Photocatalytic Degradation of Xylene by Carbon Quantum Dots/Clinoptilolite Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Catalysts
2.3. Catalyst Characterization
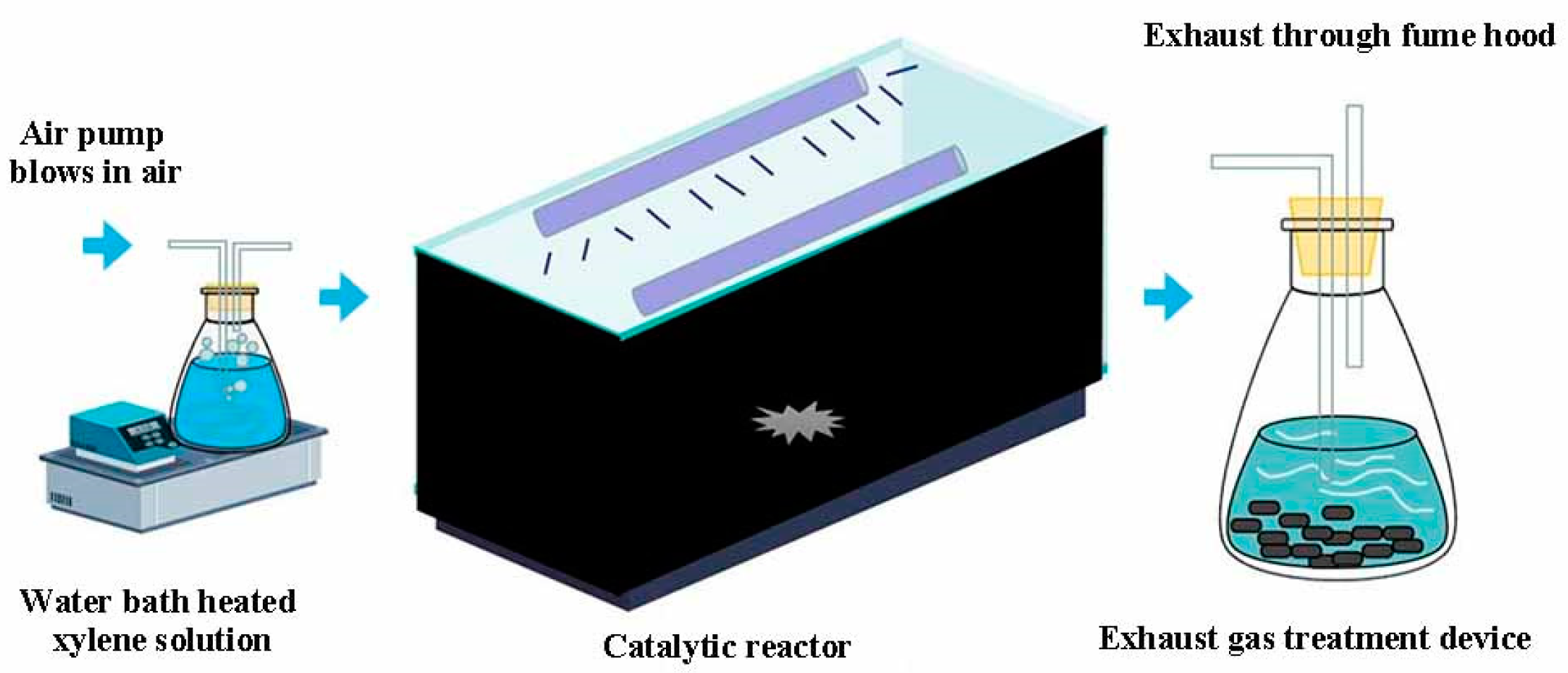
2.4. Evaluation of Photocatalytic Activity
3. Results and Discussion
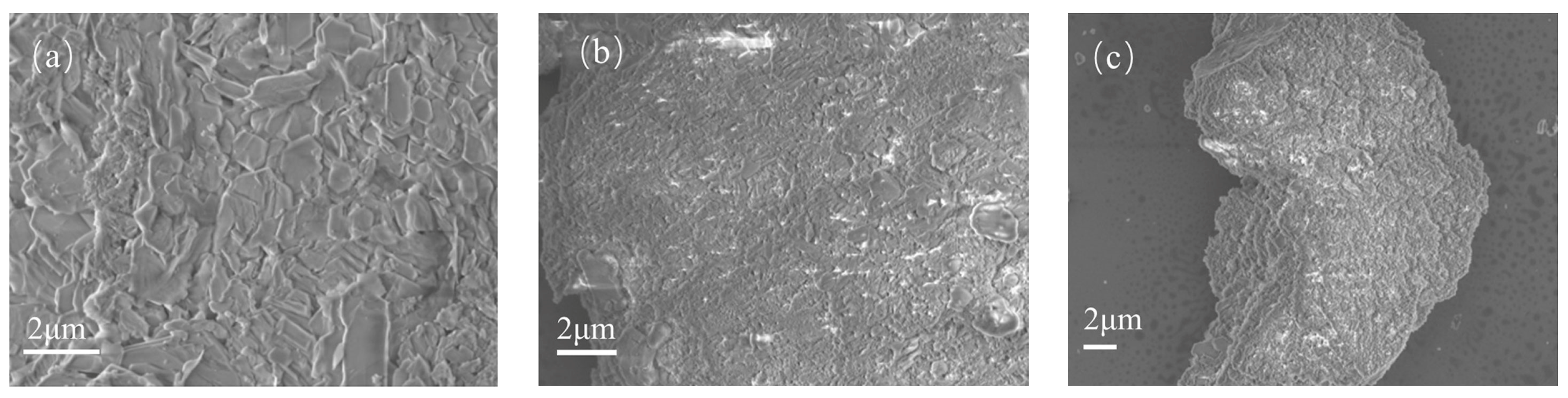
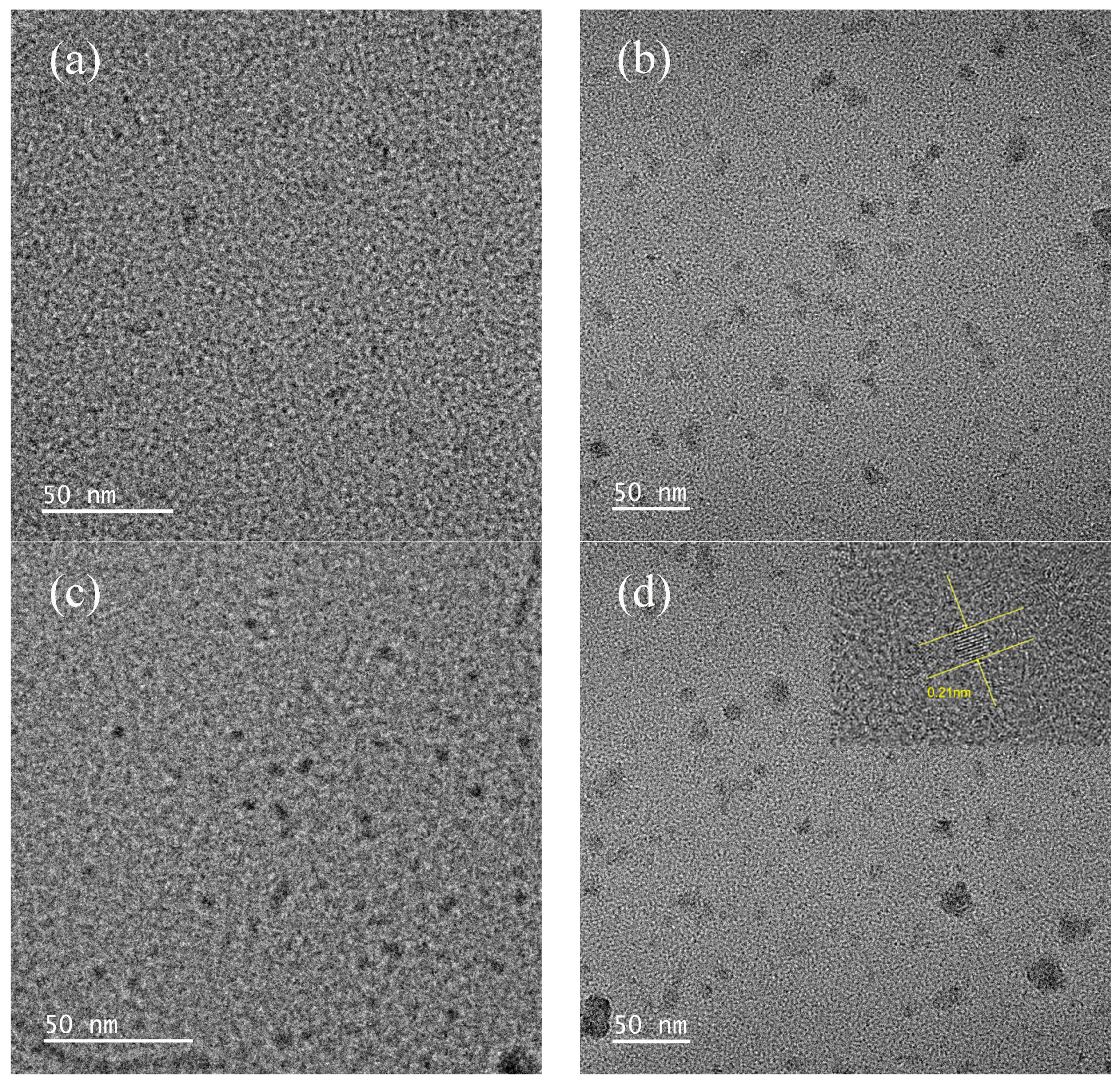
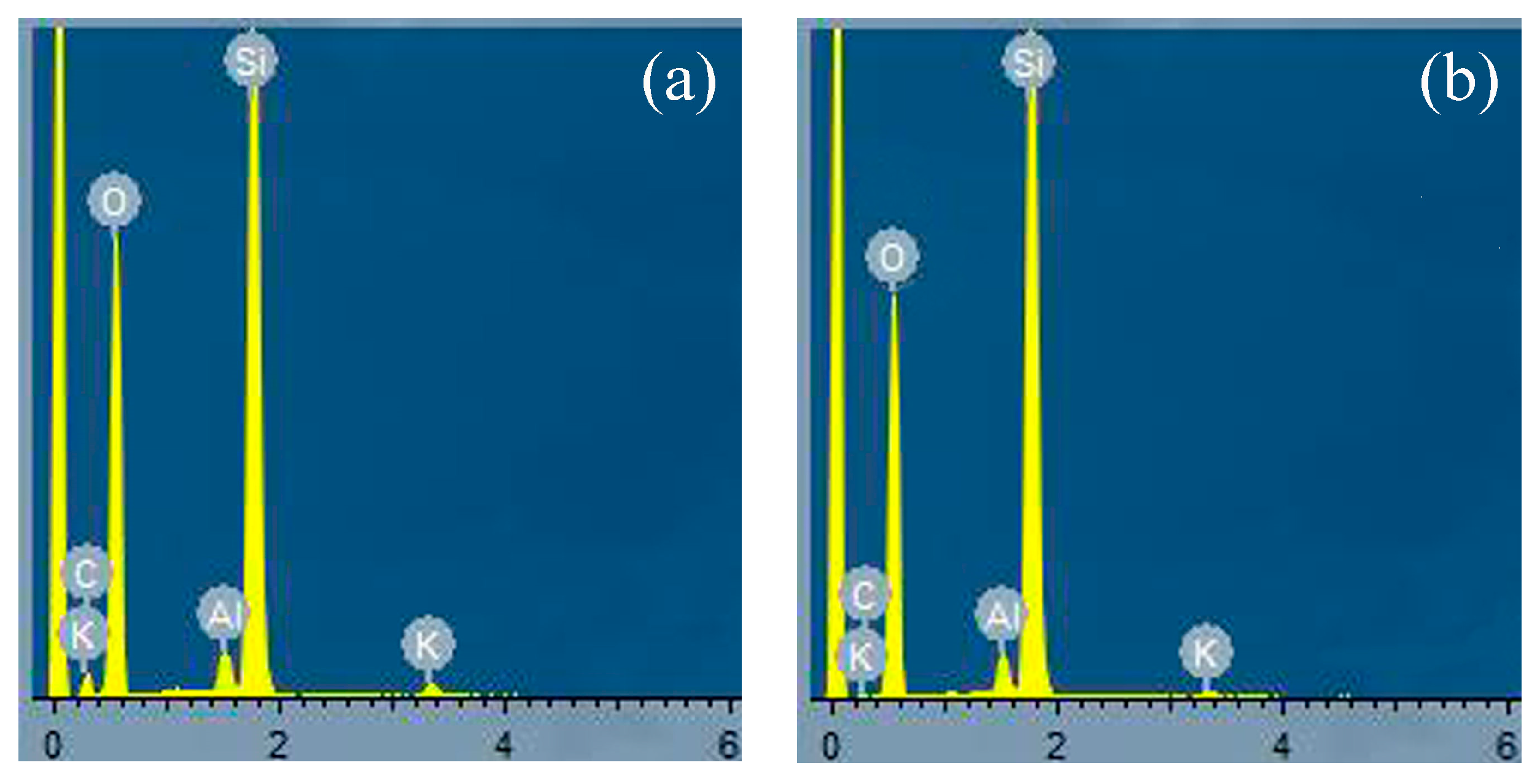
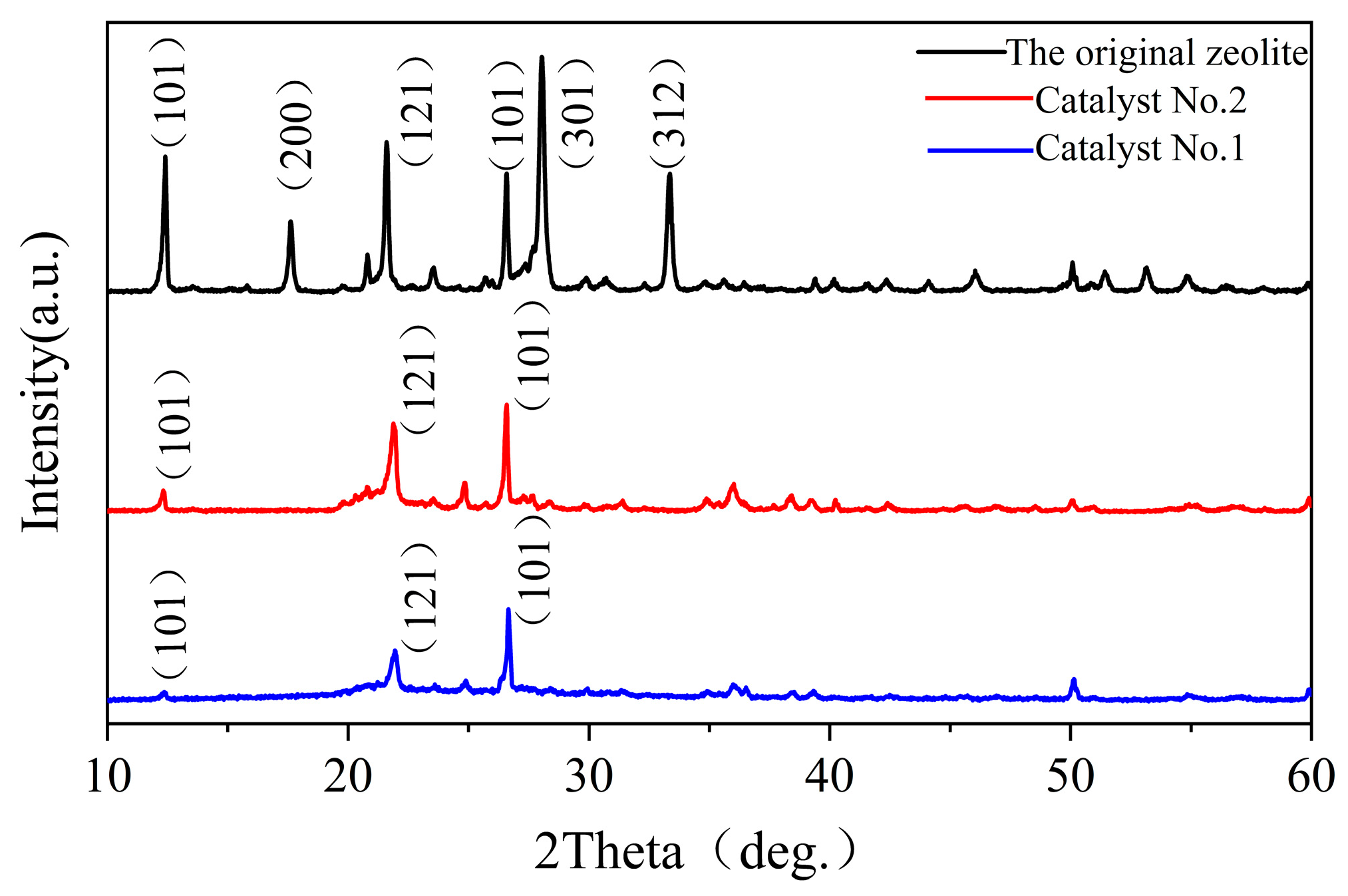
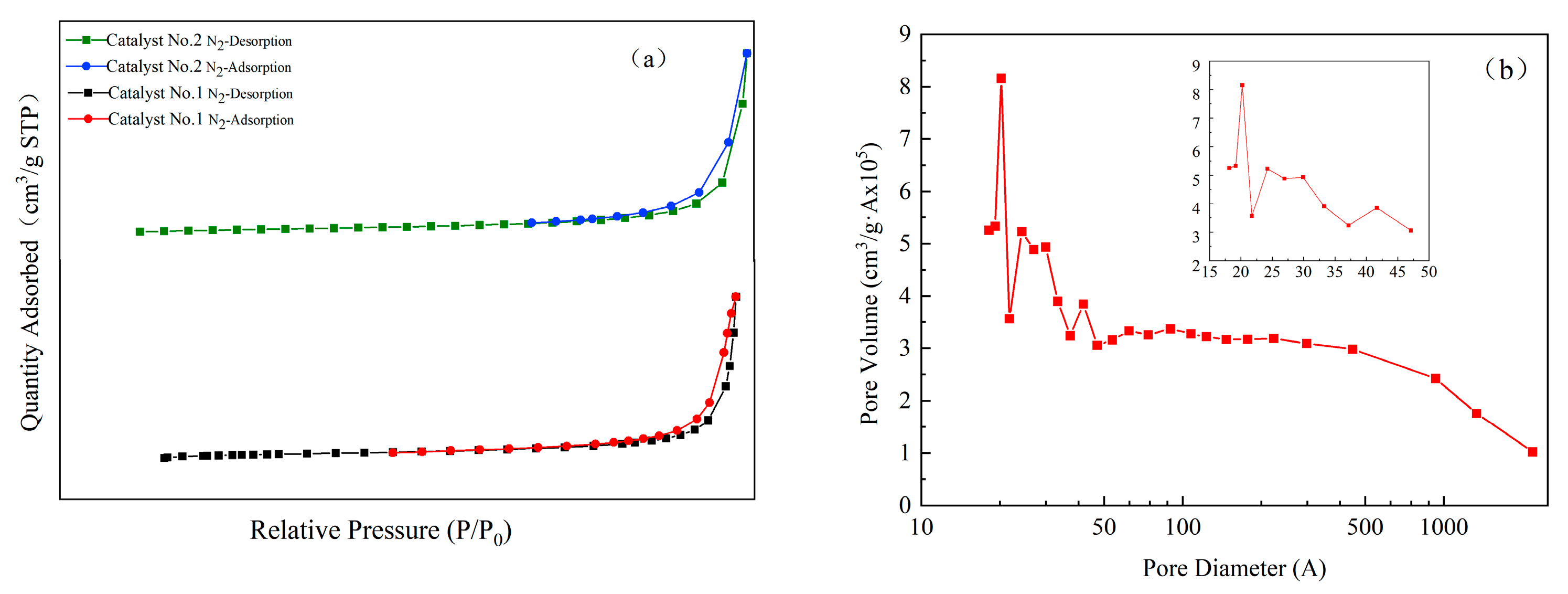
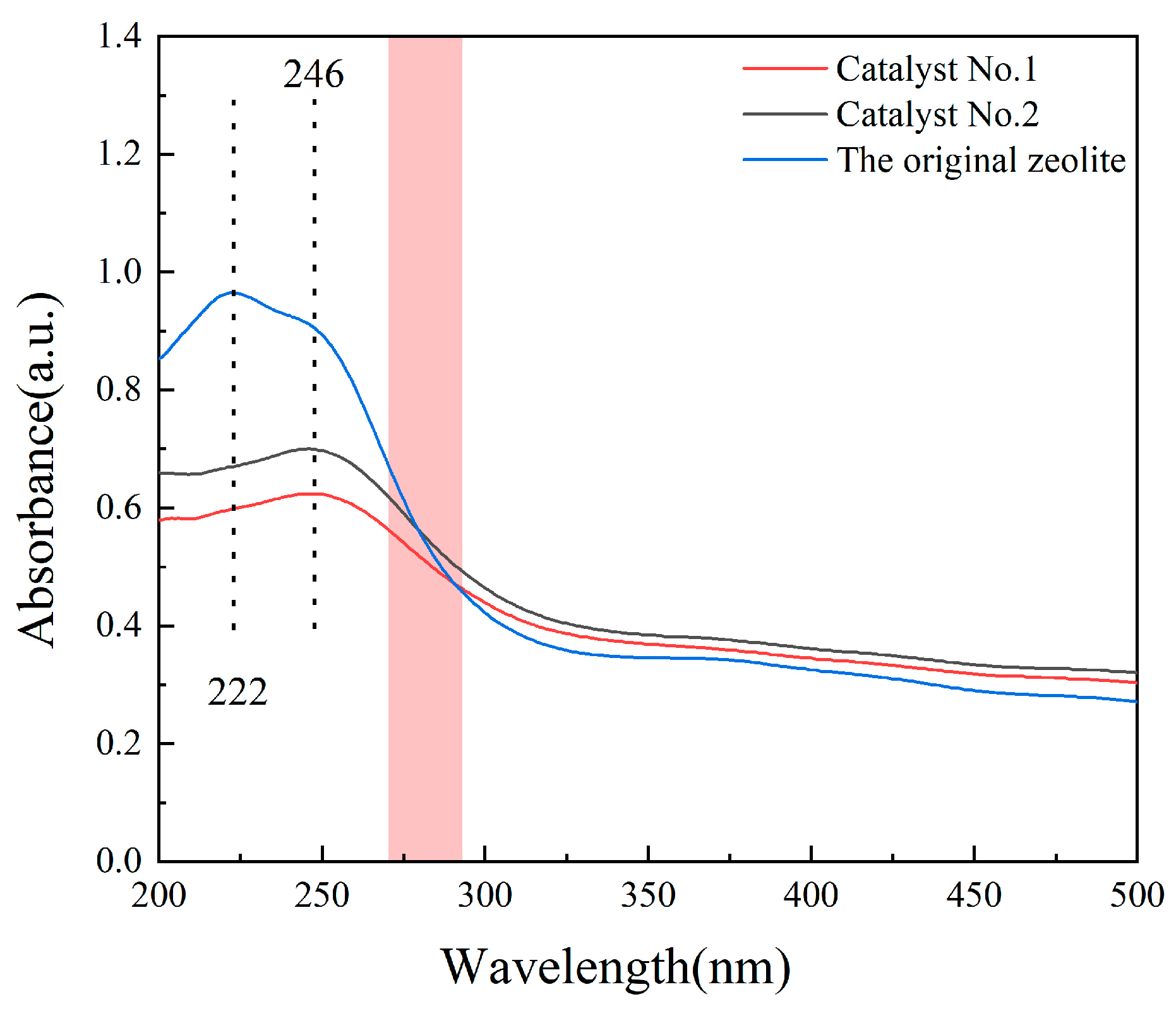
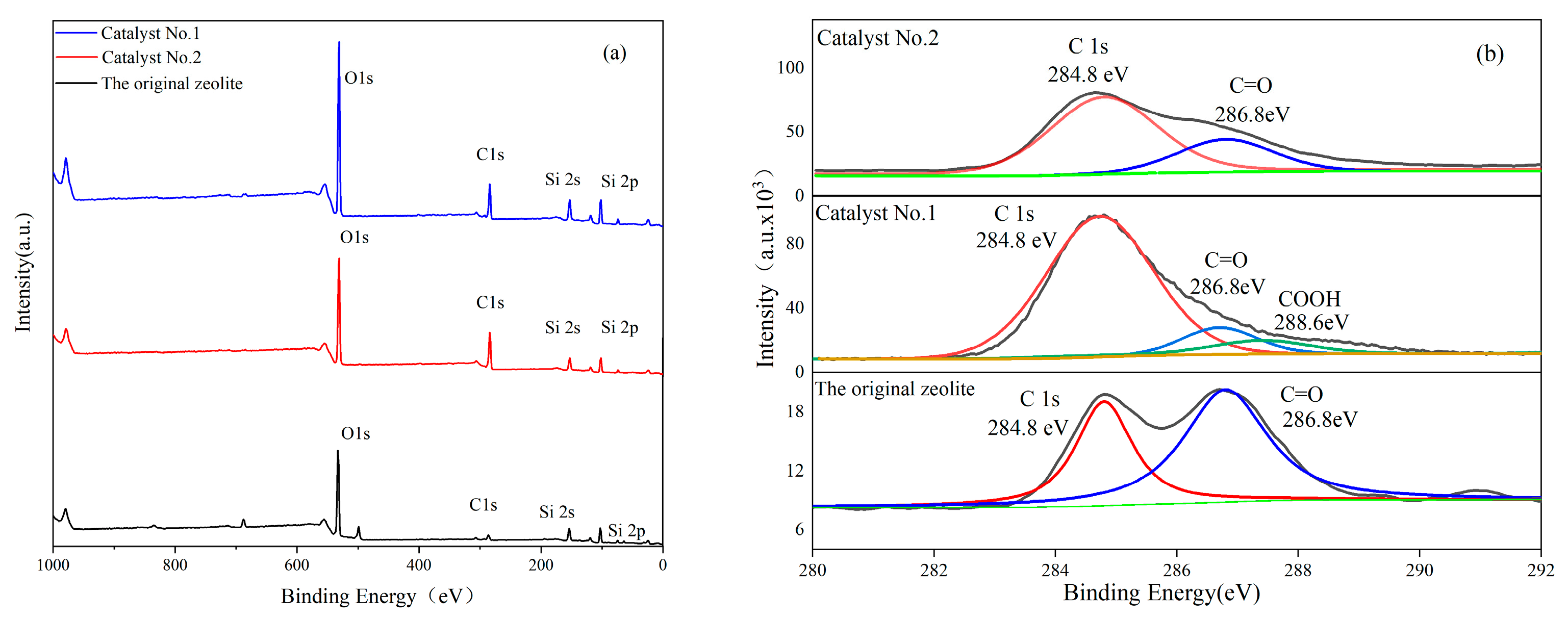
3.1. Structural Characteristics of the Catalysts
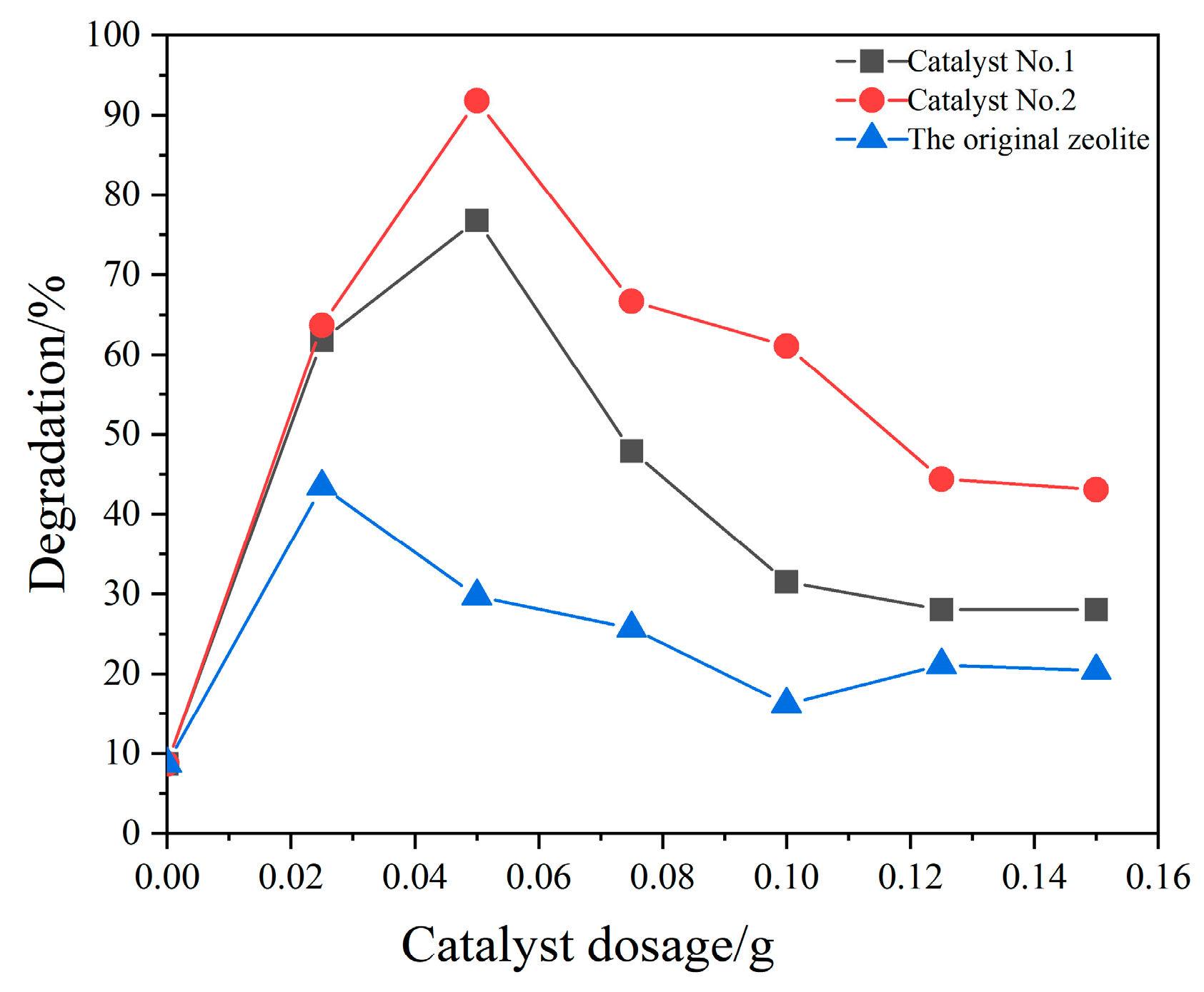
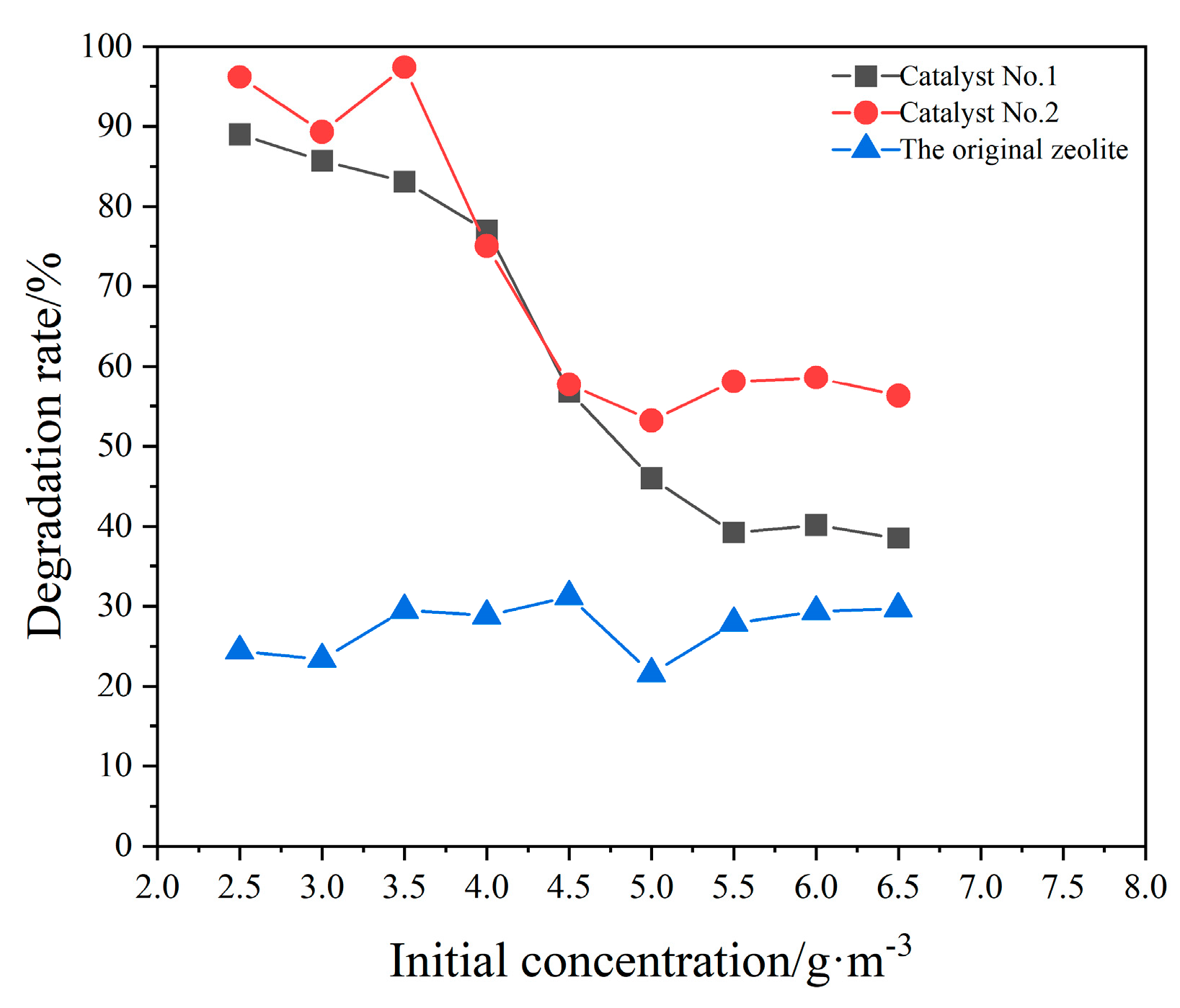
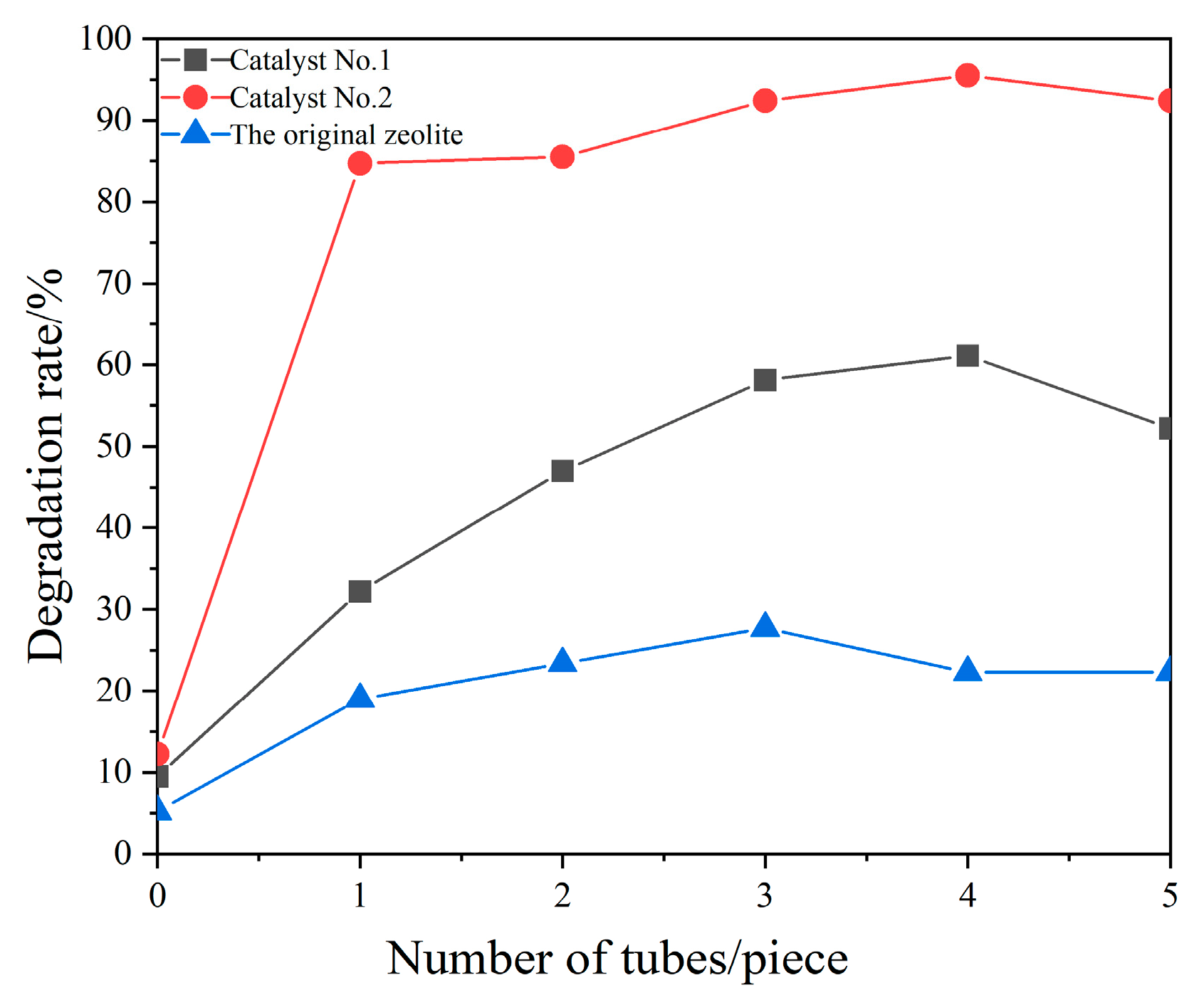
3.2. Influence of Reaction Conditions on the Degradation Effect
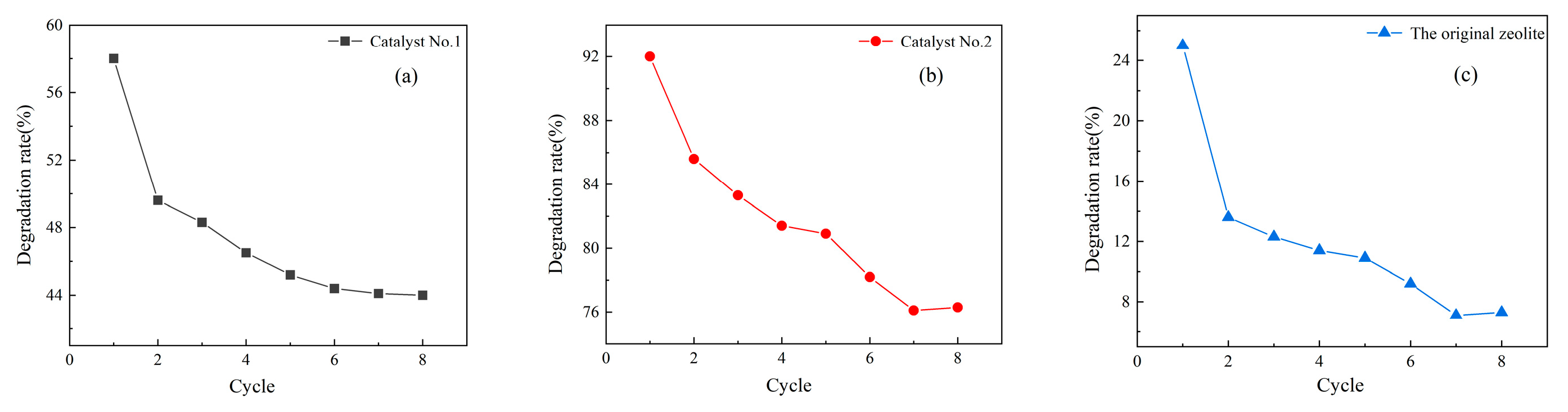
3.3. Catalyst Lifetime
3.4. Mechanistic Analysis of Photocatalytic Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tseng, H.H.; Wei, M.C.; Hsiung, S.F.; Chiou, C.W. Degradation of Xylene Vapor over Ni-Doped TiO2 Photocatalysts Prepared by Polyol-Mediated Synthesis. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ho, S.; Lu, Y.; Niu, R.; Xu, L.; Cao, J.; Lee, S. Removal of Indoor Volatile Organic Compounds via Photocatalytic Oxidation: A Short Review and Prospect. Molecules 2016, 21, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thevenet, F.; Debono, O.; Rizk, M.; Caron, F.; Verriele, M.; Locoge, N. VOC Uptakes on Gypsum Boards: Sorption Performances and Impact on Indoor Air Quality. Build. Environ. 2018, 137, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-Y.; Ahn, J.H.; Yoon, J.-W.; Lee, C.-S.; Kang, Y.C.; Abdel-Hady, F.; Wazzan, A.A.; Lee, J.-H. Highly Selective Xylene Sensor Based on NiO/NiMoO4 Nanocomposite Hierarchical Spheres for Indoor Air Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34603–34611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheson, S.; Fleck, R.; Irga, P.J.; Torpy, F.R. Phytoremediation for the Indoor Environment: A State-of-the-Art Reviews. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 22, 249–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Mo, J. Modelling and Implementation of an In-Situ Thermally Regenerated Adsorption Module for Removing Gaseous Xylene. Build. Environ. 2023, 236, 110275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardhana, Y.; Gunatilake, S.R.; Mahatantila, K.; Ginige, M.P.; Vithanage, M. Sorptive Removal of Toluene and M-Xylene by Municipal Solid Waste Biochar: Simultaneous Municipal Solid Waste Management and Remediation of Volatile Organic Compounds. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 238, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, D.; Yu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Dai, Y. Insights into Efficient Removal of Gaseous p-Xylene Using Cerium-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles through Photocatalytic Oxidation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.-L.; Han, Q.-Y.; Jiang, Y.-F.; Zhang, S.-D.; Shu, L.; Zhang, R.-X. Synergetic Effect Between Plasma and UV for Toluene Conversion in Integrated Combined Plasma Photolysis Reactor with KrCl/KrBr/XeCl/Xe2 Excilamp. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 93, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Gonçalves, J.C.; Ferreira, A.F.P.; Rodrigues, A.E. A Review of Advances in Production and Separation of Xylene Isomers. Chem. Eng. Process.—Process Intensif 2021, 169, 108603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, J.; Gandolfo, A.; Temime-Roussel, B.; Brochard, G.; Bergé, V.; Gligorovski, S.; Wortham, H. Key Parameters Influencing the Uptake of M-Xylene on Photocatalytic Paints. Build. Environ. 2020, 179, 106979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, M. Natural vs. Synthetic Zeolites. Crystals 2020, 10, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Aguiñaga, E.A.; Elizalde-González, M.P.; Sabinas-Hernández, S.A. Unpredicted Photocatalytic Activity of Clinoptilolite–Mordenite Natural Zeolite. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 39251–39260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrabadi, Z.; Faghihian, H. Clinoptilolite Modified with TiO2 for Simultaneous Elimination of Two Herbicides; 2,4-D and MCPA by UV and Sunlight-Assisted Photocatalytic Degradation. Mater. Res. Bull. 2019, 119, 110569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, S.; Li, G.; Cui, B.; Wei, D.; Shen, Y. Synthesis of Clinoptilolite-Supported BiOCl/TiO2 Heterojunction Nanocomposites with Highly-Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity for the Complete Degradation of Xanthates under Visible Light. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 126697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Zhai, X.; Wang, X.; Li, T. Carbon Quantum Dots for Advanced Electrocatalysis. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 55, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasal, A.S.; Yadav, S.; Yadav, A.; Kashale, A.A.; Manjunatha, S.T.; Altaee, A.; Chang, J.-Y. Carbon Quantum Dots for Energy Applications: A Review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 6515–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campuzano, S.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Carbon Dots and Graphene Quantum Dots in Electrochemical Biosensing. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazi, Z.; Goharshadi, E.K.; Mashreghi, M.; Jorabchi, M.N. Highly Efficient Solar Photocatalytic Degradation of a Textile Dye by TiO2/Graphene Quantum Dots Nanocomposite. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2021, 20, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Long, G.; Chen, Q.; Zhong, Q. High-Efficiency Layered Sulfur-Doped Reduced Graphene Oxide and Carbon Nanotube Composite Counter Electrode for Quantum Dot Sensitized Solar Cells. J. Power Sources 2019, 430, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.; Gaikwad, R.P.; Mishra, V.; Gawande, M.B. Synthesis and Photocatalytic Applications of Functionalized Carbon Quantum Dots. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2022, 95, 1638–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shi, H.; Yang, M.; Yan, Y.; Liu, E.; Ji, Z.; Fan, J. Facile Synthesis of Novel Carbon Quantum Dots from Biomass Waste for Highly Sensitive Detection of Iron Ions. Mater. Res. Bull. 2020, 124, 110730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaludin, N.; Tan, T.L.; Zaman, A.S.K.; Sadrolhosseini, A.R.; Rashid, S.A. Acid-Free Hydrothermal-Extraction and Molecular Structure of Carbon Quantum Dots Derived from Empty Fruit Bunch Biochar. Materials 2020, 13, 3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, Q.; Yan, X.; Mo, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, B.; Teng, L.; Xiao, W.; Ge, L.; Wang, Q. Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of the Carbon Quantum Dot-Modified BiOI Microsphere. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, G.; Cui, J.; Lu, Y.; Rong, X.; Gao, C. A Review on Mechanism, Applications and Influencing Factors of Carbon Quantum Dots Based Photocatalysis. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 35986–35999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Qi, F.; Labidi, A.; Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Xin, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, C. Chemically Bonded Carbon Quantum Dots/Bi2WO6 S-Scheme Heterojunction for Boosted Photocatalytic Antibiotic Degradation: Interfacial Engineering and Mechanism Insight. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2023, 330, 122587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, R.; Qi, W.; Su, R.; He, Z. Enhanced Photocatalytic Degradation of Antibiotics in Water over Functionalized N,S-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots Embedded ZnO Nanoflowers under Sunlight Irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 123016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Lei, X.; Xia, L.; Wu, Q.; Yao, W. Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production Activity of CdS Coated with Zn-Anchored Carbon Layer. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda-Serna, H.U.; Calderón-Domínguez, G.; García-Bórquez, A.; Salgado-Cruz, M.D.L.P.; Farrera Rebollo, R.R. Structural and Luminescent Properties of CQDs Produced by Microwave and Conventional Hydrothermal Methods Using Pelagic Sargassum as Carbon Source. Opt. Mater. 2022, 126, 112156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.; Wu, X.; Hao, Y. The Mechanism of Blue Photoluminescence from Carbon Nanodots. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 4981–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayawei, N.; Ebelegi, A.N.; Wankasi, D. Modelling and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherms. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 3039817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the Use and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherm Models: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Pramanik, P. Carbon Quantum Dots from Natural Resource: A Review. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 8, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohamy, H.S.; El-Sakhawy, M.; Kamel, S. Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots as an Effective Adsorbent. J. Fluoresc. 2023, 33, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, L.-J.; Pan, W.-G.; Wei, Z.-Z.; Liang, X.-Y.; Guo, R.-T. Granular Polymeric Carbon Nitride with Carbon Vacancies for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. Sol. RRL 2021, 5, 2000796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Song, C.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Han, Y. Shift of Microbial Diversity and Function in High-Efficiency Performance Biotrickling Filter for Gaseous Xylene Treatment. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2019, 69, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, S.; Hu, J.; Yang, X.; Huang, L.; Su, Y.; Liu, D. An Efficient Treatment for Degradation of High-Concentration Xylene Gas via Water Falling Film Discharge in Synergy with Silver Catalysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 122277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Supported C-Scorpionate Vanadium(IV) Complexes as Reusable Catalysts for Xylene Oxidation. Chem.—Asian J. 2017, 12, 1915–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, H.; Lin, H.; Humphrey, M.G.; Zhang, C. A Hydrothermal Route to Water-Stable Luminescent Carbon Dots as Nanosensors for PH and Temperature. Carbon 2015, 82, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.S.; Gao, P.F.; Zhang, H.Z.; Zheng, L.L.; Li, C.M.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.F.; Liu, F.; Li, N.; Huang, C.Z. Chiral Nanoprobes for Targeting and Long-Term Imaging of the Golgi Apparatus. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 6829–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifikar, F.; Azizian, S. Super-Stable Carbon Quantum Dots Nanofluid for Efficient Solar-Thermal Conversion. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 228, 113675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Wang, X.; Shi, G.; Wang, Z.; Xie, X.; Sun, J. Revealing Adsorption and the Photodegradation Mechanism of Gas Phase O-Xylene on Carbon Quantum Dots Modified TiO2 Nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-W.; Gong, S.; Mahmood, N.; Pan, L.; Zhang, X.; Zou, J.-J. Oxygen-Doped Nanoporous Carbon Nitride via Water-Based Homogeneous Supramolecular Assembly for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 221, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, P.; Guo, S.; Li, S.; Meng, X.; Lu, Y.; Xu, H.; Ma, H.; et al. In Situ Self-Assembly Synthesis of Carbon Self-Doped Graphite Carbon Nitride Hexagonal Tubes with Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 27354–27362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Guo, X.; Zhang, S.; Qi, Y.; Gao, S. Analysis of the Electronic Structure of β-SiO2 Intrinsic Defects Based on Density Functional Theory. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 105554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Hao, S.; Yusu, W.; Yang, J. Preparation of Goethite/Nickel Foam Catalyst and Its Application in Xylene Degradation. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 364, 132587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madannejad, R.; Shoaie, N.; Jahanpeyma, F.; Darvishi, M.H.; Azimzadeh, M.; Javadi, H. Toxicity of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials: Reviewing Recent Reports in Medical and Biological Systems. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 307, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Material Name | Glucose Dosage/mol | Clinoptilolite Mass/mol |
|---|---|---|
| The original zeolite | 0 | 5.00 × 10−3 |
| Catalyst No. 1 | 6.88 × 10−3 | 5.00 × 10−3 |
| Catalyst No. 2 | 1.38 × 10−2 | 5.00 × 10−3 |
| Element | Percentage by Weight (%) | Percentage of Atoms (%) |
|---|---|---|
| C K | 0.72 | 13.98 |
| O K | 4.29 | 62.52 |
| Al K | 0.13 | 1.16 |
| Si K | 2.61 | 21.68 |
| K K | 0.11 | 0.66 |
| Element | Atomic Percentage of Catalyst No. 1 (%) | Atomic Percentage of Catalyst No. 2 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Al 2p | 6.36 | 4.91 |
| Si 2p | 18.75 | 14.01 |
| C 1s | 19.99 | 37.96 |
| K 2p | 0.38 | 0.22 |
| O 1s | 54.52 | 42.91 |
| Capture Agent | None | TEMPO | P-Benzoquinone |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capture of active substances | ·OH | ·O2− | |
| Xylene degradation rate/% | 90 | 23 | 19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, S.; Cheng, C.; Meng, L.; Zhang, P.; Sun, B. Photocatalytic Degradation of Xylene by Carbon Quantum Dots/Clinoptilolite Composites. Materials 2023, 16, 5243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155243
Zhu S, Cheng C, Meng L, Zhang P, Sun B. Photocatalytic Degradation of Xylene by Carbon Quantum Dots/Clinoptilolite Composites. Materials. 2023; 16(15):5243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155243
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Shuguang, Chun Cheng, Li Meng, Pengyu Zhang, and Bai Sun. 2023. "Photocatalytic Degradation of Xylene by Carbon Quantum Dots/Clinoptilolite Composites" Materials 16, no. 15: 5243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155243
APA StyleZhu, S., Cheng, C., Meng, L., Zhang, P., & Sun, B. (2023). Photocatalytic Degradation of Xylene by Carbon Quantum Dots/Clinoptilolite Composites. Materials, 16(15), 5243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155243





