Effect of Intercritical Tempering Temperature on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of High Strength and Toughness Medium Manganese Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
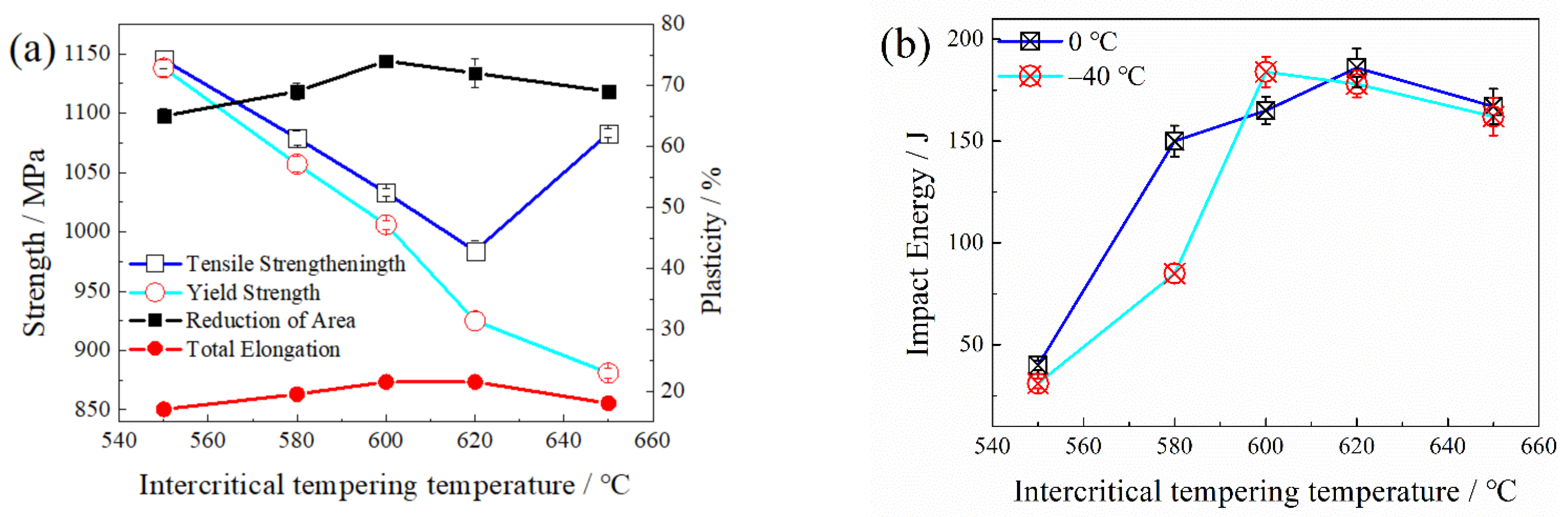
3.1. Mechanical Properties
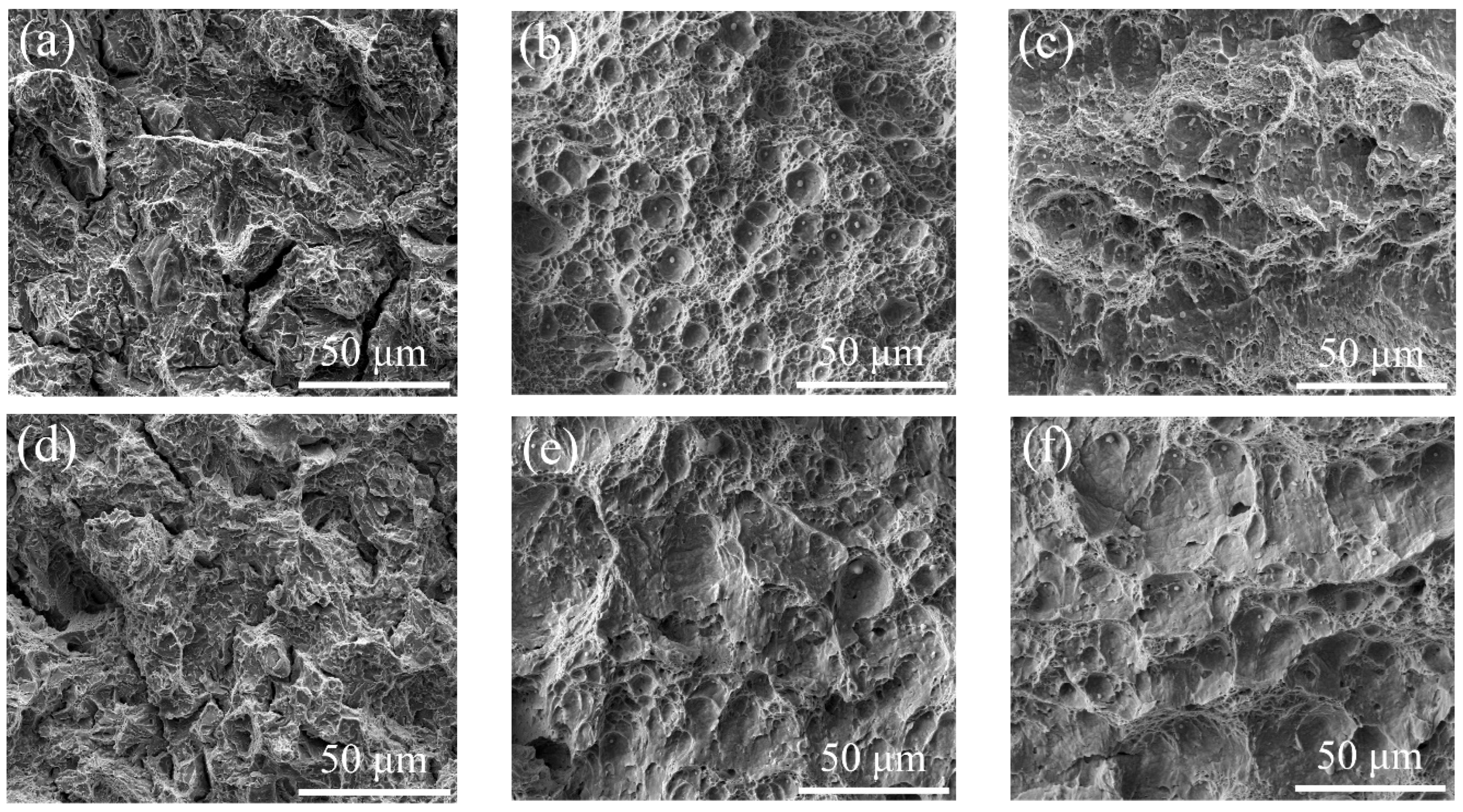
3.2. Fracture Morphology
3.3. Microstructure Characterization
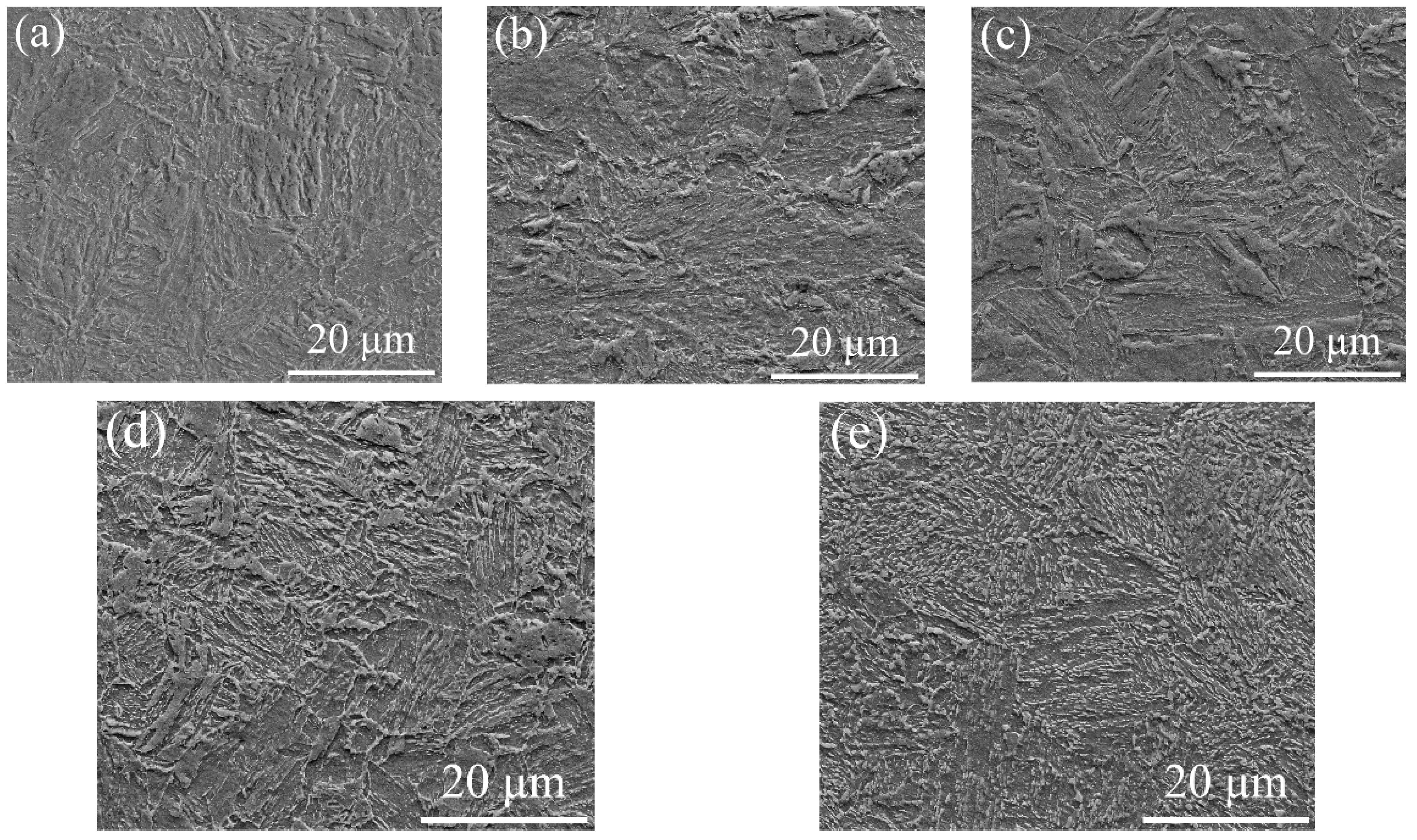
3.3.1. SEM Characterization
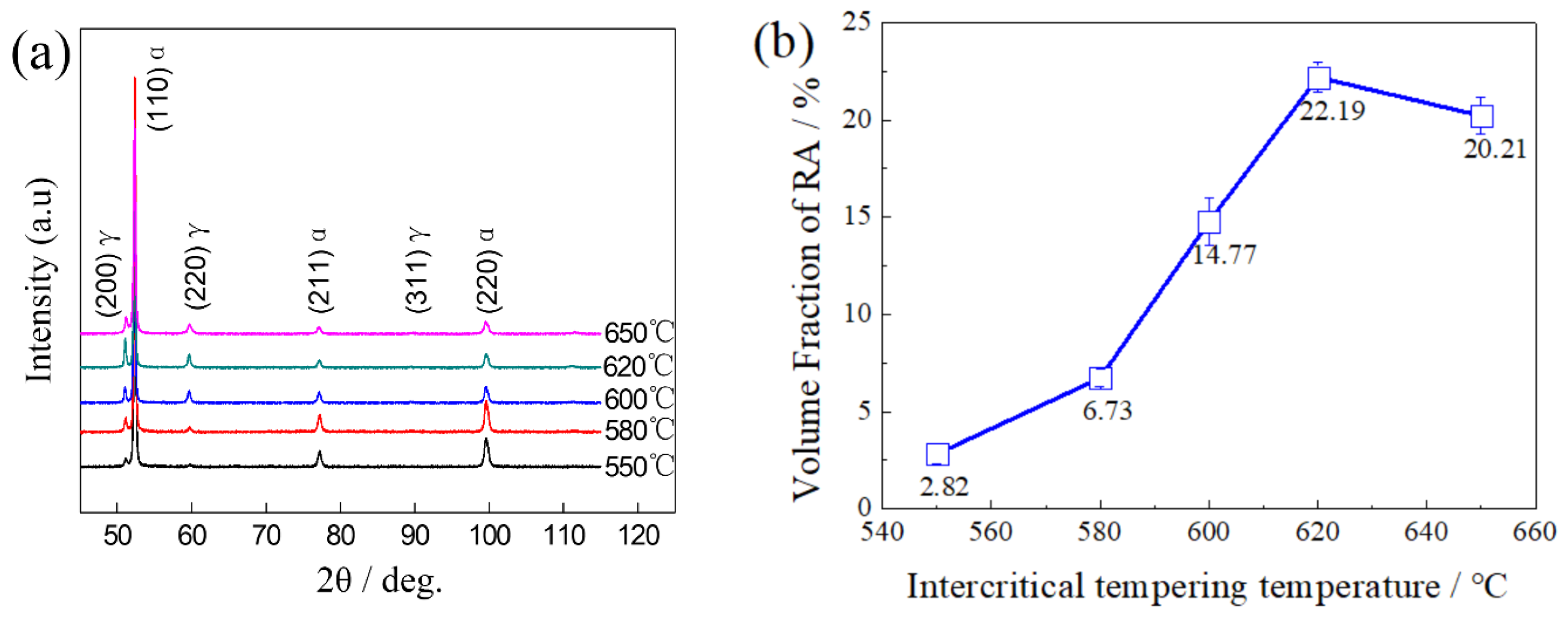
3.3.2. XRD Characterization of RA
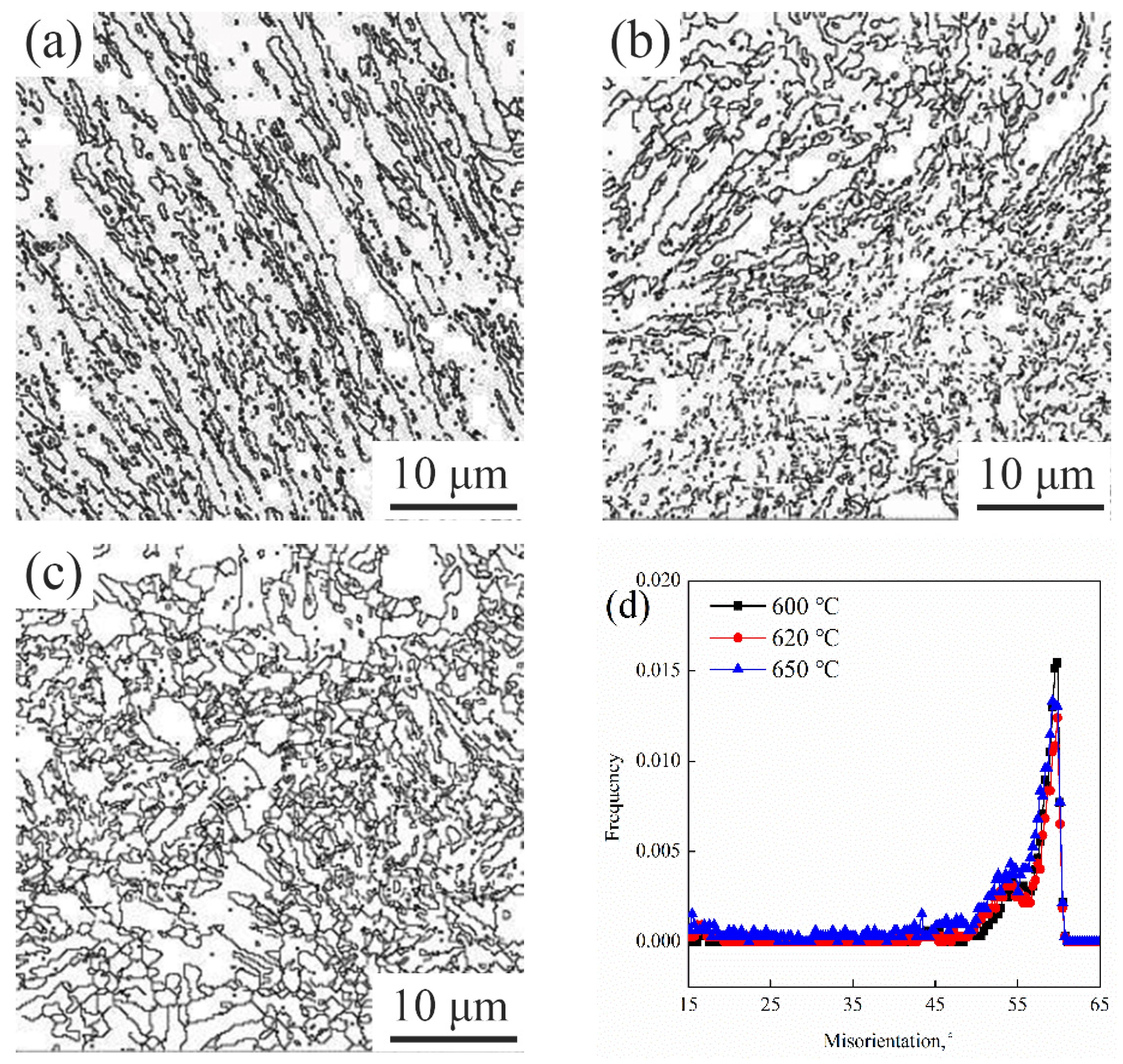
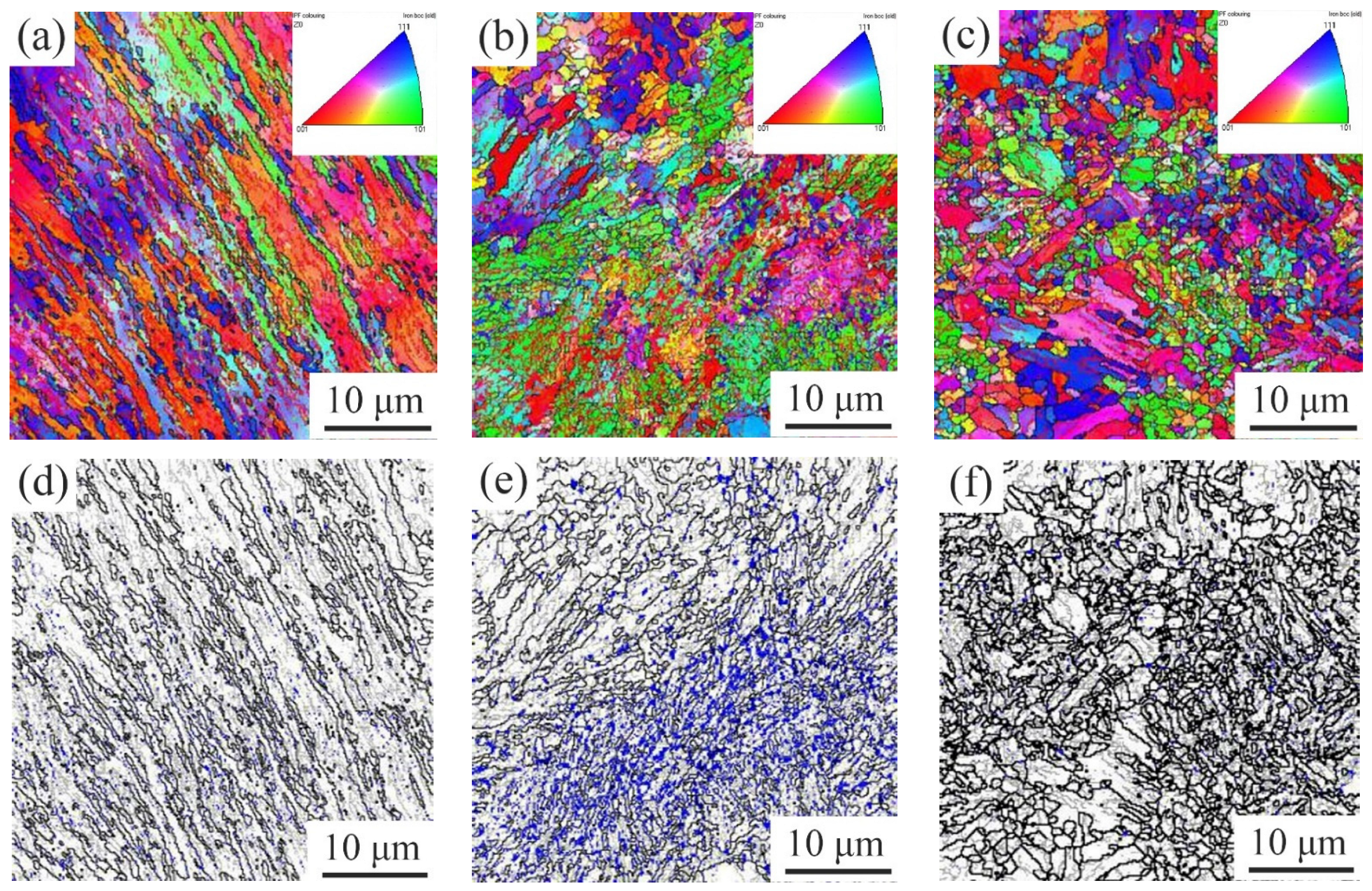
3.3.3. EBSD Characterization of Effective Grains
3.3.4. EBSD Characterization of RA
3.3.5. TEM Characterization of RA
4. Discussion
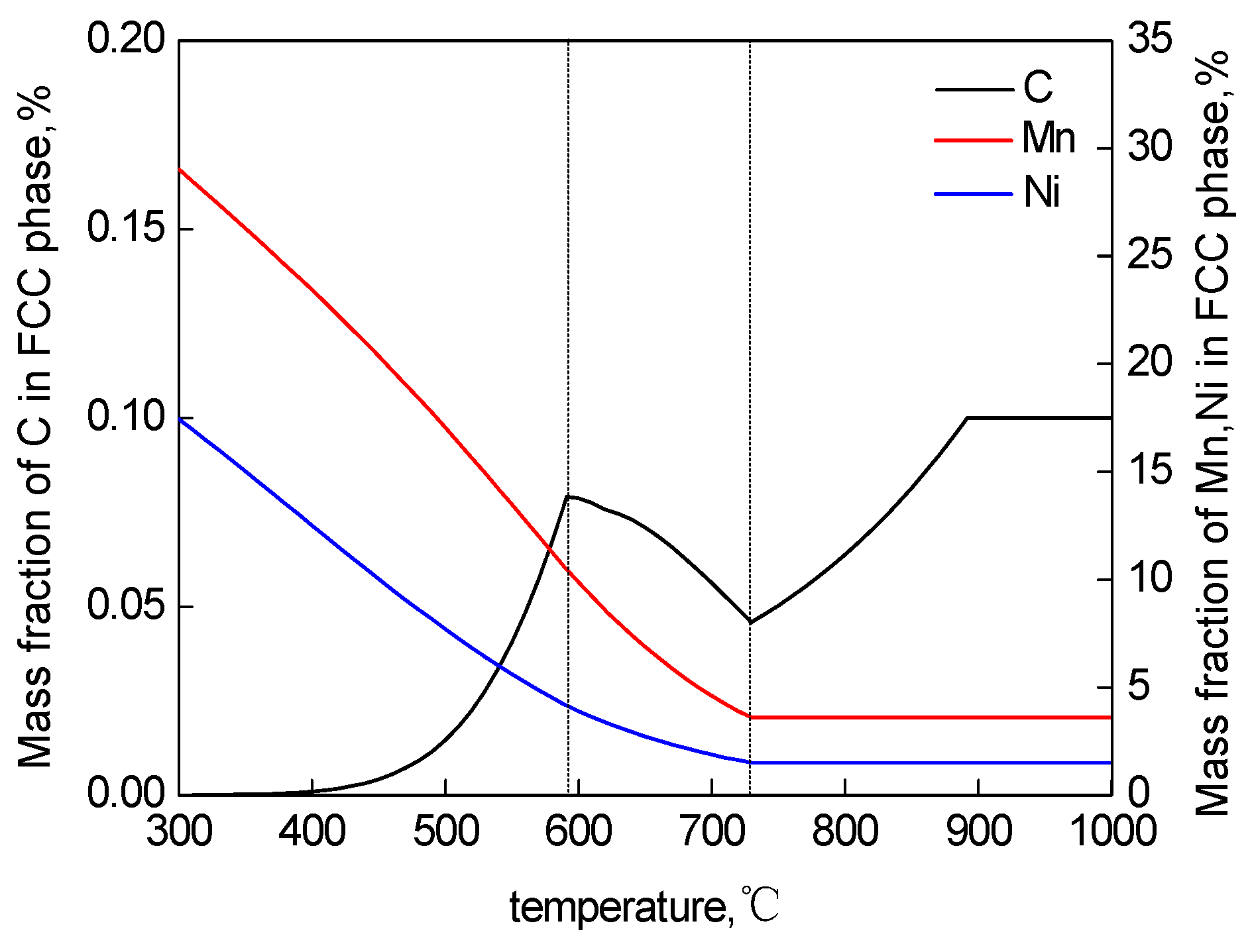
4.1. Effect of TT on RA Stability
4.2. Effect of TT on Mechanical Properties
5. Conclusions
- As the TT increases, the volume fraction of RA first increases and then decreases. When the TT is lower than 620 °C, the RA with a high stability is mainly in lath-like form displayed between martensite laths. When the TT is higher than 620 °C, the content of block RA gradually increases, and the content of stable elements such as C, Mn and Ni in RA decreases. Part of the RA transforms into fresh martensite during oil cooling, resulting in a decrease in the RA content.
- The yield strength and tensile strength gradually decrease with the increase of the TT, but the tensile strength gradually increases in view of the formation of block austenite and fresh martensite.
- Lath-like RA can significantly improve the toughness and plasticity. With the formation of block RA, the toughness and plasticity decrease slightly. When tempered at 620 °C, the plasticity and toughness reach a maximum. The fracture mode of low-temperature impact changes from a quasi-cleavage fracture mode to dimple fracture mode with the increasing content of RA.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhole, S.D.; Fox, A.G. Some interesting microstructures in very low carbon high manganese microalloyed steels. Scr. Metall. Et Mater. 1993, 29, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, C.C.; Pytlewski, K.R.; Khachaturyan, A.G.; Morris, J.J.W. The microstructure of lath martensite in quenched 9Ni steel. Acta Mater. 2014, 69, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, G.; Zhang, K.; Sun, X.; Liang, X.; Yong, Q. Effect of Nb microalloying on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties in low carbon medium manganese steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 824, 141813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.C.; Ding, H.; Misra, R.D.K.; Cai, Z.H. Microstructure-mechanical property relationship and austenite stability in medium-Mn TRIP steels: The effect of austenite-reverted transformation and quenching-tempering treatments. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 682, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Shi, J.; Wang, C.; Cao, W.; Sun, X.; Dong, H. Experimental and numerical analysis on formation of stable austenite during the intercritical annealing of 5Mn steel. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 4002–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.B.; Hu, B.; Yen, H.W.; Cheng, G.J.; Wang, Z.H.; Luo, H.W.; Huang, M.X. High dislocation density–induced large ductility in deformed and partitioned steels. Science 2017, 357, 1029–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, C.; Cao, W.Q.; Yang, Z.G. Weng, Y.Q. Observation on formation of fresh martensite from the reversed austenite during water-quenching process in Fe-0.2 C-5Mn steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 3789–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.F.; Qiu, L.N.; Sun, X.; Zuo, L.; Liaw, P.K.; Raabe, D. Effects of retained austenite volume fraction, morphology, and carbon content on strength and ductility of nanostructured TRIP-assisted steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 636, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fultz, B.; Morris, J.W. A Mössbauer spectrometry study of the mechanical transformation of precipitated austenite in 6Ni steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1985, 16, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, C.Y.; Lu, H.C.; Cao, W.Q.; Wang, C.; Dong, H.; Chen, L. Austenite transformation and work hardening of medium manganese steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2018, 25, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lv, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G. Combination of ductility and toughness by the design of fine ferrite/tempered martensite–austenite microstructure in a low carbon medium manganese alloyed steel plate. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 648, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; Cao, L.Q.; Hu, J.; Cao, W.Q.; Li, J.; Dong, H. Intercritical Rolling Induced Ultrafine Lamellar Structure and Enhanced Mechanical Properties of Medium-Mn Steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2014, 21, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; De Cooman, B.C. On the selection of the optimal intercritical annealing temperature for medium Mn TRIP steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 5018–5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, G.K.; Madhukar, D.A.; Chandan, A.K.; Ashok, K.; Mandal, G.K.; Srivastsava, V.C. On the intercritical annealing parameters and ensuing mechanical properties of low-carbon medium-Mn steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 733, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Xu, Y.B.; Hu, Z.P.; Gu, X.L.; Peng, F.; Tan, X.D.; Chen, S.Q.; Han, D.T.; Misra, R.D.K.; Wang, G.D. Austenite stability and its effect on the toughness of a high strength ultra-low carbon medium manganese steel plate. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 675, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Luo, H.W. A novel two-step intercritical annealing process to improve mechanical properties of medium Mn steel. Acta Mater. 2019, 176, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Luo, H.; Hu, C.; Pu, E.; Dong, H. Effects of intercritical annealing process on microstructures and tensile properties of cold-rolled 7Mn steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 685, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Q.; Liu, G.; Sun, X.J. The different roles of reversed austenite, athermal martensite and tempered martensite on low-temperature toughness in ultra-low carbon medium Mn steel. Mater. Lett. 2021, 297, 129958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, B.; Xu, S.; Tong, S.; Wang, X.; Liang, X.; Sun, X. Effect of intercritical annealing temperature on multiphase microstructure evolution in ultra-low carbon medium manganese steel. Mater. Charact. 2021, 173, 110920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, D.; Knott, J.F.; Davis, C.L. Charpy-impact-toughness prediction using an “effective” grain size for thermomechanically controlled rolled microalloyed steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lv, M.; Tang, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G. Correlation between mechanical properties and retained austenite characteristics in a low-carbon medium manganese alloyed steel plate. Mater. Charact. 2015, 106, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Tang, D.; Wu, H.B. Effect of Heating Rate before Tempering on Reversed Austenite in Fe-9Ni-C Alloy. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2012, 19, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Cai, Q.W.; Wu, H.B.; Wang, H. Formation of reversed austenite and its effect on cryogenic toughness of 9 Ni steel during two-phase region heat treatment. Acta Metall. Sinca 2009, 45, 270–274. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Field, D.M.; Baker, D.S.; Van Aken, D.C. On the Prediction of α-Martensite Temperatures in Medium Manganese Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 2150–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moor, E.D.; Matlock, D.K.; Speer, J.G.; Merwin, M.J. Austenite stabilization through manganese enrichment. Scr. Mater. 2011, 64, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.I.; Kim, H.J.; Morris, J.W. The role of the constituent phases in determining the low temperature toughness of 5.5Ni cryogenic steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1984, 15, 2213–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenarjhan, N.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, S.J. Effects of carbon and nitrogen on austenite stability and tensile deformation behavior of 15Cr-15Mn-4Ni based austenitic stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 742, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.B.; Hu, Z.P.; Ying, Z.; Tan, X.D.; Han, D.T.; Chen, S.Q.; Ma, D.G.; Misra, R.D.K. Effect of two-step intercritical annealing on microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-rolled medium manganese TRIP steel containing δ-ferrite. Mater. Ence Eng. A 2017, 688, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Q.L. Secondary Phases in Steels; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 33–34. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Lee, S.J.; Cooman, B. Austenite stability of ultrafine-grained transformation-induced plasticity steel with Mn partitioning. Scr. Mater. 2011, 65, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.Q.; Gao, X.H.; Zhang, D.Z.; Du, L.X.; Hu, J.; Liu, Z.G. Impact of Reversed Austenite on the Impact Toughness of the High-Strength Steel of Low Carbon Medium Manganese. JOM 2018, 70, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Cheng, B.; Chen, Y. Strengthening and Toughening of a Heavy Plate Steel for Shipbuilding with Yield Strength of Approximately 690 MPa. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, W.L.; Lee, H.C. The mechanical stability of austenite and cryogenic toughness of ferritic Fe-Mn-Al Alloys. Metall. Trans. A 1993, 24, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Sun, X.J.; Li, Z.D.; Yong, Q.L.; Wang, C.J. Effects of intercritical tempering temperature on formation of metastable austenite and mechanical properties of Mn-Mo series microalloyed steel. J. Mater. Eng. 2015, 43, 1–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Poole, W.J.; Militzer, M. Austenite formation during intercritical annealing. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 3363–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; Sun, G.J.; Ma, Q.S.; Shen, Q.Y.; Xu, L. Influence of QLT treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of a high nickel steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
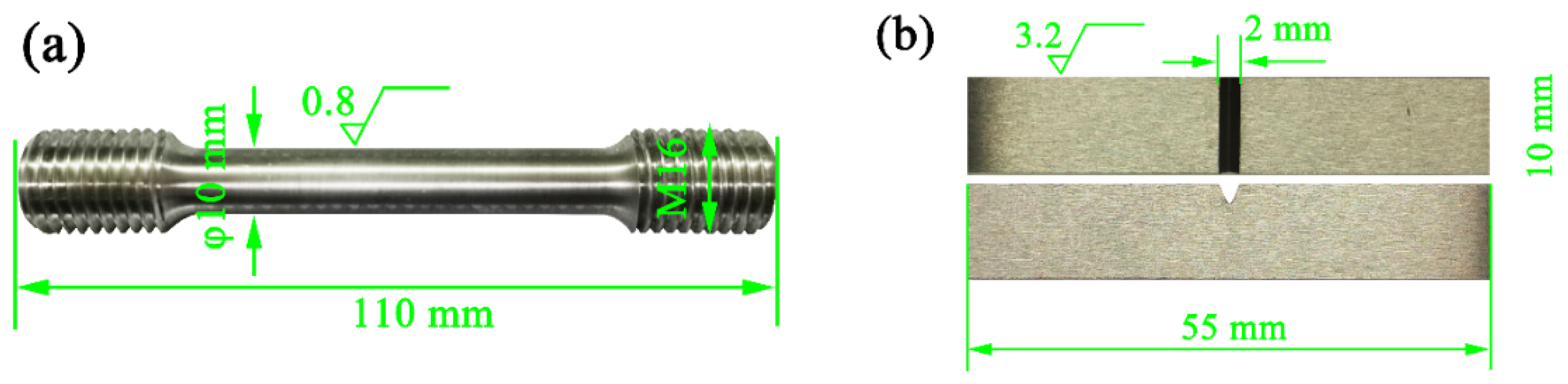


| C | Si | Mn | P | S | V + Cr + Mo + Ni + Cu | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.10 | 0.10 | 3.60 | 0.008 | 0.005 | 4.33 | Bal. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, X.; Fu, H.; Cui, M.; Liu, G. Effect of Intercritical Tempering Temperature on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of High Strength and Toughness Medium Manganese Steel. Materials 2022, 15, 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15062162
Liang X, Fu H, Cui M, Liu G. Effect of Intercritical Tempering Temperature on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of High Strength and Toughness Medium Manganese Steel. Materials. 2022; 15(6):2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15062162
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Xiaokai, Hang Fu, Mei Cui, and Gang Liu. 2022. "Effect of Intercritical Tempering Temperature on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of High Strength and Toughness Medium Manganese Steel" Materials 15, no. 6: 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15062162
APA StyleLiang, X., Fu, H., Cui, M., & Liu, G. (2022). Effect of Intercritical Tempering Temperature on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of High Strength and Toughness Medium Manganese Steel. Materials, 15(6), 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15062162






