Extracellular Electron Transfer in Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of 201 Stainless Steel by Shewanella algae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Bacterial Mutant and Culture Condition
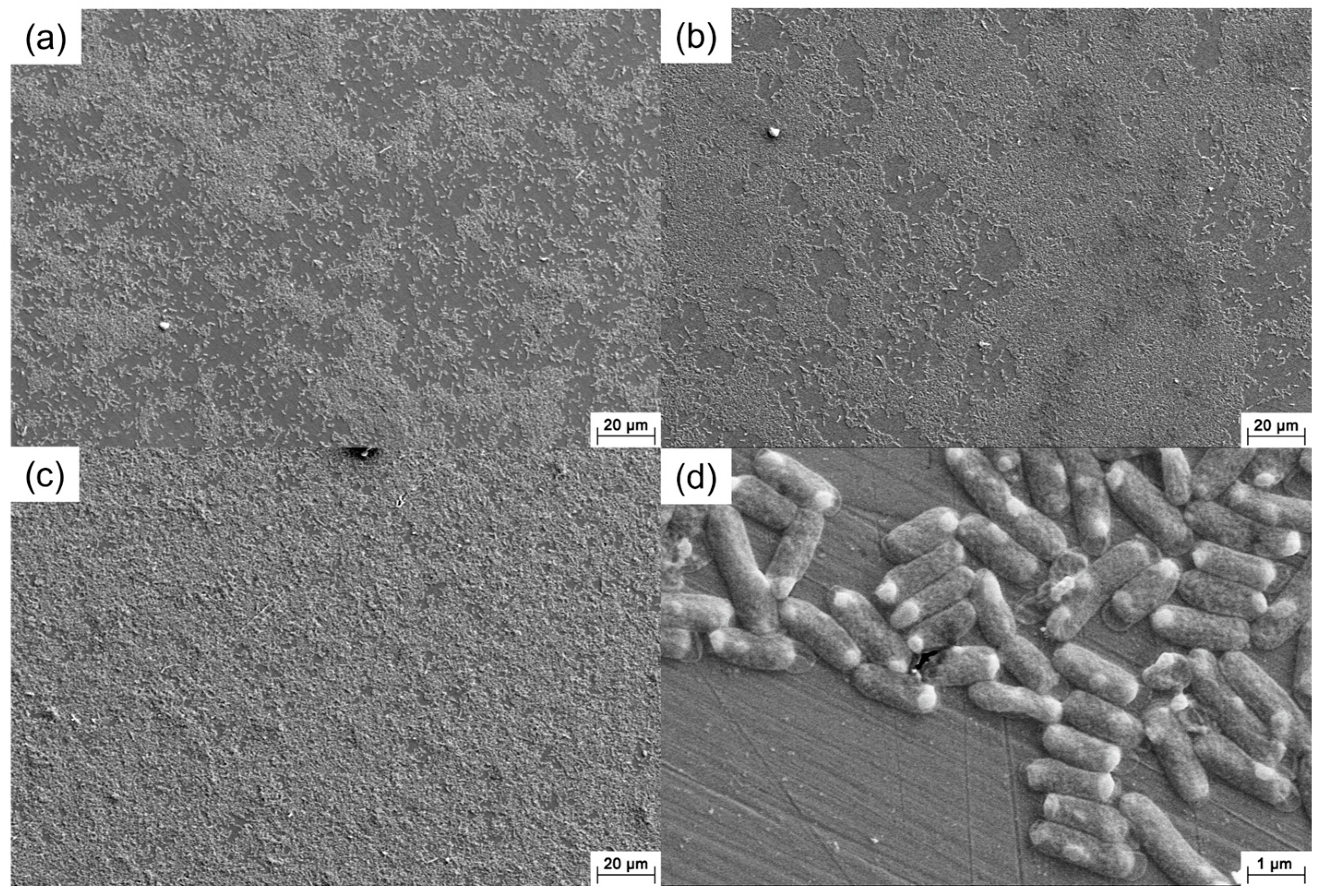
2.3. Surface Analysis
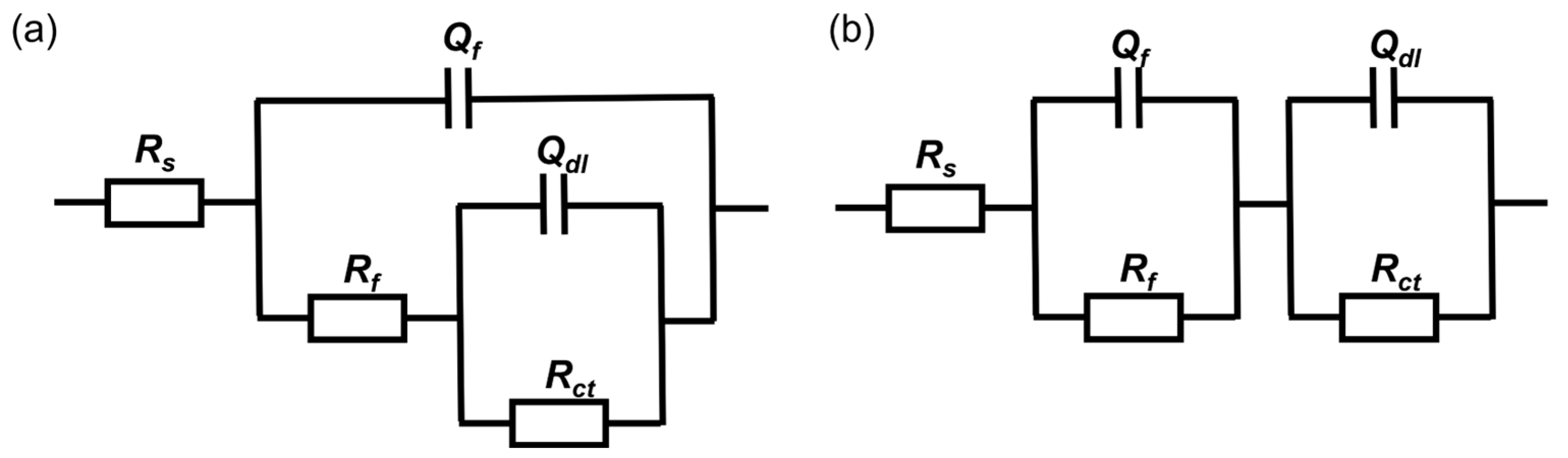
2.4. Electrochemical Tests
2.5. ICP-MS Analysis
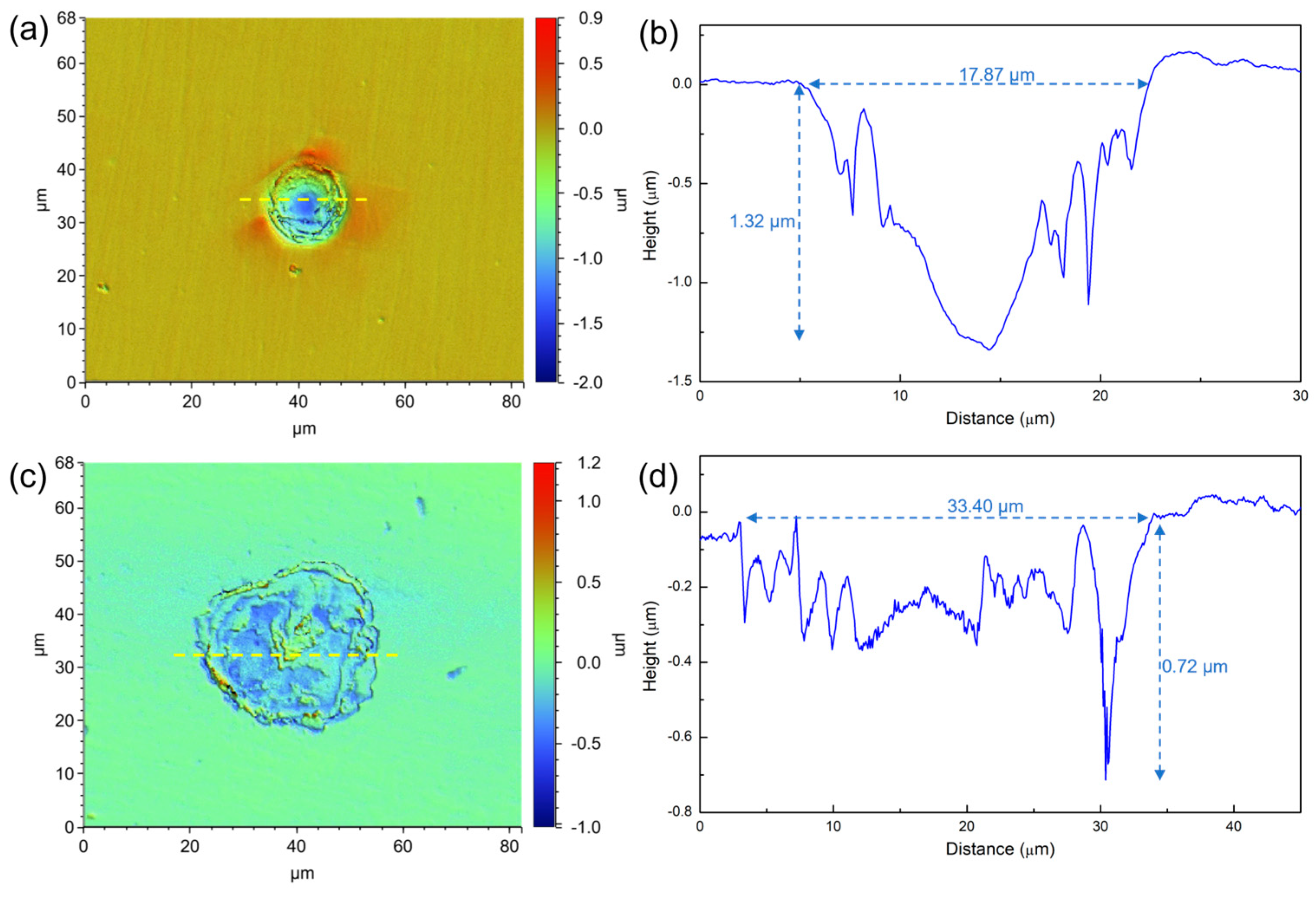
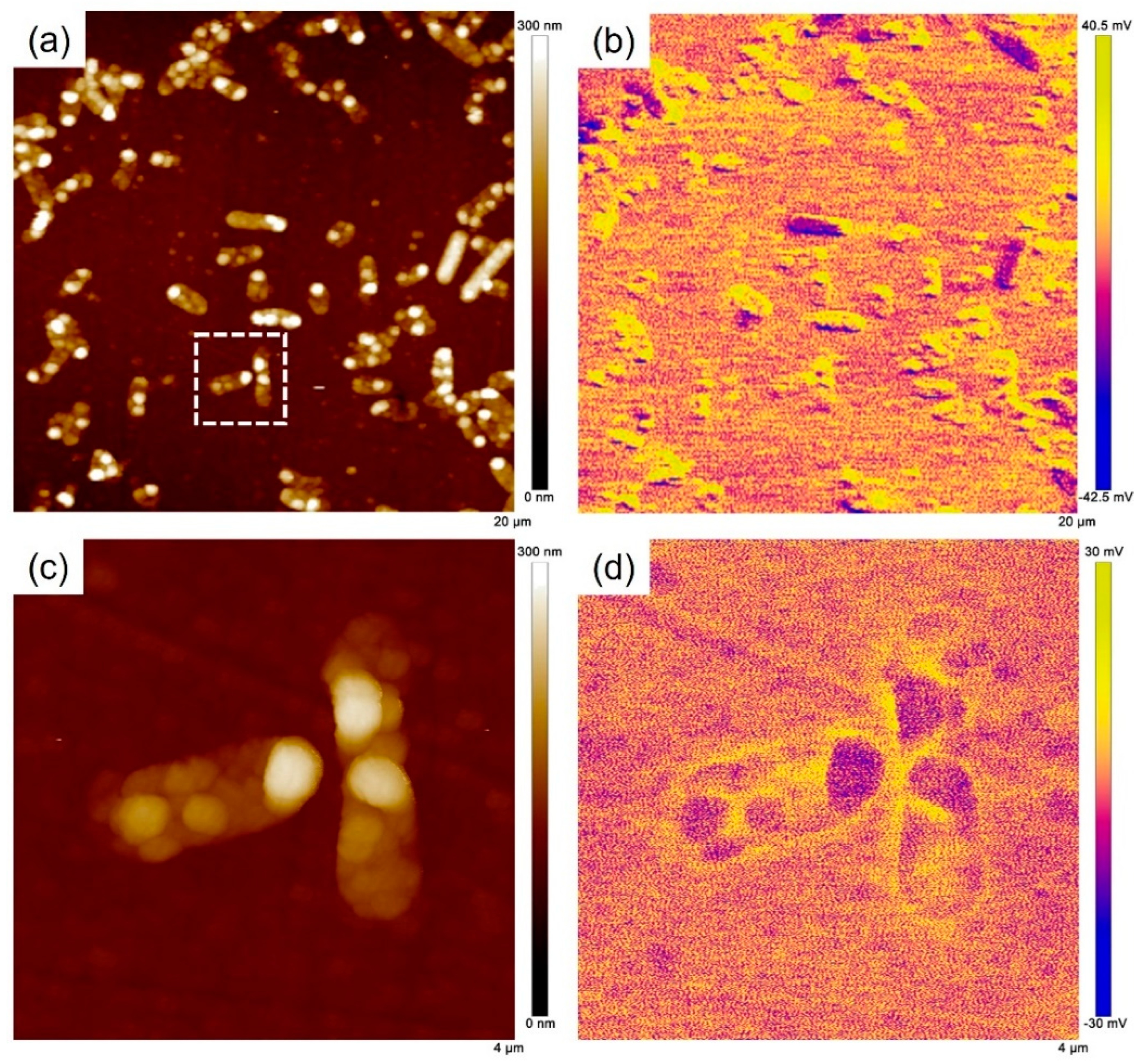
2.6. AFM Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
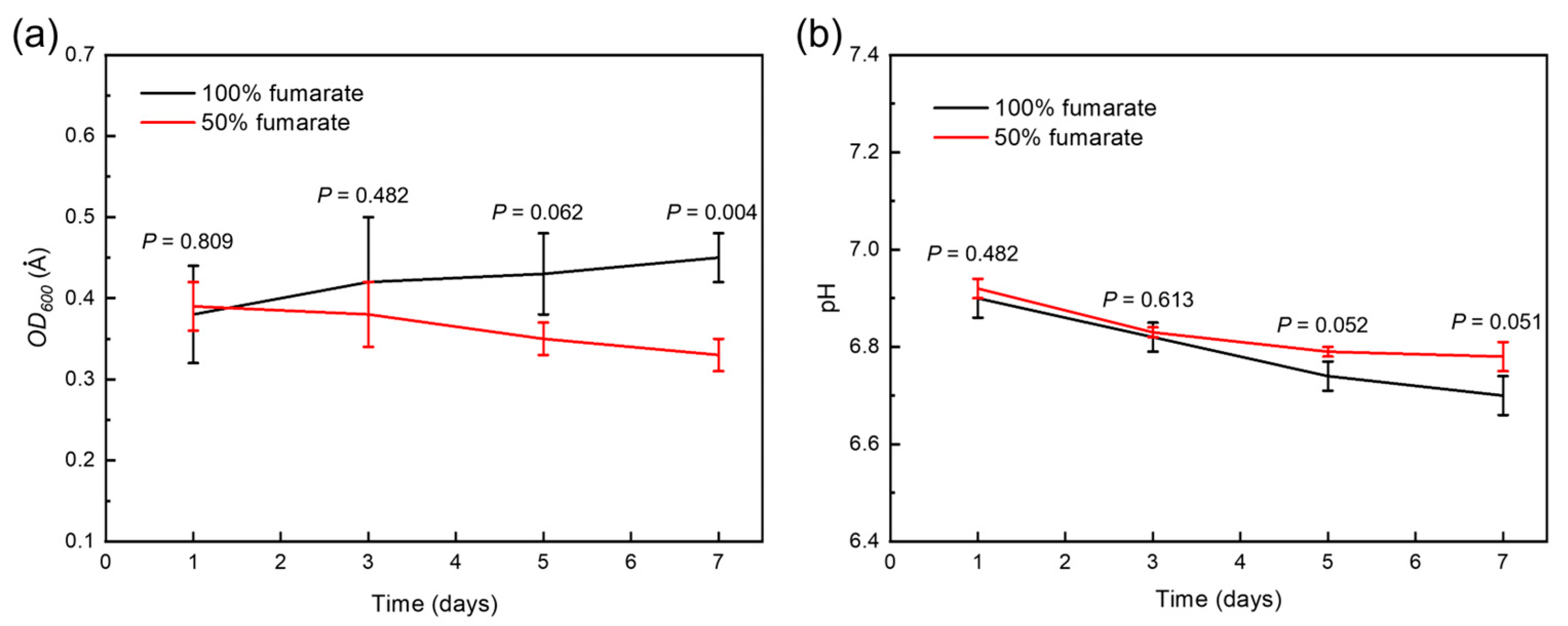
3.1. Bacterial Growth
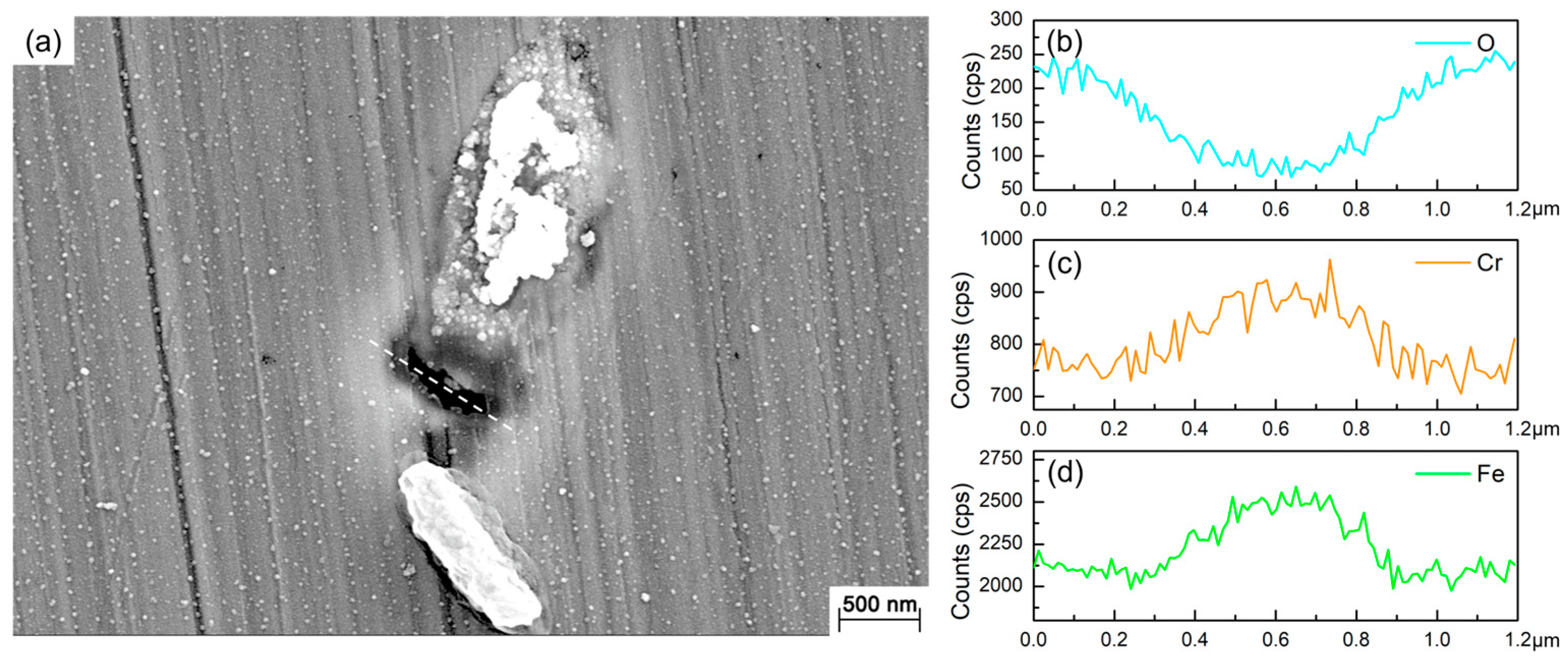
3.2. Surface Morphology
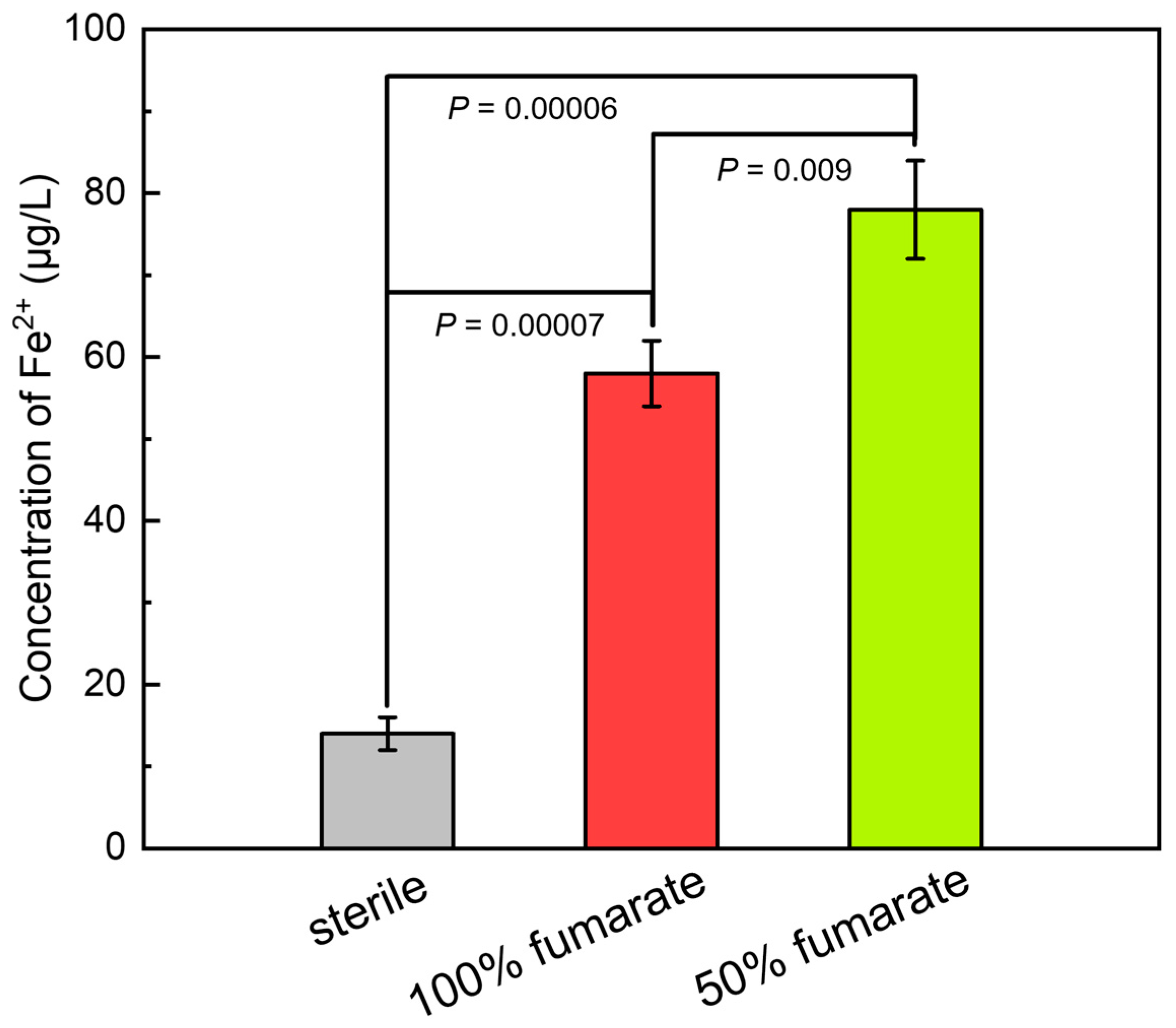
3.3. ICP-MS Results
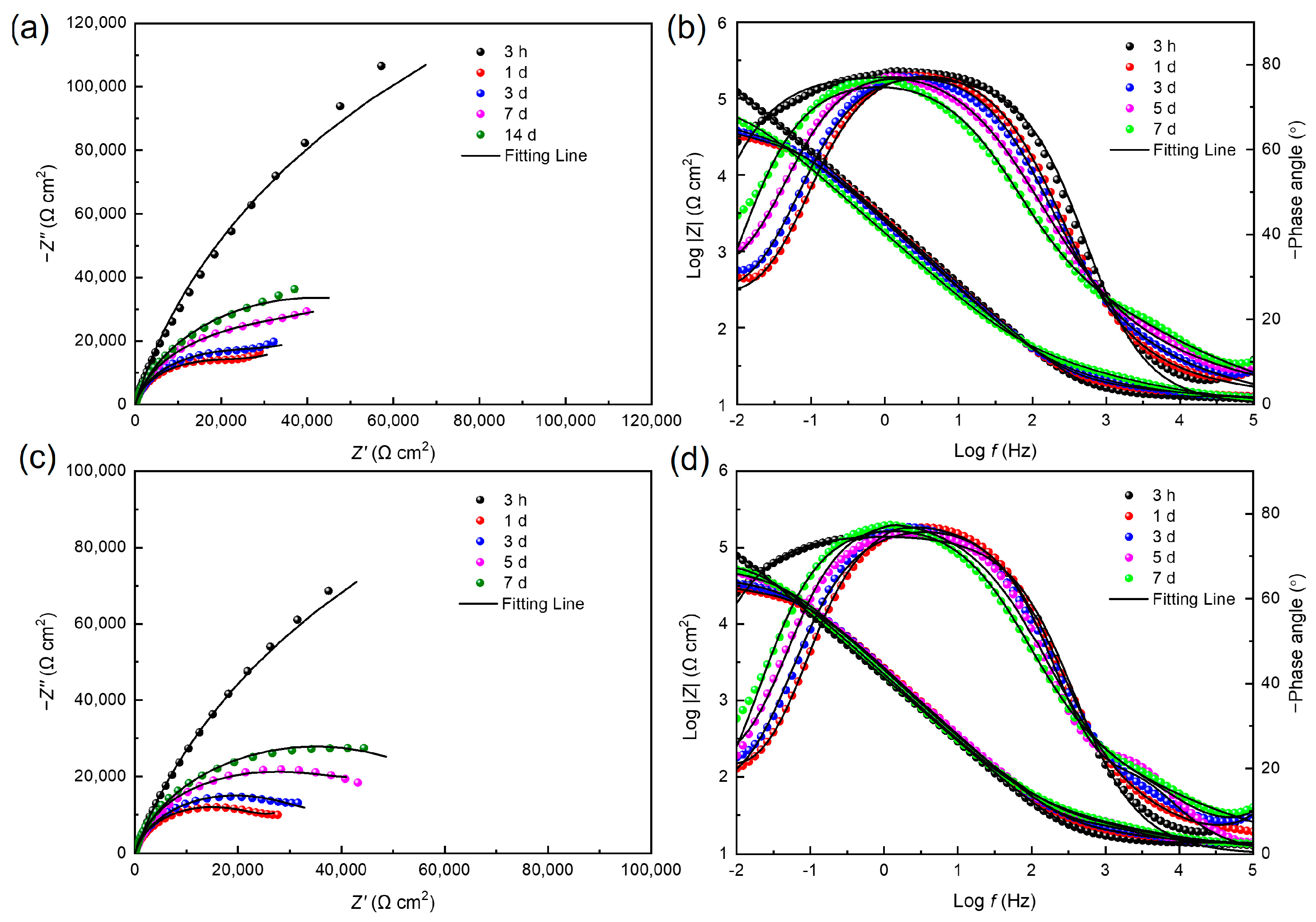
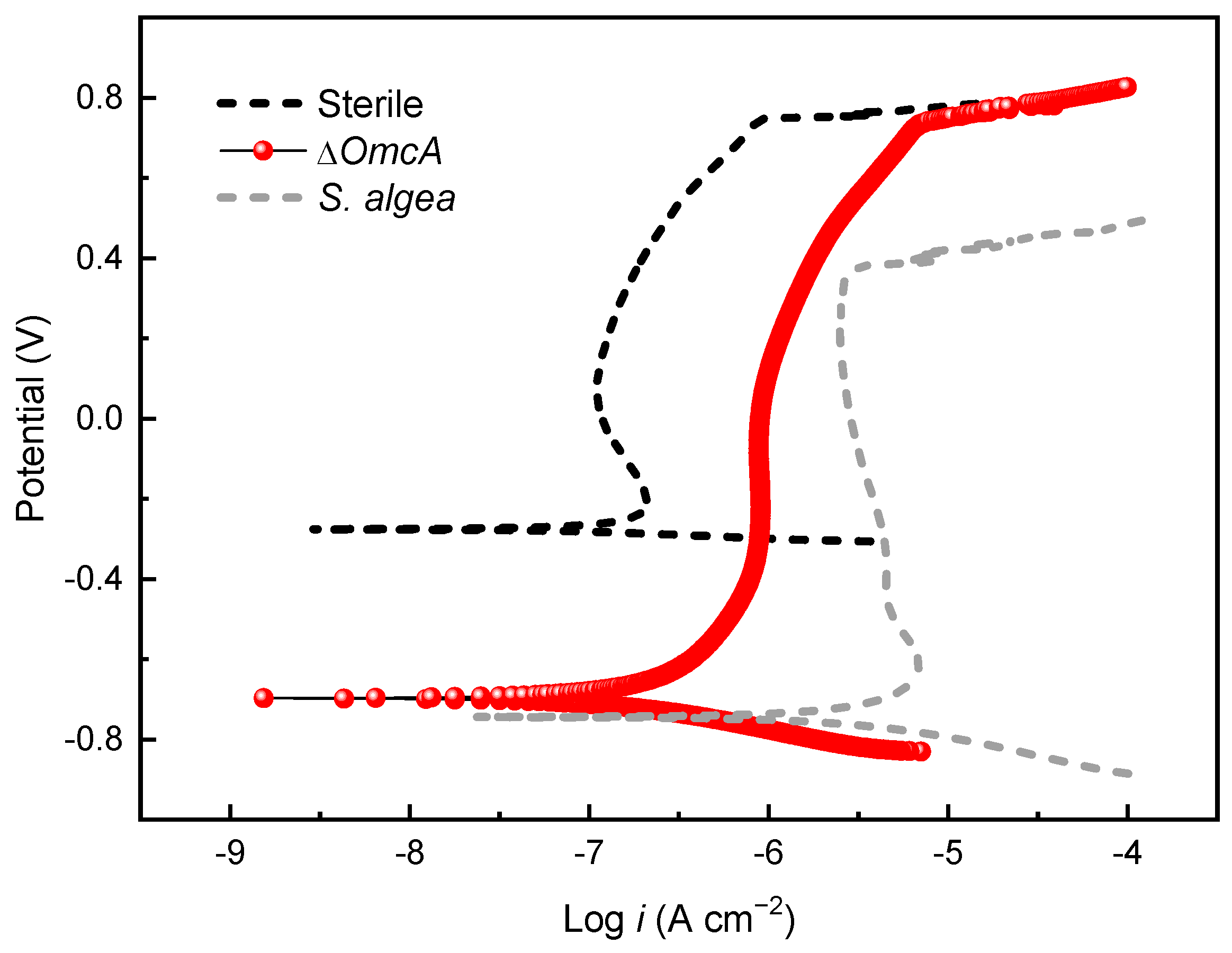
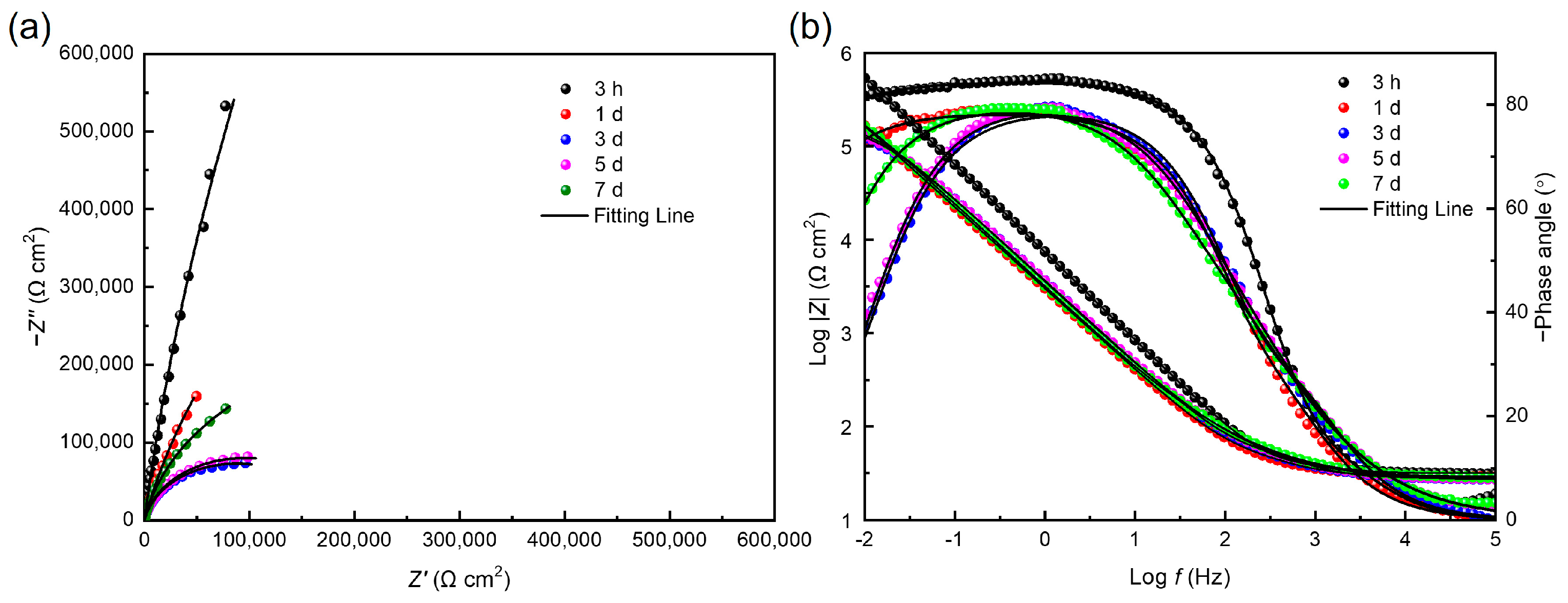
3.4. Electrochemical Analysis
3.5. Corrosion Behavior of ΔOmcA
4. Conclusions
- According to the results of the potentiodynamic polarization curves and the ICP-MS, 201 stainless steels corroded slowly in the sterile medium. The presence of S. algae enhanced the dissolution of the Fe oxides in the passive film and decreased the pitting potential of the steel, leading to the degradation of the passive film.
- The results of EIS and the morphologies of the maximum corrosion pits revealed that corrosion acceleration of 201 stainless steel was most obvious in the 50% fumarate medium in the presence of S. algae. The lack of an electron acceptor further aggravated the degradation of the passive film and mainly affected the early stage of MIC.
- In the absence of the c-type cytochrome OmcA, MIC of the 201 stainless steels induced by ΔOmcA was significantly weakened as manifested by the potentiodynamic polarization curves, EIS and AFM characterization. It further confirmed the important role of OmcA related to EET in the MIC of 201 stainless steel.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, L.; Wu, X.D.; Wang, Q.H.; Yan, Z.T.; Wen, X.; Tang, J.; Li, X.M. An overview of microbiologically influenced corrosion: Mechanisms and its control by microbes. Corros. Rev. 2022, 40, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kip, N.; van Veen, J.A. The dual role of microbes in corrosion. ISME J. 2015, 9, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procopio, L. The role of biofilms in the corrosion of steel in marine environments. World J. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.A.; Zhao, D.D.; Zheng, S.J.; Gong, A.J.; Liu, Z.P.; Su, Y.R.; Liu, Z.Y. Inhibition Effect of Pseudomonas stutzeri on the Corrosion of X70 Pipeline Steel Caused by Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria. Materials 2023, 16, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, A.; Sarkar, T.K.; Chouhan, A.; Dasgupta, D.; Khatri, O.P.; Ghosh, D. Microbiologically influenced corrosion of wastewater pipeline and its mitigation by phytochemicals: Mechanistic evaluation based on spectroscopic, microscopic and theoretical analyses. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 364, 119960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spark, A.; Wang, K.; Cole, I.; Law, D.; Ward, L. Microbiologically influenced corrosion: A review of the studies conducted on buried pipelines. Corros. Rev. 2020, 38, 231–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venzlaff, H.; Enning, D.; Srinivasan, J.; Mayrhofer, K.J.J.; Hassel, A.W.; Widdel, F.; Stratmann, M. Accelerated cathodic reaction in microbial corrosion of iron due to direct electron uptake by sulfate-reducing bacteria. Corros. Sci. 2013, 66, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Dong, H.; Reguera, G.; Beyenal, H.; Lu, A.; Liu, J.; Yu, H.Q.; Fredrickson, J.K. Extracellular electron transfer mechanisms between microorganisms and minerals. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochina, T.A.; Kondratenko, Y.A.; Shilova, O.A.; Vlasov, D.Y. Biocorrosion, Biofouling, and Advanced Methods of Controlling Them. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2022, 58, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, B.; Sheetal; Singh, M.; Thakur, S.; Pani, B.; Singh, A.K.; Saji, V.S. Extracellular Electron Transfer by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Biocorrosion: A Review. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherar, B.W.A.; Power, I.M.; Keech, P.G.; Mitlin, S.; Southam, G.; Shoesmith, D.W. Characterizing the effect of carbon steel exposure in sulfide containing solutions to microbially induced corrosion. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.W.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Lou, Y.T.; Cui, T.Y.; Qian, H.C.; Mol, A.; Zhang, D.W. The effect of riboflavin on the microbiologically influenced corrosion of pure iron by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 147, 108173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, W.W.; Liu, J.L.; Cai, W.Z.; Wang, D.; Jia, R.; Chen, S.G.; Gu, T.Y. Electrochemical investigation of increased carbon steel corrosion via extracellular electron transfer by a sulfate reducing bacterium under carbon source starvation. Corros. Sci. 2019, 150, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S. Microbial extracellular electron transfer and its relevance to iron corrosion. Microb. Biotechnol. 2016, 9, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krantz, G.P.; Lucas, K.; Wunderlich, E.L.; Hoang, L.T.; Avci, R.; Siuzdak, G.; Fields, M.W. Bulk phase resource ratio alters carbon steel corrosion rates and endogenously produced extracellular electron transfer mediators in a sulfate-reducing biofilm. Biofouling 2019, 35, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.H.; Zhong, R.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.K.; Liu, Z.Y.; Du, C.W.; Li, X.G. Characteristic and Mechanistic Investigation of Stress-Assisted Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of X80 Steel in Near-Neutral Solutions. Materials 2023, 16, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Masoumeh, M.; Zhou, E.Z.; Liu, D.; Song, Y.B.; Xu, D.K.; Wang, F.H.; Smith, J.A. Streptococcus mutans biofilms induce metabolite-mediated corrosion of 316 L stainless steel in a simulated oral environment. Corros. Sci. 2021, 182, 109286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.W.; Li, Y.Y.; Zheng, H.B.; Qian, H.C.; Guo, D.W.; Zhang, S.Y.; Lou, Y.T.; Kwok, C.T.; Tam, L.M.; Zhang, D.W. Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion Behavior of Fe40(CoCrMnNi)60 and Fe60(CoCrMnNi)40 Medium Entropy Alloys in the Presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acta Metall. Sin. 2023, 36, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.Y.; Chang, W.W.; Zhang, D.W.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Lou, Y.T.; Qian, H.C.; Jiang, C.Y.; Li, X.G.; Mol, A. Acceleration of corrosion of 304 stainless steel by outward extracellular electron transfer of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. Corros. Sci. 2022, 199, 110159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.T.; Huang, L.Y.; Lou, Y.T.; Chang, W.W.; Qian, H.C.; Zhang, D.W. Microbiologically influenced corrosion of stainless steels by Bacillus subtilis via bidirectional extracellular electron transfer. Corros. Sci. 2022, 207, 110608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovley, D.R.; Holmes, D.E.; Nevin, K.P. Dissimilatory Fe(III) and Mn(IV) reduction. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2004, 49, 219–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.X.; Gorby, Y.A.; Zachara, J.M.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Brown, C.F. Reduction kinetics of Fe(III), Co(III), U(VI) Cr(VI) and Tc(VII) in cultures of dissimilatory metal-reducing bacteria. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2002, 80, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Rosso, K.M.; Zachara, J.M.; Fredrickson, J.K. Mtr extracellular electron-transfer pathways in Fe(III)-reducing or Fe(II)-oxidizing bacteria: A genomic perspective. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2012, 40, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Canstein, H.; Ogawa, J.; Shimizu, S.; Lloyd, J.R. Secretion of flavins by Shewanella species and their role in extracellular electron transfer. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2008, 74, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, M.J.; Beliaev, A.S.; Dohnalkova, A.C.; Kennedy, D.W.; Shi, L.; Wang, Z.M.; Boyanov, M.I.; Lai, B.; Kemner, K.M.; McLean, J.S.; et al. c-Type cytochrome-dependent formation of U(IV) nanoparticles by Shewanella oneidensis. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, 1324–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, A.; Nakamura, R.; Hashimoto, K. In-vivo identification of direct electron transfer from Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 to electrodes via outer-membrane OmcA-MtrCAB protein complexes. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 5526–5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhou, E.Z.; Jiang, C.Y.; Jia, R.; Liu, S.J.; Xu, D.K.; Gu, T.Y.; Wang, F.H. Endogenous phenazine-1-carboxamide encoding gene PhzH regulated the extracellular electron transfer in biocorrosion of stainless steel by marine Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Electrochem. Commun. 2018, 94, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Chang, W.W.; Cui, T.Y.; Xu, D.K.; Zhang, D.W.; Lou, Y.T.; Qian, H.C.; Song, H.; Mol, A.; Cao, F.H.; et al. Adaptive bidirectional extracellular electron transfer during accelerated microbiologically influenced corrosion of stainless steel. Commun. Mater. 2021, 2, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, C.L.; Dohnalkova, A.C.; Nachimuthu, P.; Kennedy, D.W.; Saffarini, D.A.; Arey, B.W.; Shi, L.; Wang, Z.; Moore, D.; Mclean, J.S.; et al. Role of outer-membrane cytochromes MtrC and OmcA in the biomineralization of ferrihydrite by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Geobiology 2010, 8, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaoki, K.; Saito, N.; Nomura, T.; Konishi, Y. Microbial recovery of rhodium from dilute solutions by the metal ion-reducing bacterium Shewanella algae. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 139, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, Y.; Ohno, K.; Saitoh, N.; Nomura, T.; Nagamine, S.; Hishida, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Uruga, T. Bioreductive deposition of platinum nanoparticles on the bacterium Shewanella algae. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 128, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adaikpoh, B.I.; Fernandez, H.N.; Eustaquio, A.S. Biotechnology approaches for natural product discovery, engineering, and production based on Burkholderia bacteria. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 77, 102782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.C.; Pan, Z.M.; Wang, X.F.; Luo, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.G. Corrosion and passive behavior of AlxCrFeNi3−x (x=0.6, 0.8, 1.0) eutectic high entropy alloys in chloride environment. Corros. Sci. 2022, 208, 110666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Dou, W.W.; Chen, S.G.; Pu, Y.N.; Xu, Z.X. Influence of nutrition on Cu corrosion by Desulfovibrio vulgaris in an-aerobic environment. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 144, 108040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.Y.; Qian, H.C.; Chang, W.W.; Zheng, H.B.; Guo, D.W.; Kwok, C.T.; Tam, L.M.; Zhang, D.W. Towards understanding Shewanella algae-induced degradation of passive film of stainless steel based on electrochemical, XPS and multi-mode AFM analyses. Corros. Sci. 2023, 218, 111174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Element | C | Cr | Mn | Si | Ni | S | P | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 201 SS | 0.12 | 17.20 | 6.20 | 0.80 | 4.80 | 0.01 | 0.03 | balance |
| Time | Rs (Ω cm2) | Qf × 10−5 (Ω−1 cm−2 sn) | Rf (Ω cm2) | Qdl × 10−5 (Ω−1 cm−2 sn) | Rct × 104 (Ω cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100% fumarate medium | |||||
| 3 h | 14.52 ± 2.32 | 2.26 ± 0.76 | 40.36 ± 4.2 | 5.19 ± 0.32 | 49.5 ± 8.9 |
| 1 d | 12.05 ± 1.82 | 2.49 ± 0.30 | 11.7 ± 3.8 | 5.01 ± 0.42 | 2.81 ± 0.63 |
| 3 d | 12.70 ± 1.52 | 2.42 ± 0.29 | 15.1 ± 3.3 | 5.75 ± 0.52 | 3.47 ± 0.46 |
| 5 d | 10.12 ± 1.24 | 2.41 ± 0.47 | 22.1 ± 5.2 | 6.48 ± 0.64 | 5.76 ± 0.97 |
| 7 d | 9.68 ± 1.01 | 2.61 ± 0.36 | 49.3 ± 7.9 | 1.19 ± 0.08 | 8.40 ± 1.12 |
| 50% fumarate medium | |||||
| 3 h | 10.33 ± 1.32 | 2.10 ± 0.42 | 4.89 ± 0.10 | 8.72 ± 0.76 | 33.8 ± 6.6 |
| 1 d | 13.92 ± 1.44 | 2.25 ± 0.37 | 11.7 ± 2.6 | 5.05 ± 0.62 | 2.70 ± 0.48 |
| 3 d | 13.73 ± 1.11 | 2.21 ± 0.29 | 15.5 ± 2.9 | 5.45 ± 0.77 | 3.41 ± 0.46 |
| 5 d | 14.04 ± 1.03 | 2.28 ± 0.44 | 22.0 ± 6.2 | 5.66 ± 0.40 | 5.12 ± 0.95 |
| 7 d | 10.39 ± 0.92 | 1.80 ± 0.09 | 46.5 ± 8.3 | 9.06 ± 0.82 | 6.59 ± 1.02 |
| Time | Rs (Ω cm2) | Qf × 10−5 (Ω−1 cm−2 sn) | Rf (Ω cm2) | Qdl × 10−5 (Ω−1 cm−2 sn) | Rct × 105 (Ω cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔOmcA | |||||
| 3 h | 13.16 ± 1.77 | 0.88 ± 0.04 | 16.6 ± 3.6 | 1.54 ± 0.63 | 98.4 ± 1.7 |
| 1 d | 12.95 ± 2.01 | 3.56 ± 0.64 | 11.7 ± 3.8 | 3.13 ± 0.45 | 17.8 ± 0.8 |
| 3 d | 12.79 ± 1.14 | 2.37 ± 0.12 | 15.1 ± 3.3 | 3.03 ± 0.62 | 1.75 ± 0.12 |
| 5 d | 12.83 ± 1.62 | 2.48 ± 0.95 | 22.1 ± 5.2 | 2.97 ± 0.27 | 1.98 ± 0.43 |
| 7 d | 12.77 ± 1.36 | 53.4 ± 2.2 | 49.3 ± 7.9 | 6.20 ± 0.72 | 5.10 ± 1.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, W.; Wang, X.; Zheng, H.; Cui, T.; Qian, H.; Lou, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, S.; Guo, D. Extracellular Electron Transfer in Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of 201 Stainless Steel by Shewanella algae. Materials 2023, 16, 5209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155209
Chang W, Wang X, Zheng H, Cui T, Qian H, Lou Y, Gao J, Zhang S, Guo D. Extracellular Electron Transfer in Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of 201 Stainless Steel by Shewanella algae. Materials. 2023; 16(15):5209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155209
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Weiwei, Xiaohan Wang, Huaibei Zheng, Tianyu Cui, Hongchang Qian, Yuntian Lou, Jianguo Gao, Shuyuan Zhang, and Dawei Guo. 2023. "Extracellular Electron Transfer in Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of 201 Stainless Steel by Shewanella algae" Materials 16, no. 15: 5209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155209
APA StyleChang, W., Wang, X., Zheng, H., Cui, T., Qian, H., Lou, Y., Gao, J., Zhang, S., & Guo, D. (2023). Extracellular Electron Transfer in Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of 201 Stainless Steel by Shewanella algae. Materials, 16(15), 5209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155209





