Finite Element Analysis of Rubberized Concrete Interlocking Masonry under Vertical Loading
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Models
2.1. FE Model
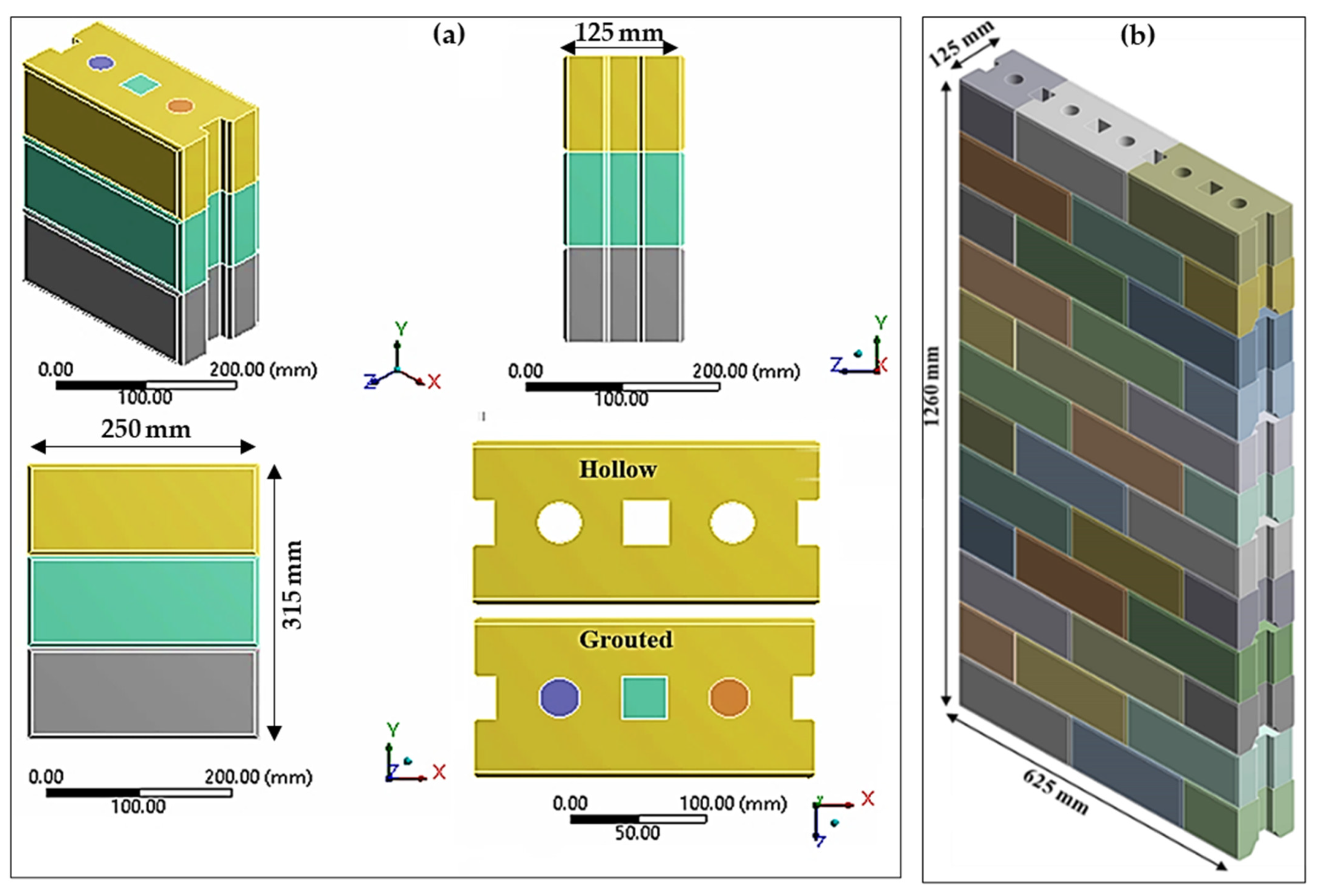
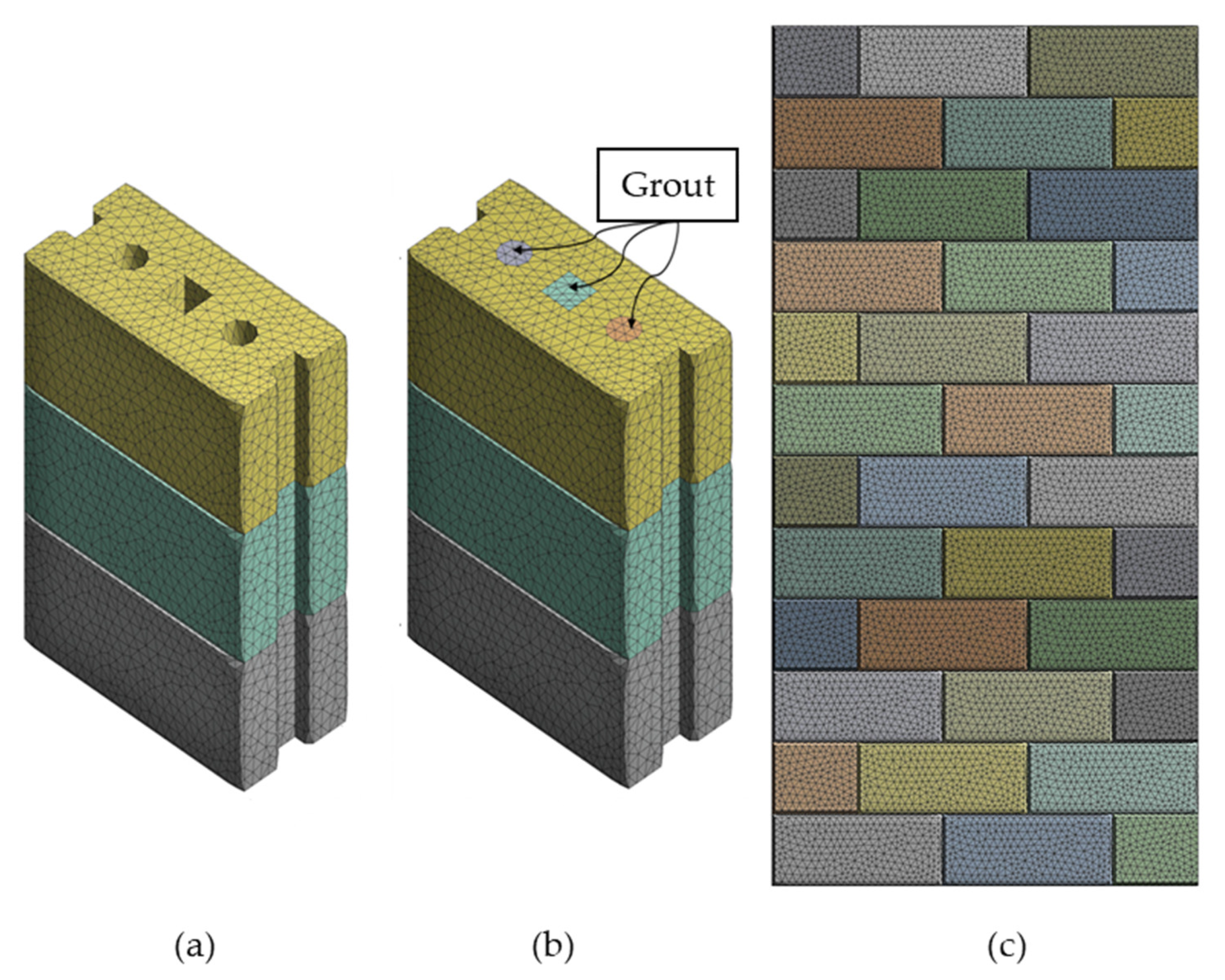
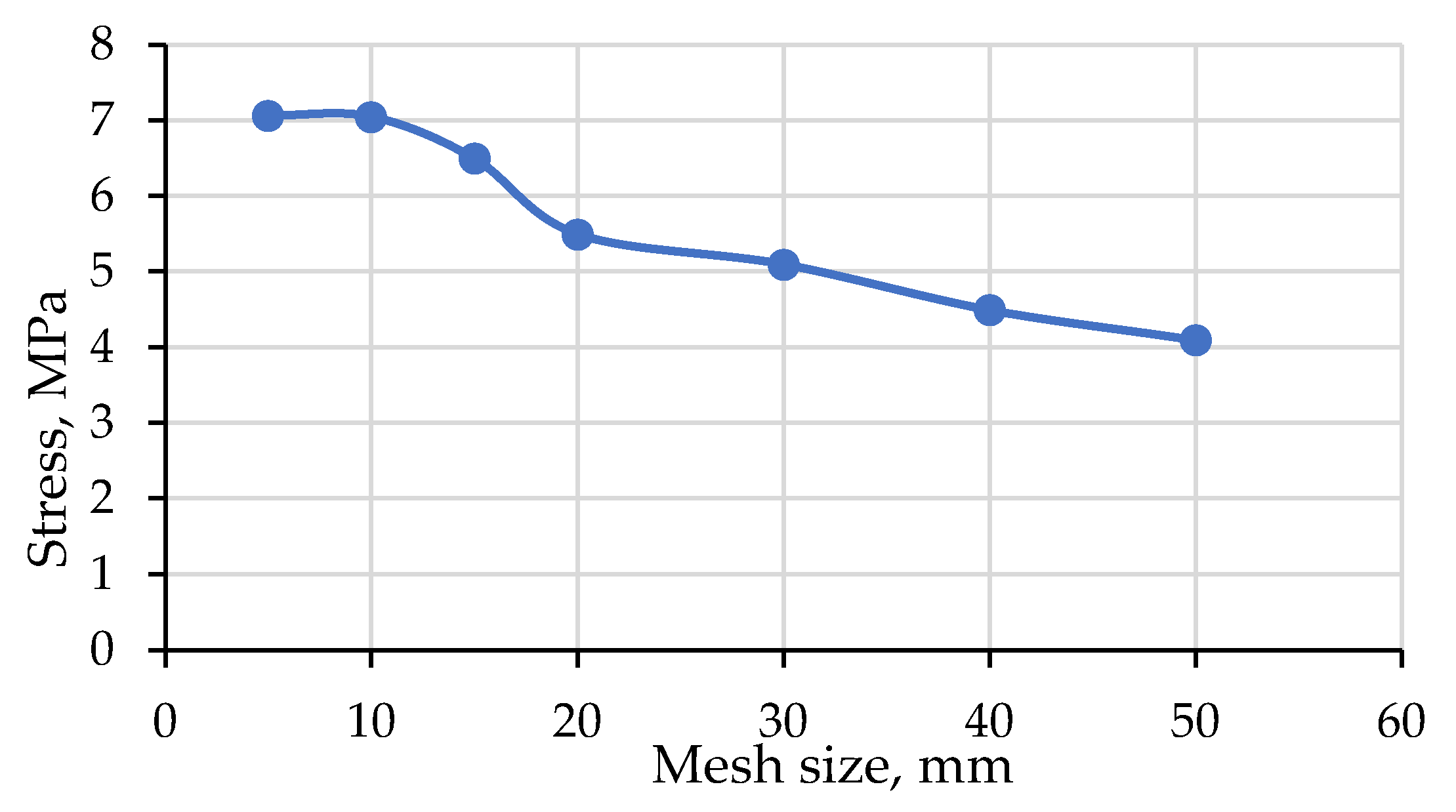
2.2. Geometry and FE Mesh
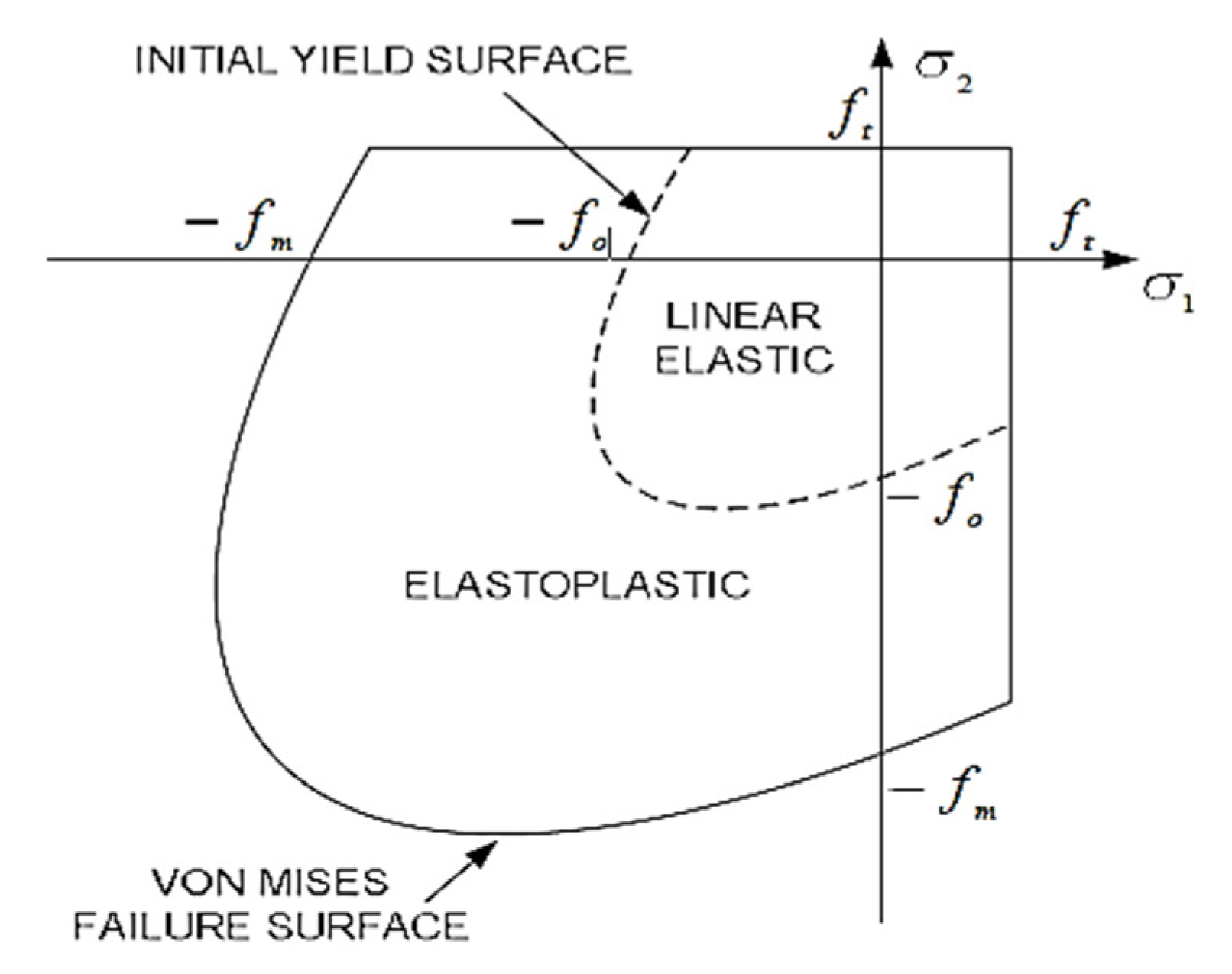
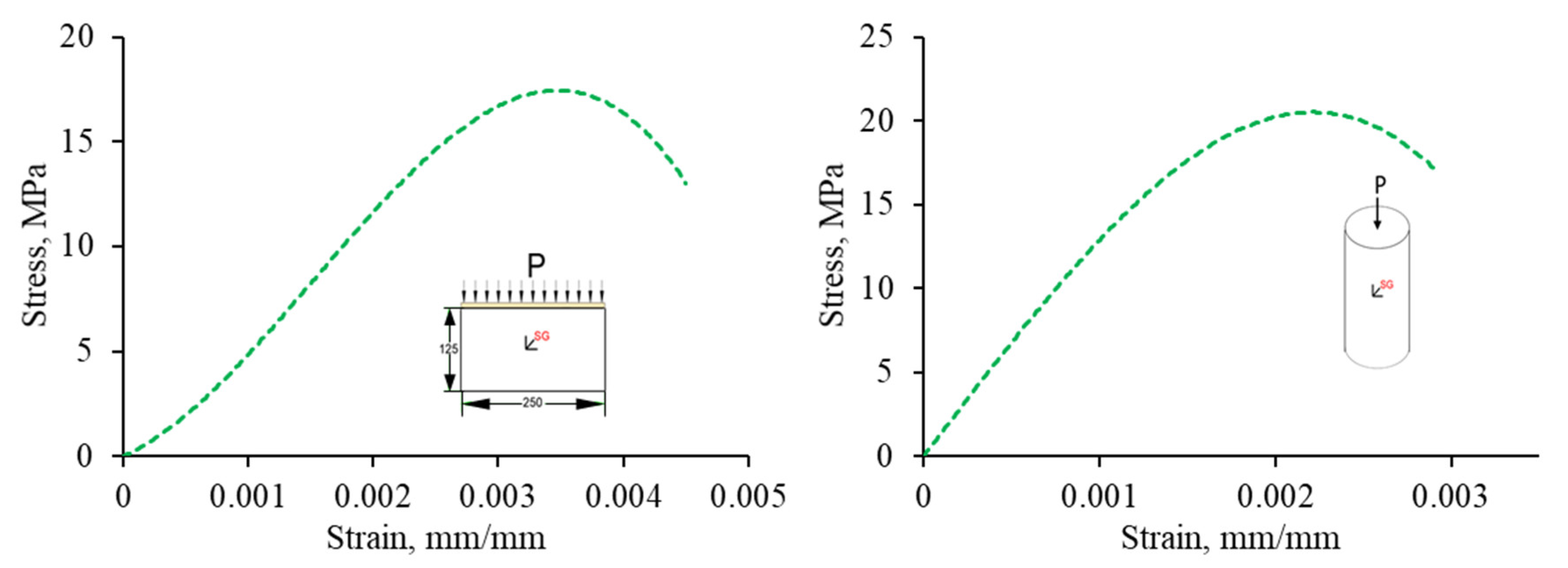
2.3. Constitutive Model
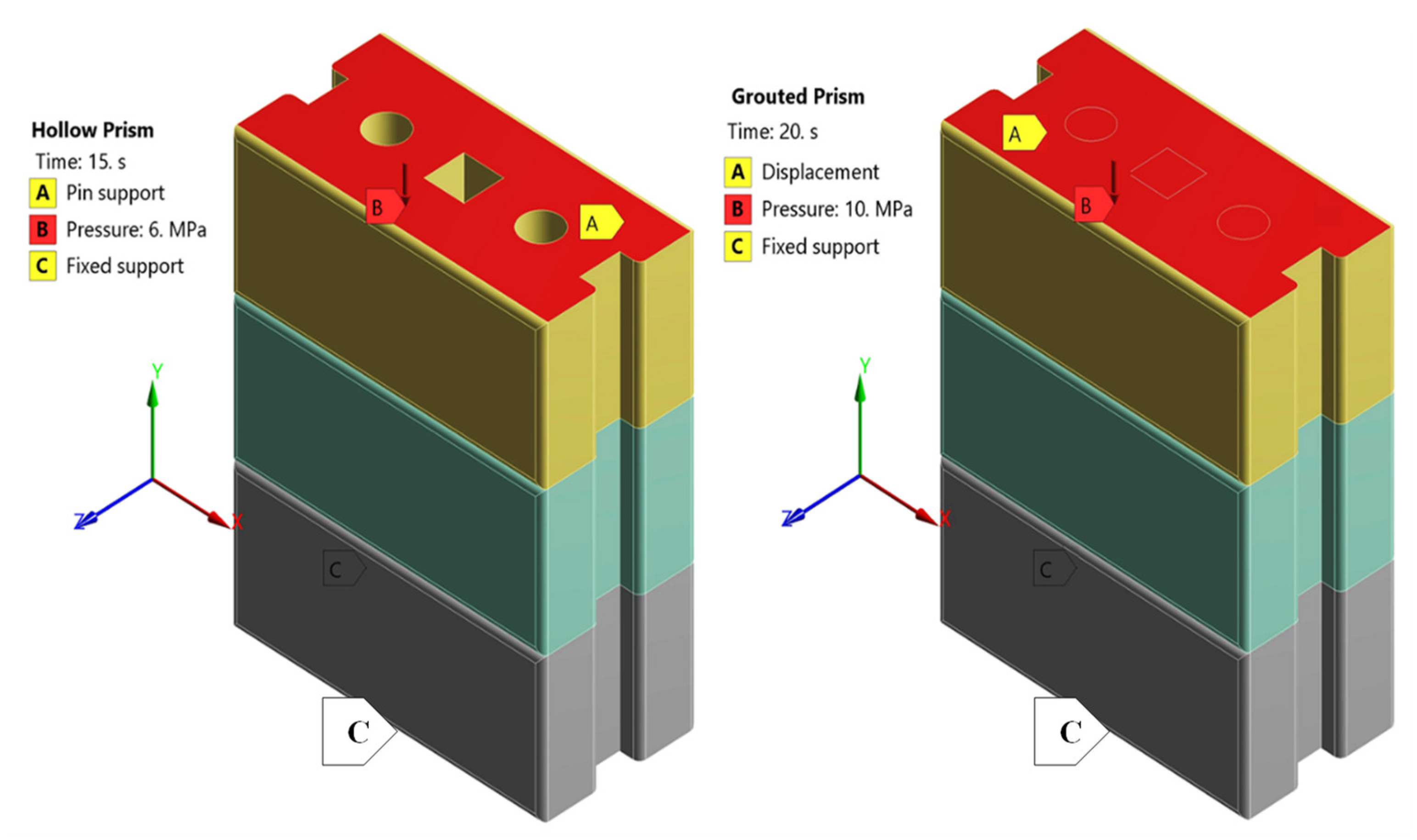
2.4. Loading and Boundary Conditions
3. Results
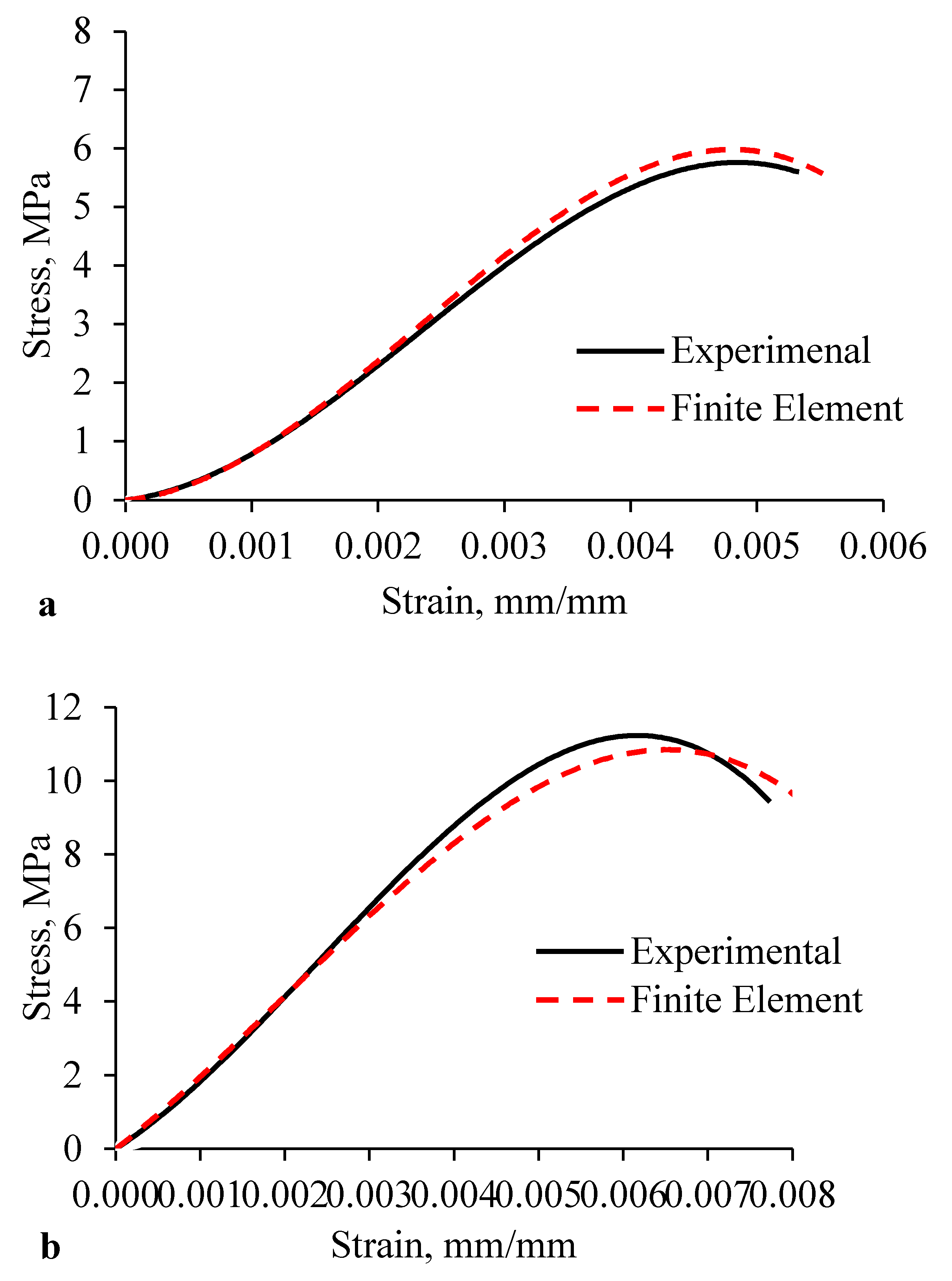
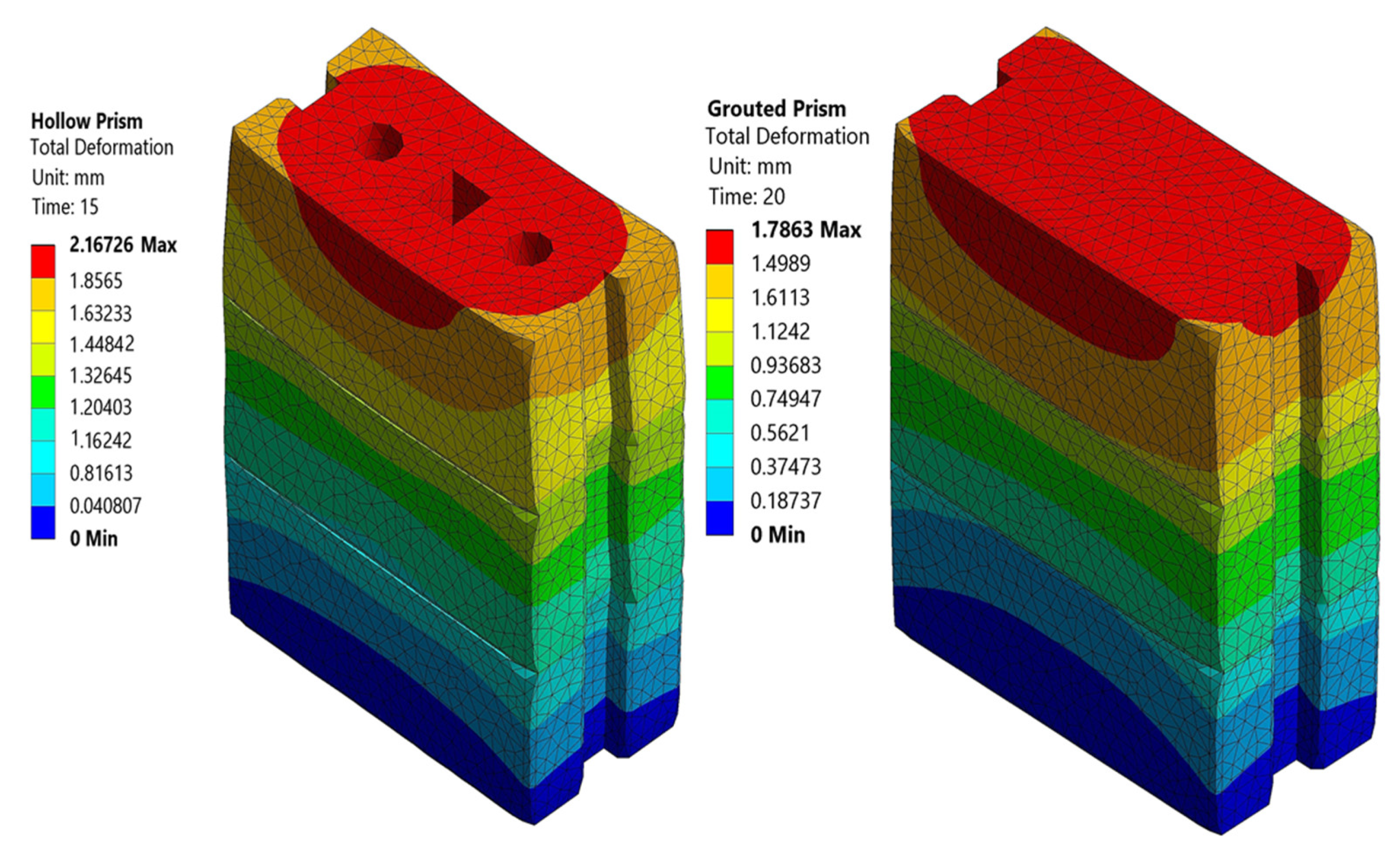
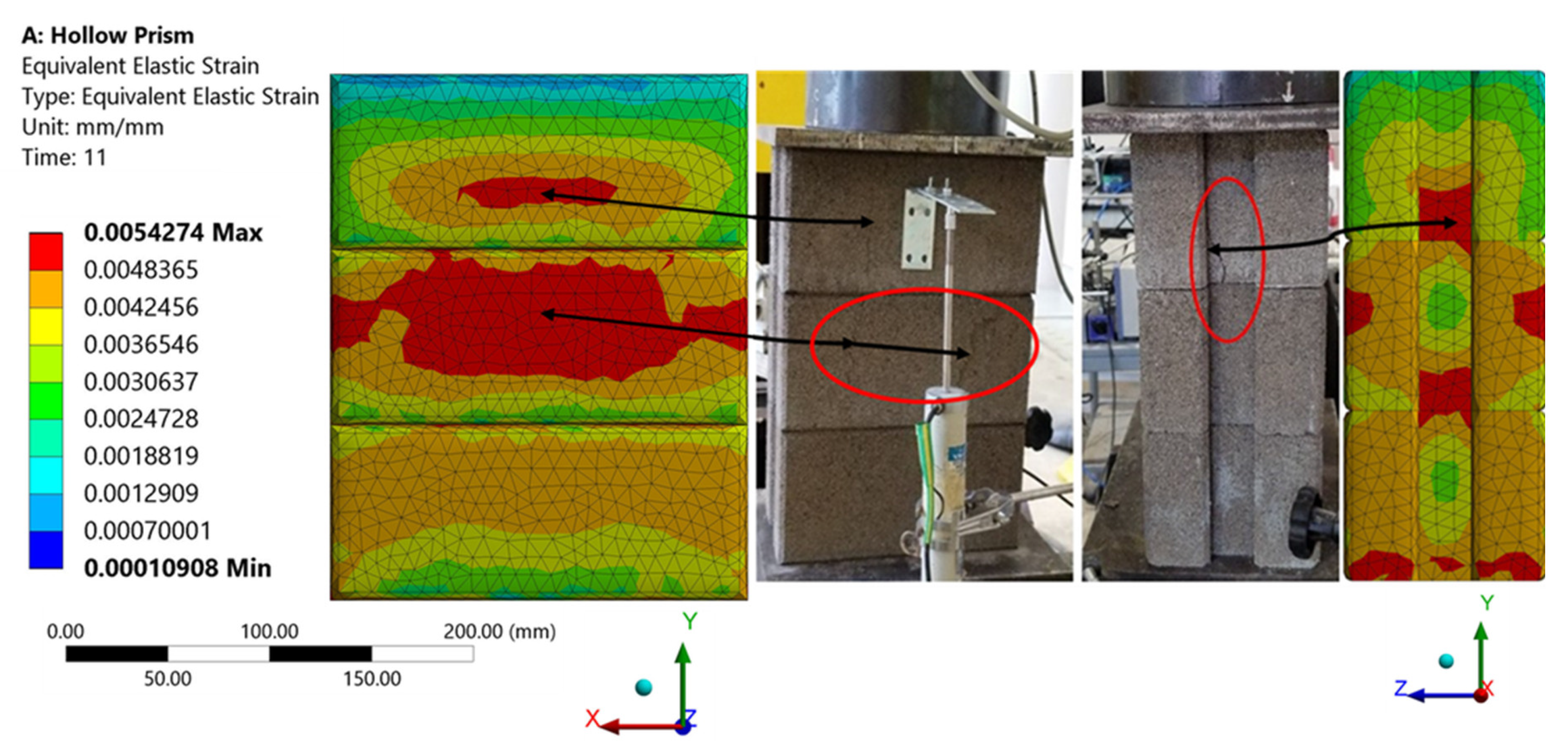
3.1. RCIB Masonry Prisms (Hollow and Grouted)
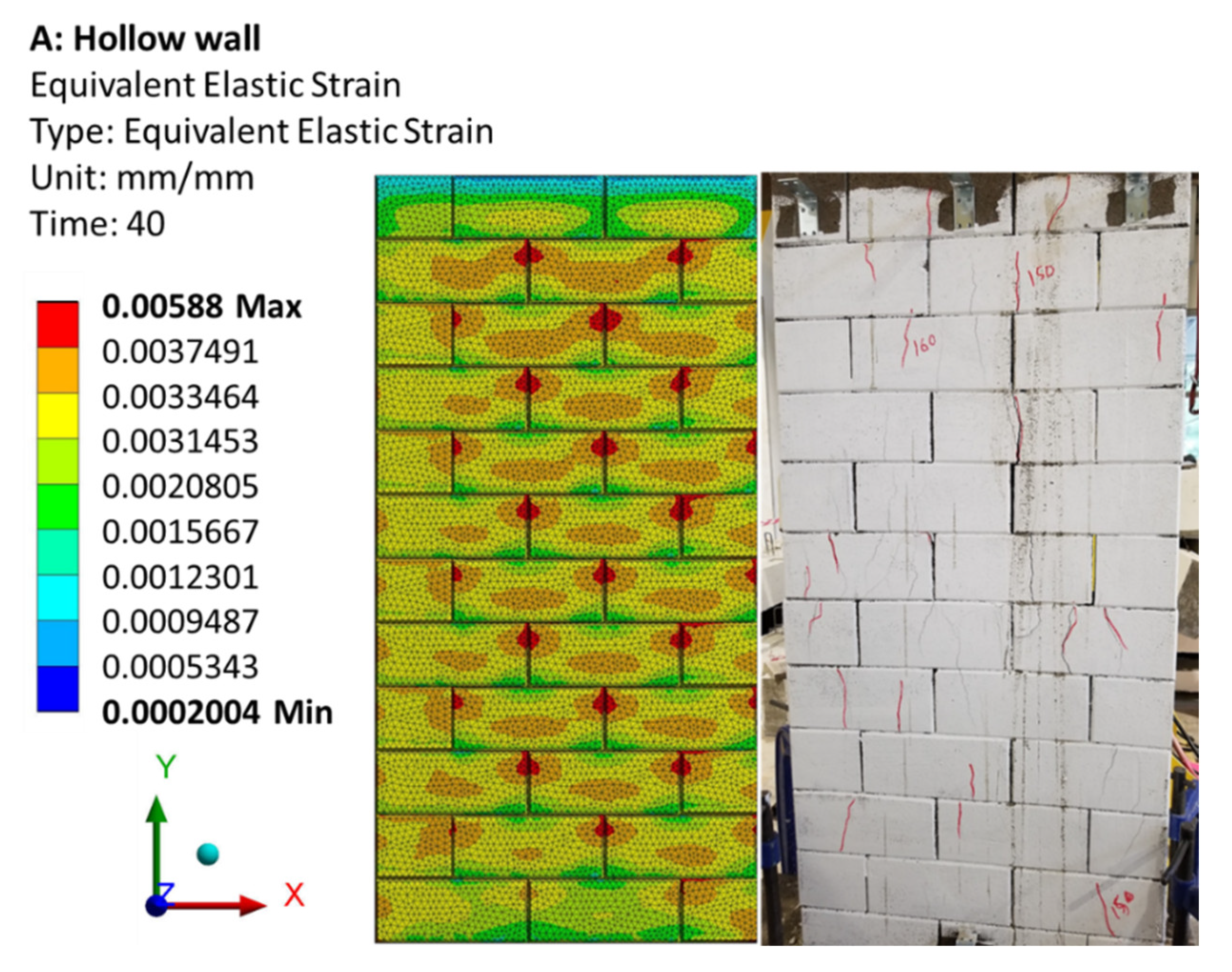
3.2. RCIB Masonry Wall (Hollow)
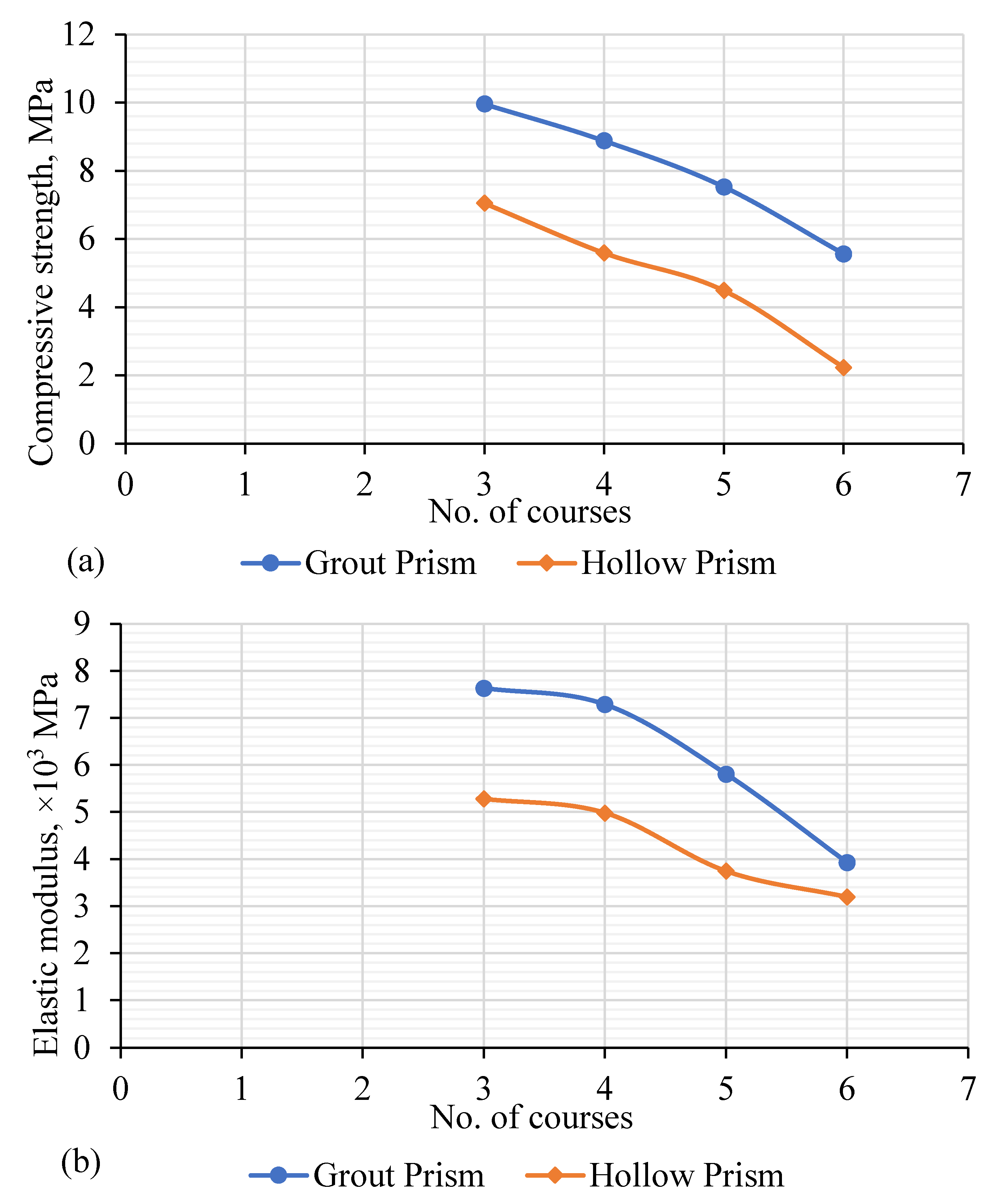
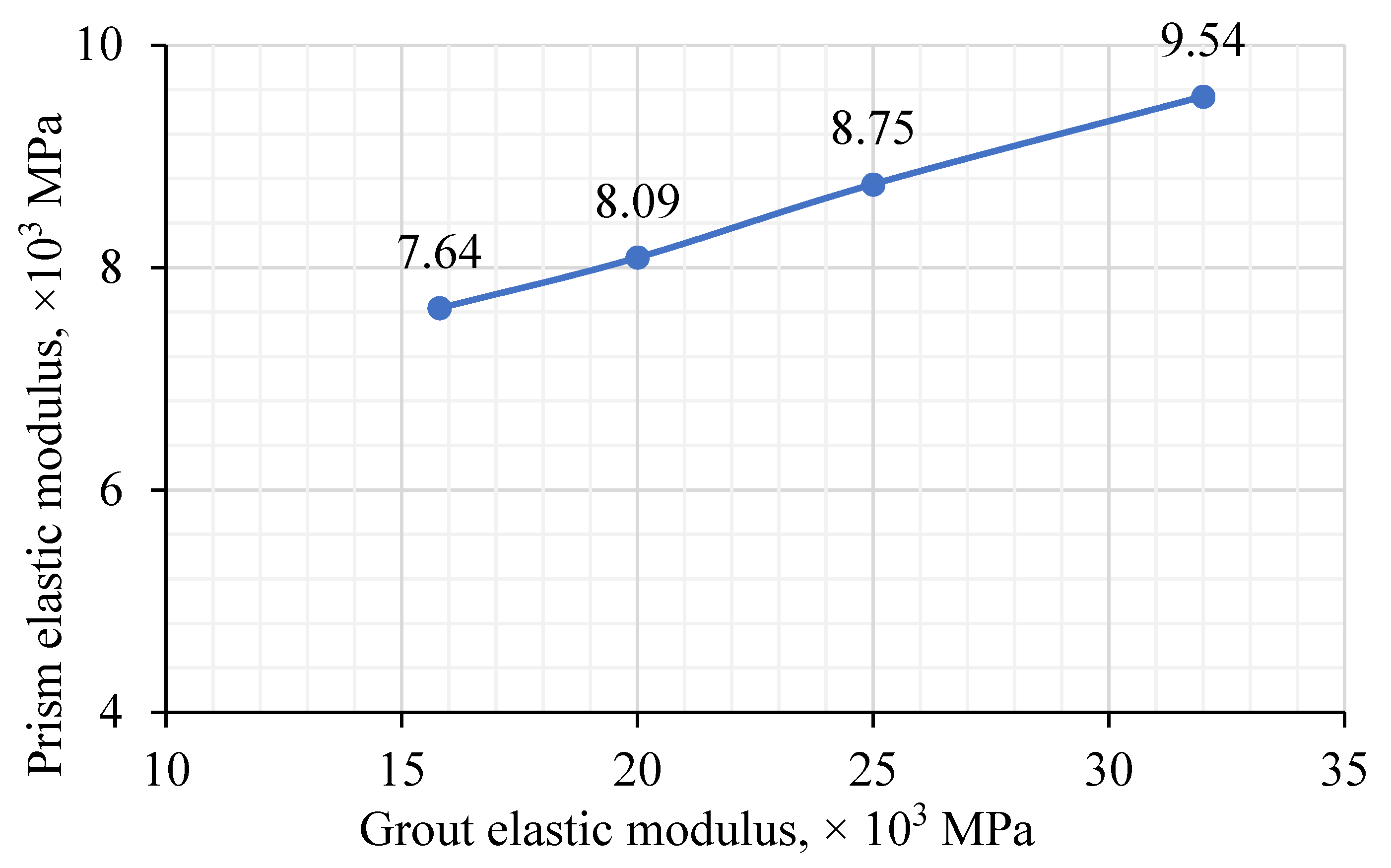
3.3. Parametric Study of RCIB Masonry Prism
4. Conclusions
- The finite element analysis emphasized the distribution of forces and stresses within the prism and the deformation mechanism of the rubberized concrete interlocking masonry prisms (hollow and grouted); 90% agreed with experimental findings.
- RCIB walls and prisms experienced higher ductility measured by the post-failure loading under compression.
- Web splitting and face spalling were the common failure mechanisms for wall panels, while shear compression failure and web splitting were the common failure mode for the hollow and grouted prisms for both the experimental specimens and simulated models.
- The differences between the FE and experimental results of the walls were less than 16%, indicating a good matching.
- With an increase in the number of courses, both prism strength and modulus of elasticity decreased.
- It is recommended to employ another plasticity model such as Willam–Warnke or Drucker–Prager yield criteria instead of the von Misses yield criterion for modeling the rubberized concrete interlocking masonry.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Fakih, A.; Wahab, M.M.A.; Mohammed, B.S.; Liew, M.S.; Wan Abdullah Zawawi, N.A.; As’ad, S. Experimental study on axial compressive behavior of rubberized interlocking masonry walls. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 29, 101107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fakih, A.; Mohammed, B.S.; Liew, M.S. Behavior of the Dry Bed Joint in the Mortarless Interlocking Masonry System: An Overview. Civ. Eng. Res. J. 2018, 4, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Fakih, A.; Mohammed, B.S.; Nuruddin, F.; Nikbakht, E. Development of Interlocking Masonry Bricks and Its’ Structural Behaviour: A Review Paper; IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; p. 012127. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, A.P.C.; Silva, B.A.; Silvestre, N.; de Brito, J.; Júlio, E. Mechanical characterization of rubberized concrete using an image-processing/XFEM coupled procedure. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 78, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubliner, J.; Oliver, J.; Oller, S.; Oñate, E. A plastic-damage model for concrete. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1989, 25, 299–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhu, H.; Ju, J.W.; Yan, Z.; Chen, Q. Modeling microcapsule-enabled self-healing cementitious composite materials using discrete element method. Int. J. Damage Mech. 2017, 26, 340–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Dong, Q.; Chen, X.; Ni, F. Meso-cracking characteristics of rubberized cement-stabilized aggregate by discrete element method. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 316, 128374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechtcherine, V.; Shyshko, S. Simulating the behaviour of fresh concrete with the Distinct Element Method–Deriving model parameters related to the yield stress. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 55, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Thoma, K.; Hofmann, J. Finite element analysis of masonry under a plane stress state. Eng. Struct. 2021, 226, 111214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Li, Y.; Cruz Noguez, C. Modeling and parameter importance investigation for simulating in-plane and out-of-plane behaviors of un-reinforced masonry walls. Eng. Struct. 2021, 248, 113233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurenco, P.; Rots, J.G.; Blaauwendraad, J. Two approaches for the analysis of masonry structures: Micro and macro-modeling. HERON 1995, 40, 313–340. [Google Scholar]
- Barraza, C.; Andrés, J.; Meskouris, K. Numerical Model for Nonlinear Analysis of Masonry Walls; Lehrstuhl für Baustatik und Baudynamik: Aachen, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rekik, A.; Allaoui, S.; Gasser, A.; Blond, E.; Andreev, K.; Sinnema, S. Experiments and nonlinear homogenization sustaining mean-field theories for refractory mortarless masonry: The classical secant procedure and its improved variants. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 2015, 49, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lourenço, P.J.B.B. Computational Strategies for Masonry Structures. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, R.L.G.; Rodrigues, J.P.C.; Pereira, J.M.; Lourenço, P.B.; Ulrich Marschall, H. Normal and tangential behaviour of dry joints in refractory masonry. Eng. Struct. 2021, 243, 112600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthivel, R.; Lourenço, P.B. Finite element modelling of deformation characteristics of historical stone masonry shear walls. Eng. Struct. 2009, 31, 1930–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, M.; Atamturktur, S. Experimental and numerical evaluation of reinforced dry-stacked concrete masonry walls. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 22, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wathaf, A.H. 3D Finite Element Analysis of Hollow Concrete Block Masonry. J. Sci. Technol. 2009, 14, 26–35. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, K.-H. Development and Investigation of Failure Mechanism of Interlocking Mortarless Block Masonry Systems. Doctoral Dissertation, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Alpa, G.; Gambarotta, L.; Monetto, I. Dry block assembly continuum modelling for the in-plane analysis of shear walls. Comput. Methods Struct. Mason. 1998, 4, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Thanoon, W.A.; Alwathaf, A.H.; Noorzaei, J.; Jaafar, M.S.; Abdulkadir, M.R. Finite element analysis of interlocking mortarless hollow block masonry prism. Comput. Struct. 2008, 86, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanoon, W.A.; Alwathaf, A.H.; Noorzaei, J.; Jaafar, M.S.; Abdulkadir, M.R. Nonlinear finite element analysis of grouted and ungrouted hollow interlocking mortarless block masonry system. Eng. Struct. 2008, 30, 1560–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Zhang, X.; Hao, H.; Chen, C. Experimental and numerical investigation on the compressive properties of interlocking blocks. Eng. Struct. 2021, 228, 111561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.L.G.; Rodrigues, J.P.C.; Pereira, J.M.; Lourenço, P.B.; Marschall, H.U. Thermomechanical behaviour of refractory dry-stacked masonry walls under uniaxial compression. Eng. Struct. 2021, 240, 112361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chewe Ngapeya, G.G.; Waldmann, D. Experimental and analytical analysis of the load-bearing capacity Pu of improved dry-stacked masonry. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 27, 100927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed, H.B.; Limam, O.; Aidi, M.; Jelidi, A. Experimental and numerical study of Interlocking Stabilized Earth Blocks mechanical behavior. J. Build. Eng. 2016, 7, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreev, K.; Sinnema, S.; Rekik, A.; Allaoui, S.; Blond, E.; Gasser, A. Compressive behaviour of dry joints in refractory ceramic masonry. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 34, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chewe Ngapeya, G.G.; Waldmann, D.; Scholzen, F. Impact of the height imperfections of masonry blocks on the load bearing capacity of dry-stack masonry walls. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 165, 898–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, A.; Terny-Rebeyrotte, K.; Boisse, P. Modelling of joint effects on refractory lining behaviour. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2004, 218, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brulin, J.; Blond, E.; de Bilbao, E.; Rekik, A.; Landreau, M.; Gasser, A.; Colleville, Y. Methodology for brick/mortar interface strength characterization at high temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 265, 120565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fakih, A.; Mohammed, B.S.; Liew, M.S.; Alaloul, W.S.; Adamu, M.; Khed, V.C.; Dahim, M.A.; Al-Mattarneh, H. Mechanical behavior of rubberized interlocking bricks for masonry structural applications. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Fakih, A.; Mohammed, B.S.; Liew, M.S.; Alaloul, W.S. Physical properties of the rubberized interlocking masonry brick. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 656–664. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Fakih, A.; Mohammed, B.S.; Wahab, M.M.A.; Liew, M.S.; Mugahed Amran, Y.H.; Alyousef, R.; Alabduljabbar, H. Characteristic compressive strength correlation of rubberized concrete interlocking masonry wall. Structures 2020, 26, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C150/C150M-17; Standard Specification for Portland Cement. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- Al-Fakih, A.; Mohammed, B.S.; Wahab, M.M.A.; Liew, M.S.; Mugahed Amran, Y.H. Flexural behavior of rubberized concrete interlocking masonry walls under out-of-plane load. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 263, 120661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.S. Finite element analysis of unreinforced masonry walls. Al-Rafidain Eng. J. (AREJ) 2010, 18, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Prism Type | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hollow | 281.19 | 309.66 | 9.2 | 109.65 | 132 | 16.9 | 4735 | 5284 | 10.4 |
| Grouted | 684.4 | 618.69 | 9.6 | 305.34 | 304 | 0.31 | 7654 | 7441 | 2.9 |
| Property | Hollow Wall Results | Grouted Wall Results | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultimate load, kN | 181 | 216 | 0.84 | 424.8 | 510 | 0.83 |
| Compressive strength, MPa | 3.87 | 3.73 | 1.04 | 5.75 | 7.62 | 0.75 |
| Elastic modulus, MPa | 727.42 | 845.4 | 0.86 | 1778.34 | 2320.2 | 0.76 |
| Ultimate strain at failure, mm/mm | 0.0055 | 0.0049 | 1.12 | 0.00436 | 0.00325 | 1.34 |
| Stiffness, kN/mm | 27 | 35 | 0.77 | 103.23 | 131.2 | 0.79 |
| Deformation, mm | 6.78 | 5.33 | 1.27 | 5.54 | 4.96 | 1.12 |
| Model | No. of Courses | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (h/t) | (MPa) | (MPa) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grouted | Slenderness effect | 3 | 315 | 250 | 125 | 2.52 | 7416 | 15,826 |
| 4 | 420 | 250 | 125 | 3.36 | 7416 | 15,826 | ||
| 5 | 525 | 250 | 125 | 4.2 | 7416 | 15,826 | ||
| 6 | 630 | 250 | 125 | 5.04 | 7416 | 15,826 | ||
| Hollow | 3 | 315 | 250 | 125 | 2.52 | 7416 | 15,826 | |
| 4 | 420 | 250 | 125 | 3.36 | 7416 | 15,826 | ||
| 5 | 525 | 250 | 125 | 4.2 | 7416 | 15,826 | ||
| 6 | 630 | 250 | 125 | 5.04 | 7416 | 15,826 | ||
| Grouted | Grout effect | 3 | 315 | 250 | 125 | 2.52 | 7416 | 15,826 |
| 3 | 315 | 250 | 125 | 2.52 | 7416 | 20,000 | ||
| 3 | 315 | 250 | 125 | 2.52 | 7416 | 25,000 | ||
| 3 | 315 | 250 | 125 | 2.52 | 7416 | 32,000 | ||
| 3 | 315 | 250 | 125 | 2.52 | 7416 | 40,000 |
| Type | No. of Courses | Load P kN | Stress, σp MPa | Strain, εp mm/mm | Deformation δp, mm | Elastic Modulus, Ep N/mm2 | Stiffness, kp kN/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grouted prism | 3 | 304.4 | 9.96 | 0.00597 | 1.79 | 7.64 | 618.69 |
| 4 | 277.4 | 8.88 | 0.00480 | 2.17 | 7.29 | 542.25 | |
| 5 | 249.0 | 7.53 | 0.00289 | 2.32 | 5.81 | 367.82 | |
| 6 | 221.1 | 5.56 | 0.00213 | 5.54 | 3.93 | 270.56 | |
| Hollow prism | 3 | 132.5 | 7.05 | 0.00540 | 2.167 | 5.28 | 309.7 |
| 4 | 121.7 | 5.59 | 0.00656 | 2.45 | 4.98 | 253.3 | |
| 5 | 95.3 | 4.49 | 0.00535 | 2.749 | 3.75 | 205.27 | |
| 6 | 75.8 | 2.23 | NA | 4.62 | 3.20 | 152.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Fakih, A.; Al-Osta, M.A. Finite Element Analysis of Rubberized Concrete Interlocking Masonry under Vertical Loading. Materials 2022, 15, 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15082858
Al-Fakih A, Al-Osta MA. Finite Element Analysis of Rubberized Concrete Interlocking Masonry under Vertical Loading. Materials. 2022; 15(8):2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15082858
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Fakih, Amin, and Mohammed A. Al-Osta. 2022. "Finite Element Analysis of Rubberized Concrete Interlocking Masonry under Vertical Loading" Materials 15, no. 8: 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15082858
APA StyleAl-Fakih, A., & Al-Osta, M. A. (2022). Finite Element Analysis of Rubberized Concrete Interlocking Masonry under Vertical Loading. Materials, 15(8), 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15082858







