Influence of the Sintering Method on the Properties of a Multiferroic Ceramic Composite Based on PZT-Type Ferroelectric Material and Ni-Zn Ferrite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Research Material
2.1.1. Spark Plasma Sintering Method
2.1.2. Hot Pressing Method
2.1.3. Free Sintering Method
2.2. Investigations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Properties of the PZT-Type Material
3.2. Structure Tests of Composite Samples
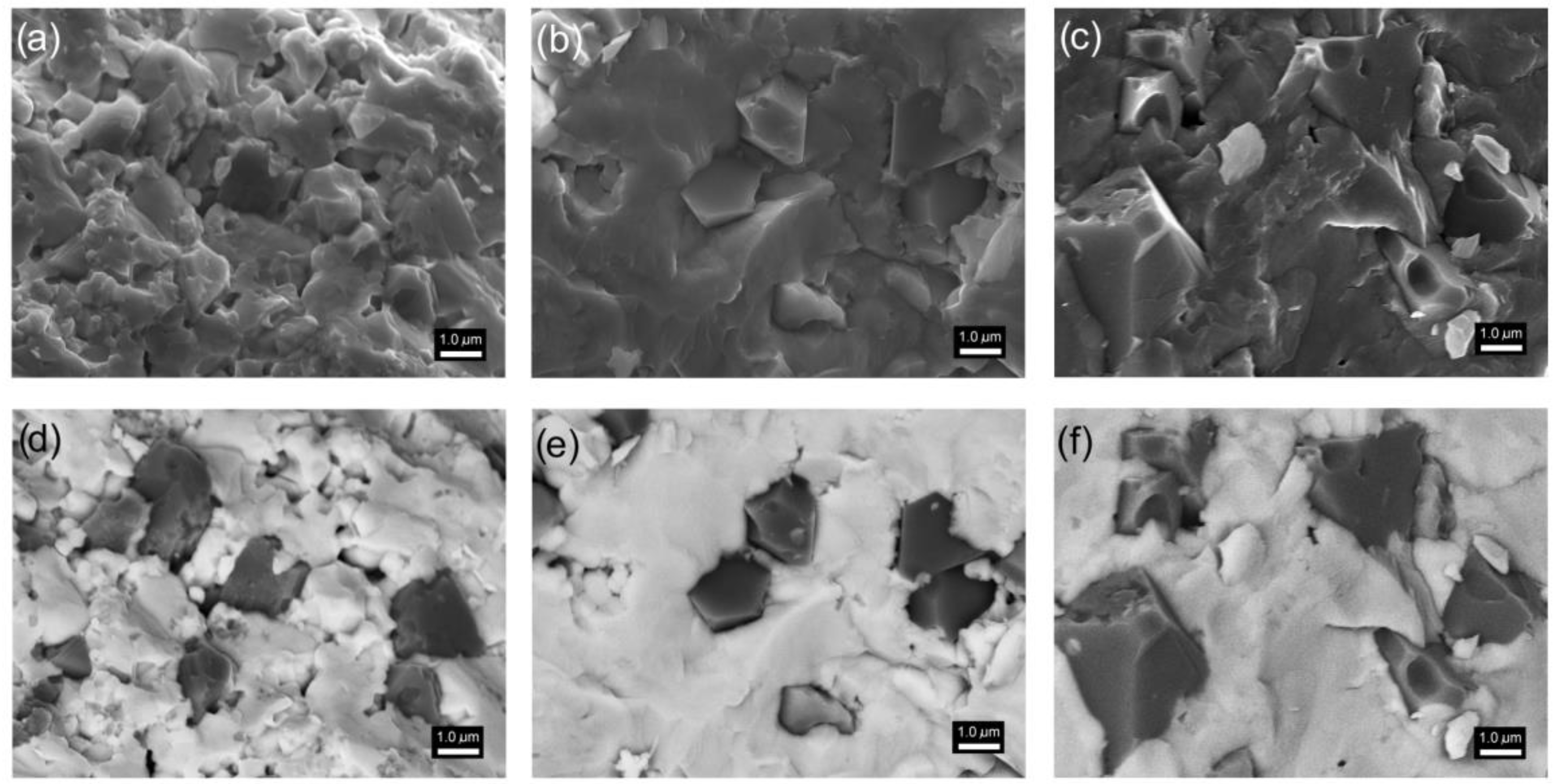
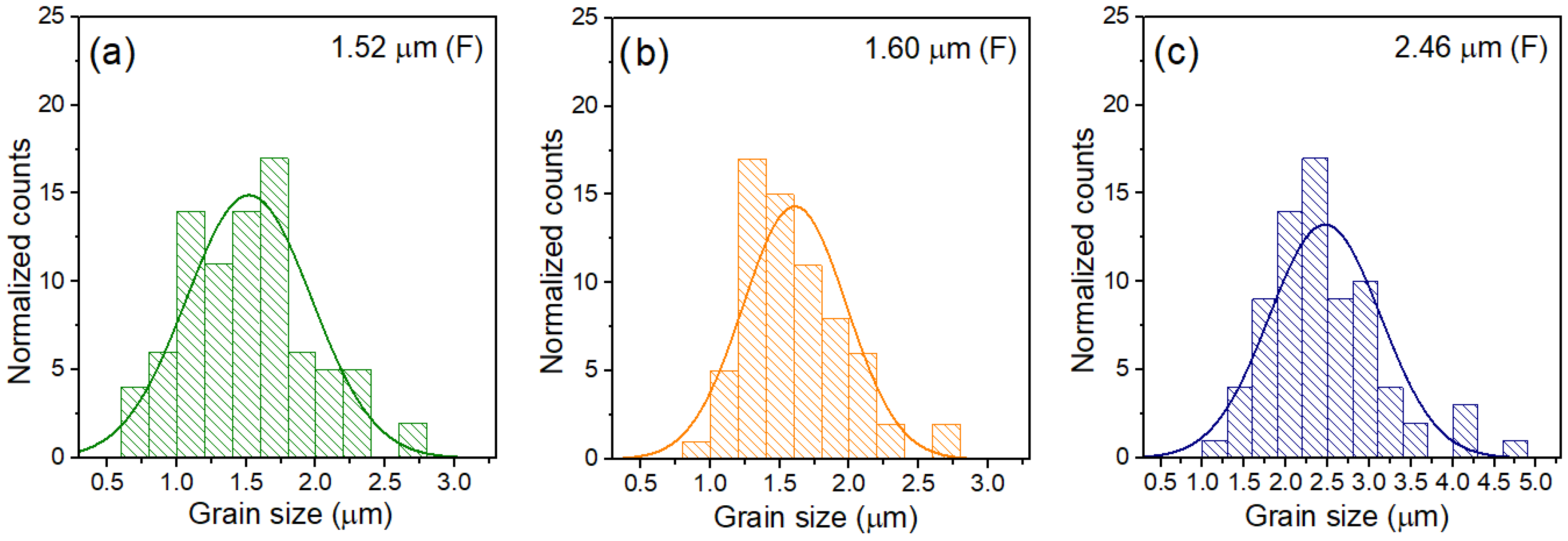
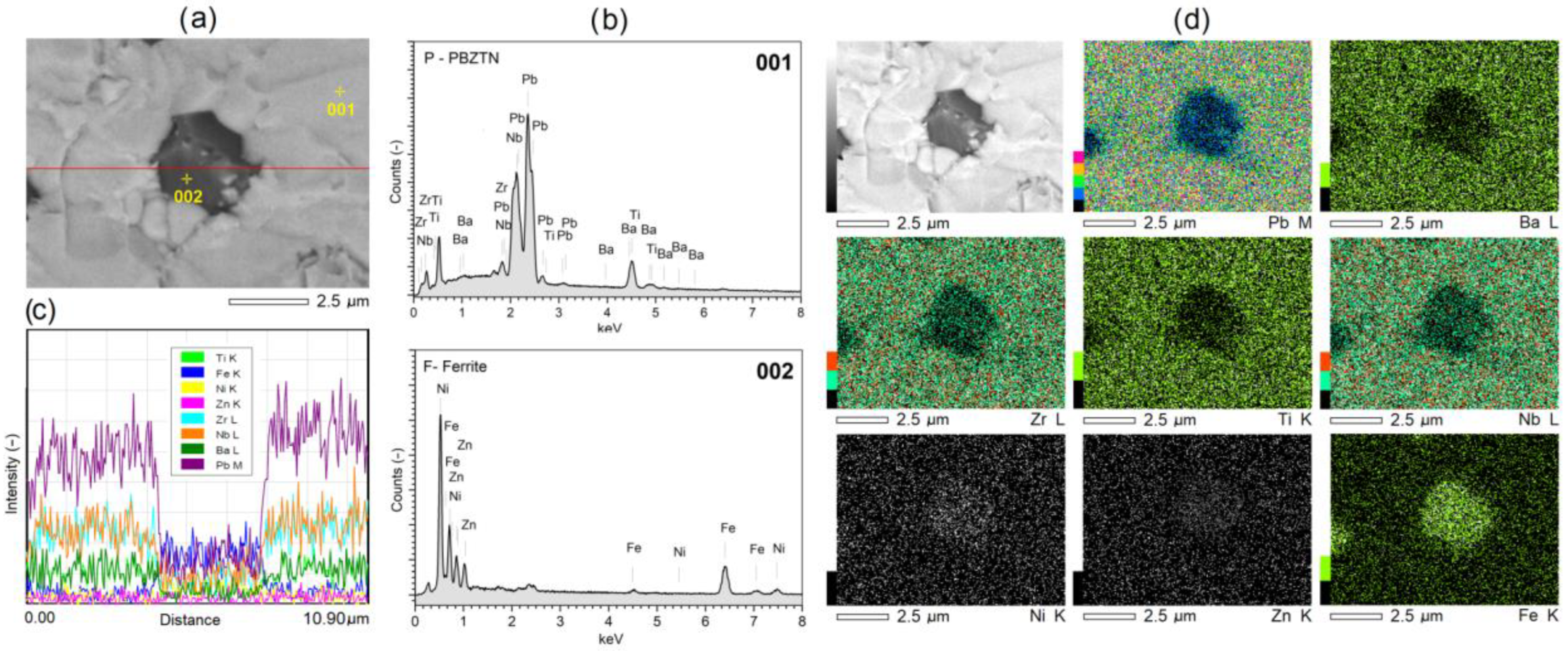
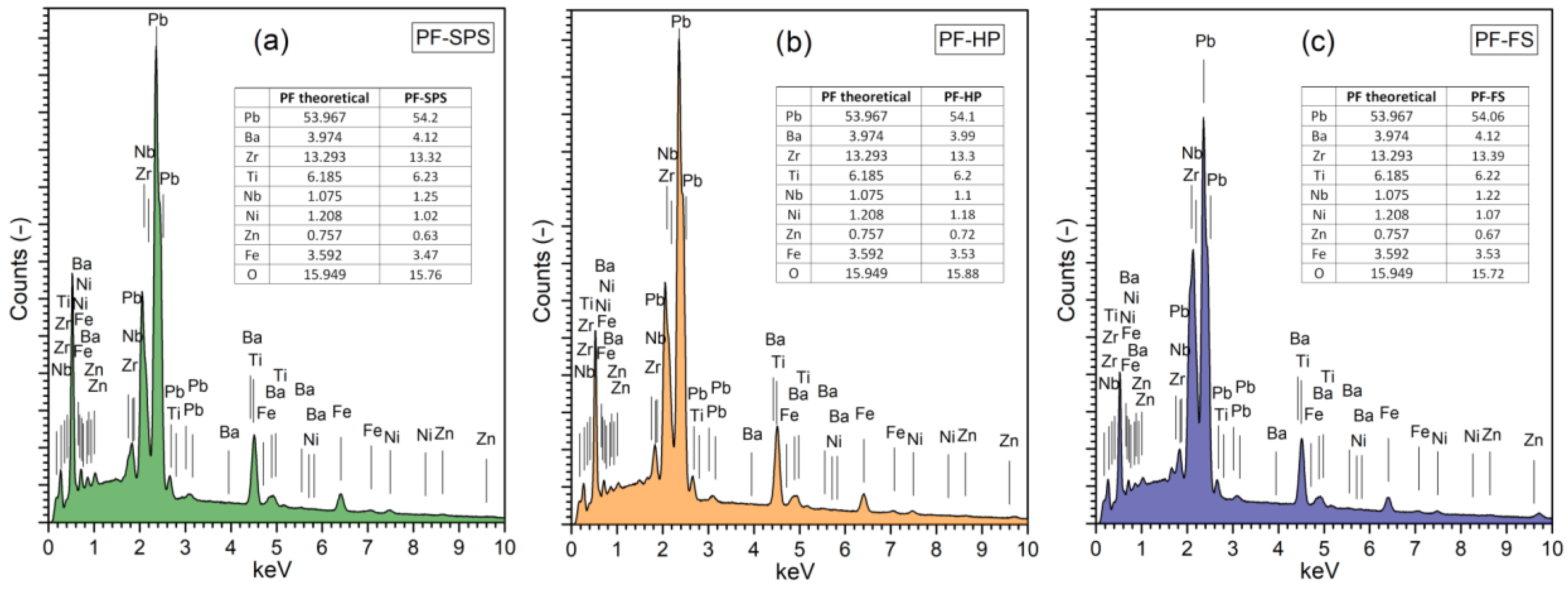
3.3. Microstructure Measurements of Composite Samples
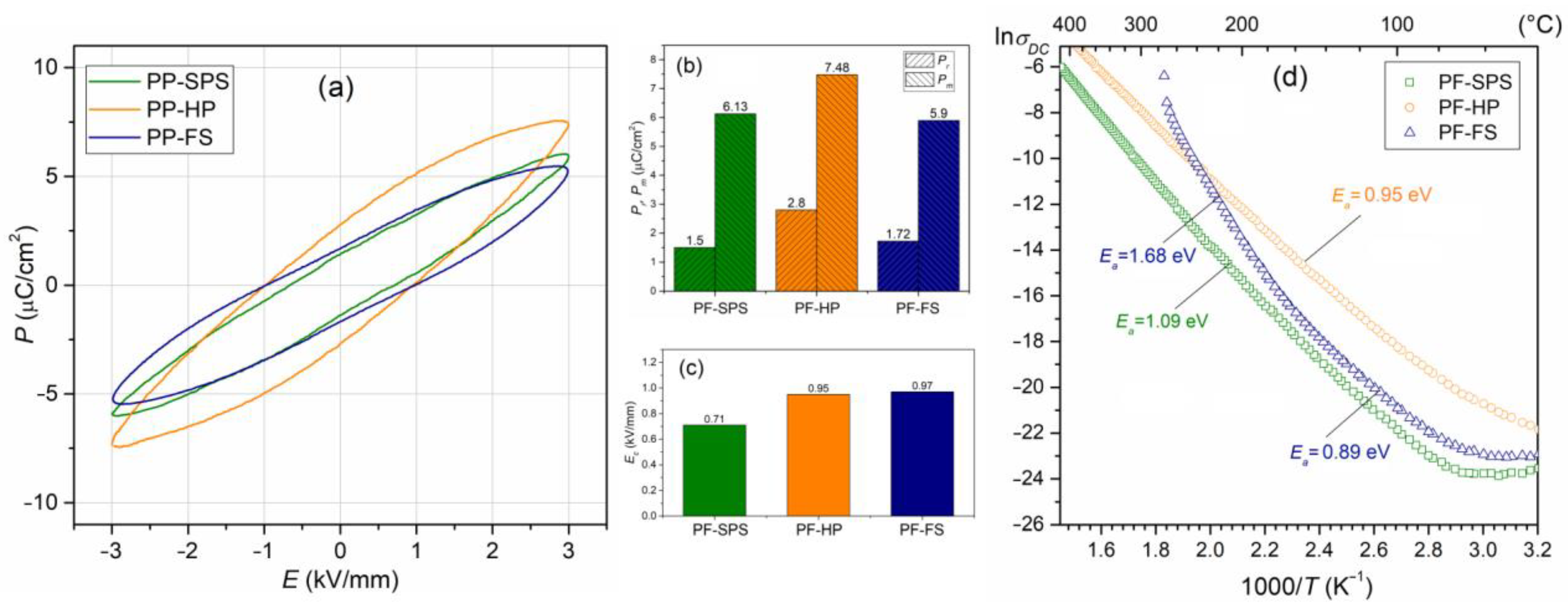
3.4. Ferroelectric Properties and Electric Conductivity of Composite Samples
3.5. Dielectric Properties of Composite Samples
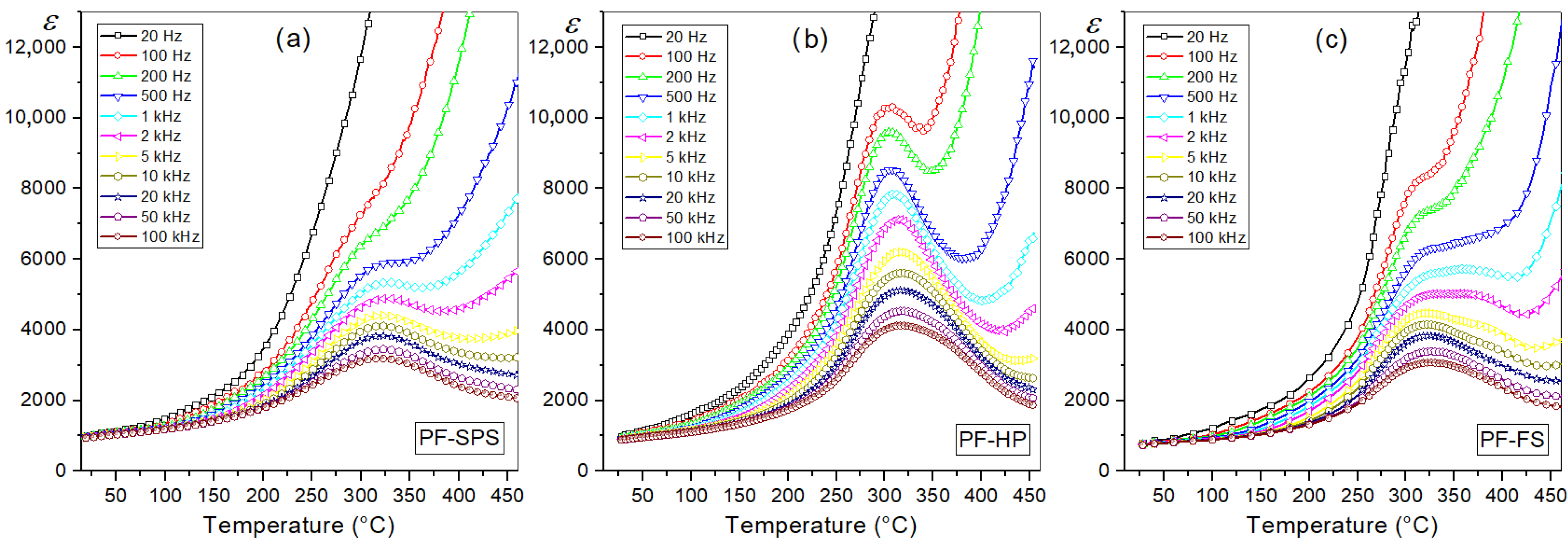
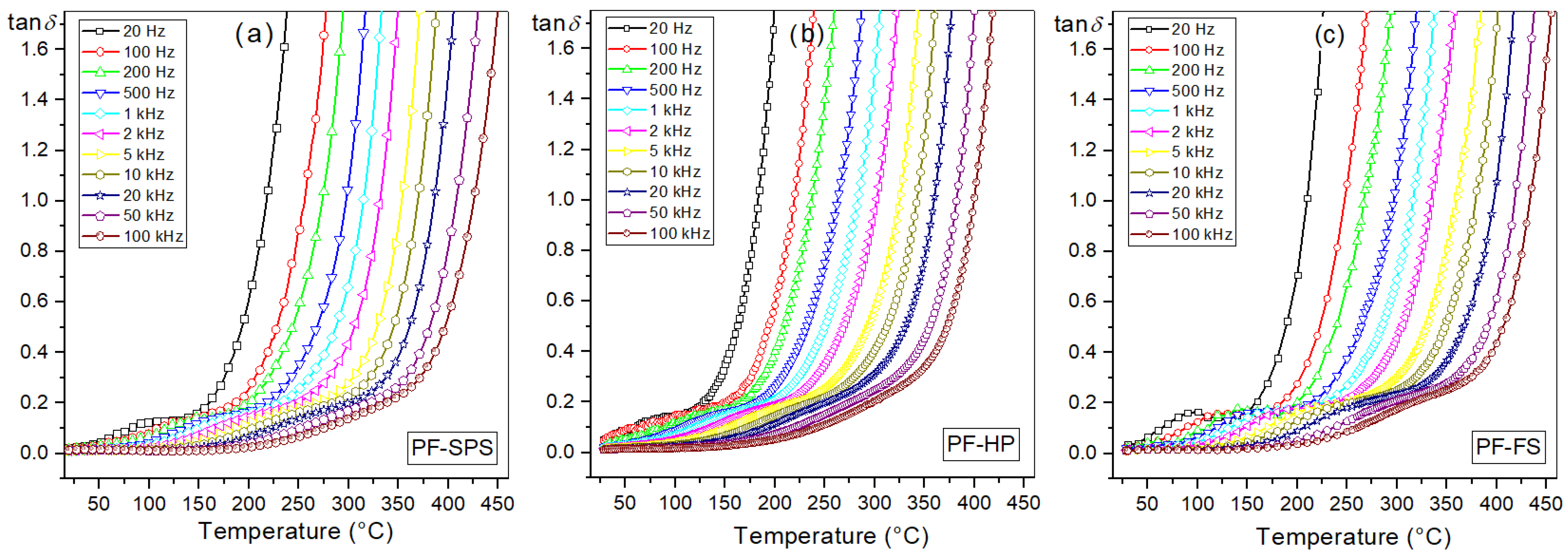
3.5.1. Temperature Dependence of Dielectric Properties
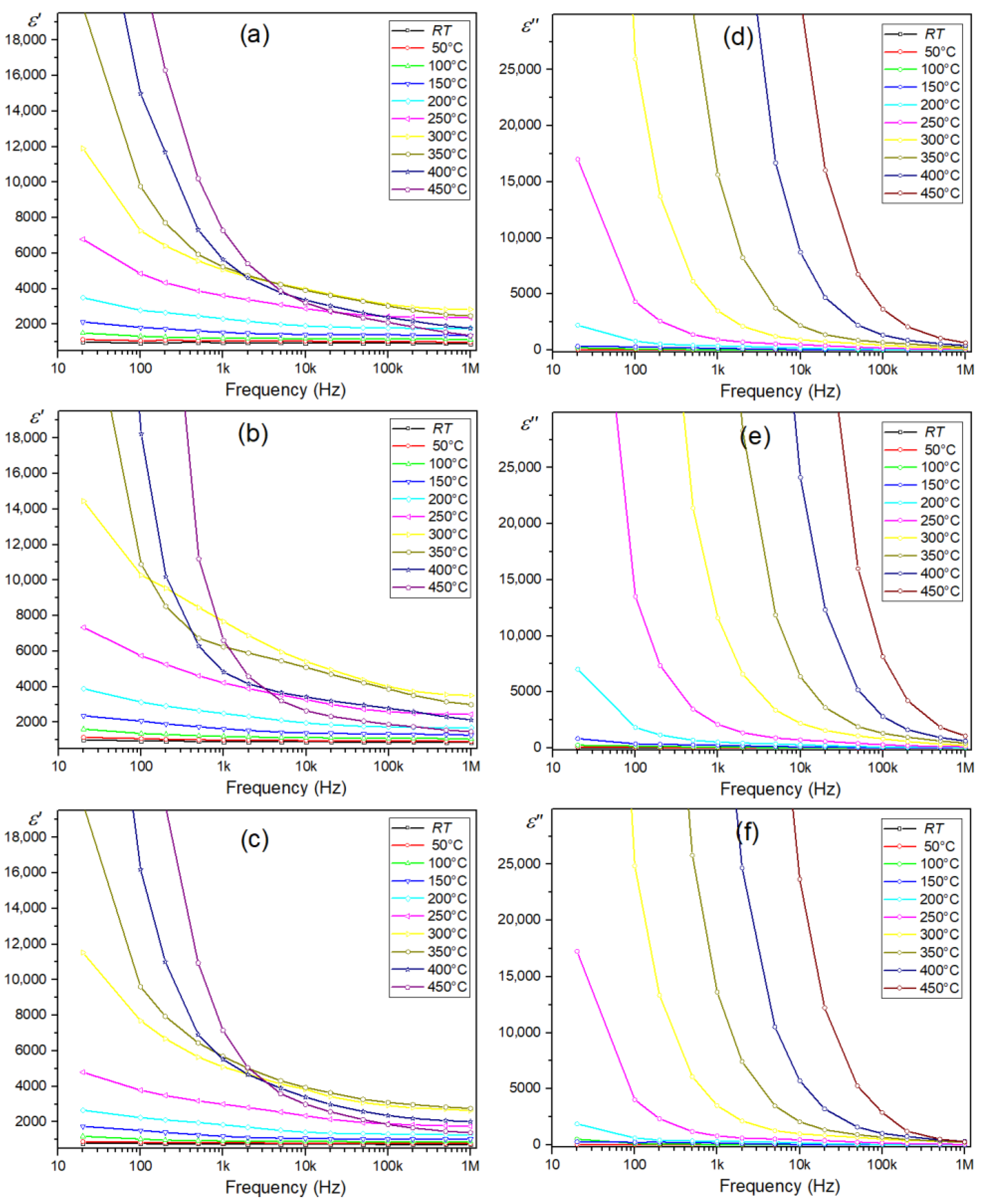
3.5.2. Frequency Dependence of Dielectric Properties
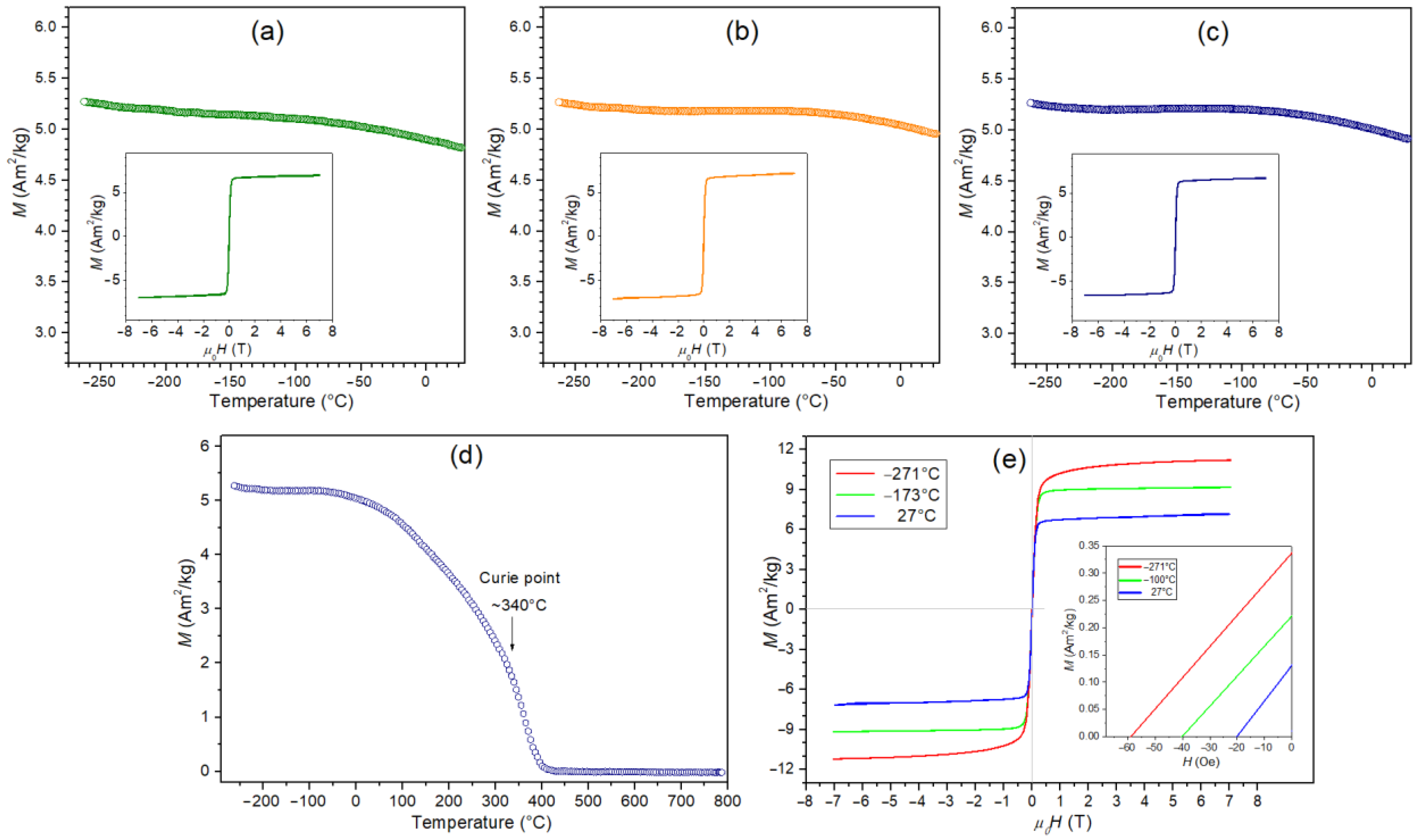
3.6. Magnetic Properties of Composite Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spaldin, N.A.; Cheong, S.-W.; Ramesh, R. Multiferroics: Past, present, and future. Phys. Today 2010, 63, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiebig, M.; Lottermoser, T.; Meier, D.; Trassin, M. The evolution of multiferroics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eerenstein, W.; Mathur, N.D.; Scott, J.F. Multiferroic and magnetoelectric materials. Nature 2006, 442, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, B.; Cook, W.R.; Jaffe, H. Piezoelectric Ceramics; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Necira, Z.; Boutarfaia, A.; Abba, M.; Abdessalem, N. Synthesis of PZT powder by conventional method at various conditions. EPJ Web Conf. 2012, 29, 00038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvecký, Ĺ.; Kmecová, M.; Saksl, K. Study of PbZr0.53Ti0.47O3 solid solution formation by interaction of perovskite phases. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 27, 2031–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpierz, M.; Suchanicz, J.; Konieczny, K.; Śmiga, W.; Czaja, P.; Sokołowski, M. Effects of PbTiO3 doping on electric properties of Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3 ceramics. Phase Transit. 2017, 90, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, M.; Kozielski, L.; Pilch, M.; Pawełczyk, M.; Soszyński, A. Influence of vanadium dopant on relaxor behavior of BaBi2Nb2O9 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 4589–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapuzha, A.S.; James, N.K.; Khanbareh, H.; van der Zwaag, S.; Groen, W.A. Structure, dielectric and piezoelectric properties of donor doped PZT ceramics across the phase diagram. Ferroelectrics 2016, 504, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, D.; Niemiec, P.; Chrobak, A.; Ziółkowski, G.; Błachowski, A. Magnetic and electric properties of the lead free ceramic composite based on the BFN and ferrite powders. Mater. Charact. 2014, 87, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipti, D.; Juneja, J.K.; Singh, S.; Raina, K.K.; Prakash, C. Enhancement in magnetoelectric coupling in PZT based composites. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 6108–6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchanicz, J.; Kluczewska, K.; Czaja, P.; Handke, B.; Sokolowski, M.; Węgrzyn, A.; Stachowski, G. Influence of sintering conditions on structural, thermal, electric and ferroelectric properties of Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3 ceramics. Phase Transit. 2018, 91, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, D.; Skulski, R.; Wawrzała, P.; Brzezińska, D. Dielectric properties of Pb0.75Ba0.25(Zr0.65Ti0.35)1-zSnzO3 ceramics. Ferroelectrics 2011, 418, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.I.; Huang, J.L.; Lin, H.P.; Wang, S.C.; Lu, H.H.; Wu, L.; Lin, J.F. Effect of drying temperature on structure, phase transformation of sol-gel derived lead zirconate titanate powders. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 414, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.P.; Camargo, E.R.; Fabbro, M.T.; Longo, E.; Leite, E.R. Wet-chemical synthesis of magnesium niobate nanoparticles powders. Ceram. Int. 2007, 33, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordan, A.R.; Airimioaiei, M.; Palamaru, M.N.; Glaassi, C.; Sandu, A.V.; Ciomaga, C.E.; Prihor, F.; Mitoseriu, L.; Lanculescu, A. Insitupreparation of CoFe2O4-Pb(ZrTi)O3 multiferroic composites by gel-combustion technique. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 29, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Hng, H.H. Ferroelectric lead scandium tantalate from mechanical activation of mixed oxides. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2002, 75, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branković, Z.; Branković, G.; Jovalekić, Č.; Maniette, Y.; Cilense, M. Mechanochemical synthesis of PZT powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 345, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.M.; Mahfoz Kotb, H. Giant dielectric properties of fine-grained Na1/2Y1/2Cu3Ti4O12 ceramics prepared by mechanosynthesis and spark plasma sintering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 8939–8948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, D.; Bartkowska, J.A.; Kozielski, L.; Szafraniak-Wiza, I. Mechanochemical activation and spark plasma sintering of the lead-free Ba(Fe1/2Nb1/2)O3 ceramics. Materials 2021, 14, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvashenkina, O.E.; Gabdullin, P.G.; Osipov, V.S. Using the novel capable of SHS-reaction multilayer nanostructured material for soldering of lead-zirconate-titanate piezoceramic elements. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1236, 012023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkovsky, I.; Morozov, Y.; Kuznetsov, M. Layering fabrication, structure, and electromagnetic properties of perovskite phases by hybrid process: Self-propagated high-temperature synthesis and selective laser sintering. Phase Transit. 2013, 86, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, M.V.; Kiran, S.R.; Reddy, N.R.; Kumar, K.S.; Murthy, V.R.; Murty, B.S. Investigation and characterization of Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 nanocrystalline ferroelectric ceramics: By conventional and microwave sintering methods. Mat. Chem. Phys. 2011, 126, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopatin, S.; Lopatina, I.; Lisnevskaya, I. Magnetoelectric PZT/ferrite composite material. Ferroelectrics 1994, 162, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fu, Z.; Wang, H.; Yuan, R. Influence of hot pressing sintering temperature and time on microstructure and mechanical properties of TiB2 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 22, 1045–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozielski, L.; Adamczyk, M.; Lisińska-Czekaj, A.; Orkisz, T.; Piechowiak, M.; Czekaj, D. Structure and dielectric properties of PZT-type ceramics with the diffuse phase transition. Phase Transit. 2006, 79, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.D.; Souza, F.L.; Longo, E.; Leite, E.R.; Camargo, E.R. Dielectric characterization of microwave sintered lead zirconate titanate ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 14423–14430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Sheu, C.I.; Lin, S.C.; Cheng, S.Y. Effects of microwave heating on dielectric and piezoelectric properties of PZT ceramic stapes. Ceram. Int. 2008, 34, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Cheng, X.-W.; Wang, F.-C.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Li, S.-L. A review of multi-physical fields induced phenomena and effects in spark plasma sintering: Fundamentals and applications. Mater. Des. 2020, 191, 108662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, B.; Enache, S.; Ghica, C.; Valeanu, M. Solid-state synthesis and spark plasma sintering of SrZrO3 ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 6395–6399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manière, C.; Riquet, G.; Marinel, S. Dielectric properties of flash spark plasma sintered BaTiO3 and CaCu3Ti4O12. Scr. Mater. 2019, 173, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, D. A combination of calcination and the spark plasma sintering method in multiferroic ceramic composite technology: Effects of process temperature and dwell time. Materials 2022, 15, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Wang, D.X.; Randall, C.A.; Trolier-McKinstry, S. Comparison of different sintering aids in cold sinter-assisted densification of lead zirconate titanate. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 104, 5479–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.P.; Chen, X.M.; Ouyang, W.Q.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Fang, J.L. Microstructure, dielectric, and energy storage properties of BaTiO3 ceramics prepared via cold sintering. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 4436–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, C.A.; Kim, N.; Kucera, J.-P.; Cao, W.; Shrout, T.R. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Size Effects in Fine-Grained Morphotropic-Phase-Boundary Lead Zirconate Titanate Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1998, 81, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surowiak, Z.; Gavrilyatchenko, S.V.; Skulski, R.; Kupriyanov, M.F.; Bochenek, D. Influence of the cyclic phase transistions on some properties of the ferroelectric perovskites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 22, 1863–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrib, L.M.; Caltun, O.F. Effects of the chemical composition of the magnetostrictive phase on the dielectric and magnetoelectric properties of cobalt ferrite–barium titanate composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 6644–6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Mak, C.-L. Impedance spectroscopic characterization of fine-grained magnetoelectric Pb(Zr0.53Ti0.47)O3-(Ni0.5Zn0.5)Fe2O4 ceramic composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 513, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Priya, S.; Uchino, K.; Kim, H.-E. Magnetoelectric effect in composites of magnetostrictive and piezoelectric materials. J. Electroceram. 2002, 8, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, J.; Yadav, K.L.; Prakash, S. Enhanced magnetodielectric effect and optical property of lead-free multiferroic (1-x)(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3/xCoFe2O4 composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 147, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bammannnavar, B.K.; Chavan, G.N.; Naik, L.R.; Chougule, B.K. Magnetic properties and magnetoelectric (ME) effect in ferroelectric rich Ni0.2Co0.8Fe2O-PbZr0.8Ti0.2O3 ME composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 117, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, D.; Niemiec, P.; Chrobak, A. Effect of chemical composition on magnetic and electrical properties of ferroelectromagnetic ceramic composites. Materials 2021, 14, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochenek, D.; Zachariasz, R.; Niemiec, P.; Ilczuk, J.; Bartkowska, J.; Brzezińska, D. Ferroelectromagnetic solid solutions on the base piezoelectric ceramic materials for components of micromechatronics. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 78, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowska, J.A.; Ilczuk, J. Microscopic origin of electric and magnetic ordering in BiFeO3. Int. J. Thermophys. 2010, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, R.J.; Sengunthar, P.; Zinzuvadiya, S.; Joshi, U.S. Investigation of magnetoelectric coupling effect in strongly ferroic oxide composites. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, D.K.; Puli, V.S.; Kumari, S.; Sahoo, S.; Das, P.T.; Pradhan, K.; Pradhan, D.K.; Scott, J.F.; Katiyar, R.S. Studies of phase transitions and magnetoelectric coupling in PFN-CZFO multiferroic composites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 1936–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.F.; Liu, J.-M.; Ren, Z.F. Multiferroicity: The coupling between magnetic and polarization orders. Adv. Phys. 2009, 58, 321–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkata Ramana, M.; Ramamanohar Reddy, N.; Siva Kumar, K.V.; Murthy, V.R.K.; Murty, B.S. Magneto-electric effect in multiferroic Ni0.93Co0.02Mn0.05Fe1.95O4−δ/PbZr0.52Ti0.48O3 particulate composites: Dielectric, piezoelectric properties. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2011, 25, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, D.; Niemiec, P.; Zachariasz, R.; Guzdek, P.; Chrobak, A.; Ziółkowski, G. Ferroelectric and ferromagnetic properties of the (1-x)NiZnFeO4-(x)Pb(Fe1/2Nb1/2)O3 composite. Inż. Mater./Mater. Eng. 2014, 35, 86–91. [Google Scholar]
- Niemiec, P.; Bochenek, D.; Chrobak, A.; Guzdek, P.; Błachowski, A. Ferroelectric–ferromagnetic ceramic composites based on PZT with added ferrite. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2015, 12, E82–E89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iulia, D.A.; Jana, P.; Delia, P.; Tudor-Gabriel, D.; Ladislau, M.; Ildiko, P. Investigation of multiferroic properties of Fe3+ and (La3+, Fe3+) doped PbZr0.53Ti0.47O3 ceramics. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Photonics (EExPolytech), St. Petersburg, Russia, 15–16 October 2020; pp. 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, E.; Guiffard, B.; Lebrun, L.; Guyomar, D. Effects of Zr/Ti ratio on structural, dielectric and piezoelectric properties of Mn-and (Mn, F)-doped lead zirconate titanate ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2006, 32, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, D.; Niemiec, P.; Skulski, R.; Adamczyk, M.; Brzezińska, D. Electrophysical properties of the multicomponent PBZT-type ceramics doped by Sn4+. J. Electroceram. 2019, 42, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khacheba, M.; Abdessalem, N.; Hamdi, A.; Khemakhem, H. Effect of acceptor and donor dopants (Na, Y) on the microstructure and dielectric characteristics of high Curie point PZT-modified ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 61–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya, C.; Muller, C.; Baudour, J.-L.; Madigou, V.; Anne, M.; Roubin, M. PbZr1-xTixO3 ceramic: Structural study and field-induced reorientation of ferroelectric domains. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2000, 75, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezińska, D.; Skulski, R.; Bochenek, D.; Niemiec, P. The properties of (1-x)(0.5PZT-0.5PFW)–xPFN ceramics. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2016, 173, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Cheng, L.-H.; Hong, R.-Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.-J.; Tian, C. Crystal structure and piezoelectric properties of xPb(Mn1/3Nb2/3)O3-(0.2-x)Pb(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3–0.8Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 1719–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Banerjee, A. Novel synthesis route to make nanocrystalline lead zirconate titanate powder. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 87, 487–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, E.R.; Gonçalves, M.D.; Kakihana, M. The oxidant peroxide method (OPM) as a new alternative for the synthesis of lead-based and bismuth-based oxides. J. Mater. Res. 2014, 29, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, E.R.; Barrado, C.M.; Ribeiro; Longo, C.E.; Leite, E.R. Nanosized lead lanthanum titanate (PLT) ceramic powders synthesized by the oxidant peroxo method. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 475, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, A.; Mazumder, R.; Sen, A.; Maiti, H.S. Fast firing of lead zirconate titanate ceramics at low temperature. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 97, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.F.; Wang, Y.R.; Mahalingam, T.; Chu, J.P.; Lin, K.U. Characterization of Hydrothermally synthesized lead zirconate titanate (PZT) ceramics. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2004, 87, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulson, A.; Herbert, J. Piezoelectric Ceramics, Electroceramics: Materials, Properties, Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, England, 2003; pp. 339–410. [Google Scholar]
- Noheda, B. Structure and high-piezoelectricity in lead oxide solid solutions. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2002, 6, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louh, R.; Reynolds, T.G., III; Buchanan, R.C. Ceramic Materials for Electronics, 3rd ed.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ajroudi, L.; Mliki, N.; Bessaïs, L.; Madigou, V.; Villain, S.; Leroux, C. Magnetic, electric and thermal properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 59, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.P.; Madhuri, W.; Reddy, N.R.; Siva Kumar, K.V.; Murthy, V.R.K.; Reddy, R.R. Magnetic properties of Ni-Zn ferrites prepared by microwave sintering method. J. Electroceram. 2012, 28, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laszkiewicz-Łukasik, J.; Putyra, P.; Klimczyk, P.; Podsiadło, M.; Bednarczyk, K. Spark plasma sintering/field assisted sintering technique as a universal method for the synthesis. Densification and bonding processes for metal, ceramic and composite materials. J. Appl. Mater. Eng. 2020, 60, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, D.; Niemiec, P.; Dercz, G.; Chrobak, A. Electrophysical properties of multiferroic PMN-PT-Ferrite composites sintered by spark plasma sintering. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 563, 169909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, D.; Płońska, M.; Dudek, J.; Surowiak, Z. Applications of the thermal analysis in preparation and investigation of the ceramic ferroics and multiferroics. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2010, 101, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marakhovsky, M.A.; Panich, A.A.; Talanov, M.V.; Marakhovskiy, V.A. Comparative study of the hard and soft PZT-based ceramics sintered by various method. Ferroelectrics 2021, 575, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, D.; Niemiec, P.; Korzekwa, J.; Durtka, B.; Stokłosa, Z. Microstructure and properties of the ferroelectric-ferromagnetic PLZT-ferrite composites. Symmetry 2018, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, A.; Graham, J.T.; Landsberger, S.; Ihlefeld, J.F.; Brennecka, G.L.; Brown, D.W.; Forrester, J.S.; Jones, J.L. Crystallographic changes in lead zirconate titanate due to neutron irradiation. AIP Adv. 2014, 4, 117125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chougule, S.S.; Patil, D.R.; Chougule, B.K. Electrical conduction and magnetoelectric effect in ferroelectric rich (x)Ni0.9Zn0.1Fe2O4-(1-x)PZT ME composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 452, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.; Badapanda, T.; Singh, A.K.; Panigrahi, S. An approach for correlating the structural and electrical properties of Zr4+-modified SrBi4Ti4O15/SBT ceramic. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 16319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Sanghi, S.; Ahlawat, N. Structural transformation and improved dielectric and magnetic properties in Ti-substituted Bi0.8La0.2FeO3 multiferroics. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 165001. [Google Scholar]
- Barick, B.K.; Mishra, K.K.; Arora, A.K.; Choudhary, R.N.; Pradhan, D.K. Impedance and raman spectroscopic studies of (Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys 2011, 44, 355402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Pu, Y.; Yao, M.; Jin, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, H. Superior electromagnetic properties obtained by enhanced resistivity on multiferroic barium titanate and hexaferrite di-phase composite ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, S85–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagar, S.; Hooda, A.; Khasa, S.; Malik, M. Structural refinement, investigation of dielectric and magnetic properties of NBT doped BaFe12O19 novel composite system. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 826, 154214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.J.; Farooq, S. Enhancement of electrical resistivity of Sr0.5Ba0.5Fe12O19 nanomaterials by doping with lanthanum and nickel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 118, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, D.K.; Chowdhury, R.N.P.; Nath, T.K. Magnetoelectric properties of PbZr0.53Ti0.47O3-Ni0.65Zn0.35Fe2O4 multiferroic nanocomposites. Appl. Nanosci. 2012, 2, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayssi, C.; Kossi, S.E.; Dhahri, J.; Khirouni, K. Frequency and temperature-dependence of dielectric permittivity and electric modulus studies of the solid solution Ca0.85Er0.1Ti1-xCo4x/3O3 (0≤x≤0.1). RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 17139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, L.; Shukla, A.K.; Sreenivas, K. Dielectric and magnetic properties of nickel ferrite ceramics using crystalline powders derived from DL alanine fuel in sol–gel auto-combustion. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 8341–8351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.J.; de Boer, F.R. Physics of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-1-4757-0567-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, R.; Momin, A.A.; Zubair, M.A.; Matin, M.A.; Akther Hossain, A.K.M. Investigation of magnetic and ferroelectric properties along with the magnetoelectric coupling behavior for asserting a room temperature bi-phase composite as multiferroics. J. Electroceram. 2020, 45, 56–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | PF-SPS | PF-HP | PF-FS |
|---|---|---|---|
| ρ (kg/m3) 1 | 6.26 × 103 | 7.12 × 103 | 6.72 × 103 |
| ra (μm) | 1.52 | 1.60 | 2.46 |
| ρDC (Ωm) 1 | 1.35 × 109 | 7.86 × 109 | 2.39 × 109 |
| M (Am2/kg) 2 | 5.27 | 5.30 | 5.26 |
| M (Am2/kg) 1 | 4.85 | 4.95 | 4.97 |
| Tm (°C) 3 | 327 | 309 | 350 |
| ε1, 3 | 1000 | 910 | 750 |
| εm 3 | 5340 | 7850 | 5720 |
| tanδ 1, 3 | 0.013 | 0.016 | 0.014 |
| Ea (eV) | 1.09 | 0.95 | 0.89 |
| Pr (µC/cm2) 1, 4 | 1.50 | 2.80 | 1.72 |
| Pm (µC/cm2) 1, 4 | 6.13 | 7.48 | 5.90 |
| Ec (kV/mm) 1, 4 | 0.71 | 0.95 | 0.97 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bochenek, D.; Chrobak, A.; Dercz, G. Influence of the Sintering Method on the Properties of a Multiferroic Ceramic Composite Based on PZT-Type Ferroelectric Material and Ni-Zn Ferrite. Materials 2022, 15, 8461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238461
Bochenek D, Chrobak A, Dercz G. Influence of the Sintering Method on the Properties of a Multiferroic Ceramic Composite Based on PZT-Type Ferroelectric Material and Ni-Zn Ferrite. Materials. 2022; 15(23):8461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238461
Chicago/Turabian StyleBochenek, Dariusz, Artur Chrobak, and Grzegorz Dercz. 2022. "Influence of the Sintering Method on the Properties of a Multiferroic Ceramic Composite Based on PZT-Type Ferroelectric Material and Ni-Zn Ferrite" Materials 15, no. 23: 8461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238461
APA StyleBochenek, D., Chrobak, A., & Dercz, G. (2022). Influence of the Sintering Method on the Properties of a Multiferroic Ceramic Composite Based on PZT-Type Ferroelectric Material and Ni-Zn Ferrite. Materials, 15(23), 8461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238461








