Mechanical Properties and Root Canal Shaping Ability of a Nickel–Titanium Rotary System for Minimally Invasive Endodontic Treatment: A Comparative In Vitro Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Size Estimation
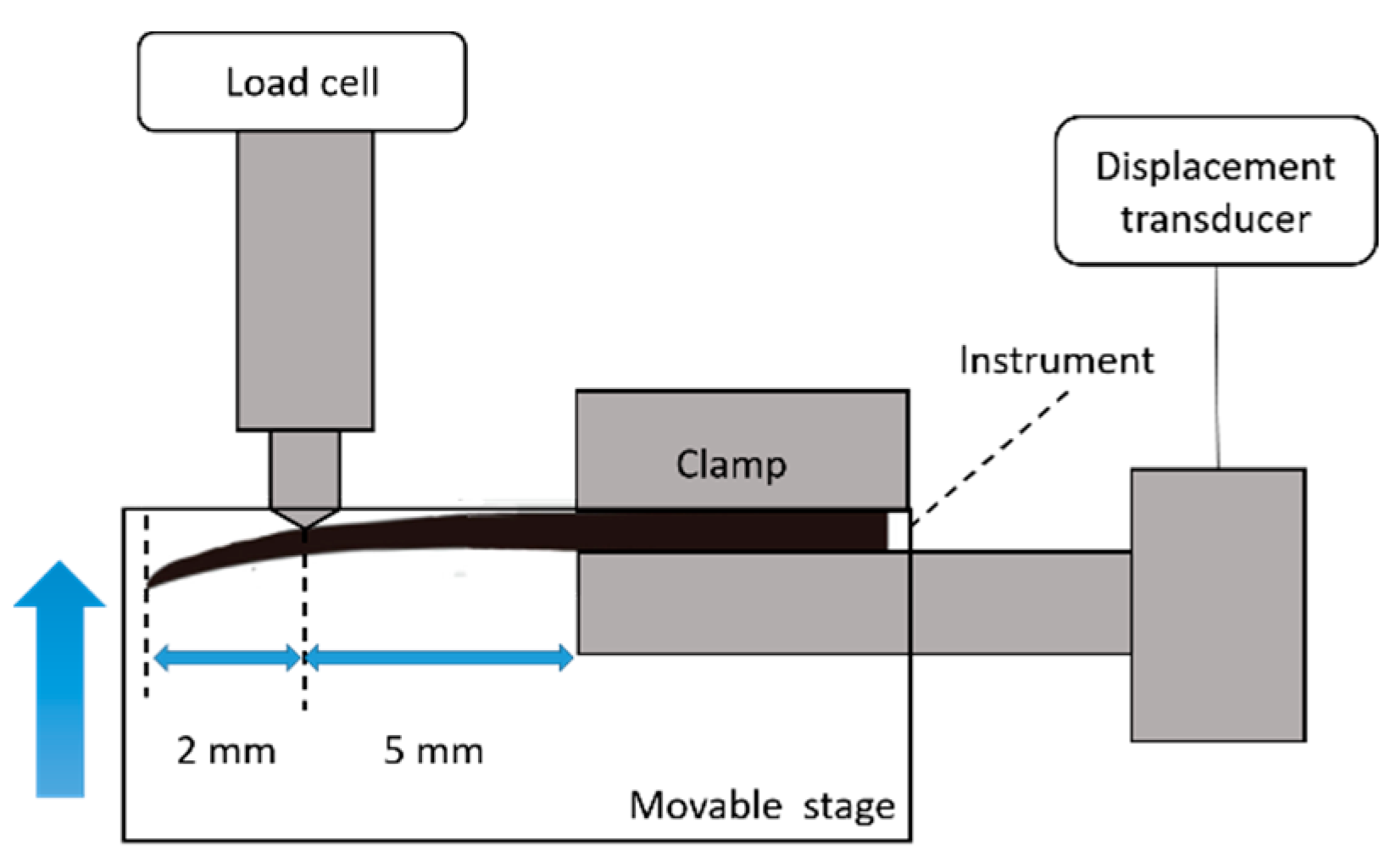
2.2. Bending Test
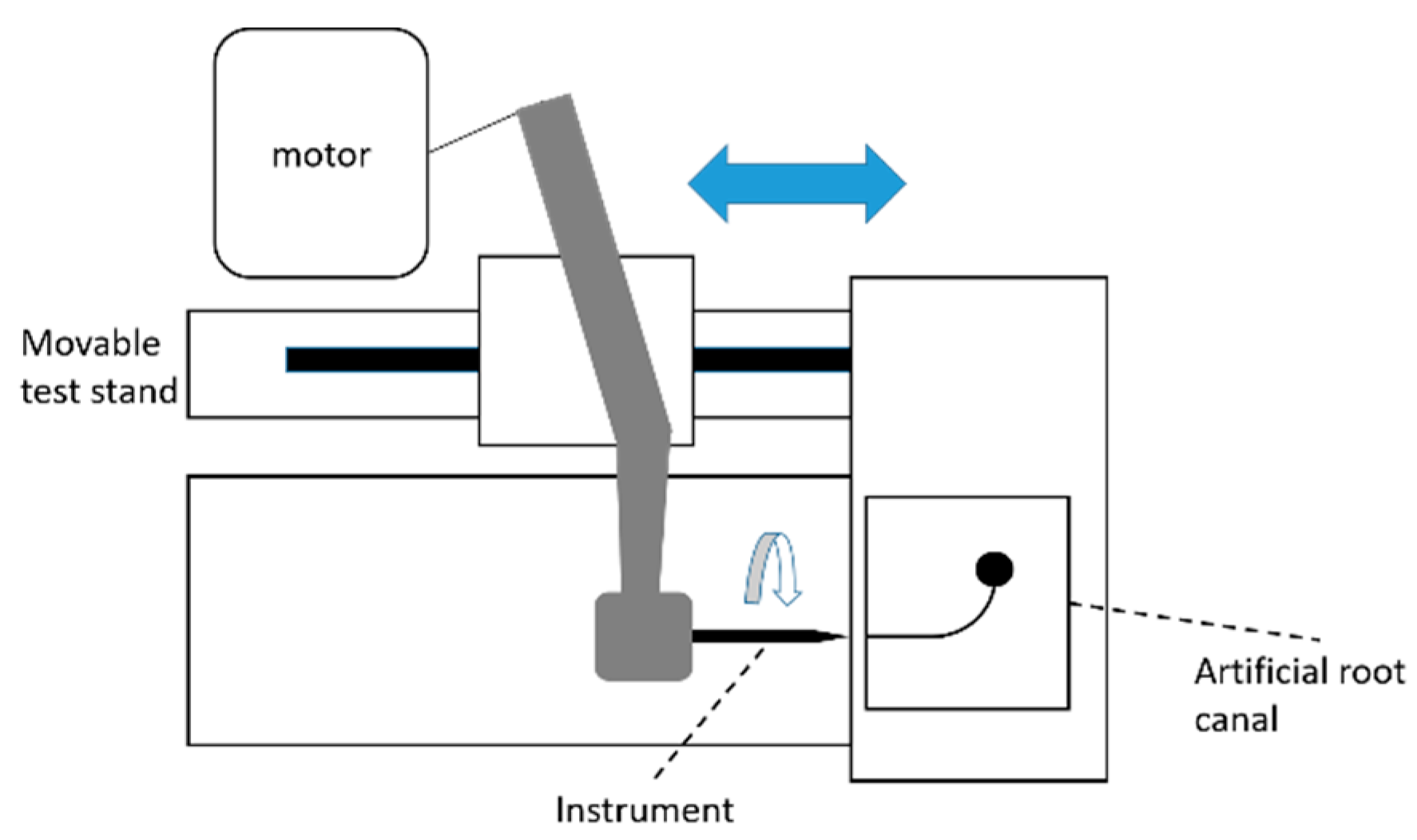
2.3. Dynamic Cyclic Fatigue Test
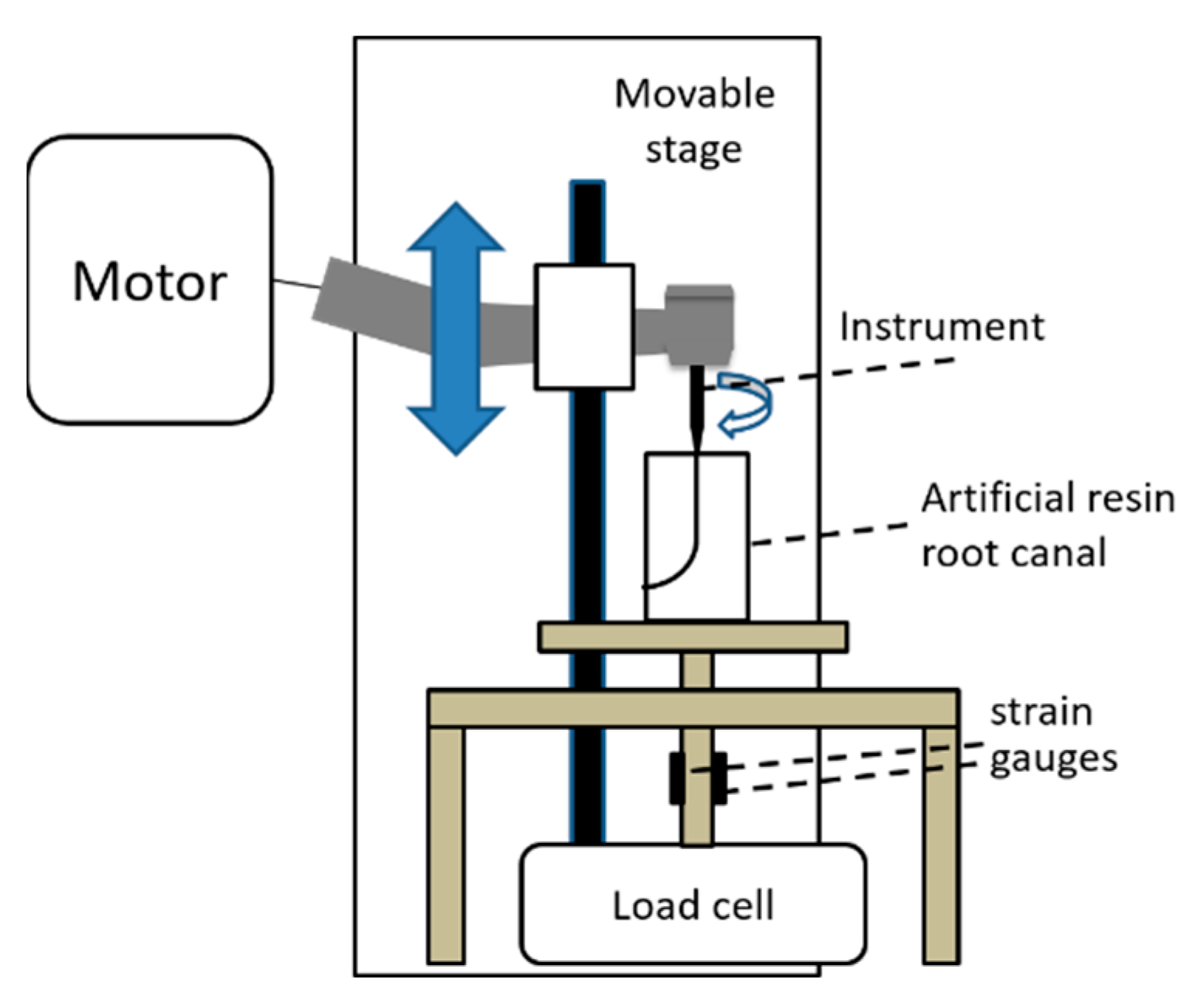
2.4. Measurement of Torque and Vertical Force
2.5. Root Canal Centering Ability
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bending Loads
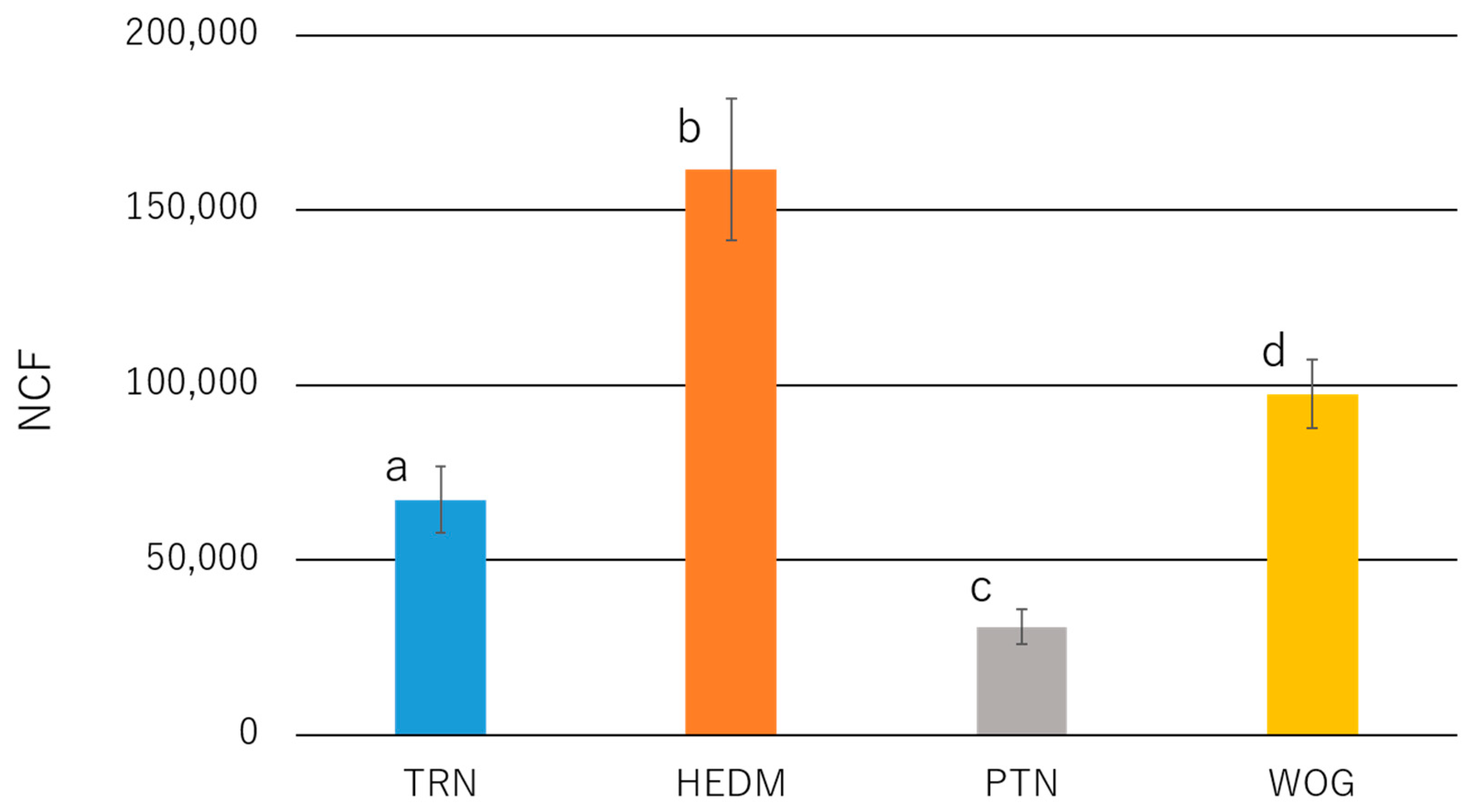
3.2. Dynamic Cyclic Fatigue Resistance
3.3. Torque and Vertical Force
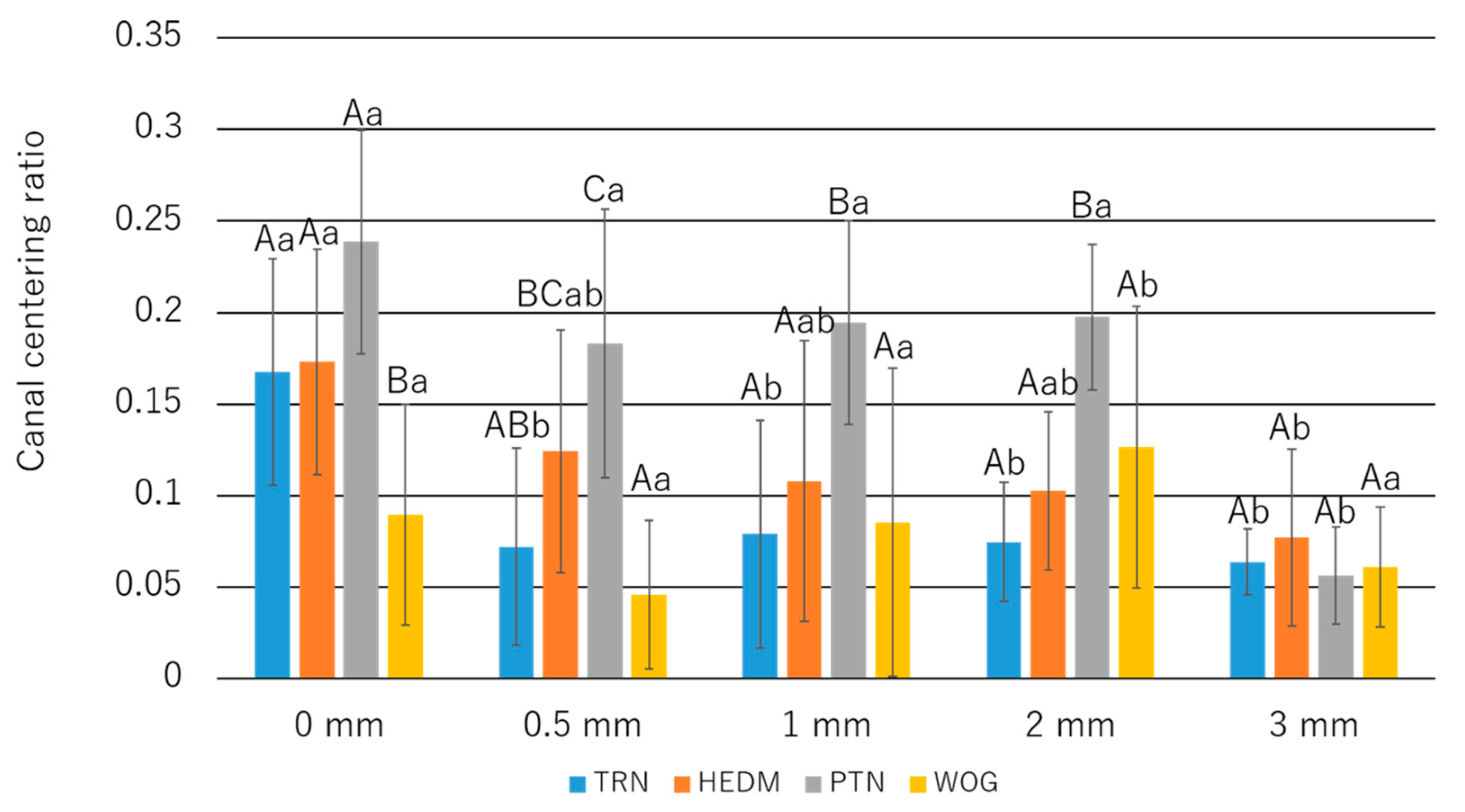
3.4. Canal Centering Ratio
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The bending load values were not significantly different between TRN, HEDM, and WOG at a 0.5 mm deflection. At a 2.0 mm deflection, the load values were ranked as TRN < HEDM < WOG < PTN.
- The number of cycles to fracture was ranked as HEDM > WOG > TRN > PTN.
- During instrumentation of J-shaped artificial resin canals, TRN showed smaller torque and vertical force values in most comparisons with the other instruments.
- The canal centering ratio for TRN was smaller than or comparable to that for the other instruments, except for WOG at the apex level.
- TRN showed higher flexibility and lower torque/force values than the other instruments, which may favor its clinical use under the concept of minimally invasive endodontic treatment.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ebihara, A.; Yahata, Y.; Miyara, K.; Nakano, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Suda, H. Heat treatment of nickel-titanium rotary endodontic instruments: Effects on bending properties and shaping abilities. Int. Endod. J. 2011, 44, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambill, J.M.; Alder, M.; Del Rio, C.E. Comparison of nickel-titanium and stainless steel hand-file instrumentation using computed tomography. J. Endod. 1996, 22, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, O.A. Current challenges and concepts in the preparation of root canal systems: A review. J. Endod. 2004, 30, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, A.; Peters, O.A. Present status and future directions: Canal shaping. Int. Endod. J. 2022, 55, 637–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhou, H.M.; Zheng, Y.F.; Peng, B.; Haapasalo, M. Current challenges and concepts of the thermomechanical treatment of nickel-titanium instruments. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.S.J.; Gomes, R.O.; Leroy, A.M.F.; Singh, R.; Peters, O.A.; Bahia, M.G.A.; Buono, V.T.L. Mechanical behavior of M-Wire and conventional NiTi wire used to manufacture rotary endodontic instruments. Dent. Mater. 2013, 29, e318–e324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçak, M.M.; Çiçek, E.; Koçak, S.; Sağlam, B.C.; Furuncuoğlu, F. Comparison of ProTaper Next and HyFlex instruments on apical debris extrusion in curved canals. Int. Endod. J. 2016, 49, 996–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, F.; Pirani, C.; Generali, L.; Bolelli, G.; Sassatelli, P.; Lusvarghi, L.; Gandolfi, M.G.; Giorgini, L.; Prati, C. Structural analysis of HyFlex EDM instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2017, 50, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedullà, E.; Lo Savio, F.; Boninelli, S.; Plotino, G.; Grande, N.M.; La Rosa, G.; Rapisarda, E. Torsional and cyclic fatigue resistance of a new nickel-titanium instrument manufactured by electrical discharge machining. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangli, T.; Maki, K.; Kimura, S.; Nishijo, M.; Tokita, D.; Ebihara, A.; Okiji, T. Assessment of mechanical properties of WaveOne Gold Primary reciprocating instruments. Dent. Mater. J. 2019, 38, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürklein, S.; Fluch, S.; Schäfer, E. Shaping ability of reciprocating single-file systems in severely curved canals: WaveOne and Reciproc versus WaveOne Gold and Reciproc blue. Odontology 2019, 107, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluskin, A.H.; Peters, C.I.; Peters, O.A. Minimally invasive endodontics: Challenging prevailing paradigms. Br. Dent. J. 2014, 216, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rundquist, B.D.; Versluis, A. How does canal taper affect root stresses? Int. Endod. J. 2006, 39, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Wu, Y.; Smales, R.J. Identifying and reducing risks for potential fractures in endodontically treated teeth. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürklein, S.; Zupanc, L.; Donnermeyer, D.; Tegtmeyer, K.; Schäfer, E. Effect of core mass and alloy on cyclic fatigue resistance of different nickel-titanium endodontic instruments in matching artificial canals. Materials 2021, 14, 5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnaghy, A.M.; Elsaka, S.E.; Mandorah, A.O. In vitro comparison of cyclic fatigue resistance of TruNatomy in single and double curvature canals compared with different nickel-titanium rotary instruments. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, O.A.; Arias, A.; Choi, A. Mechanical properties of a novel nickel-titanium root canal instrument: Stationary and dynamic tests. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Jeon, S.J.; Seo, M.S. Comparison of the canal transportation of ProTaper GOLD, WaveOne GOLD, and TruNatomy in simulated double-curved canals. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabil, E.; Katić, M.; Anić, I.; Bago, I. Micro-computed evaluation of canal transportation and centering ability of 5 rotary and reciprocating systems with different metallurgical properties and surface treatments in curved root canals. J. Endod. 2021, 47, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyaw, M.S.; Ebihara, A.; Maki, K.; Kimura, S.; Nakatsukasa, T.; Htun, P.H.; Thu, M.; Omori, S.; Okiji, T. Effect of kinematics on the torque/force generation, surface characteristics, and shaping ability of a nickel-titanium rotary glide path instrument: An ex vivo study. Int. Endod. J. 2022, 55, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyara, K.; Yahata, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Ebihara, A.; Hanawa, T.; Suda, H. The influence of heat treatment on the mechanical properties of Ni-Ti file materials. Dent. Mater. J. 2014, 33, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fukumori, Y.; Nishijyo, M.; Tokita, D.; Miyara, K.; Ebihara, A.; Okiji, T. Comparative analysis of mechanical properties of differently tapered nickel-titanium endodontic rotary instruments. Dent. Mater. J. 2018, 37, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsukasa, T.; Ebihara, A.; Kimura, S.; Maki, K.; Nisijo, M.; Tokita, D.; Okiji, T. Comparative evaluation of mechanical properties and shaping performance of heat-treated nickel titanium rotary instruments used in the single-length technique. Dent. Mater. J. 2021, 40, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruett, J.P.; Clement, D.J.; Carnes, D.L. Cyclic fatigue testing of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments. J. Endod. 1997, 23, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokita, D.; Ebihara, A.; Nishijo, M.; Miyara, K.; Okiji, T. Dynamic torque and vertical force analysis during nickel-titanium rotary root canal preparation with different modes of reciprocal rotation. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 1706–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S.; Ebihara, A.; Maki, K.; Nishijo, M.; Tokita, D.; Okiji, T. Effect of optimum torque reverse motion on torque and force generation during root canal instrumentation with crown-down and single-length techniques. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htun, P.H.; Ebihara, A.; Maki, K.; Kimura, S.; Nishijo, M.; Tokita, D.; Okiji, T. Comparison of torque, force generation and canal shaping ability between manual and nickel-titanium glide path instruments in rotary and optimum glide path motion. Odontology 2020, 108, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, K.; Ebihara, A.; Kimura, S.; Nishijo, M.; Tokita, D.; Okiji, T. Effect of different speeds of up-and-down motion on canal centering ability and vertical force and torque generation of nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2019, 45, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, K.; Ebihara, A.; Kimura, S.; Nishijo, M.; Tokita, D.; Miyara, K.; Okiji, T. Enhanced root canal-centering ability and reduced screw-in force generation of reciprocating nickel-titanium instruments with a post-machining thermal treatment. Dent. Mater. J. 2020, 39, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorster, M.; Van der Vyver, P.J.; Markou, G. The effect of different molar access cavity designs on root canal shaping times using rotation and reciprocation instruments in mandibular first molars. J. Endod. 2022, 48, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.H.; Cheung, G.S.P.; Versluis, A.; Lee, C.J.; Kwak, S.W.; Kim, H.C. ‘Screw-in’ tendency of rotary nickel-titanium files due to design geometry. Int. Endod. J. 2015, 48, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyai, K.; Ebihara, A.; Hayashi, Y.; Doi, H.; Suda, H.; Yoneyama, T. Influence of phase transformation on the torsional and bending properties of nickel-titanium rotary endodontic instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2006, 39, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zupanc, J.; Vahdat-Pajouh, N.; Schäfer, E. New thermomechanically treated NiTi alloys—A review. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 1088–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyahi, A.M.; Bashiri, A.; Alshahrani, K.; Alshahrani, S.; Alamri, H.M.; Al-Sudani, D. Cyclic fatigue comparison of TruNatomy, Twisted File, and ProTaper Next rotary systems. Int. J. Dent. 2020, 2020, 3190938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, R.; Al Omari, T.; Al-Nasrawi, S.; Al Fodeh, R.; Dkmak, A.; Haider, J. Evaluating in vitro performance of novel nickel-titanium rotary system (TruNatomy) based on debris extrusion and preparation time from severely curved canals. J. Endod. 2021, 47, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, B.N.; Murugesan, S.; Basheer, S.N.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, V.; Selvaraj, S. Comparison of cyclic fatigue resistance of novel TruNatomy files with conventional endodontic files: An in vitro SEM study. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2021, 22, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar]
- Yahata, Y.; Yoneyama, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Ebihara, A.; Doi, H.; Hanawa, T.; Suda, H. Effect of heat treatment on transformation temperatures and bending properties of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2009, 42, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.; Martins, J.N.R.; Ajuz, N.C.; Antunes, H.S.; Vieira, V.T.L.; Braz Fernandes, F.M.; Belladonna, F.G.; Versiani, M.A. A multimethod assessment of a new customized heat-treated nickel-titanium rotary file system. Materials 2022, 15, 5288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, A.C.D.; De Melo, M.C.C.; Bahia, M.G.D.; Buono, V.T.L. Relationship between flexibility and physical, chemical, and geometric characteristics of rotary nickel-titanium instruments. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2010, 110, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versluis, A.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, W.; Kim, B.M.; Lee, C.J. Flexural stiffness and stresses in nickel-titanium rotary files for various pitch and cross-sectional geometries. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 1399–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.M.; Yang, Y.J.; Qian, J. Phase transformation behaviors and mechanical properties of NiTi endodontic files after gold heat treatment and blue heat treatment. J. Oral Sci. 2020, 63, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, A.; Macorra, J.C.; Govindjee, S.; Peters, O.A. Correlation between temperature-dependent fatigue resistance and differential scanning calorimetry analysis for 2 contemporary rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, H.P.; Elias, C.N.; Vieira, M.V.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Mangelli, M.; Lopes, W.S.; Vieira, V.T.L.; Alves, F.R.F.; Oliveira, J.C.M.; Soares, T.G. Fatigue life of Reciproc and Mtwo instruments subjected to static and dynamic tests. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keleş, A.; Eymirli, A.; Uyanik, O.; Nagas, E. Influence of static and dynamic cyclic fatigue tests on the lifespan of four reciprocating systems at different temperatures. Int. Endod. J. 2019, 52, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haïkel, Y.; Serfaty, R.; Bateman, G.; Senger, B.; Allemann, C. Dynamic and cyclic fatigue of engine-driven rotary nickel-titanium endodontic instruments. J. Endod. 1999, 25, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.H.; Schwartz, S.A.; Beeson, T.J. Cyclic fatigue of three types of rotary nickel-titanium files in a dynamic model. J. Endod. 2006, 32, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, M.; Ebihara, A.; Maki, K.; Miki, N.; Okiji, T. Cyclic fatigue resistance of rotary and reciprocating nickel-titanium instruments subjected to static and dynamic tests. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 1752–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, D.L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Lin, X.W.; Tong, Z.C. Cyclic fatigue resistance for six types of nickel titanium instruments at artificial canals with different angles and radii of curvature. Dent. Mater. J. 2021, 40, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faus-Llácer, V.; Kharrat, N.H.; Ruiz-Sanchez, C.; Faus-Matoses, I.; Zubizarreta-Macho, A.; Faus-Matoses, V. The effect of taper and apical diameter on the cyclic fatigue resistance of rotary endodontic files using an experimental electronic device. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirani, C.; Iacono, F.; Generali, L.; Sassatelli, P.; Nucci, C.; Lusvarghi, L.; Gandolfi, M.G.; Prati, C. HyFlex EDM: Superficial features, metallurgical analysis and fatigue resistance of innovative electro discharge machined NiTi rotary instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2016, 49, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Deus, G.; Moreira, E.J.L.; Lopes, H.P.; Elias, C.N. Extended cyclic fatigue life of F2 ProTaper instruments used in reciprocating movement. Int. Endod. J. 2010, 43, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thu, M.; Ebihara, A.; Adel, S.; Okiji, T. Analysis of torque and force induced by rotary nickel-titanium instruments during root canal preparation: A systematic review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.W.; Lee, C.J.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, H.C.; Ha, J.H. Comparison of screw-in forces during movement of endodontic files with different geometries, alloys, and kinetics. Materials 2019, 12, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattapan, B.; Palamara, J.E.A.; Messer, H.H. Torque during canal instrumentation using rotary nickel-titanium files. J. Endod. 2000, 26, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.W.; Ha, J.H.; Lee, C.J.; El Abed, R.; Abutahun, I.H.; Kim, H.C. Effects of pitch length and heat treatment on the mechanical properties of the glide path preparation instruments. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, S.R.; Alcalde, M.P.; Vivacqua-Gomes, N.; Bramante, C.M.; Vivan, R.R.; Duarte, M.A.H.; Vasconcelos, B.C. Evaluation of apical transportation and centring ability of five thermally treated NiTi rotary systems. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieawy, A.; Haapasalo, M.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Z.J.; Shen, Y. Phase transformation behavior and resistance to bending and cyclic fatigue of ProTaper Gold and ProTaper Universal instruments. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 1134–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elashiry, M.M.; Saber, S.E.; Elashry, S.H. Comparison of shaping ability of different single-file systems using microcomputed tomography. Eur. J. Dent. 2020, 14, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.C.; Webber, J. The validity of simulated root canals for the investigation of the prepared root canal shape. Int. Endod. J. 1985, 18, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.B.; Gufran, K.; Alhabib, O.; Alafraa, O.; Alzahrani, F.; Abuelqomsan, M.S.; Karobari, M.I.; Alnajei, A.; Afroz, M.M.; Akram, S.M.; et al. CBCT based study to analyze and classify root canal morphology of maxillary molars—A retrospective study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 6550–6560. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Unno, H.; Ebihara, A.; Hirano, K.; Kasuga, Y.; Omori, S.; Nakatsukasa, T.; Kimura, S.; Maki, K.; Okiji, T. Mechanical Properties and Root Canal Shaping Ability of a Nickel–Titanium Rotary System for Minimally Invasive Endodontic Treatment: A Comparative In Vitro Study. Materials 2022, 15, 7929. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15227929
Unno H, Ebihara A, Hirano K, Kasuga Y, Omori S, Nakatsukasa T, Kimura S, Maki K, Okiji T. Mechanical Properties and Root Canal Shaping Ability of a Nickel–Titanium Rotary System for Minimally Invasive Endodontic Treatment: A Comparative In Vitro Study. Materials. 2022; 15(22):7929. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15227929
Chicago/Turabian StyleUnno, Hayate, Arata Ebihara, Keiko Hirano, Yuka Kasuga, Satoshi Omori, Taro Nakatsukasa, Shunsuke Kimura, Keiichiro Maki, and Takashi Okiji. 2022. "Mechanical Properties and Root Canal Shaping Ability of a Nickel–Titanium Rotary System for Minimally Invasive Endodontic Treatment: A Comparative In Vitro Study" Materials 15, no. 22: 7929. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15227929
APA StyleUnno, H., Ebihara, A., Hirano, K., Kasuga, Y., Omori, S., Nakatsukasa, T., Kimura, S., Maki, K., & Okiji, T. (2022). Mechanical Properties and Root Canal Shaping Ability of a Nickel–Titanium Rotary System for Minimally Invasive Endodontic Treatment: A Comparative In Vitro Study. Materials, 15(22), 7929. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15227929







