A U-Shaped Dual-Frequency-Reconfigurable Monopole Antenna Based on Liquid Metal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Antenna Design
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zohur, A.; Mopidevi, H.; Rodrigo, D.; Unlu, M.; Jofre, L.; Cetiner, B.A. RF MEMS Reconfigurable Two-Band Antenna. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2013, 12, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazin, L.; Leviatan, Y. Reconfigurable Slot Antenna for Switchable Multiband Operation in a Wide Frequency Range. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2013, 12, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Wang, J.; Ge, L. Circularly Polarized Patch Antenna with Frequency Reconfiguration. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 1770–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, G.; Qin, F.; Tian, C.; Yan, Y. Experimental investigation on an integrated thermal management system with heat pipe heat exchanger for electric vehicle. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 118, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Lu, Y.; Chen, G.; Yang, M.; Gu, Z. Advances in liquid metals for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2518–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daalkhaijav, U.; Yirmibesoglu, O.D.; Walker, S.; Mengüç, Y. Rheological Modification of Liquid Metal for Additive Manufacturing of Stretchable Electronics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1700351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J. Recent Advancements in Liquid Metal Flexible Printed Electronics: Properties, Technologies, and Applications. Micromachines 2016, 7, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, M.; Ladd, C.; Ma, S.; Holbery, J.; Tröster, G. On-skin liquid metal inertial sensor. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 3272–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J. Diverse Transformations of Liquid Metals Between Different Morphologies. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6036–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jia, Y.; Zhu, P. A Frequency- and Polarization-Reconfigurable Slot Antenna Using Liquid Metal. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 7630–7635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S. A Frequency and Polarization Reconfigurable Spiral Antenna based on Liquid Metal. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society (ACES-China) Symposium, Chengdu, China, 28–31 July 2021; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Baig, M.U.; Elassy, K.S.; Høst-Madsen, A.; Ohta, A.T.; Shiroma, W.A.; Nosratinia, A. Leveraging discrete modulation and liquid metal antennas for interference reduction. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2021, 2021, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fang, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Shao, T. A Function Reconfigurable Antenna Based on Liquid Metal. Electronics 2020, 9, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, M.; Li, X.; Kim, C.; Hashimoto, M.; Wiley, B.J.; Ham, D.; Whitesides, G.M. Stretchable Microfluidic Radiofrequency Antennas. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2749–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, R.C.; Morishita, A.M.; Dang, J.H.; Hu, W.; Shiroma, W.A.; Ohta, A.T. Continuous Electrowetting of Non-toxic Liquid Metal for RF Applications. IEEE Access 2014, 2, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Trlica, C.; Khan, M.R.; Dickey, M.D.; Adams, J.J. A reconfigurable liquid metal antenna driven by electrochemically controlled capillarity. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 194901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Guldiken, R.; Mumcu, G. Microfluidically Reconfigured Wideband Frequency-Tunable Liquid-Metal Monopole Antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 2572–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, G.H.; Pan, H.; Hartl, D.J.; Frank, G.J.; Bradford, R.L.; Baur, J.W. A Physically Reconfigurable Structurally Embedded Vascular Antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 2282–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.I.H.; Lim, S. Microfluidically Frequency-Reconfigurable Quasi-Yagi Dipole Antenna. Sensors 2018, 18, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, P.; Wang, L.; Liu, T.-Y.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Fu, J.-H.; Huang, G.-L.; Gui, L.; Liu, J.; Deng, Z.-S. The Design and Manufacturing Process of an Electrolyte-Free Liquid Metal Frequency-Reconfigurable Antenna. Sensors 2021, 21, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Huang, G.-L.; Liang, J.-J.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Fu, J.-H.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Liu, T.-Y.; Gui, L.; Liu, J.; Deng, Z.-S. A Gravity-Triggered Liquid Metal Patch Antenna with Reconfigurable Frequency. Micromachines 2021, 12, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenath Sathikbasha, M.; Nagarajan, V. Design of Multiband Frequency Reconfigurable Antenna with Defected Ground Structure for Wireless Applications. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 113, 867–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergolle, M.; Castel, X.; Himdi, M.; Besnier, P.; Parneix, P. Structural composite laminate materials with low dielectric loss: Theoretical model towards dielectric characterization. Compos. Part C Open Access 2020, 3, 100050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Guo, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, T.; Li, D. A high-efficient tunable liquid metal-based electromagnetic absorbing metamaterial. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 19242–19247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Sen, P.; Kim, C. Characterization of liquid-metal Galinstan® for droplet applications. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Hong Kong, China, 24–28 January 2010; pp. 560–563. [Google Scholar]
- Mansoul, A.; Ghanem, F.; Hamid, M.R.; Trabelsi, M. A Selective Frequency-Reconfigurable Antenna for Cognitive Radio Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2014, 13, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdil, E.; Topalli, K.; Unlu, M.; Civi, O.A.; Akin, T. Frequency Tunable Microstrip Patch Antenna Using RF MEMS Technology. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2007, 55, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, J.H.; Gough, R.C.; Morishita, A.M.; Ohta, A.T.; Shiroma, W.A. Liquid-metal frequency-reconfigurable slot antenna using air-bubble actuation. Electron. Lett. 2015, 51, 1630–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Geng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, A. Frequency-Reconfigurable Liquid Metal Magnetoelectric Dipole Antenna. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2021, 20, 2481–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
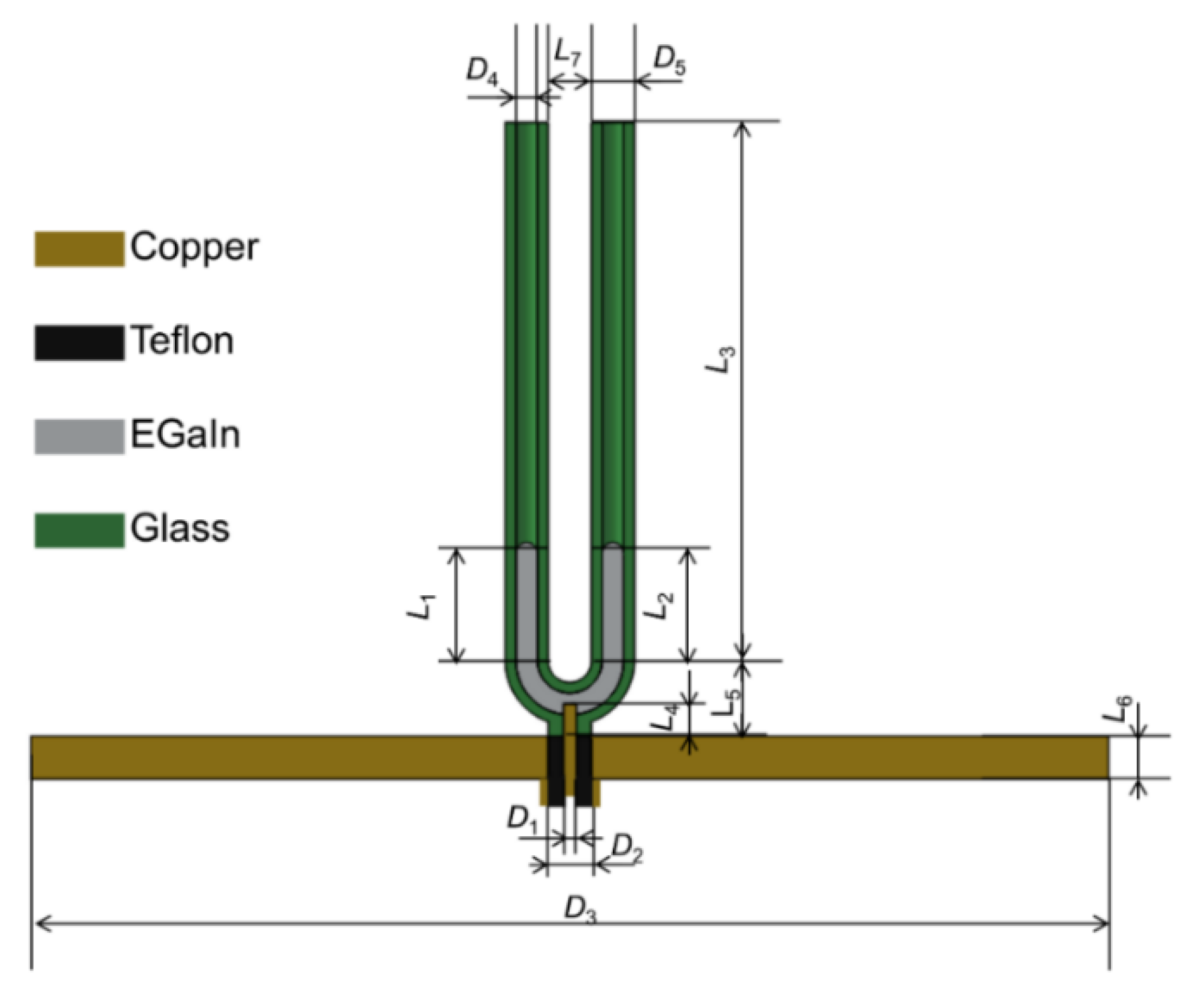
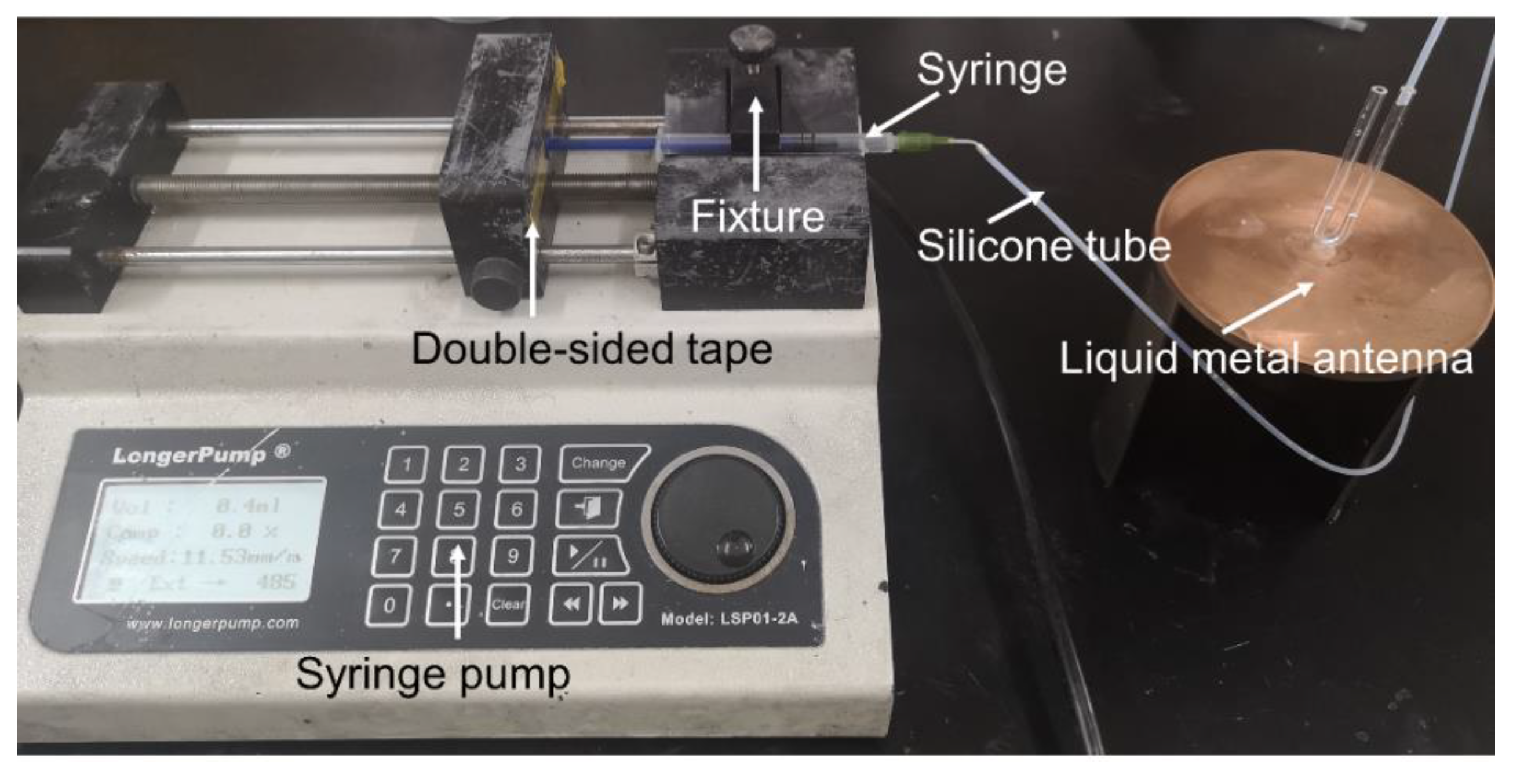







| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 |
| 1.2 | 4.0 | 100 | 2.0 |
| D5 | L1 | L2 | L3 |
| 4.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 50 |
| L4 | L5 | L6 | L7 |
| 4.0 | 8.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
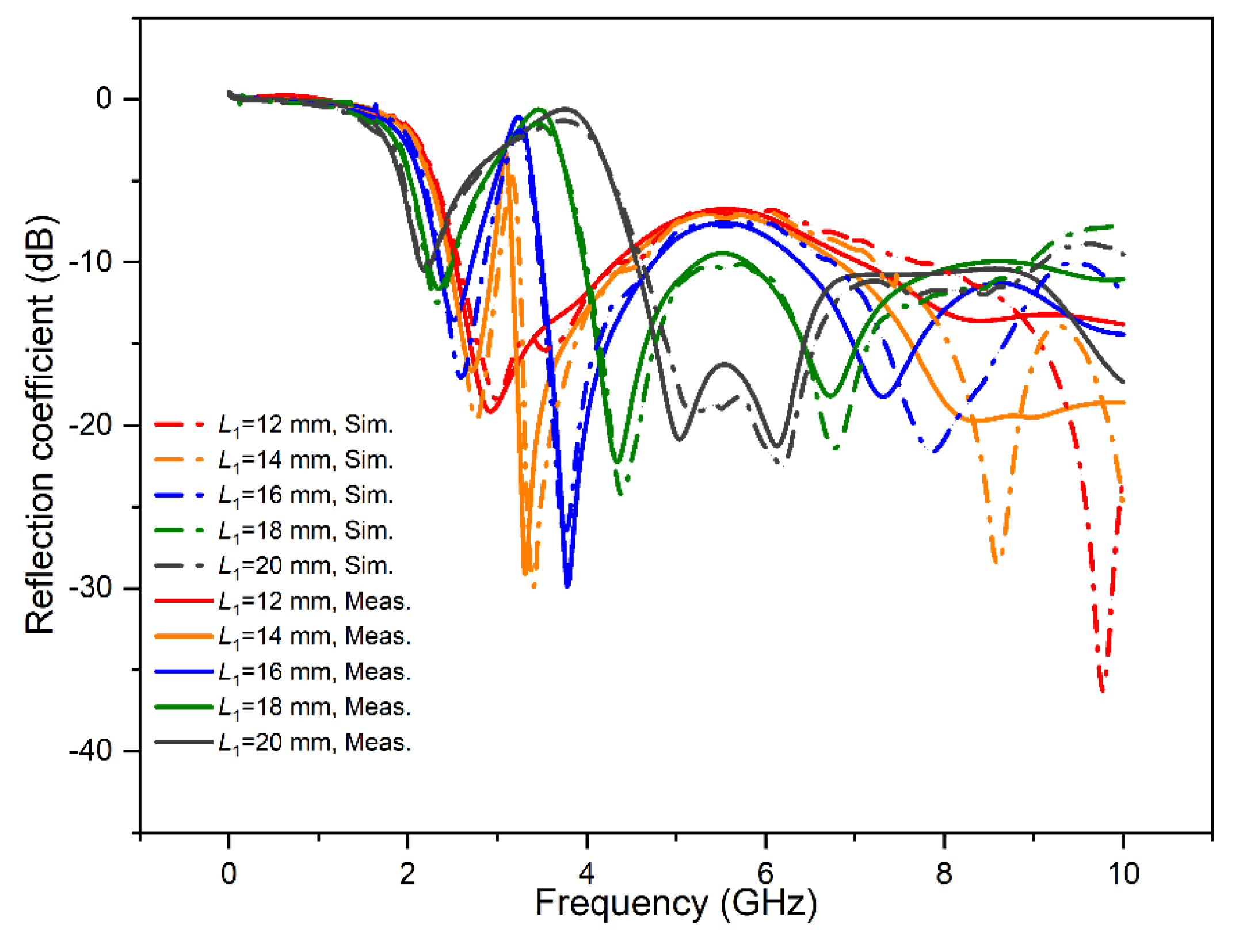
| The Length of L1 (mm) | Center Frequency (Sim., GHz) | Center Frequency (Meas., GHz) | Impedance Bandwidth (Sim.,GHz) | Impedance Bandwidth (Meas., GHz) | Peak Gain (Sim., dBi) | Peak Gain (Meas., dBi) | Average Effiency (Sim., %) | Average Effiency (Meas., %) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | f | 3.28 | 3.51 | 2.71–4.71 | 2.71–4.98 | 3.72 | 3.20 | 84 | 76 |
| 12 | fL | 2.96 | 3.03 | 2.62−3.27 | 2.65–3.38 | 3.20 | 3.60 | 88 | 79 |
| fH | 3.78 | 3.79 | 3.53–4.77 | 3.55–5.06 | 4.04 | 3.45 | 83 | 73 | |
| 14 | fL | 2.70 | 2.74 | 2.47–3.01 | 2.49–3.08 | 2.49 | 2.55 | 82 | 81 |
| fH | 4.32 | 4.42 | 3.97–5.22 | 4.03–5.45 | 3.79 | 2.33 | 93 | 73 | |
| 16 | fL | 2.50 | 2.51 | 2.33–2.72 | 2.34–2.76 | 2.03 | 2.06 | 85 | 83 |
| fH | 5.00 | 5.24 | 4.57–8.70 | 4.75–8.58 | 3.52 | 2.17 | 95 | 68 | |
| 18 | fL | 2.34 | 2.39 | 2.21–2.49 | 2.27–2.51 | 1.67 | 1.78 | 88 | 86 |
| fH | 6.14 | 5.93 | 5.35–8.64 | 5.36–8.39 | 5.44 | 4.00 | 93 | 74 | |
| The length of L1 (mm) | Center Frequency (Sim., GHz) | Center Frequency (Meas., GHz) | Impedance Bandwidth (Sim.,GHz) | Impedance Bandwidth (Meas., GHz) | Peak Gain (Sim., dBi) | Peak Gain (Meas., dBi) | Average Effiency (Sim., %) | Average Effiency (Meas., %) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | f | 2.92 | 2.98 | 2.52–4.33 | 2.57–4.32 | 3.11 | 2.60 | 83 | 75 |
| 14 | fL | 2.72 | 2.76 | 2.46–2.94 | 2.47–3.01 | 2.51 | 1.53 | 82 | 70 |
| fH | 3.32 | 3.41 | 3.17–4.45 | 3.25–4.62 | 3.67 | 2.38 | 84 | 73 | |
| 16 | fL | 2.52 | 2.59 | 2.34–2.72 | 2.36–2.85 | 1.96 | 1.40 | 85 | 75 |
| fH | 3.78 | 3.75 | 3.49–4.75 | 3.47–4.72 | 3.57 | 2.58 | 88 | 75 | |
| 18 | fL | 2.34 | 2.33 | 2.23–2.47 | 2.20–2.49 | 1.52 | −2.73 | 88 | 33 |
| fH | 4.34 | 4.39 | 3.96–5.24 | 4.00–5.37 | 3.32 | 3.72 | 94 | 63 | |
| 20 | fL | 2.20 | 2.19 | 2.13–2.26 | 2.18–2.20 | 1.26 | −4.36 | 91 | 22 |
| fH | 5.04 | 6.19 | 4.55–8.84 | 4.62–9.09 | 3.40 | 2.71 | 95 | 63 | |
| Ref. | Radiator | Methods of Reconstruction | Reconfigurable Types | Max Size (mm) | Working Bandwidth (Meas.) | Peak Gain (Meas.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [1] | Planar inverted-F | RF-MEMS | Frequency | 104 | 0.718 (2.6%) and 4.96 (7.6%) | 3.3 dBi |
| [2] | Slot | PIN diodes | Frequency | 43 | 6.0–10.6 GHz | 3.2 dBi |
| [3] | Patch | Varactor diodes | Frequency | 100 | 1.92–2.51 GHz | 5.91 dBi |
| [16] | Monopole | Liquid metal | Frequency | >75 | 0.66–3.4 GHz | 3.40 dBi |
| [17] | Monopole | Liquid metal | Frequency | 152.4 | 1.29–5.17 GHz | >1.3 dBi |
| [19] | Quasi-Yagi | Liquid metal | Frequency | 88 | 1.8–2.4 GHz | 8.5 dBi |
| [20] | Monopole | Liquid metal | Frequency | 100 | 1.25–2.00 GHz | 2.90 dBi |
| [21] | Patch | Liquid metal | Frequency | 40 | 3.69–4.95 GHz | 1.43 dBi |
| [28] | Slot | Liquid metal | Frequency | >60 | 1.41–1.84 GHz | 4.8 dBi |
| [29] | Magnetoelectric Dipole | Liquid metal | Frequency | 100 | 1.79–3.85 GHz | 9.4 dBi |
| This work | U-shape Monopole | Liquid metal | Dual frequency | 100 | 2.27–4.98 GHz and 2.71–8.58 GHz; 2.18–4.32 GHz and 2.57–9.09 GHz | 4.00 dBi; 3.72 dBi |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, P.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Fu, J.-H.; Li, C.-W.; Zhang, C.-L.; Liu, T.-Y.; Gui, L.; Liu, J.; Deng, Z.-S. A U-Shaped Dual-Frequency-Reconfigurable Monopole Antenna Based on Liquid Metal. Materials 2022, 15, 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041599
Qin P, Wang Q-Y, Fu J-H, Li C-W, Zhang C-L, Liu T-Y, Gui L, Liu J, Deng Z-S. A U-Shaped Dual-Frequency-Reconfigurable Monopole Antenna Based on Liquid Metal. Materials. 2022; 15(4):1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041599
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Peng, Qian-Yu Wang, Jun-Heng Fu, Chun-Wei Li, Cheng-Lin Zhang, Tian-Ying Liu, Lin Gui, Jing Liu, and Zhong-Shan Deng. 2022. "A U-Shaped Dual-Frequency-Reconfigurable Monopole Antenna Based on Liquid Metal" Materials 15, no. 4: 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041599
APA StyleQin, P., Wang, Q.-Y., Fu, J.-H., Li, C.-W., Zhang, C.-L., Liu, T.-Y., Gui, L., Liu, J., & Deng, Z.-S. (2022). A U-Shaped Dual-Frequency-Reconfigurable Monopole Antenna Based on Liquid Metal. Materials, 15(4), 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041599







