Effect of Tin Grain Orientation on Electromigration-Induced Dissolution of Ni Metallization in SnAg Solder Joints
Abstract
1. Introduction
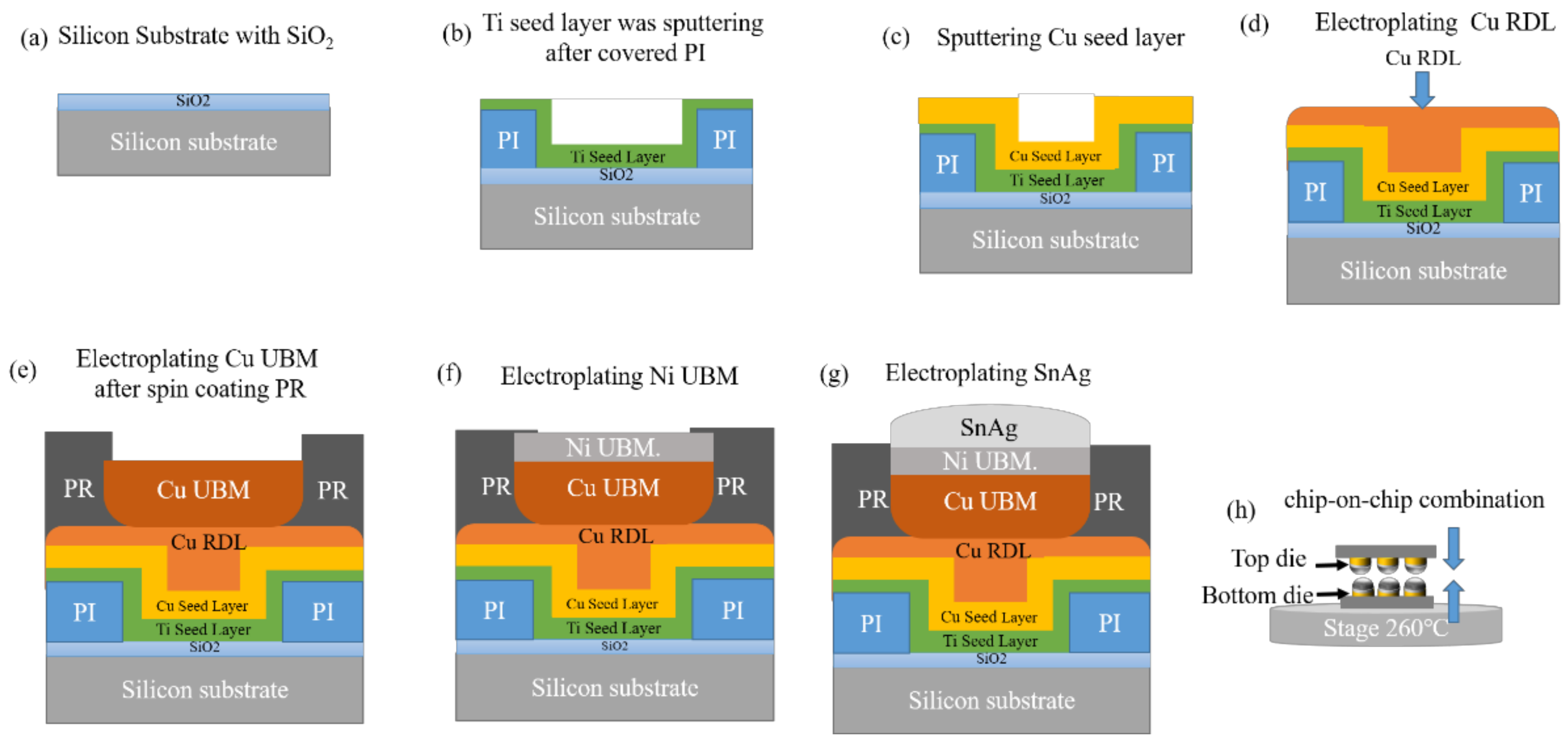
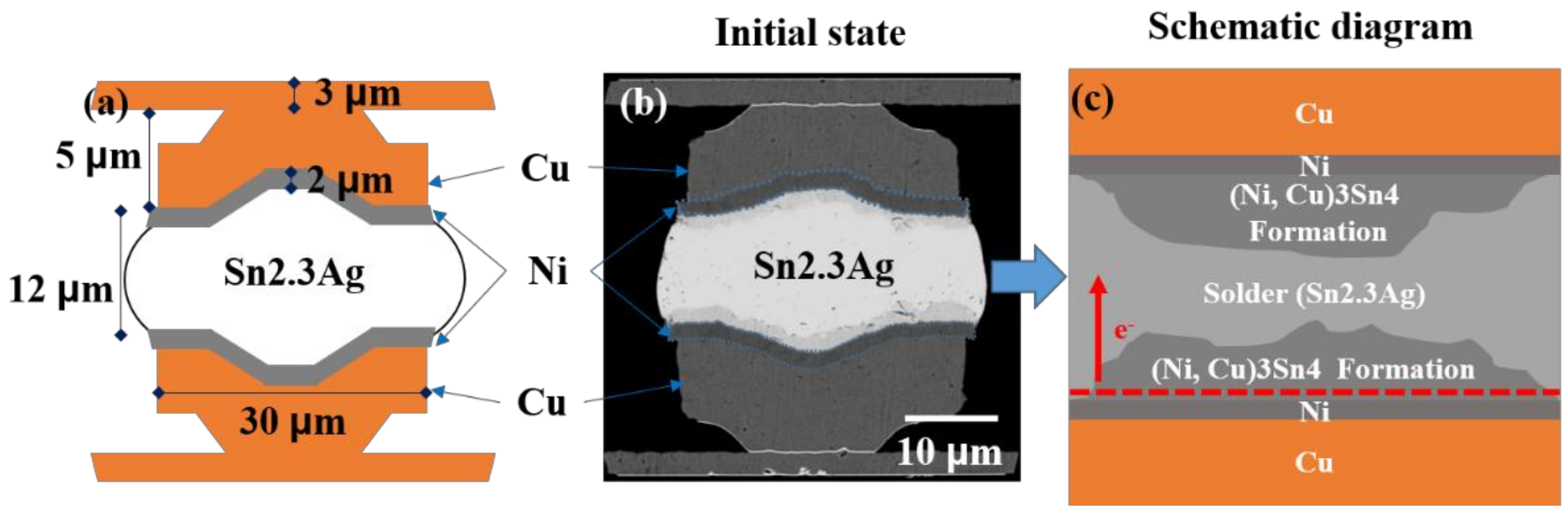
2. Materials and Methods
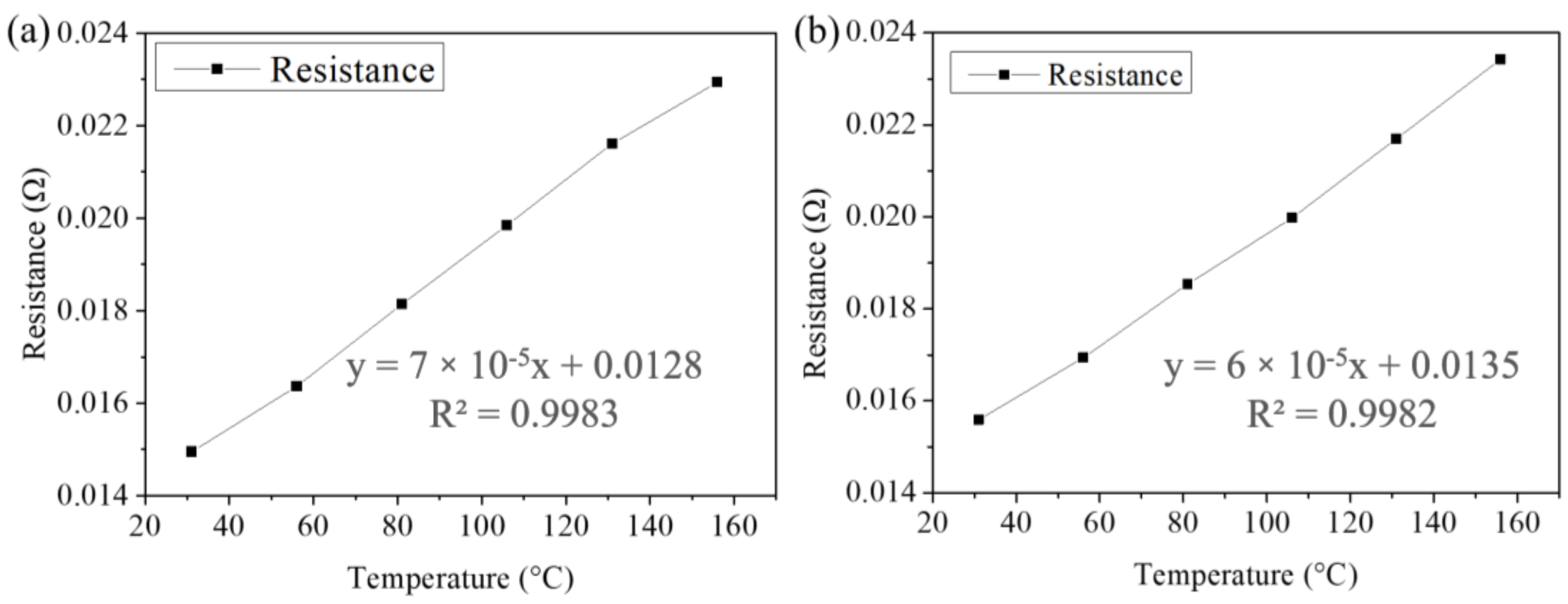
3. Results and Discussion
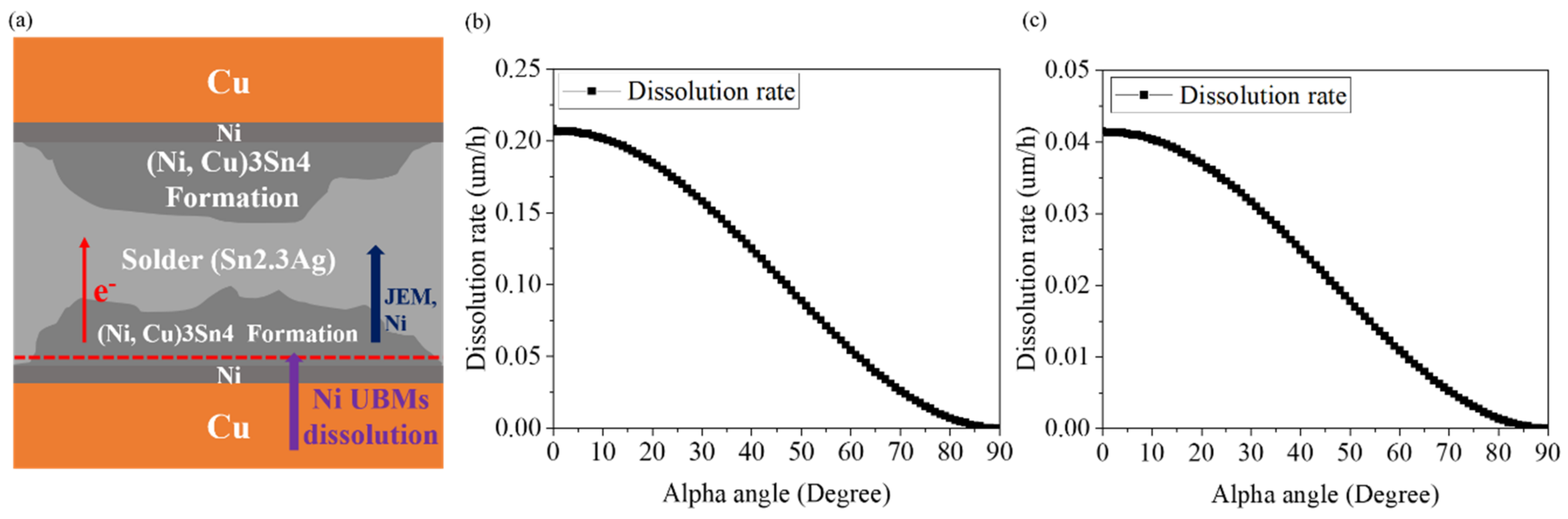
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chao, B.H.-L.; Zhang, X.; Chae, S.-H.; Ho, P.S. Recent advances on kinetic analysis of electromigration enhanced intermetallic growth and damage formation in Pb-free solder joints. Microelectron. Reliab. 2009, 49, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liang, S. Electromigration issues in lead-free solder joints. Lead-Free. Electron. Solder. 2006, 18, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.; Choi, W.; Xu, G.; Tu, K.-N. Electromigration in solder joints and solder lines. JOM 2002, 54, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Tsai, C.; Hu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Kao, C. Electromigration-induced failure in flip-chip solder joints. J. Electron. Mater. 2005, 34, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.W.; Shiozaki, K.; Yasuda, S.; Glover, M.D. Highly reliable nickel-tin transient liquid phase bonding technology for high temperature operational power electronics in electrified vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2012 Twenty-Seventh Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Orlando, FL, USA, 5–9 February 2012; pp. 478–482. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.-S.; Hyun, S.-K.; Yoon, J.-W. Cu–Sn and Ni–Sn transient liquid phase bonding for die-attach technology applications in high-temperature power electronics packaging. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 7827–7833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollefsen, T.A.; Larsson, A.; Løvvik, O.M.; Aasmundtveit, K.E. High temperature interconnect and die attach technology: Au–Sn SLID bonding. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 3, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Rai, R.; Purushothaman, S. Interfacial reactions during soldering with lead-tin eutectic and lead (Pb)-free, tin-rich solders. J. Electron. Mater. 1996, 25, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, D.; Huntington, H. Extreme fast-diffusion system: Nickel in single-crystal tin. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1984, 53, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-A.; Ouyang, F.-Y.; Chen, C. Effect of Sn grain orientation on growth of Cu-Sn intermetallic compounds during thermomigration in Cu-Sn2. 3Ag-Ni microbumps. Mater. Lett. 2019, 236, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-N.; Ouyang, F.-Y. Effects of anisotropic β-Sn alloys on Cu diffusion under a temperature gradient. Acta Mater. 2014, 81, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Ma, H.; Yu, F.; Zhao, N. Quasi-in-situ observation on diffusion anisotropy dominated asymmetrical growth of Cu-Sn IMCs under temperature gradient. Acta Mater. 2021, 217, 117168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Chen, M.-H.; Zhang, L. Microstructure evolution and grain orientation of IMC in Cu-Sn TLP bonding solder joints. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 786, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, C.-C.; Tran, D.-P.; Juang, J.-Y.; Chen, C. Effect of Intermetallic Compound Bridging on the Cracking Resistance of Sn2. 3Ag Microbumps with Different UBM Structures under Thermal Cycling. Metals 2021, 11, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Felton, L.E.; Messler, R.W. The effect of soldering process variables on the microstructure and mechanical properties of eutectic Sn-Ag/Cu solder joints. J. Electron. Mater. 1995, 24, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Yeh, E.; Tu, K.-N. Mean-time-to-failure study of flip chip solder joints on Cu/Ni (V)/Al thin-film under-bump-metallization. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 5665–5671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, T.; Su, P.; Hong, S.; Korhonen, M.; Li, C.-Y. Reactions of lead-free solders with CuNi metallizations. J. Electron. Mater. 2000, 29, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Tu, K.-N. Six cases of reliability study of Pb-free solder joints in electronic packaging technology. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2002, 38, 55–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, K.-N.; Ku, F.; Lee, T. Morphological stability of solder reaction products in flip chip technology. J. Electron. Mater. 2001, 30, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Tu, K.-N. Kinetic analysis of the soldering reaction between eutectic SnPb alloy and Cu accompanied by ripening. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 53, 16027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H.; Massalski, T. Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams; ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 1990; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, H.; Yu, J.; Kuo, M.; Tong, H.; Kao, C. Elimination of voids in reactions between Ni and Sn: A novel effect of silver. Scr. Mater. 2012, 66, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Ma, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, C. Effect of the silver content of SnAgCu solder on the interfacial reaction and on the reliability of angle joints fabricated by laser-jet soldering. J. Electron. Mater. 2015, 44, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Yu, J.; Shih, W.; Hsueh, C.; Kao, C. Effects of silver addition on Cu–Sn microjoints for chip-stacking applications. J. Alloy. Compd. 2014, 605, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, F.; Luan, J.; Baraton, X. Effect of silver content and nickel dopant on mechanical properties of Sn-Ag-based solders. In Proceedings of the 2008 58th Electronic Components and Technology Conference, Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 27–30 May 2008; pp. 485–490. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chan, Y. Effect of silver (Ag) nanoparticle size on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn58Bi–Ag composite solders. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 645, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashima, S.; Kariya, Y.; Hosoi, T.; Tanaka, M. Effect of silver content on thermal fatigue life of Sn-xAg-0.5 Cu flip-chip interconnects. J. Electron. Mater. 2003, 32, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otiaba, K.C.; Bhatti, R.; Ekere, N.; Mallik, S.; Ekpu, M. Finite element analysis of the effect of silver content for Sn–Ag–Cu alloy compositions on thermal cycling reliability of solder die attach. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2013, 28, 192–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariya, Y.; Hosoi, T.; Terashima, S.; Tanaka, M.; Otsuka, M. Effect of silver content on the shear fatigue properties of Sn-Ag-Cu flip-chip interconnects. J. Electron. Mater. 2004, 33, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.-W.; Chang, Y.-W.; Sung, W.-C.; Chen, C. Precipitation of large Ag3Sn intermetallic compounds in SnAg2. 5 microbumps after multiple reflows in 3D-IC packaging. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 134, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Frear, D.; Lee, T.; Tu, K.-N. Morphology of interfacial reaction between lead-free solders and electroless Ni–P under bump metallization. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 88, 6359–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, M.; Punch, J.; Collins, M.; Ryan, C. Effect of Ag content on the microstructure of Sn-Ag-Cu based solder alloys. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 2008, 20, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yang, C.; Lin, Y.; Hsueh, C.; Kao, C. Optimal Ag addition for the elimination of voids in Ni/SnAg/Ni micro joints for 3D IC applications. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 629, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, S.; Ye, Z. Microstructure, properties, and formation mechanisms of tungsten/steel hot isostatic pressing diffusion bonding joint utilizing a Ni-Si-B interlayer. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 299, 117303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Huang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Goodall, R. Diffusion reaction-induced microstructure and strength evolution of Cu joints bonded with Sn-based solder containing Ni-foam. Mater. Lett. 2020, 281, 128642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhao, N. Diffusion anisotropy induced uneven regional growth of Cu6Sn5 IMC in Cu/SAC305/Cu micro solder joints under temperature gradient. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 886, 161221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Liang, S.-W.; Lin, T.; Chen, C. Three-dimensional simulation on current-density distribution in flip-chip solder joints under electric current stressing. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 044509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Shih, D.-Y.; Lauro, P.; Goldsmith, C.; Henderson, D.W. Effect of Sn grain orientation on electromigration degradation mechanism in high Sn-based Pb-free solders. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 211909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
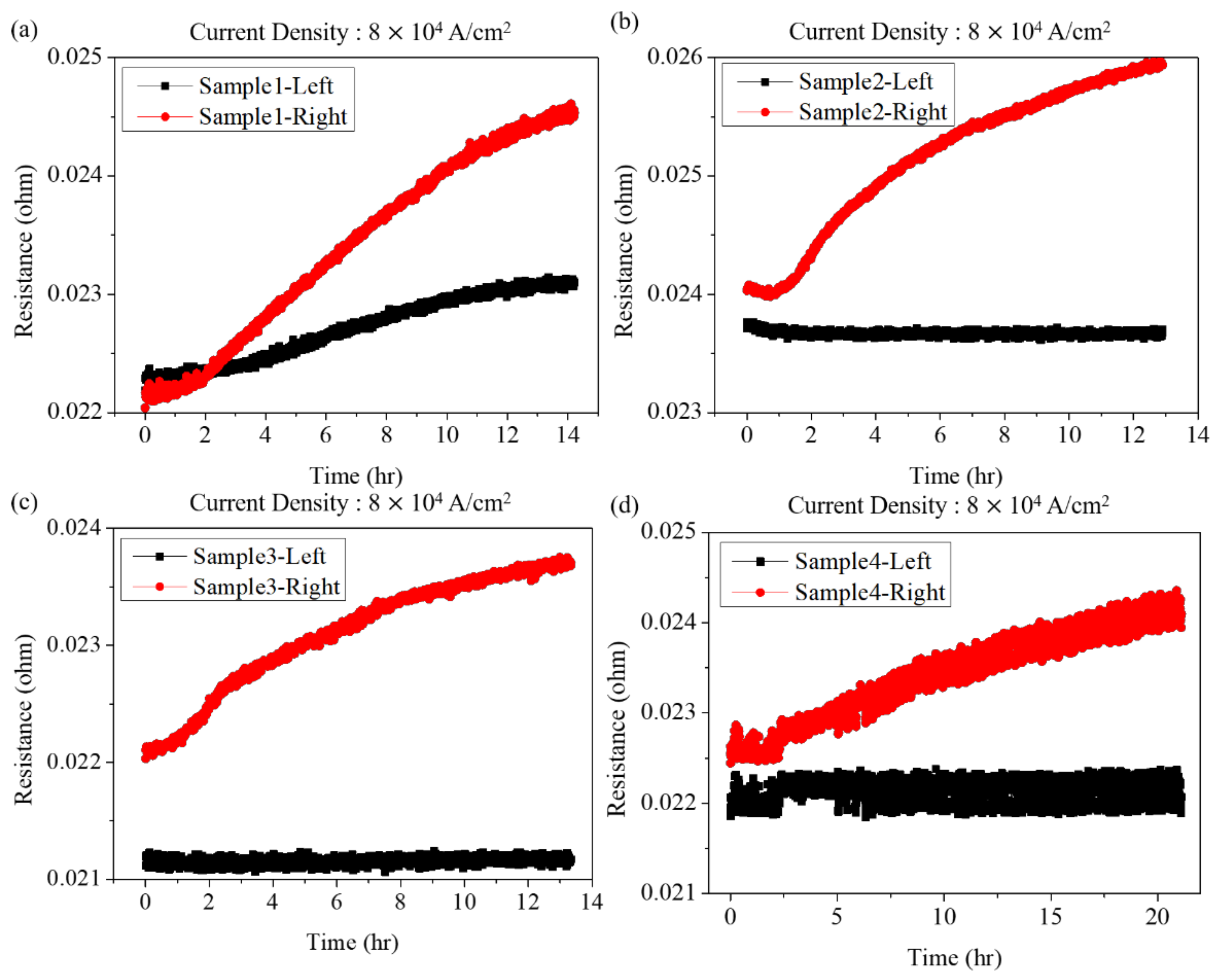
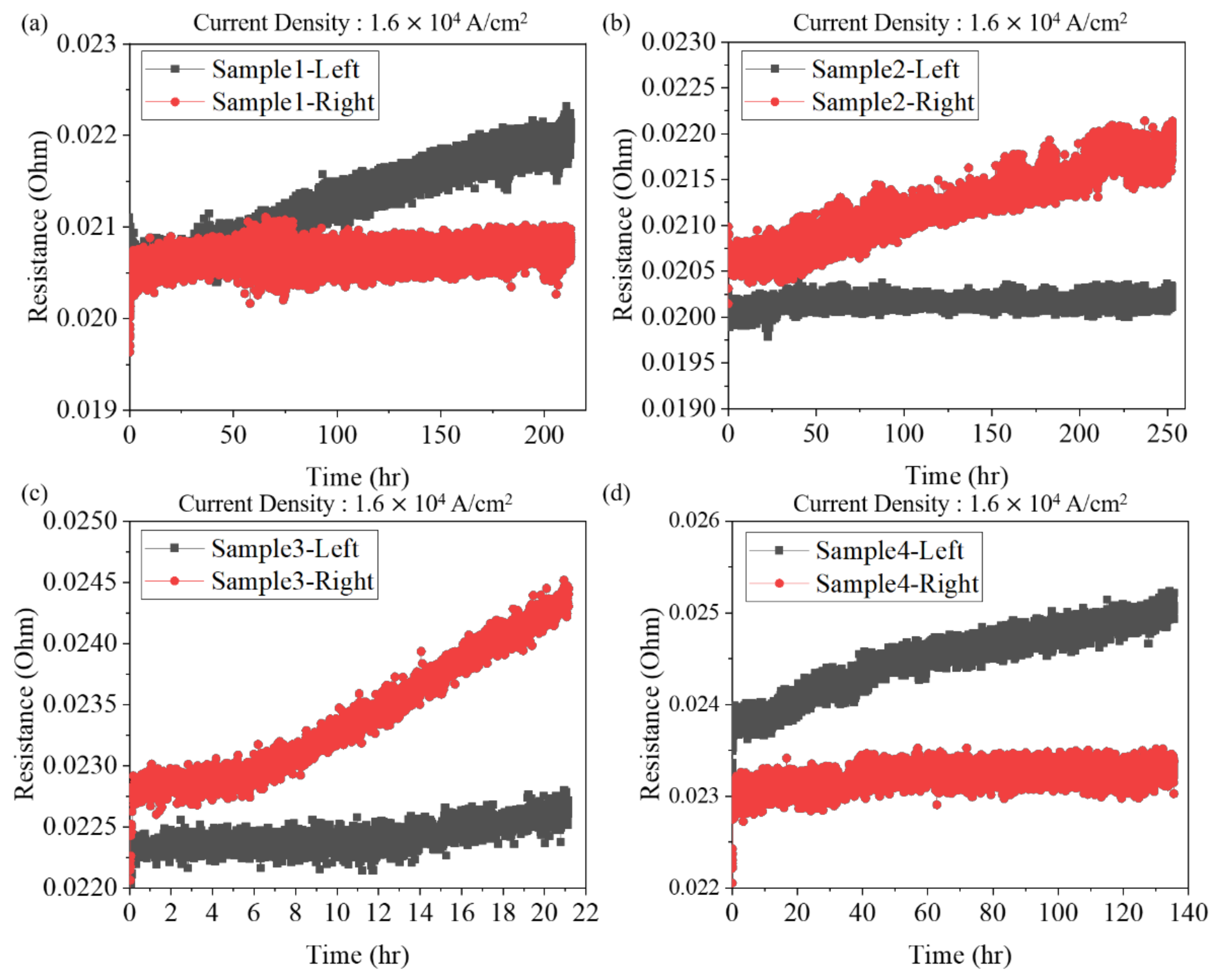
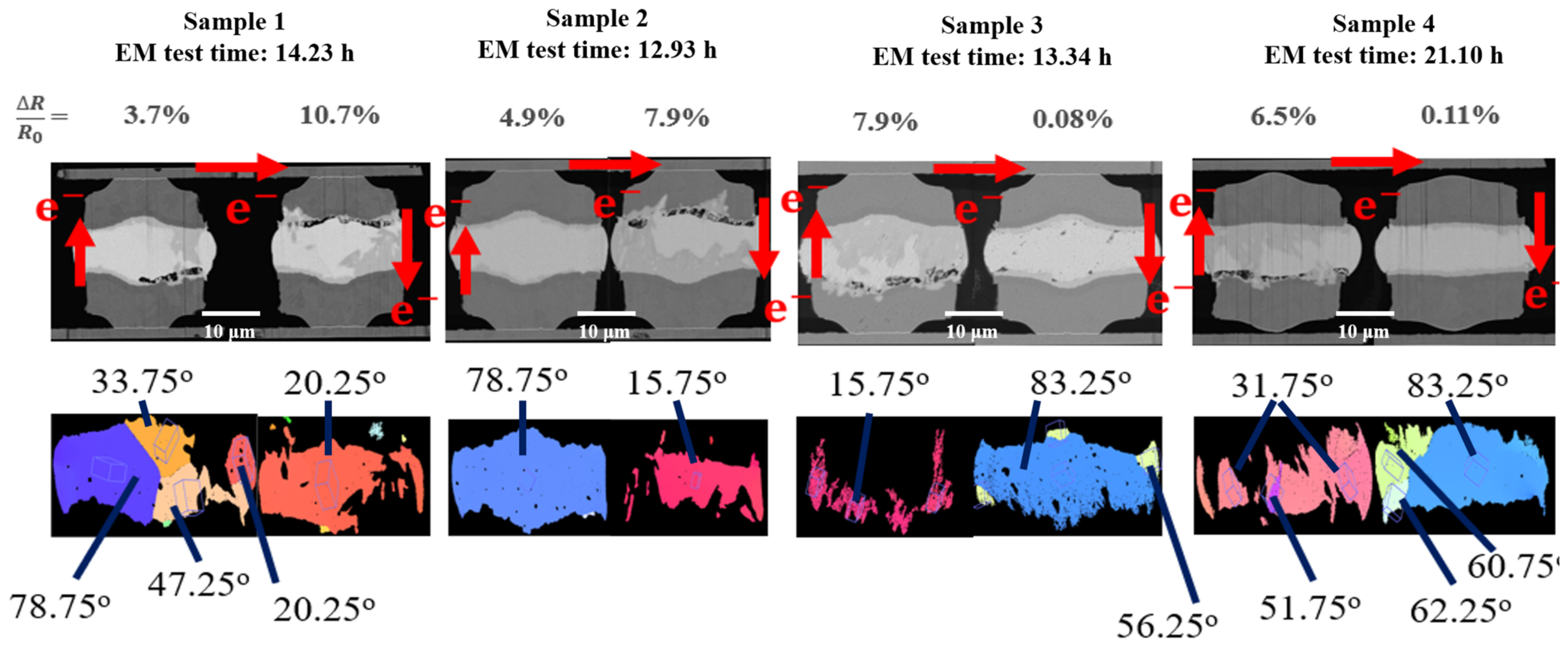
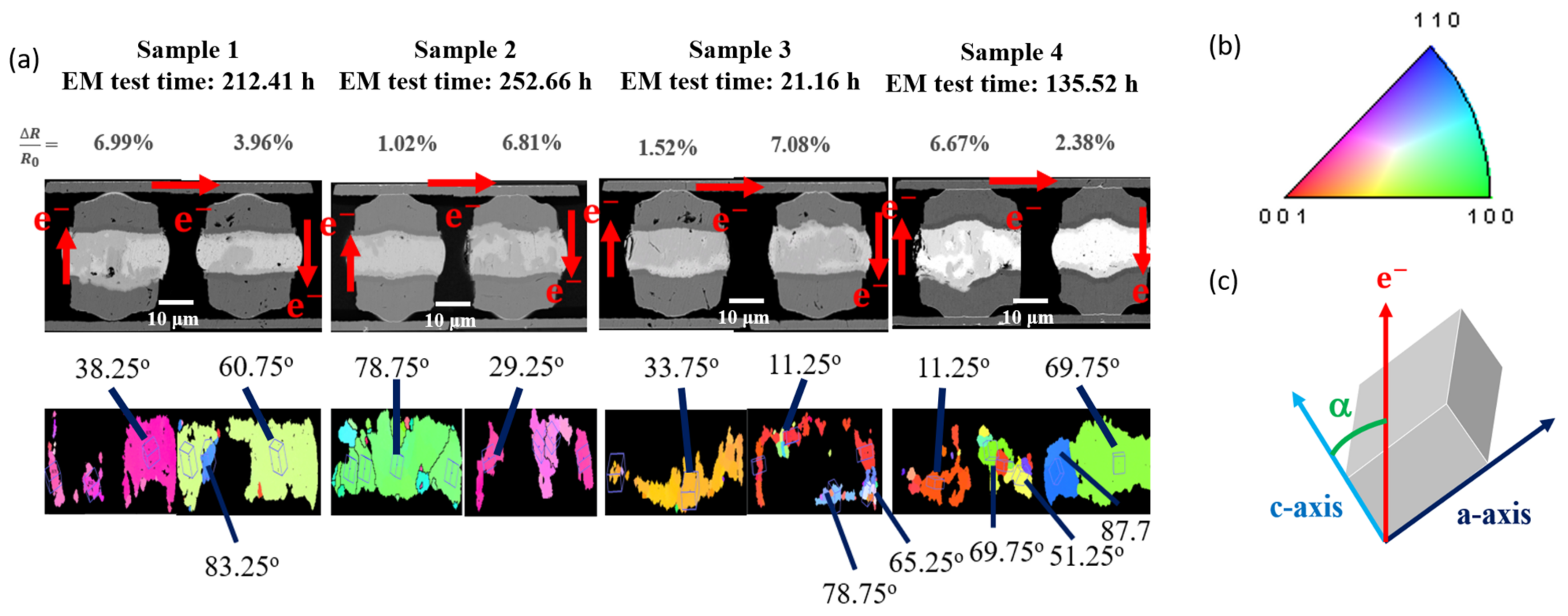
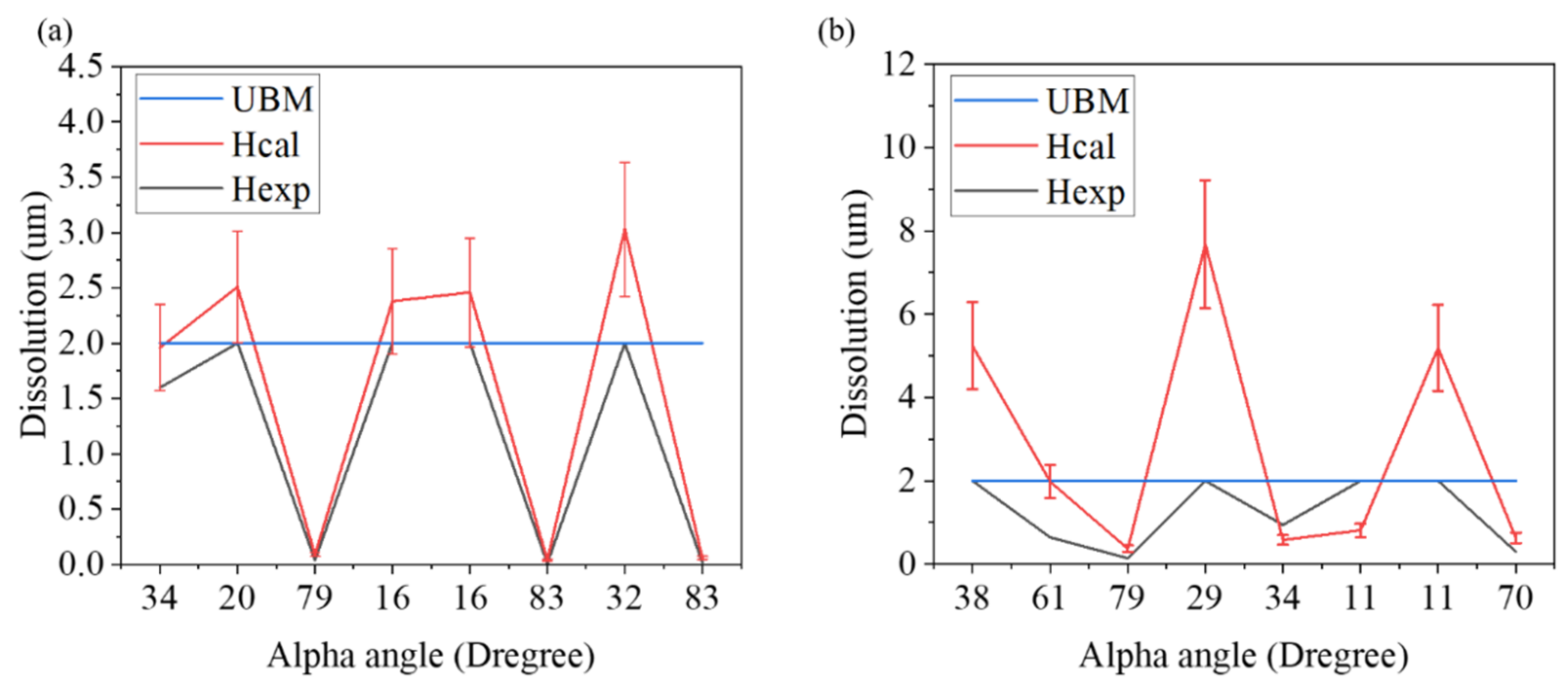
| Sample No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kelvin Position | Left | Right | Left | Right | Left | Right | Left | Right |
| Time (h) | 14.23 | 12.91 | 13.34 | 21.10 | ||||
| Rate (µm/h) | 0.137 | 0.176 | 0.007 | 0.185 | 0.185 | 0.003 | 0.144 | 0.003 |
| α-angle | 34 | 20 | 79 | 16 | 16 | 83 | 32 | 83 |
| H (exp., µm) | 1.6 | 2 | 0.04 | 2 | 2 | 0.01 | 2 | 0.02 |
| H (cal., µm) | 1.96 | 2.51 | 0.09 | 2.38 | 2.46 | 0.04 | 3.03 | 0.06 |
| Sample No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kelvin Position | Left | Right | Left | Right | Left | Right | Left | Right |
| Time (h) | 212.41 | 252.66 | 21.16 | 135.52 | ||||
| Rate (µm/h) | 0.024 | 0.009 | 0.001 | 0.030 | 0.027 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.005 |
| α-angle | 38 | 61 | 79 | 29 | 34 | 11 | 11 | 70 |
| H (exp., µm) | 2 | 0.64 | 0.14 | 2 | 0.94 | 2 | 2 | 0.3 |
| H (cal., µm) | 5.24 | 1.98 | 0.37 | 7.68 | 0.58 | 0.81 | 5.19 | 0.63 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, P.-N.; Lee, D.-L.; Tran, D.-P.; Shie, K.-C.; Tsou, N.-T.; Chen, C. Effect of Tin Grain Orientation on Electromigration-Induced Dissolution of Ni Metallization in SnAg Solder Joints. Materials 2022, 15, 7115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207115
Hsu P-N, Lee D-L, Tran D-P, Shie K-C, Tsou N-T, Chen C. Effect of Tin Grain Orientation on Electromigration-Induced Dissolution of Ni Metallization in SnAg Solder Joints. Materials. 2022; 15(20):7115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207115
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Po-Ning, Dai-Lung Lee, Dinh-Phuc Tran, Kai-Cheng Shie, Nien-Ti Tsou, and Chih Chen. 2022. "Effect of Tin Grain Orientation on Electromigration-Induced Dissolution of Ni Metallization in SnAg Solder Joints" Materials 15, no. 20: 7115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207115
APA StyleHsu, P.-N., Lee, D.-L., Tran, D.-P., Shie, K.-C., Tsou, N.-T., & Chen, C. (2022). Effect of Tin Grain Orientation on Electromigration-Induced Dissolution of Ni Metallization in SnAg Solder Joints. Materials, 15(20), 7115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207115







