Anharmonicity of Plasmons in Metallic Nanostructures Useful for Metallization of Solar Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Microscopic Description of Plasmons in a Metallic Nanoparticle
2.1. Excitation of Surface Plasmons
2.2. Dipole-Type Surface Plasmon
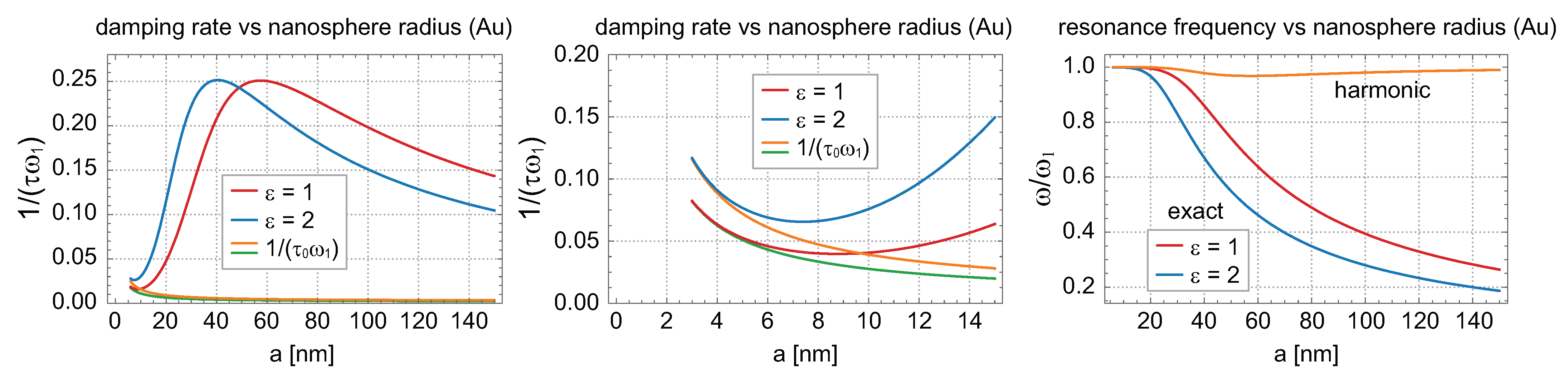
3. Anharmonicity of Dipole Surface Plasmons
4. Anharmonicity for Plasmon-Polaritons
5. Anharmonicity of Plasmons in Metallic Nanoparticles If They Are Coupled with Nearby Absorption Medium
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schaadt, D.M.; Feng, B.; Yu, E.T. Enhanced semiconductor optical absorption via surface plasmon excitation in metal nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 063106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Mar, W.; Matheu, P.; Derkacs, D.; Yu, E. Photocurrent spectroscopy of optical absorption enhancement in silicon photodiodes via scattering from surface plasmon polaritons in gold nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 104309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, M.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Chang, L.; Ao, J.; Sun, Y.; Popko, E.; Jacak, W.; Chow, L. Improving Efficiency of Multicrystalline Silicon and CIGS Solar Cells by Incorporating Metal Nanoparticles. Materials 2015, 8, 6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheu, P.; Lim, S.; Derkacs, D.; McPheeters, C.; Yu, E. Metal and dielectric nanoparticle scattering for improved optical absorption in photovoltaic devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 113108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losurdo, M.; Giangregorio, M.M.; Bianco, G.V.; Sacchetti, A.; Capezzuto, P.; Bruno, G. Enhanced absorption in Au nanoparticles/a-Si:H/c-Si heterojunction solar cells exploiting Au surface plasmon resonance. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2009, 93, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Xie, C.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y.; Wu, C.; Hu, H.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, X.; Jie, J. Surface plasmon resonance enhanced highly efficient planar silicon solar cell. Nano Energy 2014, 9, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, S.; Catchpole, K.; Trupke, T.; Green, M. Surface plasmon enhanced silicon solar cells. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 093105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, H.R.; Hall, D.G. Island size effect in nanoparticles photodetectors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 73, 3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, S.; Catchpole, K.R.; Trupke, T.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, J.; Green, M.A. Enhanced emission from Si-based light-emitting diodes using surface plasmons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 161102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacak, W.; Popko, E.; Henrykowski, A.; Zielony, E.; Luka, G.; Pietruszka, R.; Witkowski, B.; Wachnicki, L.; Godlewski, M.; Chang, L.B.; et al. On the size dependence and the spatial range for the plasmon effect in photovoltaic efficiency enhancement. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 147, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shockley, W.; Queisser, H.J. Detailed Balance Limit of Efficiency of p-n Junction Solar Cells. J. Appl. Phys. 1961, 32, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacak, W.A. Quantum Nano-Plasmonics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Saliba, M.; Stranks, S.; Sun, Y.; Shi, X.; Wiesner, U.; Snaith, H. Enhancement of perovskite-based solar cells employing core-shell metal nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.; Zhong, H.; Liu, Z.; Xiong, M.; Leng, S.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, L.; Huang, H.; et al. Plasmonic Metal Nanoparticles with Core-Bishell Structure for High-Performance Organic and Perovskite Solar Cells. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Yang, B.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhou, C.; Hao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yang, J. Prominent Efficiency Enhancement in Perovskite Solar Cells Employing Silica-Coated Gold Nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laska, M.; Krzemińska, Z.; Kluczyk-Korch, K.; Schaadt, D.; Popko, E.; Jacak, W.; Jacak, J. Metallization of solar cells, exciton channel of plasmon photovoltaic effect in perovskite cells. Nano Energy 2020, 75, 104751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacak, J.E.; Jacak, W.A. Routes for Metallization of Perovskite Solar Cells. Materials 2022, 15, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.D. Classical Electrodynamics; John Willey and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. Field Theory; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Kluczyk, K.; David, C.; Jacak, J.; Jacak, W. On Modeling of Plasmon-Induced Enhancement of the Efficiency of Solar Cells Modified by Metallic Nano-Particles. Nanomaterials 2018, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohren, C.F.; Huffman, D.R. Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mie, G. Beiträge zur Optik trüber Medien, speziell kolloidaler Metallösungen. Ann. Phys. 1908, 330, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gans, R. Über die form ultramikroskopischer goldteilchen. Ann. Phys. 1912, 342, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, M.; Kreibig, U. Optical Properties of Metal Clusters; Springer Series in Materials Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; Volume 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolwas, K.; Derkachova, A. Damping rates of surface plasmons for particles of size from nano-to micrometers; reduction of the nonradiative decay. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2013, 114, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, S.; El-Sayed, M.A. Size and Temperature Dependence of the Plasmon Absorption of Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sönnichsen, C.; Franzl, T.; Wilk, T.; von Plessen, G.; Feldmann, J. Plasmon resonances in large noble-metal clusters. New J. Phys. 2002, 4, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pines, D. Elementary Excitations in Solids; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacak, J.; Krasnyj, J.; Jacak, W.; Gonczarek, R.; Chepok, A.; Jacak, L. Surface and volume plasmons in metallic nanospheres in semiclassical RPA-type approach; near-field coupling of surface plasmons with semiconductor substrate. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 035418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pines, D.; Bohm, D. A Collective Description of Electron Interactions: II. Collective vs Individual Particle Aspects of the Interactions. Phys. Rev. 1952, 85, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitarke, J.M.; Silkin, V.M.; Chulkov, E.V.; Echenique, P.M. Theory of surface plasmons and surface-plasmon polaritons. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2007, 70, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, S.A. Plasmonics: Fundamentals and Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Abajo, F.J.G. Optical excitations in electron microscopy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010, 82, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, S.A.; Kik, P.G.; Atwater, H.A. Optical pulse propagation in metal nanoparticle chain waveguides. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 67, 205402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brongersma, M.L.; Hartman, J.W.; Atwater, H.A. Electromagnetic energy transfer and switching in nanoparticle chain arrays below the diffraction limit. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, R16356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citrin, D.S. Plasmon Polaritons in Finite-Length Metal-Nanoparticle Chains: The Role of Chain Length Unravelled. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradstein, I.S.; Rizik, I.M. Tables of Integrals; Fizmatizdat: Moscow, Russia, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Kiriejew, P.S. Physics of Semiconductors; PWN: Warsaw, Poland, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, W.; Hu, C.; Yeh, C.; Lee, Y. External quantum efficiency and photovoltaic performance of silicon cells deposited with aluminum, indium, and silver nanoparticles. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 55, 08RG03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Material | Au | Ag |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk plasmon energy, | 8.57 eV | 8.56 eV |
| Bulk plasmon frequency, | 1.302 × 1016 s−1 | 1.3 × 1016 s−1 |
| Mie dipole plasmon energy, | 4.94 eV | 4.93 eV |
| Mie frequency, | 0.752× 1016 s−1 | 0.75× 1016 s−1 |
| Constant in Equation (2), C | 1.4 | 1.4 |
| Fermi velocity, | 1.396 × 106 m/s | 1.4 × 106 m/s |
| Bulk mean free path (room temp.), | 53 nm | 57 nm |
| Metal | Size (nm) | Concentration 1/cm2 | Enhancement | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | 50 | 18% | [1] | |
| Au | 100 | % | [4] | |
| Au | 100 | 3.3% | [3] | |
| Au | 100 | % | [2] | |
| Au | ∼20 | 20% | [5] | |
| Au | 65 | 18% | [6] | |
| Ag | 40 | 127% | [8] | |
| Ag | 12 | - | 19% | [7] |
| Al | 40% of surface | 21% | [39] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krzemińska, Z.; Jacak, W.A. Anharmonicity of Plasmons in Metallic Nanostructures Useful for Metallization of Solar Cells. Materials 2023, 16, 3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16103762
Krzemińska Z, Jacak WA. Anharmonicity of Plasmons in Metallic Nanostructures Useful for Metallization of Solar Cells. Materials. 2023; 16(10):3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16103762
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrzemińska, Zofia, and Witold A. Jacak. 2023. "Anharmonicity of Plasmons in Metallic Nanostructures Useful for Metallization of Solar Cells" Materials 16, no. 10: 3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16103762
APA StyleKrzemińska, Z., & Jacak, W. A. (2023). Anharmonicity of Plasmons in Metallic Nanostructures Useful for Metallization of Solar Cells. Materials, 16(10), 3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16103762






