Effect of Initial Fe Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Recycled Al-7.0Si-Fe-Mn Alloys with Constant Mn/Fe Ratio
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. The Effect of Fe Content on Fe Removal Efficiency
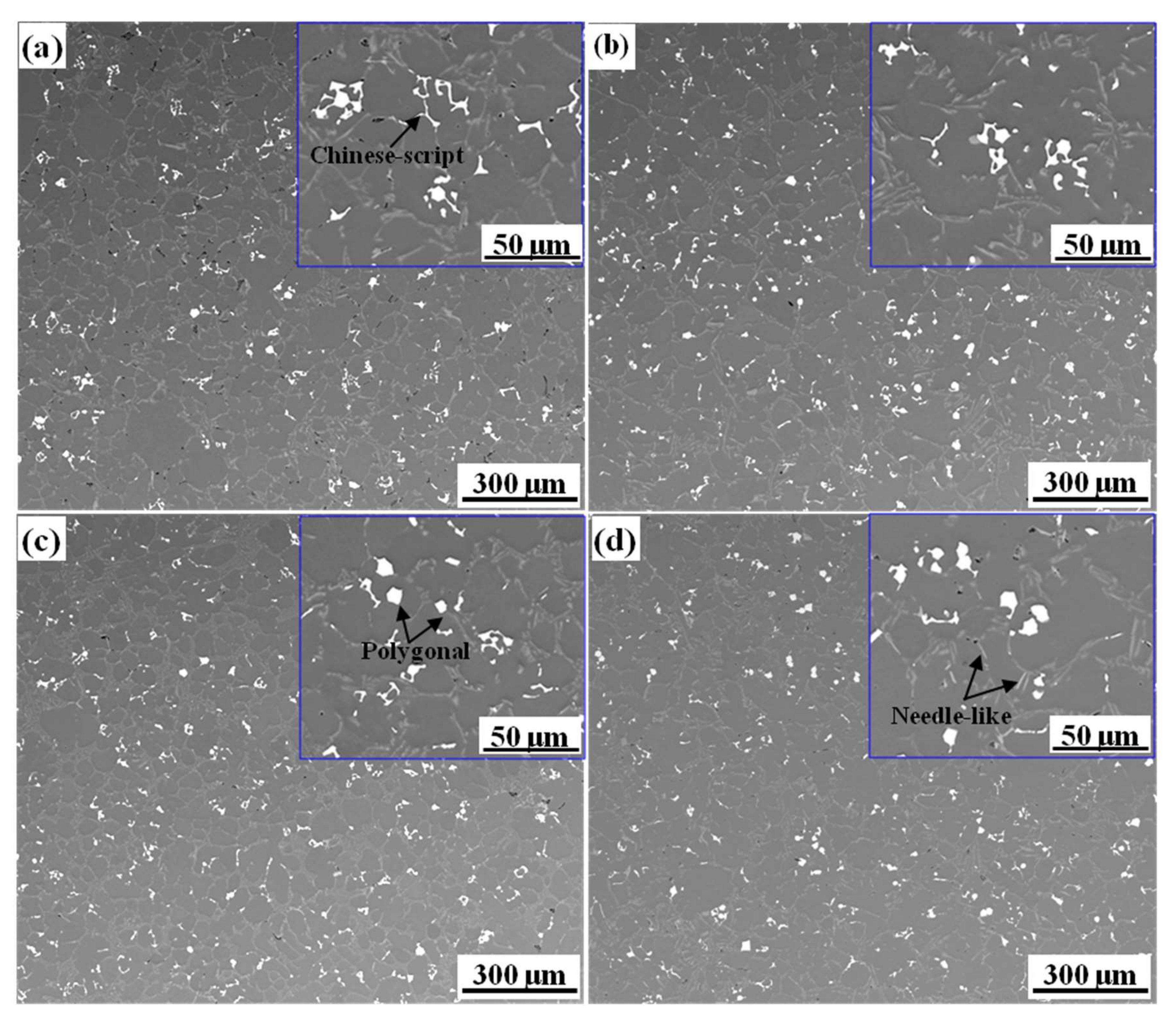
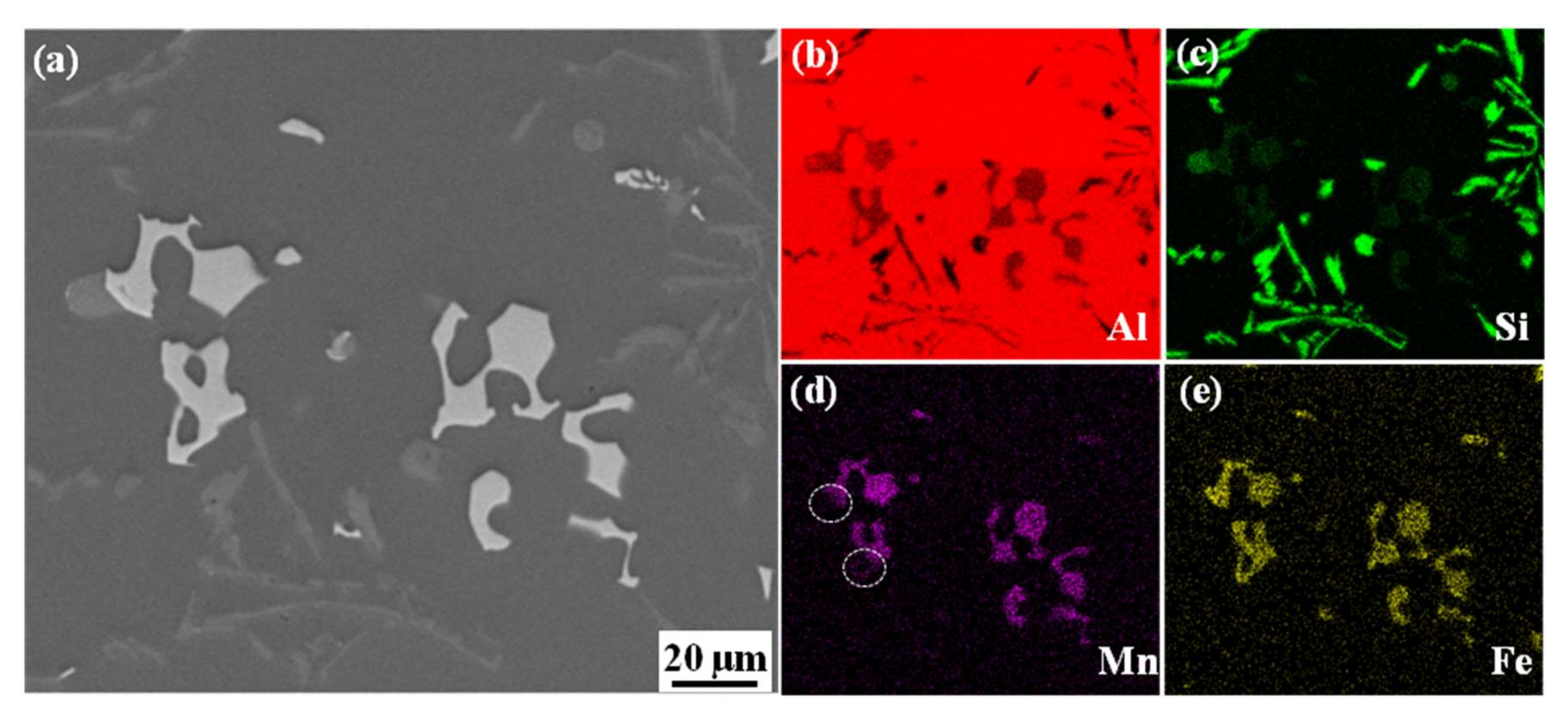
3.2. The Effect of Fe Content on Microstructure
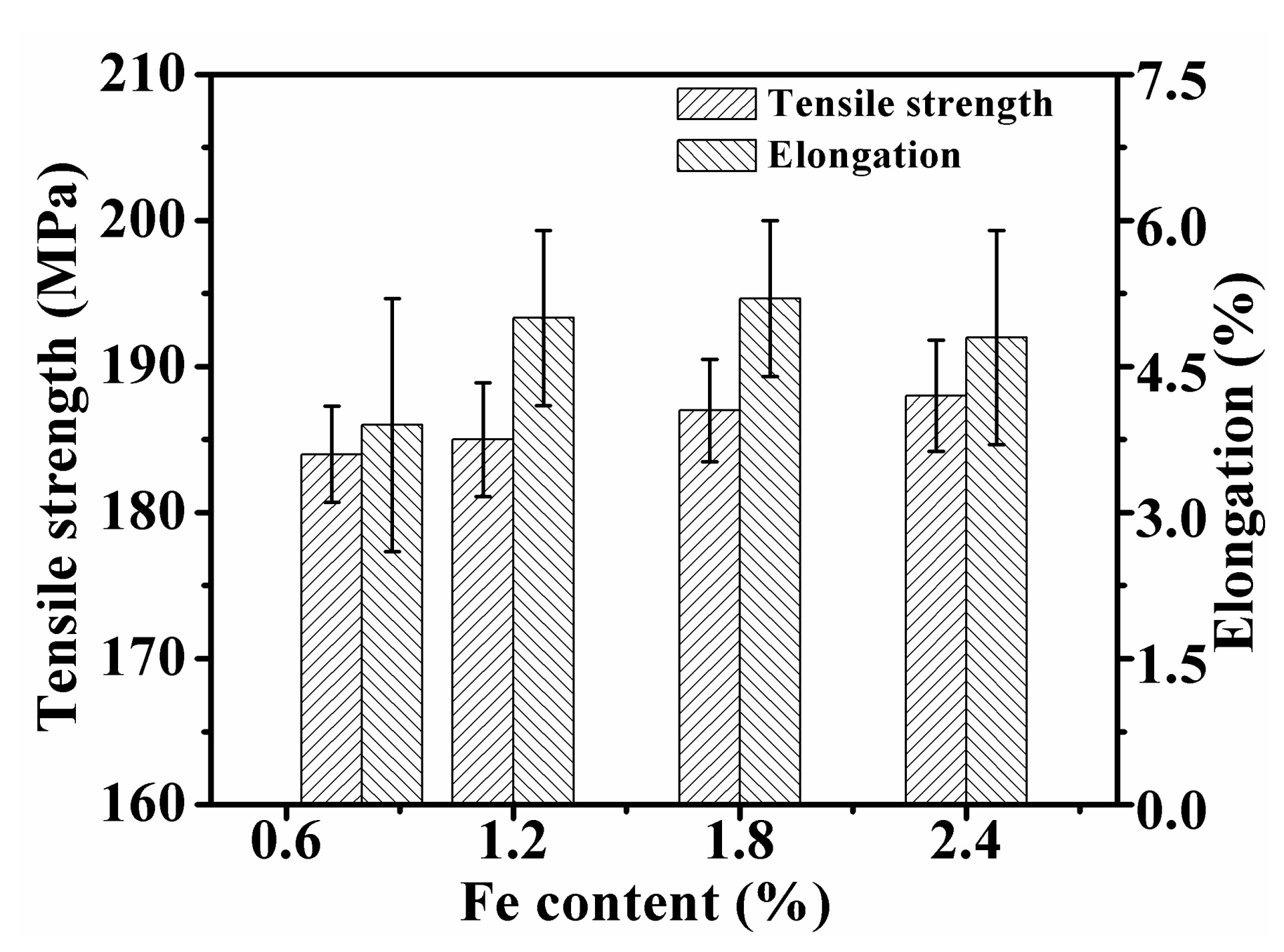
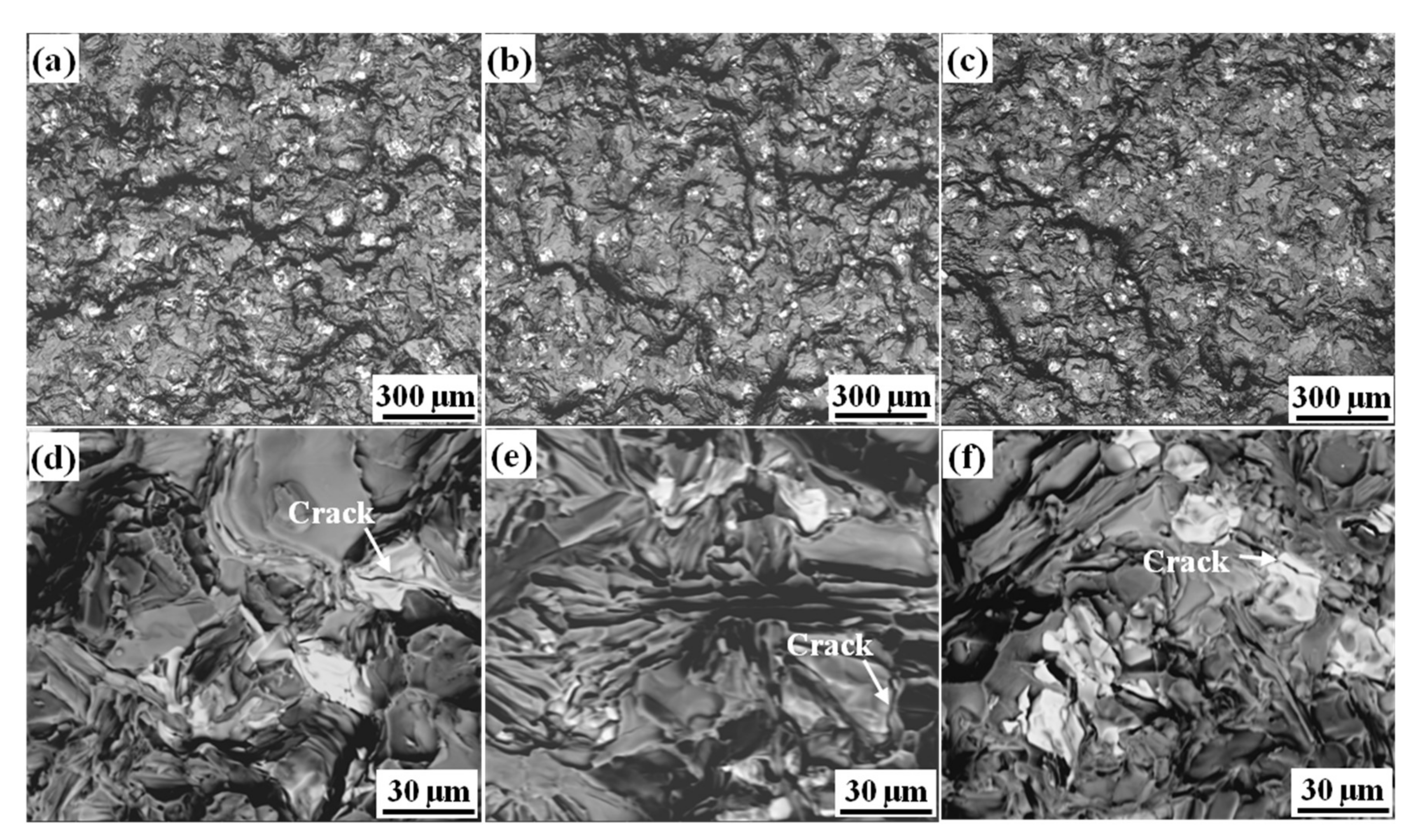
3.3. The Effect of Initial Fe on Tensile Properties
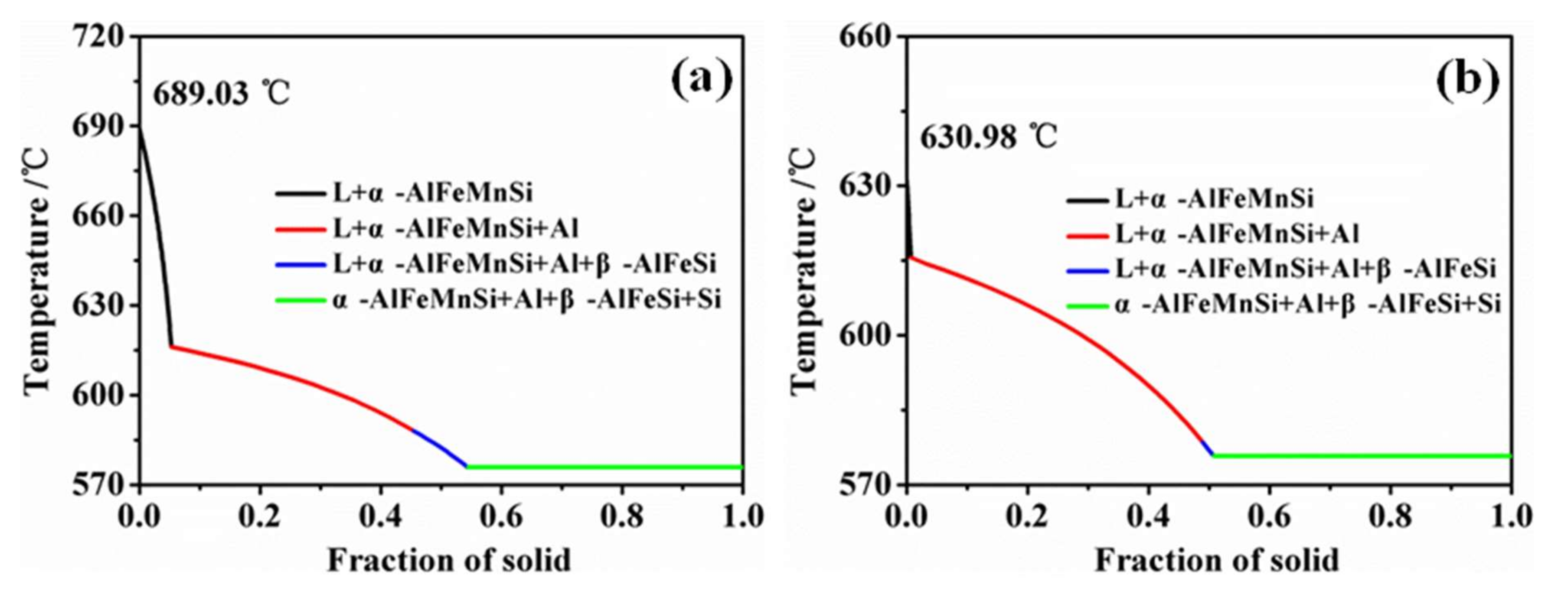
4. Analysis and Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- With the increase of the initial Fe content, the Fe content of the alloys gradually increased, while the corresponding Fe removal efficiency gradually increased to 77.67%.
- (2)
- With the increase of the initial Fe content, the Fe-rich phase type in the alloy changed from a single type of α-Fe to a mixed type of α-Fe and β-Fe. The morphological evolution of the Fe-rich phase was listed as follows: coarse Chinese-script + polygon → dense Chinese-script + polygon → polygonal + dense Chinese-script + plate-like.
- (3)
- With the increase of the initial Fe content, the morphology of the Fe-rich phase in the slag changed from a polygonal shape to an irregular-shape with a two-layer structure. The formation and increase of the inner layer with high Mn content in the irregular-shape phase was the main reason for the increase of Fe content in the alloy.
- (4)
- With the increase of the initial Fe content, the plasticity of the alloy increased obviously, but the formation of the β-Al5FeSi with plate-like morphology in higher Fe content alloy might hinder the further improvement of the plasticity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, W.S.; Zhuang, L.; Bottema, J.; Wittebrood, A.; De Smet, P.; Haszler, A.; Vieregge, A.J.M.S. Recent development in aluminium alloys for the automotive industry. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 280, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.A. Iron-Containing Intermetallic Phases in Al-Si Based Casting Alloys. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2012, 1, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, D.F.; Zhao, Y.L.; Wang, Z.; Jia, Y.W.; Li, D.X.; Fu, Y.N.; Zhang, D.T.; Zhang, W.W. 3D Fe-Rich Phases Evolution and Its Effects on the Fracture Behavior of Al-7.0Si-1.2Fe Alloys by Mn Neutralization. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2022, 35, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, M.A. Effect of iron content on the formation of β-Al5FeSi and porosity in Al–Si eutectic alloys. J. Mater. Processing Technol. 2009, 209, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, J.; Damoah, L.N.W.; Robertson, D.G. Removal of iron from aluminum: A review. Miner. Processing Extr. Metall. Rev. 2012, 33, 99–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.S.; Pillai, R.; Rajan, T.; Pai, B. Effects of individual and combined additions of Be, Mn, Ca and Sr on the solidification behaviour, structure and mechanical properties of Al–7Si–0.3Mg–0.8Fe alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 460–461, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanyathunyaroj, K.; Patakham, U.; Kou, S.; Limmaneevichitr, C. Microstructural evolution of iron-rich intermetallic compounds in scandium modified Al-7Si-0.3Mg alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 692, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaro, C.J.; Easton, M.A.; Qiu, D.; Wang, G.; StJohn, D.H.; Qian, M. The effect of ultrasonic melt treatment on macro-segregation and peritectic transformation in an Al-19Si-4Fe Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 5579–5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Z.; Jia, L.; Yang, B.; Tao, T.; Zhang, H. Effect of cooling rate and Co content on the formation of Fe-rich intermetallics in hypoeutectic Al7Si0.3Mg alloy with 0.5%Fe. Mater. Charact. 2018, 139, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Z.; Jia, L.; Yang, B.; Tao, T.; Zhang, H. Effect of B addition on the morphology of iron-rich phases in Al-Si alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2016, 45, 2133–2138. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.; Long, S.Y.; Yang, H.D.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, J.C. Influence of Ce and Mn addition on α-Fe morphology in recycled Al-Si alloy ingots. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2013, 20, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.Q.; Meng, X.C.; Yuan, Q.H.; Zeng, X.S.; Rao, X.X.; Ding, Y.; Luo, L.; Liu, Y. Morphological Evolution of Fe-Rich Phases in the AlSi9Cu3Mg0.19 (Fe)Alloy with the Addition of Minor Mn and Cr. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2018, 31, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, D.F.; Wang, S.C.; Zhou, N.; Nong, D.; Zheng, K.H. Progress in Research on Iron-rich Phase Morphology in Al-Si Alloy and Its Influencing Factors. J. Mater. Eng. 2016, 44, 120–128. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.Y.; Doty, H.W.; Kaufman, M.J. The effects of Mn additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Si-Cu casting alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2008, 488, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bösch, D.; Pogatscher, S.; Hummel, M.; Fragner, W.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Göken, M.; Höppel, H.W. Secondary Al-Si-Mg high-pressure die casting alloys with enhanced ductility. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timelli, G.; Capuzzi, S.; Fabrizi, A. Precipitation of primary Fe-rich compounds in secondary AlSi9Cu3(Fe) alloys. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 123, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.F.; Wang, S.C.; Zheng, K.H. Effects of Mn/Fe mole ratio on iron-rich phase morphology of A356 cast aluminum alloy. Chin. J. Nonferr. Met. 2015, 25, 1832–1838. [Google Scholar]
- Shabestari, S.G. The effect of iron and manganese on the formation of intermetallic compounds in aluminum–silicon alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 383, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, W. Effect of Mn/Fe ratio on Fe removal efficiency and tensile ductility of an Al-7.0Si-2.4Fe alloy. J. Mater. Res. 2021, 36, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, D.M.H.; Roberto, D.O.J.; Romano, E.D.C.; Sorares, T.J.A. Removal of iron from molten recycled aluminum through intermediate phase filtration. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 1731–1736. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, T.; Lv, G.; Bao, Y.; Duo, W.; Xu, L.; Ma, W. Electromagnetic separation of coarse Al–Si melts: The migration behavior of iron-rich phase and continuous growth of primary silicon. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 819, 153006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Im, U.H.; Cha, H.C.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, J.E.; Kim, K.Y. Removal of primary iron rich phase from aluminum-silicon melt by centrifugal separation. China Foundry 2013, 10, 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- Dhinakar, A.; Lu, P.Y.; Tang, N.K.; Chen, J.K. Iron Reduction in 356 Secondary Aluminum Alloy by Mn and Cr Addition for Sediment Separation. Int. J. Met. 2021, 15, 182–192. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Campbell, J. The solidification characteristic of Fe-rich intermetallics in Al-11.5Si-0.4Mg cast alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 1425–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, V.A.; Sukiennik, M.; Castillejos, E.A.H.; Acosta, G.F.A.; Escobedo, B.J.C. A kinetic study on the nucleation and growth of the Al8FeMnSi2 intermetallic compound for aluminum scrap purification. Intermetallics 1998, 6, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.F.; Wang, S.C.; Zhao, Y.L.; Liu, S.H.; Yong, D.U.; Kang, Y.H.; Zhi, W.; Zhang, W.W. Effect of melt holding on the morphological evolution and sedimentation behavior of iron-rich intermetallic phases in Al-Si-Fe-Mn-Mg alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2020, 30, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinnis, C.M.; Taylor, J.A.; Dahle, A.K. As-cast morphology of iron-intermetallics in Al–Si foundry alloys. Scr. Mater. 2005, 53, 955–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.S.; Song, D.F.; Zhou, H.T.; Zeng, Q.; Lou, H.S.; Wang, S.C. Effect of refinement and modification treatment on microstructrue and mechanical properties of A356 alloy. Chin. J. Nonferr. Met. 2020, 30, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraro, S.; Fabrizi, A.; Timelli, G. Evolution of sludge particles in secondary die-cast aluminum alloys as function of Fe, Mn and Cr contents. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 153, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabestari, S.G.; Gruzleski, J.E. Gravity segregation of complex intermetallic compounds in liquid aluminum-silicon alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1995, 26, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjurenstedt, A.; Ghassemali, E.; Seifeddine, S.; Dahle, A.K. The effect of Fe-rich intermetallics on crack initiation in cast aluminium: An in-situ tensile study. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 756, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.Z.; Gao, Y.X.; Lee, P.D.; Lindley, T.C. Effect of Fe-content on fatigue crack initiation and propagation in a cast aluminum–silicon alloy (A356–T6). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 386, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.Y.; Liu, C.F.; Guo, Z.P.; Tong, G.D.; Ma, S.L.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Xiong, S.M. The characterization of Fe-rich phases in a high-pressure die cast hypoeutectic aluminum-silicon alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 51, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| NO. | Initial Composition | Final Composition | Fe Removal Efficiency % | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | Fe | Mn | Al | Si | Fe | Mn | Al | ||
| Fe08 | 7.20 | 0.80 | 0.96 | Bal. | 7.29 | 0.44 | 0.48 | Bal. | 43.80 |
| Fe12 | 7.19 | 1.20 | 1.44 | Bal. | 6.85 | 0.50 | 0.50 | Bal. | 58.30 |
| Fe18 | 7.15 | 1.80 | 2.16 | Bal. | 6.90 | 0.53 | 0.41 | Bal. | 70.56 |
| Fe24 | 7.21 | 2.40 | 2.88 | Bal. | 7.23 | 0.56 | 0.34 | Bal. | 77.67 |
| Test Point | Morphology | Al | Si | Mn | Fe | Identified Compounds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Polygonal | 60.35 | 11.39 | 15.47 | 12.80 | α-Fe |
| B | Chinese script | 62.64 | 10.76 | 11.21 | 15.38 | α-Fe |
| C | Plate-like | 80.34 | 12.78 | 4.62 | 21.92 | β-Fe |
| Initial Fe Content (wt.%) | Area Fraction (%) | Average Qeuivalent Diameter (μm) | Average Roundness | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | Top 10 | All | Top 10 | ||
| 0.8 | 2.04 ± 0.09 | 9.32 ± 3.21 | 30.10 ± 2.01 | 2.72 ± 1.63 | 6.79 ± 4.53 |
| 1.2 | 2.61 ± 0.10 | 10.2 ± 3.64 | 26.70 ± 1.95 | 2.06 ± 1.00 | 3.48 ± 2.13 |
| 1.8 | 2.22 ± 0.08 | 9.35 ± 2.99 | 24.65 ± 2.21 | 2.31 ± 1.25 | 4.92 ± 2.26 |
| 2.4 | 2.49 ± 0.11 | 10.2 ± 3.60 | 26.45 ± 0.66 | 2.13 ± 1.09 | 2.90 ± 1.60 |
| Test Point | Morphology | Al | Si | Mn | Fe | Identified Compounds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Polygonal | 56.98 | 11.26 | 19.84 | 11.93 | α-Fe |
| B | Hollow polygonal | 59.38 | 9.38 | 19.18 | 12.06 | α-Fe |
| C | Inner | 54.34 | 9.00 | 33.67 | 3.00 | α-Fe |
| D | Outer | 60.34 | 8.28 | 20.10 | 10.74 | α-Fe |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, D.; Jia, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W. Effect of Initial Fe Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Recycled Al-7.0Si-Fe-Mn Alloys with Constant Mn/Fe Ratio. Materials 2022, 15, 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041618
Song D, Jia Y, Li Q, Zhao Y, Zhang W. Effect of Initial Fe Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Recycled Al-7.0Si-Fe-Mn Alloys with Constant Mn/Fe Ratio. Materials. 2022; 15(4):1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041618
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Dongfu, Yiwang Jia, Qing Li, Yuliang Zhao, and Weiwen Zhang. 2022. "Effect of Initial Fe Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Recycled Al-7.0Si-Fe-Mn Alloys with Constant Mn/Fe Ratio" Materials 15, no. 4: 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041618
APA StyleSong, D., Jia, Y., Li, Q., Zhao, Y., & Zhang, W. (2022). Effect of Initial Fe Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Recycled Al-7.0Si-Fe-Mn Alloys with Constant Mn/Fe Ratio. Materials, 15(4), 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041618






