Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles from Gold Coatings Recovered from E-Waste Processors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
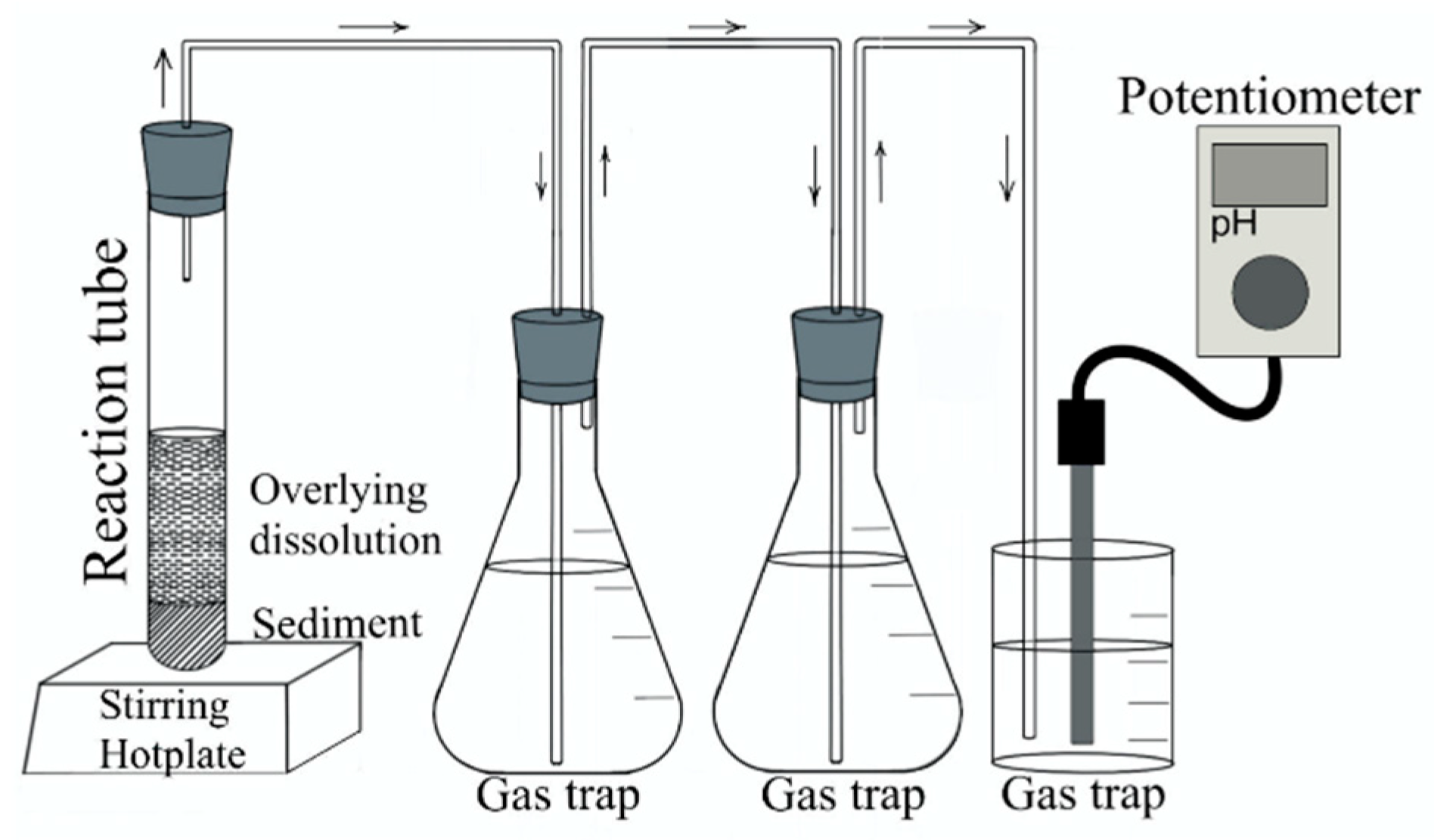
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Recovery of Pins from E-Waste Processors
2.2. Recovery of Gold Coatings from Pins
2.3. Synthesis of Tetrachoroauric Acid (HAuCl4)
2.4. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles
3. Results and Discussion
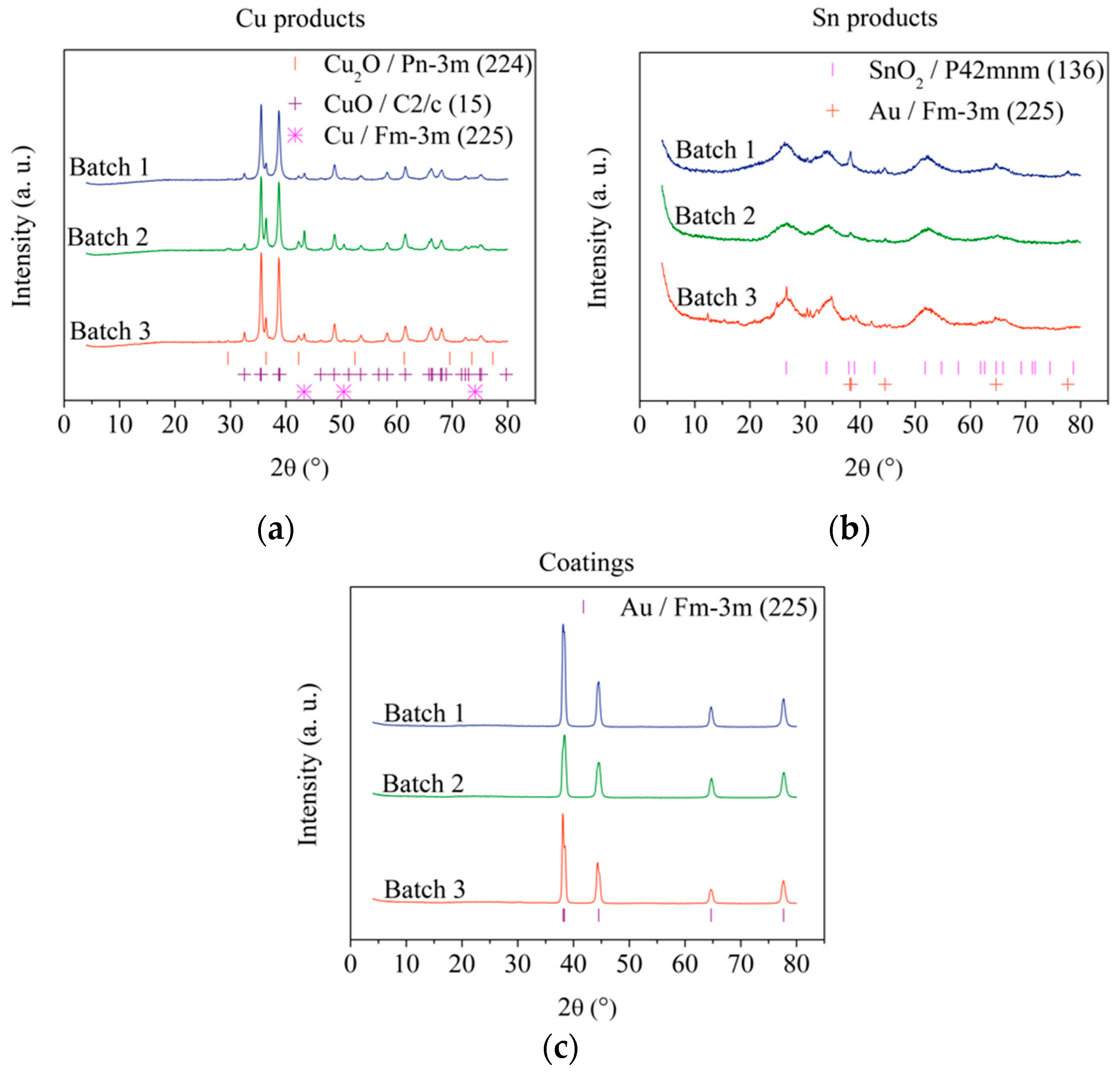
3.1. Pin Recovery from E-Waste Processors
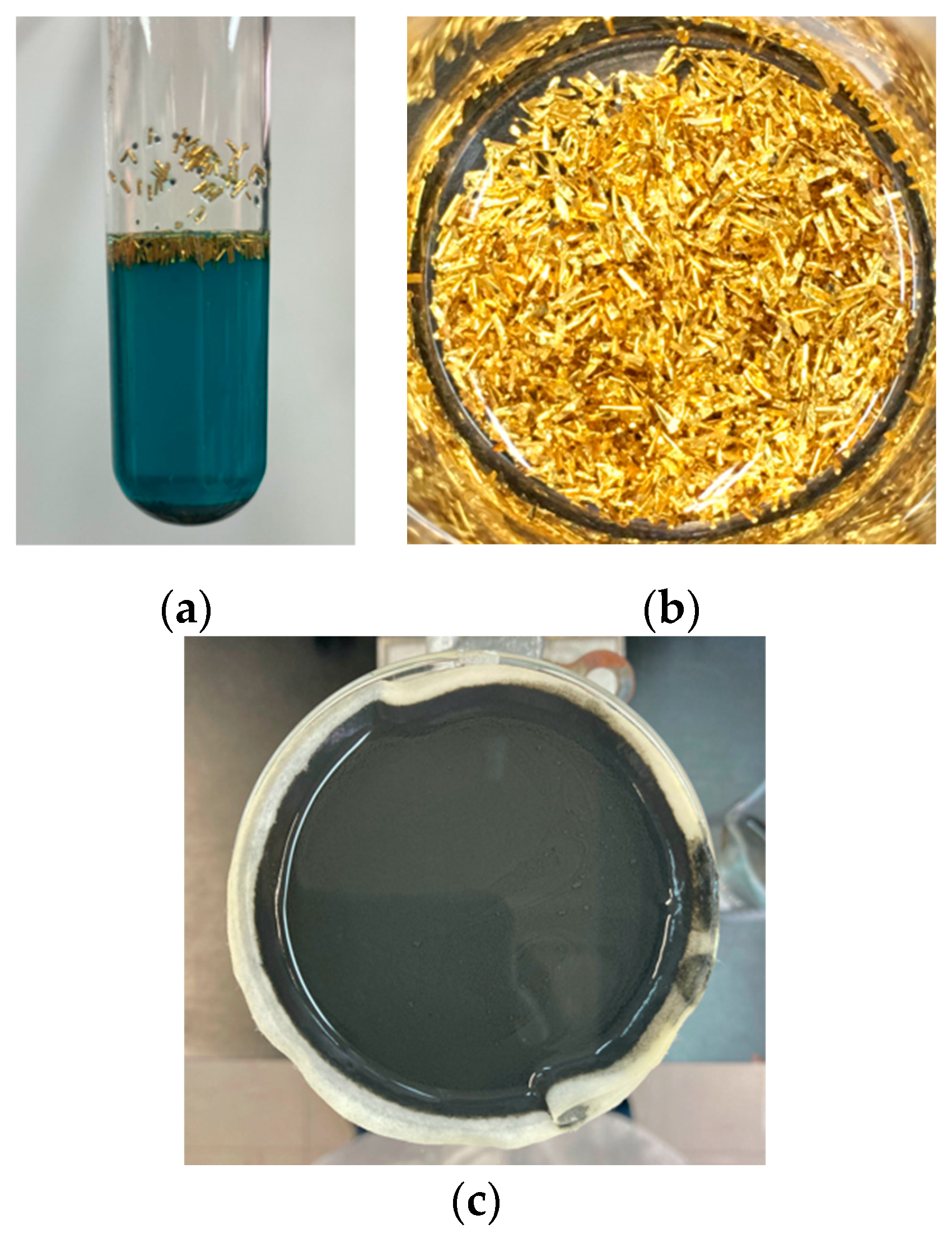
3.2. Recovery of Gold Coatings from Pins
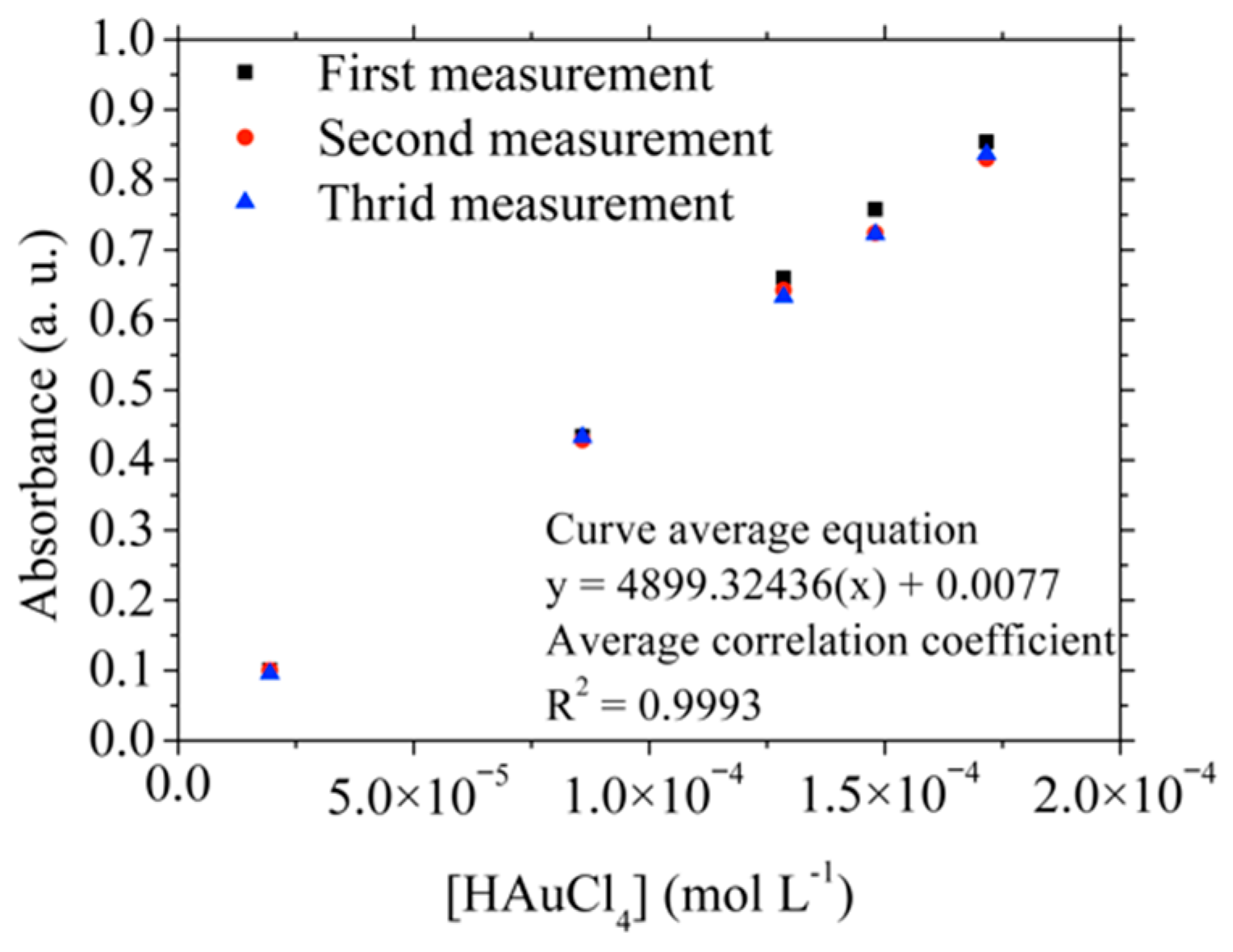
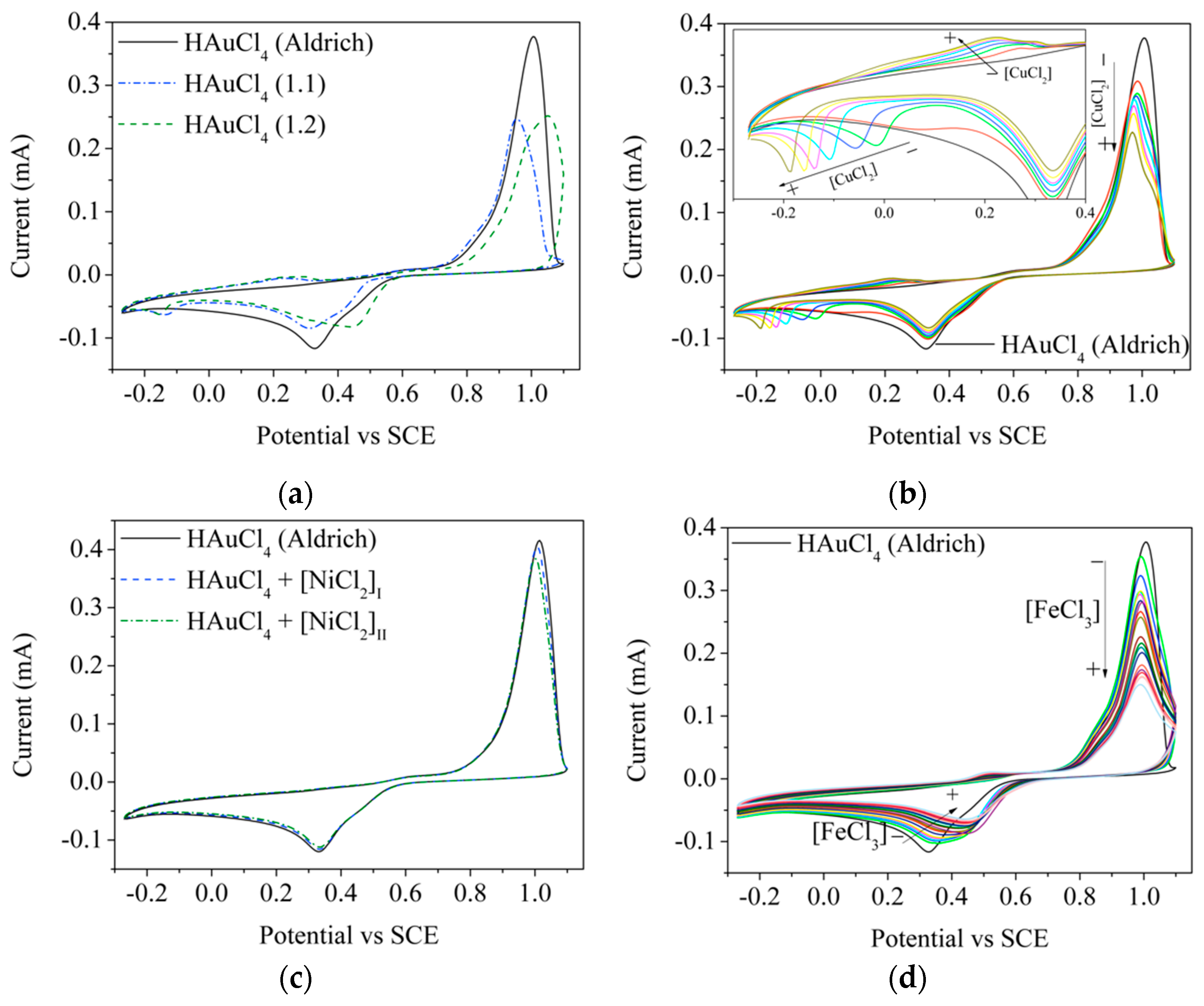
3.3. Synthesis of Tetrachloroauric Acid (HAuCl4)
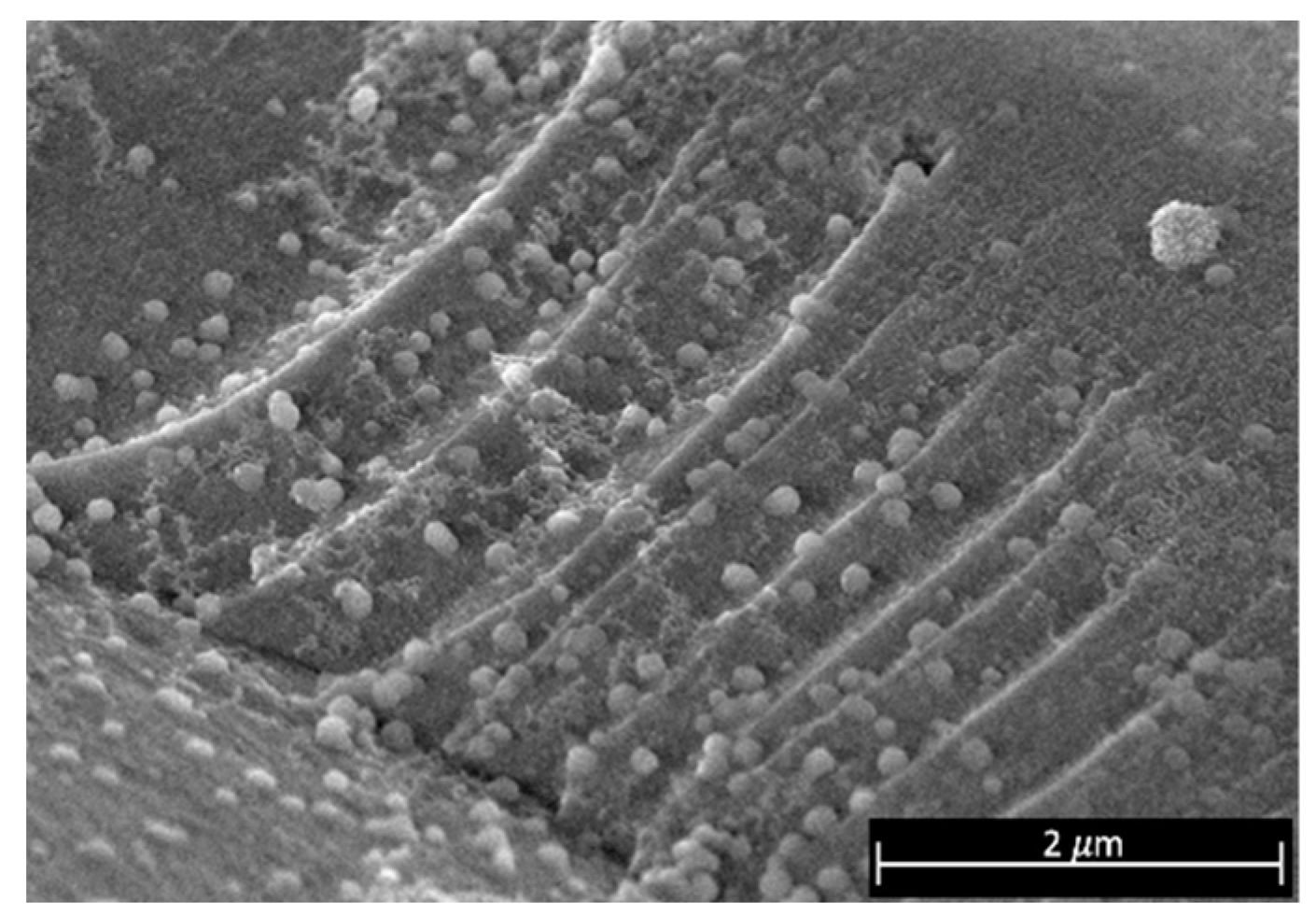
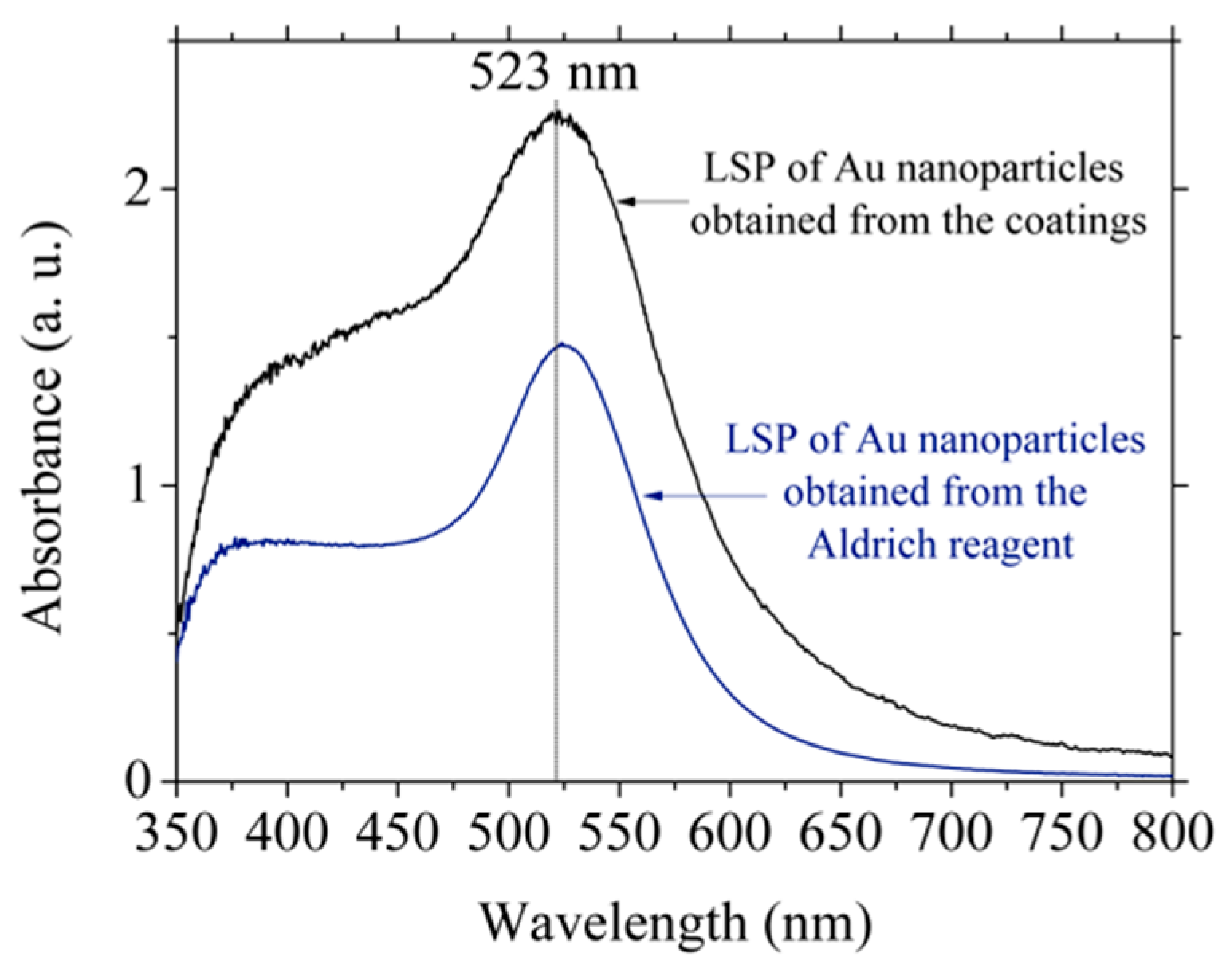
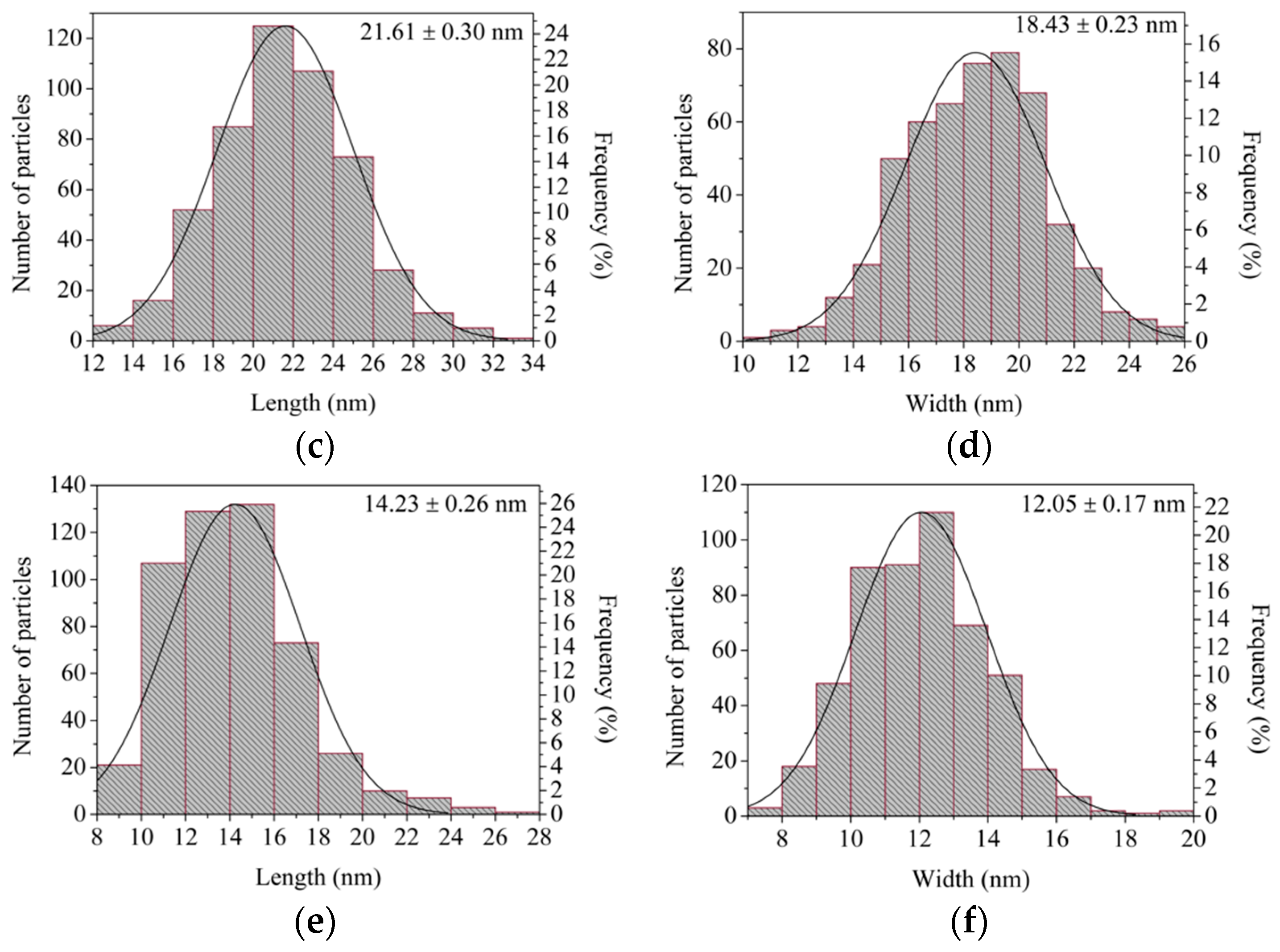
3.4. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles by the Turkevich Method
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forti, V.; Baldé, C.P.; Kuehr, R.; Bel, G. The Global E-Waste Monitor 2020; International Telecommunication Union (ITU): Geneva, Switzerland; International Solid Waste Association (ISWA): Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; ISBN 9789280891140. [Google Scholar]
- Ahirwar, R.; Tripathi, A.K. E-Waste Management: A Review of Recycling Process, Environmental and Occupational Health Hazards, and Potential Solutions. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 15, 100409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Kendall, A.; Xu, Z.; Schoenung, J.M. Waste Management of Printed Wiring Boards: A Life Cycle Assessment of the Metals Recycling Chain from Liberation through Refining. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilankoon, I.M.S.K.; Ghorbani, Y.; Chong, M.N.; Herath, G.; Moyo, T.; Petersen, J. E-Waste in the International Context—A Review of Trade Flows, Regulations, Hazards, Waste Management Strategies and Technologies for Value Recovery. Waste Manag. 2018, 82, 258–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, J.S.S.; Hacha, R.R.; D’almeida, F.S.; Almeida, C.A.; Moura, F.J.; Brocchi, E.A.; Souza, R.F.M. Electronic Waste Low-Temperature Processing: An Alternative Thermochemical Pretreatment to Improve Component Separation. Materials 2021, 14, 6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, N.; Sulke, P.; Badiye, A. E-Waste Forensics: An Overview. Forensic Sci. Int. Anim. Environ. 2021, 1, 100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, X.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, L. Elevated Emissions of Melamine and Its Derivatives in the Indoor Environments of Typical E-Waste Recycling Facilities and Adjacent Communities and Implications for Human Exposure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://www.undp.org/sustainable-development-goals (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- Abdelbasir, S.M.; Hassan, S.S.M.; Kamel, A.H.; El-Nasr, R.S. Status of Electronic Waste Recycling Techniques: A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 16533–16547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzate, A.; López, M.E.; Serna, C. Recovery of Gold from Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Using Ammonium Persulfate. Waste Manag. 2016, 57, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerecedo-Sáenz, E.; Cárdenas-Reyes, E.A.; Rojas-Calva, A.H.; Reyes-Valderrama, M.I.; Rodríguez-Lugo, V.; Toro, N.; Gálvez, E.; Acevedo-Sandoval, O.A.; Hernández-ávila, J.; Salinas-Rodríguez, E. Use of the O2-Thiosemicarbazide System, for the Leaching of: Gold and Copper from WEEE & Silver Contained in Mining Wastes. Materials 2021, 14, 7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Ahmed, T.; Awual, M.R.; Rahman, A.; Sultana, M.; Aziz, A.A.; Monir, M.U.; Teo, S.H.; Hasan, M. Advances in Sustainable Approaches to Recover Metals from E-Waste-A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Z. Identifying Extraction Technology of Gold from Solid Waste in Terms of Environmental Friendliness. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 7260–7267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, S. The Recovery of Gold from Secondary Sources; Syed, S., Simpson, M., Eds.; Imperial College Press: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2016; ISBN 9781783269907. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, F.; Liu, J.; Zhao, M.; Yu, L.; Wang, H.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Sun, Y.; Cen, J.; et al. Study of an Environmentally Friendly Method for the Dissolution of Precious Metal with Ionic Liquid and Iodoalkane. Metals 2021, 11, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zeng, B.; Lv, J.; Lu, Y.; Chen, H. Environmentally Friendly Technology for Separating Gold from Waste Printed Circuit Boards: A Combination of Suspension Electrolysis and a Chlorination Process. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 16952–16959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Sun, H.; Liu, W.-J.; Guan, B.; Deng, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, P. Environmentally Benign, Rapid, and Selective Extraction of Gold from Ores and Waste Electronic Materials. Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 9459–9463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paclawski, K.; Fitzner, K. Kinetics of Gold (III) Chloride Complex Reduction Using Sulfur (IV). Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2004, 35, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doidge, E.D.; Carson, I.; Tasker, P.A.; Ellis, R.J.; Morrison, C.A.; Love, J.B. A Simple Primary Amide for the Selective Recovery of Gold from Secondary Resources. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 12436–12439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daruich De Souza, C.; Ribeiro Nogueira, B.; Rostelato, M.E.C.M. Review of the Methodologies Used in the Synthesis Gold Nanoparticles by Chemical Reduction. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 798, 714–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, C.; Pluchery, O. Gold Nanoparticles for Physics, Chemistry and Biology, 1st ed.; Imperial College Press: Paris, France, 2012; ISBN 978-1-84816-806-0. [Google Scholar]
- Barragan, J.A.; Castro, J.R.A.; Peregrina-Lucano, A.A.; Sánchez-Amaya, M.; Rivero, E.P.; Larios-Durán, E.R. Leaching of Metals from E-Waste: From Its Thermodynamic Analysis and Design to Its Implementation and Optimization. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 12063–12071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojo, M.; Uji-Yie, Y.; Tsubota, S.; Tamura, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Okamura, K.; Isshiki, K. Can Pure Gold Be Dissolved in Seawater Mixed with Aqueous Nitric Acid? J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 194, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojo, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Okamura, K. Dilute Nitric or Nitrous Acid Solution Containing Halide Ions as Effective Media for Pure Gold Dissolution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 19948–19956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojo, M. Mechanism of Enhanced Oxidation Ability of Dilute Nitric Acid and Dissolution of Pure Gold in Seawater with Nitric Acid. Kharkiv Univ. Bull. Chem. Ser. 2019, 33, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, S.R.; Massicot, J.; McDonagh, A.M. A Straightforward Route to Tetrachloroauric Acid from Gold Metal and Molecular Chlorine for Nanoparticle Synthesis. Metals 2015, 5, 1454–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EURACHEM; CITAC. Quantifying Uncertainty in Analytical Measurement, 2nd ed.; EURACHEM: Gembloux, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Liémans, I.; Alban, B.; Tranier, J.P.; Thomas, D. SOx and NOx Absorption Based Removal into Acidic Conditions for the Flue Gas Treatment in Oxy-Fuel Combustion. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 2847–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Pan, J. Novel Process of Simultaneous Removal of Nitric Oxide and Sulfur Dioxide Using a Vacuum Ultraviolet (Vuv)-Activated O2/H2O/H2O2 System in a Wet Vuv−spraying Reactor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 12966–12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, S.; Song, F.; Bu, Y. Simultaneous Removal of NOX and SO2 from Coal-Fired Flue Gas by Catalytic Oxidation-Removal Process with H2O2. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 243, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intel. Intel® Pentium® 4 Processor with 512-KB L2 Cache on 0.13 Micron Process and Intel® Pentium® 4 Processor Extreme Edition Supporting Hyper-Threading Technology; Intel Corp.: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2004; pp. 1–85. [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich Gold Nanoparticles: Properties and Applications. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/MX/es/technical-documents/technical-article/materials-science-and-engineering/biosensors-and-imaging/gold-nanoparticles (accessed on 6 September 2022).
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
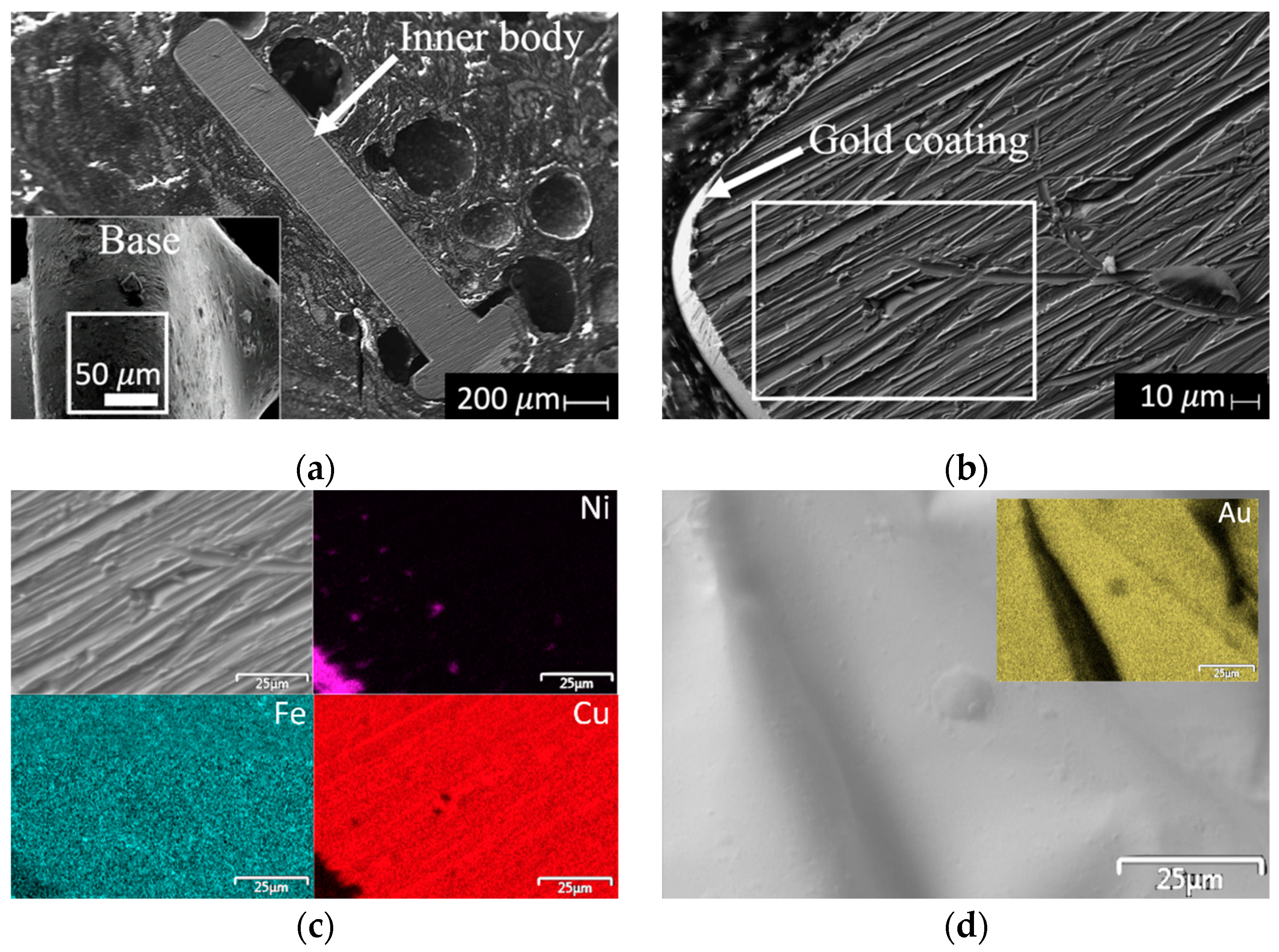

| Elements/Inner Body | Wt% |
|---|---|
| Cu | 96.05 (2.98) |
| Ni * | 1.72 (0.00) |
| Fe | 2.23 (0.04) |
| Elements/gold coating | Wt% |
| Au | 100 (0.0) |
| Elements/base | Wt% |
| Sn | 100 (0.0) |
| Element | Au | Ni | Fe | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass contained (g) | 0.0199 | 0.1050 | 0.0019 | 2.0611 |
| Percent (Wt%) | 0.9 | 4.8 | 0.1 | 94.2 |
| Variables | Batch 1 | Batch 2 | Batch 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pins mass (g) | 2.5119 (0.0004) | 2.5392 (0.0004) | 2.6118 (0.0002) |
| Au recovered (g) | 0.0164 (0.0002) | 0.0151 (0.0002) | 0.0204 (0.0002) |
| Cu recovered (g) | 1.9318 (0.0004) | 1.7865 (0.0002) | 1.6611 (0.0002) |
| Sn recovered (g) | 0.4834 (0.0008) | 0.0976 (0.0002) | 0.2485 (0.0004) |
| mT recovered (g) | 2.4316 (0.0008) | 1.8992 (0.0004) | 1.9300 (0.0005) |
| mT efficiency (%) | 96.80 (1.48) | 74.79 (1.24) | 73.90 (0.72) |
| MP-AES efficiency * (%) | 89.05 (0.02) | 82.35 (0.02) | 76.86 (0.02) |
| Variables | Synthesis 1.1 | Synthesis 1.2 |
|---|---|---|
| [HAuCl4] (mM) * | 1.04 (0.03) | 0.96 (0.03) |
| Au dissolved percent (%) | 101.9 (17.1) | 105.2 (21.1) |
| [Au]MP-AES (mM) * | 1.04 | 0.95 |
| [Ni]MP-AES | 0.08 μM * (0.48 ppm) | 0.12 μM * (0.73 ppm) |
| [Cu]MP-AES | 0.32μM * (2.03 ppm) | 0.87 μM * (5.51 ppm) |
| Element | Au | Ni | Fe | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration before | 1.07 mM * | ND | ND | 0.25 ppm |
| Concentration after | 0.63 mM * | ND | 2.5 ppm | 1.25 ppm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su-Gallegos, J.; Magallón-Cacho, L.; Ramírez-Aparicio, J.; Borja-Arco, E. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles from Gold Coatings Recovered from E-Waste Processors. Materials 2022, 15, 7307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207307
Su-Gallegos J, Magallón-Cacho L, Ramírez-Aparicio J, Borja-Arco E. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles from Gold Coatings Recovered from E-Waste Processors. Materials. 2022; 15(20):7307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207307
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu-Gallegos, Javier, Lorena Magallón-Cacho, Jeannete Ramírez-Aparicio, and Edgar Borja-Arco. 2022. "Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles from Gold Coatings Recovered from E-Waste Processors" Materials 15, no. 20: 7307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207307
APA StyleSu-Gallegos, J., Magallón-Cacho, L., Ramírez-Aparicio, J., & Borja-Arco, E. (2022). Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles from Gold Coatings Recovered from E-Waste Processors. Materials, 15(20), 7307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207307









