Microstructure and Piezoelectric Properties of Lead Zirconate Titanate Nanocomposites Reinforced with In-Situ Formed ZrO2 Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Characterization
3. Results
3.1. PZT/ZrO2 Nanocomposite Ceramics
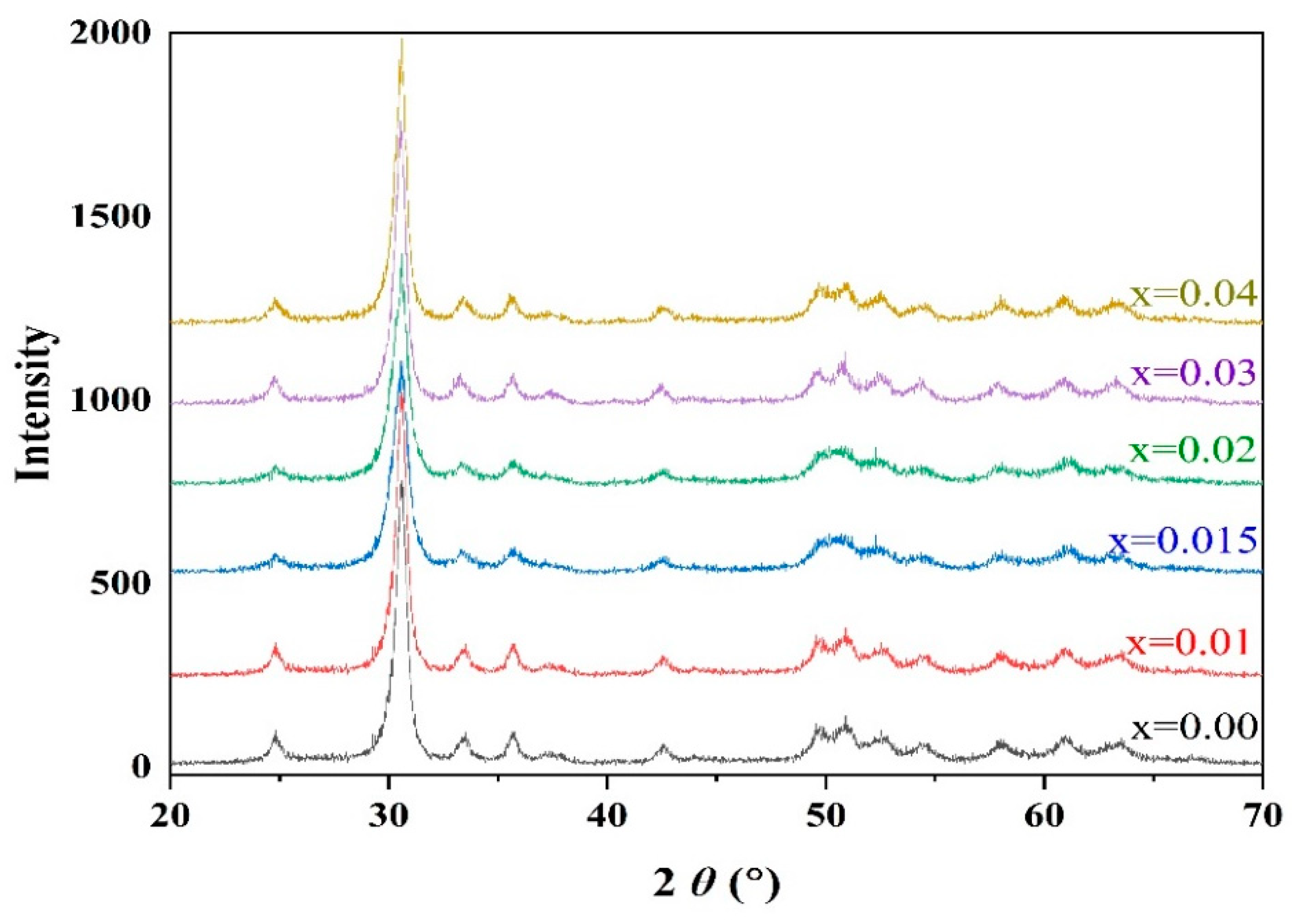
3.1.1. ZT Precursor with Pb Vacancies
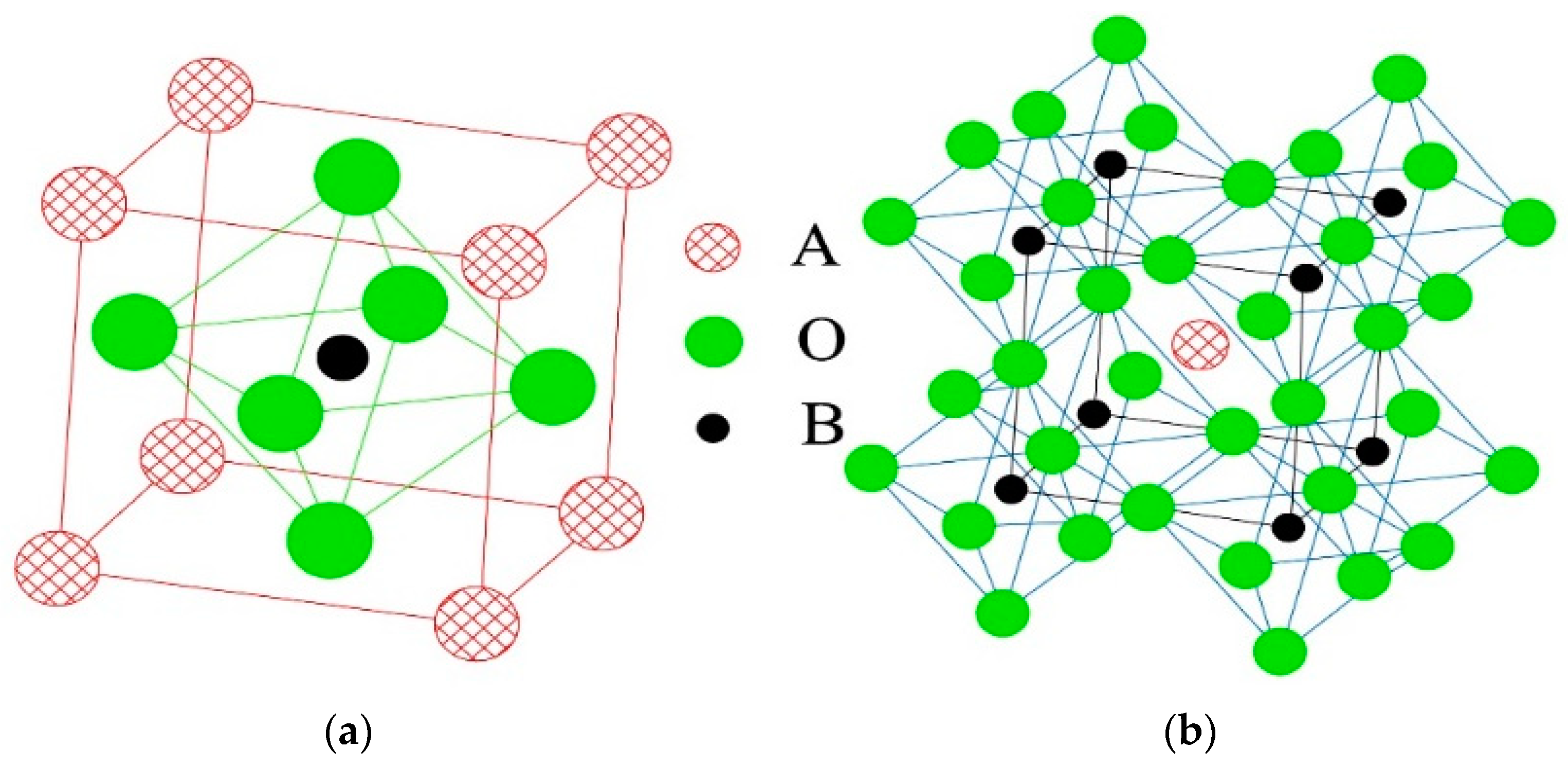
3.1.2. Metastable Perovskite-Type PZT Solid Solutions
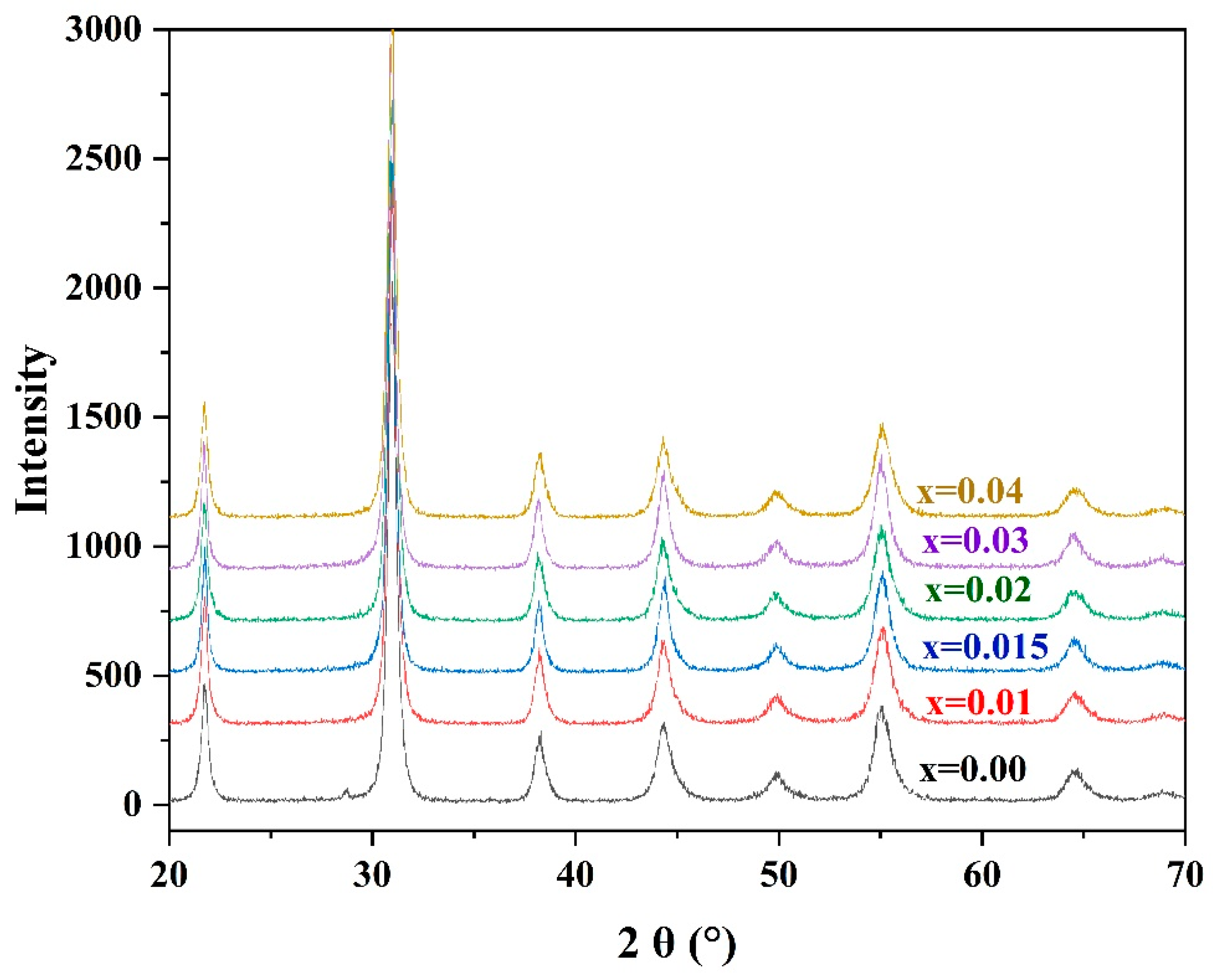
3.1.3. Intragranular PZT/ZrO2 Nanocomposite Ceramics
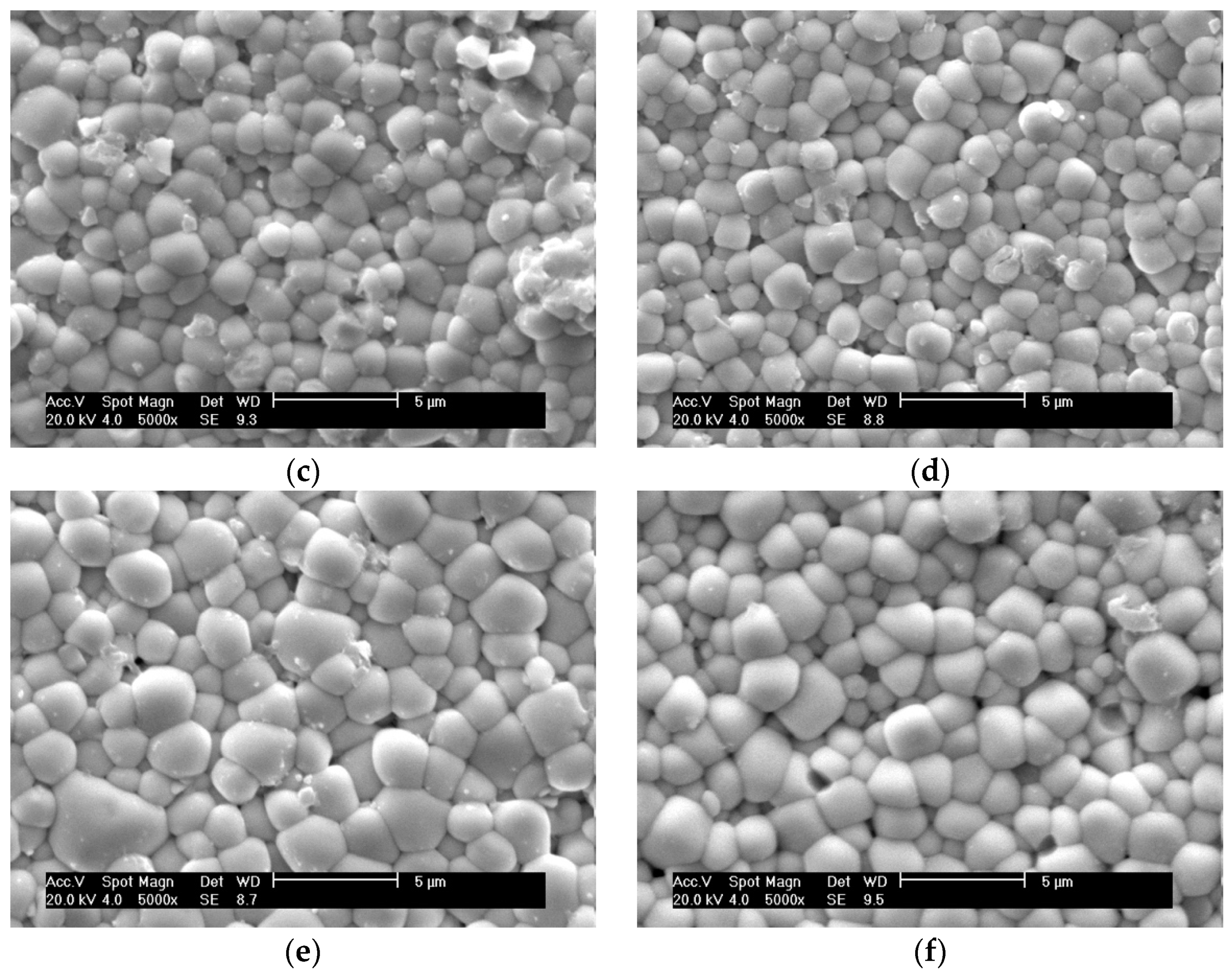
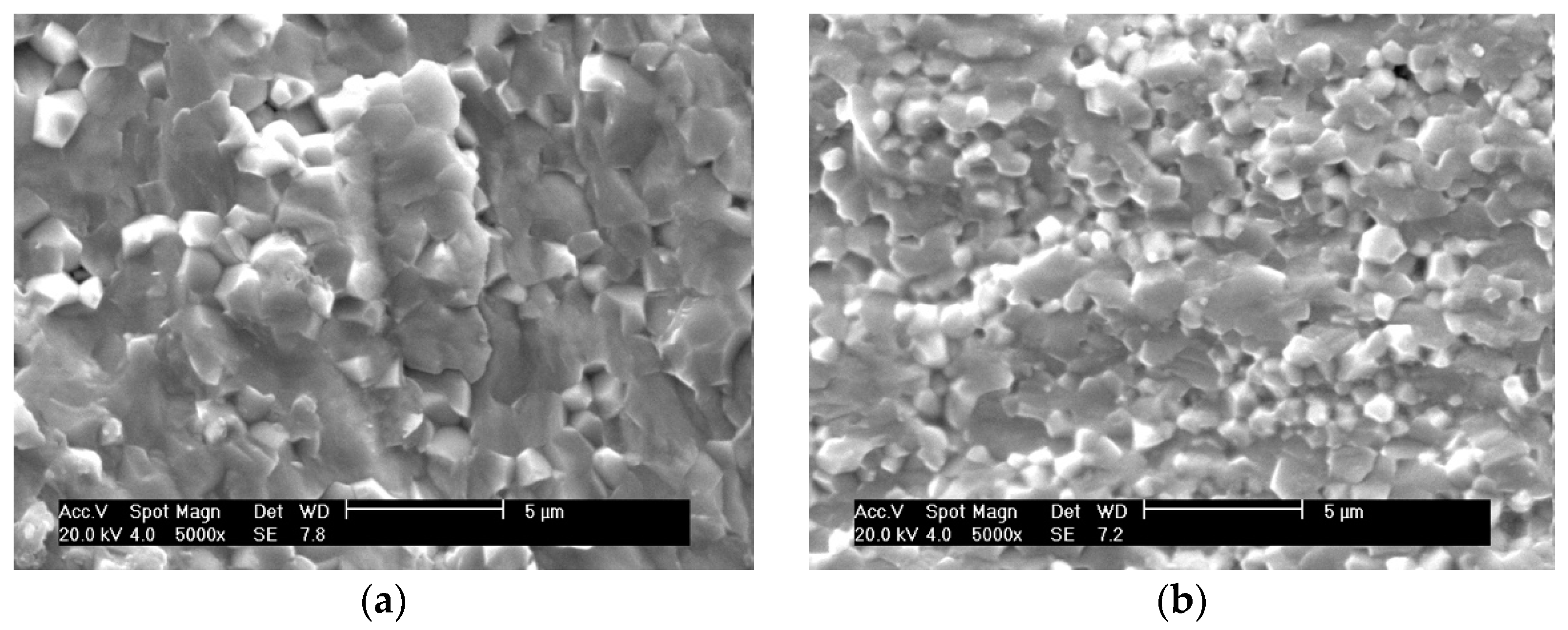
3.2. SEM Analysis of PZT/ZrO2 Nanocomposite Ceramics
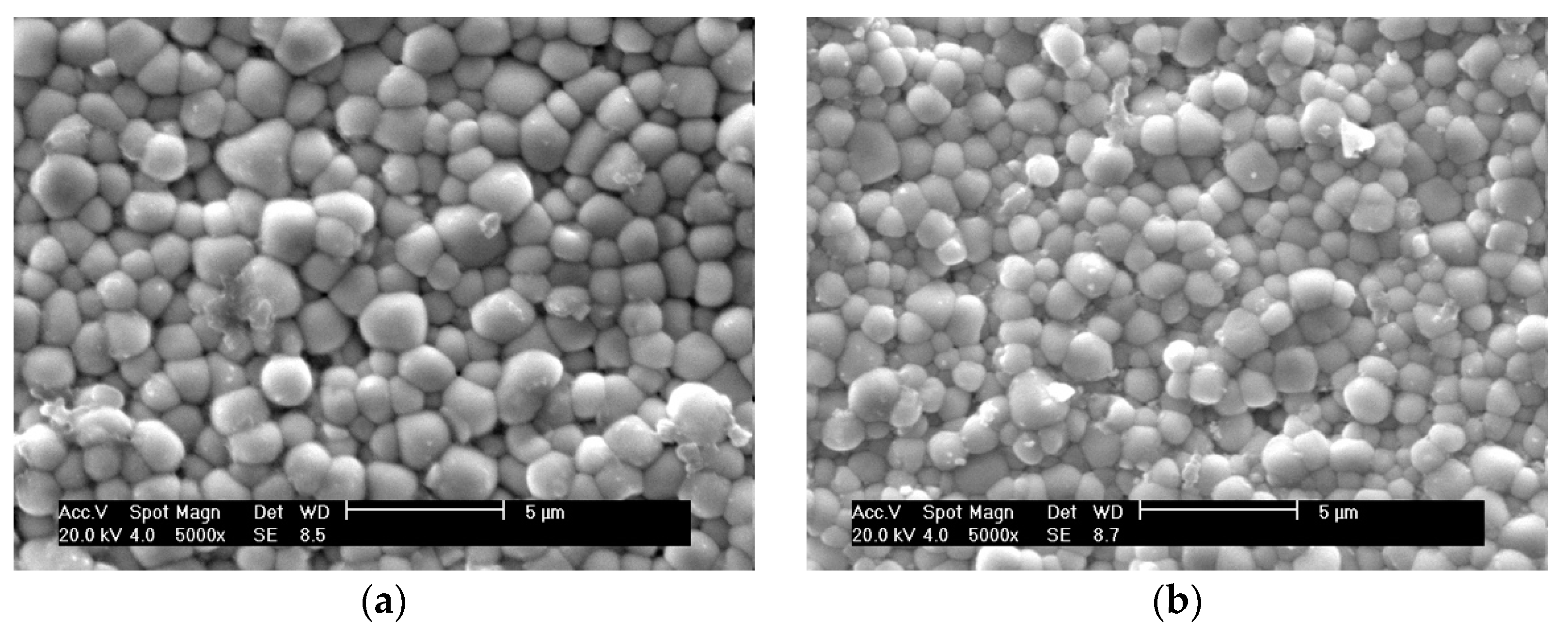
3.2.1. SEM Analysis of Natural Surfaces
3.2.2. SEM Analysis of Fractured Surfaces
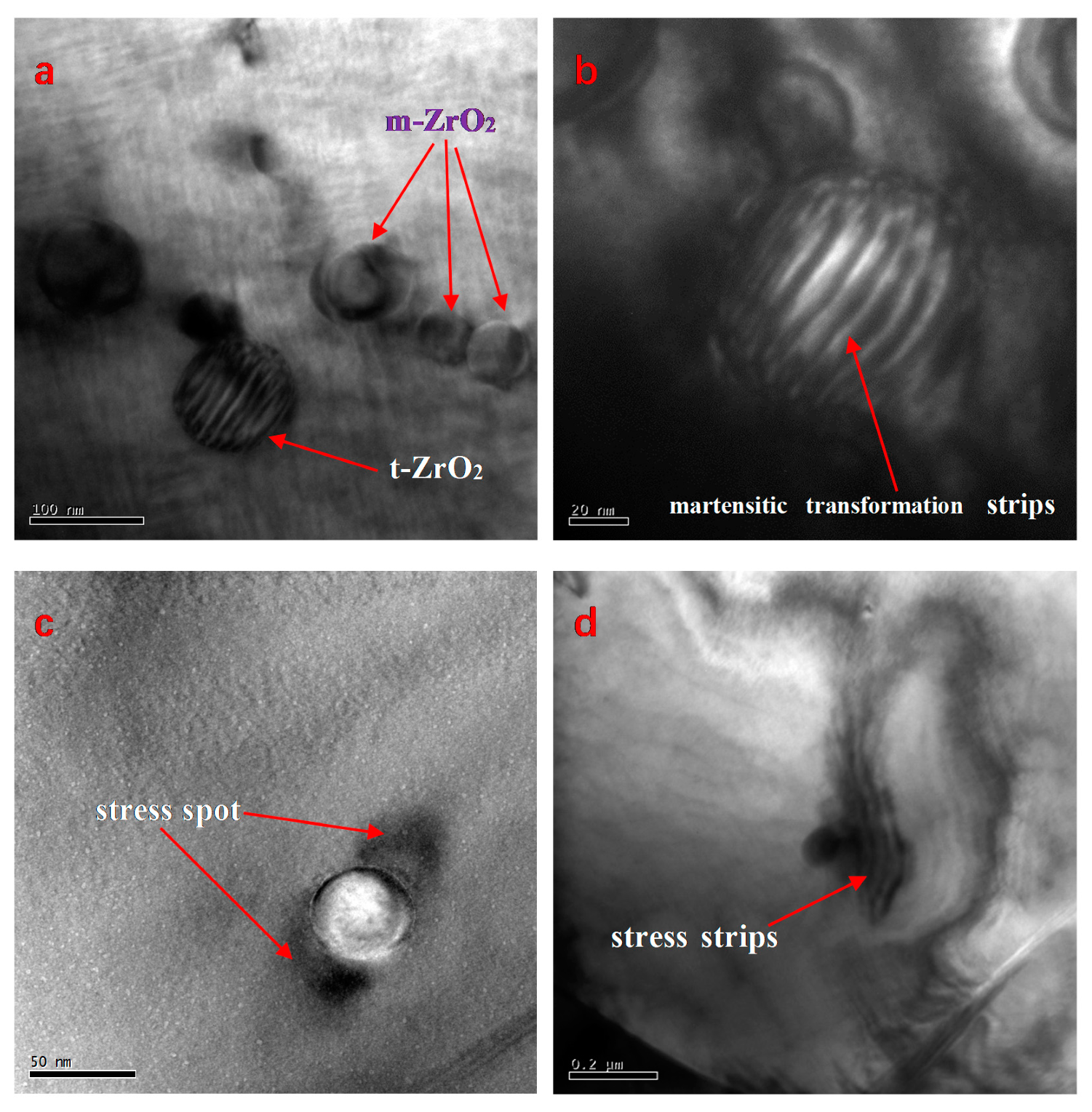
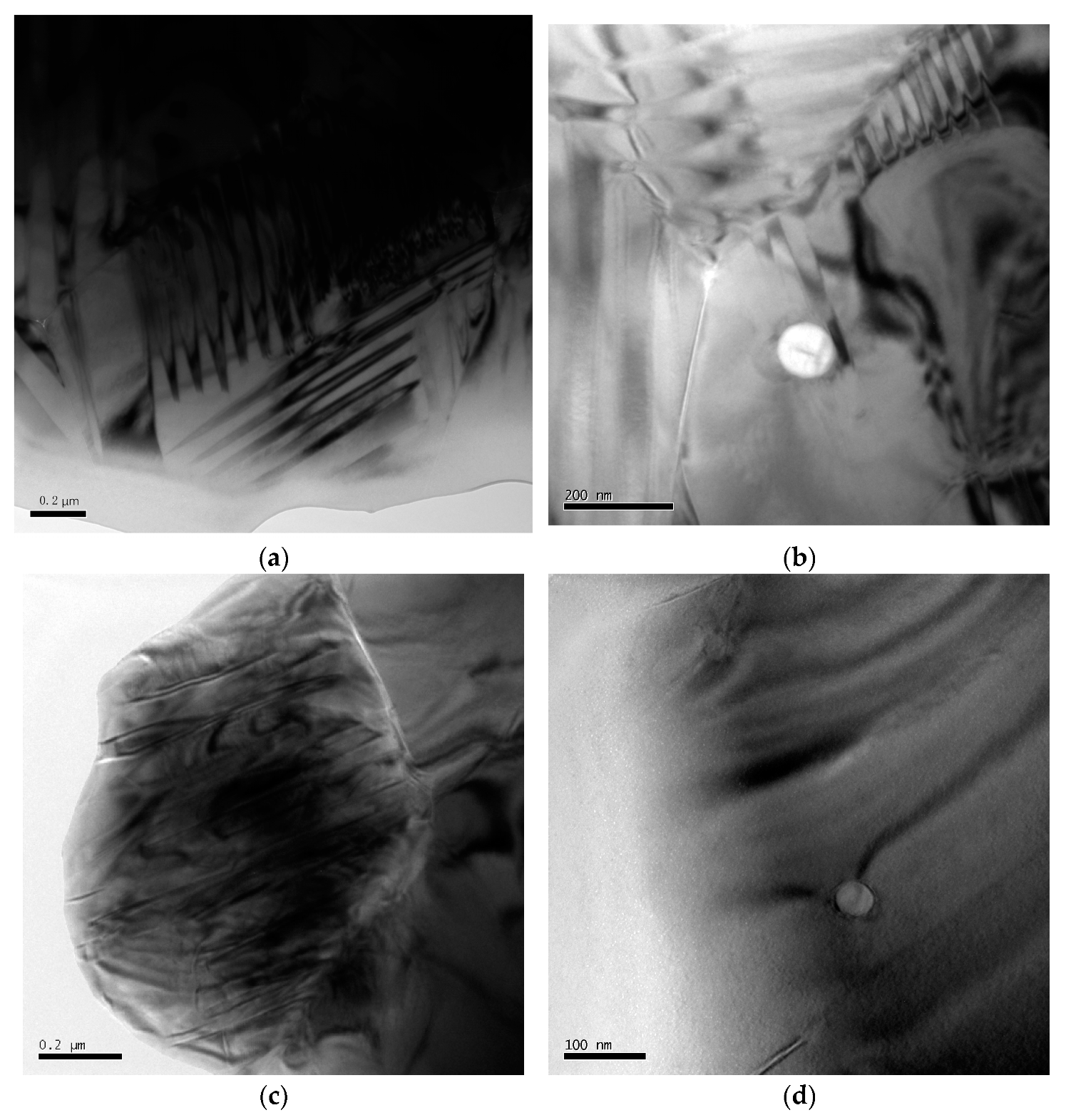
3.3. TEM and EDS Analyses
3.3.1. Nanosized ZrO2 Particles
3.3.2. Ferroelectric Domains in PZT/ZrO2 Nanocomposite Ceramics
3.4. Measured and Relative Densities
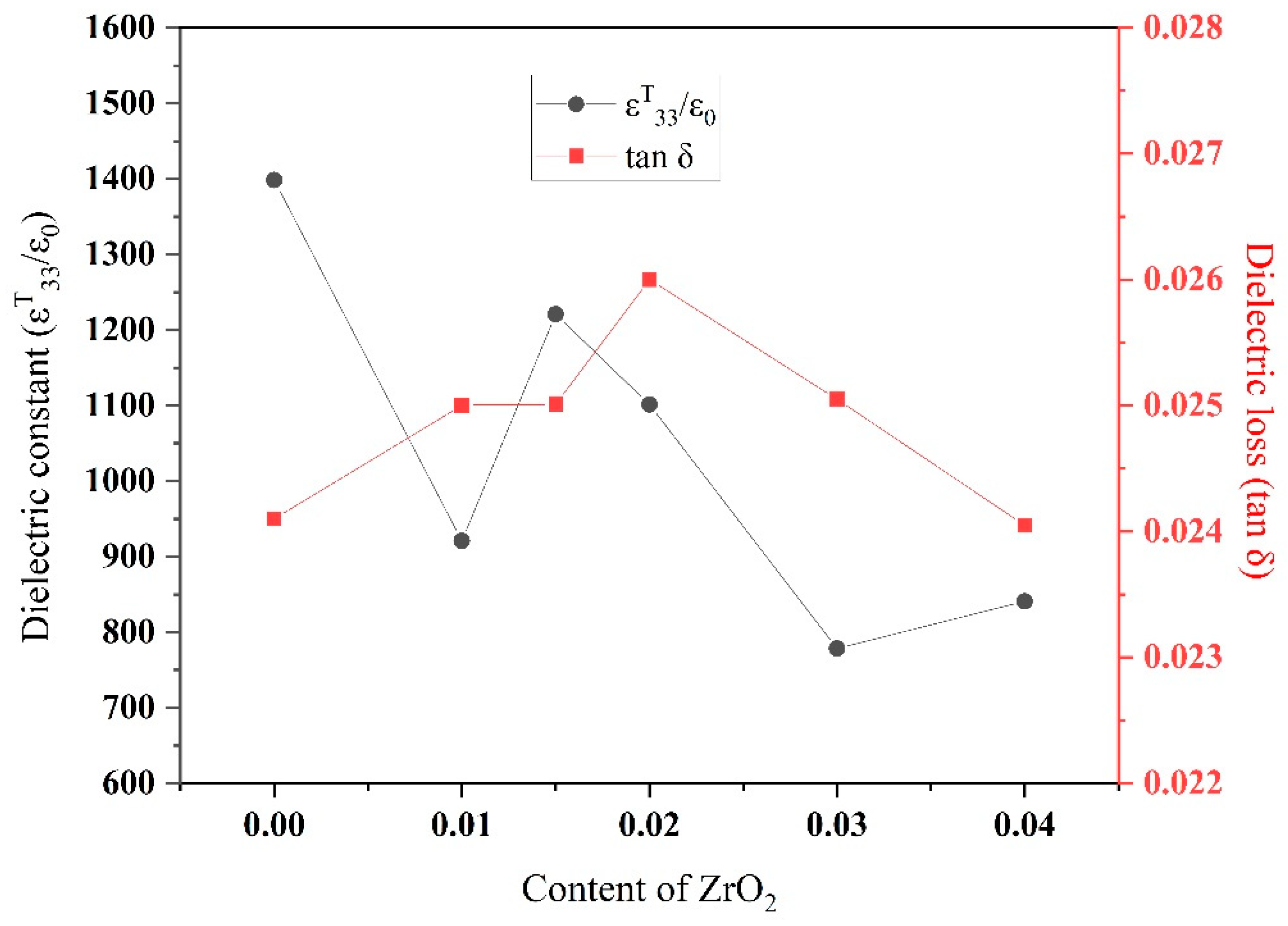
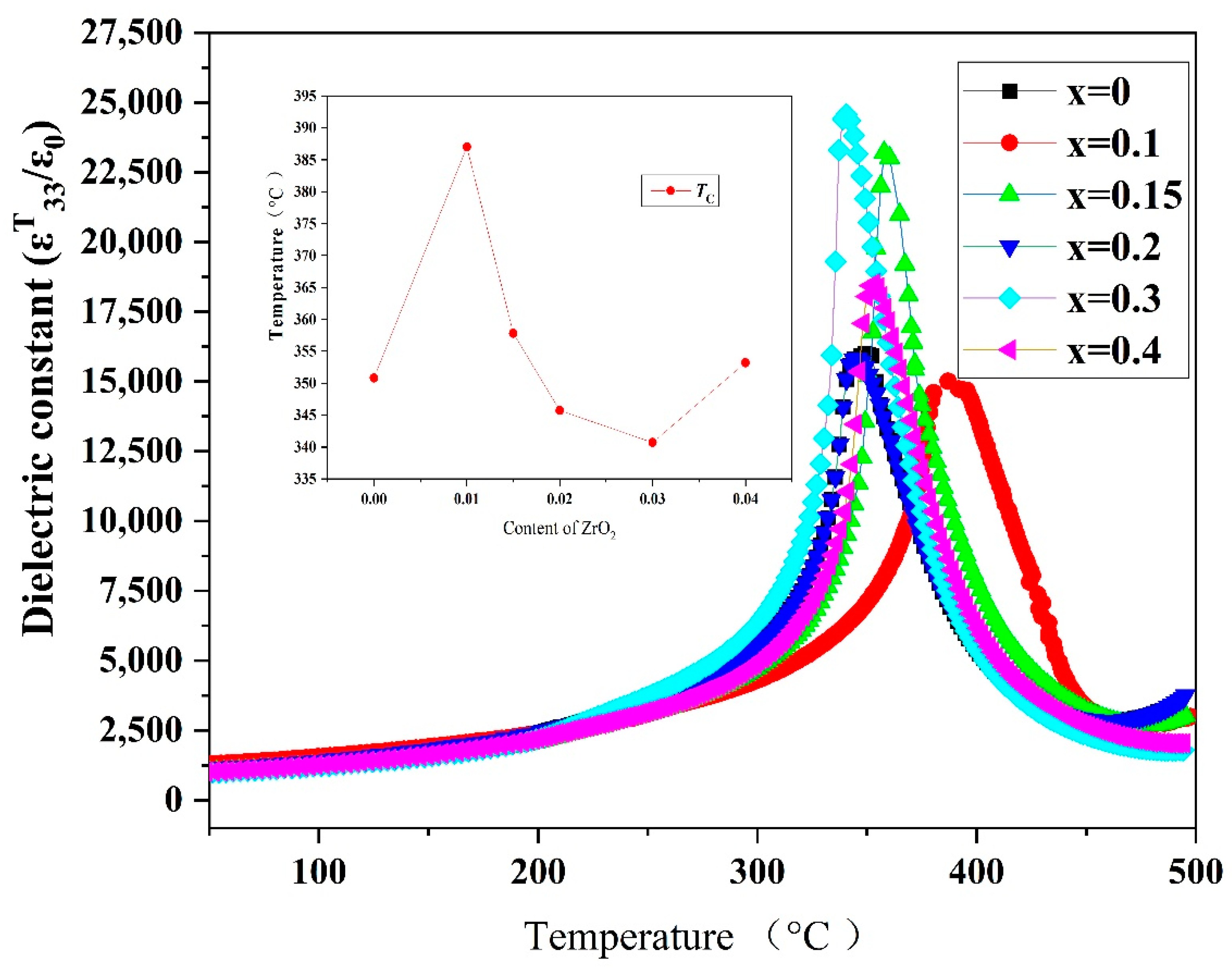
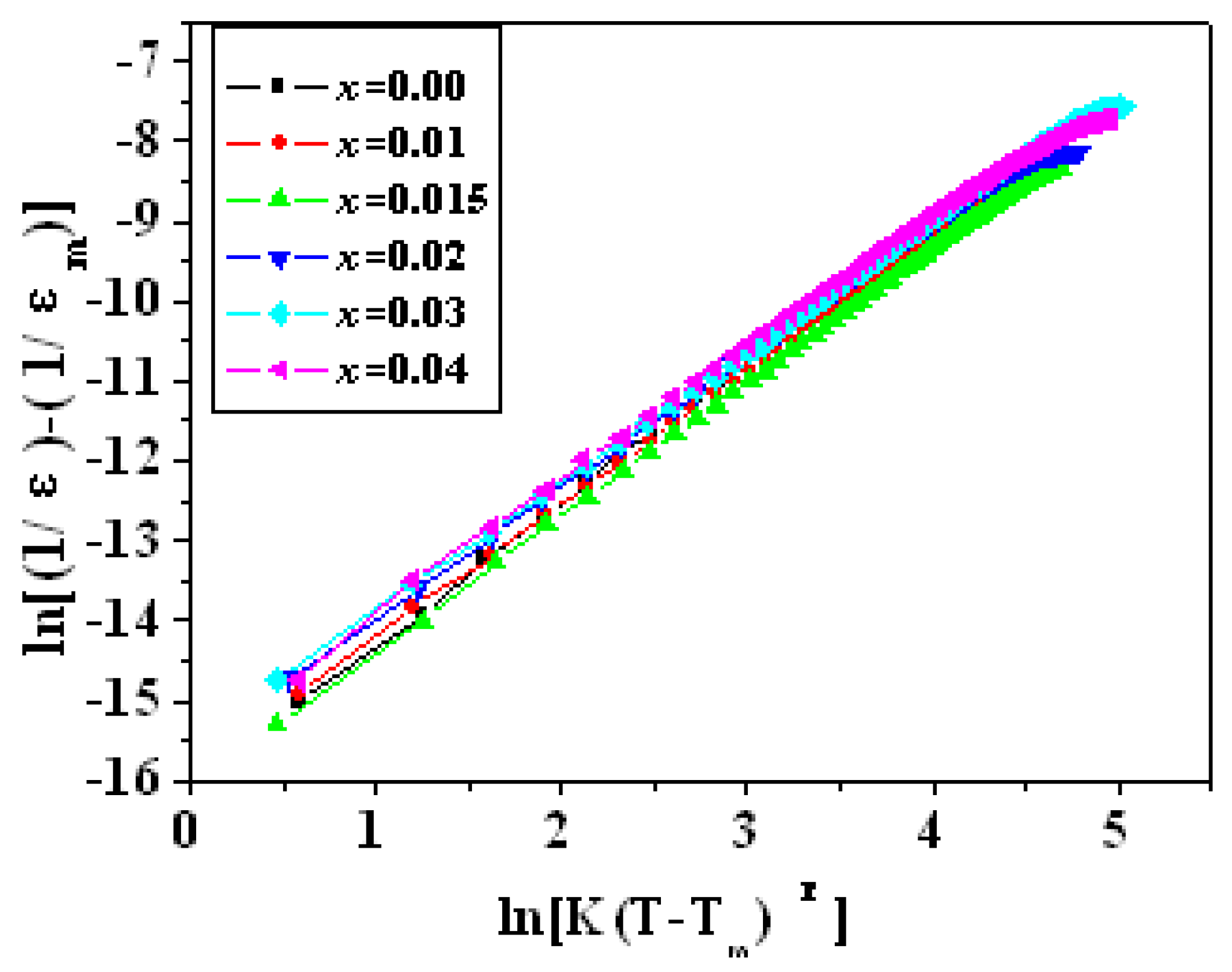
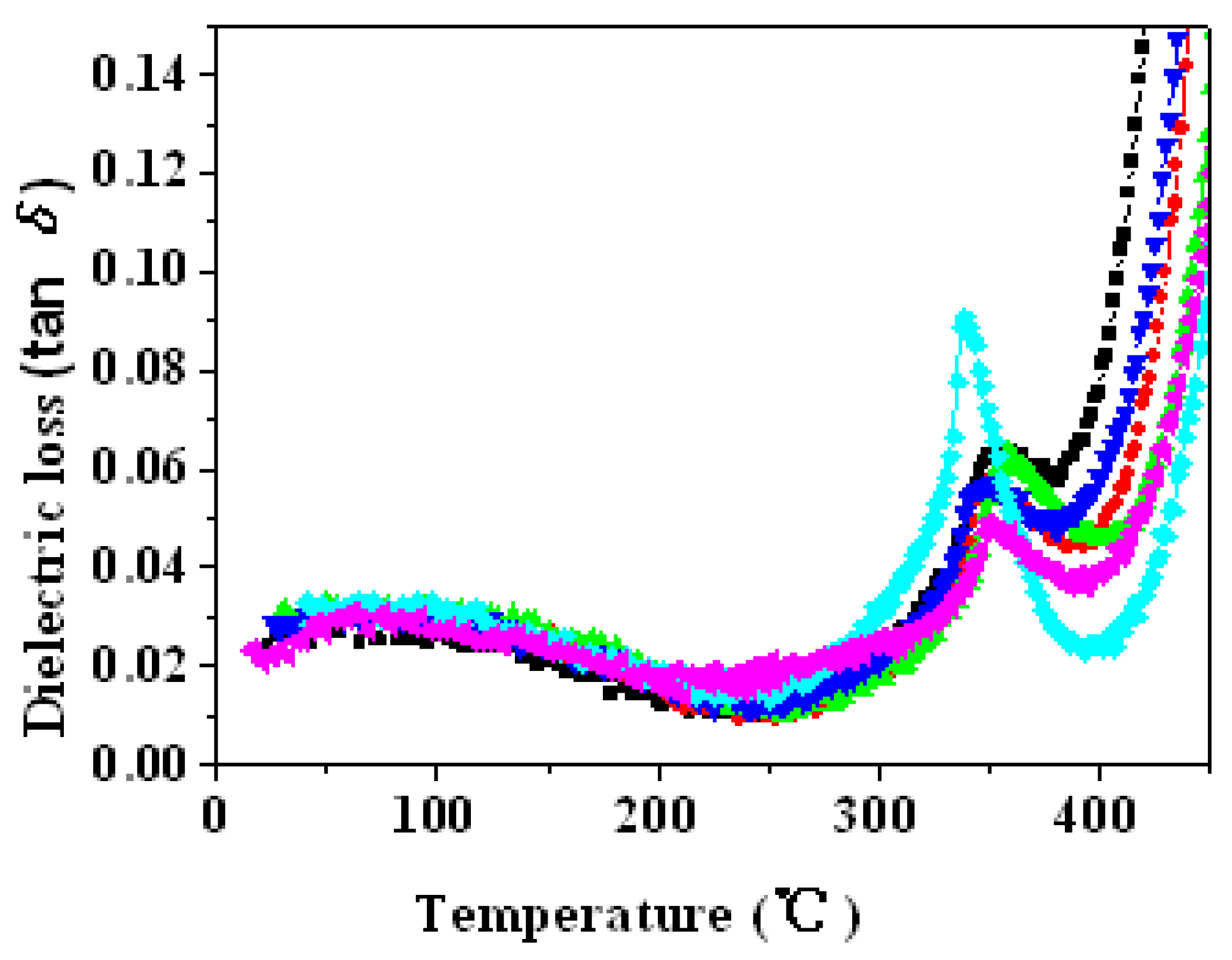
3.5. Dielectric Properties
3.5.1. Dielectric Constant and Dielectric Loss
3.5.2. Temperature Stability and Curie Temperature
3.5.3. Dielectric Loss at Different Temperature
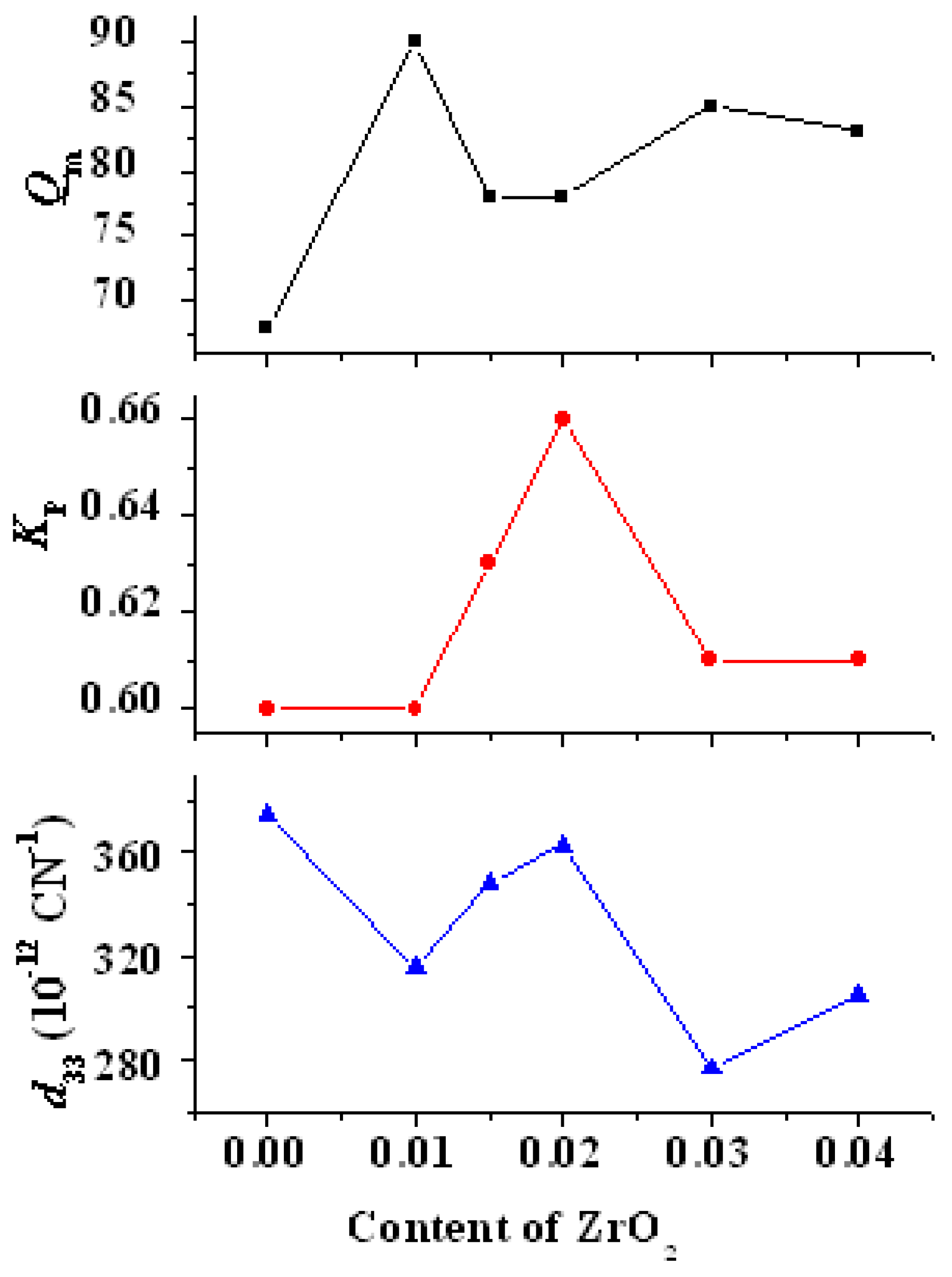
3.6. Piezoelectric Properties
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lay, R.; Deijsabc, G.S.; Malmström, J. The Intrinsic Piezoelectric Properties of Materials—A Review with a Focus on Biological Materials. RSC Adv. 2021, 49, 30657–30673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.J.; Xu, W.W.; Dong, Z.J.; Liu, Y.Q.; Wang, Q.; Shiotani, T. Piezoelectric Properties and Microstructure of Ceramicrete-Based Piezoelectric Composites. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 29681–29687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fu, J.; Zuo, R.Z. Middle-Low Temperature Sintering and Piezoelectric Properties of CuO and Bi2O3 Doped PMS-PZT Based Ceramics for Ultrasonic Motors. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 20117–20125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xing, J.; Xi, J.W.; Pu, T.; Liu, H.; Zhu, J.G. Origin of High Piezoelectricity in Low-Temperature Sintering PZT-Based Relaxor Ferroelectric Ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 860, 157930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.J.; Watari, K.; Sando, M.; Toriyama, M.; Niihara, K. Low-Temperature Sintering and High-Strength Pb(Zr,Ti)O3-Matrix Composites Incorporating Silver Particles. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1997, 80, 791–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Fujiwara, T.; Hayashi, H. Mechanical and Electromechannical Properties of Monoclinic ZrO2 Fiber/PZT Composites. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 1994, 102, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yamamoto, T.; Igarashi, H.; Okazaki, K. Electrical and Mechanical Properties of SiC Whisker Reinforced PZT Ceramic. Ferroelectrics 1985, 63, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malič, B.; Kosec, M.; Kosmač, T. Mechanical and Electric Properties of PZT-ZrO2 Composites. Ferroelectrics 1992, 129, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, B.W.; Lu, L.; Lai, M.O.; Wong, G.H.L. Effects of Complex Additives on Toughness and Electrical Properties of PZT Ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 381, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.B.; Cao, M.S.; Zhao, Q.L.; Shi, X.L.; Wang, D.; Wang, F. Mechanical Reinforcement and Piezoelectric Properties of Nanocomposites Embedded with ZnO Nanowhiskers. Scr. Mater. 2008, 59, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, P.; Sharifi, M.J. Optoelectronic Memory Capacitor Based on Manipulation of Ferroelectric Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 53067–53072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, L.H.; Zhang, F.M.; Chen, L.; Chen, L.D.; Chang, J. Preparation and Properties of β-CaSiO3/ZrO2 (3Y) Nanocomposites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 2883–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niihara, K. New design concept of structural ceramics nanocomosites. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 1990, 99, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawa, M.; Yamazaki, K.; Sekino, T.; Niihara, K. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of 3Y-TZP/Mo nanocomposites processing a novel interpenetrated intragranular microstructure. J. Mater. Sci. 1996, 31, 2849–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekino, T.; Niihara, K. Fabrication and mechanical properties of fine-tungsten-dispersed alumina-based composites. J. Mater. Sci. 1997, 32, 3943–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, K.; Hwang, H.J.; Sando, M.; Niihara, K. PZT nanocomposites reinforced by small amount of oxides. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 19, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannink, R.H.J.; Kelly, P.M.; Muddle, B.C. Transformation Toughening in Zirconia-Containing Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2000, 83, 461–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awaji, H.; Choi, S.M.; Yagi, E. Mechanisms of Toughening and Strengthening in Ceramic-Based Nanocomposites. Mech. Mater. 2002, 34, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yar, A.A.; Montazerian, M.; Abdizadeh, H.; Baharvandi, H.R. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Aluminum Alloy Matrix Composite Reinforced with Nano-Particle MgO. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 484, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H. Characterization of ZrO2/PZT Nanocomposites Ceramics Prepared by the Citrate Precursor Route. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2016, 852, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.; Paci, M.; Freer, R. Zirconium Titanate: From Polymeric Precursors to Bulk Ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 1998, 18, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). Standards on Piezoelectricity, American National Standards Institute, ANSI/IEEE Std.; The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): NewYork, NY, USA, 1987; Volume 176. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, T. Optimum Preparation Methods for Piezoelectric Ceramics and Their Evaluation. Ceram. Bull. 1992, 71, 978–984. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, P.; Arya, P.R.; Ganguli, A.K. Dielectric Properties of Lead Zirconium Titanates with Nanometer Size Grains Synthesized by the Citrate Precursor Route. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2003, 82, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.M.; Robbins, C.R.; McMurdie, H.F. Phase Diagram for Ceramist 1975 Supplemen1t; Reser, M.K., Ed.; American Ceramic Society: Columbus, OH, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Sternitzke, M.J. Structural Ceramic Nanocomposites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 1997, 17, 1061–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senda, T.; Bradt, R.C. Grain Growth in Sintered ZnO and ZnO-Bi2O3 Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1990, 73, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malic, B.; Bernard, J.; Bencan, A.; Kosec, M. Influence of Zirconia Addition on the Microstructure of K0.5Na0.5NbO3 Ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, W.H.; Chen, R.Z.; Wang, T.C.; Cheng, C.H.; Kuo, P.S. Mechanical Properties of Al2O3/ZrO2 Composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 22, 2827–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.J.; Qiu, H.B.; Todd, R.; Brook, R.J.; Guo, J.K. Processing and Mechanical Behavior of Al2O3/ZrO2 Nanocomposites. Mater. Res. Bull. 1998, 33, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.Y.; Lin, M.; Lu, H.Y. Ferroelectric Domains in Pressureless-Sintered Barium Titanate. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 3569–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Chen, C.W.; Tang, L.; Qin, L.; Zhu, H.; Cao, W. Dielectric, Elastic and Piezoelectric Properties of Single Domain Pb(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3–6.5%PbTiO3 Single Crystal with 3m Symmetry Measured Using One Sample. Scr. Mater. 2021, 194, 113634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.L.; Xu, Z.K.; Shang, J.K. In-Situ Transmission Electron Microscopy Observations of Electric-Field-Induced Domain Switching and Microcracking in Ferroelectric Ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2001, A314, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Yang, W.; Zhu, T. Crack Tip 90° Domain Switching in Tetragonal Lanthanum-Modified Lead Zirconate Titanate Under an Electric Field. J. Mater. Res. 1999, 14, 2940–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kaya, C.; Butler, E.G. Zirconia-toughened alumina ceramics of helical spring shape with improved properties from extruded sol-derived pastes. Scr. Mater. 2003, 48, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, B.; Cook, W.R.; Jaffe, H. Piezoelectric Ceramics; Academic Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillov, V.V.; Isupov, V.A. Relaxation Polarization of Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3(PMN)-A Ferroelectric with a Diffused Phase Transition. Ferroelectrics 1973, 5, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Element | Weight % | Atomic % | Uncertainty % | Correction | k-Factor | Correction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O(K) | 8.922 | 38.361 | 0.199 | 0.495 | 2.059 | 0.867 |
| Ti(K) | 0.689 | 0.989 | 0.023 | 0.993 | 1.290 | 0.993 |
| Zr(K) | 72.595 | 54.742 | 0.582 | 0.999 | 3.930 | 0.999 |
| Pb(L) | 17.792 | 5.906 | 0.342 | 0.753 | 6.528 | 0.999 |
| Secondary-Phase ZrO2 Content | γ (1 kHz) |
|---|---|
| x = 0.00 | 1.70 |
| x = 0.01 | 1.67 |
| x = 0.015 | 1.66 |
| x = 0.02 | 1.58 |
| x = 0.03 | 1.61 |
| x = 0.04 | 1.58 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J. Microstructure and Piezoelectric Properties of Lead Zirconate Titanate Nanocomposites Reinforced with In-Situ Formed ZrO2 Nanoparticles. Materials 2022, 15, 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041389
Li J. Microstructure and Piezoelectric Properties of Lead Zirconate Titanate Nanocomposites Reinforced with In-Situ Formed ZrO2 Nanoparticles. Materials. 2022; 15(4):1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041389
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jianhua. 2022. "Microstructure and Piezoelectric Properties of Lead Zirconate Titanate Nanocomposites Reinforced with In-Situ Formed ZrO2 Nanoparticles" Materials 15, no. 4: 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041389
APA StyleLi, J. (2022). Microstructure and Piezoelectric Properties of Lead Zirconate Titanate Nanocomposites Reinforced with In-Situ Formed ZrO2 Nanoparticles. Materials, 15(4), 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041389





