Experimental Identification of the Roles of Fe, Ni and Attapulgite in Nitroreduction and Dechlorination of p-Chloronitrobenzene by Attapulgite-Supported Fe/Ni Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Materials
2.3. Batch Experiments
2.4. Material Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
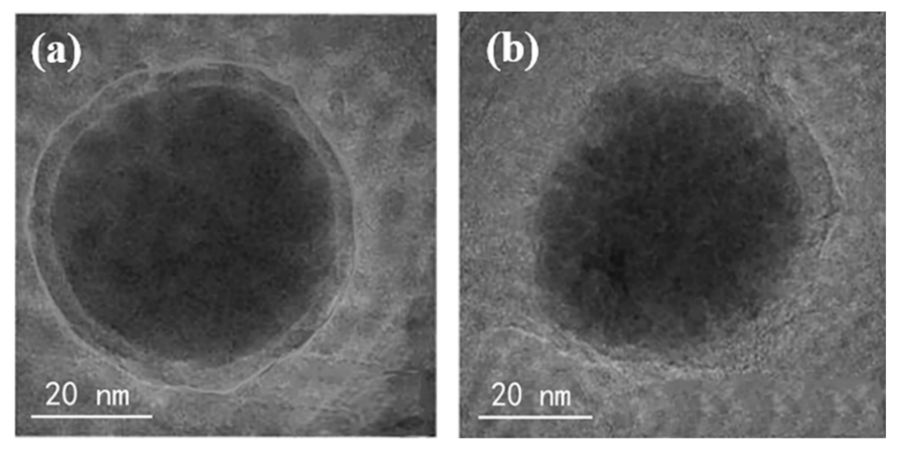
3.1. Characterizations of ATP, nFe/Ni and ATP-nFe/Ni
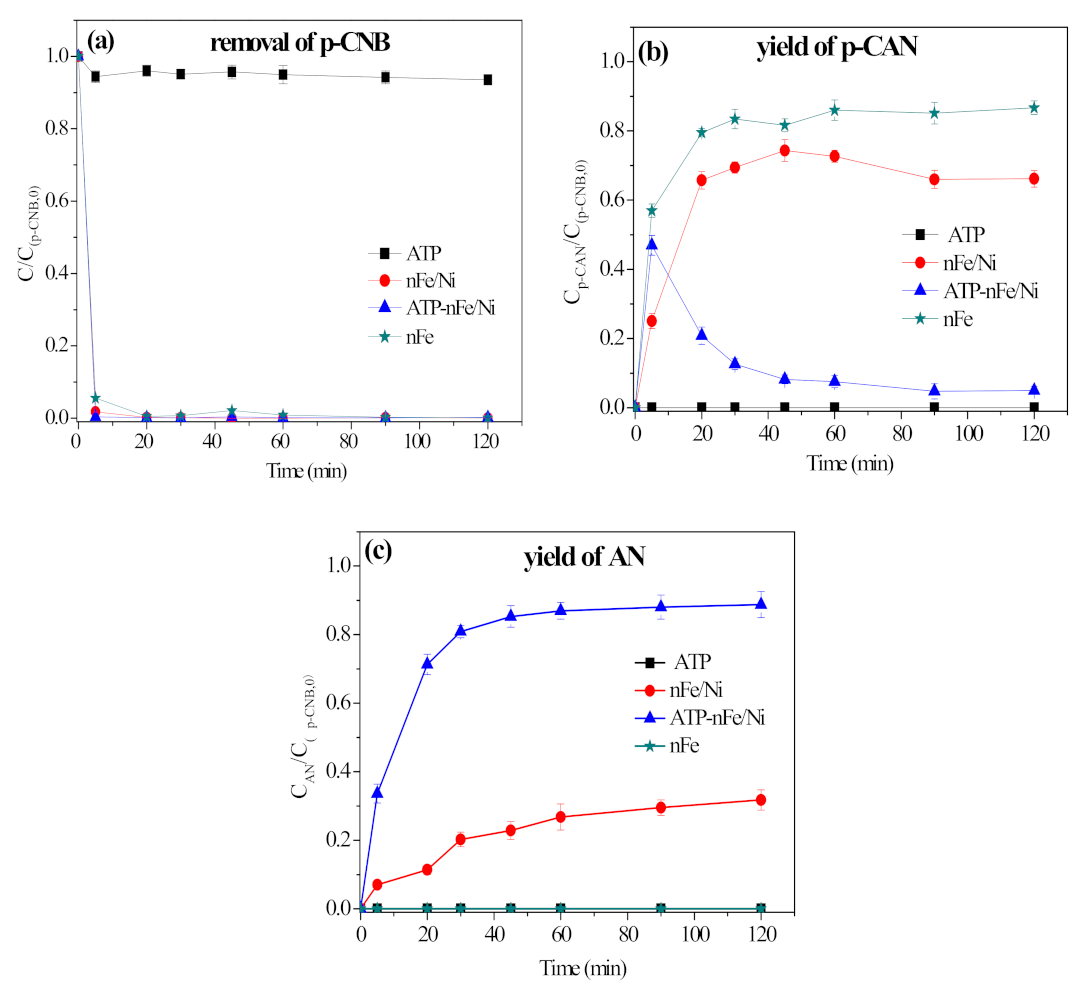
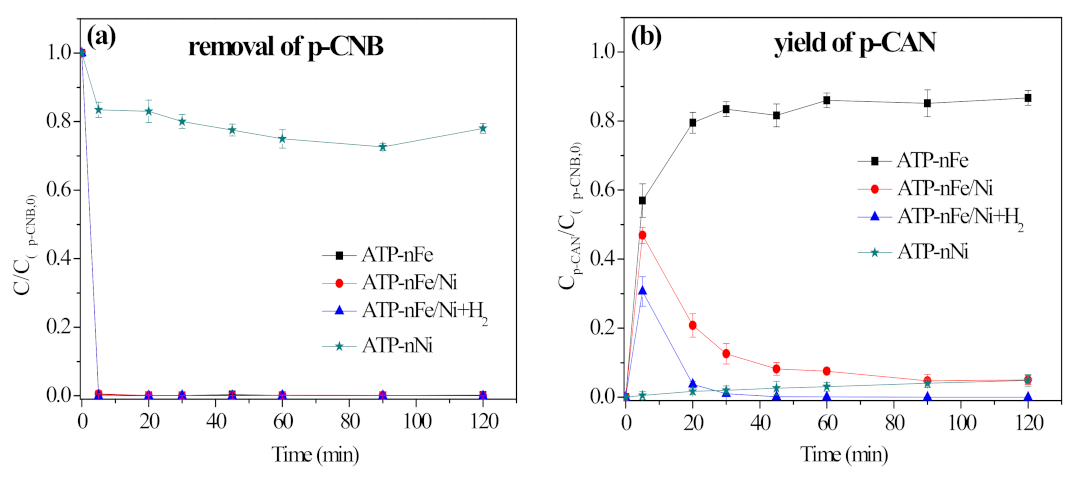
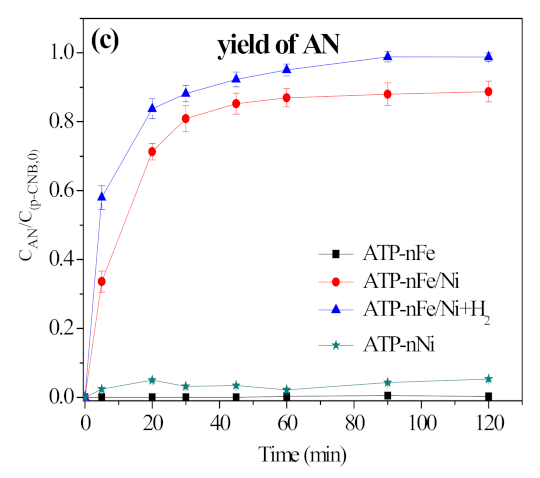
3.2. Removal, Nitroreduction and Dechlorination of p-CNB by Different Materials
3.3. Pathway and Kinetics of p-CNB Nitroreduction and Dechlorination by ATP-nFe/Ni
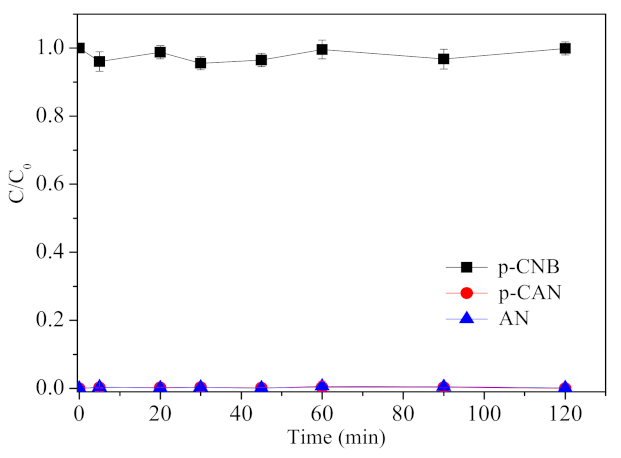
3.4. The Role of ATP in Nitroreduction and Dechlorination of p-CNB by ATP-nFe/Ni
3.5. The Role of Fe in Nitroreduction and Dechlorination of p-CNB by ATP-nFe/Ni
3.5.1. Contribution of Fe2+ in Nitroreduction and Dechlorination of p-CNB
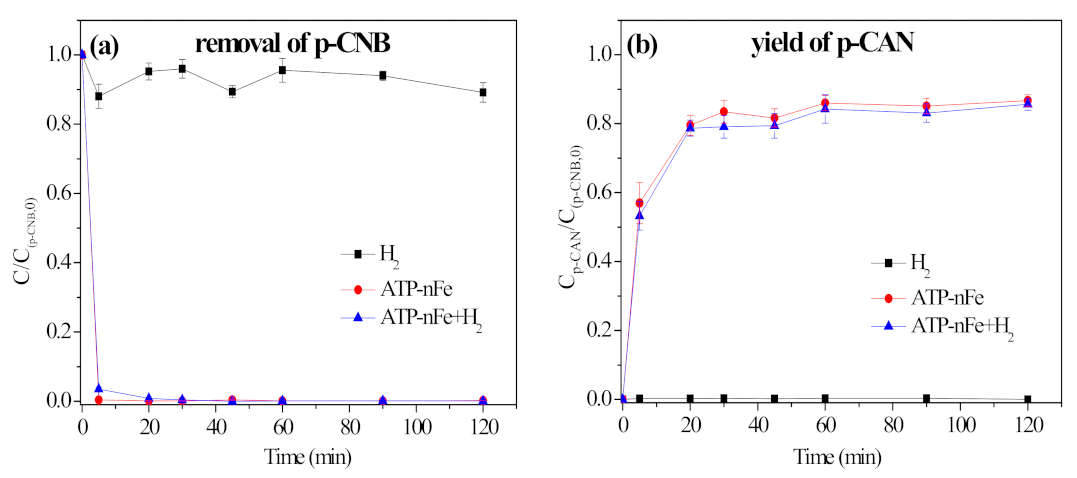
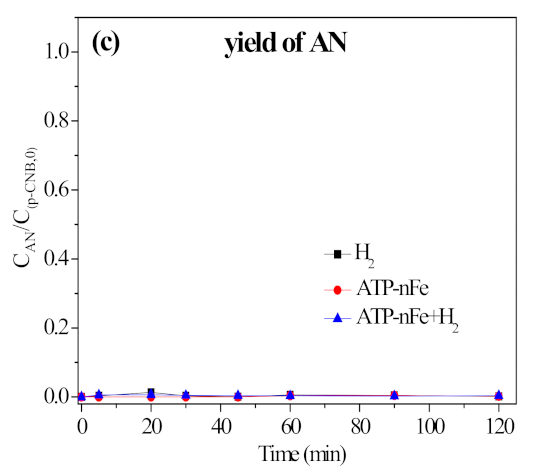
3.5.2. Contribution of H2 in Nitroreduction and Dechlorination of p-CNB
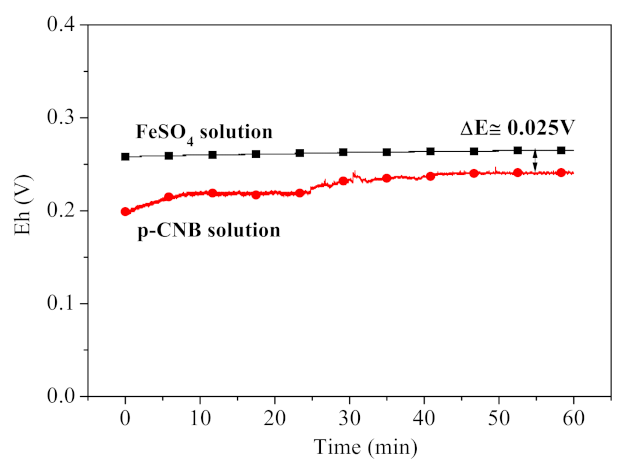
3.5.3. Contribution of Electron Transfer in Nitroreduction and Dechlorination of p-CNB
3.6. The Role of Ni in Nitroreduction and Dechlorination of p-CNB by ATP-nFe/Ni
3.6.1. Depositing on the Surface of Fe Nanoparticles to Alleviate the Oxidization of Fe
3.6.2. Acting as the Anode of Fe-Ni Galvanic Cell to Accelerate the Corrosion of Fe
3.6.3. Serving as a Hydrogenation Catalyst to Catalyze the Dissociation of H2 to H*
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, M.; Yu, W.; Liu, H. Selective hydrogenation of o-chloronitrobenzene over polymer-stabilized ruthenium colloidal catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1999, 138, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-S.; Chen, Y.-W. Hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene on La-doped NiMoB nanocluster catalysts. Chin. J. Catal. 2013, 34, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monguchi, Y.; Kume, A.; Hattori, K.; Maegawa, T.; Sajiki, H. Pd/C–Et3N-mediated catalytic hydrodechlorination of aromatic chlorides under mild conditions. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 7926–7933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.R.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Sepai, O.; Yan, H.; Sabbioni, G. Internal Exposure, Health Effects, and Cancer Risk of Humans Exposed to Chloronitrobenzene. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Jia, R.; Xie, K.; Xu, X. Bioreduction of para-chloronitrobenzene in drinking water using a continuous stirred hydrogen-based hollow fiber membrane biofilm reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arjunan, V.; Raj, A.; Sakiladevi, S.; Carthigayan, K.; Mohan, S. A comparative spectroscopic, electronic structure and chemical shift investigations of o-Chloronitrobenzene, p-Chloronitrobenzene and m-Chloronitrobenzene. J. Mol. Struct. 2012, 1007, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.M.; Chen, Z.L.; Xu, Z.Z.; Li, X.Y.; Xu, B.B.; Qi, F. Kinetics and mechanism of degradation of p-chloronitrobenzene in water by ozonation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 1325–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; You, L.; Zhang, Y. Photocatalytic reduction of p-chloronitrobenzene on illuminated nano-titanium dioxide particles. Dye. Pigment. 2006, 68, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Aqueous p-chloronitrobenzene decomposition induced by contact glow discharge electrolysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, R.; Kumar, R.; Sinha, A.; Lama, Y.; Saha, A.K. A review on synthesis, characterization, and applications of nano zero valent iron (nZVI) for environmental remediation. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 46, 443–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Liu, H. The use of zero-valent iron for groundwater remediation and wastewater treatment: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 267, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosco, T.; Petrangeli Papini, M.; Cruz Viggi, C.; Sethi, R. Nanoscale zerovalent iron particles for groundwater remediation: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 77, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Sun, Y.; Qin, H.; Li, J.; Lo, I.M.; He, D.; Dong, H. The limitations of applying zero-valent iron technology in contaminants sequestration and the corresponding countermeasures: The development in zero-valent iron technology in the last two decades (1994–2014). Water Res. 2015, 75, 1–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopal, G.; Kvg, R.; Salma, M.; Lavanya, A.A.J.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Mukherjee, A. Green synthesized Fe/Pd and in-situ Bentonite-Fe/Pd composite for efficient tetracycline removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Ruan, W.; Ai, H.; Yuan, B.; Fu, M.-L. Highly improved dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol in aqueous solution by Fe/Ni nanoparticles supported by polystyrene resin. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 128976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ding, C.; Gao, P.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wen, X.; Dai, J.; Fei, Z. Enhanced dechlorination of 2,6-dichlorophenol by carbon nanotubes supported Fe/Ni nanoparticles: Characterization, influencing factors, and kinetics. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 585, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, L.; Chu, S.; Luo, M.; Liu, J. Zeolite supported Fe/Ni bimetallic nanoparticles for simultaneous removal of nitrate and phosphate: Synergistic effect and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 347, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oruç, Z.; Ergüt, M.; Uzunoğlu, D.; Özer, A. Green synthesis of biomass-derived activated carbon/Fe-Zn bimetallic nanoparticles from lemon (Citrus limon (L.) Burm. f.) wastes for heterogeneous Fenton-like decolorization of Reactive Red 2. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103231–103241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, R.; Chen, L.; Tang, J. Enhanced dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol by recoverable Ni/Fe-Fe3O4 nanocomposites. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 48, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhou, R.; Lai, G.; Zheng, X. Influence of support and transition metal (Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni and Cu) on the hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene over supported platinum catalysts. Catal. Today 2004, 93–95, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Luo, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Chen, H. Stabilization of Fe–Pd bimetallic nanoparticles with sodium carboxymethyl cellulose for catalytic reduction of para-nitrochlorobenzene in water. Desalination 2011, 271, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-h.; Shih, Y.-h.; MacFarlane, J. Amphiphilic compounds enhance the dechlorination of pentachlorophenol with Ni/Fe bimetallic nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, D.; Fan, X. A new insight into the main mechanism of 2,4-dichlorophenol dechlorination by Fe/Ni nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzatahmadi, N.; Millarc, G.J.; Ayokoc, G.A.; Zhud, J.; Zhud, R.; Liangd, X.; Hed, H.; Xi, Y. Degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol using palygorskite-supported bimetallic Fe/Ni nanocomposite as a heterogeneous catalyst. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 168, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Pittendrigh, B.R.; Liu, S.; Jia, X.; Wong, P.K. Efficient degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A by synergistic integration of Fe/Ni bimetallic catalysis and microbial acclimation. Water Res. 2017, 122, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Huang, R.; Li, C.; Che, M.; Su, R.; Li, S.; Yu, J.; Qi, W.; He, Z. Continuous rapid dechlorination of p-chlorophenol by Fe-Pd nanoparticles promoted by procyanidin. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 201, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, X.; Liu, H.; Ning, X.; Zhao, D.; Fan, X. Screening for the action mechanisms of Fe and Ni in the reduction of Cr (VI) by Fe/Ni nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-W.; Lee, D.-S. Selective Hydrogenation of p-Chloronitrobenzene on Nanosized PdNiB Catalysts. J. Nanoparticles 2013, 2013, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Gu, C.; Ye, M.; Bian, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, F.; Yang, X.; Song, Y.; Jiang, X. Debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by attapulgite-supported Fe/Ni bimetallic nanoparticles: Influencing factors, kinetics and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 298, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzum, C.; Shahwan, T.; Eroglu, A.; Hallam, K.; Scott, T.; Lieberwirth, I. Synthesis and characterization of kaolinite-supported zero-valent iron nanoparticles and their application for the removal of aqueous Cu2+ and Co2+ ions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 43, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qian, L.; Ouyang, D.; Chen, Y.; Han, L.; Chen, M. Effective removal of Cr (VI) by attapulgite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron from aqueous solution: Enhanced adsorption and crystallization. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xi, B.; Mao, X.; Gong, B.; Li, R.; Peng, X.; Liu, H. Removal of nitrobenzene by immobilized nanoscale zero-valent iron: Effect of clay support and efficiency optimization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 370, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D. Catalytic hydrodechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol over nanoscale Pd/Fe: Reaction pathway and some experimental parameters. Water Res. 2006, 40, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Cao, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, X.; Zhou, J.L. Preparation of functionalized Pd/Fe-Fe3O4@MWCNTs nanomaterials for aqueous 2,4-dichlorophenol removal: Interactions, influence factors, and kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheson, L.J.; Tratnyek, P.G. Reductive dehalogenation of chlorinated methanes by iron metal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 2045–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, H.-L.; Zhang, W.-X. Nanoscale Pd/Fe bimetallic particles: Catalytic effects of palladium on hydrodechlorination. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 77, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Sun, J.; Xiang, Y.; Shang, C. Recycling and reuse of rusted iron particles containing core-shell Fe-FeOOH for ibuprofen removal: Adsorption and persulfate-based advanced oxidation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Mao, X.; Wang, D. Understanding the electrode reaction process of dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol over Ni/Fe nanoparticles: Effect of pH and 2,4-dichlorophenol concentration. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 84, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chen, H.; Dong, H.; Zhu, L.; Qiang, Z.; Yu, J. Transformation of iopamidol and atrazine by peroxymonosulfate under catalysis of a composite iron corrosion product (Fe/Fe3O4): Electron transfer, active species and reaction pathways. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 403, 123553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Pang, L.; Bian, Z. Electrocatalytic Reduction-oxidation of Chlorinated Phenols using a Nanostructured Pd-Fe Modified Graphene Catalyst. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 178, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Qian, W.; Yu, C.; Wang, T.; Zeng, G.; Lei, C. Effective catalytic hydrodechlorination of o -, p - and m -chloronitrobenzene over Ni/Fe nanoparticles: Effects of experimental parameter and molecule structure on the reduction kinetics and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Kumar, A.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yan, Z.; Sun, X. Boosting the bifunctional oxygen electrocatalytic performance of atomically dispersed Fe site via atomic Ni neighboring. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 274, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Jiang, Z.; Deng, J.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Hou, K.; Zhang, L.; Tang, L.; Zeng, G. Physicochemical transformation of Fe/Ni bimetallic nanoparticles during aging in simulated groundwater and the consequent effect on contaminant removal. Water Res. 2018, 129, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

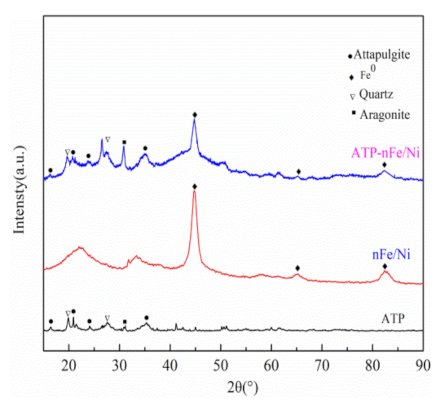
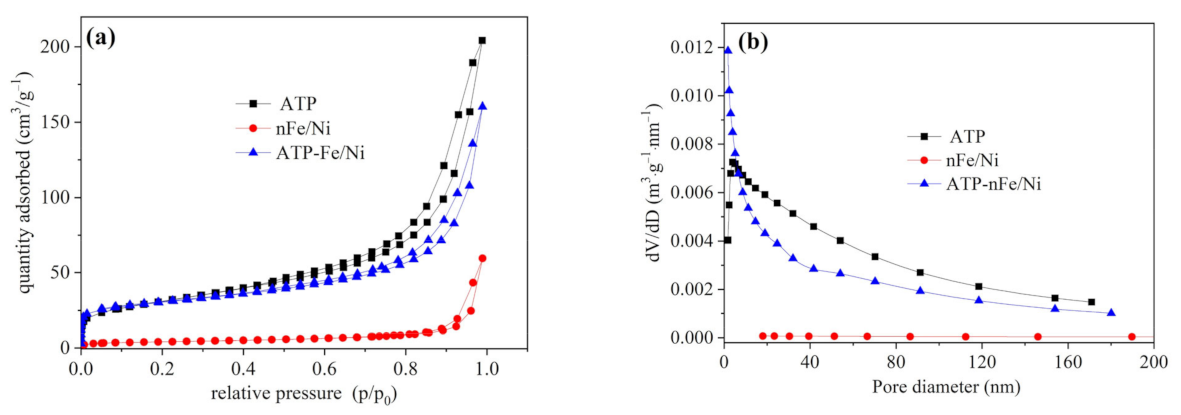


| Material | SBET (m2/g) | *Smicro (m2/g) | *Smeso (m2/g) | Vtotal (cm3/g) | *Vmicro (cm3/g) | *Vmeso (cm3/g) | Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATP | 110.16 | 7.15 | 111.04 | 0.3160 | 0.0031 | 0.3156 | 11.47 |
| nFe/Ni | 14.15 | 2.88 | 13.39 | 0.0920 | 0.0014 | 0.0919 | 26.01 |
| ATP-nFe/Ni | 101.33 | 36.58 | 77.69 | 0.2479 | 0.0188 | 0.2372 | 9.78 |
| Material | *FeT% | *Fe% | Fe/FeT% |
|---|---|---|---|
| nFe/Ni | 94.2 | 47.5 | 50.4 |
| ATP-nFe/Ni | 36.2 | 35.6 | 98.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Anang, E.; Fan, X. Experimental Identification of the Roles of Fe, Ni and Attapulgite in Nitroreduction and Dechlorination of p-Chloronitrobenzene by Attapulgite-Supported Fe/Ni Nanoparticles. Materials 2022, 15, 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031254
Liang J, Wang J, Liu H, Anang E, Fan X. Experimental Identification of the Roles of Fe, Ni and Attapulgite in Nitroreduction and Dechlorination of p-Chloronitrobenzene by Attapulgite-Supported Fe/Ni Nanoparticles. Materials. 2022; 15(3):1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031254
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Jing, Junwen Wang, Hong Liu, Emmanuella Anang, and Xianyuan Fan. 2022. "Experimental Identification of the Roles of Fe, Ni and Attapulgite in Nitroreduction and Dechlorination of p-Chloronitrobenzene by Attapulgite-Supported Fe/Ni Nanoparticles" Materials 15, no. 3: 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031254
APA StyleLiang, J., Wang, J., Liu, H., Anang, E., & Fan, X. (2022). Experimental Identification of the Roles of Fe, Ni and Attapulgite in Nitroreduction and Dechlorination of p-Chloronitrobenzene by Attapulgite-Supported Fe/Ni Nanoparticles. Materials, 15(3), 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031254





