The Influence of Heat and Cryogenic Treatment on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Laser-Welded AZ31B
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Welding Equipment
2.2. Post-Weld Treatment System
2.3. Testing Equipment
3. Results and Discussion
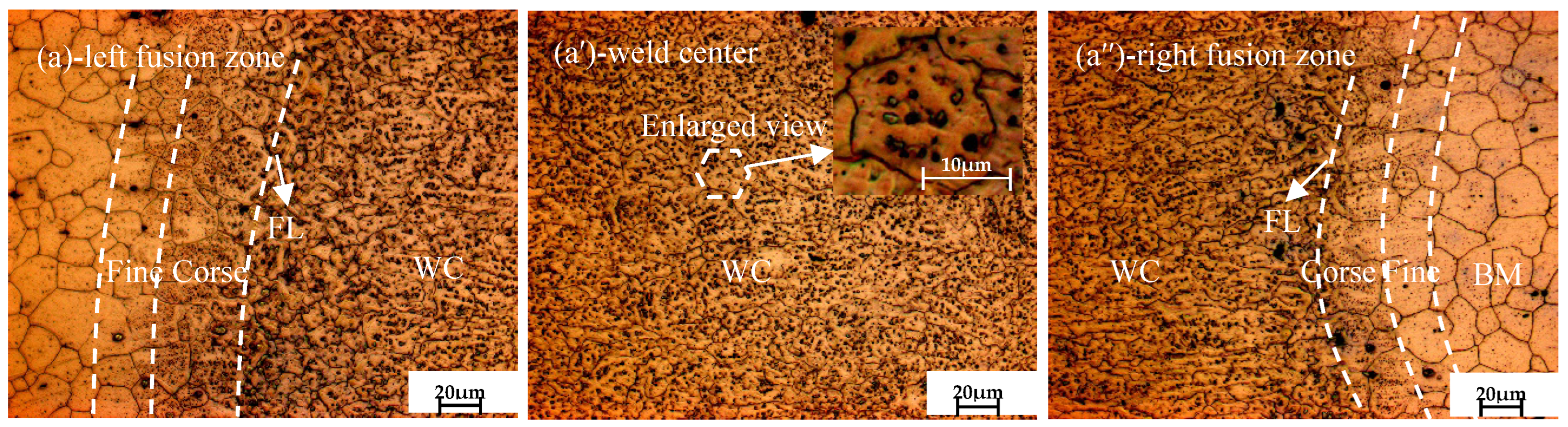
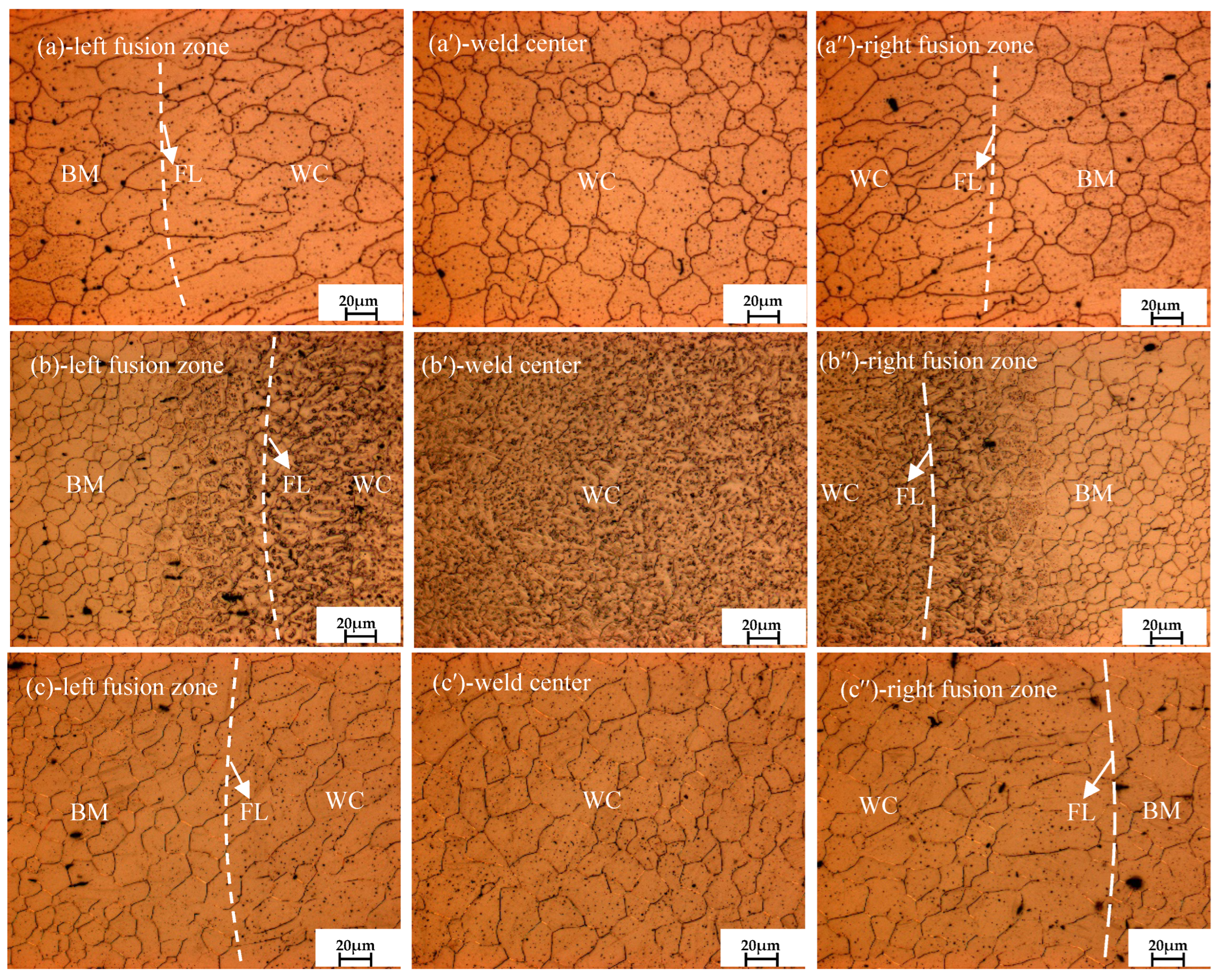
3.1. Microstructure Evolution Analysis
3.2. Phase Composition Analysis
3.2.1. XRD Analysis
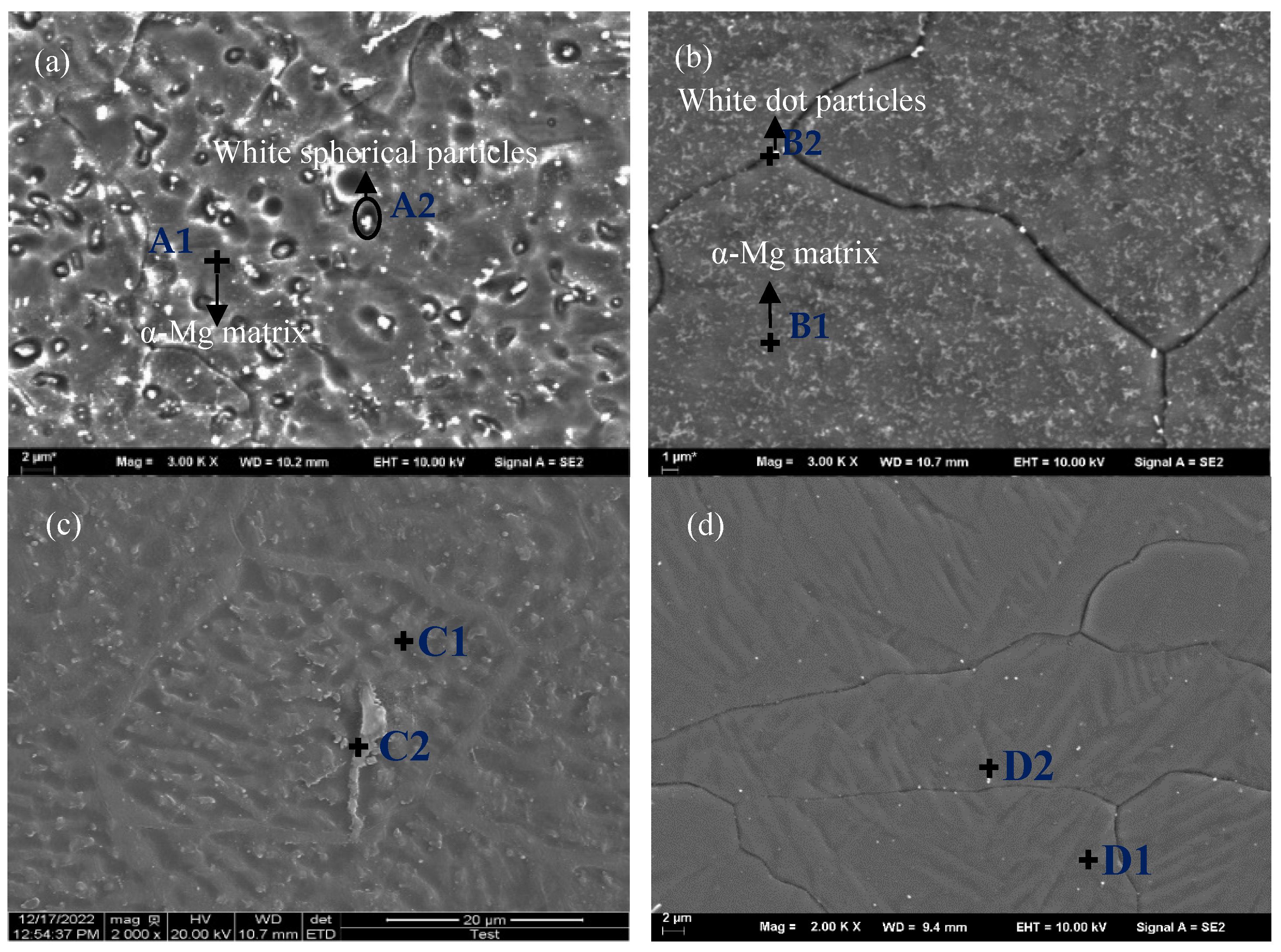
3.2.2. SEM Analysis
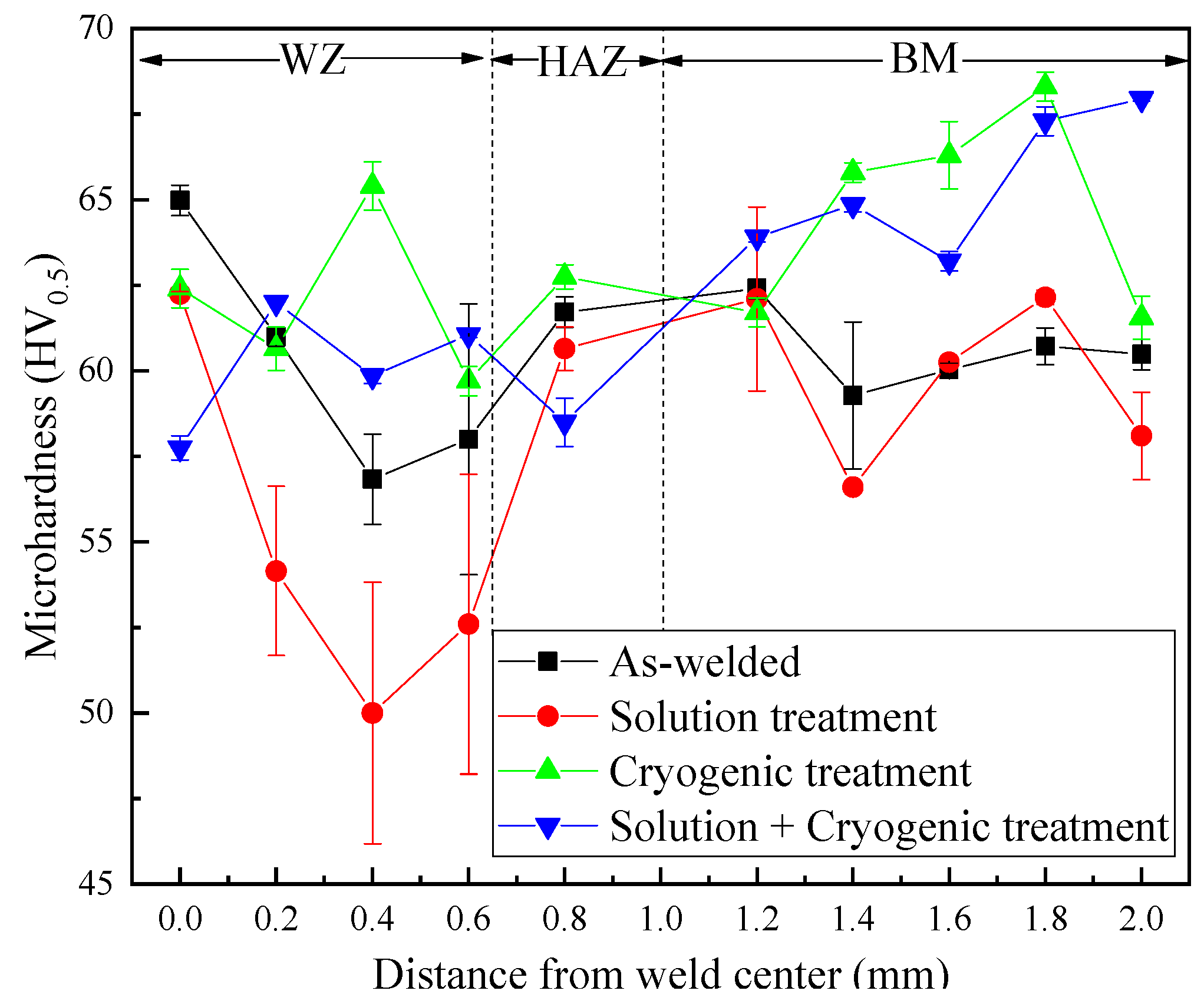
3.3. Microhardness Analysis
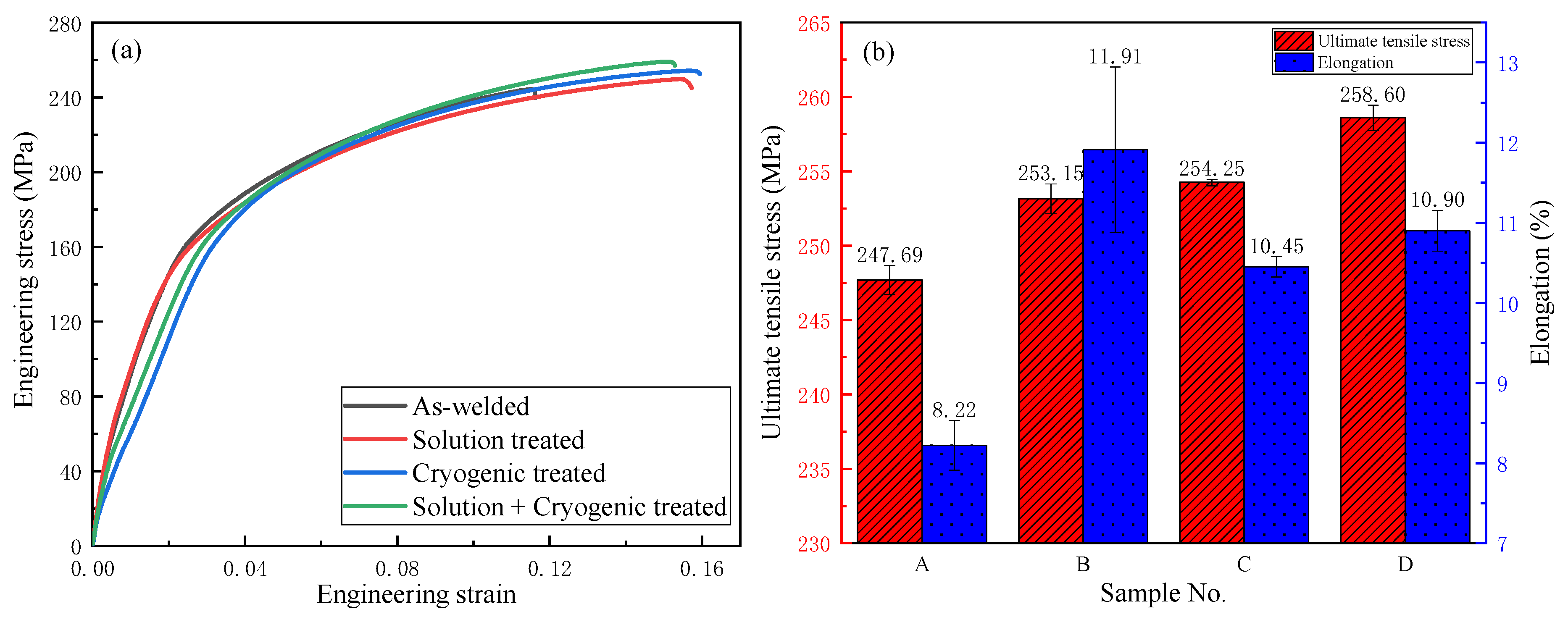
3.4. Tensile Properties
3.4.1. Comparison of Tensile Properties
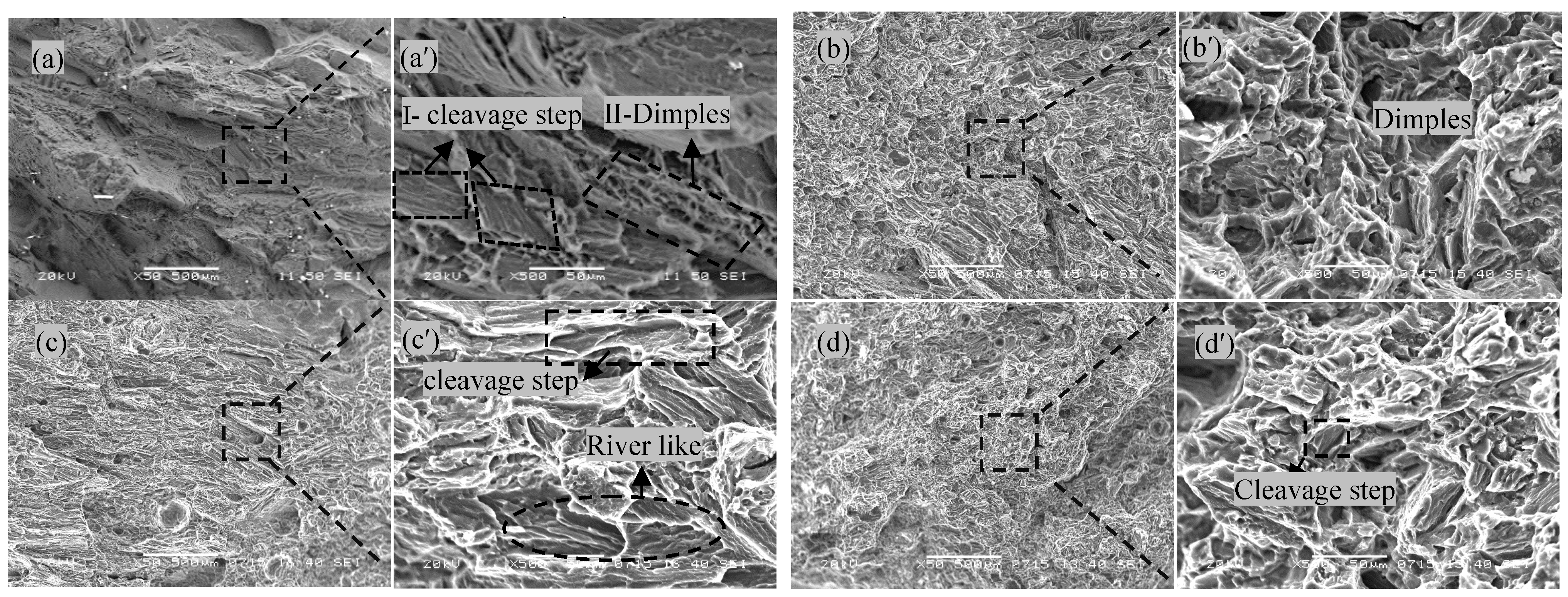
3.4.2. Comparative Analysis of Fracture Surfaces
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Solution treatment played the role of regulating the organization, reducing segregation, and improving the tensile strength of magnesium alloys. The grain size was refined under the function of cryogenic treatment, and most of lamellar Mg17Al12 was choppy.
- (2)
- After solution + cryogenic treatment, the conversion of Mg17Al12 from a lamellar state into a particle-like state as well as the appearance of dispersed Al8Mn5 particles played a major role in improving the mechanical properties of the welded joint. The tensile strength (258.60 MPa) and elongation (10.90%) of the solution + cryogenic-treated sample were 4.4% and 32.6% higher than that of the as-welded joint, and the fracture morphology exhibits quasi-cleavage fracture characteristics.
- (3)
- The hardness of the solution-treated sample in the weld zone decreased compared with that in the as-welded joint, while the hardness of the welded joint followed by cryogenic treatment or solution + cryogenic treatment was greatly improved, and was significantly higher than that of the as-welded joint.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Xiong, X.M.; Chen, J.; Peng, X.; Chen, D.; Pan, F. Research advances in magnesium and magnesium alloys worldwide in 2020. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2021, 9, 705–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.F.; Chen, J.; Xiong, X.M.; Peng, X.; Chen, D.; Pan, F. Research advances of magnesium and magnesium alloys worldwide in 2021. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2022, 10, 863–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Jiang, X.S.; Sun, H.L.; Fang, Y.; Mo, D.; Li, X.; Shu, R. Effect mechanism of cryogenic treatment on ferroalloy and nonferrous alloy and their weldments: A review. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Zhang, L.J.; Yin, X.Q.; Zhang, J.X.; Na, S.-J. Mechanism study on the effects of power modulation on energy coupling efficiency in infrared laser welding of highly-reflective materials. Mater. Des. 2019, 178, 107871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.X.; Zheng, Z.B.; Yang, H.K.; Long, J.; Han, P.X. Recent progress in microstructural evolution, mechanical and corrosion properties of medium-Mn steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2023, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitschel, R.; Kolpak, F.; Hering, O.; Tekkaya, A.E. Increasing the lightweight potential of composite cold forging by utilizing magnesium and granular cores. Metals 2020, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, J.; Al-Samman, T. Superior light metals by texture engineering: Optimized aluminum and magnesium alloys for automotive applications. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 818–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qiao, Y.X.; Zhang, L.M.; Ma, A.L.; Daniel, E.F.; Ma, R.Y.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Y.G. Effect of cavitation erosion induced surface damage on pitting and passive behaviors of 304L stainless steel. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2023, 30, 1338–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, E.F.; Mostyaev, I.V.; Anikina, M.V. Nature of High-Temperature Strength of Deformed Magnesium Alloy of the Mg-Zn-Zr- REE System. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2021, 63, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Q.; Li, F.; Wu, Z.S.; Lyu, W. Effect of heat input on the microstructure and mechanical properties of an electron-beam-welded AZ31 magnesium alloy. Mater. Technol. 2020, 54, 819–828. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.J.; Wu, J.; Mao, C.; Cheng, B.; Shakhawat, H.M.D.; Li, H.; Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Bi, Z. Impact of power modulation on weld appearance and mechanical properties during laser welding of AZ31B magnesium alloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 156, 108490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.Z.; Dong, H.; Cai, Y.; Gao, M. Effects of laser power modulation on keyhole behavior and energy absorptivity for laser welding of magnesium alloy AZ31. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 125, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.K.; Hao, K.D.; Xu, L.Y.; Han, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ren, W.; Jing, H. CNTs distribution and ductility improvement mechanisms in oscillating laser-arc hybrid welding of AZ31B magnesium alloy. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 164, 107280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Bian, S.W.; Zhao, P.F.; Ding, X.; Li, Y.; Cao, Z. Investigation on pore formation in pulsed laser spot welding of AZ31 magnesium alloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 149, 107894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, P.F. Investigation on solidification cracks in pulsed laser spot welding of an AZ31 magnesium alloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 126, 106132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorgente, D.; Palumbo, G.; Scintilla, L.D.; Tricarico, L. Evaluation of the Strain Behaviour of Butt Joints on AZ31 Magnesium Alloy Thin Sheets Welded by Nd: YAG Laser. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 67, 2753–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qiao, Y.X.; Zhang, L.M.; Li, C.T.; Liu, Z.; Ma, R.Y.; Yang, L.L.; Li, J.Y.; Zheng, Y.G. Effect of cavitation erosion induced surface damage on the corrosion behavior of TA31 titanium alloy. Ultrason Sonochem. 2023, 98, 106498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.L.; Qian, P.; Li, J.Y.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J. Effect of Solution and Aging Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of AZ31B Magnesium Alloy Laser Welded Joint. Phys. Met. Metallog. 2022, 123, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto, S.; Yamamoto, D.; Tomita, T.; Okita, K. Effect of Post Weld Heat Treatment on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of AZ31B Friction Welded Joint. Mater. Trans. 2007, 48, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.B.; Lu, R.P.; Hou, H.; Tian, J.Z.; Zhao, Y.H. Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Alloy Mg-10% Gd-3% Y-0.6% Zr. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2019, 61, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, D.; Chen, Z.H.; Liu, J. Effect of Cryogenic Treatment on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2010, 25, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Le, Q.C.; Cui, J.Z. Effect of rolling-Cryogenic Process on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AZ31 Magnesium alloy Sheets. Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 2010, 31, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wei, J.; Huang, Q.; Ma, L.; Gao, X.; Yue, Z. Effect of Cryogenic Treatment Prior to Rolling on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy. Rare Met. Mat. Eng. 2018, 47, 2942–2948. [Google Scholar]
- Che, B.; Lu, L.W.; Zhang, J.L.; Teng, J.; Chen, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Huang, L.; Wu, Z. Investigation on microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-rolled AZ31 Mg alloy with various cryogenic treatments. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 4557–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y. The influence of cryogenic and heat treatment on the mechanical properties of laser-welded AZ91D. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 86, 2615–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, S.; Xu, C.S.; Zeng, X.S.; Yang, X.J. Effect of cryogenic treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-1.5Zn-0.15Gd magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 588, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Q.; Wu, Z.S.; Cui, C.; Zhao, F.; Gong, X. Effect of Cryogenic Treatment Temperature on Corrosion Resistance of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy CMT Weld Joint. Rare Met. Mat. Eng. 2018, 47, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, Y.J. Effects of heat input on microstructure and tensile properties of laser welded magnesium alloy AZ3. Mater. Charact. 2018, 59, 1491–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Sanjari, M.; Kabir, A.S. Static Recrystallization Characteristic of Low Temperature Rolled AZ31 Magnesium Alloy During Annealing. Mater. Sci. Forum 2015, 828–829, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.M.; Nan, G.J.; Li, H.H.; Zhao, W.F.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, M. Influence of furnace cooling time on precipitation of β-Mg17Al12 phase of AZ91 magnesium alloy. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 884–885, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Sun, Y.; Ding, W. Effects of bismuth and antimony additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ91 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 308, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Finfrock, C. Temperature and Strain Rate Dependence of the Martensitic Transformation and Mechanical Properties in Advanced High Strength Steels. Ph.D. Dissertation, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.F.; Zhai, Q.Y.; Yuan, S. Rapid Solidification Characteristics of AZ91D Magnesium Alloy. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2004, 14, 939–944. [Google Scholar]

| Sample No. | Solution Treatment | Cryogenic Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| A | — | — |
| B | 410 °C—6 h | — |
| C | — | −196 °C—12 h |
| D | 410 °C—6 h | −196 °C—12 h |
| Sample No. | a (Å) | c (Å) | c/a |
|---|---|---|---|
| As-welded | 3.19414 | 5.18870 | 1.624444 |
| Solution-treated | 3.19584 | 5.19012 | 1.624024 |
| Cryogenic-treated | 3.19547 | 5.17912 | 1.620769 |
| Solution + cryogenic-treated | 3.19348 | 5.18851 | 1.624720 |
| Sample No. | Characteristic Points | Mg | Al | Zn | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | A1 (White spherical particles) | 95.38 | 3.65 | 0.91 | 0.06 |
| A2 (α-Mg matrix) | 89.13 | 7.24 | 2.92 | 0.71 | |
| B | B1 (α-Mg matrix) | 94.34 | 4.62 | 0.95 | 0.09 |
| B2 (White dot particles) | 92.17 | 7.04 | 0.59 | 1.20 | |
| C | C1 (α-Mg matrix) | 95.95 | 3.16 | 0.64 | 0.24 |
| C2 (Lamellar precipitation) | 85.65 | 13.43 | 0.48 | 0.44 | |
| D | D1 (α-Mg matrix) | 96.85 | 1.90 | 1.05 | 0.20 |
| D2 (White dot particles) | 89.56 | 5.31 | 0.77 | 4.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Qian, P.; Qiao, Y.; Yin, W.; Jiang, Z.; Li, J. The Influence of Heat and Cryogenic Treatment on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Laser-Welded AZ31B. Materials 2023, 16, 4764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16134764
Xu Y, Qian P, Qiao Y, Yin W, Jiang Z, Li J. The Influence of Heat and Cryogenic Treatment on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Laser-Welded AZ31B. Materials. 2023; 16(13):4764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16134764
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yulang, Peng Qian, Yanxin Qiao, Wujia Yin, Zhiwei Jiang, and Jingyong Li. 2023. "The Influence of Heat and Cryogenic Treatment on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Laser-Welded AZ31B" Materials 16, no. 13: 4764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16134764
APA StyleXu, Y., Qian, P., Qiao, Y., Yin, W., Jiang, Z., & Li, J. (2023). The Influence of Heat and Cryogenic Treatment on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Laser-Welded AZ31B. Materials, 16(13), 4764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16134764







