Carbon-Based Textile Sensors for Physiological-Signal Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Carbon-Based Materials Used in Textile Sensors
2.1. Graphene
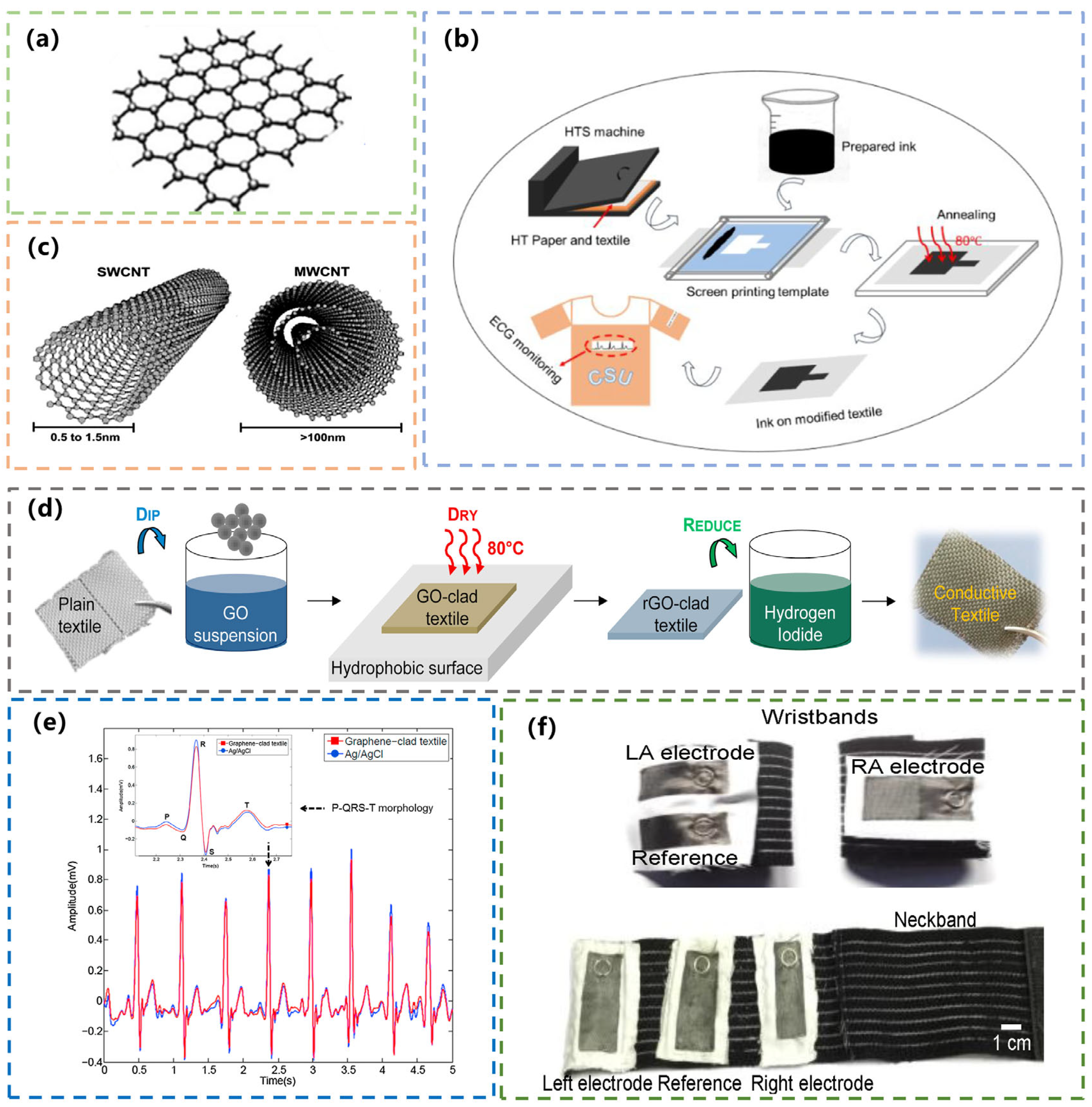
2.2. CNT
2.3. CB
3. Carbon-Based Textile Sensors for Different Physiological-Signal Monitoring
3.1. Carbon-Based ECG Textile Electrodes/Sensors
3.1.1. Graphene-Based ECG Textile Electrodes/Sensors
3.1.2. CNT/CB-Based Textile Electrodes/Sensors for ECG Monitoring
3.2. Carbon-Based Textile Sensors for Body Motion Monitoring
3.2.1. Graphene-Based Textile Sensors for Body Motion Monitoring
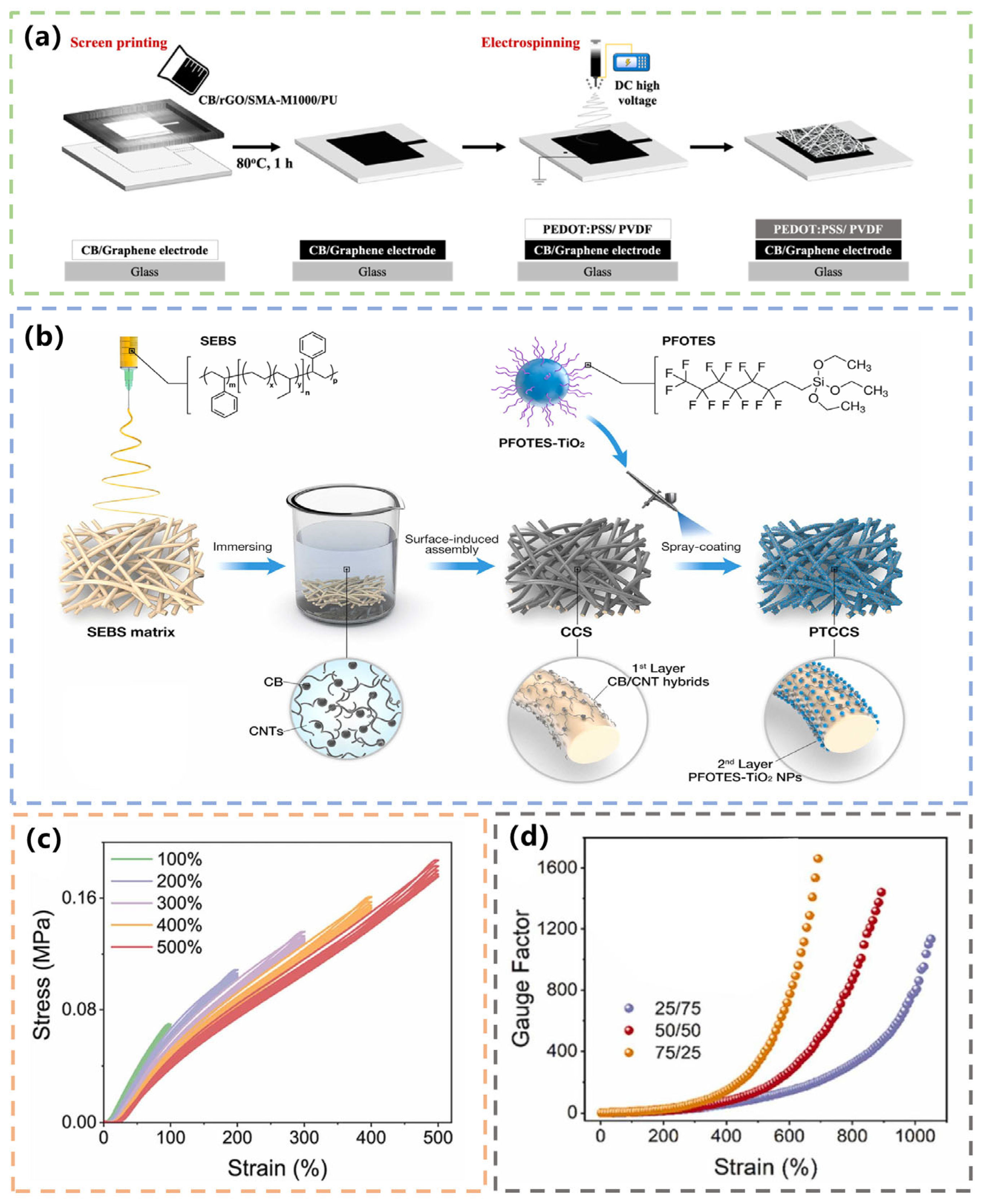

3.2.2. CNT-Based Textile Sensors for Body Motion Monitoring
3.2.3. CB-Based Textile Sensors for Body Motion Monitoring
3.2.4. Graphene/CNT-Based Textile Sensors for Body Motion Monitoring
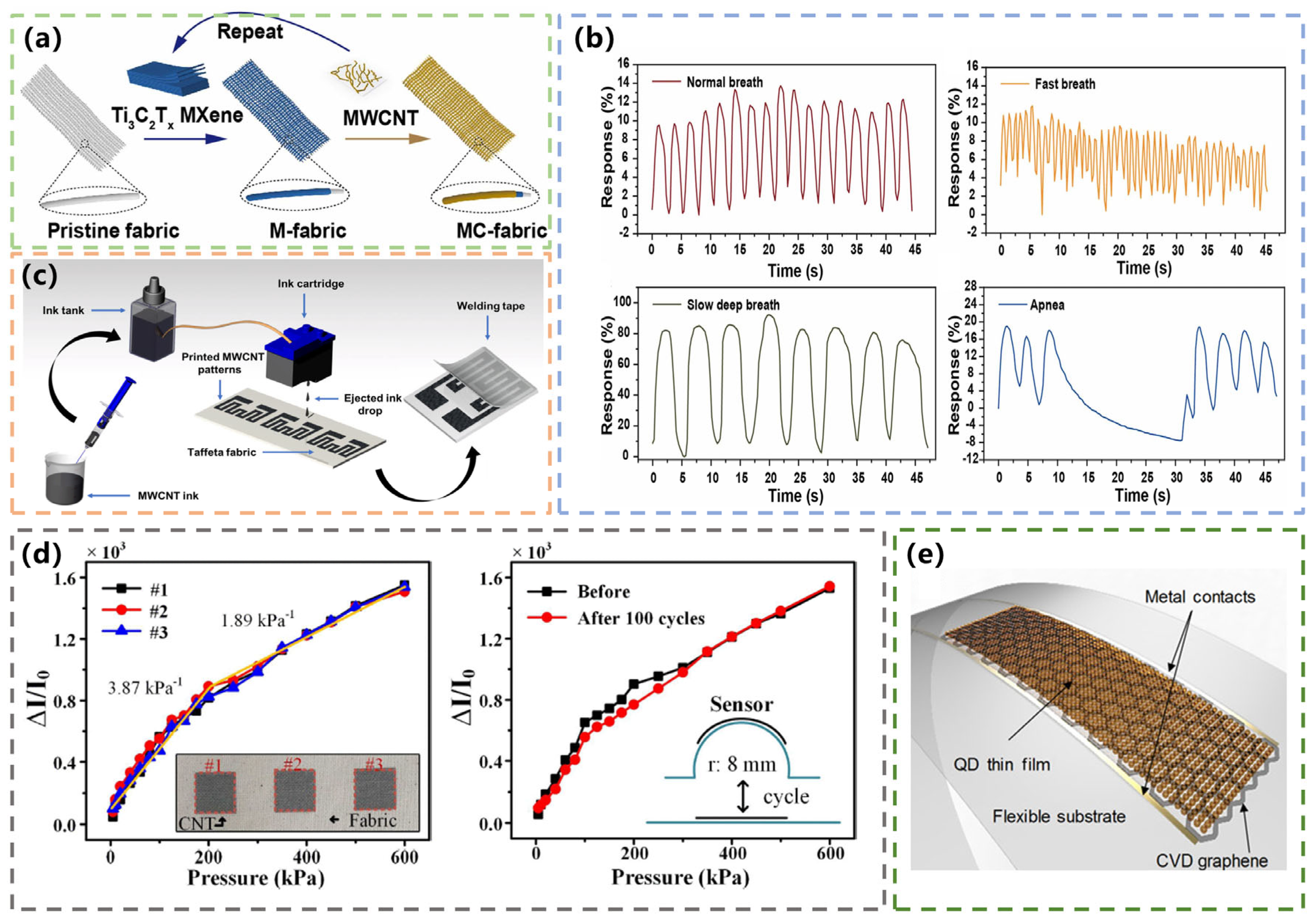
3.3. Carbon-Based Humidity Textile Sensors for Respiration Monitoring
3.4. Carbon-Based Textile Sensors for Body Temperature Monitoring
3.5. Carbon-Based Tactile Textile Sensors
3.6. Carbon-Based HR and SpO2 Sensors
4. Discussion and Outlook
4.1. Smart Textile Sensing System for Physiological-Signal Monitoring
4.2. Interconnection of Textile Sensors
4.3. Problems of Textile Sensors in Practical Application
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, G.; Chen, A.; Wang, R.; Sun, J. Research Progress of Wearable Sensors for Human Health Monitoring. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2022, 50, 1673–1684. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Li, J.; Xiao, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, K.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J.; et al. Topographic design in wearable MXene sensors with in-sensor machine learning for full-body avatar reconstruction. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Yang, A.; Li, L. Optimization of Nanofiber Wearable Heart Rate Sensor Module for Human Motion Detection. Comput. Math. Method Med. 2022, 2022, 1747822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, H.; Bhatia, K.; Jain, A.; Verma, N. IOT Based Health Monitoring System. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES), Coimbatre, India, 8–10 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Zha, L.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. Fully integrated wearable humidity sensor for respiration monitoring. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1070855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, H.; Wahab, M.A.; Will, G.; Karim, M.R.; Pan, T.; Gao, M.; Lai, D.; Lin, Y.; Miraz, M.H. Recent advances in stretchable and wearable capacitive electrophysiological sensors for long-term health monitoring. Biosensors 2022, 12, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Abidian, M.R.; Ahn, J.H.; Akinwande, D.; Andrews, A.M.; Antonietti, M.; Bao, Z.; Berggren, M.; Barkey, C.A.; Bettinger, C.J.; et al. Technology roadmap for flexible sensors. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 5211–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazoum, B.; Batoo, K.M.; Khan, M.A.A. Recent advances in flexible sensors and their applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cun, Q.; Miao, H.; Lu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Chen, S. The progress of textile-based sensor. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Optoelectronic Materials and Devices (ICOMD 2021), Guangzhou, China, 16–18 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Fu, X.; He, J.; Shi, X.; Chen, T.; Chen, P.; Wang, B.; Peng, H. Application Challenges in Fiber and Textile Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1901971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.M.; Liu, S.; Yang, B.; Zhang, L.S.; Ma, M.; Shu, L.; Wang, F. Recent advances, scientific issues, key technologies and perspective of textile electronics. Chin. Sci. Bull.-Chin. 2021, 66, 3071–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Chan, K.; Hua, T.; Niu, B.; Chen, S. Wearable strain sensors enabled by integrating one-dimensional polydopamine-enhanced graphene/polyurethane sensing fibers into textile structures. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 17266–17283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiaghadi, A.; Baima, M.; Gummeson, J.; Andrew, T.; Ganesan, D. Fabric as a sensor: Towards unobtrusive sensing of human behavior with triboelectric textiles. In Proceedings of the 16th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Shenzhen, China, 4–7 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, X.Y.; Leung, M.Y.; Tsang, J.; Tao, X.M.; Yuen, M.C.W. A flexible strain sensor from polypyrrole-coated fabrics. Synth. Met. 2005, 155, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedin, M.Z.; Razal, J.M.; Innis, P.C.; Wallace, G.G. Strain-responsive polyurethane/PEDOT: PSS elastomeric composite fibers with high electrical conductivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2957–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xiao, X.; Hu, J.; Hu, J.; Dong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, R.; Wang, X.; Islam, J. Recent advances of carbon-based flexible strain sensors in physiological signal monitoring. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2020, 2, 2282–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, Y. A review of wearable carbon-based sensors for strain detection: Fabrication methods, properties, and mechanisms. Text. Res. J. 2023, 93, 2918–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.S.; Hossain, M.F.; Kim, I. Challenges in Design and Fabrication of Flexible/Stretchable Carbon- and Textile-Based Wearable Sensors for Health Monitoring: A Critical Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xia, K.; Wang, H.; Liang, X.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Y. Advanced Carbon for Flexible and Wearable Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1801072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Tang, Z.; Ouyang, J. Highly washable e-textile prepared by ultrasonic nanosoldering of carbon nanotubes onto polymer fibers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gspann, T.S.; Juckes, S.M.; Niven, J.F.; Johnson, M.B.; Elliott, J.A.; White, M.A.; Windle, A.H. High thermal conductivities of carbon nanotube films and micro-fibres and their dependence on morphology. Carbon 2017, 114, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, J.; Hwang, H.; Jeong, S.-H. Highly stretchable and sensitive strain sensors based on single-walled carbon nanotube-coated nylon textile. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, R.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, L.; Shi, D.; Wang, E.; Zhang, G. Super-elastic graphene ripples for flexible strain sensors. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3645–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, G. High-performance strain sensors with fish-scale-like graphene-sensing layers for full-range detection of human motions. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7901–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Faruque, M.A.; Syduzzaman, M.; Sarkar, J.; Bilisik, K.; Naebe, M. A review on the production methods and applications of graphene-based materials. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Luo, M.; He, P.; Yang, J. Washable and flexible screen printed graphene electrode on textiles for wearable healthcare monitoring. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 125402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, T.; Kim, K.; Jung, M.; Bae, J.; Jeon, S. Wearable pressure sensor based on solution-coated fabric for pulse detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems (FLEPS), Vienna, Austria, 10–13 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, B.M.; Shin, H.J.; Yoon, H.W.; Park, H.B. Graphene and graphene oxide and their uses in barrier polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 39628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, B.; Botelho, E.C.; Costa, M.L.; Bandeira, C.F. Carbon nanotube buckypaper reinforced polymer composites: A review. Polimeros 2017, 27, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapici, M.K.; Alkhidir, T.; Samad, Y.A.; Liao, K. Graphene-clad textile electrodes for electrocardiogram monitoring. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2015, 221, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapici, M.K.; Alkhidir, T.E. Intelligent Medical Garments with Graphene-Functionalized Smart-Cloth ECG Sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, P.M.; Katzman, H.A.; Rellick, G.S.; Stupian, G.W. Characterization of high thermal conductivity carbon fibers and a self-reinforced graphite panel. Carbon 1998, 36, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, E.; Aubry, C.; Campagne, C.; Rochery, M.; Ensait, F. PLA/carbon nanotubes multifilament yarns for relative humidity textile sensor. J. Eng. Fiber Fabr. 2011, 6, 1558–9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, M.; Gandhi, B. CNT-based electrodes (wearable & textile-based) for cardiac monitoring in long-term & continuous fashion. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Material Science, Smart Structures and Applications (ICMSS), Erode, India, 21–22 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.M.; Lubna, M.M.; Bradford, P.D. Multifunctional and Washable Carbon Nanotube-Wrapped Textile Yarns for Wearable E-Textiles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 1944–8244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arduini, F.; Cinti, S.; Mazzaracchio, V.; Scognamiglio, V.; Amine, A.; Moscone, D. Carbon black as an outstanding and affordable nanomaterial for electrochemical (bio) sensor design. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 156, 112033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnykowycz, M.; Tschudin, M.; Clemens, F. Piezoresistive Soft Condensed Matter Sensor for Body-Mounted Vital Function Applications. Sensors 2016, 16, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J. Fabricate Graphenne-based Textile Sensors and Their Applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 Sustainability Innovation & Fashion Technology International Conference, Shanghai, China, 15–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Castano, L.M.; Flatau, A.B. Smart fabric sensors and e-textile technologies: A review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 053001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windmiller, J.R.; Wang, J. Wearable electrochemical sensors and biosensors: A review. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.-R.; Li, D.; Huang, X.-R.; Yan, A.-Z.; Dong, Y.; Xu, J.-D.; Guo, Y.-Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.-K.; Shao, W.-C.; et al. Graphene-Based Flexible Electrode for Electrocardiogram Signal Monitoring. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marozas, V.; Petrenas, A.; Daukantas, S.; Lukosevicius, A. A comparison of conductive textile-based and silver/silver chloride gel electrodes in exercise electrocardiogram recordings. J. Electrocardiol. 2011, 44, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrhop, S.; Lamparth, S.; Heuer, S. A textile integrated long-term ECG monitor with capacitively coupledelectrodes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), Beijing, China, 26–28 November 2009; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Samad, Y.A.; Li, Y.; Alhassan, S.M.; Liao, K. Non-destroyable graphene cladding on a range of textile and other fibers and fiber mats. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 16935–16938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, N.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, D.; Wu, Z.; Li, B.; Sun, C.; Guo, Z. Emerging flexible sensors based on nanomaterials: Recent status and applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 25499–25527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langner, M.; Greiner, A. Wet-Laid Meets Electrospinning: Nonwovens for Filtration Applications from Short Electrospun Polymer Nanofiber Dispersions. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2016, 37, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Chiu, C.-W. Facile Fabrication of a Stretchable and Flexible Nanofiber Carbon Film-Sensing Electrode by Electrospinning and Its Application in Smart Clothing for ECG and EMG Monitoring. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zou, G.; Doorn, S.K.; Htoon, H.; Stan, L.; Hawley, M.E.; Sheehan, C.J.; Zhu, Y.; Jia, Q. Tailoring the morphology of carbon nanotube arrays: From spinnable forests to undulating foams. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 2157–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Lee, P.; Chou, J.B.; Xu, R.; Zhao, R.; Hart, A.J.; Kim, S.J. Extremely elastic wearable carbon nanotube fiber strain sensor for monitoring of human motion. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5929–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wang, D.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lai, F.; He, G.; Ma, P.; Dong, W.; Huang, Y.; Parkin, I.P.; et al. Ultra-stretchable and superhydrophobic textile-based bioelectrodes for robust self-cleaning and personal health monitoring. Nano Energy 2022, 97, 107160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.; Hong, S.K.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, S.J.; Lim, G. Omni-purpose stretchable strain sensor based on a highly dense nanocracking structure for whole-body motion monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 41712–41721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.-Y.; Wang, P. Textile-Based Flexible Pressure Sensors: A Review. Polym. Rev. 2021, 62, 65–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Wu, Y.; Tang, J.; Pan, Z.-J. Highly sensitive strain sensor with wide strain range fabricated using carbonized natural wrapping yarns. Mater. Res. Bull. 2021, 143, 111452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Cheng, D.; Ran, J.; Li, D.; He, C.; Bi, S.; Cai, G.; Wang, X. Recent advances on the fabrication methods of nanocomposite yarn-based strain sensor. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2021, 10, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnamma, D.; Guo, Q.; Krupa, I.; Al-Maadeed, M.A.S.A.; Varughese, K.T.; Thomas, S.; Sadasivuni, K.K. Graphene and graphitic derivative filled polymer compositesas potential sensors. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 3954–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S. Properties of wool/spandex core-spun yarn produced on modified woolen spinning frame. Fiber. Polym. 2006, 7, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hua, T.; Xu, B. Electromechanical properties of a yarn strain sensor with graphene-sheath/polyurethane-core. Carbon 2017, 118, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, P. Highly flexible fabric strain sensor based on graphene nanoplatelet-polyaniline nanocomposites for human gesture recognition. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; He, P.; Wang, R.; Yang, S.; Sun, J.; Xie, X.; Ding, G. Porous Fibers Composed of Polymer Nanoball Decorated Graphene for Wearable and Highly Sensitive Strain Sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, N.; Gao, Y.; Wang, S.; Cheng, Q.; Xu, F. Strain sensing fabric integrated with carbon nanotube yarn for wearable applications. Text. Res. J. 2018, 89, 3048–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, S.M.; Murray, C.; Chaudhari, A.; Thonstenson, E.T. Carbon nanotube coated textile sensors with ultrahigh sensitivity for human motion detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Sensors, Montreal, QC, Canada, 27–30 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Ou, K.; Dai, Y.; You, X.; Wang, H.; He, J.; Qin, X.; Wang, R. Weavable and stretchable piezoresistive carbon nanotubes-embedded nanofiber sensing yarns for highly sensitive and multimodal wearable textile sensor. Carbon 2020, 170, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedin, S.; Zhang, P.; Naebe, M.; Qin, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Razal, J.M. Textile strain sensors: A review of the fabrication technologies, performance evaluation and applications. Mater. Horizons 2019, 6, 219–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, N.; Zhang, J.; Ding, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Chen, S.-C.; Hu, J.-L.; Zhao, N. Textile-Enabled Highly Reproducible Flexible Pressure Sensors for Cardiovascular Monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1700222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Choi, H.; Cho, Y.; Jeong, J.; Sun, J.; Cha, S.; Choi, M.; Bae, J.; Park, J.J. Wearable Strain Sensors with Aligned Macro Carbon Cracks Using a Two-Dimensional Triaxial-Braided Fabric Structure for Monitoring Human Health. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 22926–22934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Yao, D.; Du, D.; Ouyang, J. Highly machine-washable e-textiles with high strain sensitivity and high thermal conduction. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 2741–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Du, D.; Ouyang, J. Gas-permeable and highly sensitive, washable and wearable strain sensors based on graphene/carbon nanotubes hybrids e-textile. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 149, 106556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, X.; He, B. Flexible and self-adhesive strain sensor based on GNSs/MWCNTs coated stretchable fabric for gesture monitoring and recognition. Sens. Actuator A-Phys. 2023, 349, 114004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aakyiir, M.; Oh, J.-A.; Araby, S.; Zheng, Q.; Naeem, M.; Ma, J.; Adu, P.; Zhang, L.; Mai, Y.-W. Combining hydrophilic MXene nanosheets and hydrophobic carbon nanotubes for mechanically resilient and electrically conductive elastomer nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 214, 108997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Y.; He, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Q.; Han, R.P.S. MXene/MWCNT electronic fabric with enhanced mechanical robustness on humidity sensing for real-time respiration monitoring. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2022, 361, 131704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzubasoglu, B.A.; Sayar, E.; Cochrane, C.; Koncar, V.; Bahadir, S.K. Wearable temperature sensor for human body temperature detection. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 4784–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekertekin, Y.; Bozyel, I.; Gokcen, D. A flexible and low-cost tactile sensor produced by screen printing of carbon black/PVA composite on cellulose paper. Sensors 2020, 20, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Zhao, S.; Su, E.; Li, Y.; Wu, F. Trilayer MXene Fabric for Integrated Ultrasensitive Pressure Sensor and Wearable Heater. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2100574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, K.; Kang, Y.; Jo, E.; Sim, S.; Yang, W.; Kim, J. Washable, Inkjet-Printed Flexible Tactile Sensor on Fabric with Temperature Tolerance. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 35th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems Conference (MEMS), Tokyo, Japan, 9–13 January 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, D.; Simões-Capela, N.; Van, H.C.; Helleputte, N.V. Heart rate estimation from wrist-worn photoplethysmography: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 6560–6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T. Current progress of photoplethysmography and SPO2 for health monitoring. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2019, 9, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, E.O.; Mercier, G.; Nikitskiy, I.; Puma, E.; Galan, T.; Gupta, S.; Montagut, M.; Piqeras, J.J.; Bouwens, M.; Durduran, T.; et al. Flexible graphene photodetectors for wearable fitness monitoring. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw7846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Solino, C.; Bernalte, E.; Metcalfe, B.; Moschou, D.; Lorenzo, M.D. Power generation and autonomous glucose detection with an integrated array of abiotic fuel cells on a printed circuit board. J. Power Sources 2020, 472, 228530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, G.; Regoutz, A.; Moschou, D. Enzyme-assisted glucose quantification for a painless Lab-on-PCB patch implementation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 167, 112484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
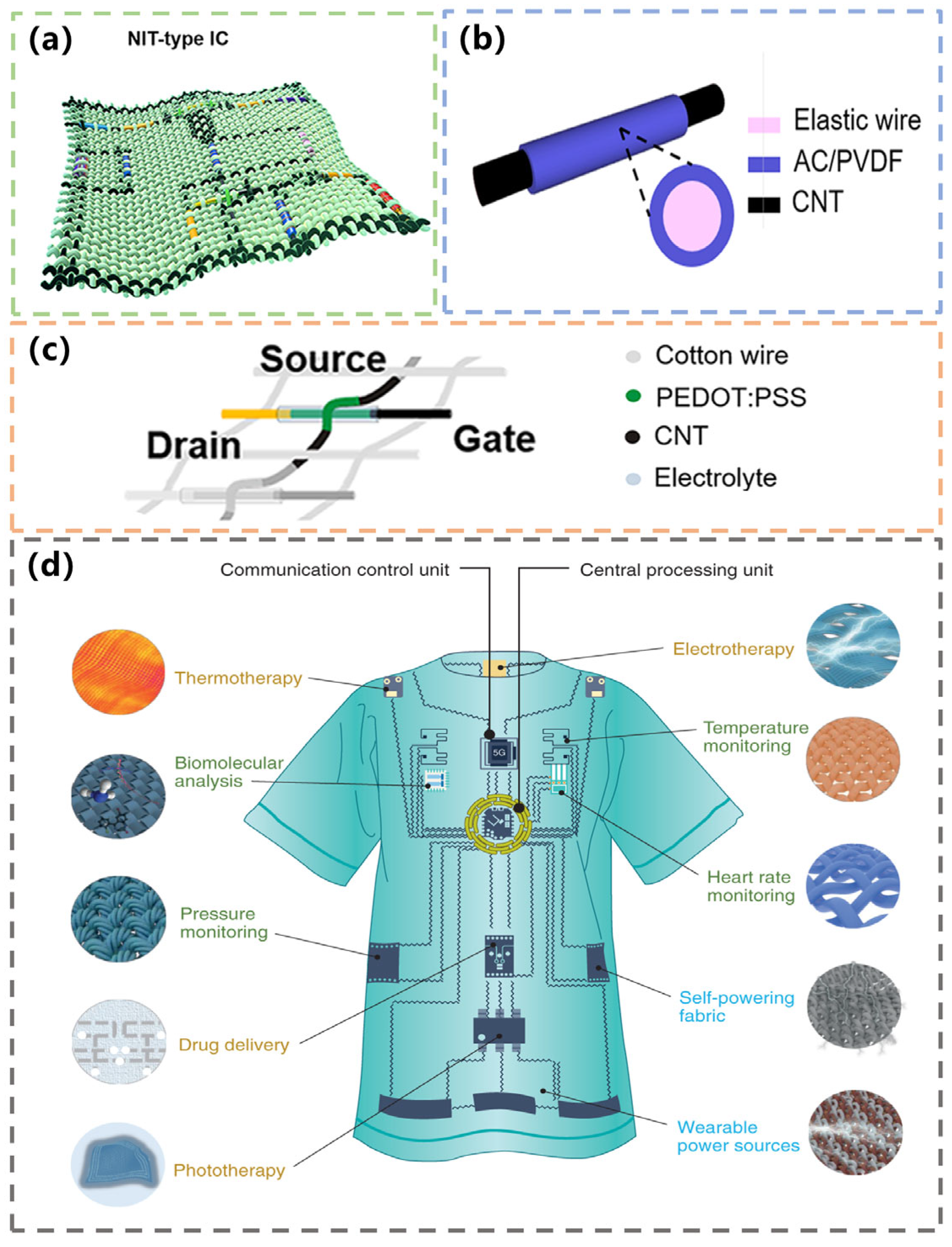
- Yang, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhang, N.; Zheng, J.; Chen, X.; Wen, Q.; Luo, X.; Lee, C.Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. A non-printed integrated-circuit textile for wireless theranostics. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libanori, A.; Chen, G.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J. Smart textiles for personalized healthcare. Nat. Electron. 2022, 5, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoane, F.; Soroudi, A.; Lu, K.; Nilsson, D.; Nilsson, M.; Abtahi, F.; Skrifvars, M. Textile-Friendly Interconnection between Wearable Measurement Instrumentation and Sensorized Garments-Initial Performance Evaluation for Electrocardiogram Recordings. Sensors 2019, 19, 4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Chu, X.; Kong, L.; Yan, X.; Kuang, M. Printing of Carbon Nanotube-Based Temperature and Bending Sensors for High-Temperature-Resistant Intelligent Textiles. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 1949–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Zhu, C.; Wan, J.; Li, Y.; Hong, X. Review of Graphene-Based Textile Strain Sensors, with Emphasis on Structure Activity Relationship. Polymers 2021, 13, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
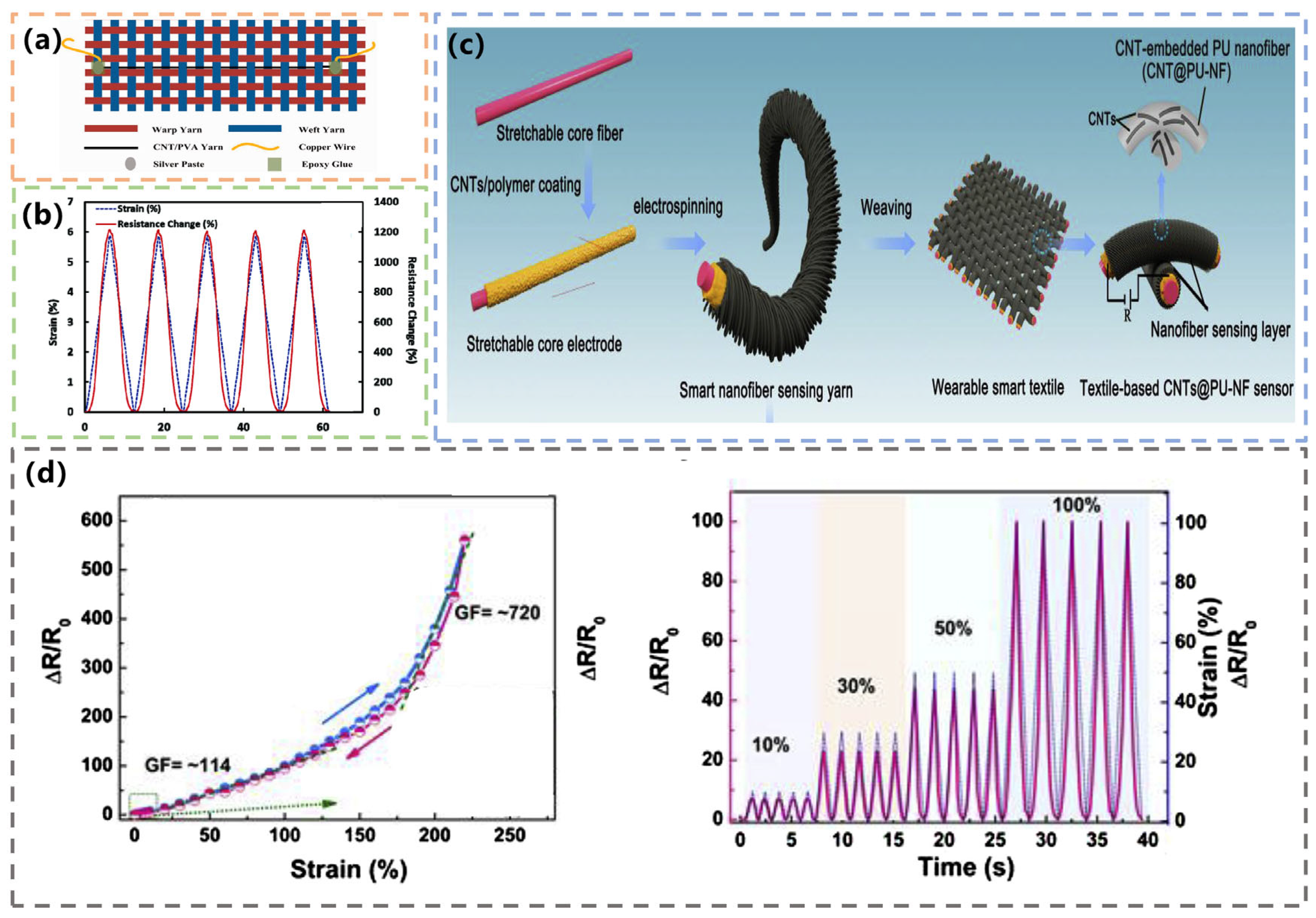

| Physiological Signals | Carbon-Based Materials | Textile | Manufacturing Method | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECG | rGO [44,45] | Nylon | Dipping | Cost-effective |
| rGO, CB [32] | PU | Electrospinning | Good skin contact | |
| CNTs, CB [49] | Nonwoven | Dipping | Anti-fouling | |
| Human motions [56] | Graphene | PU | Dip-coating | Sensing yarn, high sensitivity |
| Motion detection of figures [57] | GNPs | Lycra | Spin-coating | Excellent strain-resistance |
| Pulse, motions [58] | Graphene fibers | PVDF, PU | / | High GF, fast response time |
| Motion detection of figures [59] | CNTs | PVA yarn | Coating | Excellent stability |
| Human motions [60] | CNTs | Nylon–polyester- –spandex fabrics | Electrophoretic deposition | High comfortability |
| Human motions [61] | CNTs | PU | Electrospinning | High-pressure sensitivity, broad sensing range |
| Pulse [63] | CB | Nylon | / | High sensor repeatability |
| Human motions, biosignals [64] | CB | Fabric | Two-dimensional triaxial-braided weaving, dip coating | good stability and durability, environment-friendly |
| Human motions, pulse [65] | rGO, CNTs | Nonwoven | Nano-soldering | High sensitivity |
| Human motions [66] | rGO, CNTs | Nonwoven | Nano-soldering | High sensitivity, good washability and durability |
| Motion detection of figures [67] | GNSs, MWCNTs | Cloth | Screen-printing | Cost-effective, good stability |
| Respiration [69] | MWCNTs | Fabric | / | Improved humidity response and favorable response stability |
| Body temperature [70] | MWCNTs | Taffeta fabric | Inkjet printing | Negative temperature coefficient characteristic |
| Tactile perception [73] | CNTs | Cotton | Inkjet printing | High sensitivity, wide pressure- sensing range |
| HR and SpO2 [76] | Graphene | / | / | Long-term monitoring |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, W.; Cui, T.; Li, D.; Jian, J.; Li, Z.; Ji, S.; Cheng, A.; Li, X.; Liu, K.; Liu, H.; et al. Carbon-Based Textile Sensors for Physiological-Signal Monitoring. Materials 2023, 16, 3932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16113932
Shao W, Cui T, Li D, Jian J, Li Z, Ji S, Cheng A, Li X, Liu K, Liu H, et al. Carbon-Based Textile Sensors for Physiological-Signal Monitoring. Materials. 2023; 16(11):3932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16113932
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Wancheng, Tianrui Cui, Ding Li, Jinming Jian, Zhen Li, Shourui Ji, Aobo Cheng, Xinyue Li, Kaiyin Liu, Houfang Liu, and et al. 2023. "Carbon-Based Textile Sensors for Physiological-Signal Monitoring" Materials 16, no. 11: 3932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16113932
APA StyleShao, W., Cui, T., Li, D., Jian, J., Li, Z., Ji, S., Cheng, A., Li, X., Liu, K., Liu, H., Yang, Y., & Ren, T. (2023). Carbon-Based Textile Sensors for Physiological-Signal Monitoring. Materials, 16(11), 3932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16113932






