Highly Photostable Carbon Dots from Citric Acid for Bioimaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
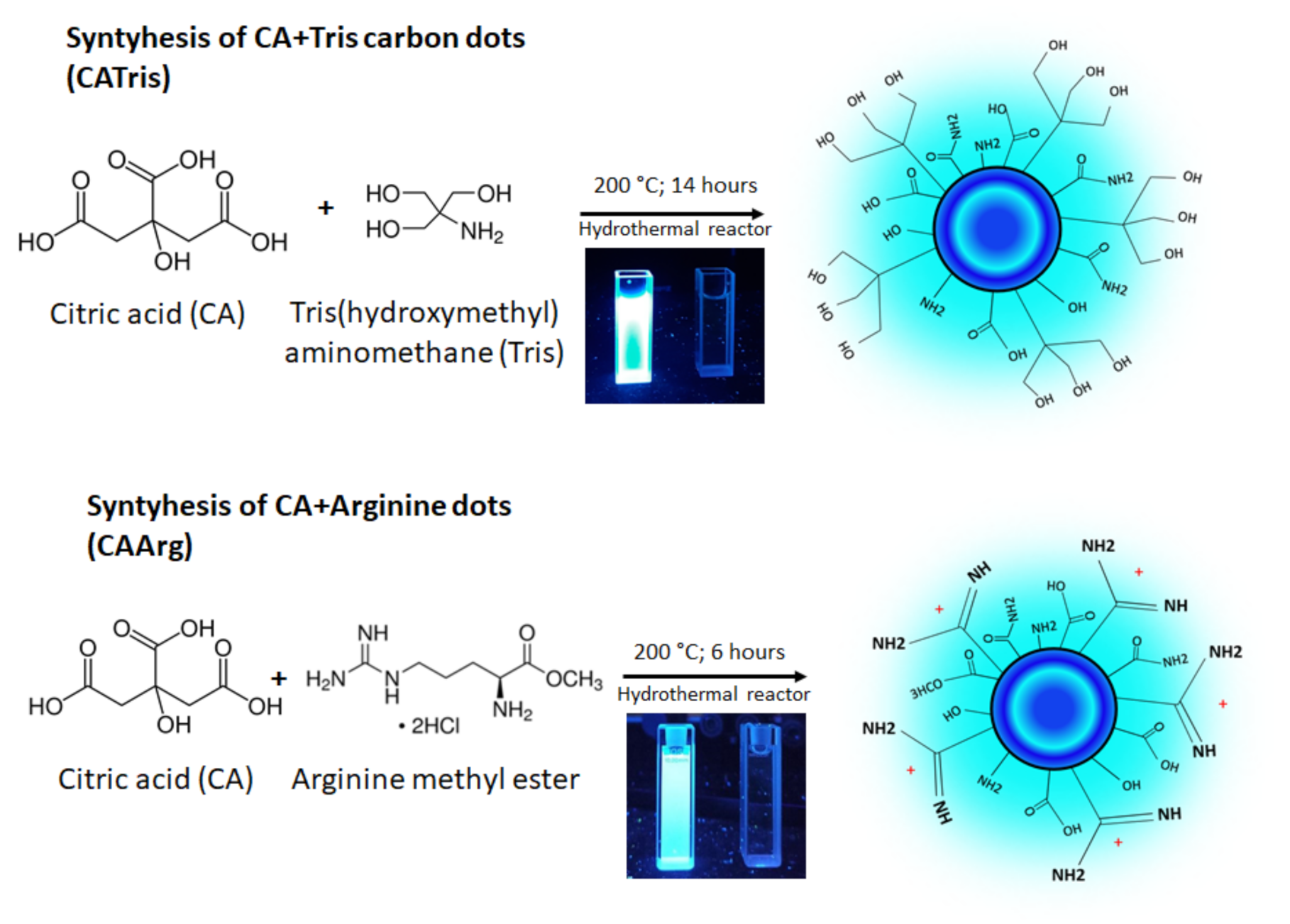
2.1. Synthesis of Carbon Dots
2.2. Characterization Techniques
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Cell Imaging
2.5. Cytotoxicity
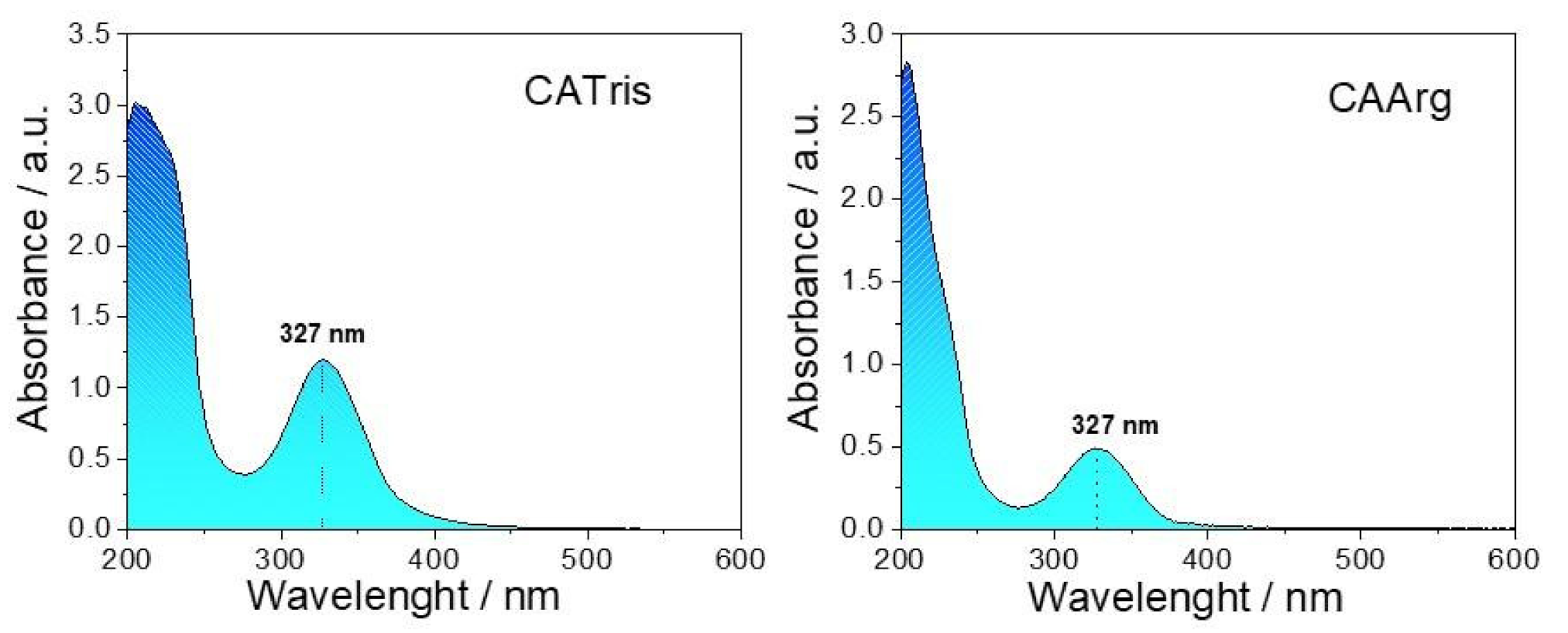
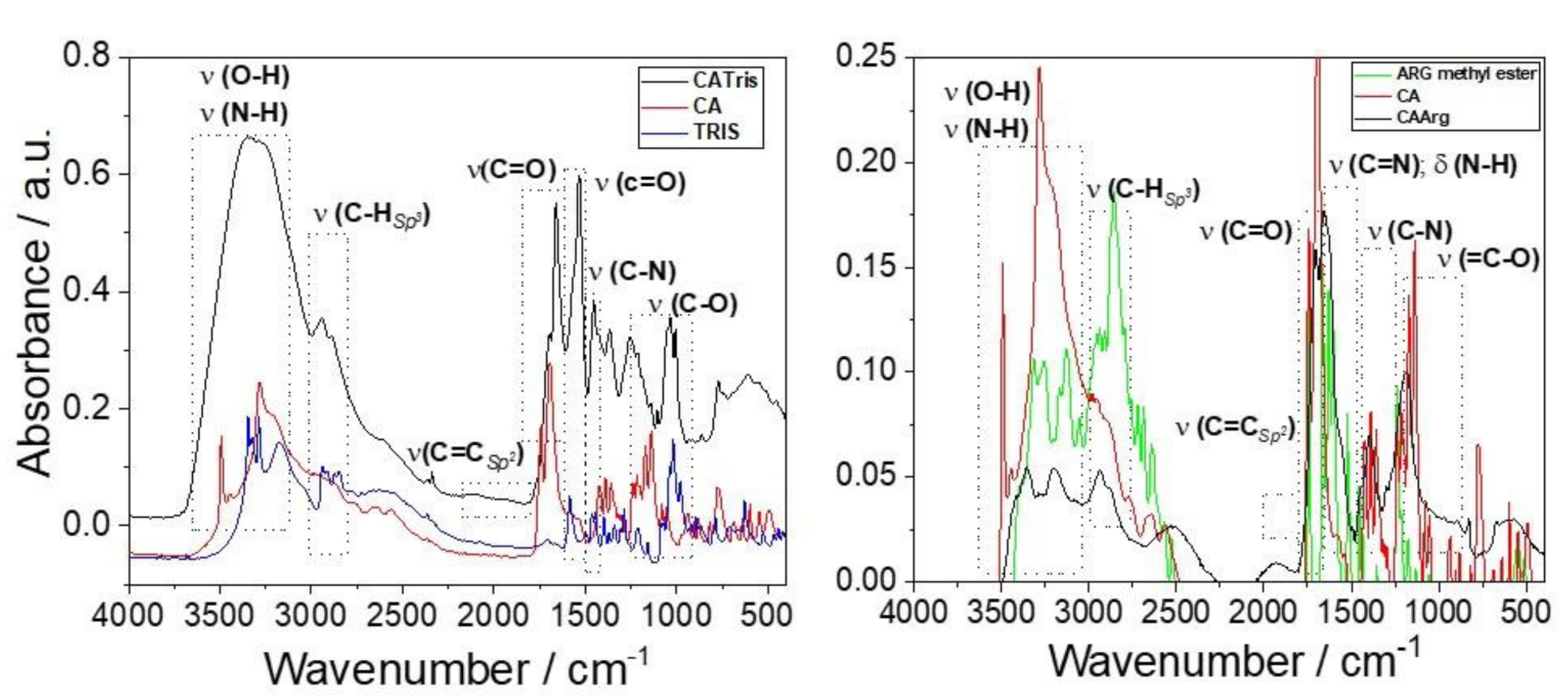
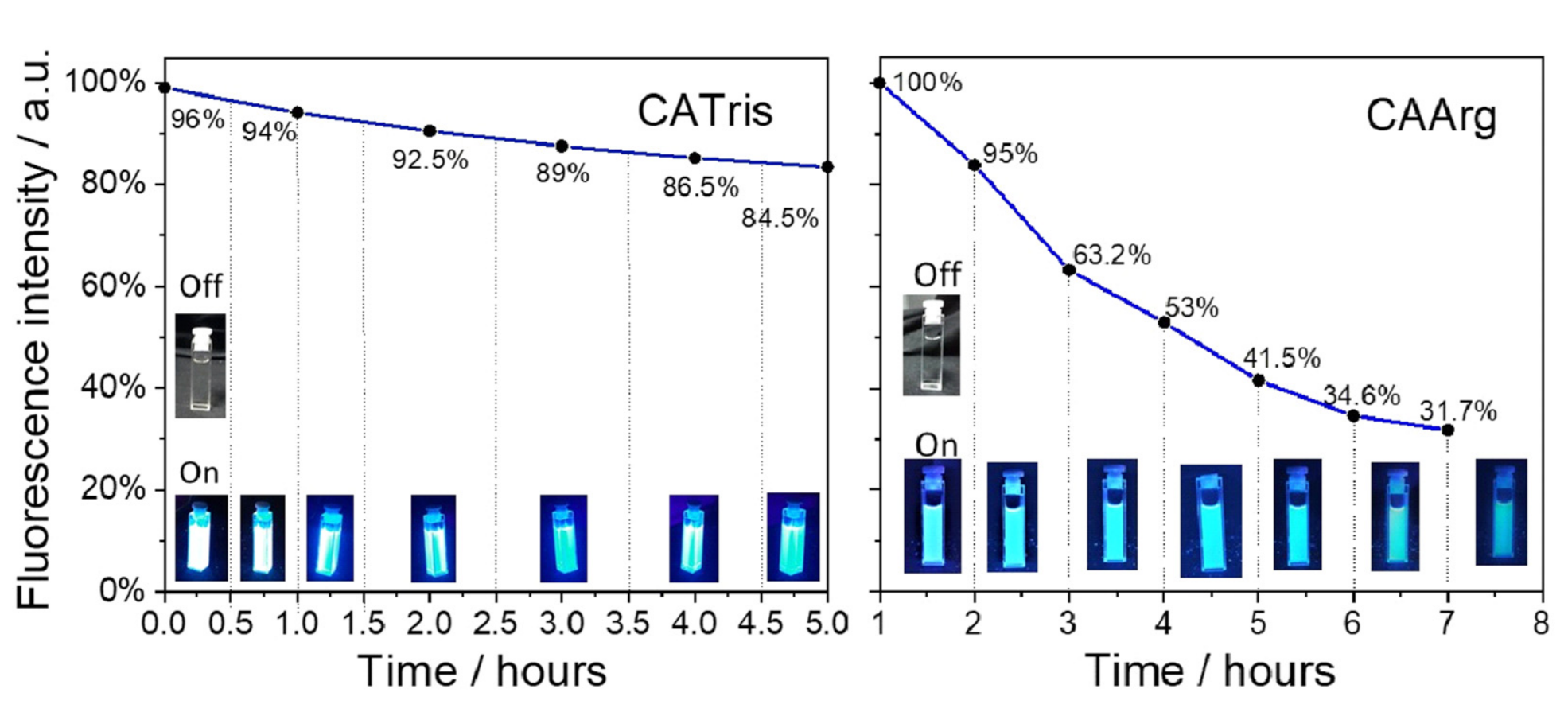
3. Results and Discussion
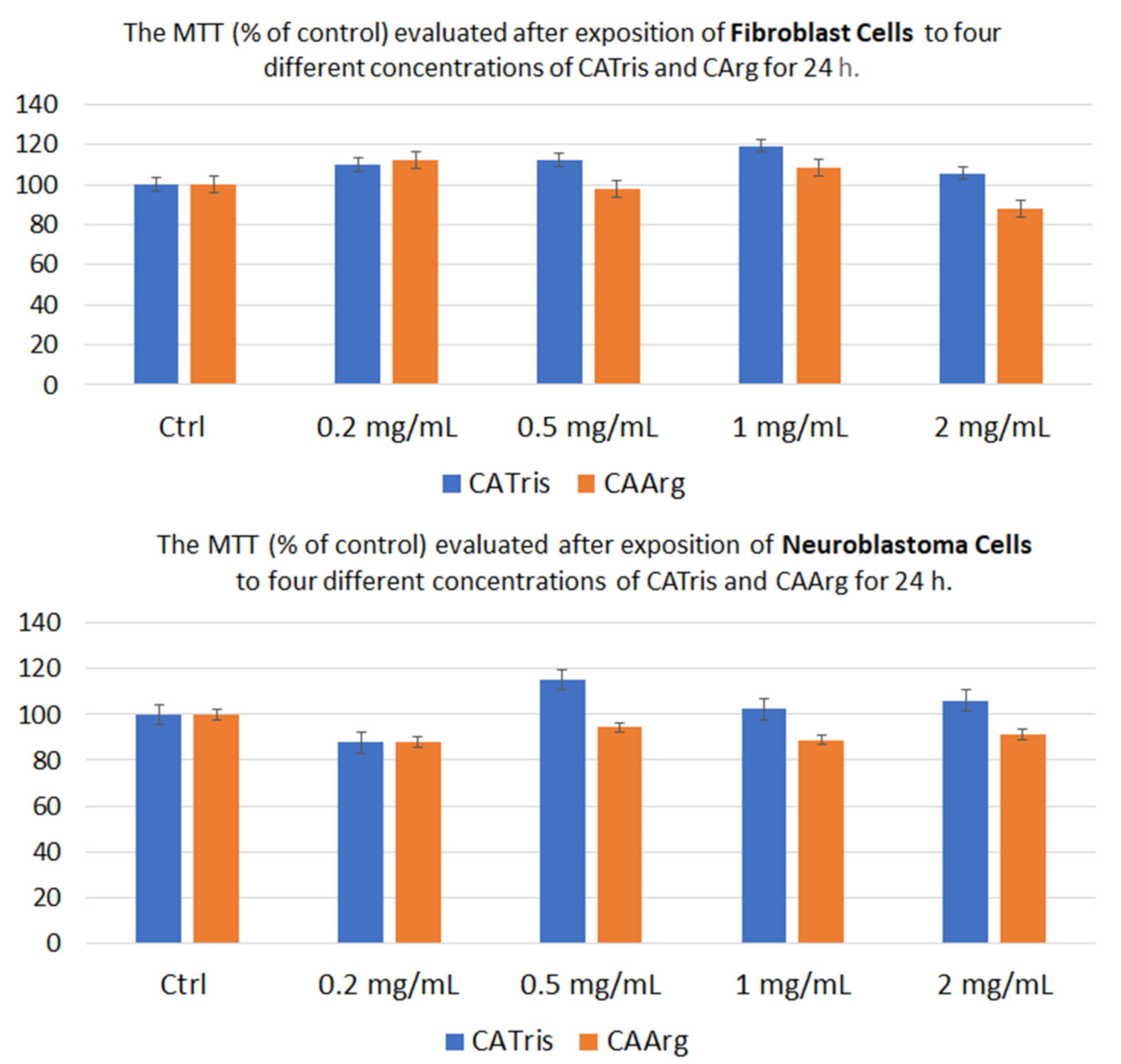
3.1. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Studies
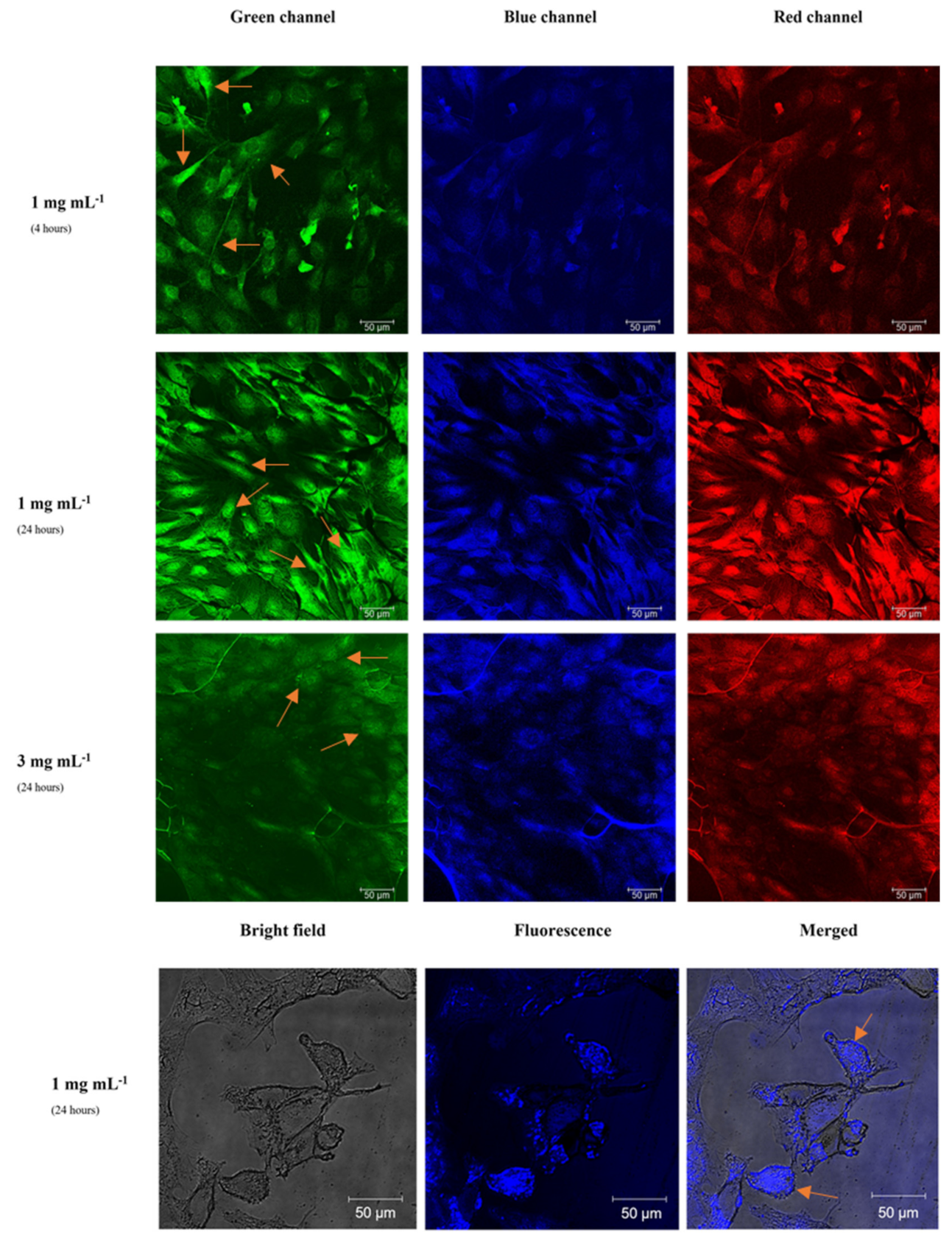
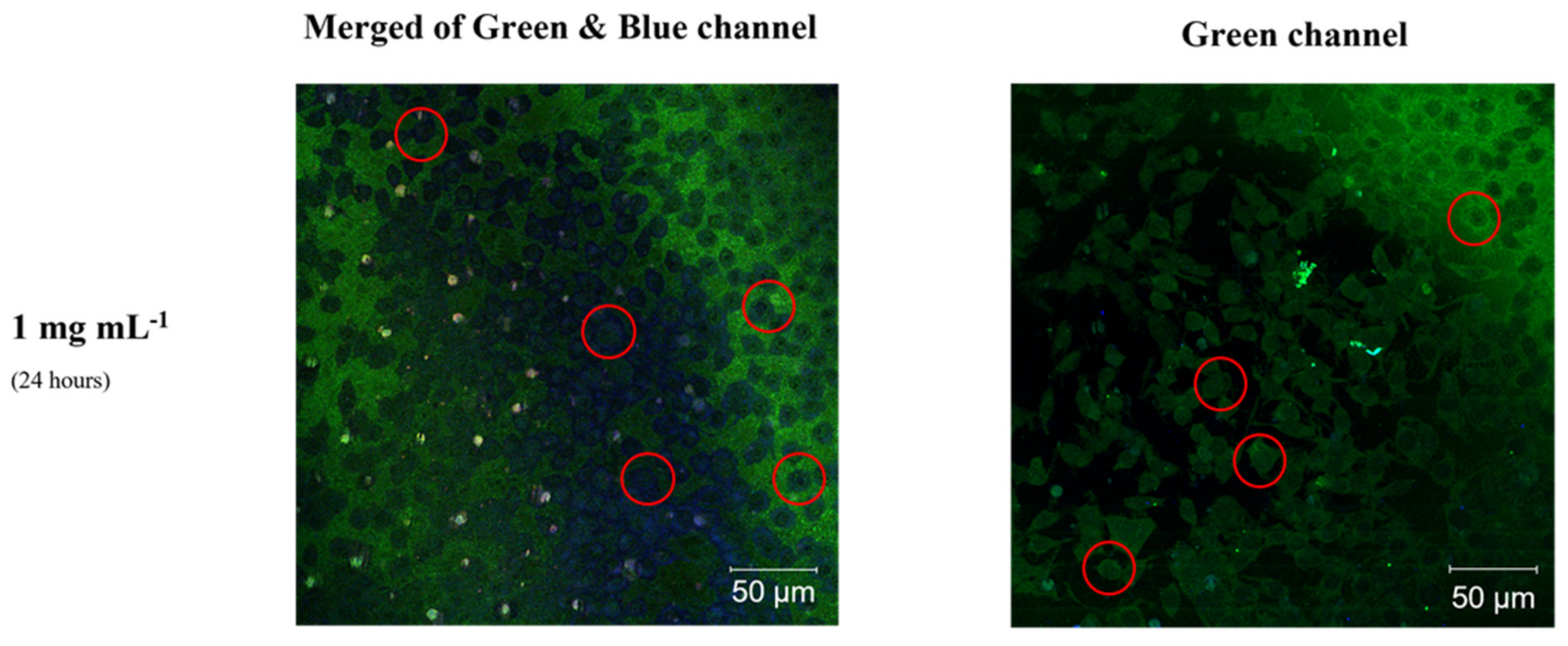
3.2. Bioimaging
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Yan, X.; Kong, D.; Jin, R.; Sun, C.; Du, D.; Lin, Y.; Lu, G. Recent advances in carbon dots for bioimaging applications. Nanoscale Horiz. 2019, 5, 218–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, P.; Lu, X.; Sun, Z.; Guo, Y.; He, H. A review on syntheses, properties, characterization and bioanalytical applications of fluorescent carbon dots. Mikrochim. Acta 2015, 183, 519–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, L.; Hallaj, S.; Hallaj, T.; Amjadi, M. Doped-carbon dots: Recent advances in their biosensing, bioimaging and therapy applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 203, 111743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Wu, A.; Cai, C.; Lin, H. Red, Green, and Blue Luminescence by Carbon Dots: Full-Color Emission Tuning and Multicolor Cellular Imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 5360–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Wen, X.; Zhang, G.; Yang, J.; Dong, C.; Shuang, S. Facile and eco-friendly synthesis of green fluorescent carbon nanodots for applications in bioimaging, patterning and staining. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 7394–7401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.; Lizhe, L.; Wang, L.; Luo, G.; Moc, C.; Changa, C. Bright, stable, and tunable solid-state luminescence of carbon nanodot organogels. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 18089–18096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Das, P.; Samanta, S.; Xiong, J.; Pan, W.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Qu, J.; Yang, Z. Redefining the photo-stability of common fluorophores with triplet state quenchers: Mechanistic insights and recent updates. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 8695–8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadwater, D.; Bates, M.; Jayaram, M.; Young, M.; He, J.; Raithel, A.L.; Hamann, T.W.; Zhang, W.; Borhan, B.; Lunt, R.R.; et al. Modulating cellular cytotoxicity and phototoxicity of fluorescent organic salts through counterion pairing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, B.A.; Kumar, P.; Elangovan, T.; Ramalingam, G.; Ravi, G.; Mohanapriya, P.; Natarajan, T. Surface functionalization of core-shell QDs for solar photovoltaic and anti-cancer applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2021, 5, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekaliuk, M.; Pyrshev, K.; Demchenko, A. Visualization and detection of live and apoptotic cells with fluorescent carbon nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mura, S.; Ludmerczki, R.; Stagi, L.; Garroni, S.; Carbonaro, C.M.; Ricci, P.C.; Casula, M.F.; Malfatti, L.; Innocenzi, P. Integrating sol-gel and carbon dots chemistry for the fabrication of fluorescent hybrid organic-inorganic films. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ludmerczki, R.; Malfatti, L.; Stagi, L.; Meloni, M.; Carbonaro, C.M.; Casula, M.F.; Bogdán, D.; Mura, S.; Mándity, I.M.; Innocenzi, P. Polymerization-Driven Photoluminescence in Alkanolamine-Based C-Dots. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 2543–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Deng, R.; Zhang, H. Highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots with excellent thermal and photo stability applied as invisible ink for loading important information and anti-counterfeiting. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, M.; Zhou, Z.; Gong, A.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q. Synthesis of highly photoluminescent carbon dots via citric acid and Tris for iron(III) ions sensors and bioimaging. Talanta 2015, 143, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suner, S.S.; Sahiner, M.; Ayyala, R.S.; Bhethanabotla, V.R.; Sahiner, N. Nitrogen-Doped Arginine Carbon Dots and Its Metal Nanoparticle Composites as Antibacterial Agent. C 2020, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Qian, K.; Fu, A. Arginine-modified carbon dots probe for live cell imaging and sensing by increasing cellular uptake efficiency. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 76, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melikov, K.; Chernomordik, L.V. Arginine-rich cell penetrating peptides: From endosomal uptake to nuclear delivery. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2739–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludmerczki, R.; Mura, S.; Carbonaro, C.M.; Mandity, I.M.; Carraro, M.; Senes, N.; Garroni, S.; Granozzi, G.; Calvillo, L.; Marras, S.; et al. Carbon Dots from Citric Acid and its Intermediates Formed by Thermal Decomposition. Chem. A Eur. J. 2019, 25, 11963–11974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Malfatti, L.; Innocenzi, P. Citric Acid Derived Carbon Dots, the Challenge of Understanding the Synthesis–Structure Relationship. C 2020, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagi, L.; Malfatti, L.; Caboi, F.; Innocenzi, P. Thermal Induced Polymerization of l-Lysine forms Branched Particles with Blue Fluorescence. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2021, 222, 2100242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, C.; Piehler, A.J.; Schrader, T. Arginine- and Lysine-Specific Polymers for Protein Recognition and Immobilization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 128, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahiner, N.; Suner, S.S.; Sahiner, M.; Silan, C. Nitrogen and Sulfur Doped Carbon Dots from Amino Acids for Potential Applications. J. Fluoresc. 2019, 29, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroozandeh, P.; Aziz, A.A. Insight into Cellular Uptake and Intracellular Trafficking of Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tiruppathi, C.; Minshall, R.D.; Malik, A.B. Size and Dynamics of Caveolae Studied Using Nanoparticles in Living Endothelial Cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 4110–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sciortino, A.; Cannizzo, A.; Messina, F. Carbon Nanodots: A Review—From the Current Understanding of the Fundamental Photophysics to the Full Control of the Optical Response. C 2018, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fröhlich, E. The role of surface charge in cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of medical nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5577–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, Y.-F.; Fang, Y.-W.; Li, Y.-H.; Li, W.; Yin, X.-B. Nucleus-staining with biomolecule-mimicking nitrogen-doped carbon dots prepared by a fast neutralization heat strategy. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 16956–16959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, C.; Liu, L.; Fang, L.; Liang, J.; Xiao, S. Blue and cyan fluorescent carbon dots: One-pot synthesis, selective cell imaging and their antiviral activity. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 28016–28023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, M.C.; Crist, R.; Clogston, J.D.; McNeil, S.E. Zeta potential: A case study of cationic, anionic, and neutral liposomes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 5779–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Hashemi, E. A pseudohomogeneous nanocarrier based on carbon quantum dots decorated with arginine as an efficient gene delivery vehicle. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnikrishnan, B.; Wu, R.-S.; Wei, S.-C.; Huang, C.-C.; Chang, H.-T. Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Selective Labeling of Subcellular Organelles. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 11248–11261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fiori, F.; Moukham, H.; Olia, F.; Piras, D.; Ledda, S.; Salis, A.; Stagi, L.; Malfatti, L.; Innocenzi, P. Highly Photostable Carbon Dots from Citric Acid for Bioimaging. Materials 2022, 15, 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15072395
Fiori F, Moukham H, Olia F, Piras D, Ledda S, Salis A, Stagi L, Malfatti L, Innocenzi P. Highly Photostable Carbon Dots from Citric Acid for Bioimaging. Materials. 2022; 15(7):2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15072395
Chicago/Turabian StyleFiori, Federico, Hind Moukham, Federico Olia, Davide Piras, Sergio Ledda, Andrea Salis, Luigi Stagi, Luca Malfatti, and Plinio Innocenzi. 2022. "Highly Photostable Carbon Dots from Citric Acid for Bioimaging" Materials 15, no. 7: 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15072395
APA StyleFiori, F., Moukham, H., Olia, F., Piras, D., Ledda, S., Salis, A., Stagi, L., Malfatti, L., & Innocenzi, P. (2022). Highly Photostable Carbon Dots from Citric Acid for Bioimaging. Materials, 15(7), 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15072395







