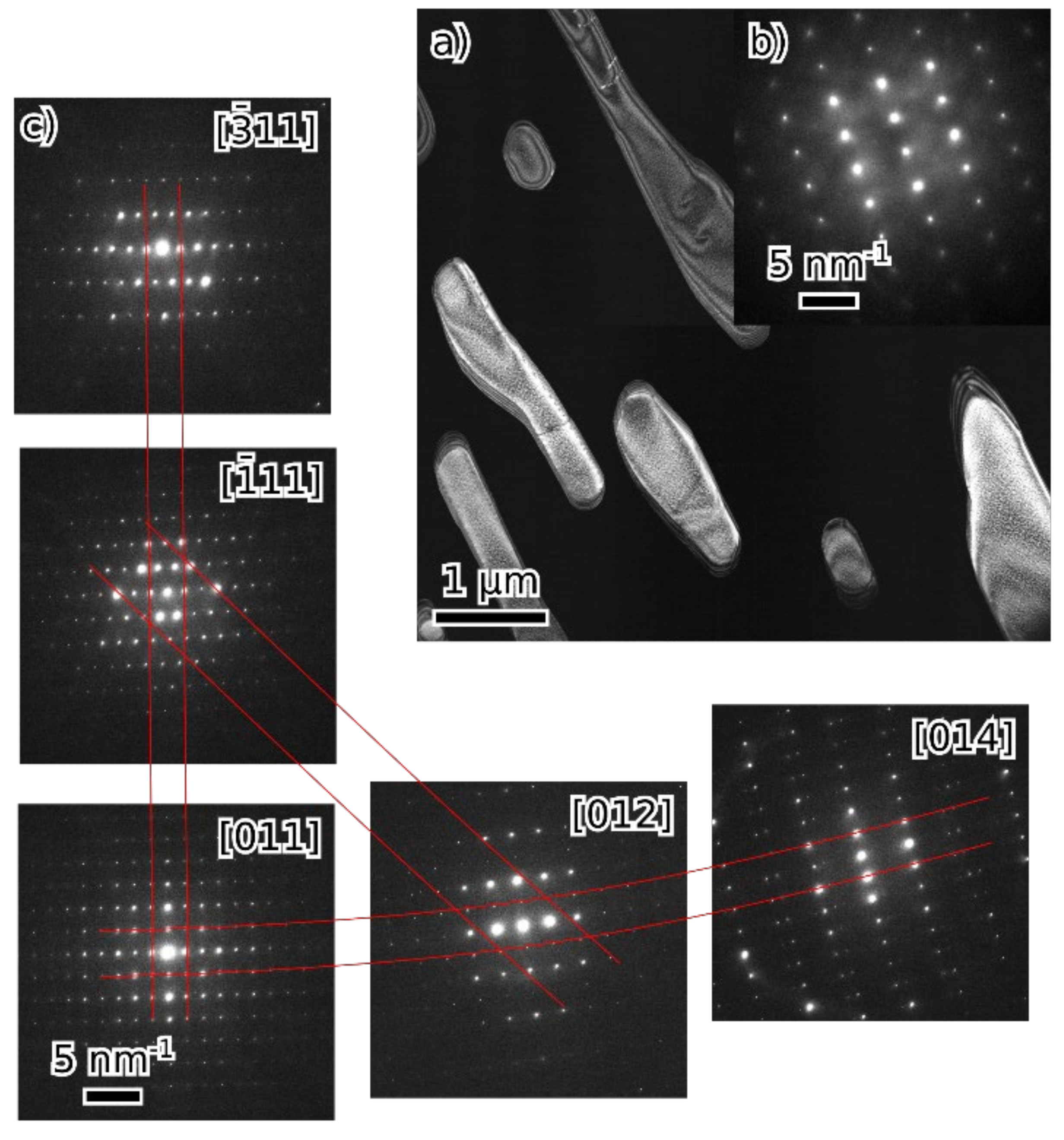
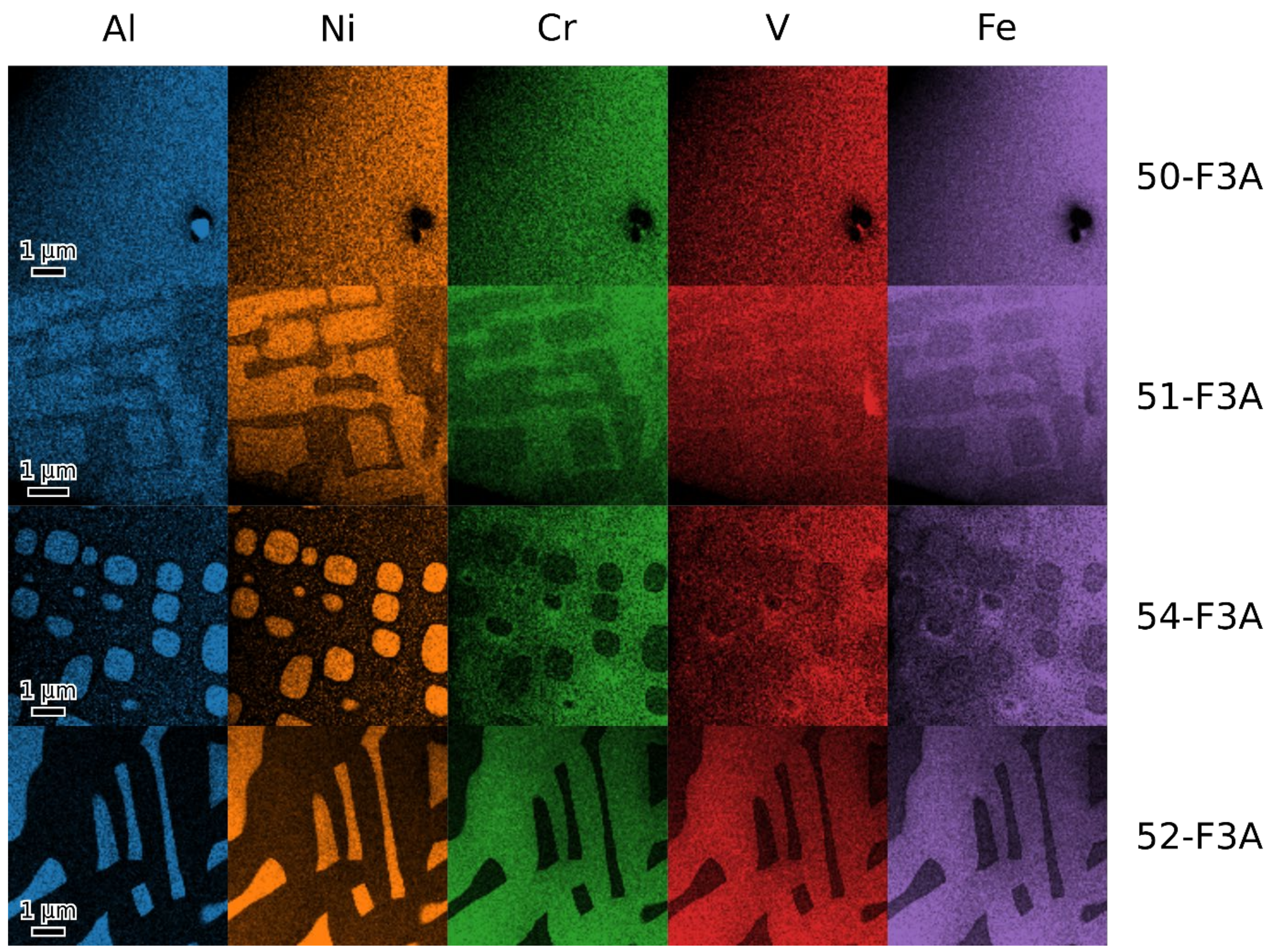
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- Fe3Al maintains the D03 structure up to at least 24 at. % of combined alloying with V, Cr and Ni.
- Beyond that (36 and 45 at. % of combined alloying by V, Cr and Ni), the alloys are composed of B2 NiAl together with bcc solid solution. Coherent phase separation occurs on two length scales down to a few nanometers.
- After the amount of alloyed Ni exceeds the amount of Al present in the alloy (the total combined alloying by V, Cr and Ni of 60 at. %), the alloy forms FeNiCrV σ-phase together with B2 NiAl.
- The original TCHEA5 database overestimates the stability of the σ phase. The present experimental results can thus serve to its improvement.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Babu, N.; Balasubramaniam, R.; Ghosh, A. High-temperature oxidation of Fe3Al-based iron aluminides in oxygen. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 2239–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotař, A.; Palm, M. Oxidation resistance of Fe-25Al-2Ta (at. %) in air. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1390–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hao, J.; Bi, Q.; Fu, L.C.; Yang, J.; Liu, W. Tribological properties of a Fe3Al material in sulfuric acid corrosive environment. Wear 2010, 268, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.G.; Muñoz-Morris, M.A.; Requejo, L.M. New iron–aluminium alloy with thermally stable coherent intermetallic nanoprecipitates for enhanced high-temperature creep strength. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 2335–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kwong, F.-L.; Shi, R.-X.; Dickon, H.L.; Yin, Y.-S. Microstructure and properties of in situ nanometric Al2O3 reinforced-Fe(Al)–Fe3Al-based composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 526, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvíl, P.; Vodičková, V.; Hakl, J.; Vlasák, T.; Hanus, P.; Pešička, J. High temperature mechanical properties of Fe28Al4Cr alloy with additives TiB2 and Zr. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.X.; Pan, Y.; Oliveira, F.J.; Baptista, J.L.; Vieira, J.M. High strength TiC matrix Fe28Al toughened composites prepared by spontaneous melt infiltration. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 26, 3853–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krein, R.; Friak, M.; Neugebauer, J.; Palm, M.; Heilmaier, M. L21-ordered Fe–Al–Ti alloys. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1360–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Ma, J.; Bi, Q.; Cheng, J.; Liang, Y.; Liu, W. Microstructures and mechanical properties of Fe–28Al–5Cr/TiC composites produced by hot-pressing sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 6819–6824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.-M.; Sakamoto, K.; Makoto Tamura, M.; Kunihiko Iwasaki, K. Comparative study of the high temperature deformation behavior of Fe-25Al and Fe-25Al-10Ti alloys. Scr. Mater. 2000, 42, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvíl, P.; Daniš, S.; Minárik, P.; Pešička, J.; Král, R. Strengthening of Fe3Al Aluminides by One or Two Solute Elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 4135–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvíl, P.; Daniš, S.; Pešička, J.; Minárik, P.; Král, R. Fe3Al Iron Aluminides Alloyed with High Concentrations of V and Cr: Their Structure and High Temperature Strength. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 6046–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Fu, F. Effects of annealing treatment on properties of CoCrFeNiTiAlx multi-component alloys. Intermetallics 2012, 28, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhou, K.; Lu, Y.; Gao, X.; Wang, T.; Li, T. Effect of vanadium addition on the microstructure and properties of AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 2014, 57, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.D.; Cai, Y.H.; Chen, X.H.; Wang, T.; Si, J.J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.D.; Hui, X.D. Phase composition and solid solution strengthening effect in TiZrNbMoV high-entropy alloys. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Chen, W.; Wen, H.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, B.; Zhou, Y.; Lavernia, E.J. Microstructure and strengthening mechanisms in an FCC structured single-phase nanocrystalline Co25Ni25Fe25Al7.5Cu17.5 high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2016, 107, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wang, Z.; Niu, S.; Wu, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.T.; Dang, Y. Strengthening the CoCrFeNiNb0.25 high entropy alloy by FCC precipitate. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 667, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Pang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, T. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al20-xCr20+0.5xFe20Co20Ni20+0.5x high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 659, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.J.; Chen, M.R.; Chen, S.K.; Yeh, J.W.; Shun, T.T.; Lin, S.J.; Chang, S.Y. Mechanical performance of the AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Bei, H.; Pharr, G.M.; Georgie, E.P. Temperature dependence of the mechanical properties of equiatomic solid solution alloys with face-centered cubic crystal structures. Acta Mater. 2015, 81, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-W.; Tsai, M.-H.; Yeh, J.-W.; Yang, C.-C. Effect of temperature on mechanical properties of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi wrought alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 490, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.R.; Lin, S.J.; Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Huang, Y.C.; Tu, C.P. Microstructure and Properties of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNiTix (x = 0–2.0) High-Entropy Alloys. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 1395–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, S.; Manzoni, A.M.; Holzinger, M.; Glatzel, U. Influence of high melting elements on microstructure, tensile strength and creep resistance of the compositionally complex alloy Al10Co25Cr8Fe15Ni36Ti6. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 274, 125163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Vechio, K. Processing, microstructure evolution and mechanical property improvements of an Al–V–Cr–Mn–Fe–Ni CCA with an as-cast BCC/B2 coherent nanostructure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 852, 143698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Liu, W.H.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Nieh, T.G.; Lu, Z.P. Effects of Al addition on structural evolution and tensile properties of the FeCoNiCrMn high-entropy alloy system. Acta Mater. 2014, 62, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.-F.; Chen, T.-J.; Chen, S.-K.; Yeh, J.-W. Microstructure and mechanical property of as-cast, -homogenized, and -deformed AlxCoCrFeNi (0 ≤ x ≤ 2) high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 488, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvíl, P.; Král, R.; Daniš, S.; Pešička, J.; Minárik, P.; Veselý, J. Atom Location by Channeling-Enhanced Microanalysis (ALCHEMI) Study of Structure of Complex Concentrated Alloys Derived from FeAl Iron Aluminide. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2022, 53, 3967–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, H.E.; Tatge, E.; Gilfrich, N.T.; Ugrinic, G.M. Standard X-ray diffraction powder patterns. Natl. Bur. Stand. Circ. 1955, 539, 1–75. [Google Scholar]
- Neuburger, M.C. Praezisionsmessung der Gitterkonstante von reinem Vanadium. Zeitsch. Krist. 1936, 93, 314–315. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, A.J.; Taylor, A. An X-ray analysis of the nickel-aluminium system. Proc. Roy. Soc. Lon. 1937, 159, 56–72. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, A.J.; Jay, A.H. The lattice spacings of iron-aluminium alloys. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1932, 125, 339–357. [Google Scholar]
- Bergman, G.; Shoemaker, D.P. The determination of the crystal structure of the sigma-phase in the Fe-Cr and Fe-Mo systems. Acta Cryst. 1954, 7, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanneman, R.E.; Mariano, A.N. Lattice-parameter and volumetric data of the iron-vanadium system. Trans. Met. Soc. AIME 1964, 230, 937–938. [Google Scholar]
- Kasper, J.S.; Waterstrat, R.M. Ordering of atoms in the sigma phase. Acta Cryst. 1956, 9, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.L.; Wang, X. The effect of electronic structure on the defect properties of FeAl. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 1997, 239–240, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Chen, H.-L.; Chen, Q. TCHEA1: A Thermodynamic Database Not Limited for “High Entropy” Alloys. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2017, 38, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-L.; Mao, H.; Chen, Q. Database development and Calphad calculations for high entropy alloys: Challenges, strategies, and tips. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 210, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
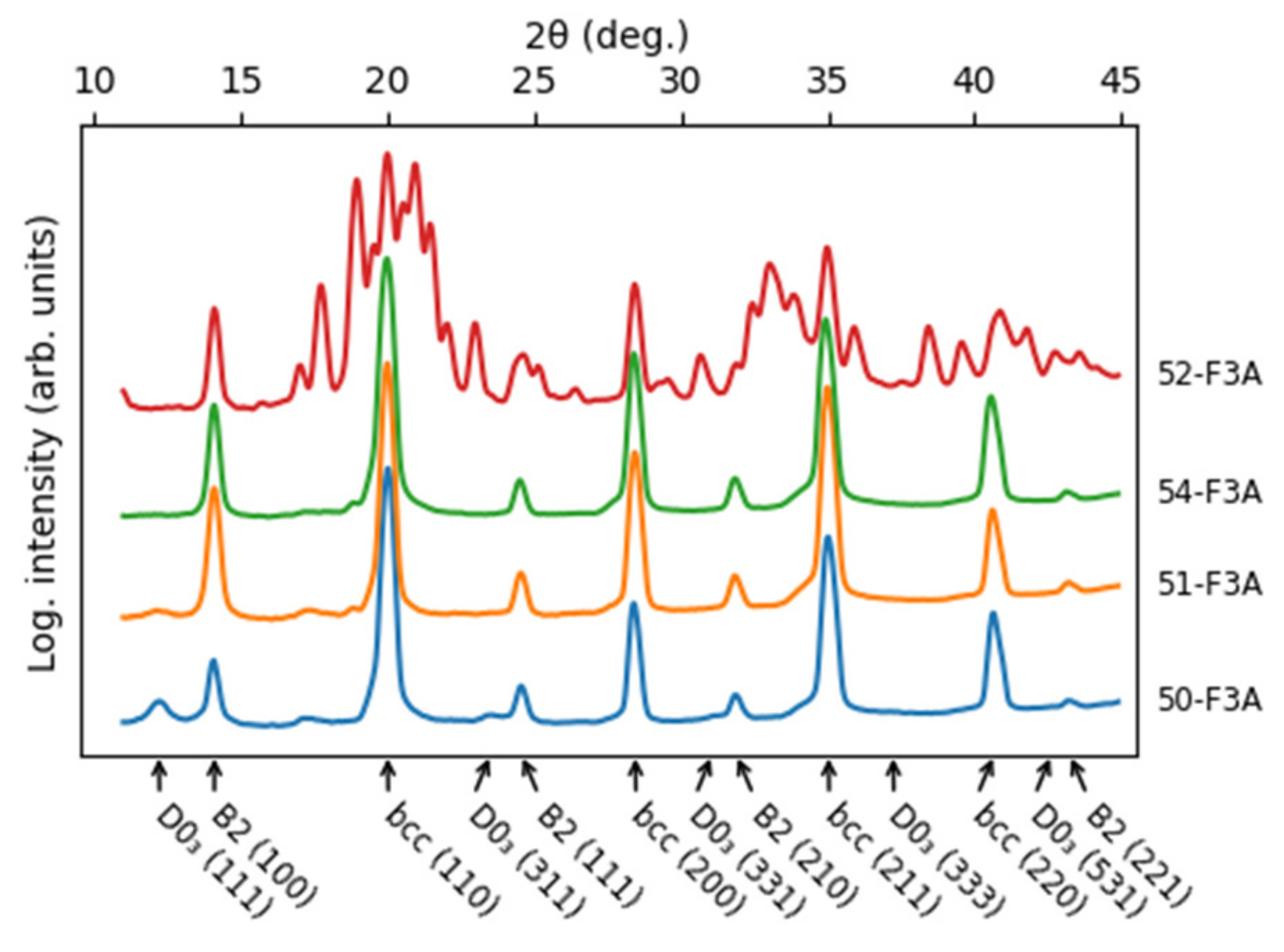
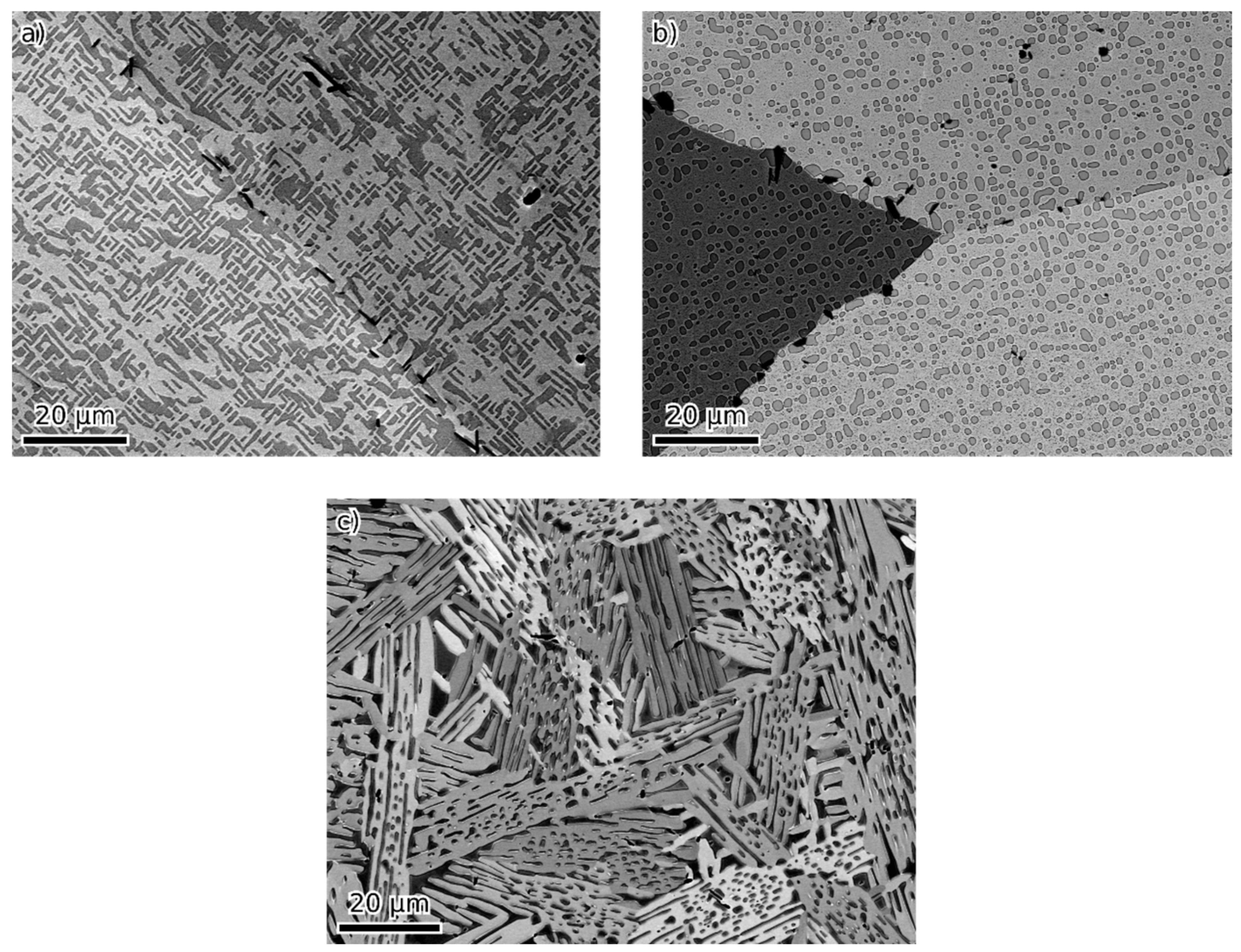
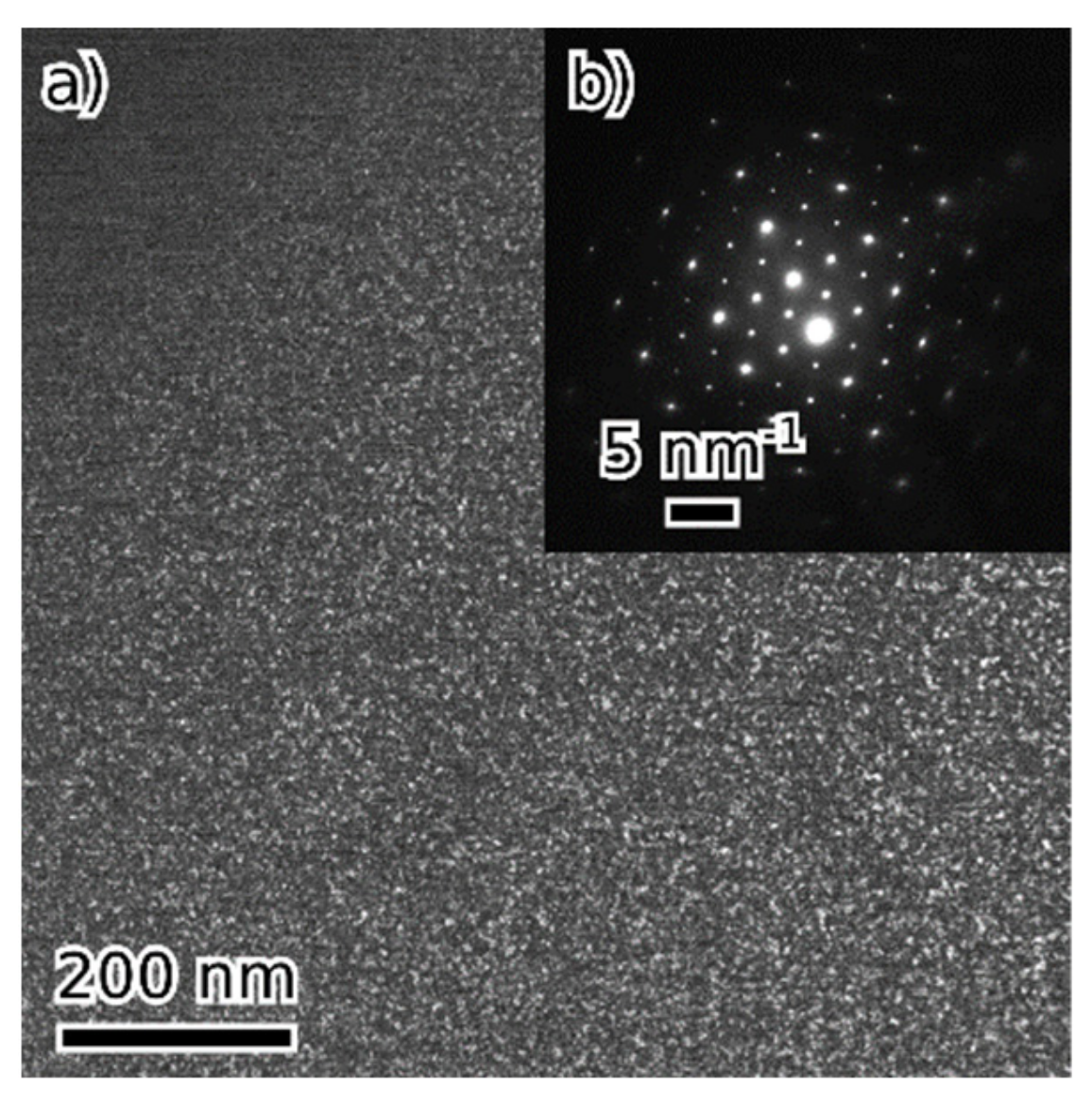
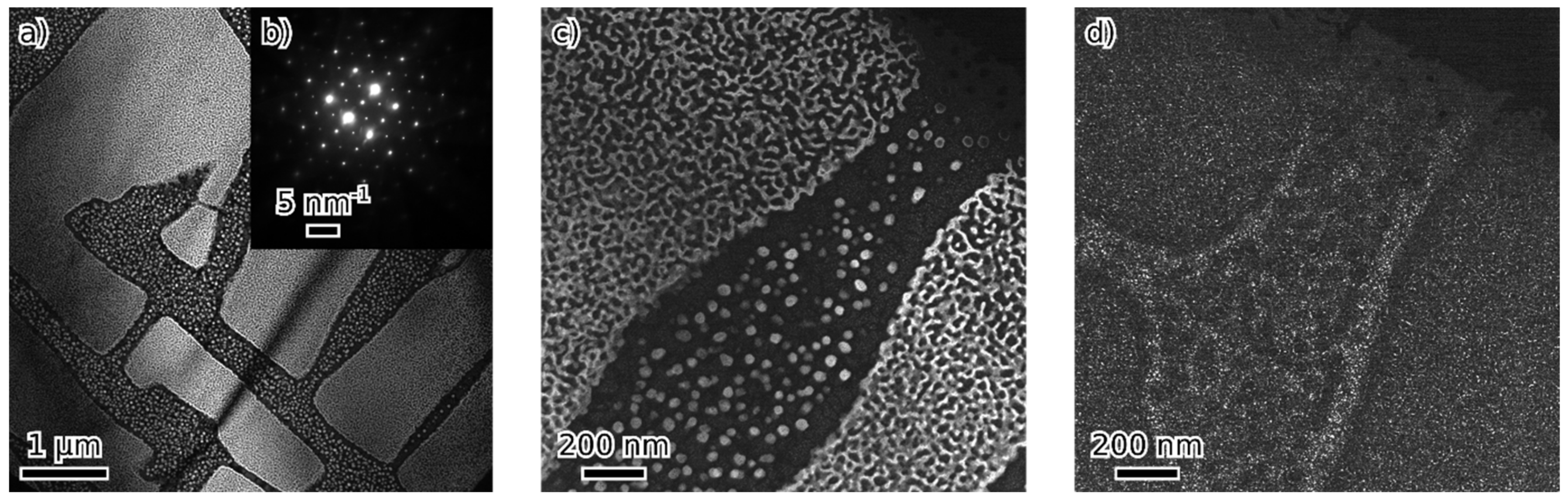

| at. % | Fe | Al | Ni | V | Cr | Phases | Lattice Parameters (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50-F3A | 56.8 | 19.1 | 8.1 | 8.0 | 8.5 | D03 | a = 0.2890(3) |
| 51-F3A | 46.5 | 18.0 | 11.5 | 11.5 | 11.6 | bcc + B2 + D03 | a = 0.2890(1) |
| 54-F3A | 40.1 | 14.4 | 15.5 | 15.1 | 14.8 | bcc + B2 (+D03) | a = 0.2893(2) |
| 52-F3A | 29.8 | 9.4 | 19.9 | 20.5 | 20.4 | B2 + σ | a = 0.2888(1) aσ = 0.8887(2) cσ = 0.4605(2) |
| at. % ± ~3 at. % | Al | V | Cr | Fe | Ni | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51-F3A | exp. | bcc | 13.6 | 12.6 | 13.5 | 51.7 | 8.5 |
| B2′ | 23.1 | 10.4 | 9.5 | 41.6 | 15.3 | ||
| TC | B2 | 15.1 | 12.4 | 12.5 | 49.2 | 10.9 | |
| B2′ | 33.4 | 4.2 | 2.6 | 26.5 | 33.3 | ||
| 54-F3A | exp. | bcc | 6.3 | 18.7 | 20.6 | 50.0 | 4.3 |
| B2′ | 26.0 | 9.8 | 6.0 | 25.9 | 32.3 | ||
| TC | bcc | 9.8 | 17.1 | 17.4 | 45.4 | 10.3 | |
| B2′ | 34.8 | 3.9 | 2.1 | 18.9 | 40.3 | ||
| 52-F3A | exp. | σ | 4.0 | 24.0 | 24.9 | 34.1 | 12.9 |
| B2′ | 26.6 | 8.7 | 5.0 | 14.7 | 44.9 | ||
| TC | σ | 0.02 | 26.3 | 27.3 | 37.9 | 8.5 | |
| B2′ | 33.8 | 5.0 | 2.6 | 11.1 | 47.5 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pešička, J.; Kratochvíl, P.; Král, R.; Veselý, J.; Jača, E.; Preisler, D.; Daniš, S.; Minárik, P.; Čamek, L. Structure of Complex Concentrated Alloys Derived from Iron Aluminide Fe3Al. Materials 2023, 16, 5388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155388
Pešička J, Kratochvíl P, Král R, Veselý J, Jača E, Preisler D, Daniš S, Minárik P, Čamek L. Structure of Complex Concentrated Alloys Derived from Iron Aluminide Fe3Al. Materials. 2023; 16(15):5388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155388
Chicago/Turabian StylePešička, Josef, Petr Kratochvíl, Robert Král, Jozef Veselý, Eliška Jača, Dalibor Preisler, Stanislav Daniš, Peter Minárik, and Libor Čamek. 2023. "Structure of Complex Concentrated Alloys Derived from Iron Aluminide Fe3Al" Materials 16, no. 15: 5388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155388
APA StylePešička, J., Kratochvíl, P., Král, R., Veselý, J., Jača, E., Preisler, D., Daniš, S., Minárik, P., & Čamek, L. (2023). Structure of Complex Concentrated Alloys Derived from Iron Aluminide Fe3Al. Materials, 16(15), 5388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155388





