Refinement of the Magnesium–Aluminium Alloy Microstructure with Zirconium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
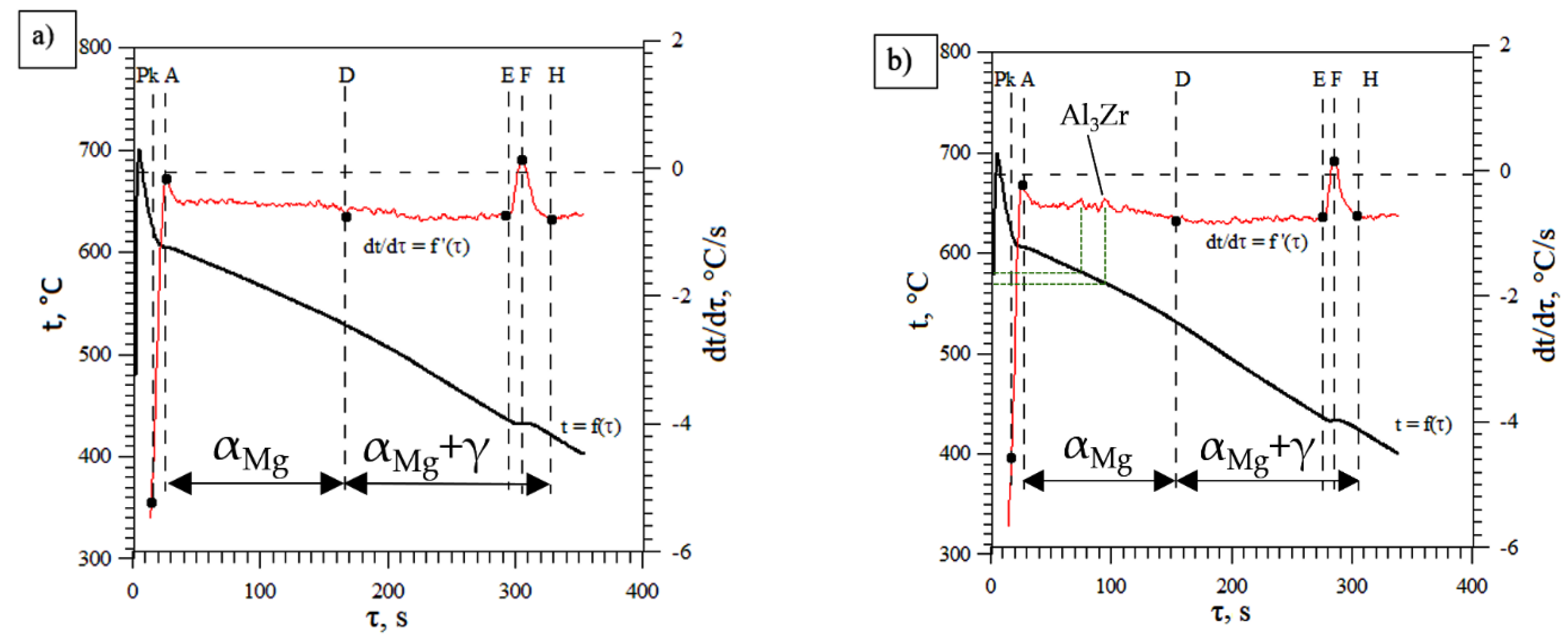
- the phase αMg: Δτα = τD − τpk,
- the eutectic αMg + γ(Mg17Al12): Δτγ = τH − τD.
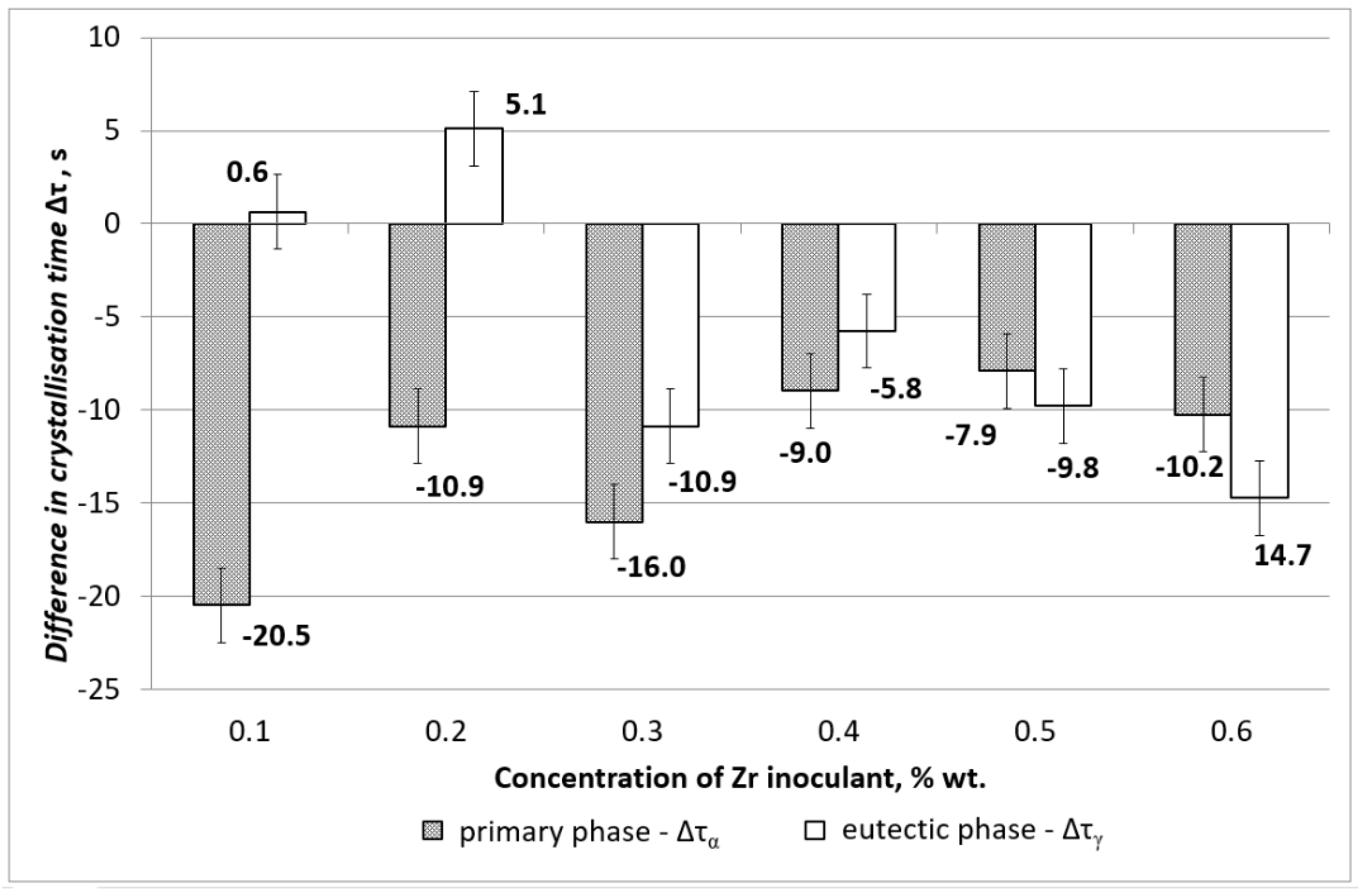
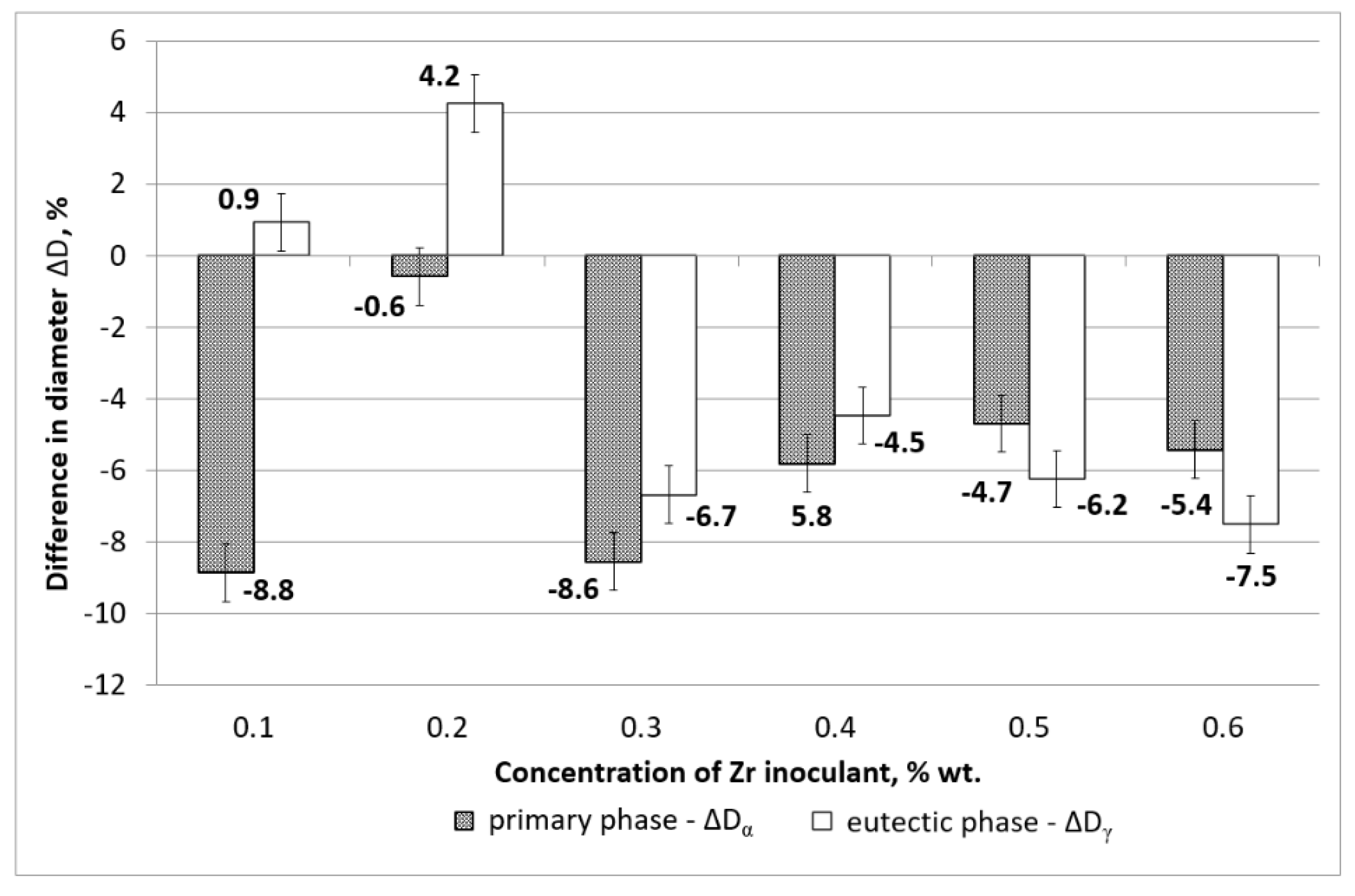
- a difference in solidification times of the primary phase αMg: ΔτDα= ΔταAZ91 − ΔταAZ91inX,
- a difference in solidification times of the eutectic phase αMg + γ(Mg17Al12):
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Derivative and Thermal Analysis of Crystallisation Process Dynamics
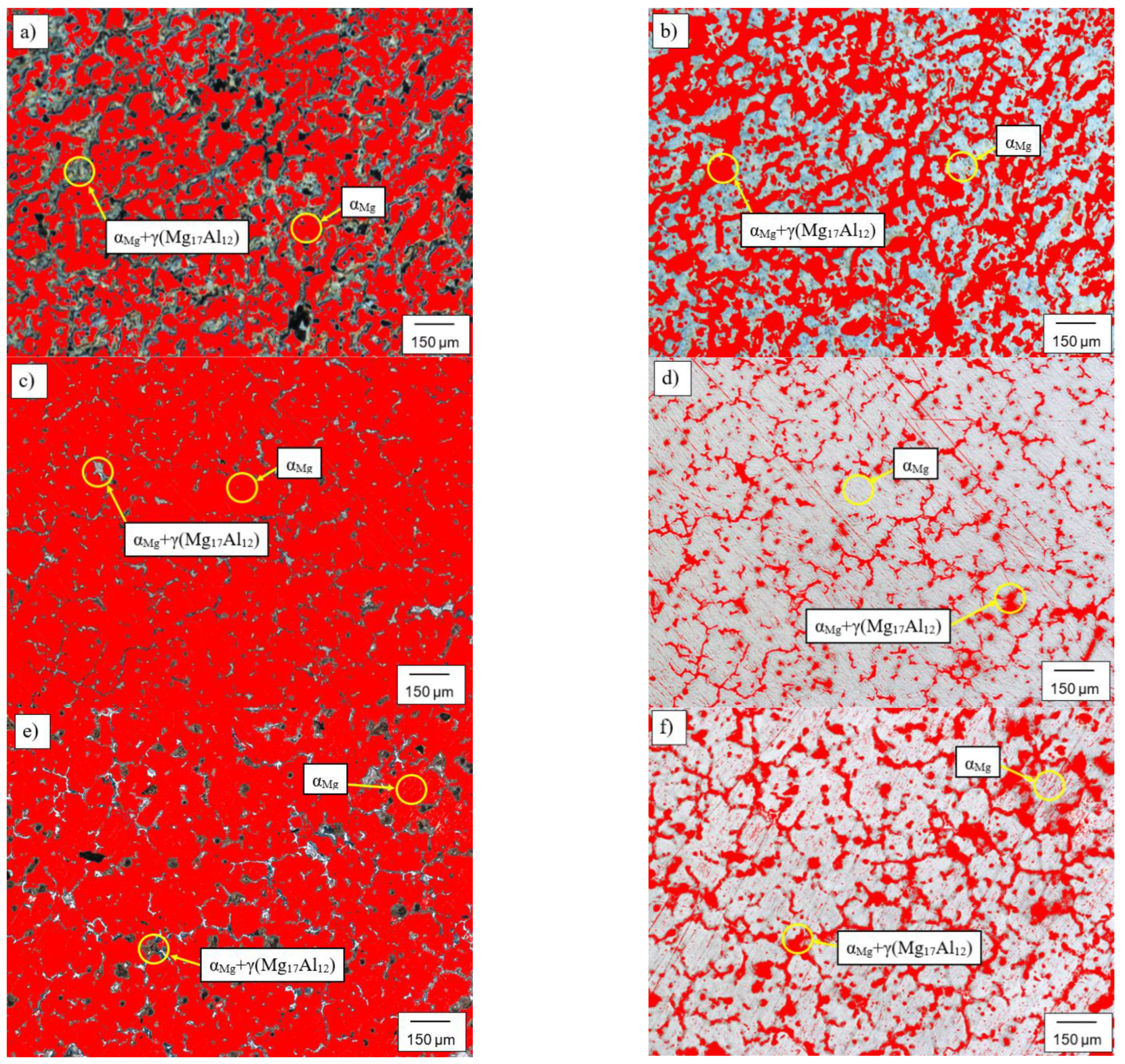
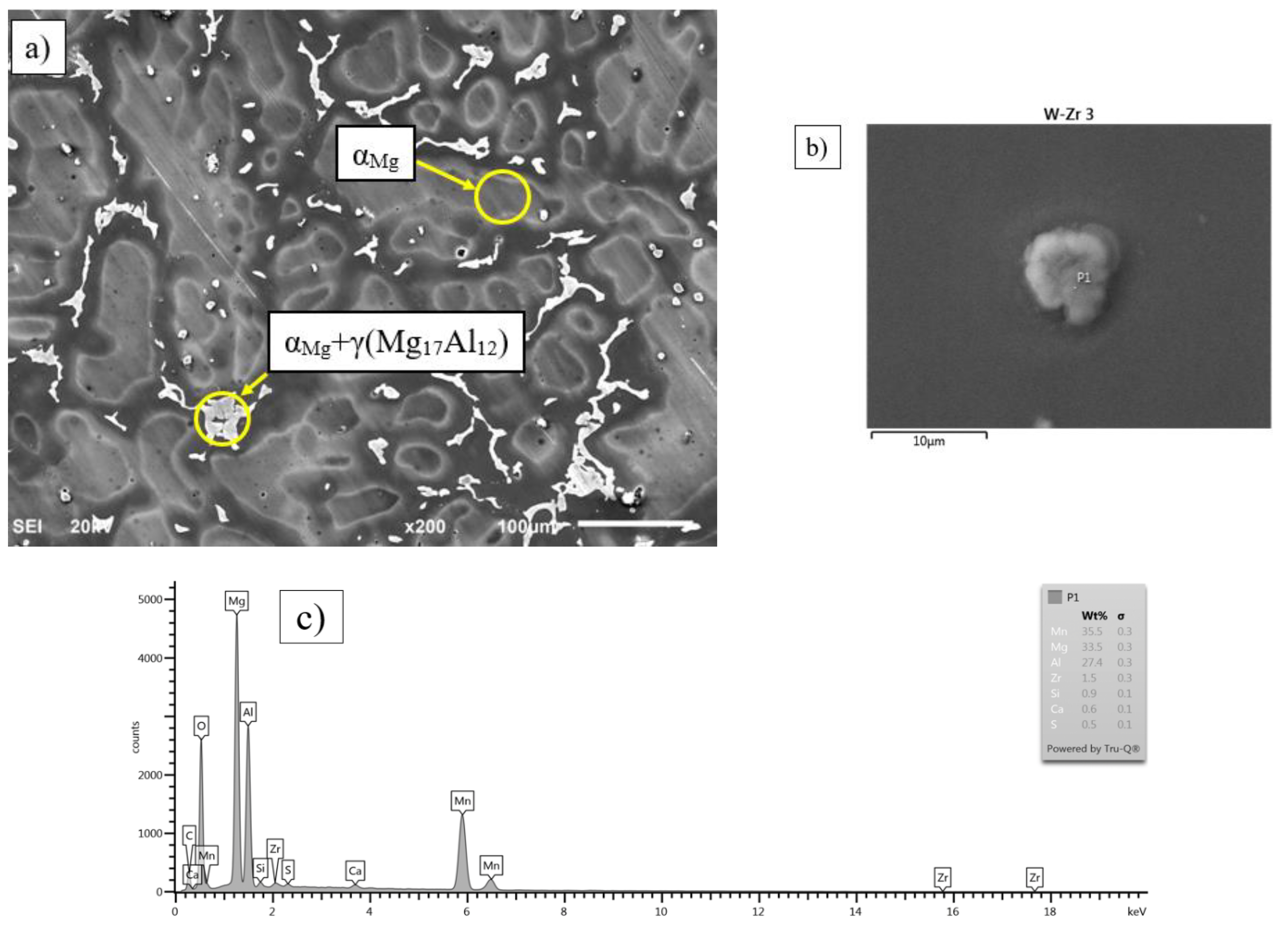
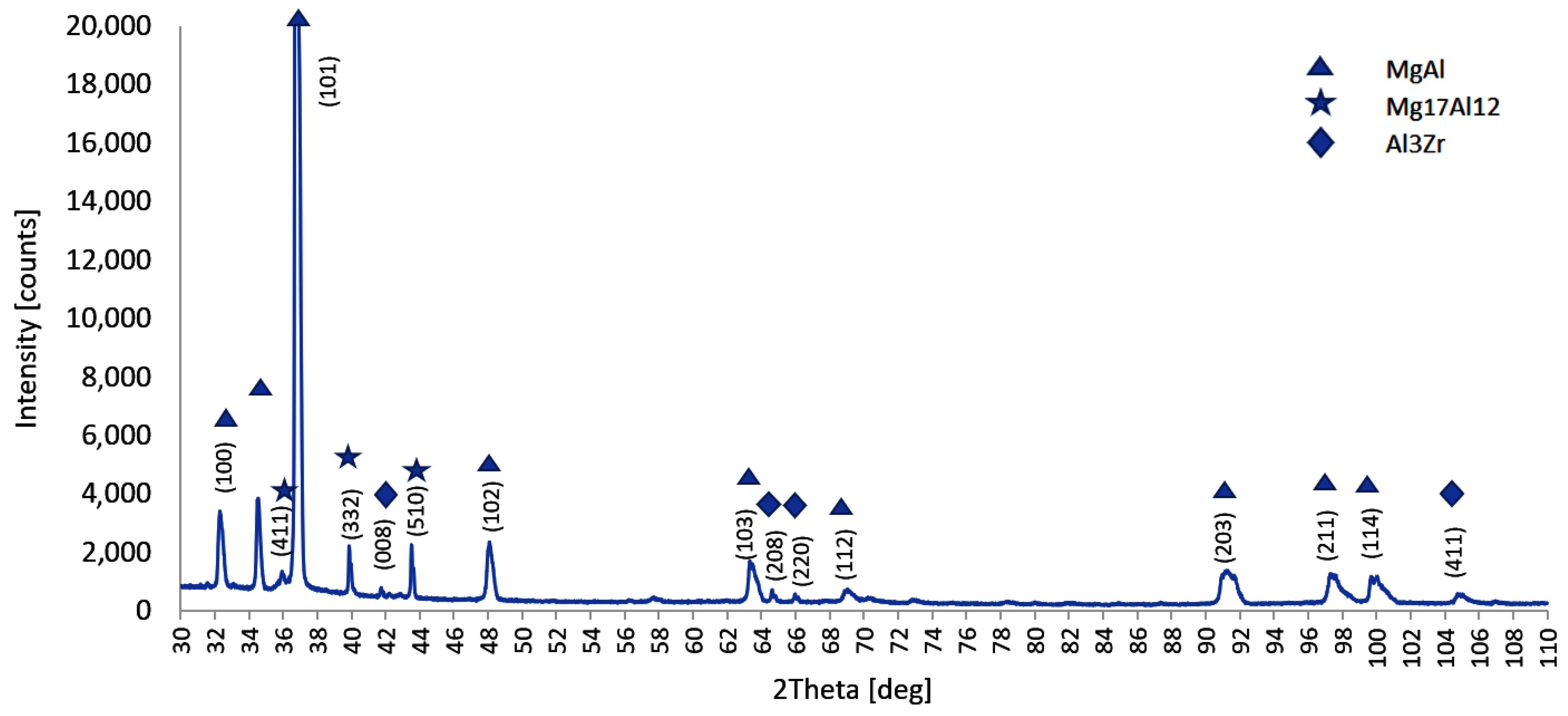
3.2. Microstructure Analysis
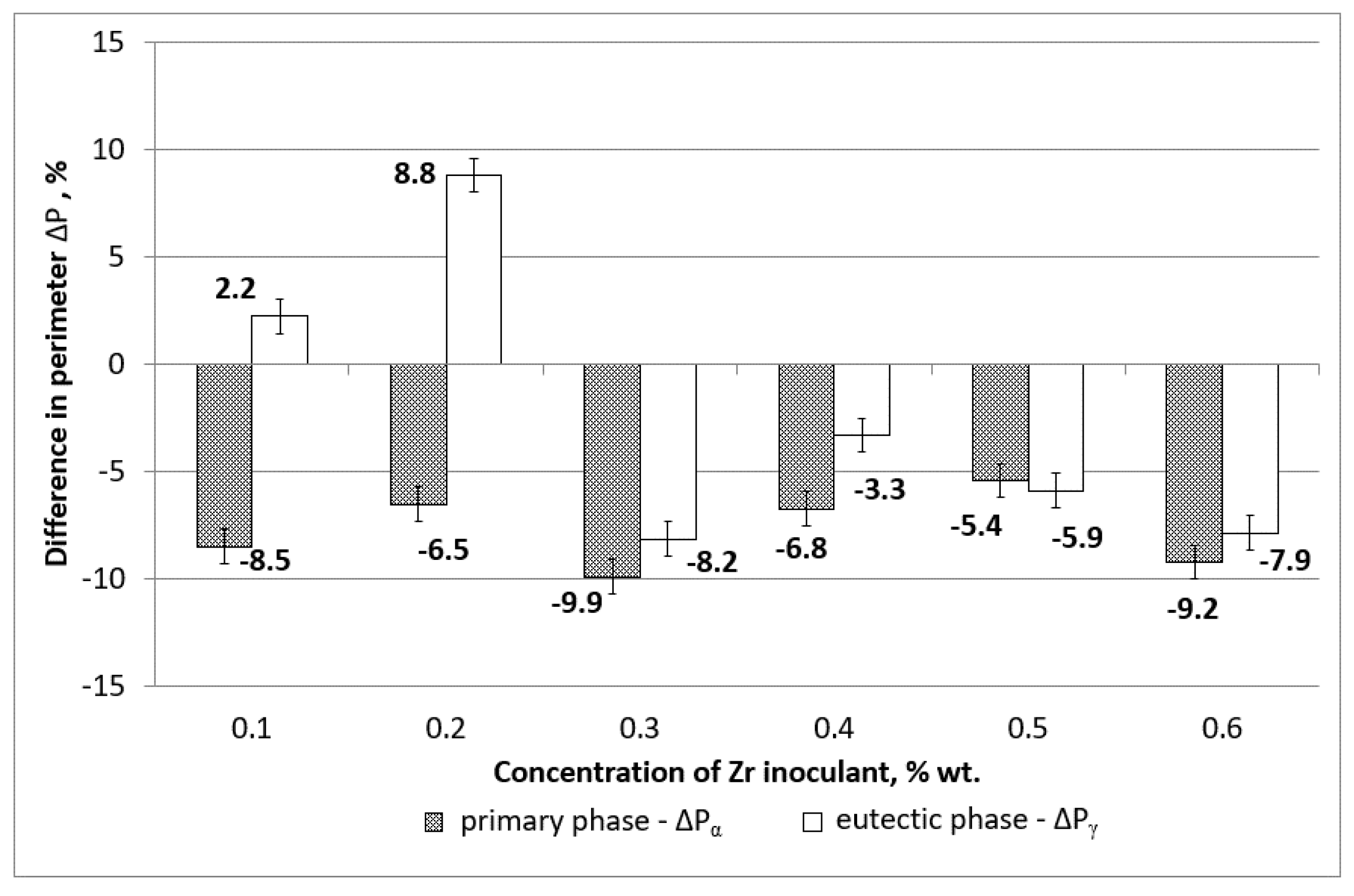
3.3. Image Analysis
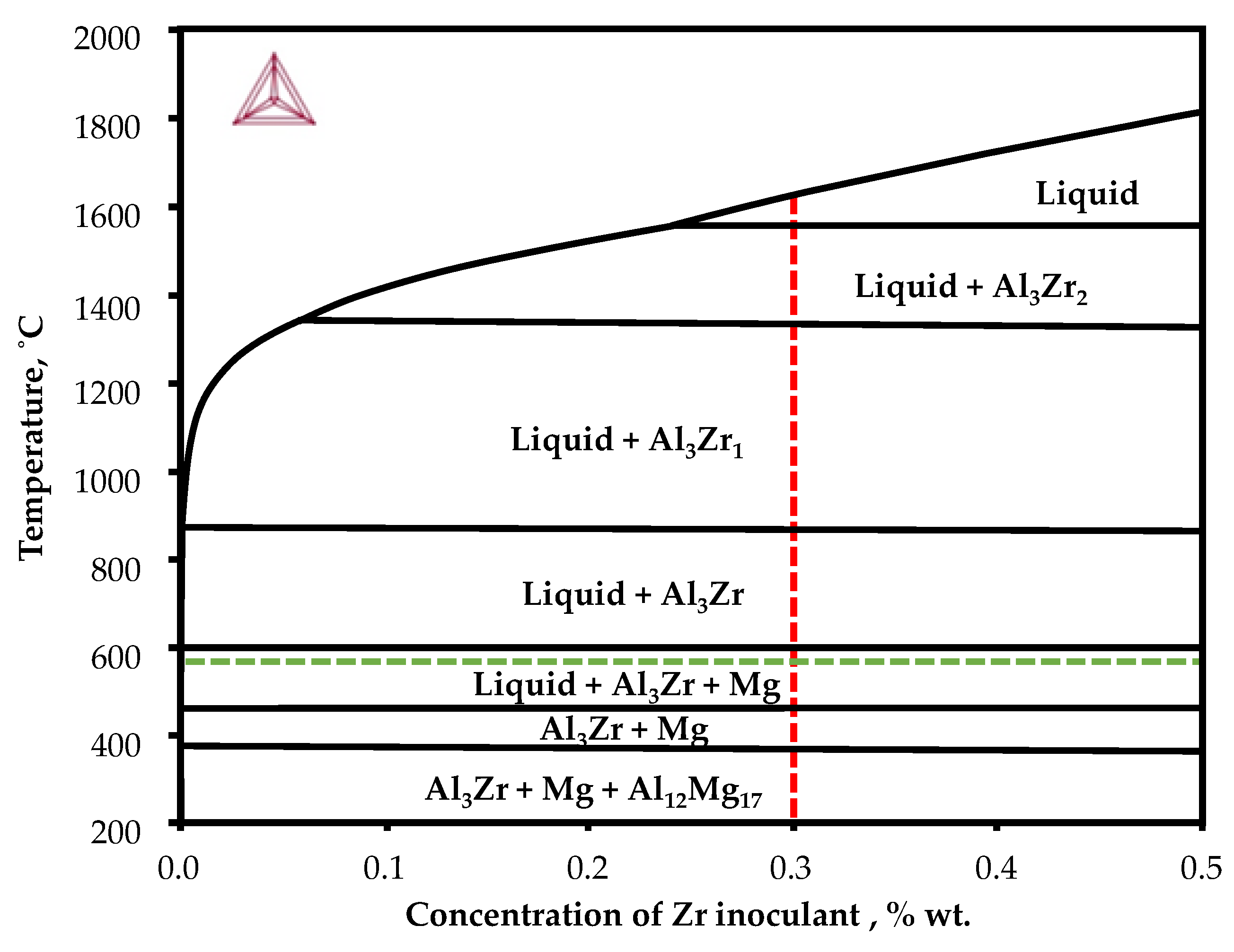
3.4. Equilibrium Phase Diagram Analysis
4. Summary
5. Conclusions
- There is a change in the solidification mechanism at 0.3 wt % of Zn, with larger grains formed at lower concentrations and smaller grains formed at 0.3 wt % of Zn and above,
- Crystallisation time is shorter when grains are refined at the zirconium concentration above 0.3 wt %,
- Larger concentration of zirconium inoculant above 0.3 wt % are not beneficial,
- In early stages of primary magnesium phase solidification, additional peaks have been found on the temperature derivative curve (Figure 1), indicating the formation of additional intermetallic Al3Zr phases, which were directly detected in the bulk material.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fico, D.; Rizzo, D.; De Carolis, V.; Montagna, F.; Corcione, C.E. Sustainable Polymer Composites Manufacturing through 3D Printing Technologies by Using Recycled Polymer and Filler. Polymers 2022, 14, 3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Hu, S.; Wang, T.; Xie, W.; Guo, T.; Li, F.; Luo, R. Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of 7075 Aluminium Alloy during Semi-Solid Compression Deformation. Crystals 2022, 12, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, W.; Kubiak, K.J.; Wendler, B.G.; Mathia, T.G. Wear resistant multilayer nanocomposite WC 1 − x/C coating on Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy. Tribol. Int. 2015, 82, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, Z.; Ma, Y.; Hao, Y. Effects of samarium addition on as-cast microstructure, grain refinement and mechanical properties of Mg-6Zn-0.4Zr magnesium alloy. J. Rare Earths 2017, 35, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; You, G.; Bai, S.; Guo, W. Effects of heat treatment on the thermal properties of AZ91D magnesium alloys in different casting processes. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 766, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzychoń, T. The Sand-Cast Mg-Al-Ca-Sr Alloys: The Structure Properties and Strengthening Mechanisms, 1st ed.; Silesian University of Technology: Gliwice, Poland, 2018; pp. 15–25. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Mordike, B.L.; Ebert, T. Magnesium: Properties—applications—potential. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 302, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapiejko, C.; Pisarek, B.; Pacyniak, T. Effect of Intensive Cooling of Alloy AZ91 with a Chromium Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Casting. Arch. Met. Mater. 2017, 62, 2199–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapiejko, C.; Pisarek, B.; Czekaj, E.; Pacyniak, T. Analysis of AM60 and AZ91 Alloy Crystallisation in ceramic moulds by thermal derivative analysis (TDA). Arch. Met. Mater. 2014, 59, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Yang, M.; Tang, H.; Pan, F. Effect of minor Sc on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ91 Magnesium Alloy. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2018, 28, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.-F.; Ma, Y.; Chen, T.-J.; Li, Y.-D.; Hao, Y. Effects of Cu addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of as-cast Mg-6Zn magnesium alloy. China Foundry 2017, 14, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhingole, P.; Chaudhari, G. Synergy of nano carbon black inoculation and high intensity ultrasonic processing in cast magnesium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 556, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolibruchová, D.; Kuriš, M.; Matejka, M.; Kasińska, J. Study of the Influence of Zirconium, Titanium and Strontium on the Properties and Microstructure of AlSi7Mg0.3Cu0.5 Alloy. Materials 2022, 15, 3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cug, H.; Ahlatci, H. Effect of Zn and Mn Additions on the Wear Resistance of Cast Alloy Mg–5% Al–1% Si. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2017, 59, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo-dong, T.; Hai-feng, L.; Yao-hui, L. Effect of rare earth additions on microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ91 magnesium alloys. T Nonferr. Metal. Soc. China 2010, 20, 336–340. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Lei, J. Effect of mischmetal on mechanical properties and microstructure of die-cast magnesium alloy AZ91D. J. Rare Earths 2016, 34, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Hao, H. Effect of calcium addition on microstructure, casting fluidity and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-Ce-Zr magnesium alloy. J. Rare Earths 2017, 35, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-S.; Zhang, Z.-G.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Li, S.-H.; Liu, Y.-L. Effect of Sb on microstructure and mechanical properties in Mg-10Zn-5Al high zinc magnesium alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Chiu, Y.L.; Jones, I. Characterisation of nano-sized Al–Mn–(Mg) particles in AZ91 and their effect on Mg17Al12 precipitation. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 579, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnesium Alloys Encyclopaedia, Metallurgy of Magnesium Alloy. Available online: http://www.magnesium.com/w3/data-bank/article.php?mgw=7&magnesium=183 (accessed on 27 July 2021).
- Qian, M.; Stjohn, D.H.; Frost, M.T. Effect of soluble and insoluble zirconium on the grain refinement of magnesium alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2003, 419-4, 593–598. [Google Scholar]
- Vinotha, D.; Raghukandan, K.; Pillai, U.T.S.; Pai, B.C. Grain refining mechanisms in magnesium alloys—An overview. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2009, 62, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, H.; Amiryavari, P. The effects of zirconium and beryllium on microstructure evolution, mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of as-cast AZ63 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 654, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltygin, A.V.; Bazhenov, V.E.; Nikitina, A.A. Effect of Neodymium and Zirconium on the Structure of Castable Magnesium Alloy ML10 (NZ30K). Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2017, 59, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltygin, A.V.; Belov, V.D.; Bazhenov, V.E. Effect of the specific features of solidification of an ML10 magnesium alloy on the zirconium segregation during melting. Russ. Met. 2013, 2013, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Das, A. Grain refinement of magnesium alloys by zirconium: Formation of equiaxed grains. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, J.; Paa-Rai, C. The interaction of grain refinement and ageing in magnesium–zinc–zirconium (ZK) alloys. Acta Mater. 2015, 95, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polish Committee for Standarization. PN-EN 1753:2001; Standard, Magnesium and Magnesium Alloys. Magnesium Alloy Ingots and Coastings. The Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2001.
- Pietrowski, S.; Rapiejko, C. Temperature and microstructure characteristics of silumin casting AlSi9 made with investment casting method. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2011, 11, 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- StJohn, D.H.; Qian, M.; Easton, M.A.; Cao, P.; Hildebrand, Z. Grain Refinement of Magnesium Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; StJohn, D.H.; Frost, M.T. Magnesium Alloys and Their Applications; Kainer, K.U., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Wolfsburg, Germany, 2003; pp. 706–712. [Google Scholar]

| Chemical Composition, wt % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | Al | Zn | Mn | Fe | Si |
| 90.08 | 8.47 | 0.52 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Sample | Zirconium Inoculant Content, wt % |
|---|---|
| Baseline | 0.0 |
| 1 | 0.1 |
| 2 | 0.2 |
| 3 | 0.3 |
| 4 | 0.4 |
| 5 | 0.5 |
| 6 | 0.6 |
| Point | τ, s | t, °C | dt/dτ, °C/s | Crystallising Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pk | 14.7 | 631.3 | −5.2332 | αMg |
| A | 26.2 | 604.4 | −0.1646 | |
| D | 167.7 | 527.8 | −0.7499 | |
| E | 293.1 | 436.6 | −0.7371 | αMg + γ(Mg17Al12) |
| F | 305.3 | 432.1 | 0.1340 | |
| H | 329.0 | 420.2 | −0.8102 |
| Point | τ, s | t, °C | dt/dτ, °C/s | Crystallising Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pk | 17.3 | 622.8 | −4.5792 | αMg |
| A | 26.2 | 605.9 | −0.2219 | |
| D | 154.2 | 530.9 | −0.7911 | |
| E | 275.2 | 436.3 | −0.7298 | αMg + γ(Mg17Al12) |
| F | 284.8 | 432.8 | 0.1443 | |
| H | 304.6 | 424.6 | −0.7161 |
| Element | wt % | wt % Sigma | Atomic, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | 23.37 | 0.31 | 32.81 |
| Al | 30.06 | 0.36 | 38.03 |
| Si | 0.94 | 0.13 | 1.14 |
| Ca | 0.74 | 0.10 | 0.63 |
| Mn | 41.09 | 0.42 | 25.53 |
| Fe | 1.85 | 0.26 | 1.13 |
| Zr | 1.95 | 0.34 | 0.73 |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rapiejko, C.; Mikusek, D.; Januszewicz, B.; Kubiak, K.J.; Pacyniak, T. Refinement of the Magnesium–Aluminium Alloy Microstructure with Zirconium. Materials 2022, 15, 8982. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248982
Rapiejko C, Mikusek D, Januszewicz B, Kubiak KJ, Pacyniak T. Refinement of the Magnesium–Aluminium Alloy Microstructure with Zirconium. Materials. 2022; 15(24):8982. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248982
Chicago/Turabian StyleRapiejko, Cezary, Dominik Mikusek, Bartłomiej Januszewicz, Krzysztof J. Kubiak, and Tadeusz Pacyniak. 2022. "Refinement of the Magnesium–Aluminium Alloy Microstructure with Zirconium" Materials 15, no. 24: 8982. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248982
APA StyleRapiejko, C., Mikusek, D., Januszewicz, B., Kubiak, K. J., & Pacyniak, T. (2022). Refinement of the Magnesium–Aluminium Alloy Microstructure with Zirconium. Materials, 15(24), 8982. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248982









