Effect of Multi-Pass Power Spinning on Microstructure Homogenization and Mechanical-Property Strengthening of Ti2AlNb-Based Alloy Using Welded Tube Blank
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Material and Method
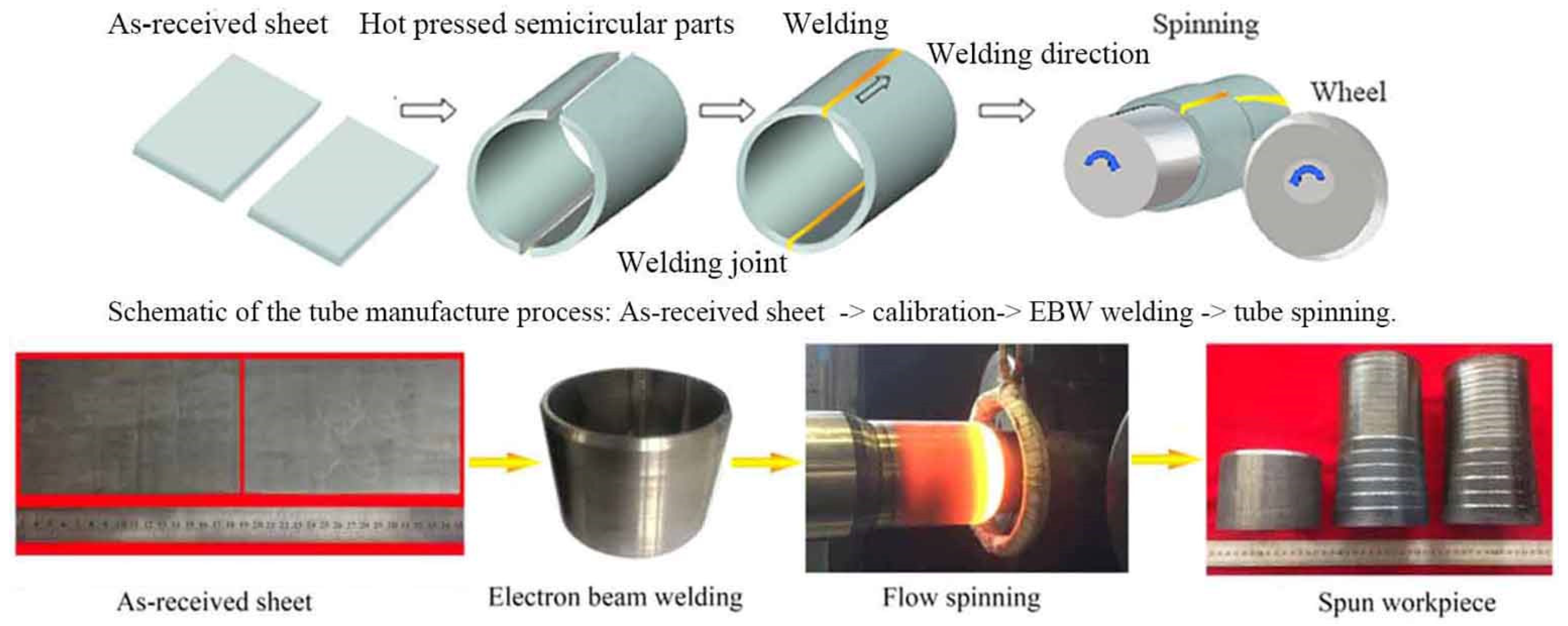
2.1. Material Selection and Experimental Procedure
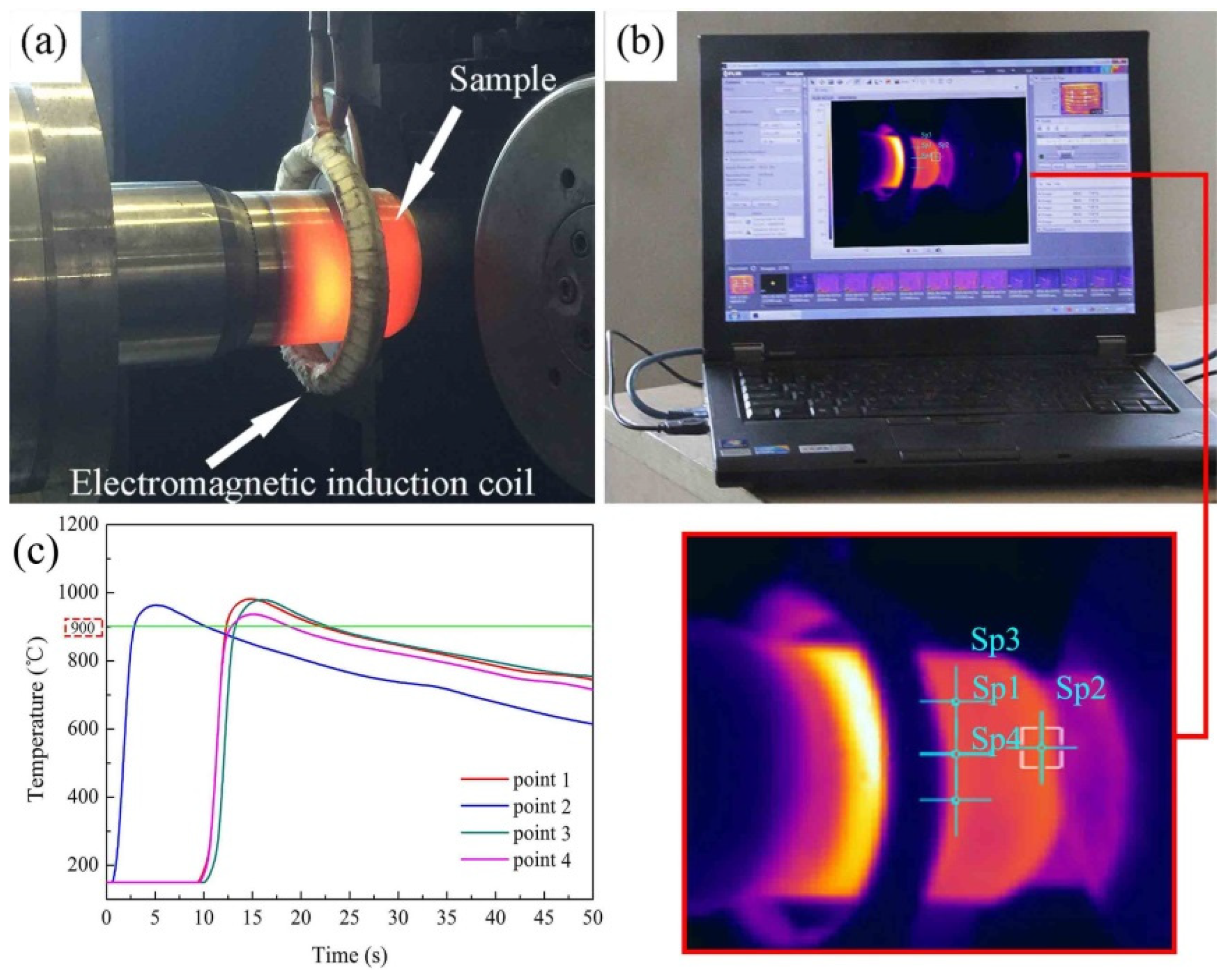
2.2. Temperature Control System
2.3. Spinning Process Scheme
2.4. Mechanical-Property Evaluation and Microstructures Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
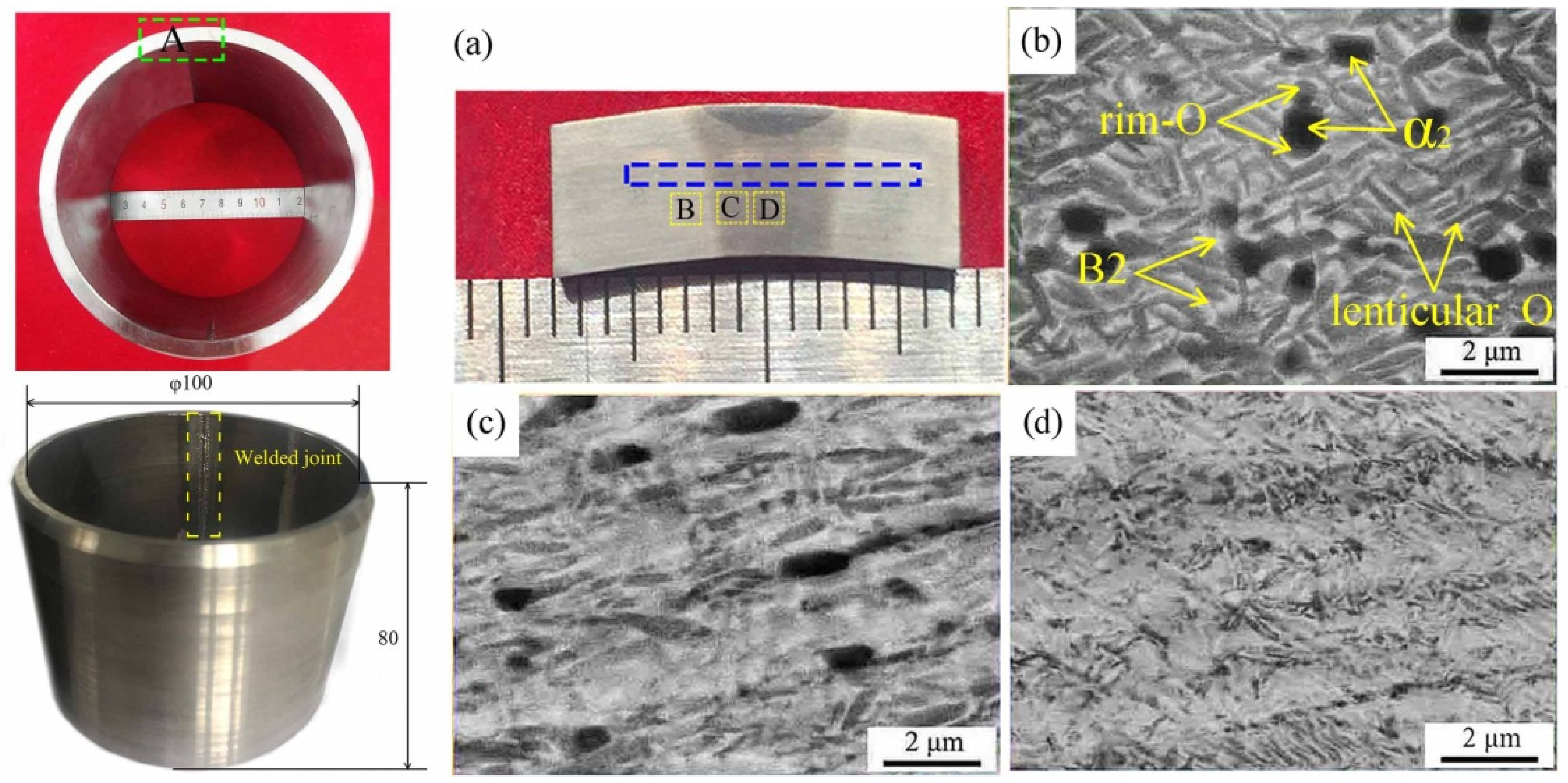
3.1. Initial Microstructures
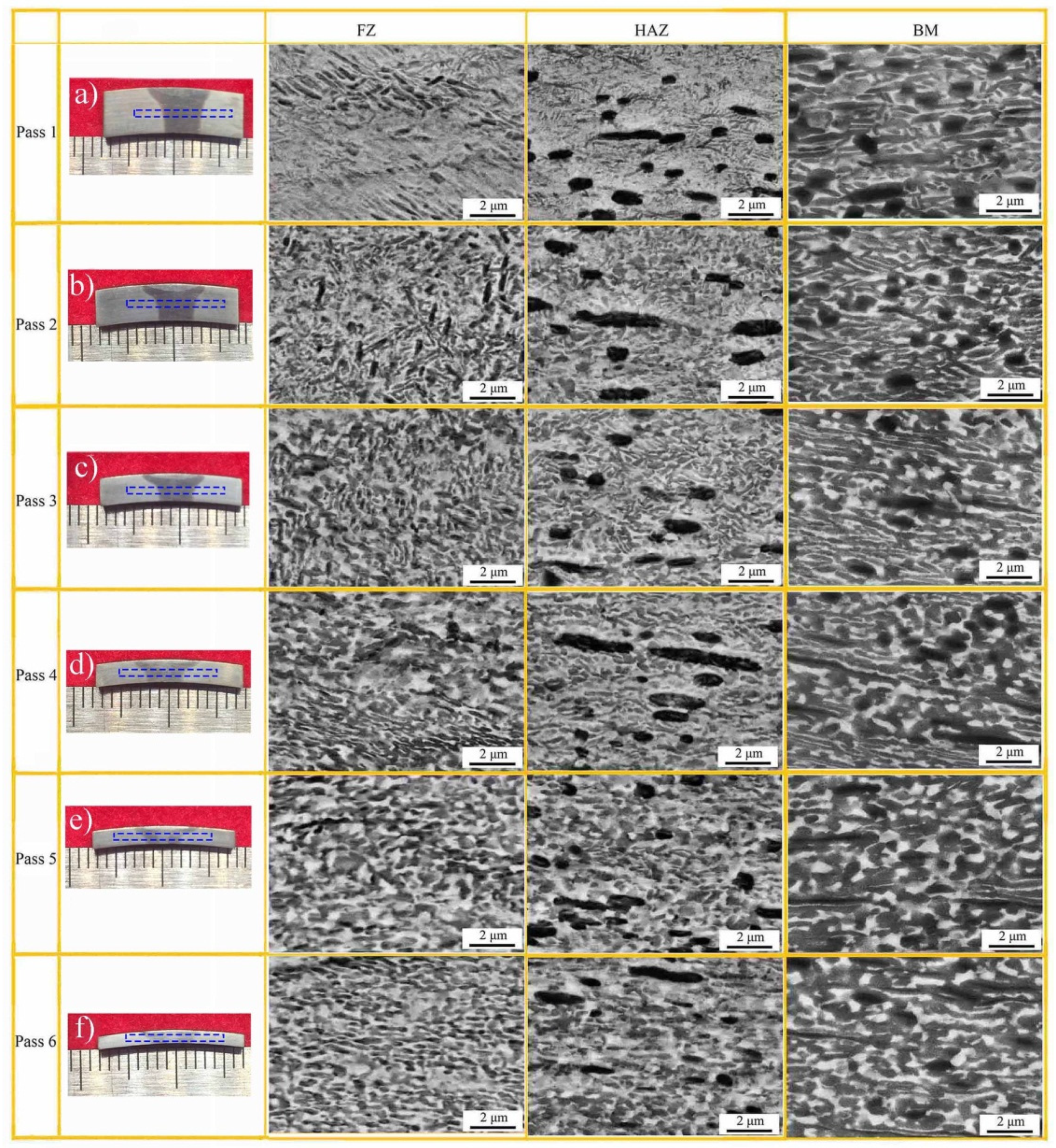
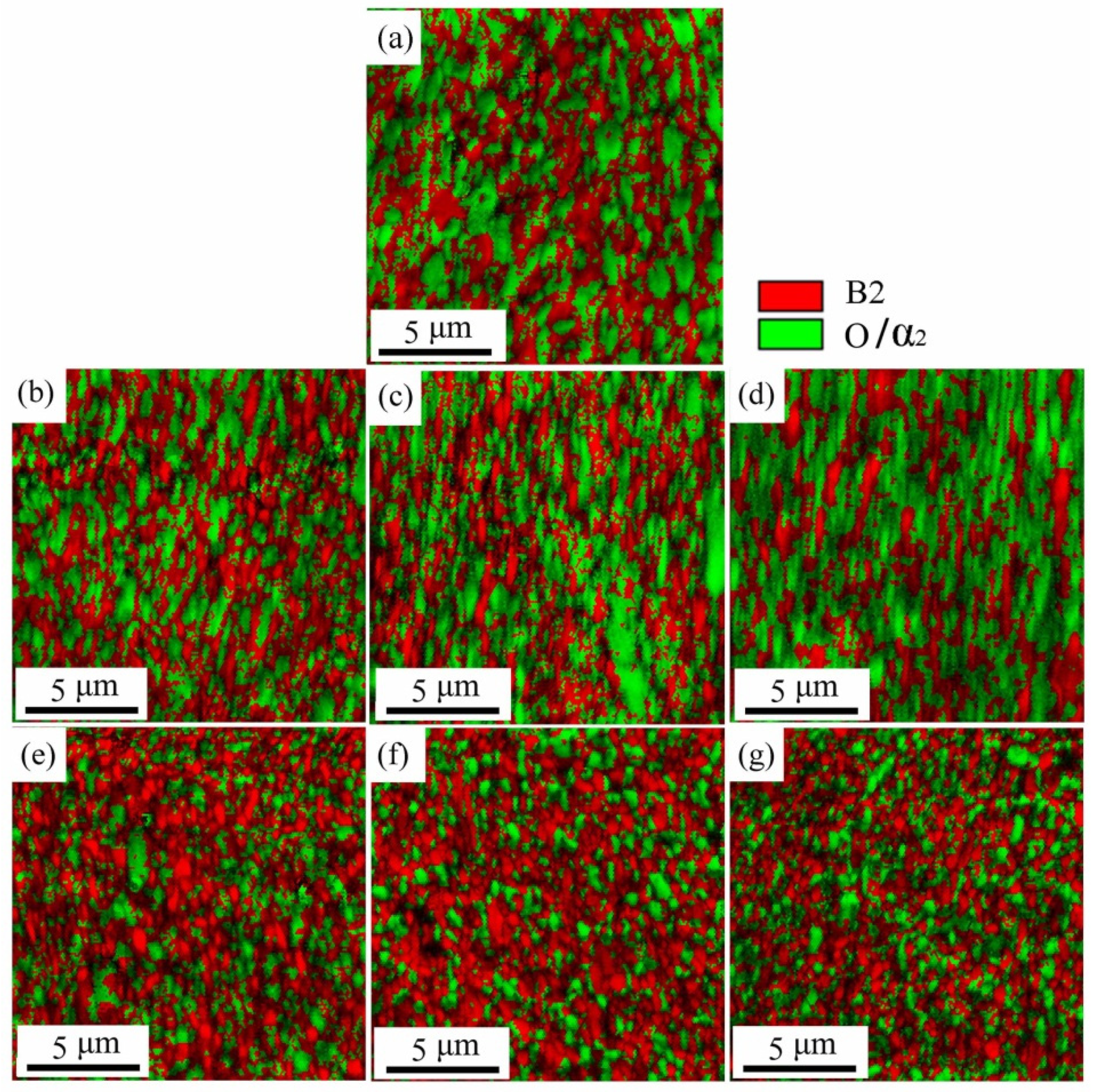
3.2. Microstructure Evolution during Multi-Pass Power Spinning
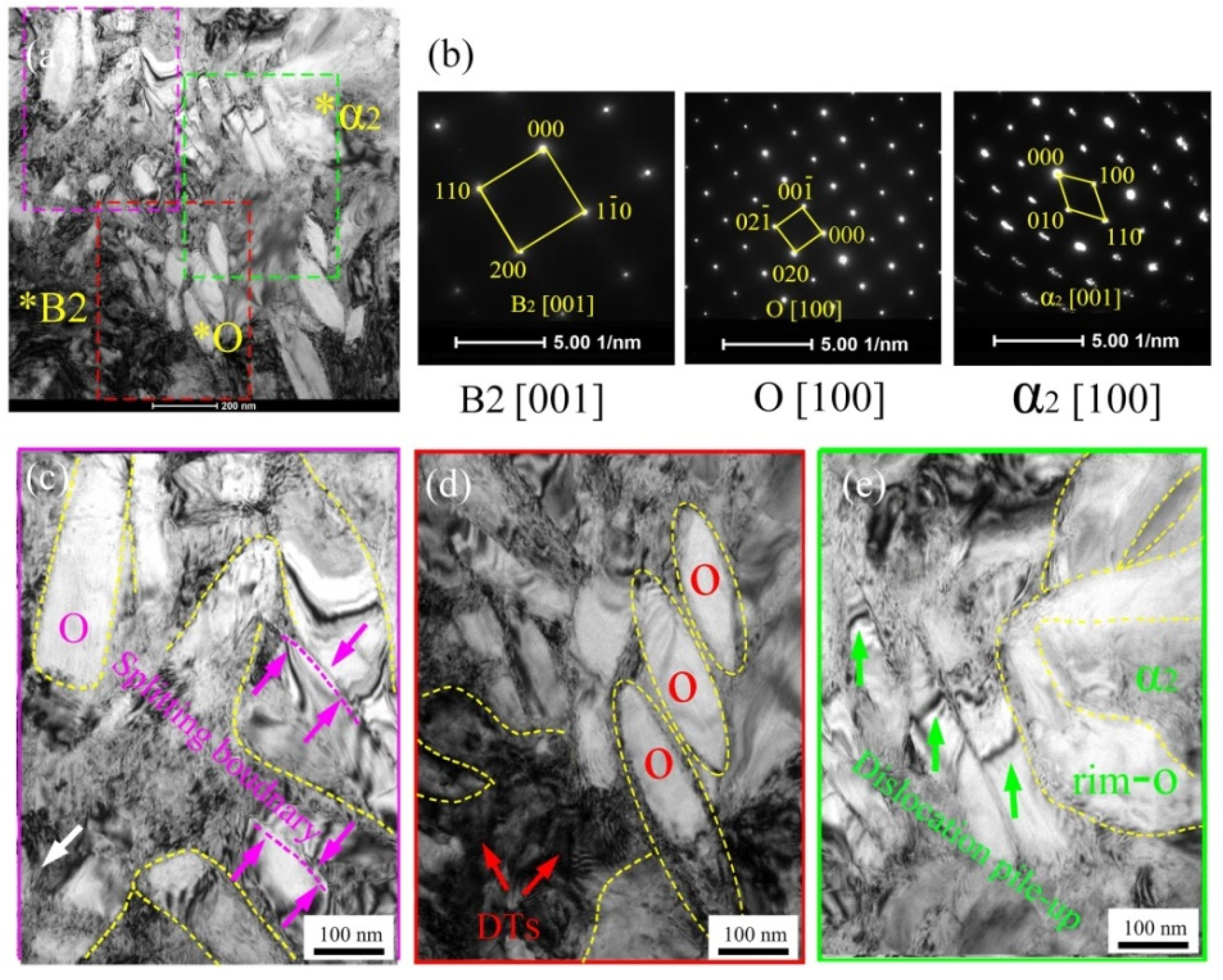
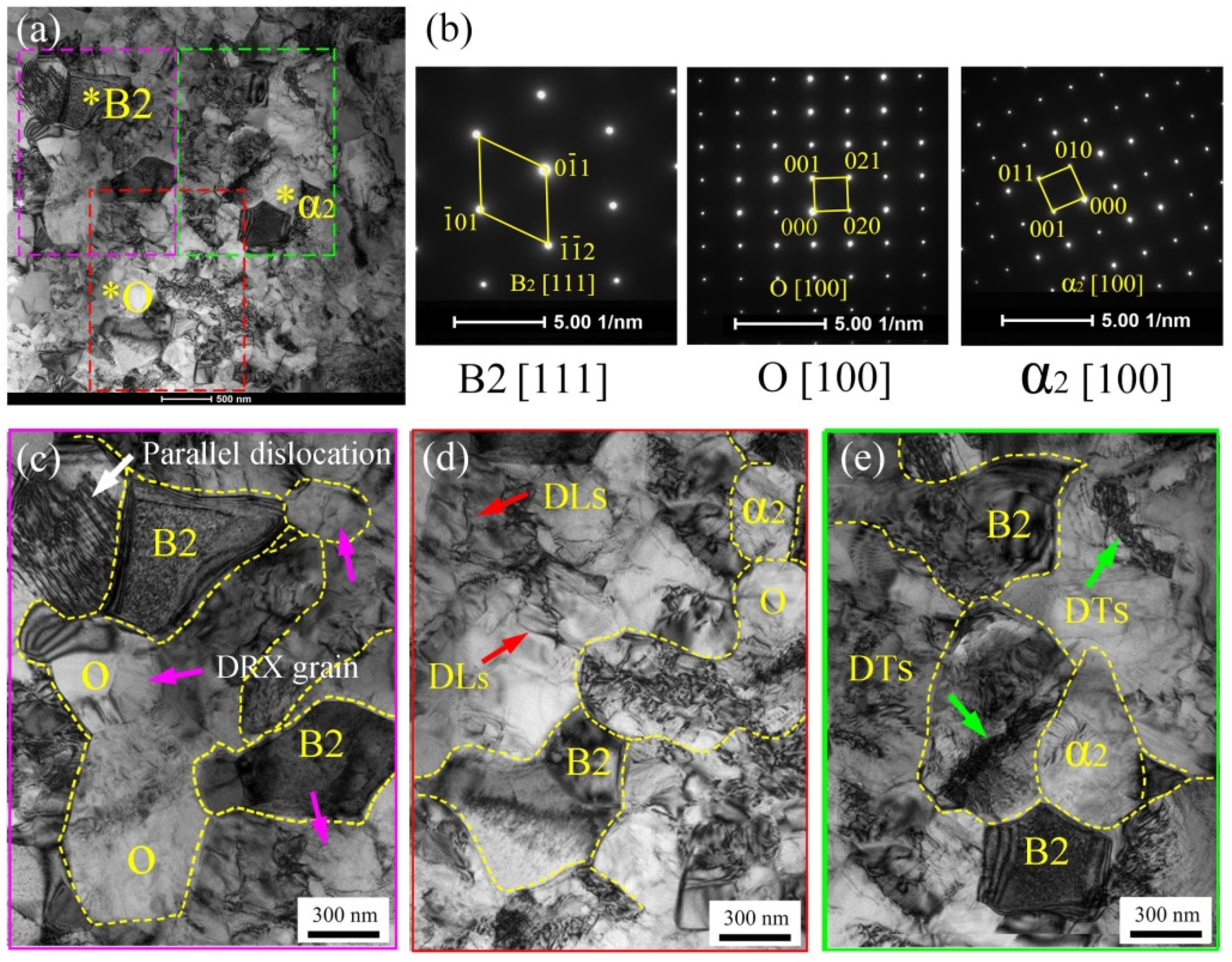
3.2.1. Microstructure Evolution of BM
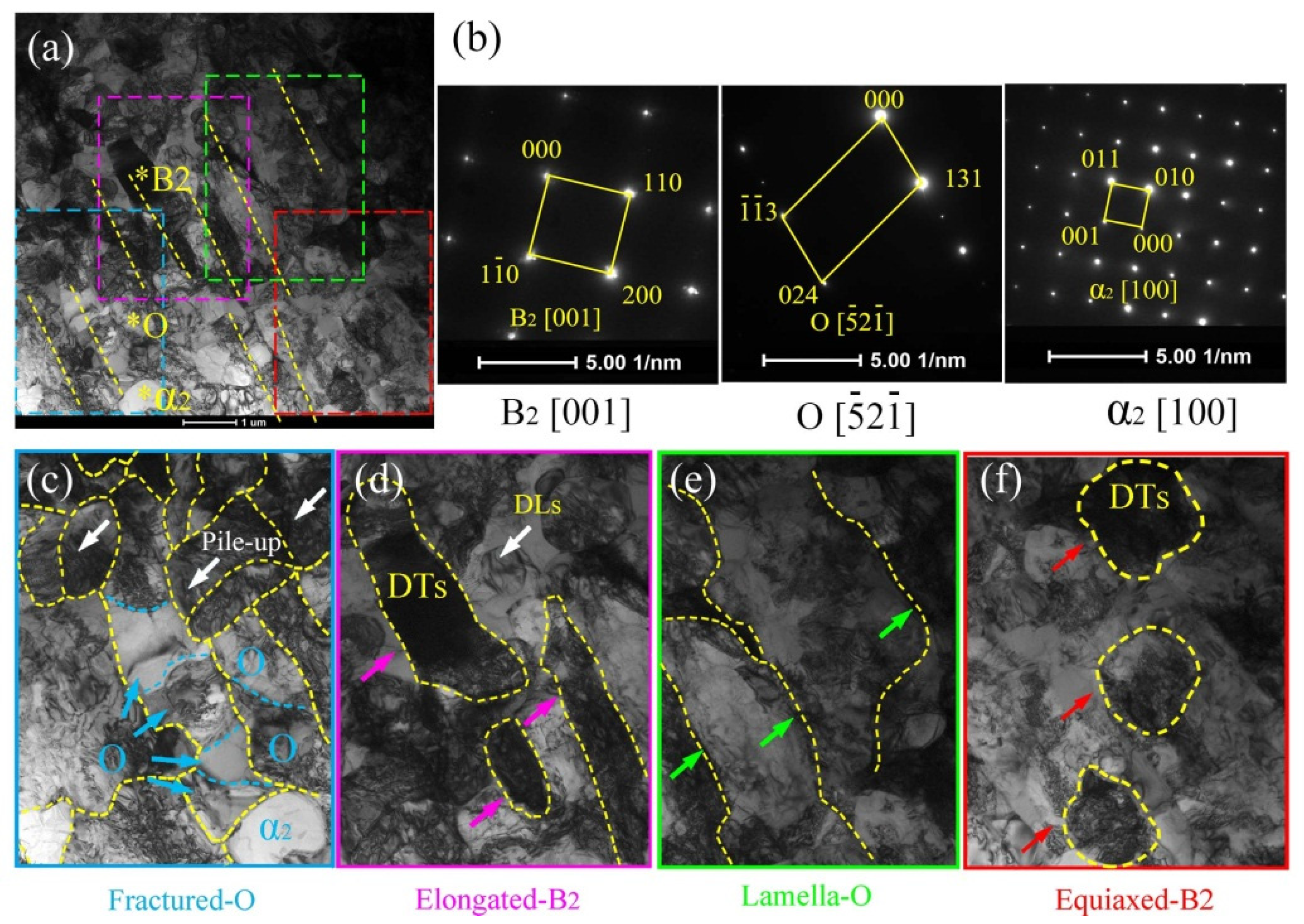
3.2.2. Microstructure Evolution of FZ
3.3. Mechanical-Property Analysis during Multi-Pass Power Spinning
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shao, B.; Shan, D.; Guo, B.; Zong, Y. Plastic deformation mechanism and interaction of B2, α2, and O phases in Ti22Al25Nb alloy at room temperature. Int. J. Plast. 2019, 113, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpfert, J. Intermetallic Alloys Based on Orthorhombic Titanium Aluminide. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2010, 3, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehlert, C.J.; Bingert, J.F. Microstructure, tensile, and creep behavior of O+BCC Ti2AlNb alloys processed using induction-float-zone melting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2001, 117, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, J.P.; Boehlert, C.J. Comparison of the Microstructure, Tensile, and Creep Behavior for Ti-24Al-17Nb-0.66Mo (Atomic Percent) and Ti-24Al-17Nb-2.3Mo (Atomic Percent) Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2007, 38, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zeng, W.; Li, D.; Liang, X.; Zhang, J.; Ma, X. Effect of orthorhombic case on the creep rupture of Ti-22Al-25Nb (at%) orthorhombic alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 696, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriev, A.; Polozov, I.; Sufiiarov, V.; Popovich, A. In-situ synthesis of Ti2AlNb-based intermetallic alloy by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 704, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cai, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yu, J. Dual structure O+B2 for enhancement of hardness in furnace-cooled Ti2AlNb-based alloys by powder metallurgy. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Liu, W.; Xu, Y.; Lu, C.; Liu, H.; Gu, Y.; Luo, J. Microstructure evolution, B2 grain growth kinetics and fracture behaviour of a powder metallurgy Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 730, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobbili, R.; Madhu, V. Physically-based constitutive model for flow behavior of a Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy at high strain rates. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 762, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.R.; Suwas, S.; Fundenberger, J.J.; Ray, R.K. Evolution of crystallographic texture and microstructure in the orthorhombic phase of a two-phase alloy Ti–22Al–25Nb. Intermetallics 2009, 17, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehlert, C.J. Microstructure, creep, and tensile behavior of a Ti-12Al-38Nb (at%) beta+orthorhombic alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 267, 82–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chen, Z.Y.; Wu, C.C.; Li, J.W.; Tang, Z.Y.; Wang, Q.J. The effect of annealing on microstructure and tensile properties of Ti-22Al-25Nb electron beam weld joint. Intermetallics 2016, 75, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyens, C.; Peters, M. Titanium and Titanium Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications; Wiley-VCH: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, K.; Lu, Z.; Li, B.; Zhang, D. The structural design and superplastic forming/diffusion bonding of Ti2AlNb based alloy for four-layer structure. Mater. Des. 2016, 104, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-W.; Zhao, T.; Wang, G.; Gao, J.; Fang, H. Superplastic forming and diffusion bonding of Ti-22Al-24Nb alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 222, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, G.; Jin, S.; Liu, Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti2AlNb cup-shaped part prepared by hot gas forming: Determining forming temperature, strain rate, and heat treatment. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 92, 4583–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Xiao, G.; Long, H.; Cheng, X.; Sheng, X. A review of process advancement of novel metal spinning. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2014, 85, 100–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhao, X.; Ma, H.; Shan, D.; Lin, H. Influence of roller distribution modes on spinning force during tube spinning. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2016, 113, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-J.; Wu, A.-P.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, R.-C.; Wang, G.-Q. Effects of welding parameters on weld shape and residual stresses in electron beam welded Ti2AlNb alloy joints. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2019, 29, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.L.; Yuan, S.J.; Wang, X.S.; Liu, G.; Liu, H.J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–Cu–Mg alloy tube fabricated by friction stir welding and tube spinning. Scr. Mater. 2012, 66, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, W.; Zong, Y.; Zhong, X.; Shan, D. Effect of Initial Microstructures on Hot Deformation Behavior and Workability of Ti2AlNb-Based Alloy. Metals 2018, 8, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, B.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, J. Study on Spinning Properties of Titanium Alloy. Rare Met. 2004, 28, 271–273. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Weidong, Z.; Wei, W.; Xiaobo, L.; Jianwei, Z. Coarsening behavior of lamellar orthorhombic phase and its effect on tensile properties for the Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 611 (Suppl. C), 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Zeng, W.; Wang, W.; Liang, X.; Zhang, J. Quantitative analysis on microstructure evolution and tensile property for the isothermally forged Ti2AlNb based alloy during heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 573, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Zeng, W.; Chen, X.; Liang, X.; Zhang, J. Quantitative analysis of the effect of heat treatment on microstructural evolution and microhardness of an isothermally forged Ti-22Al-25Nb (at%) orthorhombic alloy. Intermetallics 2014, 45, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Boehlert, C.J.; Majumdar, B.S.; Seetharaman, V.; Miracle, D.B. Part I. The microstructural evolution in Ti-Al-Nb O+Bcc orthorhombic alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1999, 30, 2305–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Dai, X.; Liu, J.; Si, X.; Feng, J. Relationship between microstructure and mechanical properties of TiAl/Ti2AlNb joint brazed using Ti-27Co eutectic filler metal. Mater. Des. 2017, 121, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Kong, B.; Tao, W.; Liu, G.; Ning, H. Effects of annealing on microstructure and deformation uniformity of Ti-22Al-24Nb-0.5Mo laser-welded joints. Mater. Des. 2017, 130, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpfert, J.; Leyens, C. Microstructure Evolution, Phase Transformations and Oxidation of an Orthorhombic Titanium Aluminide Alloy. Struct. Intermet. 1997, 895–904. [Google Scholar]
- Bendersky, L.A.; Roytburd, A.; Boettinger, W.J. Phase transformations in the (Ti, Al)3 Nb section of the TiAlNb system—I. Microstructural predictions based on a subgroup relation between phases. Acta Metall. Mater. 1994, 42, 2323–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.P.; Zou, G.S.; Ren, J.L.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, G.Q.; Liu, X.; Xie, M.R. Microstructures and mechanical properties of Ti-24Al-17Nb (at%) laser beam welding joints. Intermetallics 2002, 10, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, S.; Shen, J. Strain rate sensitivity of Ti-22Al-25Nb (at%) alloy during high temperature deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 710, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvage, X.; Wilde, G.; Divinski, S.V.; Horita, Z.; Valiev, R.Z. Grain boundaries in ultrafine grained materials processed by severe plastic deformation and related phenomena. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 540, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.; Zhu, Y.T.; Butt, D.P.; Alexandrov, I.V.; Lowe, T.C. Microstructural evolution, microhardness and thermal stability of HPT-processed Cu. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 290, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, M.; Horita, Z.; Nemoto, M.; Langdon, T.G. The use of severe plastic deformation for microstructural control. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 324, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Wang, D.; Yang, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, G. Microstructure analysis on enhancing mechanical properties at 750 °C and room temperature of Ti-22Al-24Nb-0.5Mo alloy tubes fabricated by hot gas forming. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 789, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





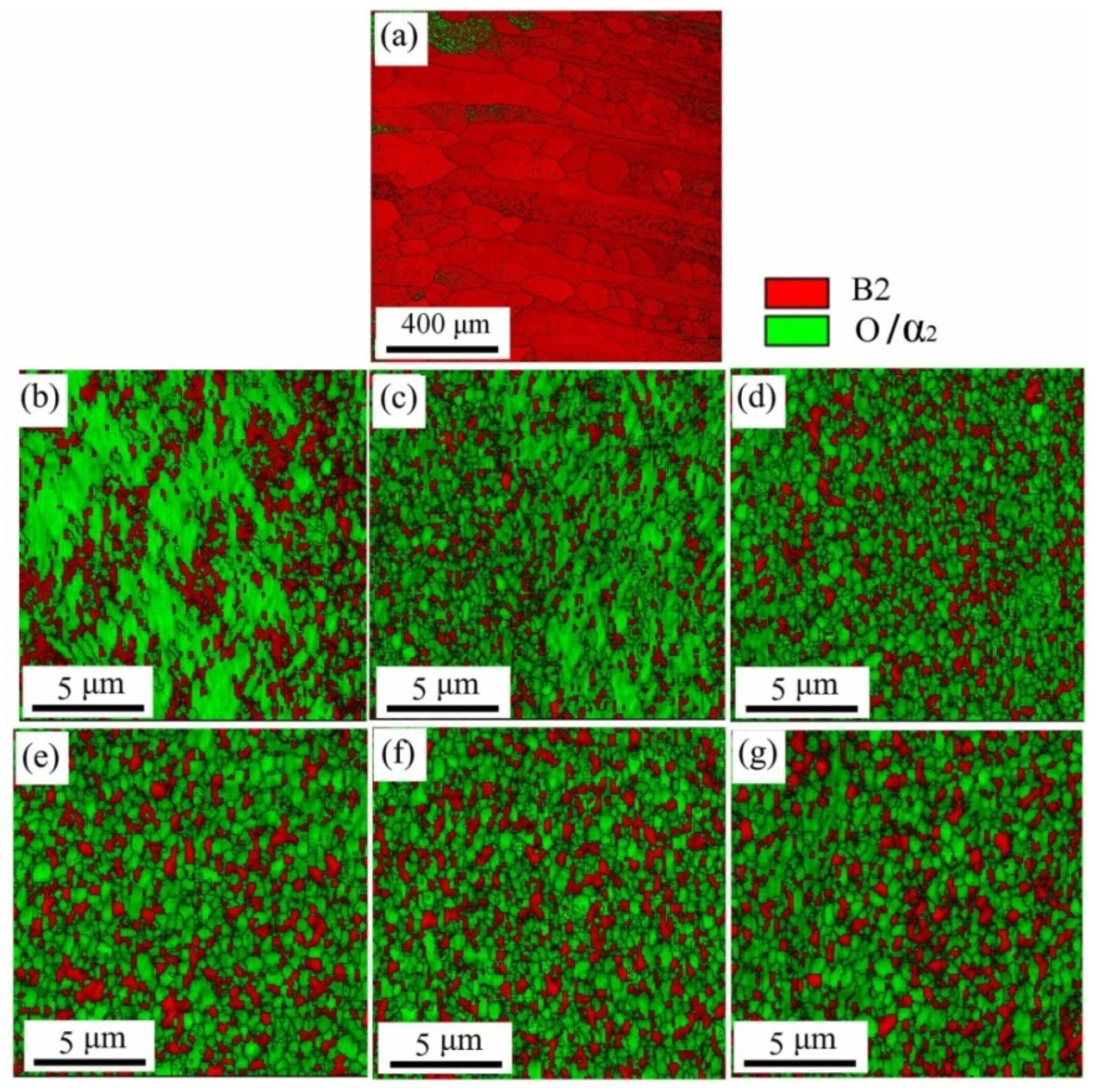
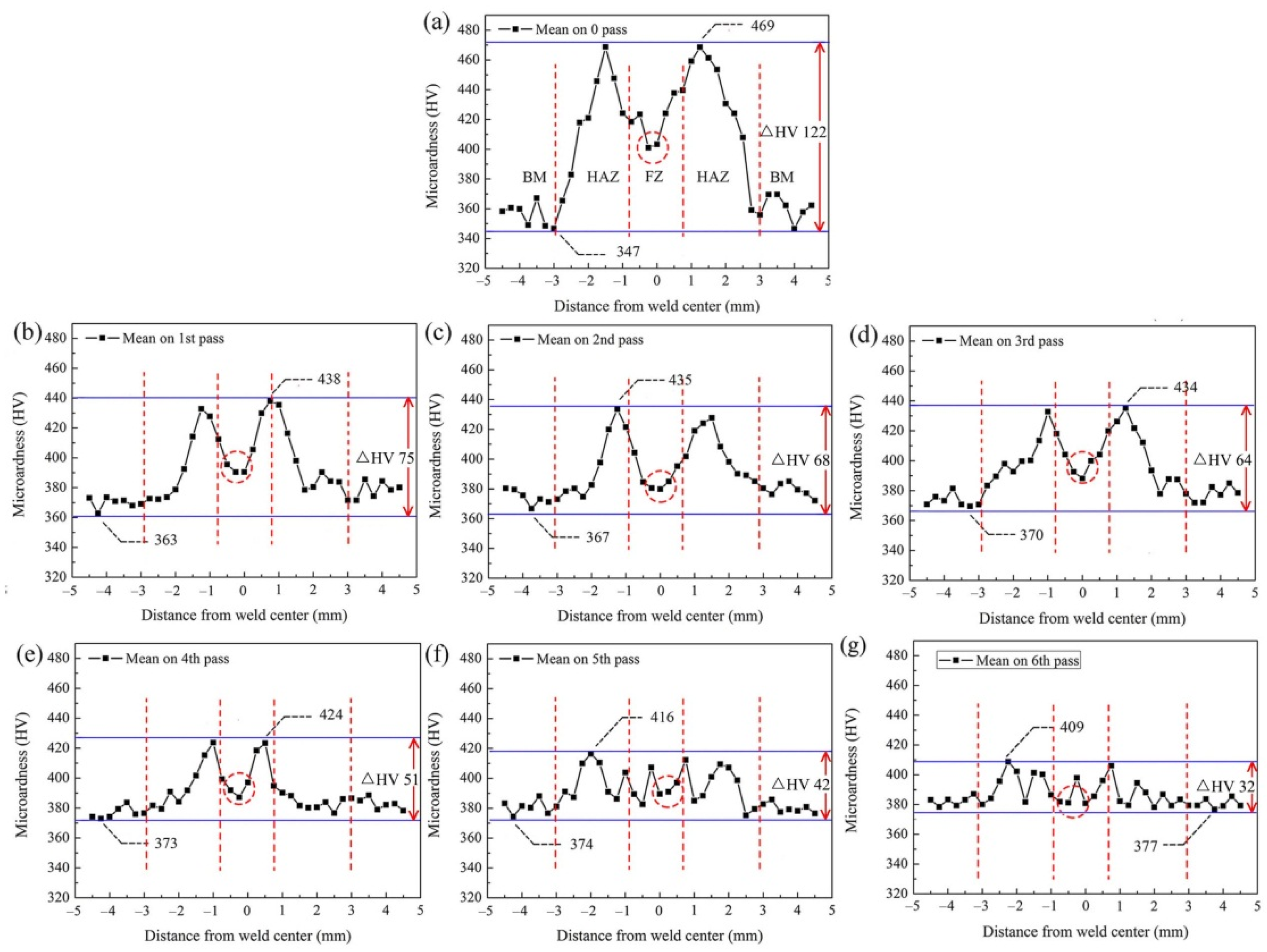
| Forming Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Initial tube blank length, L (mm) | 80 |
| Initial tube blank thickness, t0 (mm) | 6 |
| Mandrel diameter Dm (mm) | 100 |
| Roller diameter, Dr (mm) | 200 |
| Roller feed rate, f (mm/r) | 1 |
| Front angle of roller, αρ (deg) | 20 |
| Fillet radius of roller, r (mm) | 5 |
| Rotation speed of mandrel, n (rpm) | 200 |
| Reduction, ψt (%) | 20, 36, 49, 59, 67, 74 |
| Thickness of spun workpiece, mm | 6.0, 4.8, 3.84, 3.07, 2.46, 1.97, 1.58 |
| Roller number | 2 |
| Temperature (°C) | 950 ± 30 |
| FZ | HAZ Close to BM | BM | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B2 | α2 | O | B2 | α2 | O | B2 | α2 | O | |
| As-welded | 95.5 ± 4.5 | 4.5 ± 0.2 | / | 81.5 ± 4.1 | 12.8 ± 0.7 | 5.7 ± 0.3 | 55.4 ± 2.8 | 13.2 ± 0.7 | 31.4 ± 1.6 |
| Pass 1 | 42.6 ± 2.8 | 10.3 ± 0.2 | 47.1 ± 0.9 | 48.7 ± 2.4 | 12.5 ± 0.7 | 38.8 ± 1.9 | 52.3 ± 2.8 | 13.3 ± 0.7 | 34.4 ± 1.7 |
| Pass 2 | 41.7 ± 2.8 | 10.7 ± 0.4 | 47.6 ± 1.3 | 46.6 ± 2.3 | 12.5 ± 0.7 | 40.9 ± 2.1 | 49.1 ± 2.5 | 12.8 ± 0.7 | 38.1 ± 1.9 |
| Pass 3 | 40.4 ± 2.1 | 11.5 ± 0.4 | 48.1 ± 1.3 | 45.2 ± 2.3 | 12.2 ± 0.7 | 42.6 ± 2.1 | 48.1 ± 2.5 | 12.8 ± 0.7 | 39.1 ± 2.1 |
| Pass 4 | 39.1 ± 2.1 | 11.7 ± 0.4 | 49.2 ± 1.4 | 42.6 ± 2.1 | 12.2 ± 0.7 | 45.2 ± 2.3 | 44.3 ± 2.2 | 12.5 ± 0.7 | 43.2 ± 2.1 |
| Pass 5 | 38.5 ± 1.9 | 11.9 ± 0.5 | 49.6 ± 1.4 | 42.3 ± 2.1 | 12.1 ± 0.6 | 45.6 ± 2.3 | 44.2 ± 2.2 | 12.3 ± 0.7 | 43.5 ± 2.2 |
| Pass 6 | 38.4 ± 1.8 | 12.1 ± 0.5 | 49.5 ± 1.5 | 42.2 ± 2.1 | 12.1 ± 0.6 | 45.7 ± 2.3 | 44.1 ± 2.2 | 12.1 ± 0.6 | 43.8 ± 2.2 |
| Slip System | Pass | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| {110}<111>B2-axial direction | 0.43 | 0.44 | 0.46 | 0.43 | 0.47 | 0.42 | 0.46 |
| {110}<111>B2-tangential direction | 0.47 | 0.45 | 0.47 | 0.45 | 0.47 | 0.45 | 0.47 |
| {112}<111> B2-axial direction | 0.47 | 0.46 | 0.47 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.44 | 0.46 |
| {112}<111> B2-tangential direction | 0.47 | 0.49 | 0.47 | 0.48 | 0.47 | 0.48 | 0.46 |
| Pass | BM-Axial | BM-Tangential | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTS/MPa | Total Elongation % | UTS/MPa | Total Elongation % | |
| 0 | 1206 ± 16 | 14.3 ± 0.7 | 1010 ± 46 | 14.6 ± 0.7 |
| 1 | 1212 ± 26 | 13.1 ± 0.7 | 1043 ± 27 | 11.9 ± 0.6 |
| 2 | 1224 ± 16 | 9.4 ± 0.5 | 1109 ± 30 | 9.0 ± 0.5 |
| 3 | 1237 ± 20 | 9.4 ± 0.5 | 1152 ± 38 | 9.0 ± 0.5 |
| 4 | 1242 ± 15 | 9.4 ± 0.5 | 1196 ± 28 | 7.5 ± 0.4 |
| 5 | 1252 ± 8 | 9.5 ± 0.5 | 1247 ± 70 | 7.9 ± 0.4 |
| 6 | 1245 ± 26 | 8.1 ± 0.4 | 1299 ± 40 | 7.3 ± 0.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Xu, W.; Wang, B.; Yang, G.; Shan, D. Effect of Multi-Pass Power Spinning on Microstructure Homogenization and Mechanical-Property Strengthening of Ti2AlNb-Based Alloy Using Welded Tube Blank. Materials 2022, 15, 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031013
Wang S, Xu W, Wang B, Yang G, Shan D. Effect of Multi-Pass Power Spinning on Microstructure Homogenization and Mechanical-Property Strengthening of Ti2AlNb-Based Alloy Using Welded Tube Blank. Materials. 2022; 15(3):1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031013
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Sibing, Wenchen Xu, Bo Wang, Guoping Yang, and Debin Shan. 2022. "Effect of Multi-Pass Power Spinning on Microstructure Homogenization and Mechanical-Property Strengthening of Ti2AlNb-Based Alloy Using Welded Tube Blank" Materials 15, no. 3: 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031013
APA StyleWang, S., Xu, W., Wang, B., Yang, G., & Shan, D. (2022). Effect of Multi-Pass Power Spinning on Microstructure Homogenization and Mechanical-Property Strengthening of Ti2AlNb-Based Alloy Using Welded Tube Blank. Materials, 15(3), 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031013







