Abstract
The main objective of this study is to examine the impact of reinforcements on the strength of natural fiber composites. Recent advancements in natural fiber composites have minimized the usage of man-made fibers, especially in the field of structural applications such as aircraft stiffeners and rotor blades. However, large variations in the strength and modulus of natural fiber degrade the properties of the composites and lower the safety level of the structures under dynamic load. Without compromising the safety of the composite structure, it is significant to enrich the strength and modulus of natural fiber reinforcement for real-time applications. The strength and durability of natural fiber can be enriched by reinforcing natural fiber. The reinforcement effect on natural fiber in their woven, braided, and knit forms enhances their structural properties. It improves the properties of natural fiber composites related to reinforcement with short and random-orientation fibers. The article also reviews the effect of the hybridization of natural fiber with cellulosic fiber, synthetic fiber, and intra-ply hybridization on its mechanical properties, dynamic mechanical properties, and free vibration characteristics, which are important for predicting the life and performance of natural fiber composites for weight-sensitive applications under dynamic load.
1. Introduction
This century has already perceived notable achievements in green technology, especially in the domain of materials science, with the evolution of high-performance materials made from natural resources for various structural, manufacturing, bio-medical, aerospace, and automotive applications [1,2]. Due to their natural abundance, ease of processing, design flexibility, and feasibility of manufacturing complex shapes, natural fiber composites are good alternatives to conventional materials. They are also light in weight and hazardless to the environment [3,4]. The main problem with natural fibers is the variation of properties and characteristics, such as strength and modulus [5]. The cellulose composition of the cell wall, environmental circumstances during growth, geographical considerations, microfibrillar angle, and other factors all influence the fiber’s strength [6]. The structure of the natural fiber is shown in Figure 1. Properties of natural fiber composites depend on several parameters, such as processing technique, fiber strength, interfacial bonding between fiber and matrix, type of reinforcement, weaving pattern, and fiber orientation [7].
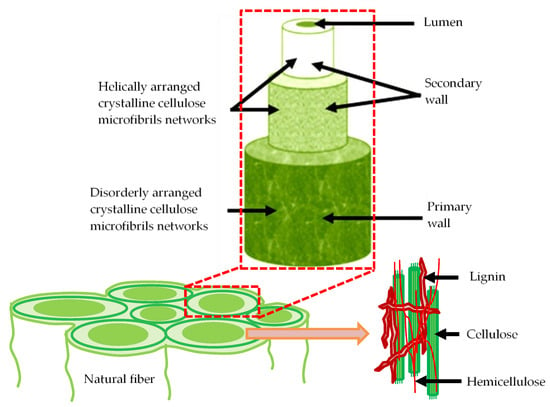
Figure 1.
Structure of natural fiber.
In the last two decades, natural fiber has found extensive usage in aerospace, naval, and structural fields [8]. The main reasons behind the higher usage of natural fiber composites for weight-sensitive and structural applications such as stiffener, truss members, bio-medical, automobile interior parts, etc., by industries are the potential environmental, end-of-life discarding, and health advantages in contrast to man-made composite materials [9]. Furthermore, man-made composite materials have a high density, are expensive, and are hazardous to the environment compared to natural fiber composites [10]. As proof, natural fibers such as jute, flax, banana, hemp, and sisal have replaced synthetic fibers such as glass, carbon, Kevlar, and boron in fields that require a load-carrying capacity in the medium and low range [11]. Tarasen and Reddy [12] established the usage of natural fibers (bamboo and jute) in several areas, such as fiber-reinforced columns, special joints, packaging material, and pillars. Moreover, some natural fibers are the best sources for extracting nanocellulose fibers. These nanofibers can be added as a second reinforcement to naturally based composites. Figure 2 depicts different natural fibers utilized in composites, and Figure 3 displays the classification of natural fibers. Moreover, composites consist of two phases: One is the matrix phase and the other is the reinforcement phase. The reinforcement phase consists of lignocellulose, which is generally referred to as natural fiber composite. The fibers directly extracted from a living organism are called natural fibers. The fibers derived from synthetic materials are called synthetic fibers.

Figure 2.
Common natural fibers used in composites: (a) bamboo (grass fiber type); (b) banana (leaf fiber type); (c) coir (fruit fiber type); (d) cotton (seed fiber type); (e) kenaf (bast fiber type); (f) flax (bast fiber type); (g) hemp (bast fiber type); (h) jute (bast fiber type); (i) nettle (grass fiber type); (j) oil palm (fruit fiber type); (k) ramie (bast fiber type); (l) sisal (leaf fiber type).
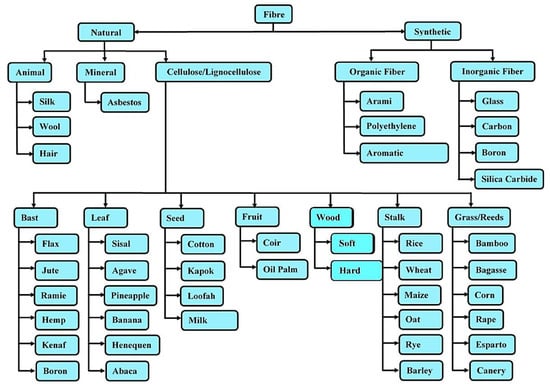
Figure 3.
Classification of natural fibers.
The large variation in strength and modulus makes NFCs incompatible under dynamic load and minimizes the safety level of the component. To overcome this drawback, NFCs are reinforced with NFRs in the polymer matrix to improve the structural applications’ strength, modulus, and safety.
Most researchers have developed NFCs with random orientation and short natural fibers as reinforcements in the polymer matrix, creating non-uniform stress distribution due to fiber discontinuity, which further leads to early failure of composites. The modulus of natural fibers can be enriched by reinforcing them with natural fibers in plain, braided, and knitted arrangements. It is observed that the Young’s modulus of NFCs reinforced with NFRs in distinctive patterns in weavings such as basket, plain, stain, twill, etc. have increased promisingly. Similarly, braided NRCs enriched the Young’s modulus of jute-fiber reinforcement by 30% compared to conventional weaving [12,13]. Sapuan and Maleque [13] developed less expensive telephone stands using banana fabric (woven type) in an epoxy matrix. By substituting fiberglass with jute fiber composites, Alves et al. [14] highlighted the advantages of NFCs in the manufacture of automobile hoods.
Reinforcing the NFC with synthetic fiber enhances its mechanical properties and load-carrying capacities and can be used for different structural applications [15]. Damodaran et al. [16] applied a basic sandwich model to develop a traditional drum (Chenda) using a carbon epoxy composite and balsa core material. Comparing the acoustic performance of the traditional drum and a composite drum suggested that the high damping properties of sandwich composites could replace the wood used in the traditional drum. Based on the mechanical properties, many researchers are focusing on working on identifying fibers (plant-based) suitable for use in medium and low load applications [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. The benefits of woven fabric natural composites (WFNCs) have led to an increase in their use in a variety of structural applications. When compared to randomly oriented and unidirectional NFCs, WFNCs provide higher stiffness and strength for the same amount of fibers employed. NFCs’ fracture toughness is also improved by the usage of woven fabric. Riedel et al. studied the usage of WFNCs in several structural applications and concluded that using woven fabric would improve composite stiffness [25].
In this paper, a systematic review of NFC enhancement by modifying the Young’s modulus of natural fiber reinforcement is reported. A critical review was done on various processes such as weaving, braiding, and knitting concerning mechanical, dynamic mechanical, and free vibration properties. Further hybridization effects of natural fiber with synthetic fiber in the context of mechanical, dynamic mechanical, and dynamic properties were reviewed. In addition, the fabrication and advantages of intra-ply woven NFC made with two different yarn fibers are also discussed.
2. Disadvantages of Composites including Short Natural Fibers
Many researchers have investigated the mechanical, dynamic mechanical, and tribological properties of randomly oriented and short natural fibers as reinforcements in the polymer matrix. The main problem associated with short-form reinforcement in a high-density polymer matrix is that achieving uniform distribution is difficult. It affects the advantages of natural fiber composites seriously and makes them incompatible for structural applications. Almeida et al. [26] investigated the mechanical characteristics of coir fiber in a polyester matrix with a fraction of up to 80 wt% coir fiber. They found that composites with 50 wt% exhibited enhanced mechanical properties. Further addition resulted in less strength and a lower modulus of the composites due to random distribution and poor bonding between the fiber and matrix.
Another problem associated with randomly distributed short natural fibers is that the polymer matrix is agglomerates as it affects the composites properties. A similar problem was reported by Joseph et al. [27] regarding the mechanical properties of sisal/polypropylene composites. The authors concluded that fiber length, loading, and orientation affect the performance of the composites. A schematic diagram of a randomly oriented short fiber-reinforced composite is illustrated in Figure 4.
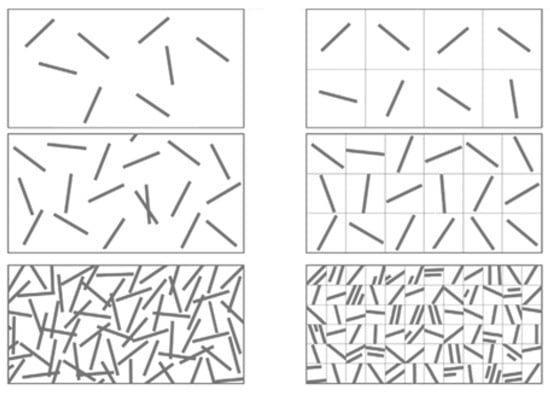
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of randomly oriented short fiber composite.
Arib et al. [28] studied the mechanical properties of pineapple leaf fiber-reinforced polypropylene composites and found that a higher volume percentage diminished the mechanical properties of the pineapple composites. Shekeil et al. [29] investigated the mechanical characteristics of kenaf fiber–thermoplastic polyurethane composites as a function of fiber weight %. They discovered that adding 30 wt% to the composites enhanced the mechanical characteristics of the composites and that adding more resulted in the composites’ modulus, flexural, and tensile strength decreasing.
Researchers also found that the random distribution of NFR affects the stiffness of composites due to poor stress transfer at the interface during loading. The dynamic behavior of banana–sisal hybrid short fiber-reinforced polyester composites was investigated by Idicula et al. [30]. At 0.40 Vf, they observed a minimum peak height and maximum width for the material loss factor. It was revealed that composites with 0.40 Vf possessed higher stiffness and maximum energy. Further increasing the fiber content in the matrix reduced its stiffness due to the non-uniform fiber distribution. Similar variations were observed by Doan et al. in jute fiber/polypropylene composites [31]. Pothan et al. [32] found that 40 wt% fiber loading enhanced the storage modulus and glass transition temperature of banana fiber composite materials. They also observed that high fiber loading decreased the stiffness of the composites.
Kumar et al. [33] compared the free vibration and damping behavior of short banana and sisal fiber polyester composites. The authors found that banana fiber with a length of 4 mm and sisal fiber with a length of 3 mm at 50 wt% improved the damping and mechanical characteristics. For longer fiber length, the damping properties of composites decreased due to agglomeration. Tayeb [34] investigated the tribological properties of sugarcane fiber–polyester composites and found that the wear rate of composites decreased when fiber length varied from 1 to 5 mm. Further, increasing the length of the fiber resulted in an increased wear rate and friction coefficient of the composite material. Higher fiber length increased the amorphous nature of the composite. Shalwan and Yousif [35] investigated the mechanical and tribological behavior of polymeric composites based on natural fibers. They came to the conclusion that the properties of composite materials are impacted by fiber orientation, fiber length, and volume fraction. Yusuf et al. [36] looked into the tribological characteristics of oil-palm fiber-reinforced polyester composites and discovered that oil palm/polyester composites had better wear properties.
From the results of these reported studies, it is concluded that the properties of natural fibers with short form depend on the fiber aspect ratio, and improvements in properties are generally observed only up to a certain wt%. The main problem associated with short and randomly oriented fibers in composites is achieving uniform distribution in the polymer matrix [37]. Furthermore, it creates a poor interfacing bond between the fiber and the matrix due to a higher weight percentage, resulting in poor mechanical properties.
3. Woven Natural Fiber Composite
To overcome the disadvantage of natural fiber with short and random orientation, researchers focused more on the reinforcement effect by incorporating WNFR to enhance the properties of NFCs for low and medium load applications. Because of its ease of processing, low fabrication cost, and improved characteristics, the idea of employing WNFR to produce NFCs was generally adopted. Due to stronger fiber–matrix bonding, the gap between warp and weft acts as a mechanical interlock among the polymer matrix, increasing resistance to failure under load. In addition, the chances of failure are less/delayed due to fiber pullout under dynamic loading conditions. In recent years, tremendous development in the textile sector has motivated researchers to explore the possibilities of improving natural fiber composite properties, making them suitable for many applications. Nowadays, natural fibers are used in continuous and woven forms, which further increases the inherent properties of NFCs. Several researchers analyzed the outcome of weaving patterns such as plain, twill, stain, and basket weaving patterns on the mechanical properties of NFCs. Results revealed that NFCs reinforced with NFR with varied weaving patterns exhibit improved mechanical properties. John et al. [38] and Pothan et al. [39] explained the advantages of various weaving structures such as plain, basket, twill, and satin. Out of these four patterns, plain weave gives uniform distribution, good stability, and porosity. A continuous yarn moves in the warp and weft directions in a regular 1x1 pattern in a plain weave. Plain weave has the major drawback of having a larger crimp in the warp, and the weft impacts the properties of the succeeding composite. To enhance the properties of composite materials, researchers investigated various weaving patterns and evaluated them against plain weave as a reference. Alavudeen et al. [40] tested a woven banana/kenaf polyester composite against a randomly oriented fiber composite with the same wt%. In comparison to the short fiber composite, they discovered that the woven composite had better mechanical characteristics. As a result, it has been demonstrated that continuous natural fiber improves composite performance when compared to composites made with short natural fiber with random distribution.
3.1. Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties of natural fiber composites, such as impact, flexural, and tensile strength, are influenced by fiber percentage in the matrix, fiber strength, fiber–matrix adhesion, fiber orientation, concentration, and treatment type [41,42]. Steel, titanium, and aluminum were formerly the materials of choice for engineering, civil, aircraft, and automotive applications. WNFR composites, on the other hand, offer favorable weight characteristics and bulk strength, making them a feasible substitute for traditional materials since they have stiffness and superior strength [43,44,45]. Schematic diagrams of basic weaving patterns used in the composite field are illustrated in Figure 5.
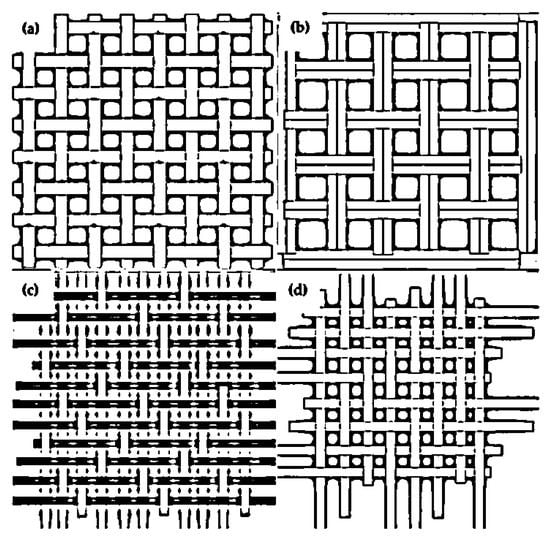
Figure 5.
Schematic of various woven mats: (a) plain; (b) basket; (c) twill; (d) satin.
In an experimental investigation, Asim et al. [46] evaluated the flexural characteristics and tensile strength of tri-layer palm oil and woven jute fiber–epoxy composites to palm oil–epoxy and woven jute–epoxy composites. Three-layer palm oil and woven jute fiber–epoxy composites had greater mechanical properties than identical composites made with other combinations. It was also discovered that the kind of fiber and its hybridization had an impact on composite characteristics. The mechanical characteristics of Cotton and Kapok fabrics as reinforcing components in a polypropylene matrix were examined by Mwaikambo et al. [47]. They discovered that adding fabric to the composite material enhanced its rigidity. Sapuan et al. [48] studied the mechanical characteristics of woven banana/epoxy composites and discovered that woven banana composites had a higher strength and modulus. The influence of a stacking arrangement on the mechanical properties of sansevieria cylindrical–coconut sheath polyester composites was investigated by Bennet et al. [49]. The maximum modulus was seen when the mat fiber was kept as an exterior layer and short-fiber mat was used as the core material.
Carmisciano et al. [50] investigated the flexural properties of a basalt woven fiber-reinforced vinyl ester composite and a glass fiber composite. Basalt woven fiber composites outperformed glass fiber composites. Venkateshwaran and Elayaperumal [51] investigated the mechanical properties of woven banana–jute–epoxy composites with various stacking sequences. They discovered that adding jute fiber as a core layer increased the flexural and tensile properties of the composite over the jute and banana composites individually. The flexural characteristics of woven pandanus and banana fabric composites with short fiber reinforcement were compared by Mariatti et al. [52]. They discovered that at the same volume %, the woven fabric composite exhibited a high modulus and strength. Finally, Khan et al. [53] investigated the mechanical characteristics of non-woven jute and plain-woven jute composites in the warp direction. They observed that in the warp direction, the woven mat composite outperformed the non-woven composite in terms of mechanical properties.
Rajesh and Pitchaimani [54] analyzed the effect of weaving patterns on mechanical properties compared with composites reinforced with randomly oriented natural fibers. Results revealed that for the same weight percentage, the woven composite improved the mechanical properties of the composites whereas randomly oriented SNFR failed relatively. Short-form reinforcement experienced higher stress concentrations as fiber discontinuity affected the bonding strength between the fibers and the matrix. It led to early failure of the composites compared to woven fabric reinforcement. The individual strength of the yarn and the amount of fiber present in the reinforcement influenced the load-carrying behavior of the composites. Similar observations were made by Alavudeen et al. [40]. They analyzed the effect of fiber strength and weaving patterns on the mechanical properties of polyester composites and compared them with randomly oriented composites. They found that irrespective of fiber strength, the weaving pattern significantly affected the strength of the composites.
Figure 5 depicts commonly used weaving patterns in the composite field, such as plain, basket, twill, and satin weaves. The main advantage associated with plain and basket weaving is the uniform orientation of the fibers in the weft and warp directions. In satin and twill weaves, the fabric will bias diagonally, which influences the load-carrying behavior of the composites. In plain and basket weaves, stress is distributed uniformly along with the warp and weft directions, which affects the mechanical properties of the composites. In twill and satin weaves, stress transfers non-uniformly and diagonally to the warp and weft directions, leading to earlier failure of the composite under loading. In the textile industry, the huckaback style is commonly used in fabrics. Due to the periodic yarn arrangement in both the warp and weft directions, the huckaback pattern enhances the fabric’s surface roughness. The gaps between subsequent strands in the warp and weft orientations are the fundamental drawback of huckaback woven composites, which causes them to break prematurely. As a result, there is a higher concentration of tension during loading. Goutianos et al. [55] studied the effects of yarn twist for woven composites. Results indicated that a higher yarn twist improved the properties of the composites, whereas a lower yarn twist exacerbated insufficient loading capacity. Pothan et al. [56] evaluated the mechanical characteristics of several types of woven sisal fiber composites and discovered that plain-woven fabric improved the composite’s properties. Shibata et al. [57] investigated the flexural strength of bamboo/kenaf fiber-reinforced composites that were unidirectional and randomly oriented. They concluded that the woven fabric, regardless of material, flexural strength, and modulus of the composite, was improved. Table 1 shows the mechanical properties of frequently used plant fibers in the field of composites.

Table 1.
Mechanical properties of plant fiber-reinforced polymeric biocomposites.
3.2. Dynamic Mechanical Properties
Thermal and dynamic mechanical characteristics of newly developed materials are significant parameters to be examined primarily for structural applications. At higher temperatures, the interactions between molecules in materials made out of conventional materials will be higher, which increases energy dissipation and lowers the stiffness. The fiber or yarn arrangement, reinforcement, amount of fiber in the matrix, and adhesion between the matrix in the space between two fiber yarns influence the dynamic characteristics of composite materials. Rajesh and Pitchaimani [83] investigated the dynamic mechanical characteristics of composite materials using weaving patterns and fiber strengths. They discovered that in the glassy zone, regardless of the weaving pattern, the composite had a small change in storage modulus. However, compared to satin, plain, huckaback, and twill woven composites, the basket-design jute composite significantly increased the storage modulus after the glassy area. At higher temperatures, the basket-design composite enhanced structural stiffness and improved resistance to free molecular movement. The basket-woven fabric’s fiber yarn arrangement also reduced stress concentration and supported more weight between two consecutive yarns in the weft and warp directions. Furthermore, the list of published research work that has been conducted to demonstrate the dynamic mechanical properties is tabulated in Table 2.

Table 2.
Some of the research work related to dynamic mechanical properties.
The impact of weaving patterns on the dynamic mechanical behavior of banana–epoxy composites was investigated by Venkateshwaran and Elayaperumal [51]. The composite enhanced the storage modulus of the composite laminate while having no influence on the glass transition temperature compared to twill and satin weaves. According to the authors, the orientation of natural fiber yarns in the warp and weft directions influenced the storage modulus of the plain-woven composite. In plain weave, a different strand arrangement in the warp and weft orientations enhances stability and minimizes porosity. The high crimp present in both the warp and weft directions is the fundamental issue with plain weave. Plain weave, however, is more rigid than satin or twill. Fangueiro and Rana [99] investigated the viscoelastic behavior of twill and plain-woven hemp fiber-reinforced polylactic acid composites. They discovered that twill weave improved the composites’ viscoelastic and mechanical characteristics, as well as their loss and storage moduli. Gupta [100] discovered that plain-weave reinforcement improved the composite’s dynamic mechanical characteristics more than short fibers. A dynamic mechanical investigation of oil-palm empty fruit bunch (EFB)/woven jute fiber (Jw) epoxy hybrid composites was explored by Jawaid et al. [101]. The woven jute composite’s storage modulus was found to be higher than that of the hybrid composites. It revealed that the hybridization of oil-palm empty fruit bunches with woven jute fabric affects the performance of the composite under the thermal environment due to the addition of oil-palm empty fruit bunches minimizing the resistance of free molecule movement in the polymer chain. Thus, it minimizes the resistance against free molecular movement and reduces stiffness. Asim et al. [102] studied the influence of jute fiber loading on the dynamic mechanical behavior of oil-palm epoxy composites. The inclusion of jute fiber in the oil-palm–epoxy composites increased their storage modulus. It showed that adding high-strength jute fiber to the matrix prevented free molecule movement and improved the composite material’s stiffness at higher temperatures. The dynamic mechanical behavior of PLA–hemp bio-composites was studied by Durante et al. [103]. They discovered that increasing the fiber ratio in the PLA matrix enhanced the composite material’s glass transition temperature and storage modulus. The dynamic mechanical behavior of aliphatic–aromatic co-polyester and green composites consisting of woven flax cloth matrix was studied by Chandrasekar et al. [104]. Conferring to the results, the addition of woven fabric significantly increased the storage modulus of the green composite.
3.3. Free Vibration Behaviour
The materials used for structural applications must have superior damping properties, along with strength and stiffness. These properties are significantly influenced by the manufacturing process, type of reinforcement, and matrix. Researchers have fabricated composite laminates using a compression-molding process and compared them with a hand lay-up technique. Results revealed that composites fabricated using the compression-molding technique exhibited improved properties compared to those produced using the hand lay-up method. Kumar et al. [33] reported that the compression-molding process showed enhanced material properties and stiffness, along with energy dissipating properties. For structural applications, it is important to reduce the resonant amplitude of vibration to protect the components and structures from failure. The modal damping associated with each mode of the structure has a considerable impact on the resonant amplitude of vibration. A small exciting force can induce high amplitude vibrations at resonance due to any sizeable vibratory inertia force. In general, fiber-reinforced composites have higher damping properties than conventional materials due to viscoelastic behavior and fiber–matrix interaction.
Free vibration properties such as natural frequency and damping characteristics of fiber-reinforced composites have been analyzed by several researchers using experimental, analytical, and numerical methods. In free vibration analysis, the composite material’s natural frequency and corresponding damping factor were found using the fast Fourier transfer (FFT) algorithm. It changes a time-domain signal to a frequency response signal and provides an incessant peak for the corresponding natural frequency of the composite material. Chandradass et al. [105] experimentally analyzed the outcome of nanoclay additions on free vibration characteristics of a glass fiber-reinforced composite structure. The second-phase nanoscale dispersion in the matrix and E-glass fiber greatly improved the internal damping of the hybrid composites, according to the dynamic results. Gibson [106] analyzed the modal vibration response quantities of composite materials and structures. Results revealed that impulsive excitation methods gave accurate values for the characterization of intrinsic material properties.
Recently, synthetic fibers have been replaced by natural fibers as reinforcements in the polymer matrix because of their better energy-dissipating behavior [107,108]. The development of green composites increases the usage of plant wastes, thereby reducing their carbon footprint. The free vibration behavior of woven reinforced materials improves the natural frequency of the composite material [109,110]. Rouf [111] analyzed the influence of plain, twill, and satin weaving patterns on the dynamic behavior of woven fabric composites. The author found that plain weave increased the damping properties of composites more than satin composites. Duc et al. [112] conducted a modal analysis to determine the natural frequency and damping behavior of unidirectional, laminated, and woven flax fiber (FF)/epoxy composites. They critically evaluated the factors affecting the natural frequency and damping factor of the composite material. They found that the impregnation quality, fiber/matrix adhesion, strength of the fibers, twist of the fiber yarns, and yarn crimp significantly affected the fundamental natural frequency and corresponding damping factor of the composite structure.
Similarly, the effects of structure type, type of fibers, and physical properties such as density, thickness, and manufacturing process on the stiffness of the composite laminate influence the dynamic properties [113]. Mishra and Sahu [114] carried out extensive experimental work on the free vibrational behavior of woven composites with different boundary conditions. They found that the number of layers, fiber orientation, aspect ratio, and different boundary conditions of the woven fiber composite significantly influenced their stiffness values.
According to Chandra et al. [115], fiber-reinforced composites offer better strength and stiffness, as well as a stronger damping effect, than traditional materials. Da et al. [116] measured the frequency and conducted modal damping analysis for jute/sisal hybrid polyester composites using the impulse hammer technique. They found that the average damping factor attained for the jute/sisal hybrid composite was 1.15 times higher than the composite reinforced with the jute layer alone. It was due to differences in the flexural stiffness of the jute/sisal hybrid polyester composite. Rajini et al. [117] discussed the free vibration behavior of coconut woven mat with different percentages of nanoclay added to the polyester composite. The introduction of nanoclay increased the natural frequency of the composite by up to 3 wt%, whereas further addition reduced the matrix stiffness. The damping characteristics of the composite material improved as the wt% of the nanoclay increased, owing to the efficient interaction between the fiber and matrix, which boosted the composite material’s energy dissipation. Rajesh et al. [83,118] reported similar observations for a banana–jute intra-ply hybrid composite. Results showed that the use of a basket-woven composite as reinforcement enhanced the first three fundamental natural frequencies of the composite material. Fiber orientation within the yarn plays an essential role in determining natural frequencies [119,120]. Rajesh and Pitchaimani [121] analyzed the natural frequency of woven natural fiber composites under a buckling load. Results revealed that the weaving patterns influenced the resistance against a buckling load.
4. Effect of Hybridization
Hybridization offers substantial improvement in the properties of composites, which has attracted the attention of researchers for structural applications. In general, a significant weight percentage of synthetic fibers such as carbon, glass, etc., are hybridized to enhance the inherent properties of natural fiber composites for the intended applications. For compressive applications, jute fibers are reinforced with glass fiber. However, the hybridization effect is not significant for tensile load applications. Thus, it reveals that the procedure requires applications regarding the hybridization of natural fiber with synthetic fiber to achieve the desired goals/applications. For example, Mansor et al. [122] carried out an experimental investigation, selecting natural fiber and its hybridization for automotive brake lever applications. They found that kenaf fiber with glass fiber provided superior properties for the intended application compared to other natural fibers. The enhancement in the hybridization performance increased the load-carrying behavior of the composites compared to when they were reinforced in the matrix alone. However, the addition of synthetic fiber improved the properties of the natural fiber composite, and the compatibility between the fiber/filler and matrix influenced the failure of the hybrid composites. The list of research work carried out in natural fiber hybrid polymer composites is illustrated in Table 3.

Table 3.
Various studies on natural fiber hybrid polymer composites.
The primary purpose of the hybridization of synthetic fiber/filler in the polymer matrix with natural fiber is to enrich the properties of composites, especially mechanical properties. It is determined by the filler dispersion in the polymer matrix, fiber distribution, fiber adherence to the matrix, fiber contact area, reinforcement high load-bearing behavior, fiber origin, surface treatment (physical or chemical), and stacking sequence. Through experimental studies, most researchers reported that strength enhancement depends on fiber loading, treatment, aspect ratio, and contact area [151,152,153]. Due to hybrid composites’ enhanced strength and land-bearing capacity, they are used in many automotive applications such as car interior components and door panels.
4.1. Hybridization of Natural Fiber with Man-Made Fiber
The hybridization of synthetic fiber with natural fiber helps to enrich the properties and to increase the resistance against water absorption and minimize environmental issues and cost. Though natural fibers have many advantages over man-made fibers, many hydroxyl groups present in cellulosic substances such as cellulose, hemi-cellulose, and lignin increase the interaction rate with moisture present in the environment, making them incompatible with hydrophobic applications. Researchers carried out a lot of experimentation on the hybridization of synthetic fiber with natural fiber. They established that the hybridization of synthetic fiber enhanced the mechanical properties of the composite. The improvement is due to the decrease in water absorption and enhancement in bonding. The major problems of natural fibers are moisture absorption due to the interaction of cellulosic substances available in the fiber cell wall. It can restrict the applications of natural fiber composites in various applications, especially outdoor applications, where the interaction of water particles is high. The water absorption of natural fiber composites is affected by the nature of the fiber, growing environment, volume fraction, and diffusivity. Water can enter through available micro-cracks in the matrix and microgaps between the fiber and matrix. Transportation of water particles can happen due to capillary action in the interface gap due to poor wetting. Therefore, composites exposed to the moisture environment can experience debonding and crack formation. In addition, those water molecules act as a plasticizer and reduce the load-carrying capacity, thus minimizing the mechanical properties of natural fiber composites. Henceforth, it is important to improve the resistance to water absorption behavior. Physical and chemical surface modification of natural fiber improves the compatibility of natural fiber with the polymer matrix. However, using a high concentration of harsh chemical treatment affects human health and the environment differently. Hence, to overcome the problem related to the moisture absorption and wettability of natural fibers, the hybridization of synthetic fiber and natural fiber is a better choice. It reduces the water molecule interaction and enhances the properties under various loading conditions for intended applications.
Panthapulakkal and Sain [153] analyzed the impact of the water absorption of hemp fiber composites on tensile strength. They found that the inclusion of glass fiber in the hemp composite increased the tensile properties. In the case of neat hemp composite, debonding arose between the fiber and matrix due to the penetration of water molecules and reduced the strength of the composites. Similarly, the inclusion of glass fiber in the jute composite enhanced the tensile strength of the composite for water-immersed samples. Results revealed that the inclusion of synthetic fiber in the natural fiber composite enhanced durability [154].
Kureemun et al. [155] and Ramprasad [156] found that replacing a small wt% of jute fiber from the polyester matrix with carbon fiber enhanced the mechanical properties of the composites. Due to the high modulus of carbon fiber reinforcement, it compensated for the shortcomings of jute fiber and enhanced its properties. Ridzuan et al. [157] hybridized grass fiber with glass fiber. They found that the hybridization effect enhanced the composites’ storage modulus and increased the composites’ glass transition temperature. The addition of glass fiber in the matrix increased the resistance against free molecule movement in the polymer chain. A similar effect was observed by Romanzini et al. [158], who found that neat resin had a high damping factor, whereas hybridization exhibited a high modulus.
Thwe et al. [159] compared the mechanical properties of short-fiber bamboo composites with hybrid bamboo–glass–polypropylene composites. They reported that the addition of glass fiber up to 20 wt% enhanced the mechanical characteristic of the composite material. Comparable outcomes were observed by Sreekala et al. [160] and Thwe et al. [161] for hybrid phenol–formaldehyde-based glass and oil-palm fibers. Ahmed and Vijayarangan [162] prepared woven jute fiber with woven glass fiber composites to investigate flexural and tensile strength. They found that the properties of the jute composite improved when the glass fiber was maintained as an external layer. The effects of glass and ramie natural fibers on dynamic mechanical behavior were investigated by Romanzini et al. [157]. They discovered that adding glass fiber to the composite material made it stiffer. Ramesh et al. [163] found that incorporating glass fiber into the jute–sisal composite improved the mechanical properties due to minimized internal cracks. It also improved the rigidity and stiffness of the composite. A similar nature was observed by Kumar et al. [164], who found that the addition of glass fiber to bamboo increased the storage modulus. Anuar et al. [165] observed that the hybridization of carbon and kenaf fibers increased the stiffness of the composite material. Simultaneously, it reduced the damping of the composite material, with similar effects observed by other researchers [166,167,168,169,170]. The inclusion of glass fiber in wood polymer composites increased the wear resistance of the composite due to hybridization effects. The impact characteristics of sisal–glass composites were studied by John and Naidu [171]. They discovered that combining sisal and glass fibers improved the composite’s impact resistance compared to a pure sisal fiber composite. Pothan et al. [172] identified that the addition of glass woven fabric in a banana composite enhanced the composite material’s structural properties. The addition of small amounts of glass fiber also increased the modulus and load-carrying capacities of the composites [173,174]. The influence of glass and jute on the woven fabric-stacking sequence on tensile and flexural characteristics was tested. They found that the inclusion of glass woven mat increased the properties of the jute composite. Valente et al. [175] studied the effect of wood flour and glass fiber in the thermoplastic on its flexural properties. They found that the addition of recycled glass fiber in the wood flour thermoplastic composite enhanced the properties of the composite. Amuthakannan et al. [176] found that combining woven basalt and jute fiber composites with varied stacking sequences improved the composites’ deformation. The impact of glass fiber reinforcement on the mechanical characteristics of sisal and jute fiber composites was investigated by Ramesh et al. [177]. They came to the conclusion that adding glass fiber to composite materials improved their properties. Bennet et al. [178] investigated the dynamic properties of coconut sheath–sansevieria cylindrical fiber composite materials. They found that composites with a coconut sheath–sansevieria cylindrica–coconut sheath stacking sequence enhanced the fundamental natural frequency of the composite material. Kumar et al. [179] analyzed the influence of the layering sequence of coconut sheath and banana fiber on the composite. They observed that composites with a higher amount of banana fiber enhanced the mechanical properties. The influence of sequencing on the dynamic mechanical characteristics of plain-woven jute fabric–carbon composites was investigated by Sezgin et al. [180].
Results showed that composites with carbon fiber as the outer skin layer exhibited enhanced dynamic properties and an increased glass transition temperature of 75 °C. Mochane et al. [181] found that 40 wt% sisal/hemp fiber-reinforced hybrid composite gave the best flexural strength compared to hybrid composites with different wt%. Vaghasia and Rachchh [182] found that 9 wt% bamboo fiber in woven bamboo glass–polyester hybrid composite material gave excellent tensile and flexural properties. Flax fiber reinforced with glass fiber was studied for its mechanical properties as a substitute for bone plate fracture fixation. They found that compared to metallic plates, glass/flax/epoxy hybrid composite was significantly more flexible [183]. Sanjay et al. [184] fabricated a hybrid composite using jute/kenaf and a glass layer, and compared the impact properties with a composite prepared with pure jute, kenaf, and glass fiber composites. Results showed that hybridization improved the impact properties of the composite.
4.2. Hybridization of Natural Fiber with Natural Fiber
Natural fiber composites with two or more types of natural fiber reinforced in the polymer matrix have better inherent properties and are more compatible than conventional materials for low/medium load applications and automobile applications such as home applications, outer car body, agricultural, interior parts, and packing applications. Edhirej et al. [185] found that natural–natural fiber hybridization alters the tensile properties of the composites. Results revealed that the hybridization of natural fiber with other types of natural fiber composites is a suitable alternative to man-made composites. Das [186] hybridized jute fiber polyester composite with an un-shredded newspaper. They used two stacking sequences, such as jute/newspaper/jute and newspaper/jute/ newspaper. They found that the tensile properties of the hybrid composite were higher than pure newspaper/polyester composite but less than pure jute composite. This revealed that the selection of reinforcement for hybridization depends on the types of fiber and its strength. In addition, it was observed from the result that newspaper reinforcement in the jute composite had a short form and random distribution. Thus, it decreased the modulus of the composites and decreased the load-carrying capacity. Fragassa et al. [187] carried out an experimental investigation on the mechanical properties of flax and basalt fibers and their hybridization. The inclusion of flax fiber reduced the basalt fiber composite’s brittleness, enhanced its plastic behavior, and further postponed the composites’ failure. Dhakal et al. [188] analyzed post-impact mechanical properties of basalt/hemp fiber hybrid composites. Hybrid laminates were subjected to impact load (3, 6, and 9 J) and subjected to quasi-static and cyclic flexural tests. It was found that the addition of basalt fiber enhanced the damage tolerance of the hybrid composite. Kona [189] studied banana fiber-reinforced composite mechanical properties using groundnut shell ash as filler. Results revealed that the accumulation of filler enhanced the mechanical properties of the composites, as the addition of filler enhanced the adhesion between the banana fiber and the matrix. The reinforcement of the filler along with the fiber increased the resistance against the crack formation and microvoids. Thus, it enhanced the properties of the composites. Sarasini et al. [190] used ramie and borassus fibers and developed biodegradable composites using polycaprolactone. Results revealed that the ramie fiber composite increased the brittle nature of the composites, whereas borassus enhanced the elasticity of the composites. The inclusion of both fibers in the matrix raised the tensile strength and crystallinity of the composites, demonstrating improved performance. Jumaidin et al. [191] created a hybrid composite using seaweed and sugar-palm fibers with starch as a matrix and discovered that hybridization improved the composites’ tensile characteristics compared to seaweed and sugar-palm-reinforced composites.
Though hybridization addresses the drawbacks of single-fiber reinforcement, the incompatibility of hybrid reinforcement in the hydrophobic matrix is exacerbated by the presence of additional hydroxyl groups in the cellulose and hemicellulose in the fiber cell wall. As a result, the benefits of natural–natural fiber-reinforcing hybridization are diminished. As a consequence, increasing the interfacial bonding strength of hybrid reinforcement and matrix is essential. For example, when two stronger natural fibers are reinforced (jute/flax, jute/hemp, sisal/jute, etc.) in the hydrophobic matrix, it increases the interaction with water molecules present in the environment. The reason behind higher interaction with water molecules associated with stronger natural fibers is that the presence of more cellulose contributes to interaction with moisture. Thus, it reduces the interfacial adhesive bonding. Major parts of cellulose have a significant –OH-to-C ratio, which interacts with water molecules. Cellulose is semi-crystalline, and the crystalline region provides a barrier against water penetration, whereas the amorphous region of the cellulose allows the water molecules to pass through. Therefore, it affects the cellulosic chain and losses its stiffness. Hence, it minimizes the advantages of natural–natural fiber hybridization by increasing the incompatibility between fiber and matrix, generating more microvoids and delamination. King et al. [192] analyzed the influence of bagasse/basalt hybrid reinforcement of polylactic acid (PLA) composites on tensile, flexural, and water absorption behavior. They found that as the amount of fiber increased in the matrix, the weight loss rate increased. This is due to the interaction of moisture increasing the degradation rate of the composites. Gupta and Srivastava [193] analyzed the effect of sisal/jute fiber hybridization on mechanical properties and water absorption behavior. They found the maximum water uptake, sorption, diffusion, and permeability coefficient. Almansour et al. [194] investigated the effect of water absorption on the fracture toughness of flax/basalt-reinforced vinyl ester hybrid composites.
Researchers modified the fiber surface using physical and chemical methods to improve the adhesive strength between fiber and matrix. In the chemical modification, alkali treatment is commonly used by researchers and has been noticed to improve the adhesion between fiber and matrix by removing a substantial amount of hemicellulose and lignin from the fiber cell wall. Kabir et al. [195] used alkali, acetyl, and silane chemical treatments and separated cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin from the hemp fiber. TGA results revealed that hemicellulose degraded faster than cellulose and lignin. They found that the hydrophilic nature of hemp fiber was reduced by treating it with a higher concentration of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), followed by acetylation, whereas silane treatment acted as a coupling agent. The fiber cell wall of Napier fiber collapsed by treating it with 2% and 5% alkali solution [196]. Cao et al. [197] treated bagasse fiber with alkaline solution and found that a lower concentration enhanced the mechanical properties. The bonding strength between the fiber and matrix was further enhanced by changes made to the fiber surface, such as raising the aspect ratio and improving mechanical interlock. Gassan and Bledzki [198] investigated jute/epoxy composite mechanical properties using alkaline treatment. Alkaline treatment enhanced the fiber’s stiffness, which helped to increase the inherent properties of the composite. Other than alkali chemical treatment, silane, acetylation, benzoylation, acrylation, maleated coupling agents, isocyanates, and permanganate have also been used by researchers and have enhanced the properties of composites [199]. Zaman et al. [200] investigated the effects of urea and potassium permanganate on the mechanical characteristics of jute/polypropylene composites. A lower concentration of urea and potassium permanganate improved the mechanical characteristics of the composites, whereas higher concentrations reduced the properties of the composites due to the collapse of the cellulosic structure of the fibers. Morphology analysis revealed that the fibers became thin and rough due to removing a certain quantity of hemicellulose and lignin. NaOCl, NaOCl/NaOH, and H2O2 solution removed the hemicellulose and lignin from green coconut fiber. SEM results revealed that H2O2 removed a high amount of the waxy and fatty acid but did not alter the surface.
In contrast, NaOCl/NaOH minimized the hemicellulose content from the fiber wall. NaOCl treatment did not affect it because it increased the hydrophilic nature of the fiber [200,201]. The storage and loss moduli of jute fiber-reinforced composite was enhanced using an alkaline treatment by Ray et al. [202]. The treatment enhanced the glass transition temperature of the composites. Similarly, researchers adopted physical modification using coating technology to enhance the adhesive strength of the fiber reinforcement in the matrix. Costa et al. [203] used a graphene oxide coating to prepare acuraua fiber-reinforced epoxy composite. Results revealed that surface coating enhanced the adhesion. Kan [204] used plasma treatment and modified the surface properties of textile material. They found that plasma treatment introduced a functional effect. Vellguth et al. [205] enhanced the thermal stability of a natural fiber composite through an epoxy coating on the natural fiber using the spray-coating method. Esen et al. [206] used thermal vacuum evaporation and coated Al and Zn on textile material. Both the coatings improved the electromagnetic interference and UV/IR (ultraviolet/infrared)-shielding properties. Jute fibers were treated with cold argon plasma for 5, 10, and 15 min and reinforced in the polyester matrix. Plasma treatment altered the fiber from hydrophilic to hydrophobic. It enhanced the fiber/matrix adhesion [207].
4.3. Hybridization of Natural Fiber with Filler
A higher contact area associated with filler material helps to establish better bonding between natural fiber reinforcement and polymer matrix, leading to improved mechanical properties by increasing the resistance against debonding and the initiation of cracks and the random propagation of them, and increasing the rigidity of the composites. However, reinforcement by fillers in polymer composites sometimes decreases the composites’ strength, stiffness, and modulus. This is due to the depression of the fillers in the polymer matrix, thus affecting the properties of the composites [208]. In general, oil-palm nanofiller, montmorillonite (MMT), organically modified montmorillonite, fly ash, graphine, carbon nanotube, coir nanofiller, carbon black and cellulosic nanofiller, and rice husk ash fillers are reinforced along with natural fiber reinforcement in the polymer matrix, which leads to enriching the properties of composites [209]. Arrakhiz et al. [210] observed that the weight percentage of clay in the polymer composite enhanced the properties. However, a higher weight percentage showed no improvement in properties. They reinforced clay filler along with pinecone fibers. Results revealed that the addition of clay filler enhanced the properties of the composite for 30 wt% loading, whereas for a higher wt% filler did not show a significant contribution to strength improvement. Njuguna et al. [211] compared the influence of filler diameter on strength and the stiffness of various polymers such as polyesters, polyamides (PAs), polypropylenes (pps), polyurethanes (PUs), and high-performance/temperature engineering polymers such as polyarylacetylene (PAA), polyimide (PI), poly (ether ether ketone) (PEEK), and polyphenylenee benzobisoxazole (PBO). They found that when the particles shrank from macro to sub-micro and nano-level, it led to superior mechanical properties due to the large surface area-to-volume ratio of the fillers. Saba et al. [212] investigated the influence of nano oil-palm empty fruit bunch reinforcement on the dynamic mechanical behavior of the composites. They found that the addition of nano oil-palm empty fruit bunch enhanced the modulus value of the composite, and 3 wt% altered the damping factor. Thus, it increased the usage of structural applications because it required both strength- and energy-dissipating behavior.
Similarly, the tensile properties of madar fiber were enhanced by adding nanoclay to the polyester matrix [213]. The decrement in the mechanical properties of the composite with high filler loading is because the random dispersion of the higher filler loading in the polymers increased the agglomeration. Thus, it increased the incompatibility nature of the enhancement of its strength and stiffness. This is understood from the study carried out by Ravichandran et al. [214]. They reinforced the halloysite nanotube in the epoxy polymer and found that compared to neat epoxy composite, the accumulation of filler decreased the properties of the composites. The reason was the lack of interfacial bonding due to the uniform dispersion of particles. Furthermore, they developed techniques for particle dispersion and found that an ultrasonic homogenized nanocomposite improved the properties of the composites compared to other dispersion methods. Thus, it reveals that the quality of the filler and its dispersion in the polymer influenced the strength and stiffness enhancement of the composites. In addition, it increased the resistance against the failure of the composite by minimizing the initiation of cracks and the random propagation of them in the matrix. Thus, it helped to transfers the stress uniformly from the matrix to the particle under loading.
4.4. Intra-Ply Hybridization
Fiber yarn orientation influences the excellent properties of natural fiber composite. The relatively strong natural fiber yarn orientation in the loading direction exhibits a higher modulus and stiffness in natural fiber composites. In general, natural fiber composites are reinforced in a single-matrix system using natural fiber, synthetic fiber, or filler material to improve their properties. Many researchers investigated the hybridization of natural fiber with synthetic fiber and cellulosic fiber with natural fiber in a polymer matrix in an experimental investigation. They found that hybridization enhanced the mechanical properties of the natural fiber composites compared to natural fiber-reinforced composites alone in the matrix [215,216]. Inter- and intra-ply hybridization is a technique for improving the characteristics of natural fiber composites. Two or more natural fiber yarns are aligned in the warp and weft directions in the hybridization process, avoiding the stacking sequence and fiber orientation of natural fibers in the matrix. Maslinda et al. [217] reinforced the epoxy matrix with interwoven kenaf/jute and kenaf/hemp fabrics and investigated the effect of fiber yarns on the mechanical parameters of the composites. They discovered that hybridization interplay improved the composite’s tensile characteristics due to the presence of more muscular fibers such as kenaf, hemp, and jute in the loading direction, which increased the load-carrying capacity compared to when those fibers were reinforced individually in the matrix. Another reason is that the presence of different yarn fibers in the single woven fabric provided more resistance against fiber yarn failure and compensated for the effect. Figure 6 and Figure 7 shows the various intra-ply hybrid woven mats (natural–natural, natural–glass) [83,181].
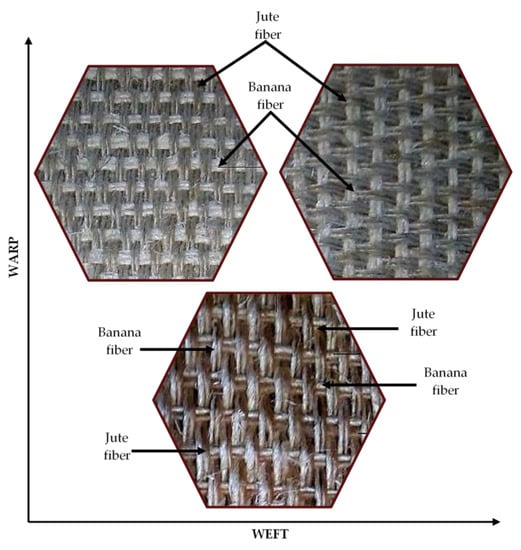
Figure 6.
Various intra-ply hybrid woven natural fiber mats.
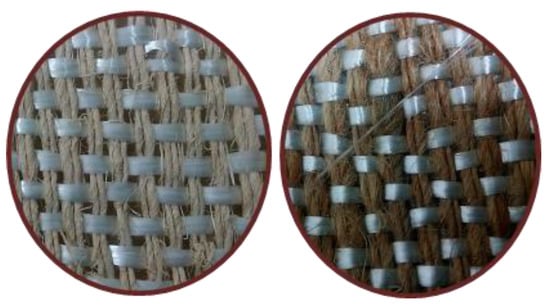
Figure 7.
Different types of intra-ply hybrid woven natural/glass fiber mats.
Park and Jang [218] fabricated intra-ply fabrics using aramid and polyethylene fiber yarn and carried out an experimental investigation on flexural and interlaminar shear strength (ILSS). They found that compared to intra-ply hybridization, aramid fiber oriented in the loading direction enhanced the flexural strength, and intra-ply hybridization exhibited a lower value of ILSS. This was due to the difference in the failure modes in the flexural and ILSS tests. This revealed that a vast difference in the properties of the fiber yarns present in the woven fabric’s warp and weft directions reduced the performance but increased the resistance against failure. In contrast, the tensile and impact characteristics of E-glass fabric reinforced composite were enhanced by hybridization of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) polyester fiber in the fabric. They found that the presence of the PVA fiber in the intra-ply fabric enhanced the specific impact energy of the laminates and increased their resistance to crack propagation [219]. Attia et al. [220] compared the intra- and inter-ply hybrid composition mechanical properties of the composites. Results revealed that the presence of the E-glass and polypropylene improved the intra-ply hybrid composite and enhanced the resistance against tensile and flexural loading more than the inter-ply composite. Dehkordi et al. [221] enhanced the impact behavior of basalt and nylon composite using interplay hybridization. The results showed that impact energy, hybridization, and variation in basalt/nylon fiber content all had an effect on the impact performance of composite plates. The dynamic properties of the jute and banana natural fiber composite were enhanced through intra-ply reinforcement [83]. They analyzed the factors affecting the composites’ modulus and energy-dissipating properties, such as fiber strength, fiber orientation, weaving pattern, and several layers. They found that the relatively stronger jute fiber in the loading direction with braided weaving architecture enhanced the storage modulus.
In contrast, the banana fiber in the loading direction enriched the energy-dissipating properties. However, the combination of jute and banana in the single-woven fabric enhanced both the modulus and the damping factor of the intra-ply hybrid composites. The review found that the selection of fiber and its orientation with the exemplary weaving architecture helped improve the properties of the natural fiber composite through intra and inter-ply hybridization.
5. Braided Reinforcement
Inherent properties of composite material can be enhanced by reinforcing stiff fiber in the polymer matrix. In natural fiber composites, the stiffness of the natural fiber can be enhanced by replacing short natural fibers extracted from the natural source with continuous fiber yarn, which can be substituted into woven form. Though the woven form enhances the stiffness and modulus of the reinforcement, weaving architecture and interlacing between fiber yarn in the warp and weft directions influences the strength and modulus of the composite. Furthermore, to improve the properties of the composites, researchers have used advanced techniques such as braiding and knitting for natural fiber reinforcement. Compared to conventional yarn, braided yarn enhances the modulus value, enhancing the load-carrying behavior of the yarn. Reinforcement of those braided yarns increases the composites’ inherent properties compared to those reinforced using conventional twisted yarn [221]. Furthermore, it can be used as woven fabric, which can improve the properties of the composites, which is incomparable to natural fibers reinforced in any other form. The properties of braided fabrics depend on the braiding angle. A lower braiding angle enhances the strength and modulus value more than a higher braiding angle [222]. Composites reinforced with braided woven fabric are used in a variety of engineering applications, including structural parts, air ducts, and motor car and household applications. In a study comparing the mechanical qualities of braided, woven, and knitted fabric-reinforced natural fiber composites, it was observed that braided woven jute fabric composites had better mechanical characterization than conventional and knitted woven fabric reinforcement. The fabric Young’s modulus was improved by braided-form natural fiber reinforcement, which also improved load resistance. For confirmation, Rajesh and Pitchaimani [54] carried out an experimental investigation on the tensile strength of braided and conventional yarns and their fabrics. Results revealed that the braided woven fabric and its yarn had a higher Young’s modulus than the other types, which helped enhance the composite laminate’s overall performance. The discoveries showed that a banana–jute intra-ply composite was compared to separate banana and jute woven textiles. Individual jute braided fabric increased the mechanical parameters of the braided composite compared to the banana–jute intra-ply composite. In contrast to the normal woven fabric, the intra-ply banana–jute woven fabric increased the mechanical properties of the composite material. They concluded that the kind of yarn had a higher influence on the mechanical properties of composite materials than the fiber strength. The amount of fiber and the degree of twist defined the braided yarn’s strength. Rajesh and Pitchaimani [83] investigated the dynamic mechanical and free vibration properties of composites experimentally. They observed that jute-braided woven fabric improved the composite material’s storage modulus, whereas knitted jute increased the composite material’s loss factor. Because there is a high level of contact between the fibers and the matrix in knitted fabric, the stress concentration between the fibers in the fabric increases, thus, in turn, increasing the energy-dissipating behavior of knitted composites, irrespective of the fiber or yarn. In addition, free vibration studies on braided composites revealed similar variations. The braided composite showed enhanced fundamental natural frequencies irrespective of fiber or yarn arrangement, whereas knitted fabric composites enhanced the damping factors. From these results, it was concluded that composites with woven fabrics and braided yarn enhanced the properties of the composite [54,119]. The potential of braided composites was discussed by Ayranci et al. [222]. They determined that braided composites may be used in a variety of applications without losing stiffness, stability, or strength and that they are an excellent alternative to conventional materials in structural rods, columns, shafts, pressure vessels, and plates. Sun and Qiao [223] conducted experimental and theoretical studies on the mechanical characteristics of braided composites and discovered that the braiding angle affected the composites’ mechanical properties. The volume average compliance approach was utilized by Sun and Sun [224] to assess the mechanical characteristics of the 3D braided composite. They found that, compared to straight yarn-woven fabric, braided-woven fabric greatly improved the mechanical characteristics. The parameters affecting the mechanical characteristics of braided composites were investigated by Goyal et al. [225]. They observed that the mechanical properties were controlled by the braid angle, waviness ratio, and cross-sectional form. Ye et al. [226] investigated the impact characteristics of a sandwich composite in an experimental setting and found that a sandwich composite with a stiff woven fabric as a face layer and two weak knitted core layers improved the properties. The performance of knitted composites for diverse applications was examined by Leong et al. [227]. Muralidhar et al. [228] compared plain-woven composites to knitted fabric composites in terms of flexural properties. The composite with knitted-woven fabric in the outer layer had higher mechanical characteristics, according to the results. Hu et al. [229] discovered similar patterns. They discovered that the 3D knitted basalt increased the composite material’s Young’s modulus and gave better deformation resistance.
6. Knitted Reinforcement
Knitted reinforcement is a special kind of reinforcement that helps overcome the delinquents associated with natural fiber reinforced in short form. It provides good stability and properties compared to unidirectional reinforcement. Woven-fabric reinforcement provides good stability and balances properties in the warp and weft directions due to the high crimp in the warp and weft directions’ tensile modulus of the composites [230,231]. A loop structure associated with knitted fabric tends to deform considerably, but it reduces the mechanical properties of the composites. The development of multi-axial knitted fabric is a good alternative to conventional reinforcement [232]. It can improve the composites’ dynamic properties, as fiber yarns are not crimped [233]. Xue and Hu [234] developed a modified flat knitting machine and fabricated a biaxial weft-knitted structure. The knitted structure lowered the mechanical characteristics of the composites, according to the findings. Muralidhar [235] improved the mechanical characteristics of the composites by using flax plain-woven, rib-knitted fabric. The authors stacked rib-knitted/plain-woven fabric in the epoxy matrix. Results showed that composite with knitted fabric in the outer layer enhanced the flexural and impact properties of the composites. Kannan et al. [236] developed double-faced plain and rib-knitted fabric and found that parallel lamination enhanced the flexural and impact strength of the composites. Carvalho et al. [237] compared the mechanical behavior of plain-woven fabric and knitted fabric-reinforced composites. They observed that woven-reinforced composites outperformed plain weft-knitted fabric composites in terms of mechanical characteristics. Both woven and knitted fabric-reinforced composites had a higher impact strength than plain composites.
7. Conclusions and Future Scope
- The influence of reinforcement on the strength improvement of natural fiber composites was thoroughly examined in this report. Short natural fiber reinforcement with random orientations provides poor resistance under loading due to high-stress concentration and rapid crack propagation. Thus, it increases the water-absorbing behavior and reduces the composites’ mechanical properties due to the significant surface contact of cellulosic natural fiber with moisture available in the environment.
- On the other hand, woven reinforcement enhances the tensile, flexural, and impact strength of natural fiber composite due to the presence of natural fiber in continuous yarn form. Thus, it increases the rigidity of the reinforcement and enriches the properties of the composite. However, it reduces the modulus value of the composites due to the high crimp in the fiber yarn in the warp and weft directions. In addition, various chemical and physical surface treatments were reviewed, and it was shown that they increase the interfacial bonding between fiber and matrix. Further, the hybridization of natural fiber with synthetic fiber, cellulosic fiber, and various fillers was reviewed.
- Furthermore, sophisticated weaving techniques such as braiding and knitting were reviewed, with the conclusion that braided composites significantly improve the characteristics of the composite material.
- Knitted composites, on the other hand, improve the energy dissipation capabilities of the composite materials, implying that braided fabric composites could be used in biological and structural applications.
- In future, natural fiber-reinforced composites should be further studied for their fatigue properties and biocompatible properties for possible considerations in biomedical fields such as orthopedic bone plates, total hip replacement, and prosthesis applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.A., J.K., S.V., R.M. and V.L.N.; writing—original draft preparation, S.A. and V.L.N.; writing—review and editing, M.T.H.S., F.S.S. and A.U.M.S.; supervision, J.K., S.V. and R.M.; project administration, J.K., T.A.S., M.T.H.S., F.S.S., T.K. and A.U.M.S.; funding, M.T.H.S., T.K. and T.A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by VIT SEEDGRANT. The APC was funded by the Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia, through the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme FGRS/1/2019/STG07/UPM/02/2, grant number 5540320.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore, for funding this research by VIT SEEDGRANT. The authors would like to thank the Department of Aerospace Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia, and the Laboratory of Bio-composite Technology, Institute of Tropical Forestry and Forest Product (INTROP), Universiti Putra Malaysia (HICOE), for the close collaboration in this research. The authors would like to acknowledge the support of Prince Sultan University for paying the Article Processing Charges (APC) for this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Foulk, J.A.; Akin, D.E.; Dodd, R.B. New Low Cost Flax Fibers for Composites. SAE Technol. Pap. Ser. 2000, 1, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateshwaran, N.; Elayaperumal, A. Banana Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites—A Review. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2010, 29, 2387–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.V.; Drzal, L.T.; Mohanty, A.K.; Arora, S. Are natural fiber composites environmentally superior to glass fiber reinforced composites? Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2004, 35, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbery, J.; Houston, D. Natural-fiber-reinforced polymer composites in automotive applications. JOM 2006, 58, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, T.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. A review of the recent developments in biocomposites based on natural fibres and their application perspectives. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 77, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargiullo, L.; Del Chierico, F.; D’Argenio, P.; Putignani, L. Gut microbiota modulation for multidrug-resistant organism decoloni-zation: Present and future perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Oqla, F.M. Sapuan, S.M. Natural fiber reinforced polymer composites in industrial applications: Feasibility of date palm fibers for sustainable automotive industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 66, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthanarieswaran, V.P.; Kumaravel, A.; Kathirselvam, M. Evaluation of mechanical properties of banana and sisal fiber reinforced epoxy composites: Influence of glass fiber hybridization. Mater. Des. 2014, 64, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundhar, A.; Jayakrishna, K. Investigations on mechanical and morphological characterization of chitosan reinforced polymer nanocomposites. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjay, M.R.; Madhu, P.; Jawaid, M.; Senthamaraikannan, P.; Senthil, S.; Pradeep, S. Characterization and properties of natural fiber polymer composites: A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 566–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, M.U.; Siddique, A.; Abraha, K.G.; Yao, L.; Li, W.; Khan, M.Q.; Kim, I.S. Performance Evaluation of Jute/Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) Hybrid Composites with Different Layering Configurations. Materials 2022, 15, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, T.; Reddy, H.J. Strengthening of RC beams in flexure using natural jute fibre textile reinforced composite system and its comparative study with CFRP and GFRP strengthening systems. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2013, 2, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sapuan, S.M.; Maleque, M.A. Design and fabrication of natural woven fabric reinforced epoxy composite for household telephone stand. Mater. Des. 2005, 26, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.; Ferrão, P.; Silva, A.J.; Reis, L.G.; Freitas, M.; Rodrigues, L.B.; Alves, D.E. Ecodesign of automotive components making use of natural jute fiber composites. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoodi, M.M.; Sapuan, M.S.M.; Ahmad, D.; Ali, A.; Khalina, A.; Jonoobi, M. Mechanical properties of hybrid kenaf/glass reinforced epoxy composite for passenger car bumper beam. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 4927–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodaran, A.; Mansour, H.; Lessard, L.; Scavone, G.; Babu, A.S. Application of composite materials to the chenda, an Indian percussion instrument. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 88, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Shuai, H.; Cheng, Q.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired green composite lotus fibers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 3358–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Zhang, L. Aligned ramie fiber reinforced arylated soy protein composites with improved properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, A. Hemp fiber and its composites–A review. J. Compos. Mater. 2012, 46, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, S.M.; Hassan, M.L.; Oksman, K. Improving tensile strength and moisture barrier properties of gelatin using microfibrillated cellulose. J. Compos. Mater. 2013, 47, 1977–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, A.; Dweib, M.; Wool, R. Natural fiber composites with plant oil-based resin. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2004, 64, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abral, H.; Kadriadi, D.; Rodianus, A.; Mastariyanto, P.; Ilhamdi; Arief, S.; Sapuan, S.; Ishak, M. Mechanical properties of water hyacinth fibers—Polyester composites before and after immersion in water. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayandi, K.; Rajini, N.; Pitchipoo, P.; Sreenivasan, V.; Jappes, J.W.; Alavudeen, A. A comparative study on characterisations of Cissus quadrangularis and Phoenix reclinata natural fibres. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2015, 34, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoti, A.; Soundhar, A.; Rajesh, M.; Jayakrishna, K.; Hameed, M.T. Enhancement of mechanical properties of an epoxy composite reinforced with Hibiscuss sabdariffa var. altissima fiber micro cellulose. Int. J. Recent Technol. 2019, 8, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnik, E.; Briassoulis, D. Comparative Biodegradation in Soil Behaviour of two Biodegradable Polymers Based on Renewable Resources. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 19, 18–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.R.; Monterio, S.N.; Terrones, L.A. Mechanical properties of coir/polyester composites. Elsevier Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 591–595. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, P.V.; Joseph, K.; Thomas, S. Effect of processing variables on the mechanical properties of sisal-fiber-reinforced polypro-pylene composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1999, 59, 1625–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arib, R.M.; Sapuan, S.M.; Ahmad, M.M.; Paridah, M.T.; Zaman, H.K. Mechanical properties of pineapple leaf fibre reinforced poly-propylene composites. Mater. Des. 2006, 27, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shekeil, Y.A.; Sapuan, S.M.; Abdan, K.; Zainudin, E.S. Influence of fiber content on the mechanical and thermal properties of Kenaf fiber reinforced thermoplastic polyurethane composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idicula, M.; Malhotra, S.K.; Joseph, K.; Thomas, S. Dynamic mechanical analysis of randomly oriented intimately mixed short ba-nana/sisal hybrid fibre reinforced polyester composites. Compos. Sci. Tech. 2005, 65, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, T.-T.-L.; Brodowsky, H.; Mäder, E. Jute fibre/polypropylene composites II. Thermal, hydrothermal and dynamic mechanical behaviour. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 2707–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothan, L.A.; Oommen, Z.; Thomas, S. Dynamic mechanical analysis of banana fiber reinforced polyester composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.S.; Siva, I.; Jeyaraj, P.; Jappes, J.W.; Amico, S.C.; Rajini, N. Synergy of fiber length and content on free vibration and damping behavior of natural fiber reinforced polyester composite beams. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tayeb, N. A study on the potential of sugarcane fibers/polyester composite for tribological applications. Wear 2008, 265, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalwan, A.; Yousif, B.F. In State of Art: Mechanical and tribological behaviour of polymeric composites based on natural fibres. Mater. Des. 2013, 48, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, B.F.; El-Tayeb, N.S.M. The effect of oil palm fibers as reinforcement on tribological performance of polyester composite. Surf. Rev. Lett. 2007, 14, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, S.A.; Gibson, R.F.; Sun, C.T.; Chaturvedi, S.K. The influence of fiber length and fiber orientation on damping and stiffness of polymer composite materials. Exp. Mech. 1986, 26, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.J.; Thomas, S. Biofibres and biocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Pothan, L.A.; Cherian, B.M. Natural fibre reinforced polymer composites: From macro to nanoscale. Arch. Contemp. 2009, 36, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavudeen, A.; Rajini, N.; Karthikeyan, S.; Thiruchitrambalam, M.; Venkateshwaren, N. Mechanical properties of banana/kenaf fiber-reinforced hybrid polyester composites: Effect of woven fabric and random orientation. Mater. Des. 2015, 66, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, M.; Deepa, C. Processing of Green Composites. In Textile Science and Clothing Technology; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 47–72. [Google Scholar]
- Saheb, D.N.; Jog, J.P. Natural fiber polymer composites: A review. Adv. Polym. Technol. J. Polym. Process. Inst. 1999, 18, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez, C.; Durán, A.; Valdez-Tamez, P.L.; Fajardo, G. Performance of “Agave lecheguilla” natural fiber in portland cement composites exposed to severe environment conditions. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, A.K.; Mamun, A.A.; Faruk, O. Abaca fibre reinforced PP composites and comparison with jute and flax fibre PP composites. Express Polym. Lett. 2007, 1, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Kasal, B.; Huang, L. A review of recent research on the use of cellulosic fibres, their fibre fabric reinforced cementitious, geo-polymer and polymer composites in civil engineering. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 92, 94–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, M.; Jawaid, M.; Abdan, K.; Ishak, M.R.; Alothman, O.Y. Effect of Hybridization on the Mechanical Properties of Pineapple Leaf Fiber/Kenaf Phenolic Hybrid Composites. J. Renew. Mater. 2018, 6, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwaikambo, L.Y.; Martuscelli, E.; Avella, M. Kapok/cotton fabric–polypropylene composites. Polym. Test. 2000, 19, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapuan, S.; Leenie, A.; Harimi, M.; Beng, Y. Mechanical properties of woven banana fibre reinforced epoxy composites. Mater. Des. 2006, 27, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennet, C.; Rajini, N.; Winowlin Jappes, J.T.; Venkatesh, A.; Harinarayanan, S.; Vinothkumar, G. Effect of Lamina Fiber Orientation on Tensile and Free Vibration (by Impulse Hammer Technique) Properties of Coconut Sheath/Sansevieria cylindrica Hybrid Composites. AMR 2014, 984–985, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmisciano, S.; De Rosa, I.M.; Sarasini, F.; Tamburrano, A.; Valente, M. Basalt woven fiber reinforced vinylester composites: Flexural and electrical properties. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateshwaran, N.; ElayaPerumal, A.; Raj, R.A. Mechanical and dynamic mechanical analysis of woven banana/epoxy com-posite. J. Polym. Environ. 2012, 20, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariatti, M.; Jannah, M.; Abu Bakar, A.; Khalil, H.A. Properties of Banana and Pandanus Woven Fabric Reinforced Unsaturated Polyester Composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2008, 42, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, G.A.; Terano, M.; Gafur, M.; Alam, M.S. Studies on the mechanical properties of woven jute fabric reinforced poly(l-lactic acid) composites. J. King Saud Univ.—Eng. Sci. 2016, 28, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajesh, M.; Pitchaimani, J. Mechanical Properties of Natural Fiber Braided Yarn Woven Composite: Comparison with Conventional Yarn Woven Composite. J. Bionic Eng. 2017, 14, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutianos, S.; Peijs, T.; Nystrom, B.; Skrifvars, M.O.V. Development of Flax Fibre based Textile Reinforcements for Composite Applications. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2006, 13, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pothan, L.A.; Mai, Y.-W.; Thomas, S.; Li, R. Tensile and Flexural Behavior of Sisal Fabric/Polyester Textile Composites Prepared by Resin Transfer Molding Technique. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2008, 27, 1847–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, S.; Cao, Y.; Fukumoto, I. Flexural modulus of the unidirectional and random composites made from biodegradable resin and bamboo and kenaf fibres. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandekar, H.; Chaudhari, V.; Waigaonkar, S. A review of jute fiber reinforced polymer composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 2079–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darshan, S.M.; Suresha, B. Effect of basalt fiber hybridization on mechanical properties of silk fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 43, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.N.; Sulong, A.B.; Radzi, M.K.F.M.; Ismail, N.; Raza, M.; Muhamad, N.; Khan, M.A. Influence of alkaline treatment and fiber loading on the physical and mechanical properties of kenaf/polypropylene composites for variety of applications. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2016, 26, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Srivastava, R. Tensile and Flexural Properties of Sisal Fibre Reinforced Epoxy Composite: A Comparison between Unidirectional and Mat form of Fibres. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 5, 2434–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, T.; Huang, H.; Wu, G.; Sun, E.; Jin, X.; Tang, W. The characteristic changes of rice straw fibers in anaerobic digestion and its effect on rice straw-reinforced composites. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 121, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odusote, J.K.; Oyewo, A.T. Mechanical properties of pineapple leaf fiber reinforced polymer composites for application as a prosthetic socket. J. Eng. Technol. 2016, 7, 125–139. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo-Salazar, M.A.; Salinas, E. Mechanical, thermal, viscoelastic performance and product application of PP-rice husk Co-lombian biocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 176, 107135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrandez-Garcia, M.T.; Ferrandez-Garcia, C.E.; Garcia-Ortuño, T.; Ferrandez-Garcia, A.; Ferrandez-Villena, M. Experimental Evaluation of a New Giant Reed (Arundo donax L.) Composite Using Citric Acid as a Natural Binder. Agronomy 2019, 9, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgiopoulos, P.; Christopoulos, A.; Koutsoumpis, S.; Kontou, E. The effect of surface treatment on the performance of flax/biodegradable composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 106, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, T.; Naveen, J.; Navaneethakrishnan, P.; Satheeshkumar, S.; Rajini, N. Characterization of sisal/cotton fibre woven mat reinforced polymer hybrid composites. J. Ind. Text. 2016, 47, 429–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagamani, S.M.K.; Krishnasamy, S.; Muthukumar, C.; Tengsuthiwat, J.; Nagarajan, R.; Siengchin, S.; Ismail, S.O. Investigation into mechanical, absorption and swelling behaviour of hemp/sisal fibre reinforced bioepoxy hybrid composites: Effects of stacking sequences. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundhar, A.; Kandasamy, J. Mechanical, Chemical and Morphological Analysis of Crab shell/Sisal Natural Fiber Hybrid Composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2021, 18, 1518–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, D.J.D.; Manoharan, S.; Saikrishnan, G.; Arjun, S. Influence of bagasse/sisal fibre stacking sequence on the mechanical characteristics of hybrid-epoxy composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2020, 17, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Bajpai, P.K.; Maheshwari, S. An investigation on wear and dynamic mechanical behavior of jute/hemp/flax reinforced composites and its hybrids for tribological applications. Fibers Polym. 2018, 19, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, G.S.; Shanmugasundar, G.; Vanitha, M.; Sivashanmugam, N. Mechanical Properties of Chemically Treated Banana and Ramie Fibre Reinforced Polypropylene Composites. IOP Conf. Series Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 961, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, A.; Sivaramakrishnan, K.; Karthikeyan, B.; Purushothaman, R.; Swaminathan, J.; Kannan, S.; Udhayasankar, R.; Madieen, A.H. Study on mechanical and morphological properties of sisal/banana/coir fiber-reinforced hybrid polymer composites. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2019, 41, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.; Farag, M.; Megahed, H.; Mehanny, S. Characteristics of starch-based biodegradable composites reinforced with date palm and flax fibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Grewal, J.S.; Singh, T.; Kumar, N. Mechanical and thermal properties of chemically treated Kenaf natural fiber rein-forced polymer composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, S.; Sozhamannan, G.G.; Saravanan, L.; Venkatachalapathy, V.S. Study on mechanical behaviour of natural fiber rein-forced vinylester hybrid composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 4526–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, G.S.; Shanmugasundar, G.; Vanitha, M.; Srinivasan, S.; Suresh, G. Investigation on the Mechanical and Morphological Properties of Red banana/Ramie Fiber vinyl ester composites. IOP Conf. Series Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 961, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaduman, Y.; Onal, L.; Rawal, A. Effect of stacking sequence on mechanical properties of hybrid flax/jute fibers reinforced thermoplastic composites. Polym. Compos. 2015, 36, 2167–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.M.S.; Duraibabu, D.; Subramanian, K. Studies on mechanical, thermal and dynamics mechanical properties of untreated (raw) and treated coconut sheath fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Mater. Des. 2014, 59, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, S.; Gunda, Y.; Mohan, S.R.; Raghunathan, V.; Dhilip, J.D. Influence of stacking sequence on the mechanical and water absorption characteristics of areca sheath-palm leaf sheath fibers reinforced epoxy composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Shah, A.U.M.; Ariffin, A.H.; Jawaid, M. The Effects of Stacking Sequence on the Tensile and Flexural Properties of Kenaf/Jute Fibre Hybrid Composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2021, 18, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathish, P.; Kesavan, R.; Ramnath, B.V.; Vishal, C. Effect of Fiber Orientation and Stacking Sequence on Mechanical and Thermal Characteristics of Banana-Kenaf Hybrid Epoxy Composite. Silicon 2017, 9, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, M.; Pitchaimani, J. Dynamic mechanical analysis and free vibration behavior of intra-ply woven natural fiber hybrid polymer composite. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2015, 35, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.H.; Ansell, M.P. The effect of alkalization and fibre alignment on the mechanical and thermal properties of kenaf and hemp bast fibre composites: Part 1—Polyester resin matrix. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2004, 64, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Franco, P.J.; Valadez-González, A. A study of the mechanical properties of short natural-fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2005, 36, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethamma, V.G.; Kalaprasad, G.; Groeninckx, G.; Thomas, S. Dynamic mechanical behavior of short coir fiber reinforced natural rubber composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2005, 36, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.K.; Dewan, M.W.; Hosur, M.; Jeelani, S. Mechanical performances of surface modified jute fiber reinforced biopol nanophased green composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2011, 42, 1701–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essabir, H.; Elkhaoulani, A.; Benmoussa, K.; Bouhfid, R.; Arrakhiz, F.; Qaiss, A.E.K. Dynamic mechanical thermal behavior analysis of doum fibers reinforced polypropylene composites. Mater. Des. 2013, 51, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L. Effect of alkali treatment on vibration characteristics and mechanical properties of natural fabric reinforced composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2012, 31, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.S.; Siva, I.; Rajini, N.; Jeyaraj, P.; Jappes, J.W. Tensile, impact, and vibration properties of coconut sheath/sisal hybrid composites: Effect of stacking sequence. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 1802–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indira, K.N.; Jyotishkumar, P.; Thomas, S. Viscoelastic behaviour of untreated and chemically treated banana Fiber/PF composites. Fibers Polym. 2014, 15, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajini, N.; Jappes, J.T.W.; Jeyaraj, P.; Rajakarunakaran, S.; Bennet, C. Effect of montmorillonite nanoclay on temperature dependence mechanical properties of naturally woven coconut sheath/polyester composite. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2013, 32, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabu, V.A.; Uthayakumar, M.; Manikandan, V.; Rajini, N.; Jeyaraj, P. Influence of redmud on the mechanical, damping and chemical resistance properties of banana/polyester hybrid composites. Mater. Des. 2014, 64, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negawo, T.A.; Polat, Y.; Buyuknalcaci, F.N.; Kilic, A.; Saba, N.; Jawaid, M. Mechanical, morphological, structural and dynamic me-chanical properties of alkali treated Ensete stem fibers reinforced unsaturated polyester composites. Compos. Struct. 2019, 207, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheith, M.H.; Aziz, M.A.; Ghori, W.; Saba, N.; Asim, M.; Jawaid, M.; Alothman, O.Y. Flexural, thermal and dynamic mechanical properties of date palm fibres reinforced epoxy composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satapathy, S.; Kothapalli, R.V.S. Mechanical, Dynamic Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Banana Fiber/Recycled High Density Polyethylene Biocomposites Filled with Flyash Cenospheres. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doddi, P.R.V.; Chanamala, R.; Dora, S.P. Effect of fiber orientation on dynamic mechanical properties of PALF hybridized with basalt reinforced epoxy composites. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 015329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalusuraman, G.; Siva, I.; Munde, Y.; Pon Selvan, C.; Kumar, S.A.; Amico, S.C. Dynamic-mechanical properties as a function of luffa fibre content and adhesion in a polyester composite. Polym. Test. 2020, 87, 106538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangueiro, R.; Rana, S. Natural Fibres: Advances in Science and Technology towards Industrial Applications; Fangueiro, R., Rana, S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, K.M. Engineering Materials: Research, Applications and Advances; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jawaid, M.; Khalil, H.A.; Alattas, O.S. Woven hybrid biocomposites: Dynamic mechanical and thermal properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, M.; Jawaid, M.; Abdan, K.; Ishak, M.R. Effect of pineapple leaf fibre and kenaf fibre treatment on mechanical performance of phenolic hybrid composites. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, M.; Langella, A.; Formisano, A.; Boccarusso, L.; Carrino, L. Dynamic-Mechanical Behaviour of Bio-composites. Procedia Eng. 2016, 167, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, M.; Ishak, M.R.; Sapuan, S.M.; Leman, Z.; Jawaid, M. A review on the characterisation of natural fibres and their composites after alkali treatment and water absorption. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2017, 46, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandradass, J.; Kumar, M.R.; Velmurugan, R. Effect of nanoclay addition on vibration properties of glass fibre reinforced vinyl ester composites. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 4385–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.F. A review of recent research on mechanics of multifunctional composite materials and structures. Compos. Struct. 2010, 92, 2793–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambua, P.; Ivens, J.; Verpoest, I. Natural fibres: Can they replace glass in fibre reinforced plastics? Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, S.; Kaith, B.; Kaur, I. Pretreatments of natural fibers and their application as reinforcing material in polymer composites-A review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 1253–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, Y.M. Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials: Volume 2: Dynamic Loading and Intelligent Material Systems; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Chou, T.-W. Free vibration analysis of orthogonal-woven fabric composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1999, 30, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouf, K.; Denton, N.L.; French, R.M. Effect of fabric weaves on the dynamic response of two-dimensional woven fabric composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 10581–10591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, F.; Bourban, E.; Manson, E. Damping performance of flax fibre composites. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Composite Materials, Seville, Spain, 22–26 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Tan, J.; Fernandes, L.; Qu, Z.; Li, Y. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis on Delaminated Flax Fiber Reinforced Composites. Material 2019, 12, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, I.; Sahu, S.K. Modal Analysis of Woven Fiber Composite Plates with Different Boundary Conditions. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2015, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, R.; Singh, S.P.; Gupta, K. Damping studies in fiber-reinforced composites–A review. Compos. Struct. 1999, 46, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akash, D.A.; Thyagaraj, N.R.; Sudev, L.J. Experimental study of dynamic behaviour of hybrid jute/sisal fibre reinforced polyester composites. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2013, 2, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajini, N.; Jappes, J.W.; Rajakarunakaran, S.; Jeyaraj, P. Dynamic mechanical analysis and free vibration behavior in chemical modifications of coconut sheath/nano-clay reinforced hybrid polyester composite. J. Compos. Mater. 2013, 47, 3105–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, M.; Jeyaraj, P.; Rajini, N. Mechanical, Dynamic Mechanical and Vibration Behavior of Nanoclay Dispersed Natural Fiber Hybrid Intra-ply Woven Fabric Composite. In Nanoclay Reinforced Polymer Composites; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 281–296. [Google Scholar]
- Rajesh, M.; Pitchaimani, J. Dynamic mechanical and free vibration behavior of natural fiber braided fabric composite: Com-parison with conventional and knitted fabric composites. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 2479–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, M.; Pitchaimani, J.; Rajini, N. Free Vibration Characteristics of Banana/Sisal Natural Fibers Reinforced Hybrid Polymer Composite Beam. Procedia Eng. 2016, 144, 1055–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajesh, M.; Pitchaimani, J. Experimental investigation on buckling and free vibration behavior of woven natural fiber fabric composite under axial compression. Compos. Struct. 2017, 163, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansor, M.; Sapuan, S.; Zainudin, E.; Nuraini, A.; Hambali, A. Hybrid natural and glass fibers reinforced polymer composites material selection using Analytical Hierarchy Process for automotive brake lever design. Mater. Des. 2013, 51, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, G.P.; Moisés, M.P.; Carvalho, G.; Rinaldi, A.W.; Garcia, J.C.; Radovanovic, E.; Fávaro, S.L. Mechanical properties of a polyurethane hybrid composite with natural lignocellulosic fibers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 110, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna Venkatesh, R.; Ramanathan, K.; Srinivasa Raman, V. Tensile, flexual, impact and water absorption properties of natural fibre reinforced polyester hybrid composites. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2016, 117, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Bajpai, P.K.; Maheshwari, S. Studies on Mechanical and Morphological Characterization of Developed Jute/Hemp/Flax Reinforced Hybrid Composites for Structural Applications. J. Nat. Fibers 2018, 15, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanavel, V.; Raja, T.; Yadav, A.; Ravichandran, M.; Winczek, J. Evaluation of Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Jute and Ramie Reinforced Epoxy-based Hybrid Composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2021, 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedom, F.; Sakthivel, S.; Asfaw, D.; Melese, B.; Solomon, E.; Kumar, S.S. Development of Natural Fiber Hybrid Composites Using Sugarcane Bagasse and Bamboo Charcoal for Automotive Thermal Insulation Materials. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmakuri, A.; Palevicius, A.; Kolli, L.; Vilkauskas, A.; Janusas, G. Development and Analysis of Mechanical Properties of Caryota and Sisal Natural Fibers Reinforced Epoxy Hybrid Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.L.; Banea, M.D.; Neto, J.S.; Cavalcanti, D.K. Mechanical and Thermal Characterization of Natural Intralaminar Hybrid Composites Based on Sisal. Polymers 2020, 12, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Senthilkumar, K.; Siva, I.; Rajini, N.; Jappes, J.W.; Siengchin, S. Mechanical characteristics of tri-layer eco-friendly polymer composites for interior parts of aerospace application. In Sustainable Composites for Aerospace Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, M.; Ajith Arul, D.; Nithya, S.M.; Kumar, S.; Pugazhenthi, R. Characterization of natural–Synthetic fiber reinforced epoxy based composite–Hybridization of kenaf fiber and kevlar fiber. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 37, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Živković, I.; Fragassa, C.; Pavlović, A.; Brugo, T. Influence of moisture absorption on the impact properties of flax, basalt and hybrid flax/basalt fiber reinforced green composites. Compos. B Eng. 2017, 111, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Shah, A.U.M.; Safri, S.N.A. Investigations on fatigue analysis and biomimetic mineralization of glass fiber/sisal fiber/chitosan reinforced hybrid polymer sandwich composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 10, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasini, F.; Tirillò, J.; D’Altilia, S.; Valente, T.; Santulli, C.; Touchard, F.; Chocinski-Arnault, L.; Mellier, D.; Lampani, L.; Gaudenzi, P. Damage tolerance of carbon/flax hybrid composites subjected to low velocity impact. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 91, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapuan, S.M.; Aulia, H.S.; Ilyas, R.A.; Atiqah, A.; Dele-Afolabi, T.T.; Nurazzi, M.N.; Supian, A.B.M.; Atikah, M.S.N. Mechanical Properties of Longitudinal Basalt/Woven-Glass-Fiber-reinforced Unsaturated Polyester-Resin Hybrid Composites. Polymers 2020, 12, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhudi, N.Z.; Lin, R.J.; Jayaraman, K. Flammability, thermal and dynamic mechanical properties of bamboo–glass hybrid com-posites. J. Compos. Mater. 2016, 29, 1210–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baihaqi, N.N.M.Z.; Khalina, A.; Mohd Nurazzi, N.; Aisyah, H.A.; Sapuan, S.M.; Ilyas, R.M. Effect of fiber content and their hybridization on bending and torsional strength of hybrid epoxy composites reinforced with carbon and sugar palm fibers. Polimery 2021, 66, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothibasu, S.; Mohanamurugan, S.; Vijay, R.; Lenin Singaravelu, D.L.; Vinod, A.; Sanjay, M.R. Investigation on the mechanical behavior of areca sheath fibers/jute fibers/glass fabrics reinforced hybrid composite for light weight applications. J. Ind. Text. 2020, 49, 1036–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandaru, A.K.; Patel, S.; Sachan, Y.; Alagirusamy, R.; Bhatnagar, N.; Ahmad, S. Low velocity impact response of 3D angle-interlock Kevlar/basalt reinforced polypropylene composites. Mater. Des. 2016, 105, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, S.D.; Sharba, M.J.; Leman, Z.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Ishak, M.R.; Cardona, F. Tension-Compression Fatigue Behavior of Plain Woven Kenaf/Kevlar Hybrid Composites. Bioresources 2016, 11, 3575–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Sharif, A.; Hussain, M.; Hassan, I. Synergic effect of recycled cotton fabric and wood saw dust reinforced biodegradable polypropylene composites. Bangladesh J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2019, 54, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, P.V.; Prasad, P.R.; Krishnudu, D.M.; Hussain, P. Influence of fillers on mechanical properties of prosopis juliflora fiber rein-forced hybrid composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 19, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, N.; Alothman, O.Y.; Almutairi, Z.; Jawaid, M. Magnesium hydroxide reinforced kenaf fibers/epoxy hybrid composites: Mechanical and thermomechanical properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, T.V.; Chowdary, M.S.; Babu, C.S.S.; Sumanth, C.M. Effect of Bamboo Fiber on Mechanical Properties of Fly Ash with Polypropylene Composites. In Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 437–446. [Google Scholar]
- Abdellaoui, H.; Raji, M.; Essabir, H.; Bouhfid, R.; Qaiss, A.E.K. Mechanical behavior of carbon/natural fiber-based hybrid composites. In Mechanical and Physical Testing of Biocomposites, Fibre-Reinforced Composites and Hybrid Composites; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 103–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kauser, B.; Upadhyay, V.; Chak, V.; Hasan, F. Moisture Absorption Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Banana Fiber-Reinforced Fly Ash/Epoxy Composites. In Innovation in Materials Science and Engineering; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, T.; Gangil, B.; Ranakoti, L.; Joshi, A. Effect of silica nanoparticles on physical, mechanical, and wear properties of natural fiber reinforced polymer composites. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 2396–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, Y.; Gangil, B.; Patel, V.K. Effects of Agro-Waste and Bio-Particulate Fillers on Mechanical and Wear Properties of Sisal Fibre Based Polymer Composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 10144–10147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udaya Kumar, P.A.; Suresha, B.; Rajini, N.; Satyanarayana, K.G. Effect of treated coir fiber/coconut shell powder and aramid fiber on mechanical properties of vinyl ester. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 4542–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbakumar, J.P.; Ramesh, S. Mechanical, wear and thermal behaviour of hemp fibre/egg shell particle reinforced epoxy resin bio composite. Trans. Can. Soc. Mech. Eng. 2018, 42, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisaria, H.; Gupta, M.K.; Shandilya, P.A.; Srivastava, R. Effect of Fibre Length on Mechanical Properties of Randomly Oriented Short Jute Fibre Reinforced Epoxy Composite. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Srivastava, R. Effect of Sisal Fibre Loading on Dynamic Mechanical Analysis and Water Absorption Behaviour of Jute Fibre Epoxy Composite. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 2909–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthapulakkal, S.; Sain, M. Studies on the water absorption properties of short hemp—Glass fiber hybrid polypropylene com-posites. J. Compos. Mater. 2007, 41, 1871–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Shi, S.Q.; Cai, L.; Hua, J. Property enhancement of kenaf fiber composites by means of vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding (VARTM). Holzforschung 2015, 69, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kureemun, U.; Ravandi, M.; Tran, L.Q.; Teo, W.S.; Tay, T.E.; Lee, H.P. Effects of hybridization and hybrid fibre dispersion on the me-chanical properties of woven flax-carbon epoxy at low carbon fibre volume fractions. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 134, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, M.V.; Ramprasad, S. Experimental Investigation on Jute/Carbon Fibre reinforced Epoxy based Hybrid Composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 8654–8664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanzini, D.; Ornaghi, H.L., Jr.; Amico, S.C.; Zattera, A.J. Influence of fiber hybridization on the dynamic mechanical properties of glass/ramie fiber-reinforced polyester composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2012, 31, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanzini, D.; Lavoratti, A.; Ornaghi, H.L., Jr.; Amico, S.C.; Zattera, A.J. Influence of fiber content on the mechanical and dynamic mechanical properties of glass/ramie polymer composites. Mater. Des. 2013, 47, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thwe, M.M.; Liao, K. Effects of environmental aging on the mechanical properties of bamboo–glass fiber reinforced polymer matrix hybrid composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2002, 33, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekala, M.S.; George, J.; Kumaran, M.G.; Thomas, S. The mechanical performance of hybrid phenol-formaldehyde-based compo-sites reinforced with glass and oil palm fibres. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thwe, M.M.; Liao, K. Durability of bamboo-glass fiber reinforced polymer matrix hybrid composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.S.; Vijayarangan, S. Withdrawn: Tensile, flexural and interlaminar shear properties of woven jute and jute-glass fabric reinforced polyester composites. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 207, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, M.; Palanikumar, K.; Reddy, K.H. Mechanical property evaluation of sisal–jute–glass fiber reinforced polyester compo-sites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 48, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Samal, S.K.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Epoxidized Soybean Oil-Based Epoxy Blend Cured with Anhydride-Based Cross-Linker: Thermal and Mechanical Characterization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar, H.; Ahmad, S.H.; Rasid, R.; Ahmad, A.; Busu, W.W. Mechanical properties and dynamic mechanical analysis of thermo-plastic-natural-rubber-reinforced short carbon fiber and kenaf fiber hybrid composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 4043–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.K.; Mohanty, S.; Samal, S.K. Influence of short bamboo/glass fiber on the thermal, dynamic mechanical and rheological properties of polypropylene hybrid composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 523, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, L.U.; Bhagawan, S.; Thomas, S. Dynamic mechanical analysis of pineapple leaf/glass hybrid fiber reinforced polyester composites. Polym. Compos. 2009, 31, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornaghi, H.L., Jr.; Bolner, A.S.; Fiorio, R.; Zattera, A.J.; Amico, S.C. Mechanical and dynamic mechanical analysis of hybrid composites molded by resin transfer molding. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 118, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.K.; Mohanty, S. Sisal Glass Fiber Reinforced PP Hybrid Composites: Effect of MAPP on the Dynamic Mechanical and Thermal Properties. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2009, 29, 1551–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kositchaiyong, A.; Rosarpitak, V.; Prapagdee, B.; Sombatsompop, N. Molecular characterizations, mechanical properties and anti-algal activities for PVC and wood/PVC composites containing urea- and triazine-based algaecides. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 53, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, K.; Naidu, S.V. Sisal Fiber/Glass Fiber Hybrid Composites: The Impact and Compressive Properties. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2004, 23, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothan, L.A.; Potschke, P.; Habler, R.; Thomas, S. The Static and Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Banana and Glass Fiber Woven Fabric-Reinforced Polyester Composite. J. Compos. Mater. 2005, 39, 1007–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuciel, S.; Bazan, P.; Liber-Kneć, A.; Gądek-Moszczak, A. Physico-Mechanical Properties of the Poly(oxymethylene) Composites Reinforced with Glass Fibers under Dynamical Loading. Polymers 2019, 11, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Selver, E.; Ucar, N.; Gulmez, T. Effect of stacking sequence on tensile, flexural and thermomechanical properties of hybrid flax/glass and jute/glass thermoset composites. J. Ind. Text. 2018, 48, 494–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M.; Sarasini, F.; Marra, F.; Tirillò, J.; Pulci, G. Hybrid recycled glass fiber/wood flour thermoplastic composites: Manufacturing and mechanical characterization. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amuthakkannan, P.; Manikandan, V.; Jappes, J.T.W.; Uthayakumar, M. Influence of stacking sequence on mechanical properties of basalt-jute fiber-reinforced polymer hybrid composites. J. Polym. Eng. 2012, 32, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, M.; Palanikumar, K.; Reddy, K.H. Comparative evaluation on properties of hybrid glass fiber-sisal/jute reinforced epoxy composites. Procedia Eng. 2013, 51, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bennet, C.; Rajini, N.; Jappes, J.W.; Siva, I.; Sreenivasan, V.; Amico, S. Effect of the stacking sequence on vibrational behavior of Sansevieria cylindrica/coconut sheath polyester hybrid composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2015, 34, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.S.; Siva, I.; Rajini, N.; Jappes, J.W.; Amico, S.C. Layering pattern effects on vibrational behavior of coconut sheath/banana fiber hybrid composites. Mater. Des. 2016, 15, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin, H.; Berkalp, O.B.; Mishra, R.; Militky, J. Investigation of dynamic mechanical properties of jute/carbon reinforced composites. Composites 2016, 14, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Mochane, M.J.; Mokhena, T.C.; Mokhothu, T.H.; Mtibe, A.; Sadiku, E.R.; Ray, S.S.; Ibrahim, I.D.; Daramola, O.O. Recent progress on natural fiber hybrid composites for advanced applications: A review. Express Polym. Lett. 2019, 13, 159–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghasia, B.; Rachchh, N. Evaluation of Physical and Mechanical Properties of Woven Bamboo Glass Polyester Hybrid Composite Material. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 7930–7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manteghi, S.; Mahboob, Z.; Fawaz, Z.; Bougherara, H. Investigation of the mechanical properties and failure modes of hybrid natural fiber composites for potential bone fracture fixation plates. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 65, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjay, M.R.; Arpitha, G.R.; Senthamaraikannan, P.; Kathiresan, M.; Balaji, S.; Yogesha, B. The Hybrid Effect of Jute/Kenaf/E-Glass Woven Fabric Epoxy Composites for Medium Load Applications: Impact, Inter-Laminar Strength, and Failure Surface Characterization. J. Nat. Fibers 2018, 16, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edhirej, A.; Sapuan, S.; Jawaid, M.; Zahari, N.I. Cassava/sugar palm fiber reinforced cassava starch hybrid composites: Physical, thermal and structural properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S. Mechanical properties of waste paper/jute fabric reinforced polyester resin matrix hybrid composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 172, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fragassa, C.; Pavlovic, A.; Santulli, C. Mechanical and impact characterisation of flax and basalt fibre vinylester composites and their hybrids. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 137, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, H.N.; Sarasini, F.; Santulli, C.; Tirillò, J.; Zhang, Z.; Arumugam, V. Effect of basalt fibre hybridisation on post-impact me-chanical behaviour of hemp fibre reinforced composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 75, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kona, S. Experimental study of the mechanical properties of banana fiber and groundnut shell ash reinforced epoxy hybrid composite. Int. J. Eng. 2018, 31, 659–665. [Google Scholar]
- Sarasini, F.; Tirillò, J.; Puglia, D.; Dominici, F.; Santulli, C.; Boimau, K.; Valente, T.; Torre, L. Biodegradable polycaprolactone-based composites reinforced with ramie and borassus fibres. Compos. Struct. 2017, 167, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumaidin, R.; Sapuan, S.M.; Jawaid, M.; Ishak, M.R.; Sahari, J. Thermal, mechanical, and physical properties of seaweed/sugar palm fibre reinforced thermoplastic sugar palm Starch/Agar hybrid composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, F.L.; Kumar, A.J.; Srinivasan, V. Investigation of Mechanical Behaviour on Bagasse/Basalt Reinforced Poly Lactic Acid Hybrid Composites: Tensile, Flexural, Impact and Water Absorption. J. Adv. Microsc. Res. 2018, 13, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K.; Srivastava, R.K. Mechanical, thermal and water absorption properties of hybrid sisal/jute fiber reinforced polymer composite. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2016, 23, 231–238. [Google Scholar]
- Almansour, F.; Dhakal, H.; Zhang, Z. Effect of water absorption on Mode I interlaminar fracture toughness of flax/basalt reinforced vinyl ester hybrid composites. Compos. Struct. 2017, 168, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabir, M.M.; Wang, H.; Lau, K.T.; Cardona, F. Effects of chemical treatments on hemp fibre structure. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 276, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.O.; Maheswari, C.U.; Shukla, M.; Rajulu, A. Chemical composition and structural characterization of Napier grass fibers. Mater. Lett. 2012, 67, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Shibata, S.; Fukumoto, I. Mechanical properties of biodegradable composites reinforced with bagasse fibre before and after alkali treatments. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassan, J.; Bledzki, A.K. Possibilities for improving the mechanical properties of jute/epoxy composites by alkali treatment of fibres. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1999, 59, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tabil, L.G.; Panigrahi, S. Chemical Treatments of Natural Fiber for Use in Natural Fiber-Reinforced Composites: A Review. J. Polym. Environ. 2007, 15, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, H.U.; Khan, M.A.; Khan, R.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Das, L.R.; Mamun, A. Role of potassium permanganate and urea on the improvement of the mechanical properties of jute polypropylene composites. Fibers Polym. 2010, 11, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brígida, A.; Calado, V.; Gonçalves, L.; Coelho, M. Effect of chemical treatments on properties of green coconut fiber. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, D.; Sarkar, B.K.; Das, S.; Rana, A. Dynamic mechanical and thermal analysis of vinylester-resin-matrix composites reinforced with untreated and alkali-treated jute fibres. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, U.O.; Nascimento, L.F.C.; Garcia, J.M.; Monteiro, S.N.; Da Luz, F.S.; Pinheiro, W.A.; Filho, F.C.G. Effect of Graphene Oxide Coating on Natural Fiber Composite for Multilayered Ballistic Armor. Polymers 2019, 11, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kan, C.-W. Plasma treatments for sustainable textile processing. In Sustainable Apparel; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 49–118. [Google Scholar]
- Vellguth, N.; Rudeck, T.; Shamsuyeva, M.; Renz, F.; Endres, H.J. Thermal Stability of Natural Fibers via Thermoset Coating for Application in Engineering Thermoplastics. Key Eng. Mater. 2019, 809, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, M.; Ilhan, I.; Karaaslan, M.; Esen, R. Investigation of electromagnetic and ultraviolet properties of nano-metal-coated textile surfaces. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, E.; Panigrahi, S. Effect of Plasma Treatment on Structure, Wettability of Jute Fiber and Flexural Strength of its Composite. J. Compos. Mater. 2009, 43, 1791–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappu, A.; Thakur, V.K. Towards sustainable micro and nano composites from fly ash and natural fibers for multifunctional applications. Vacuum 2017, 146, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saba, N.; Tahir, P.M.; Jawaid, M. A Review on Potentiality of Nano Filler/Natural Fiber Filled Polymer Hybrid Composites. Polymers 2014, 6, 2247–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrakhiz, F.; Benmoussa, K.; Bouhfid, R.; Qaiss, A. Pine cone fiber/clay hybrid composite: Mechanical and thermal properties. Mater. Des. 2013, 50, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njuguna, J.; Pielichowski, K.; Desai, S. Nanofiller-reinforced polymer nanocomposites. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2008, 19, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saba, N.; Jawaid, M.; Alothman, O.Y.; Almutairi, Z. Evaluation of dynamic properties of nano oil palm empty fruit bunch fill-er/epoxy composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 1470–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, G.; Rao, M.V.R.; Vijay, K.; Gopinath, S. Evaluation of Tensile Properties of Nanoclay-Filled Madar Fiber-Reinforced Polyester Hybrid Composites. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Experimental and Computational Mechanics in Engineering, Banda Aceh, Indonesia, 13–14 October 2021; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ravichandran, G.; Rathnakar, G.; Santhosh, N.; Chennakeshava, R.; Hashmi, M.A. Enhancement of mechanical properties of epoxy/halloysite nanotube (HNT) nanocomposites. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 296. [Google Scholar]
- Yahaya, R.; Sapuan, S.; Jawaid, M.; Leman, Z.; Zainudin, E. Mechanical performance of woven kenaf-Kevlar hybrid composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 2242–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swolfs, Y.; Gorbatikh, L.; Verpoest, I. Fibre hybridisation in polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 67, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslinda, A.; Majid, M.S.A.; Ridzuan, M.; Afendi, M.; Gibson, A. Effect of water absorption on the mechanical properties of hybrid interwoven cellulosic-cellulosic fibre reinforced epoxy composites. Compos. Struct. 2017, 167, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, R.; Jang, J. The effects of Hybridization on the mechanical performance of aramid/polyethylene intraply fabric composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1998, 58, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegoretti, A.; Fabbri, E.; Migliaresi, C.; Pilati, F. Intraply and interply hybrid composites based on E-glass and poly(vinyl alcohol) woven fabrics: Tensile and impact properties. Polym. Int. 2004, 53, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, M.; El-Baky, M.A.; Alshorbagy, A. Mechanical performance of intraply and inter-intraply hybrid composites based on e-glass and polypropylene unidirectional fibers. J. Compos. Mater. 2017, 51, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehkordi, M.T.; Nosraty, H.; Shokrieh, M.M.; Minak, G.; Ghelli, D. The influence of hybridization on impact damage behavior and residual compression strength of intraply basalt/nylon hybrid composites. Mater. Des. 2013, 43, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayranci, C.; Carey, J. 2D braided composites: A review for stiffness critical applications. Compos. Struct. 2008, 85, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.-Y.; Qiao, X. Prediction of the mechanical properties of three-dimensionally braided composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1997, 57, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Sun, C. Mechanical properties of three-dimensional braided composites. Compos. Struct. 2004, 65, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, D.; Tang, X.; Whitcomb, J.D.; Kelkar, A.D. Effect of Various Parameters on Effective Engineering Properties of 2 × 2 Braided Composites. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2005, 12, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Mai, Y.W.; Su, Z. (Eds.) Composite Technologies for 2020. In Proceedings of the Fourth Asian-Australasian Conference on Composite Materials (Accm 4), Sydney, Australia, 6–9 July 2004; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Leong, K.; Ramakrishna, S.; Huang, Z.; Bibo, G. The potential of knitting for engineering composites—A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2000, 31, 197–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidhar, B.; Giridev, V.; Raghunathan, K. Flexural and impact properties of flax woven, knitted and sequentially stacked knitted/woven preform reinforced epoxy composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2012, 31, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, M.; Fangueiro, R.; De Araujo, M. Mechanical Properties of Composite Materials Made of 3D Stitched Woven-knitted Preforms. J. Compos. Mater. 2010, 44, 1753–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van de Velde, K.; Kiekens, P. Influence of fibre and matrix modifications on mechanical and physical properties of flax fibre reinforced poly (propylene). Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2001, 286, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-X.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Y.-W.; Huang, G. Flax/PP Weft-knitted Thermoplastic Composites and its Tensile Properties. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2009, 29, 1820–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongxing, Z.; Hong, H.; Nanliang, C.; Xunwei, F. An experimental and numerical study on the impact energy absorption char-acteristics of the multiaxial warp knitted (MWK) reinforced composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2005, 39, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Sun, B.Z.; Hu, H.; Gu, B.H. Responses of 3D biaxial spacer weft-knitted composite circular plate under impact loading. Part II: Impact tests and FEM calculation. J. Text. Inst. 2010, 101, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Hu, H. Mechanical properties of biaxial weft-knitted flax composites. Mater. Des. 2013, 46, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidhar, B.A. Tensile and compressive behaviour of multilayer flax-rib knitted preform reinforced epoxy composites. Mater. Des. 2013, 49, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, T.G.; Wu, C.M.; Cheng, K.B. Effect of different knitted structure on the mechanical properties and damage behavior of Flax/PLA (Poly Lactic acid) double covered uncommingled yarn composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 2836–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, L.H.; Cavalcante, J.M.; d’Almeida, J.R. Comparison of the mechanical behavior of plain weave and plain weft knit jute fabric-polyester-reinforced composites. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2006, 45, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).