Early-Age Performance Analysis of Sludge Water Incorporation in High-Temperature Steam Cured Green High-Performance Concrete
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Preparation of High Performance Concrete Incorporating Sludge Water (HPC-SW)
2.3. Measurement of Mechanical Properties
2.4. Characterization
3. Results
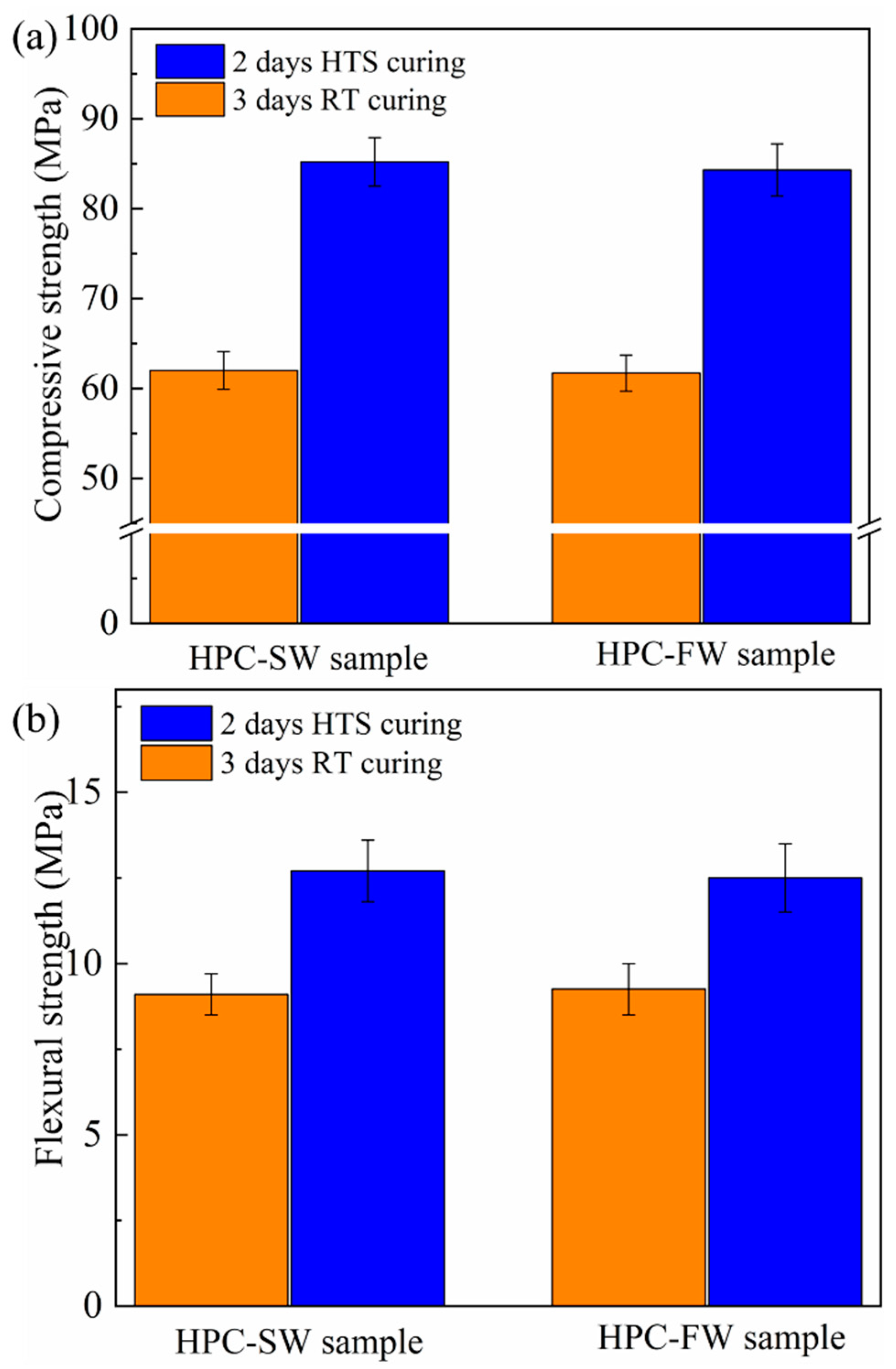
3.1. Mechanical Properties
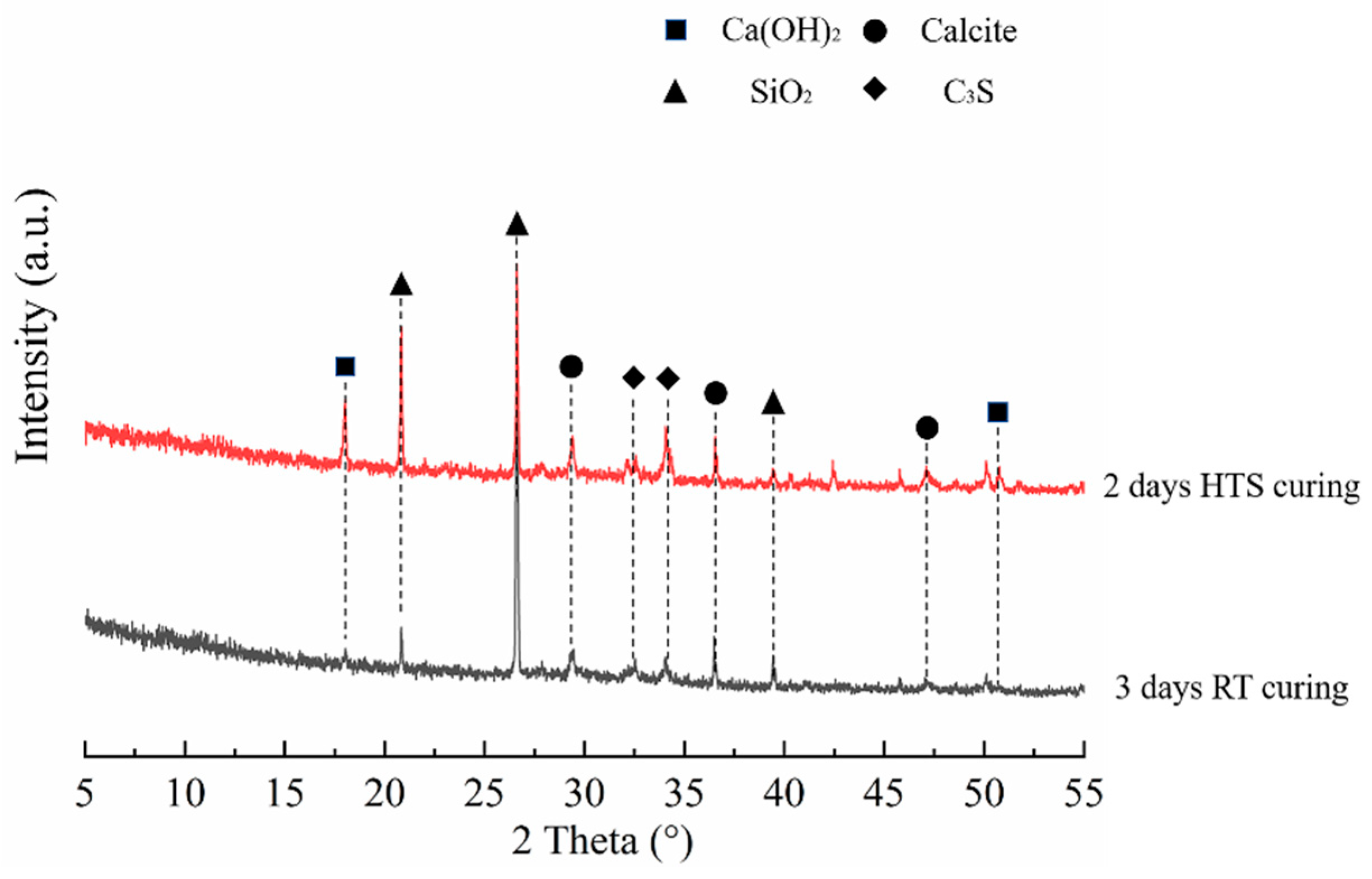
3.2. XRD Analysis
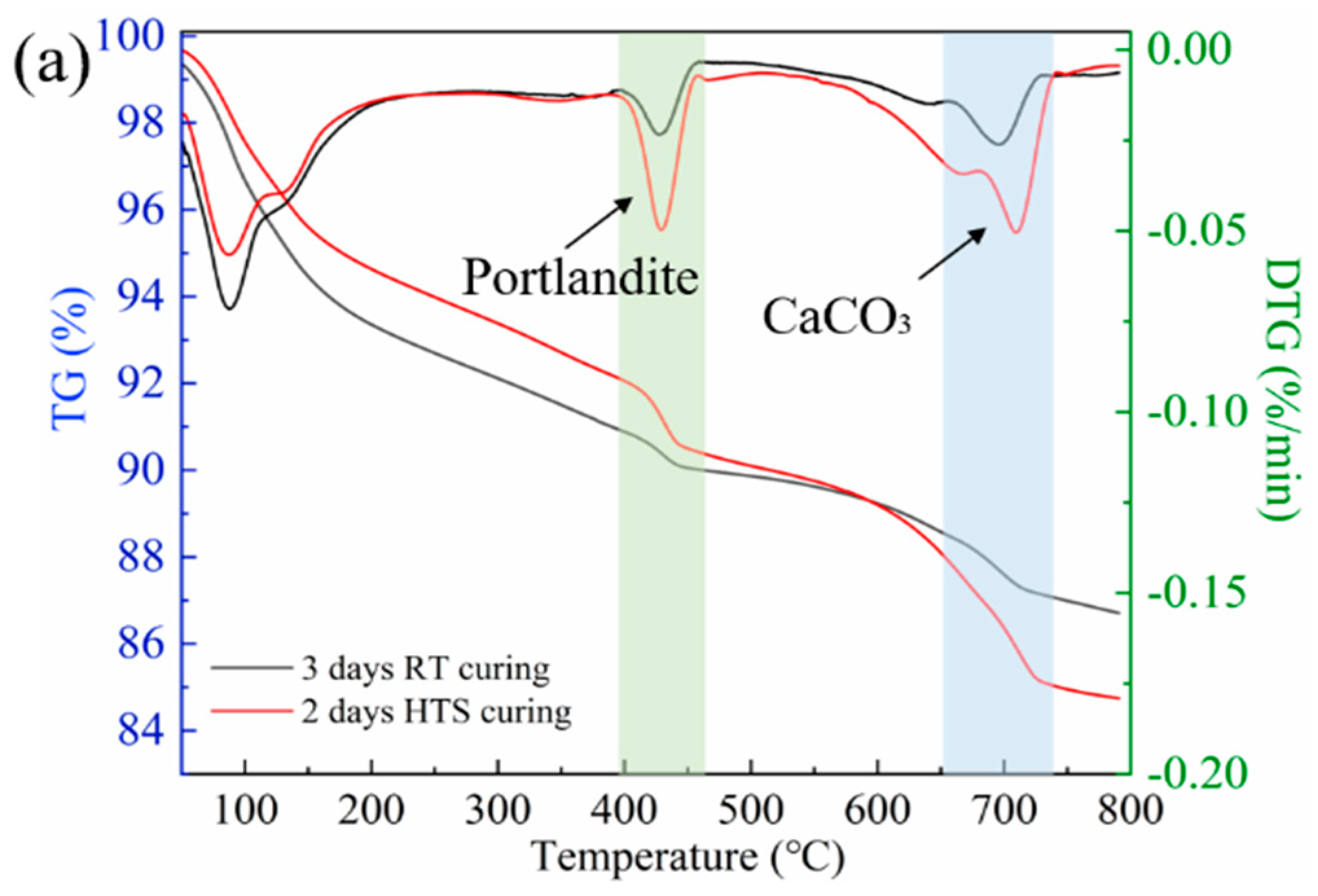
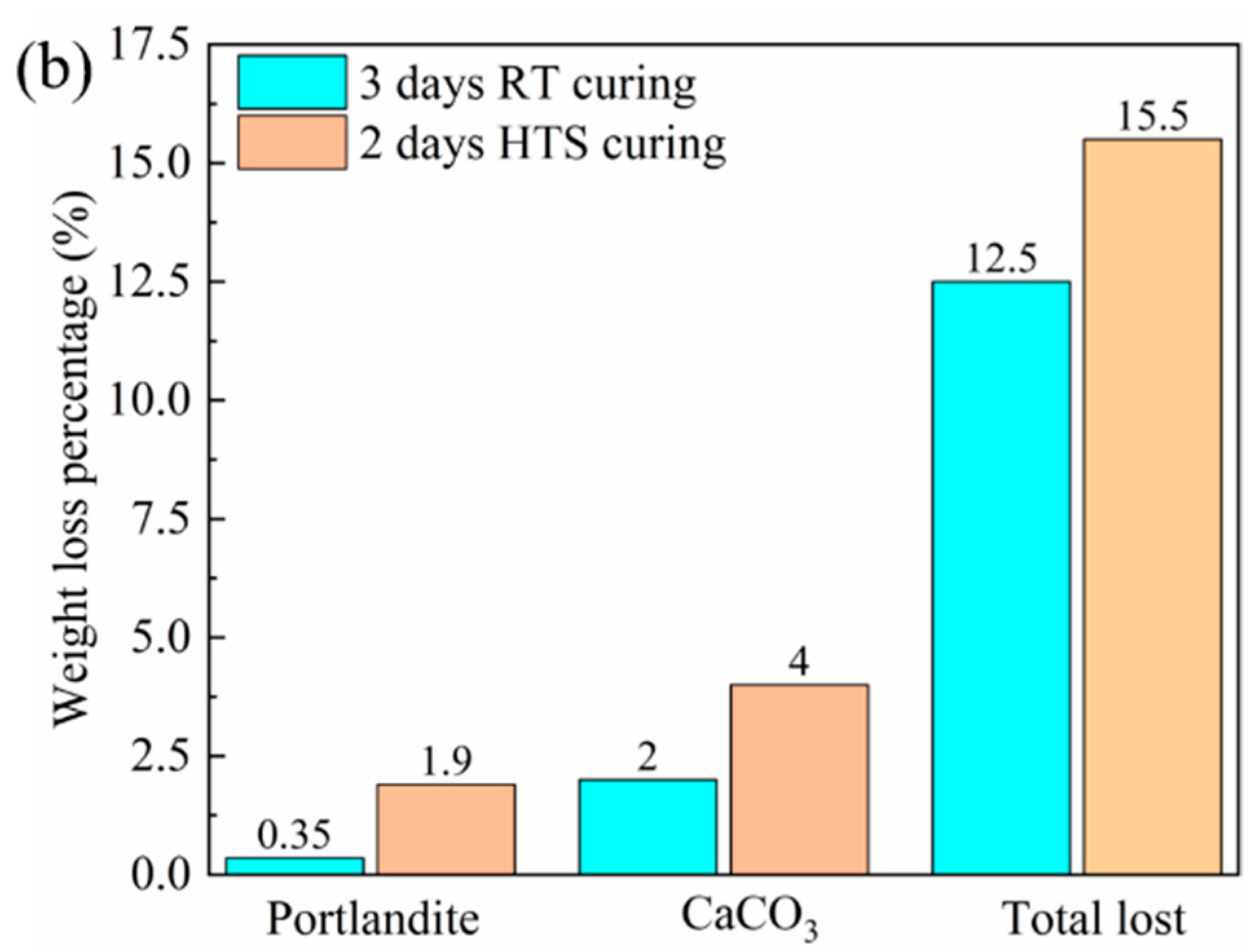
3.3. TG Analysis
3.4. MIP Analysis
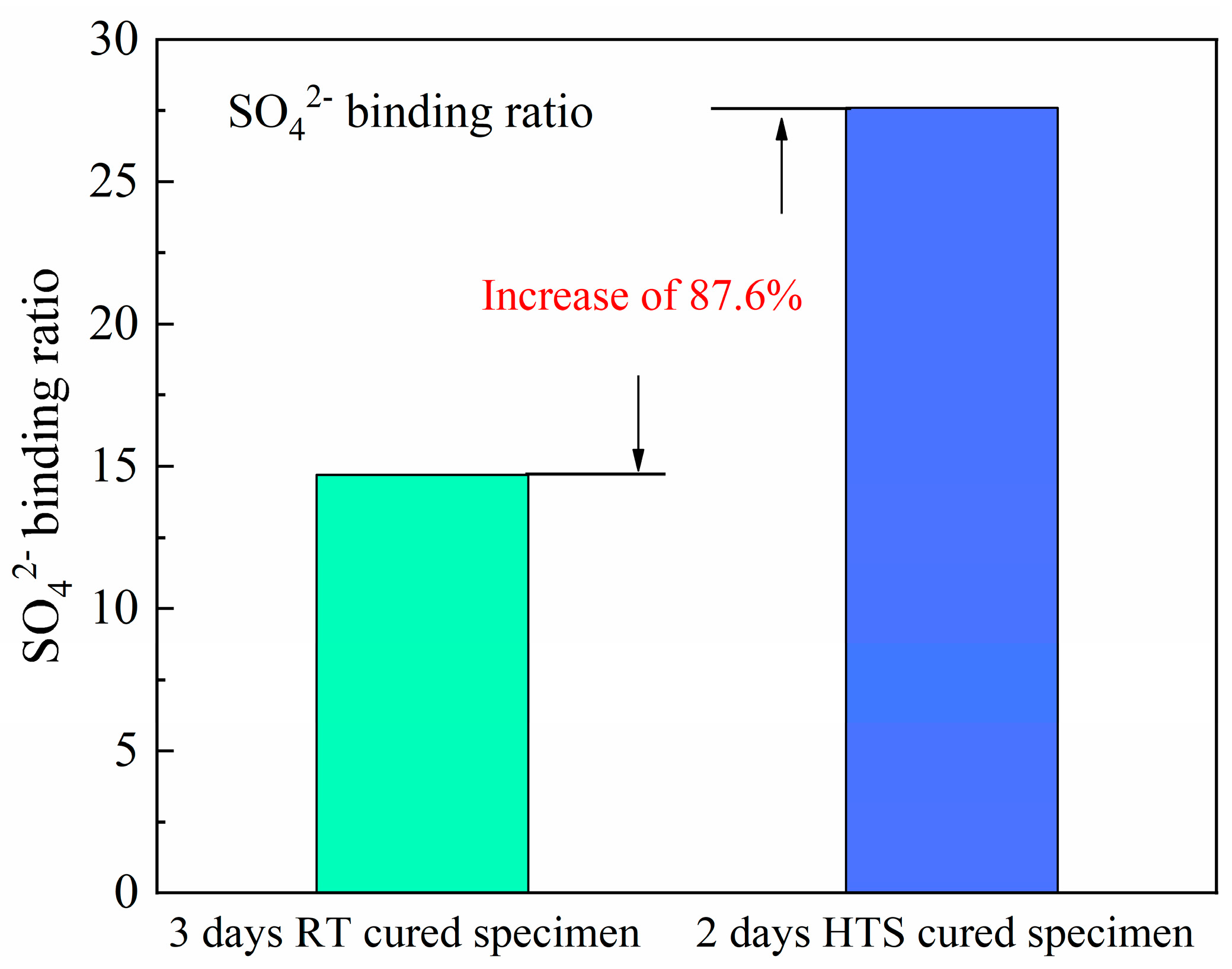
3.5. Ion’s Content
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L.; Chen, X.; Chu, S.; Ouyang, Y.; Kwan, A. Seawater cement paste: Effects of seawater and roles of water film thickness and superplasticizer dosage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimi, A.; Federici, S.; Depero, L.E.; Valentim, B.; Vassura, I.; Ceruti, F.; Cutaia, L.; Bontempi, E. Evaluation of the sustainability of technologies to recover phosphorus from sewage sludge ash based on embodied energy and CO2 footprint. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.J.; Jiang, N.J.; Shen, S.L.; Jin, F. Experimental investigation of influence of acid rain on leaching and hydraulic charac-teristics of cement-based solidified/stabilized lead contaminated clay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 225–226, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Lu, S.; Chi, L. Functionalized PP fiber to improve compressive strength and solidifica-tion/stabilization performance of cement with heavy metals. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 278, 122412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.S.; Pant, K.K. Solidification/stabilization of arsenic containing solid wastes using portland cement, fly ash and polymeric materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 131, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Shi, C.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, Z. Durability of ultra-high performance concrete—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 255, 119296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhnoukh, A.K.; Buckhalter, C. Ultra-High-Performance Concrete: Constituents, Mechanical Properties, Applications and Current Challenges. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahwia, A.M.; Elgendy, G.M.; Amin, M. Durability and microstructure of eco-efficient ultra-high-performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 303, 124491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Bo, Y. Effect of Casting Position on Mechanical Performance of Ultra-High Performance Concrete. Materials 2022, 15, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Gao, X.; Chen, T. Influence of mineral admixtures on carbonation curing of cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 212, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nmai, C.K. Recent Advances in Ultra-high Performance Concrete. J. Korean Recycl. Constr. Resour. Inst. 2013, 1, 163–172. [Google Scholar]
- Von Werder, J.; Simon, S.; Lehmann, C.; Selleng, C.; Fontana, P.; Meng, B. Autoclaving of Ultra-High Performance Con-Crete (UHPC); Ce/Papers 2018; Volume 2, pp. 131–136. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cepa.866 (accessed on 2 December 2021).
- Qin, L.; Gao, X.; Li, Q. Influences of coal fly ash containing ammonium salts on properties of cement paste. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Mei, J.; Tan, H.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, T. Effect of Nano Silica on Hydration and Microstructure Characteris-tics of Cement High Volume Fly Ash System under Steam Curing. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2019, 34, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Choi, Y.C. Hydration and pore-structure characteristics of high-volume fly ash cement pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 278, 122390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhu, X.; Liu, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, M. Modification of water absorption and pore structure of high-volume fly ash cement pastes by incorporating nanosilica. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 33, 101638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Diao, L.; Lai, Z.; He, Y.; Lv, S. Effects of bentonite on pore structure and permeability of cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 224, 276–283. [Google Scholar]
- Glasser, F.; Kindness, A.; Stronach, S. Stability and solubility relationships in AFm phases: Part I. Chloride, sulfate and hydroxide. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Huo, B.; Cao, R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Sulfate resistance of steam cured ferronickel slag blended cement mortar. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 96, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Materials | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | 20.86 | 5.47 | 3.94 | 1.73 | 62.23 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, B. Early-Age Performance Analysis of Sludge Water Incorporation in High-Temperature Steam Cured Green High-Performance Concrete. Materials 2022, 15, 1912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051912
Qi B. Early-Age Performance Analysis of Sludge Water Incorporation in High-Temperature Steam Cured Green High-Performance Concrete. Materials. 2022; 15(5):1912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051912
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Beimeng. 2022. "Early-Age Performance Analysis of Sludge Water Incorporation in High-Temperature Steam Cured Green High-Performance Concrete" Materials 15, no. 5: 1912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051912
APA StyleQi, B. (2022). Early-Age Performance Analysis of Sludge Water Incorporation in High-Temperature Steam Cured Green High-Performance Concrete. Materials, 15(5), 1912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051912





