Effects of Micro-Arc Oxidation Discharge Parameters on Formation and Biomedical Properties of Hydroxyapatite-Containing Flower-like Structure Coatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Specimens
2.2. Preparation of Coatings by MAO Process
2.3. Measurement of Surface Roughness and Wettability (Contact Angle)
2.4. In Vitro Bone-like Apatite Inducement Tests
2.5. Initial In Vitro Cell Culture Tests
2.6. Microstructure and Phase Composition
3. Results and Discussion
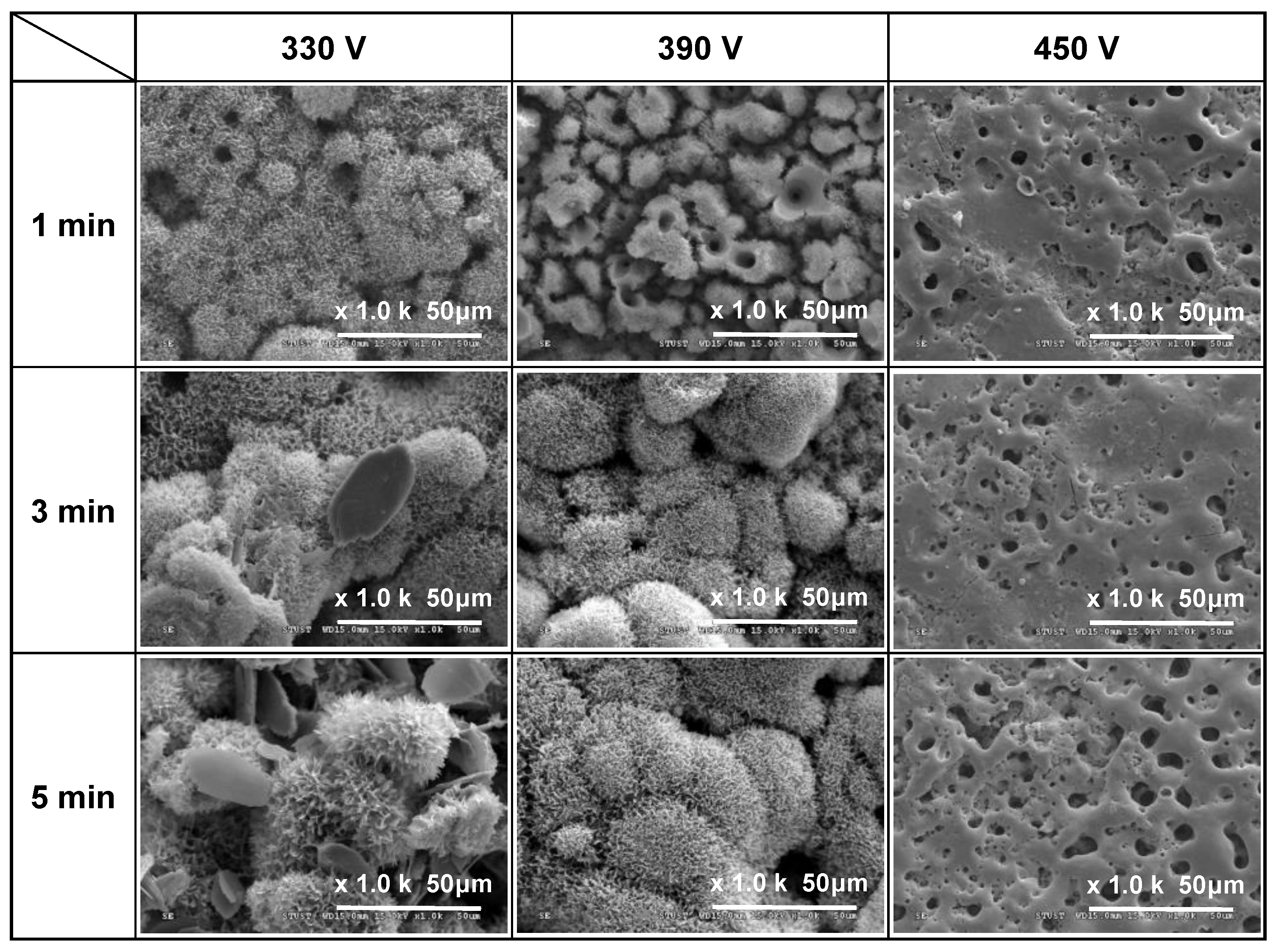
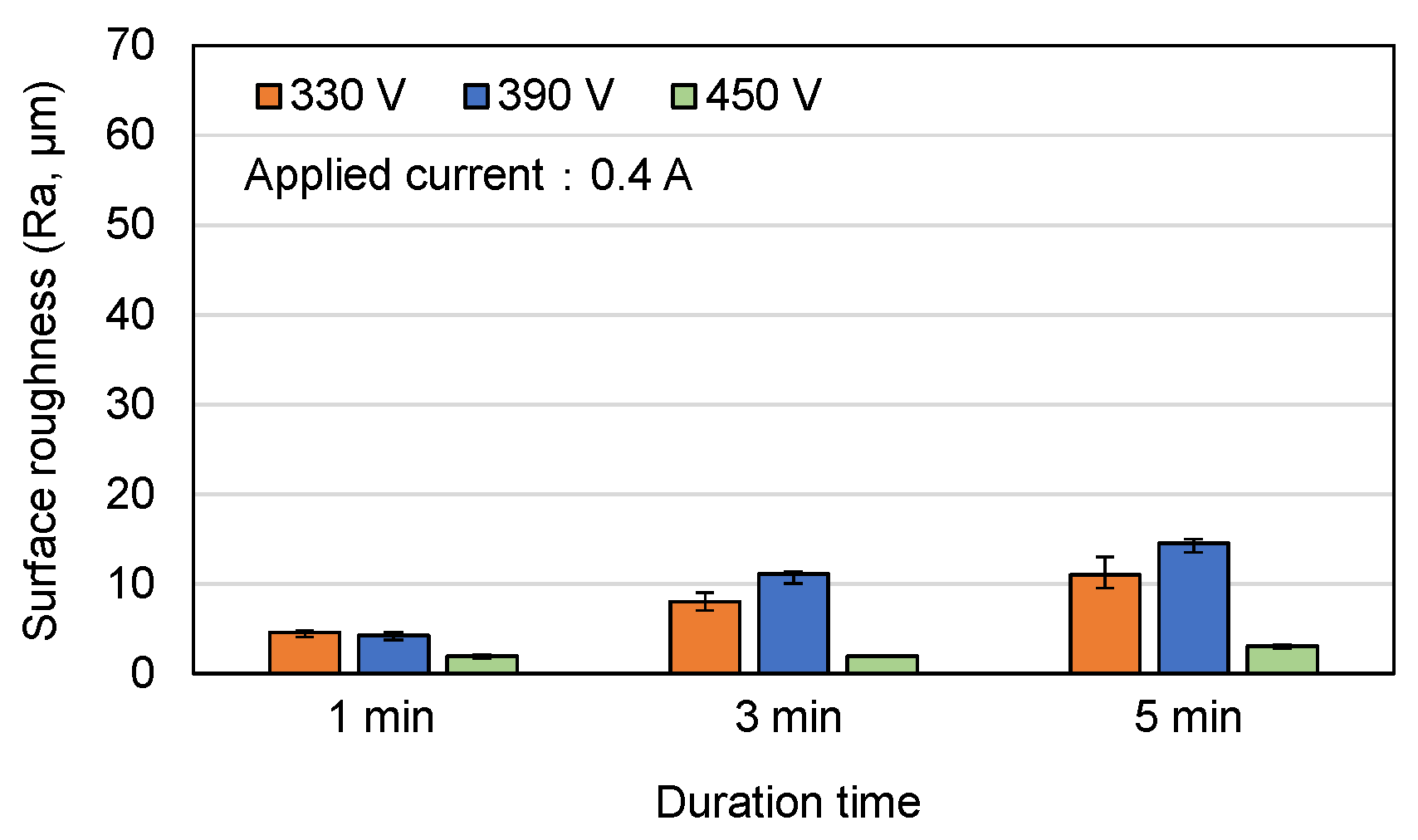
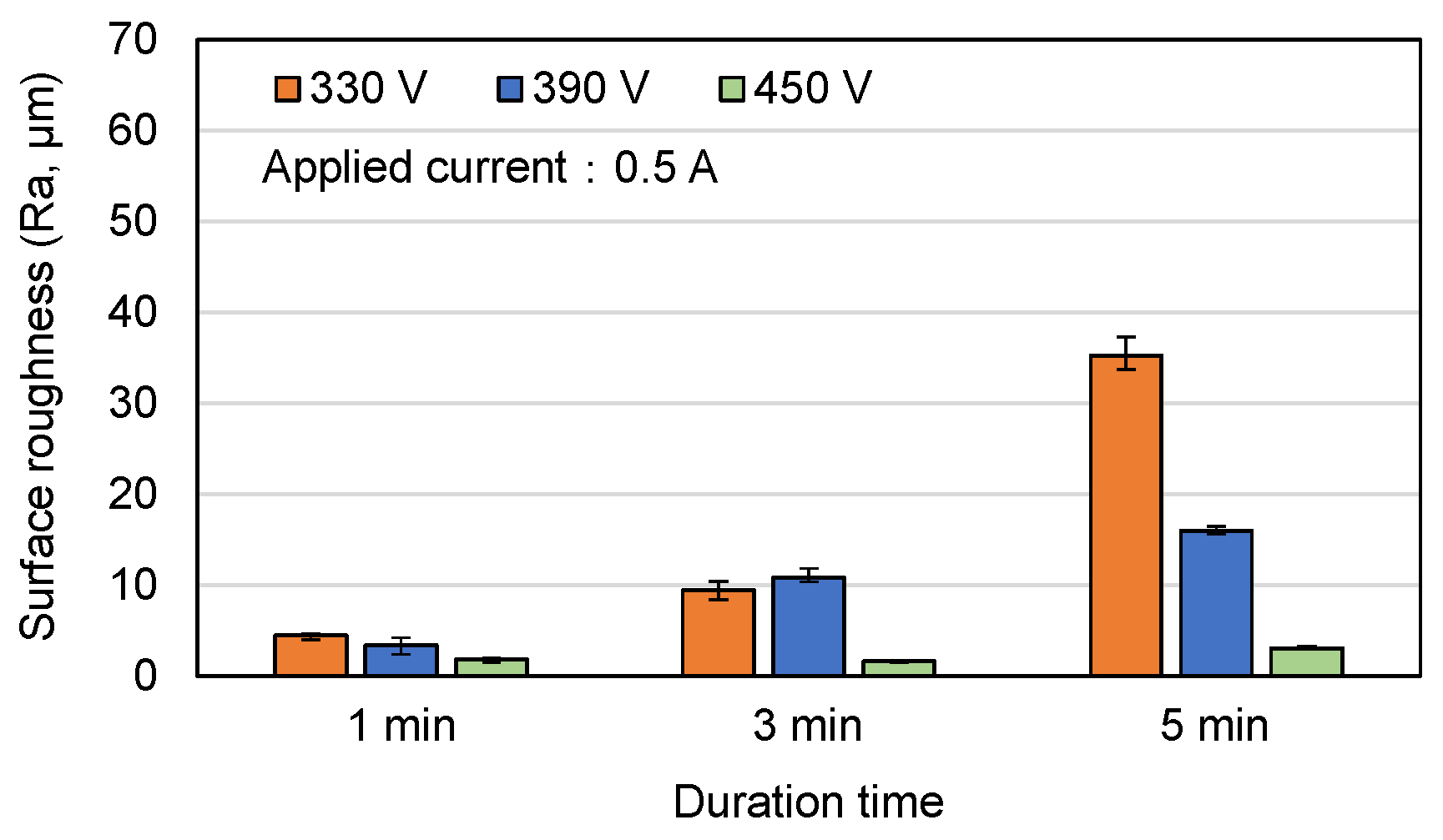
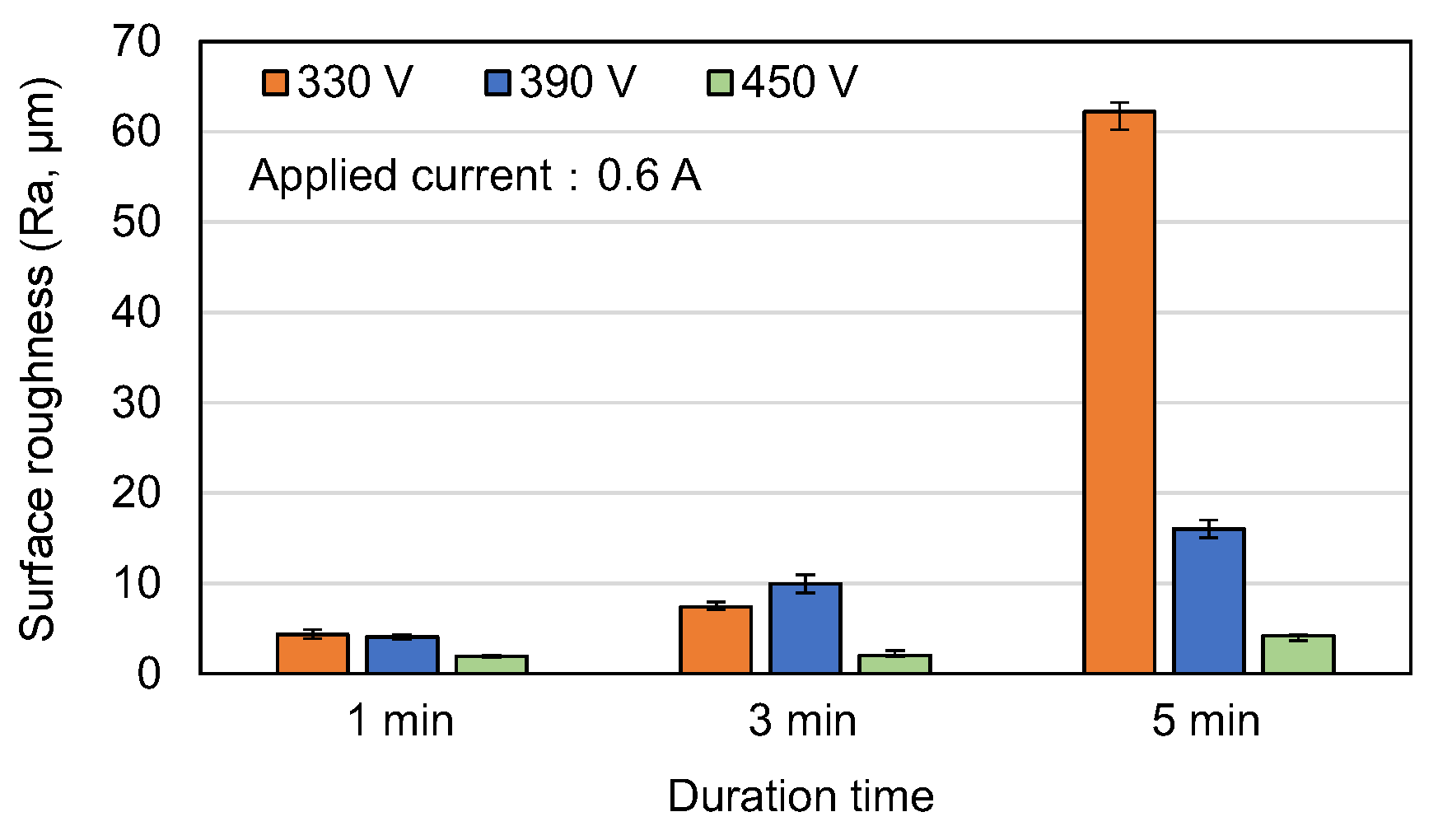
3.1. Surface Morphology and Roughness of MAO Coatings
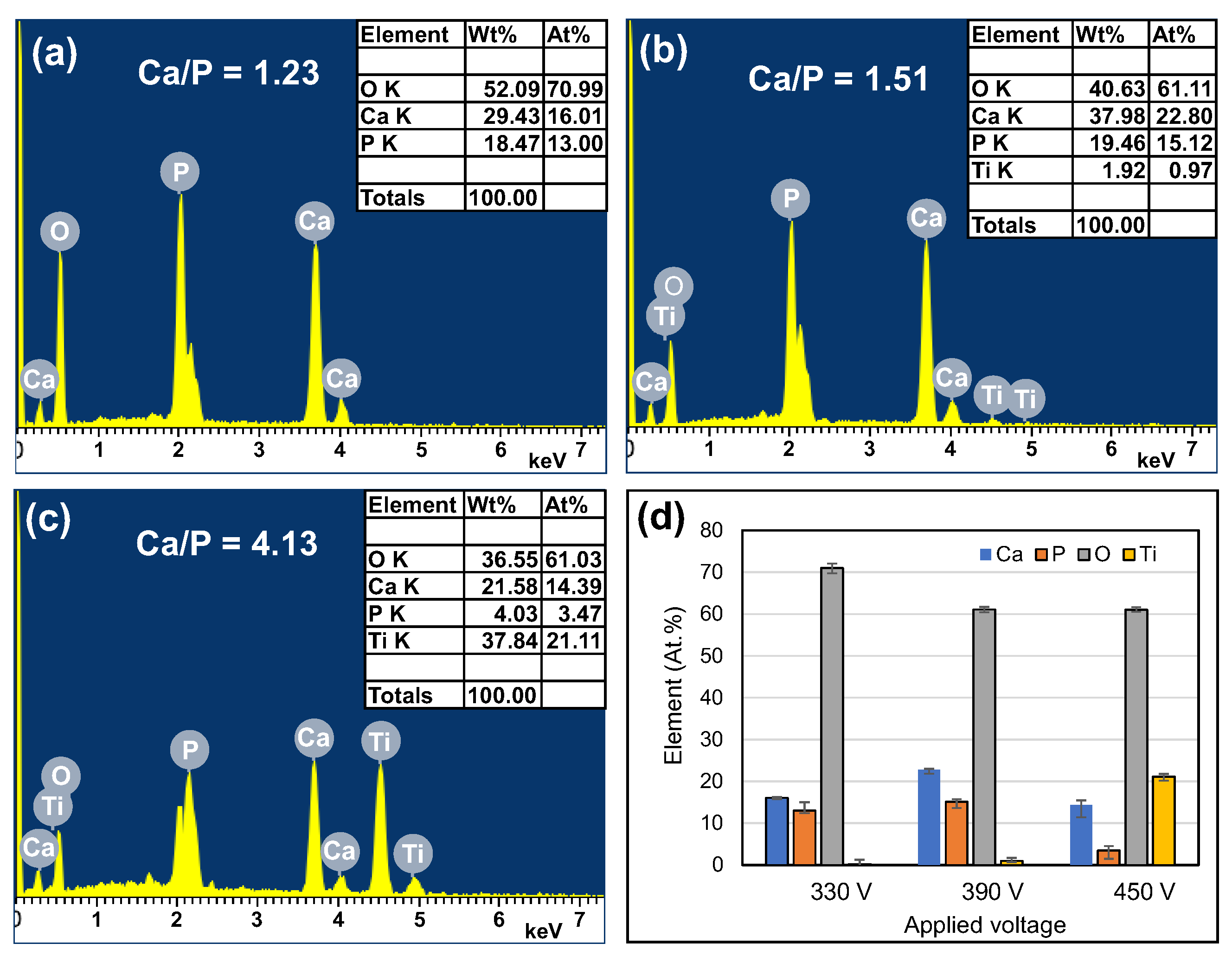
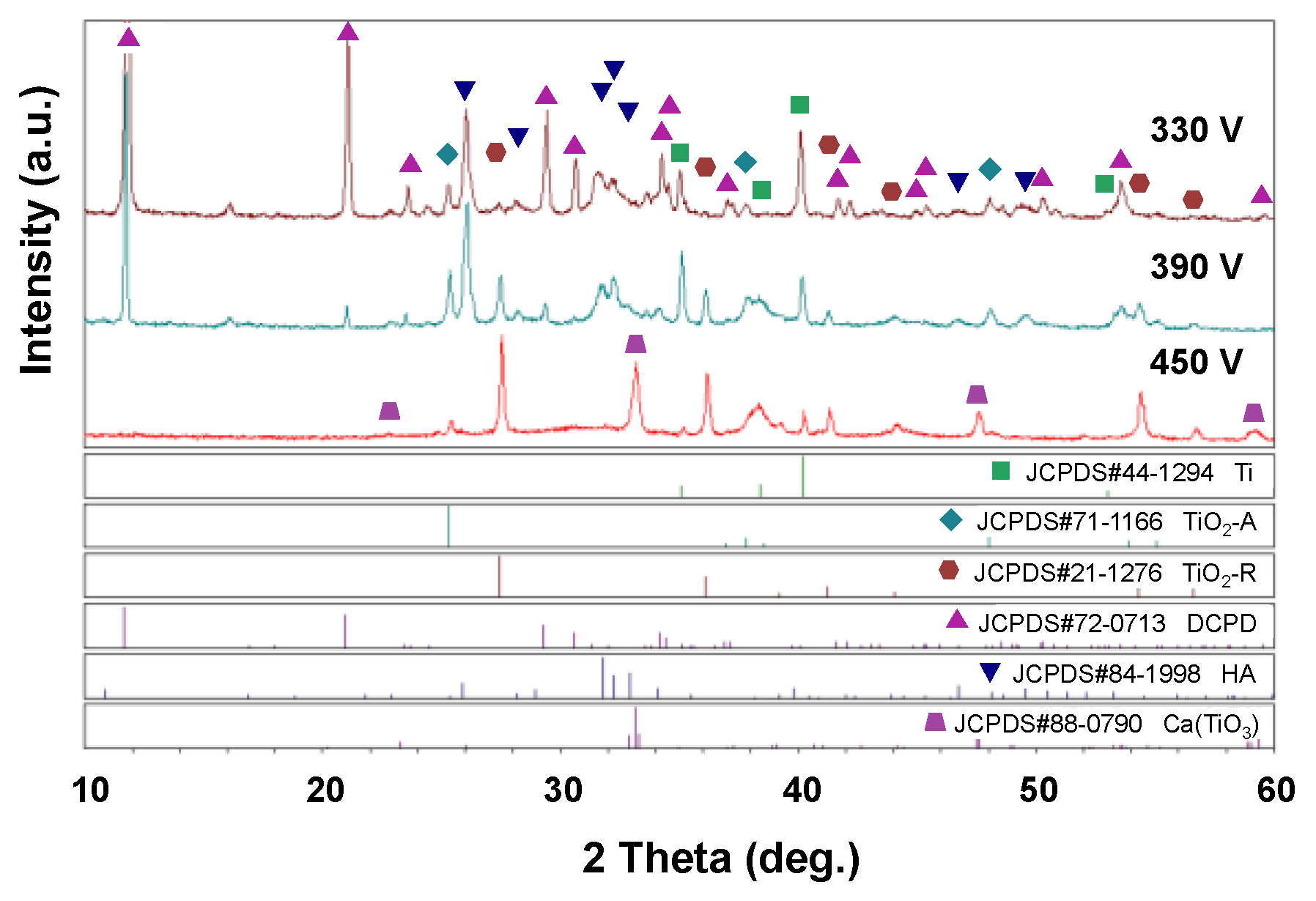
3.2. EDS and XRD Analysis Results for MAO Coating Surfaces
3.3. Wettability of MAO Coatings
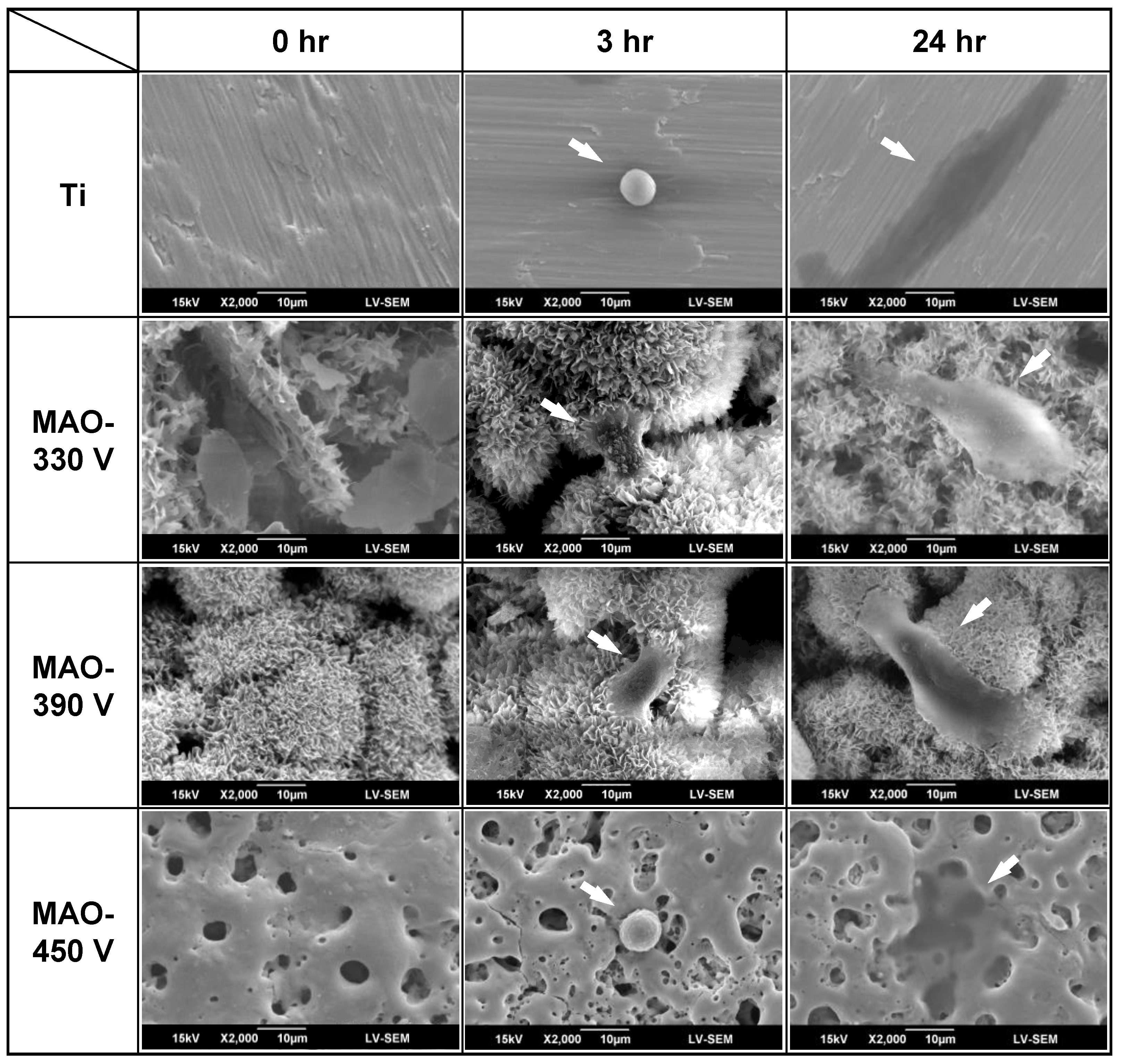
3.4. In Vitro Bioactivity of MAO-Formed Coatings
3.5. Initial In Vitro Biocompatibility of MAO-Formed Coatings
4. Conclusions
- Among the various discharge parameters considered in this study, the applied voltage had the greatest effect on the surface structure and morphology of the coatings. In particular, the 330 V coating had a mixed flower-like/plate-like structure, while the 390 V and 450 V coatings had a flower-like structure and a typical MAO porous morphology, respectively. The applied current mainly determined the coating formation speed, while the duration time governed the petal size of the flower-like structure. Among all the samples, the 0.6 A/5 min samples showed the greatest variation in the coating surface morphology with changes in the discharge voltage.
- The 330 V and 390 V coatings prepared with an applied current of 0.6 A and duration time of 5 min consisted mainly of Ti, TiO2-A, TiO2-R, DCPD, and HA. Of the two coatings, the 390 V coating contained less DCPD and thus had a higher HA/DCPD ratio and a Ca/P ratio close to the ideal value of HA. The flower-like structures consisted mainly of HA-containing compounds, while the plate-like structures consisted of DCPD. The 450 V coatings consisted mainly of Ti, TiO2-A, TiO2-R, and CaTiO3.
- The contact angle (CA) of the ground Ti surface was around 47°. By contrast, the CA values of the 330 V and 390 V coatings, with flower-like/plate-like and flower-like structures on the surface, respectively, were close to 0°, while the CA value of the 450 V sample was approximately 3°. In other words, the Ti substrate and MAO coatings had sufficient hydrophilicity, with the flower-like/plate-like and flower-like structure surfaces having a better wettability than the traditional MAO porous surface.
- The 330 V, 390 V, and 450 V coatings were completely covered with apatite after 7 days, 3 days, and 7 days immersion in SBF, respectively. However, no apatite was formed on the surface of the bare Ti substrate. The Ca/P ratios of the 330 V and 390 V samples increased from 1.23 to 1.74 and 1.51 to 1.66, respectively, following immersion in SBF for 7 days. By contrast, the Ca/P ratio of the 450 V sample fell from 4.13 to 1.91. The bioactivity of the MAO coatings was significantly correlated with the HA and CaTiO3 contents of the coating prior to immersion in SBF.
- In MG-63 cell culture tests, the flower-like/plate-like structure coatings (330 V) and flower-like structure coatings (390 V) showed partial cell coverage and protruded filopodia after 3 h. The 450 V coating and bare Ti substrate exhibited obvious cell expansion after 24 h, but no filopodia growth. The samples are ranked in order of decreasing in vitro biocompatibility as follows: 390 V > 330 V > 450 V > Ti substrate.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sidambe, A.T. Biocompatibility of advanced manufactured titanium implants—A Review. Materials 2014, 7, 8168–8188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Bose, S. Induction plasma sprayed nano hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium for orthopaedic and dental implants. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 2785–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchanek, W.; Yoshimura, M. Processing and properties of hydroxyapatite based biomaterials for use as hard tissue replacement implants. Mater. Res. 1998, 13, 94–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadow, R.; Killinger, A.; Stiegler, N. Hydroxyapatite coatings for biomedical applications deposited by different thermal spray techniques. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmenev, R. A review of plasma-assisted methods for calcium phosphate-based coatings fabrication. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 2035–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carayon, M.T.; Lacout, J.L. Study of the Ca/P atomic ratio of the amorphous phase in plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings. J. Solid State Chem. 2003, 172, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, B.Y.; Chang, E.; Yao, S.Y.; Chen, J.M. Phase transformation during plasma spraying of hydroxyapatite-10-wt%-zirconia composite coating. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 85, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanawa, T. Metal ion release from metal implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2004, 24, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, C.S.; Liao, T.Y.; Hong, T.F.; Kuo, T.Y.; Chang, C.H.; Yeh, M.L.; Lee, T.M. Surface microstructure and bioactivity of hydroxyapatite and fluorapatite coatings deposited on Ti-6Al-4V substrates using Nd-YAG laser. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2014, 4, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, A.; Schimpf, C.; Mandel, M.; Hecker, C.; Rafaja, D.; Krüger, L.; Arki, P.; Joseph, Y. Sol–gel derived hydroxyapatite coating on titanium implants: Optimization of sol–gel process and engineering the interface. J. Mater. Res. 2022, 37, 2558–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, A.; Hecker, C.; Árki, P.; Joseph, Y. Sol-gel derived hydroxyapatite coatings for titanium implants: A Review. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Estrada, O.A.; Pertuz Comas, A.D.; Ospina, R. Characterization of hydroxyapatite coatings produced by pulsed-laser deposition on additive manufacturing Ti6Al4V ELI. Thin Solid Films 2022, 763, 139592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duta, L.; Popescu, A.C. Current status on pulsed laser deposition of coatings from animal-origin calcium phosphate sources. Coatings 2019, 9, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, R.; Uvillús, A.; Fernández, L.; Bonilla, O.; Jara, A.; González, G. Electrochemical deposition of hydroxyapatite on stainless steel coated with tantalum/tantalum nitride using simulated body fluid as an electrolytic medium. Coatings 2022, 12, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Chen, H.; Yuan, B.; Zhou, Y.; Min, L.; Xiao, Z.; Zhu, X.; Tu, C.; Zhang, X. Electrochemical deposition of nanostructured hydroxyapatite coating on titanium with enhanced early stage osteogenic activity and osseointegration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 6605–6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pani, R.; Ranjan Behera, R.; Roy, S. Electrophoretic deposition of hydroxyapatite Coating: A state of art. Mater. Today 2022, 62, 4086–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmadani, S.; Anawati, A.; Gumelar, M.D.; Hanafi, R.; Jujur, I.N. Optimizing parameter for electrophoretic deposition of hydroxyapatite coating with superior corrosion resistance on pure titanium. Mater. Res. Express 2022, 9, 115402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhao, M.C.; Tan, L.; Zhao, Y.C.; Xie, B.; Huang, L.; Yin, D.; Yang, K.; Atrens, A. Biodegradation behaviour of hydroxyapatite-containing self-sealing micro-arc-oxidation coating on pure Mg. Surf. Eng. 2021, 37, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziaduszewska, M.; Shimabukuro, M.; Seramak, T.; Zielinski, A.; Hanawa, T. Effects of micro-arc oxidation process parameters on characteristics of calcium-phosphate containing oxide layers on the selective laser melted Ti13Zr13Nb alloy. Coatings 2020, 10, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerokhin, A.L.; Nie, X.; Leyland, A.; Matthews, A.; Dowey, S.J. Plasma electrolysis for surface engineering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 122, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.F.; Jin, L.; Zhou, L. Surface characteristics and electrochemical corrosion behavior of a pre-anodized microarc oxidation coating on titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 3775–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.C.; Ni, Y.J.; Wang, Z.C. Preparation of hydroxyapatite functionally gradient coating on titanium substrate using a combination of electrophoretic deposition and reaction bonding process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 3387–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasia, S.; Bayati, M.R.; Golestani-Fard, F.; Rezaei, H.R.; Zargar, H.R.; Samanipour, F.; Shoaei-Rad, V. Micro arc oxidized HAp-TiO2 nanostructured hybrid layers-part I: Effect of voltage and growth time. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 5944–5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, B.; Liang, C.; Wang, H.; Qiao, Z. Formation mechanism and adhesive strength of a hydroxyapatite/TiO2 composite coating on a titanium surface prepared by micro-arc oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 362, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Fang, Y.J.; Zheng, H.; Tan, G.; Cheng, H.; Ning, C. Effect of applied voltage on phase components of composite coatings prepared by micro-arc oxidation. Thin Solid Films 2013, 544, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, P.K. Effects of micropitted/nanotubular titania topographies on bone mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2629–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kossenko, A.; Lugovskoy, S.; Astashina, N.; Lugovskoy, A.; Zinigrad, M. Effect of time on the formation of hydroxyapatite in PEO process with hydrothermal treatment of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Glas. Phys. Chem. 2013, 39, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, X.; Cui, Z.; Zhu, S.; Wei, Q. One-step synthesis of petal-like apatite/titania composite coating on a titanium by micro-arc oxidation. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1041–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, B.; Zhou, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Liang, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, H. Influence of surface structures on biocompatibility of TiO2/HA coatings prepared by MAO. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 215, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, T.; Takadama, H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Z.; Tian, J.M.; Tian, J.T.; Chen, Z.Q.; Deng, X.J.; Zhang, D.H. Preparation of graded porous titanium coatings on titanium implant materials by plasma spraying. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikada, Y. (Ed.) Tissue Engineering: Fundamentals and Applications. In Interface Science and Technology; Elsevier, Ltd.: Edinburgh, UK, 2011; Volume 8, pp. 443–448. [Google Scholar]
- Budiraharjo, R.; Neoh, K.G.; Kang, E.T. Hydroxyapatite-coated carboxymethyl chitosan scaffolds for promoting osteoblast and stem cell differentiation. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2012, 366, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guéhennec, L.; Soueidan, A.; Layrolle, P.; Amouriq, Y. Review: Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeets, R.; Stadlinger, B.; Schwarz, F.; Beck-Broichsitter, B.; Jung, O.; Precht, C.; Kloss, F.; Gröbe, A.; Heiland, M.; Ebker, T. Impact of dental implant surface modifications on osseointegration. BioMed. Res. Int. 2016, 2, 6285620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakngarm, A.; Mutoh, Y. Electrochemical depositions of calcium phosphate film on commercial pure titanium and Ti-6Al-4V in two types of electrolyte at room temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Jeong, Y. Generation mechanism of micro discharges during plasma electrolytic oxidation of Al in aqueous solutions. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 1506–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafieerad, A.R.; Ashra, M.R.; Mahmoodian, R.; Bushroa, A.R. Surface characterization and corrosion behavior of calcium phosphate-base composite layer on titanium and its alloys via plasma electrolytic oxidation: A review paper. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 57, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, R.O.; Northwood, D.O. Production of anti-corrosion coatings on light alloys (Al, Mg, Ti) by plasma-electrolytic oxidation (PEO). In Developments in Corrosion Protection; Aliofkhazraei, M., Ed.; InTech Open Access: Rijeka, Croatia, 2014; pp. 201–240. [Google Scholar]
- Sundararajan, G.; Rama, L. Mechanisms underlying the formation of thick alumina coatings through the MAO coating technology. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 167, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, L.R.; Somaraju, K.R.C.; Sundararajan, G. The tribological performance of ultra-hard ceramic composite coatings obtained through microarc oxidation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 163–164, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Yu, Y.; Dong, Z. Formation mechanism, corrosion behaviour and biological property of hydroxyapatite/TiO2 coatings fabricated by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 25, 125483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundager Madsen, H.E.; Thorvardarson, G. Precipitation of calcium phosphate from moderately acid solution. J. Cryst. Growth 1984, 66, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbona, F.; Madsen, H.E.L.; Boistelle, R. The initial phases of calcium and magnesium phosphates precipitated from solutions of high to medium concentrations. J. Cryst. Growth 1986, 74, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, H.E.L. Influence of foreign metal ions on crystal growth and morphology of brushite (CaHPO4, 2H2O) and its transformation to octacalcium phosphate and apatite. J. Cryst. Growth 2008, 310, 2602–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boanini, E.; Silingardi, F.; Gazzano, M.; Bigi, A. Synthesis and hydrolysis of brushite (DCPD): The Role of ionic substitution. Cryst. Growth Des. 2021, 211, 689–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Luthringer, B.; Tang, S.; Hu, J.; Blawert, C.; Zheludkevich, M.L. Evolution and performance of a MgO/HA/DCPD gradient coating on pure magnesium. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 883, 160793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, M.D.; Webb, N.C. Hydroxyapatite formation from a hydrated calcium monohydrogen phosphate precursor. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1970, 6, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, K.; Kikuchi, M.; Tanaka, J.; Eda, H. Synthesis of c axes oriented hydroxyapatite aggregate. Chem. Lett. 2002, 31, 894–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Han, B.; Li, W.; Du, J.; Guo, P.; Han, D. Study on the microstructural evolution of BaTiO3 on titanium substrate during MAO. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 1801–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, X.; Chu, C.L.; Sun, Q. Synthesis of porous Ce-doped titania coating containing CaTiO3 by MAO and its apatite inducing ability. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 302, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, K.; Wu, C.; Lei, X.; Ding, J.; Shi, X.; Liu, C. Micro-arc oxidation enhances the blood compatibility of ultrafine-grained pure titanium. Materials 2017, 10, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redey, S.A.; Nardin, M.; Bernache-Assolant, D.; Rey, C.; Delannoy, P.; Sedel, L.; Marie, P.J. Behavior of human osteoblastic cells on stoichiometric hydroxyapatite and type A carbonate apatite: Role of surface energy. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 50, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Scheideler, L.; Reichl, R.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J. Effects of topography and composition of titanium surface oxides on osteoblast responses. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4087–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.H.; Chien, C.S.; Kuo, T.Y.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Huang, J.W.; Chin, W.H.; Chang, C.P.; Lee, T.M.; Lee, H.T. Biomedical evaluation of vacuum plasma sprayed tantalum coatings processed by alkali treatment and alkali-heat treatment with different NaOH concentrations. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 403, 126400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Sirghi, L.; Aoki, T.; Hatanaka, Y. Study on hydrophilic property of hydro-oxygenated amorphous TiOx:OH thin films. Surf. Sci. 2002, 507–510, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X.; Pan, W. Effect of surface morphology on wettability conversion. J. Adv. Ceram. 2016, 5, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M.; Lim, J.Y.; Donahue, H.J.; Dhurjati, R.; Mastro, A.M.; Vogler, E.A. Influence of substratum surface chemistry/energy and topography on the human fetal osteoblastic cell line hFOB 1.19: Phenotypic and genotypic responses observed in vitro. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4535–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Hockey, J.A. Infra-red studies of rutile surfaces. Part 2. Hydroxylation, hydration and structure of rutile surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1971, 67, 2679–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primet, M.; Pichat, P.; Mathieu, M.V. Infrared study of the surface of titanium dioxides. I. Hydroxyl Groups. J. Phys. Chem. 1971, 75, 1216–1220. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Y.; Liu, P.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. Influence of applied voltage on surface morphology and wettability of biological coatings on Ti6-Al-4V by micro-arc oxidation treatment. Mater. Res. 2020, 23, 20200002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurella, A.; Dahotre, N.B. Laser induced hierarchical calcium phosphate structures. Acta Biomater. 2006, 2, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Leng, Y. Theoretical analysis of calcium phosphate precipitation in simulated body fluid. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verron, E.; Bouler, J.M.; Guicheux, J. Controlling the biological function of calcium phosphate bone substitutes with drugs. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 3541–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, D.; Wang, Y. Structure of calcium titanate/titania bioceramic composite coatings on titanium alloy and apatite deposition on their surfaces in a simulated body fluid. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 8715–8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coreño, J.; Coreño, O. Evaluation of calcium titanate as apatite growth promoter. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2005, 75, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toworfe, G.K.; Composto, R.J.; Shapiro, I.M.; Ducheyne, P. Nucleation and growth of calcium phosphate on amine-, carboxyl- and hydroxyl-silane self-assembled monolayers. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Tu, B.; Lin, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Shen, M.; Hu, R. Evaluation of the biocompatibility of a hydroxyapatite-CaTiO3 coating in vivo. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 35, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, C.S.; Hung, Y.C.; Hong, T.F.; Wu, C.C.; Kuo, T.Y.; Lee, T.M.; Liao, T.Y.; Lin, H.C.; Chuang, C.H. Preparation and characterization of porous bioceramic layers on pure titanium surfaces obtained by micro-arc oxidation process. Appl. Phys. A 2017, 123, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampin, M.; Warocquier-Clerout, R.; Legris, C.; Degrange, M.; Sigot-Luizard, M.F. Correlation between substratum roughness and wettability, cell adhesion, and cell migration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1997, 36, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.J.; Oshida, Y.; Andres, C.J.; Barco, M.T. Surface characterization of variously treated titanium materials. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2001, 16, 333–342. [Google Scholar]
- Lincks, J.; Boyan, B.D.; Blanchard, C.R.; Lohmann, C.H.; Liu, Y.; Cochran, D.L.; Dean, D.D.; Schwartz, Z. Response of MG63 osteoblast-like cells to titanium and titanium alloy is dependent on surface roughness and composition. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 2219–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.C.; Carlier, A.; Bolander, J.; Roberts, S.J.; Geris, L.; Schrooten, J.; Van Oosterwyck, H.; Luyten, F.P. Current views on calcium phosphate osteogenicity and the translation into effective bone regeneration strategies. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 3876–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Yang, Z.; Du, R.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Bao, C.; Ma, J. Impact of implant surface micropatterns on epithelial cell behavior. Implant Dent. 2017, 26, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Yang, G.; Liu, L.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, S. Cell adhesive spectra along surface wettability gradient from superhydrophilicity to superhydrophobicity. Sci. China Chem. 2017, 60, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuma, A.; Quéré, D. Superhydrophobic states. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtsu, N.; Sato, K.; Yanagawa, A.; Saito, K.; Imai, Y.; Kohgo, T.; Yokoyama, A.; Asami, K.; Hanawa, T. CaTiO3 coating on titanium for biomaterial application—Optimum thickness and tissue response. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 82, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Akao, M. Preparation and characterization of double layered coating composed of hydroxyapatite and perovskite by thermal decomposition. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 1997, 7, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, T.J.; Ergun, C.; Doremus, R.H.; Lanford, W.A. Increased osteoblast adhesion on titanium-coated hydroxylapatite that forms CaTiO3. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2003, 67, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, M.; Zu, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, L. The corrosion resistance, biocompatibility and biomineralization of the dicalcium phosphate dihydrate coating on the surface of the additively manufactured NiTi alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, S.; Anada, T.; Honda, Y.; Suzuki, O. Comparative study on in vitro biocompatibility of synthetic octacalcium phosphate and calcium phosphate ceramics used clinically. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 7, 045020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Grover, L.M.; Huang, Y.; Adamopoulos, I.E.; Gbureck, U.; Triffitt, J.T.; Shelton, R.M.; Barralet, J.E. In vitro biodegradation of three brushite calcium phosphate cements by a macrophage cell-line. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4557–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, C.; Lausmaa, J.; Nygren, H. Interactions between human whole blood and modified TiO2-surfaces: Influence of surface topography and oxide thickness on leukocyte adhesion and activation. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 1987–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunette, D.M. The effects of implant surface topography on the behavior of cells. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1988, 3, 231–246. [Google Scholar]
- Rupp, F.; Scheideler, L.; Rehbein, D.; Axmann, D.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J. Roughness induced dynamic changes of wettability of acid etched titanium implant modifications. Biomaterials 2004, 5, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, K.; Yamaguchi, M. Role of albumin in osteoblastic cells: Enhancement of cell proliferation and suppression of alkaline phosphatase activity. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2004, 14, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| (mM) | Na+ | K+ | Ca+2 | Mg+2 | Cl− | HCO3− | HPO4−2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBF | 142.0 | 5.0 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 148.8 | 4.2 | 1.0 |
| Blood | 142.0 | 5.0 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 103.0 | 27.0 | 1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, K.-T.; Huang, J.-W.; Lin, W.-T.; Kuo, T.-Y.; Chien, C.-S.; Chang, C.-P.; Lin, Y.-D. Effects of Micro-Arc Oxidation Discharge Parameters on Formation and Biomedical Properties of Hydroxyapatite-Containing Flower-like Structure Coatings. Materials 2023, 16, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010057
Chen K-T, Huang J-W, Lin W-T, Kuo T-Y, Chien C-S, Chang C-P, Lin Y-D. Effects of Micro-Arc Oxidation Discharge Parameters on Formation and Biomedical Properties of Hydroxyapatite-Containing Flower-like Structure Coatings. Materials. 2023; 16(1):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010057
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Kuan-Ting, Jun-Wei Huang, Wei-Ting Lin, Tsung-Yuan Kuo, Chi-Sheng Chien, Ching-Ping Chang, and Yung-Ding Lin. 2023. "Effects of Micro-Arc Oxidation Discharge Parameters on Formation and Biomedical Properties of Hydroxyapatite-Containing Flower-like Structure Coatings" Materials 16, no. 1: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010057
APA StyleChen, K.-T., Huang, J.-W., Lin, W.-T., Kuo, T.-Y., Chien, C.-S., Chang, C.-P., & Lin, Y.-D. (2023). Effects of Micro-Arc Oxidation Discharge Parameters on Formation and Biomedical Properties of Hydroxyapatite-Containing Flower-like Structure Coatings. Materials, 16(1), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010057







