Can Mesoporous Silica Speed Up Degradation of Benzodiazepines? Hints from Quantum Mechanical Investigations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Computational Details
2.1. Static Quantum Mechanical Calculations
2.2. Frequency Calculations
2.3. Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Amorphous Silica Surfaces
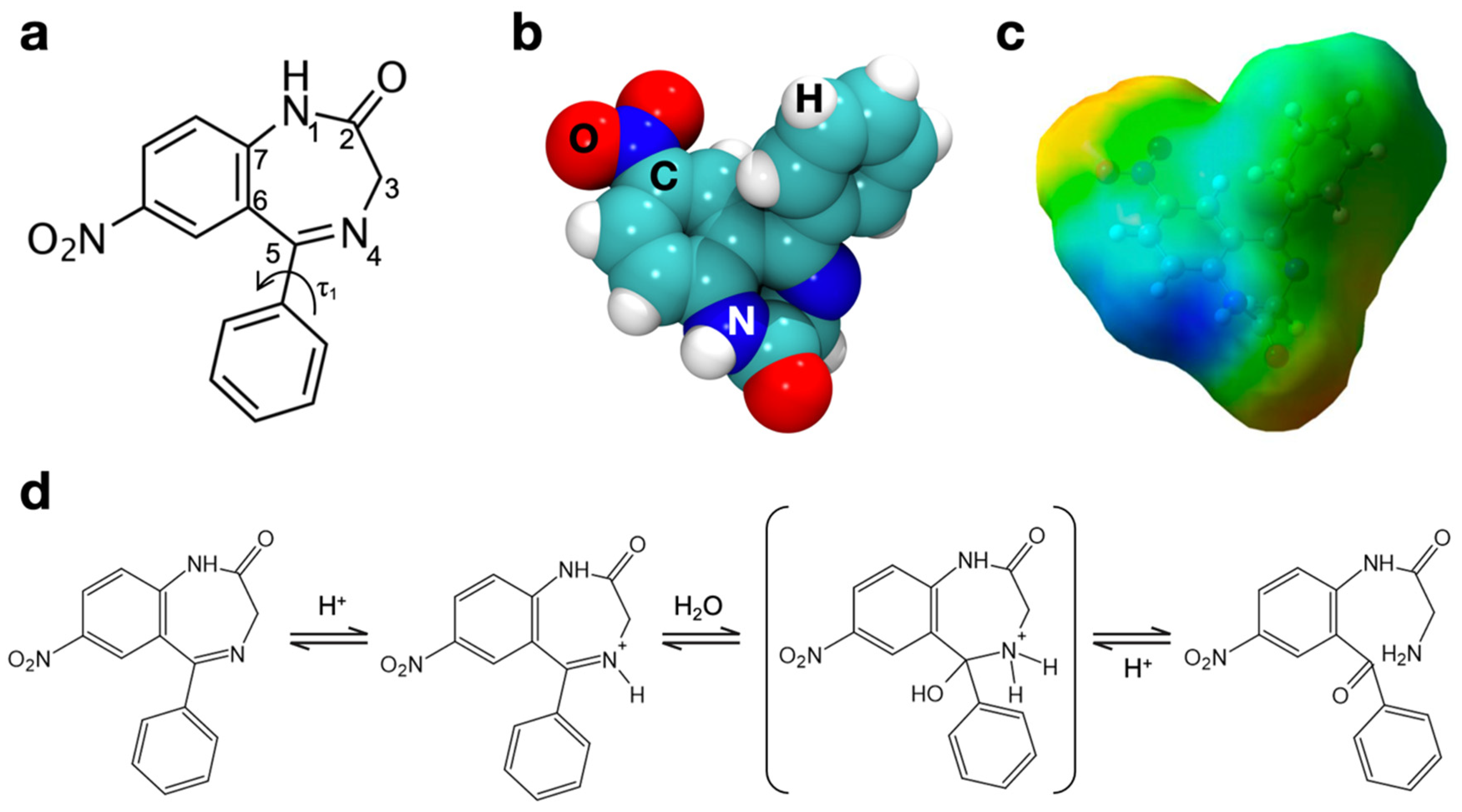
3.2. Nitrazepam
3.3. Nitrazepam Adsorption on Amorpohous Silica Surfaces
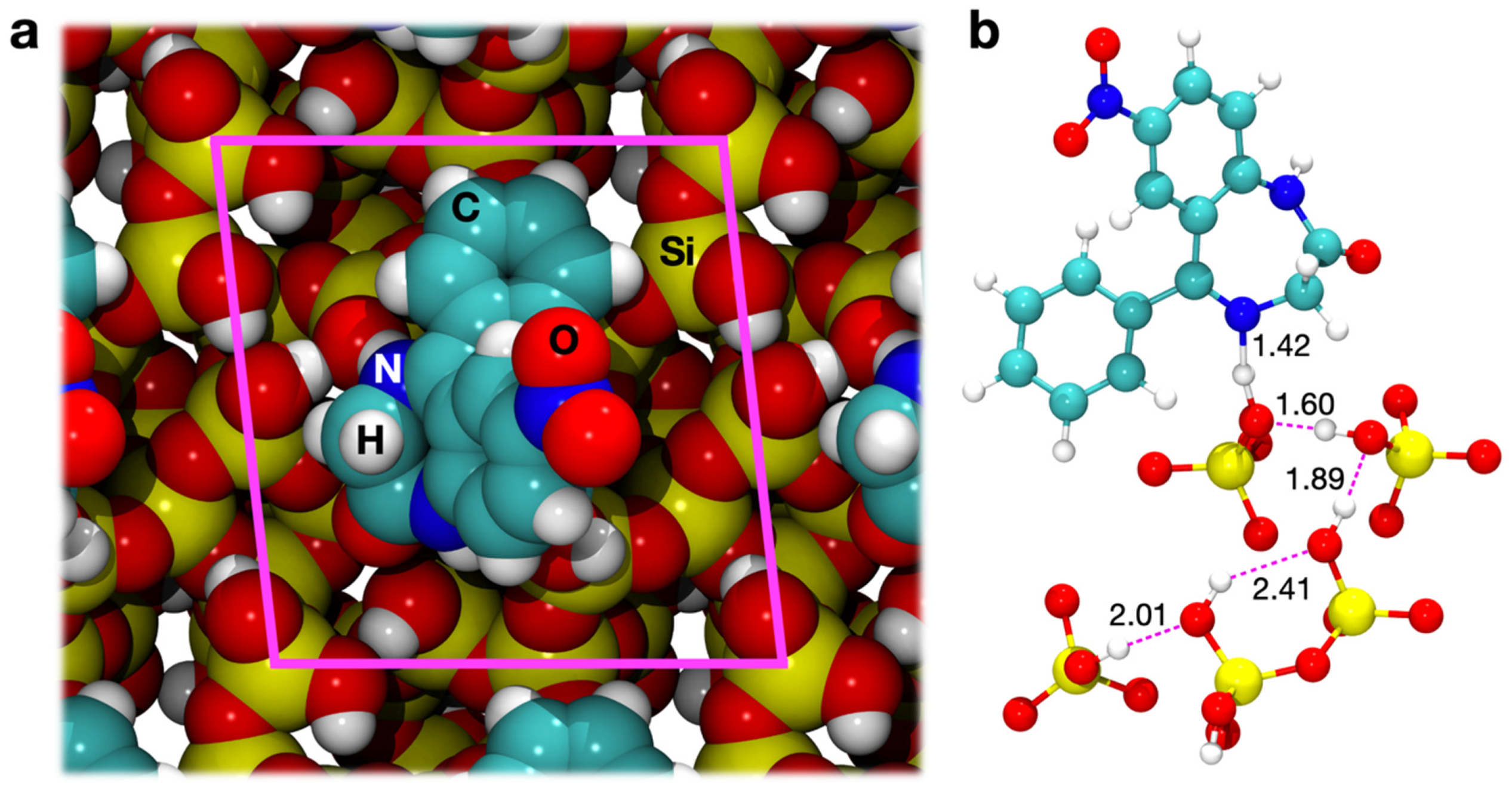
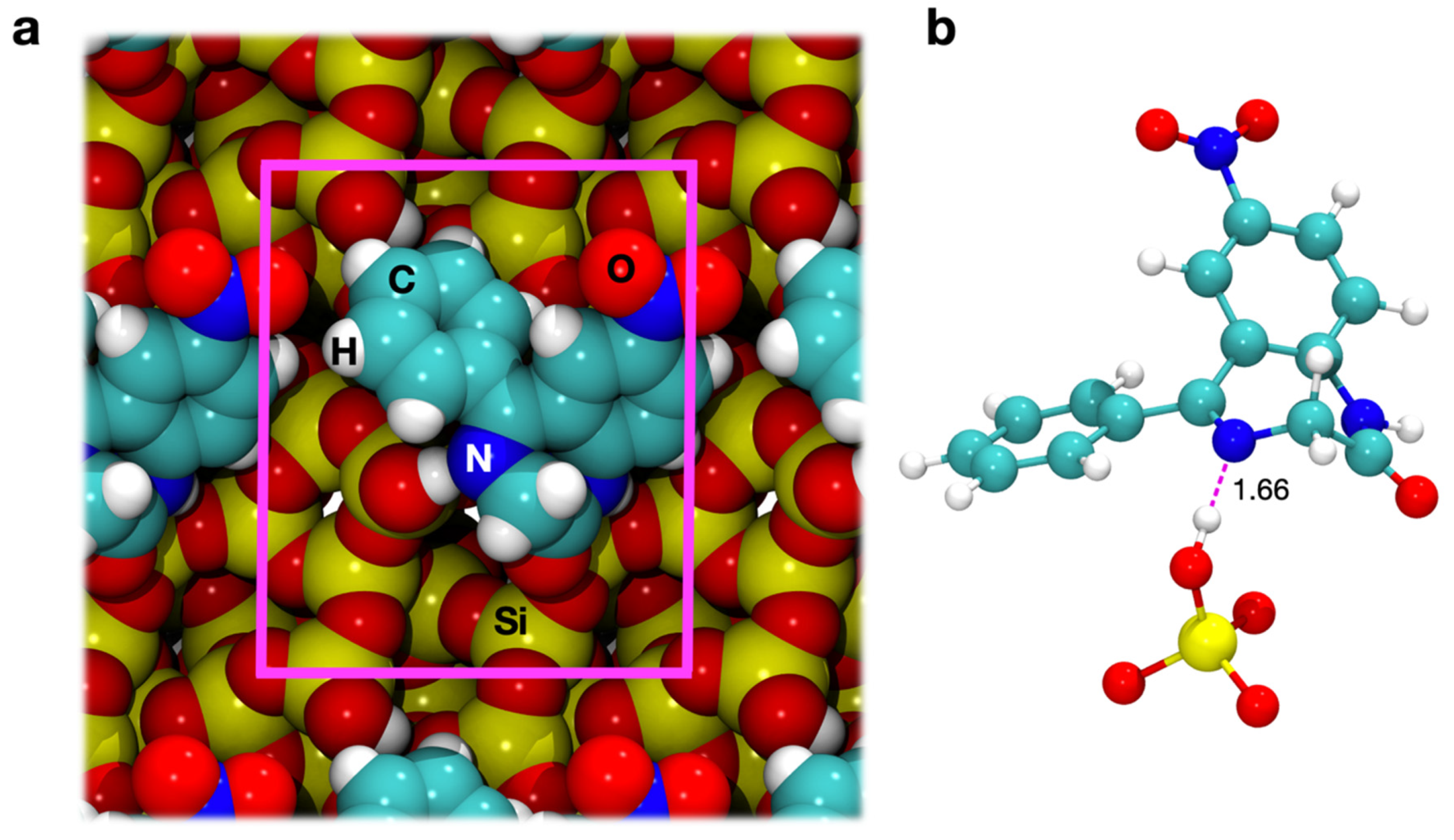
3.3.1. Geometry Optimization
3.3.2. Energetics
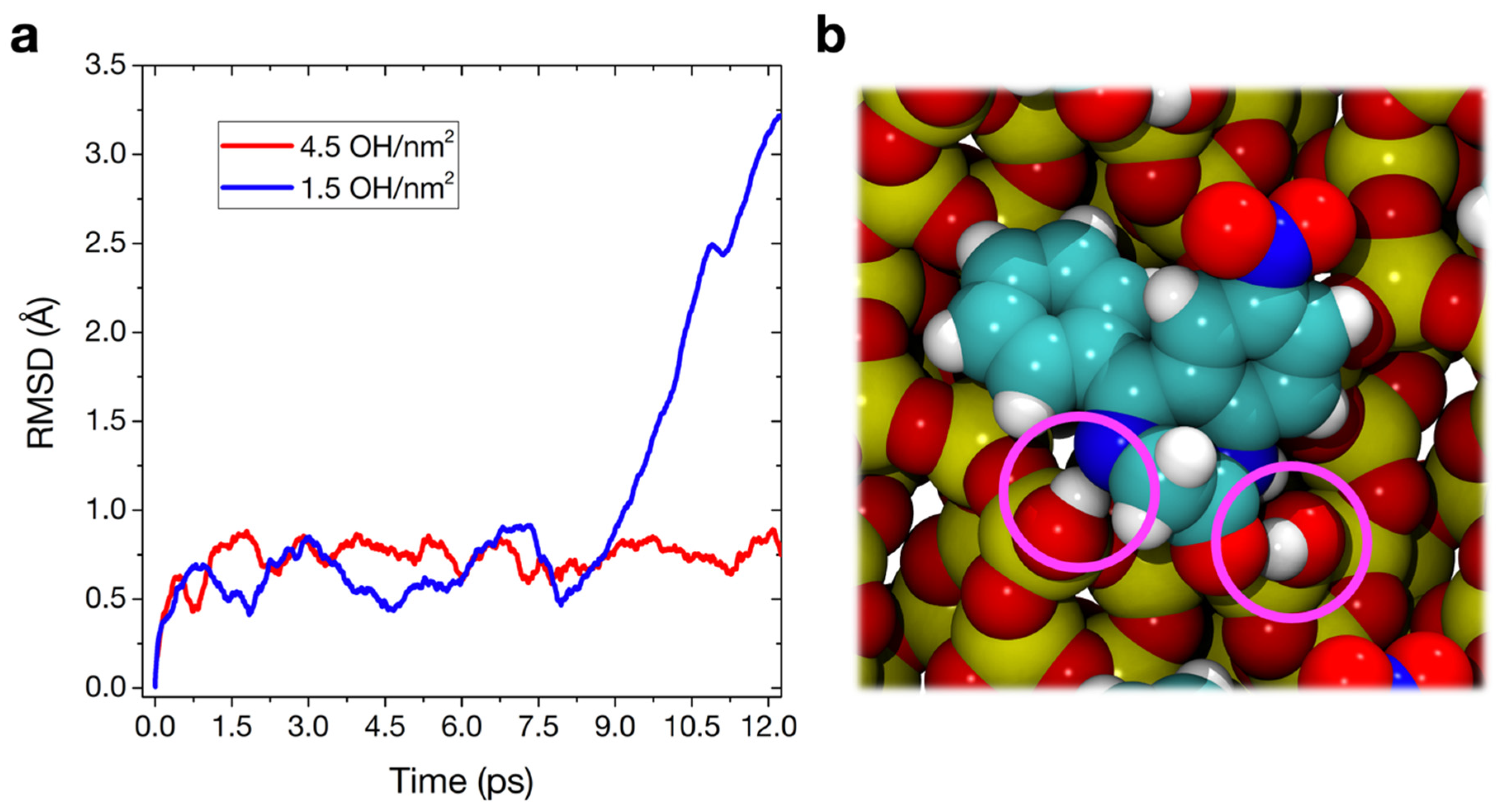
3.3.3. Molecular Dynamics
3.3.4. IR Frequencies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pifferi, G.; Santoro, P.; Pedrani, M. Quality and Functionality of Excipients. Farmaco 1999, 54, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pifferi, G.; Restani, P. The safety of pharmaceutical excipients. Farmaco 2003, 58, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delle Piane, M.; Corno, M.; Ugliengo, P. Does dispersion dominate over H-bonds in drug-surface interactions? The case of silica-based materials as excipients and drug-delivery agents. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 2404–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narang, A.S.; Desai, D.; Badawy, S. Impact of excipient interactions on solid dosage form stability. In Excipient Applications in Formulation Design and Drug Delivery; Narang, A.S., Boddu, S.H.S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 93–137. ISBN 978-3-319-20206-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Dali, M.; Gupta, A.; Raghavan, K. Understanding drug-excipient compatibility: Oxidation of compound A in a solid dosage form. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2009, 14, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Hoag, S.W. The Influence of Excipients on the Stability of the Moisture Sensitive Drugs Aspirin and Niacinamide: Comparison of Tablets Containing Lactose Monohydrate with Tablets Containing Anhydrous Lactose. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2001, 6, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delle Piane, M.; Corno, M.; Ugliengo, P. Propionic acid derivatives confined in mesoporous silica: Monomers or dimers? The case of ibuprofen investigated by static and dynamic ab initio simulations. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2016, 135, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimola, A.; Costa, D.; Sodupe, M.; Lambert, J.-F.; Ugliengo, P. Silica Surface Features and Their Role in the Adsorption of Biomolecules: Computational Modeling and Experiments. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 4216–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laitinen, R.; Löbmann, K.; Strachan, C.J.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T. Emerging trends in the stabilization of amorphous drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahr, A.; Liu, X. Drug delivery strategies for poorly water-soluble drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2007, 4, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regi, M.; Rámila, A.; Del Real, R.P.; Pérez-Pariente, J. A new property of MCM-41: Drug delivery system. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Riikonen, J.; Lehto, V.-P. Mesoporous systems for poorly soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gignone, A.; Delle Piane, M.; Corno, M.; Ugliengo, P.; Onida, B. Simulation and Experiment Reveal a Complex Scenario for the Adsorption of an Antifungal Drug in Ordered Mesoporous Silica. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 13068–13079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gignone, A.; Manna, L.; Ronchetti, S.; Banchero, M.; Onida, B. Incorporation of Clotrimazole in Ordered Mesoporous Silica by supercritical CO2. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2014, 200, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, A.P.; Grillet, Y.; Burneau, A.; Papirer, E.; Fubini, B. The Surface Properties of Silicas; Legrand, A.P., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; ISBN 0471953326. [Google Scholar]
- Iler, R.K. The Chemistry of Silica, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Sadowska, A.; Świderski, F. Sources, Bioavailability, and Safety of Silicon Derived from Foods and Other Sources Added for Nutritional Purposes in Food Supplements and Functional Foods. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresge, C.T.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Roth, W.J.; Vartuli, J.C.; Beck, J.S. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesizad by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 1992, 359, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M.; Ko, C.H.; Ryoo, R. Characterization of the porous structure of SBA-15. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Piane, M.; Corno, M.; Pedone, A.; Dovesi, R.; Ugliengo, P. Large-Scale B3LYP Simulations of Ibuprofen Adsorbed in MCM-41 Mesoporous Silica as Drug Delivery System. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 26737–26749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Piane, M.; Corno, M.; Ugliengo, P. Chapter 9—Ab initio modeling of hydrogen bond interaction at silica surfaces with focus on silica/drugs systems. In Modelling and Simulation in the Science of Micro- and Meso-Porous Materials; Catlow, C.R.A., Van Speybroeck, V., van Santen, R.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 297–328. ISBN 978-0-12-805057-6. [Google Scholar]
- Mamaeva, V.; Sahlgren, C.; Lindén, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in medicine—Recent advances. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Balas, F.; Arcos, D. Mesoporous Materials for Drug Delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7548–7558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, M.A.; Ashraf, A.; Rehman, S.S.; Shahid, S.A.; Mahmood, A.; Faruq, M. 1, 4-diazepines: A review on synthesis, reactions and biological significance. Curr. Org. Synth. 2019, 16, 709–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, J.H.; Smith, J.A.; Hyland, C.; Meyer, A.G.; Williams, C.C.; Bissember, A.C.; Just, J. Seven-membered rings. Prog. Heterocycl. Chem. 2014, 26, 521–571. [Google Scholar]
- Sternbach, L.H. 1, 4-benzodiazepines. Chemistry and some aspects of the structure-activity relationship. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 1971, 10, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skolnick, P.; Paul, S.M. The mechanism(s) of action of the benzodiazepines. Med. Res. Rev. 1981, 1, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kangas, L.; Breimer, D.D. Clinical pharmacokinetics of nitrazepam. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1981, 6, 346–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Guðmundsdóttir, H.; Sigurjonsdottir, J.F.; Sigurðsson, H.H.; Sigfússon, S.D.; Masson, M.; Stefansson, E. Cyclodextrin solubilization of benzodiazepines: Formulation of midazolam nasal spray. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 212, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, J.; Mielck, J.B. Solid-state degradation kinetics of nitrazepam in the presence of colloidal silica. Pharm. Acta Helv. 1982, 57, 144–153. [Google Scholar]
- Dovesi, R.; Erba, A.; Orlando, R.; Zicovich-Wilson, C.M.; Civalleri, B.; Maschio, L.; Rérat, M.; Casassa, S.; Baima, J.; Salustro, S.; et al. Quantum-mechanical condensed matter simulations with CRYSTAL. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2018, 8, e1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, R.; Delle Piane, M.; Bush, I.J.; Ugliengo, P.; Ferrabone, M.; Dovesi, R. A new massively parallel version of CRYSTAL for large systems on high performance computing architectures. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 2276–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Enzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation for the exchange-correlation hole of a many-electron system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grimme, S. Semiempirical GGA-type density functional constructed with a long-range dispersion correction. J. Comput. Chem. 2006, 27, 1787–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.; Horn, H.; Ahlrichs, R. Fully Optimized Contracted Gaussian Basis Sets for Atoms: Li to Kr. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 97, 2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nada, R.; Nicholas, J.B.; McCarthy, M.I.; Hess, A.C. Basis Sets for ab initio Periodic Hartree-Fock Studies of Zeolite/Adsorbate Interactions: He, Ne, and Ar in Silica Sodalite. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 1996, 60, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boys, S.F.; Bernardi, F. The calculation of small molecular interactions by the differences of separate total energies. Some procedures with reduced errors. Mol. Phys. 1970, 19, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Olio, S.; Dovesi, R.; Resta, R. Spontaneous polarization as a Berry phase of the Hartree-Fock wave function: The case of KNbO3. Phys. Rev. B 1997, 56, 10105–10114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutter, J.; Iannuzzi, M.; Schiffmann, F.; Vandevondele, J. Cp2k: Atomistic simulations of condensed matter systems. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2014, 4, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- VandeVondele, J.; Krack, M.; Mohamed, F.; Parrinello, M.; Chassaing, T.; Hutter, J. Quickstep: Fast and accurate density functional calculations using a mixed Gaussian and plane waves approach. Comp. Phys. Comm. 2005, 167, 103–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goedecker, S.; Teter, M.; Hutter, J. Separable Dual Space Gaussian Pseudo-potentials. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 1703–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- VandeVondele, J.; Hutter, J. Gaussian basis sets for accurate calculations on molecular systems in gas and condensed phases. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 127, 114105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bussi, G.; Donadio, D.; Parrinello, M. Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.C.; Maciel, G.E. The fumed silica surface: A study by NMR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 5103–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravlev, L.T. Concentration of Hydroxyl-Groups on the Surface of Amorphous Silica. Langmuir 1987, 3, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugliengo, P.; Sodupe, M.; Musso, F.; Bush, I.J.J.; Orlando, R.; Dovesi, R. Realistic Models of Hydroxylated Amorphous Silica Surfaces and MCM-41 Mesoporous Material Simulated by Large-scale Periodic B3LYP Calculations. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 4579–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Y.; Bryant, S.H. PubChem as a public resource for drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 1052–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gunasekaran, S.; ArunBalaji, R.; Kumaresan, S.; Anand, G.; VivekAnand, M. Computation and interpretation of vibrational spectra on the structure of Nitrazepam using semi-empirical and density functional methods. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2009, 4, 1109. [Google Scholar]
- Archer, G.A.; Sternbach, L.H. Chemistry of benzodiazepines. Chem. Rev. 1968, 68, 747–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azais, T.; Tourne-Peteilh, C.; Aussenac, F.; Baccile, N.; Coelho, C.; Devoisselle, J.M.; Babonneau, F. Solid-state NMR study of ibuprofen confined in MCM-41 material. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 6382–6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenneau, F.; Panesar, K.; Nossov, A.; Springuel-Huet, M.-A.; Azais, T.; Babonneau, F.; Tourne-Peteilh, C.; Devoisselle, J.-M.; Gedeon, A. Probing the mobility of ibuprofen confined in MCM-41 materials using MAS-PFG NMR and hyperpolarised-129Xe NMR spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 18805–18808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Piane, M.; Vaccari, S.; Corno, M.; Ugliengo, P. Silica-based materials as drug adsorbents: First principle investigation on the role of water microsolvation on ibuprofen adsorption. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 118, 5801–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, S.; Arunbalaji, R.; Seshadri, S.; Muthu, S. Vibrational spectra and normal coordinate analysis on structure of nitrazepam. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 2008, 46, 162–168. [Google Scholar]
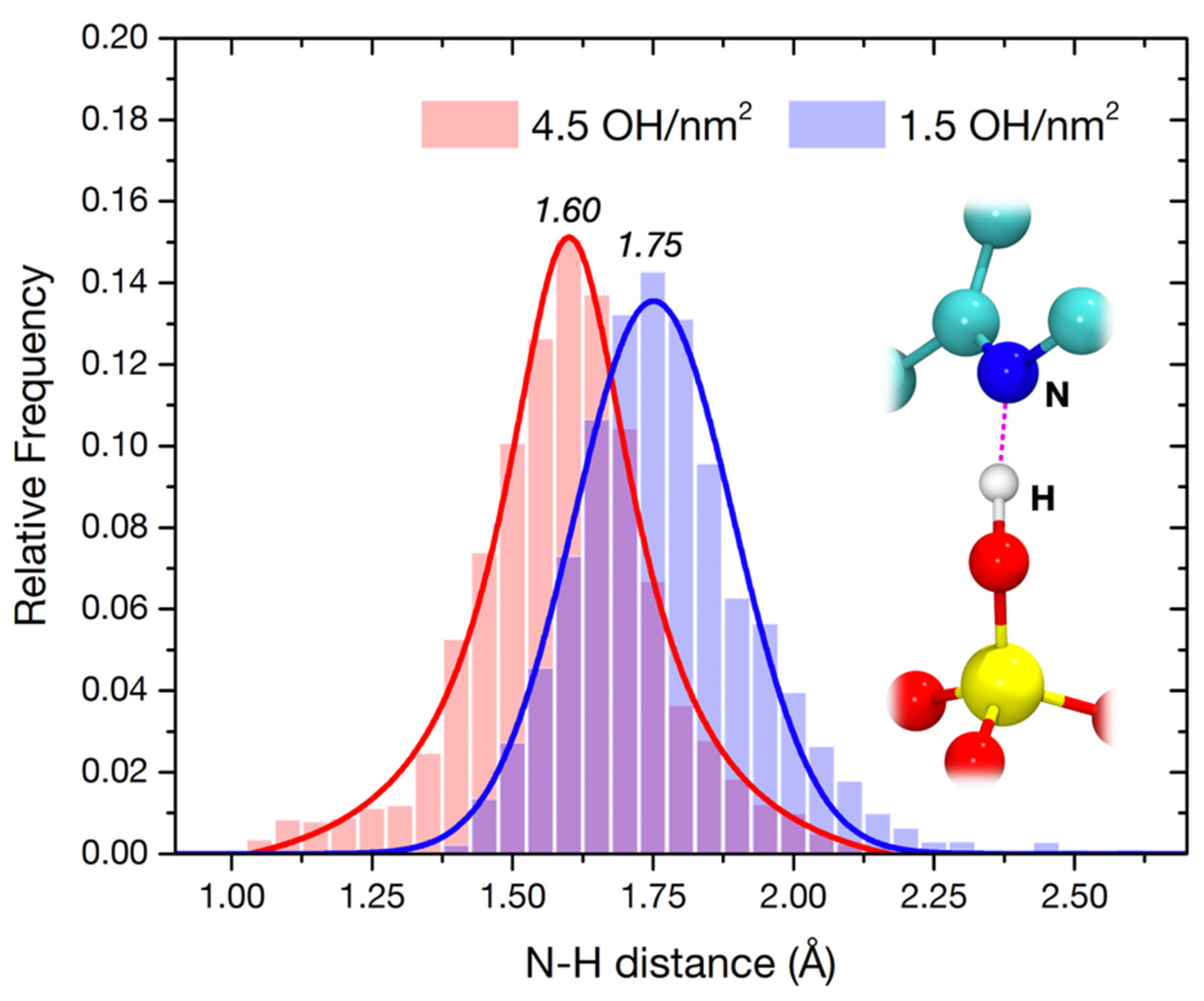
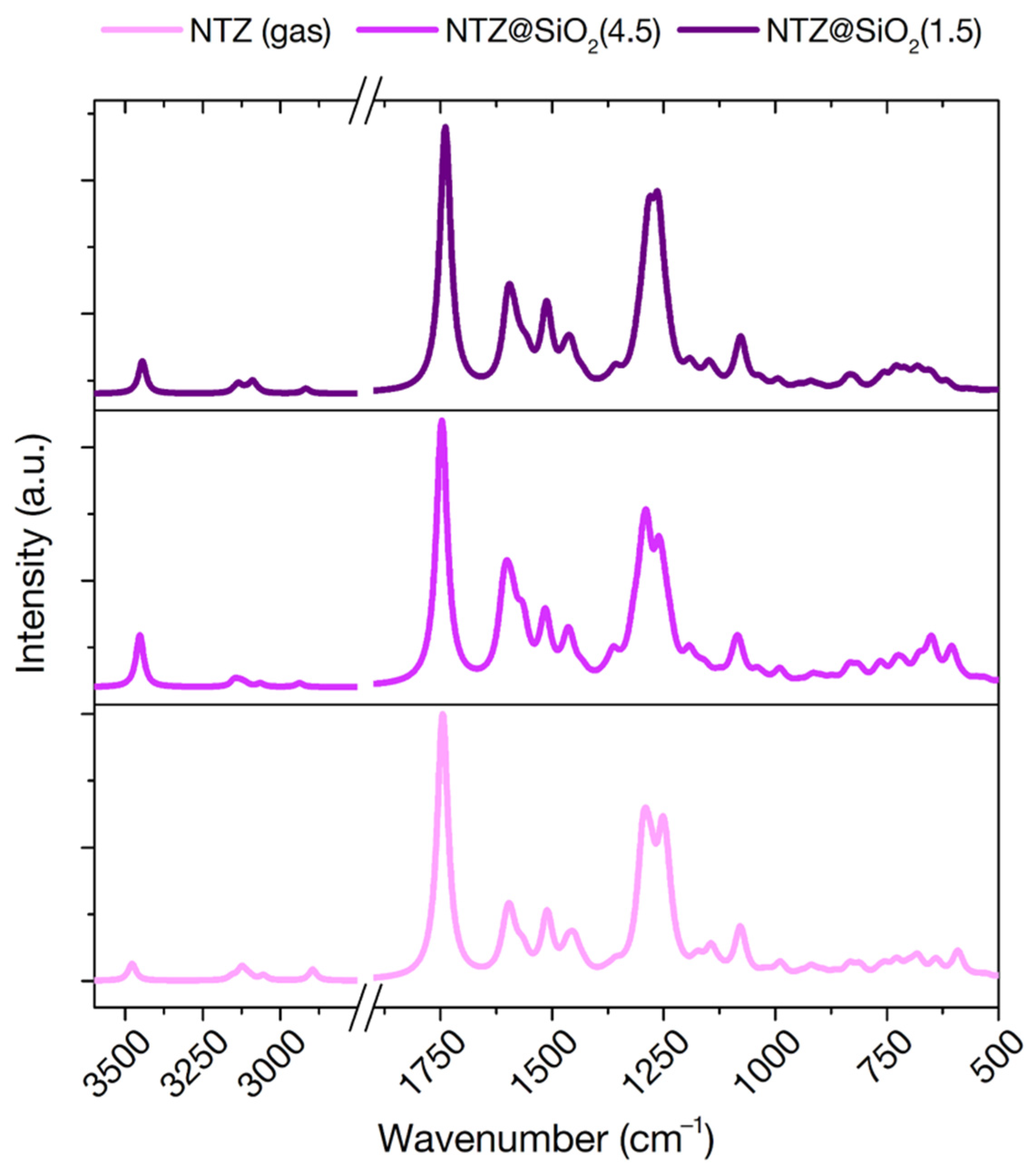
| ∆E | ∆ED | Disp. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.5 OH/nm2 | PBE | −30.8 | – | – |
| PBE-D2 | −10.1 | −104.9 (−128.0) | −94.8 | |
| 1.5 OH/nm2 | PBE | −38.7 | – | – |
| PBE-D2 | −28.2 | −131.9 (−100.2) | −103.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Delle Piane, M.; Corno, M. Can Mesoporous Silica Speed Up Degradation of Benzodiazepines? Hints from Quantum Mechanical Investigations. Materials 2022, 15, 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041357
Delle Piane M, Corno M. Can Mesoporous Silica Speed Up Degradation of Benzodiazepines? Hints from Quantum Mechanical Investigations. Materials. 2022; 15(4):1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041357
Chicago/Turabian StyleDelle Piane, Massimo, and Marta Corno. 2022. "Can Mesoporous Silica Speed Up Degradation of Benzodiazepines? Hints from Quantum Mechanical Investigations" Materials 15, no. 4: 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041357
APA StyleDelle Piane, M., & Corno, M. (2022). Can Mesoporous Silica Speed Up Degradation of Benzodiazepines? Hints from Quantum Mechanical Investigations. Materials, 15(4), 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041357







