Optimization of Thermo-Mechanical Fatigue Life for Eutectic Al–Si Alloy by the Ultrasonic Melt Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Preparation Process and Micro-Structure Analysis
2.2. Thermo-Mechanical Fatigue Process
3. Results and Discussion
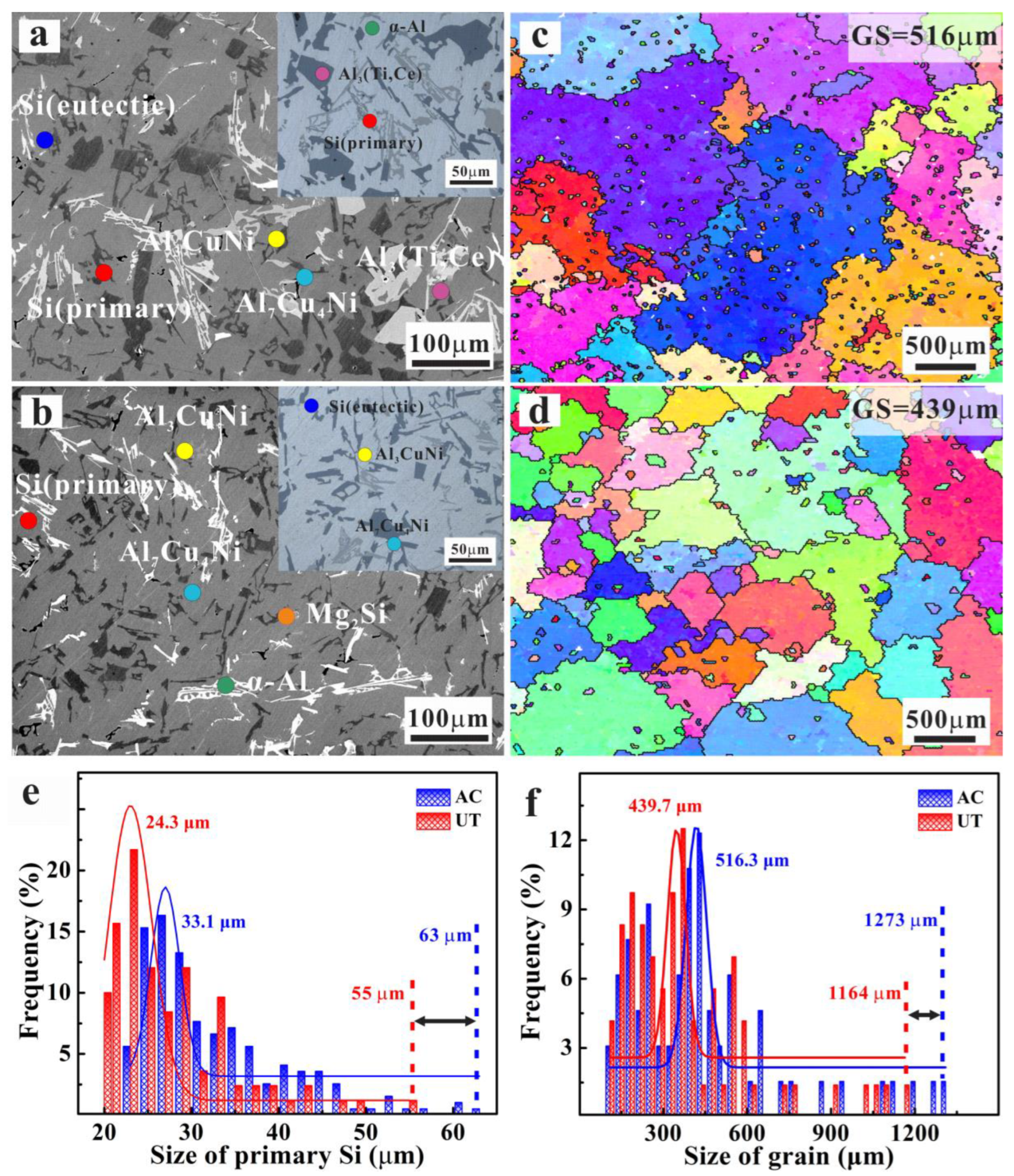
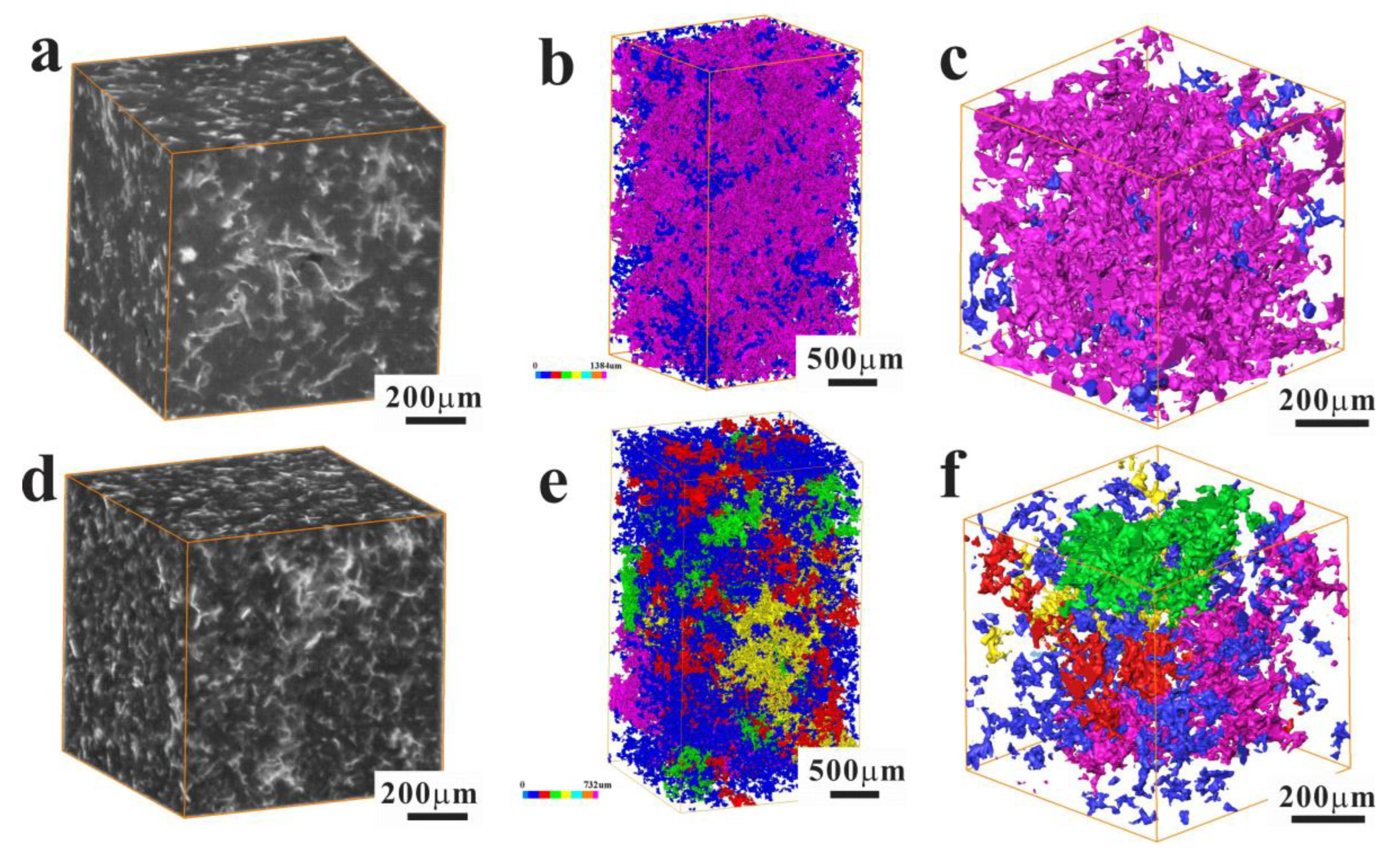
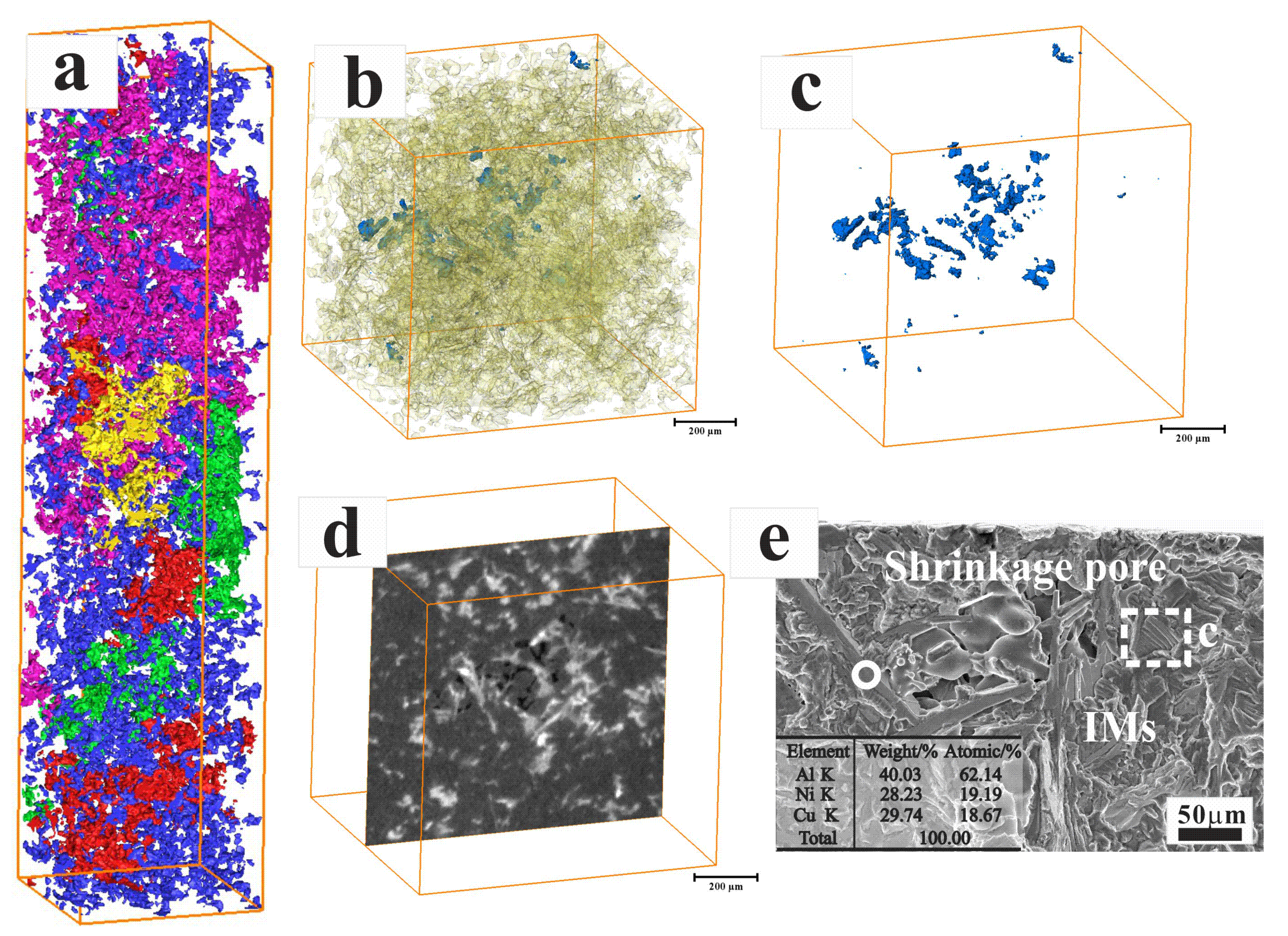
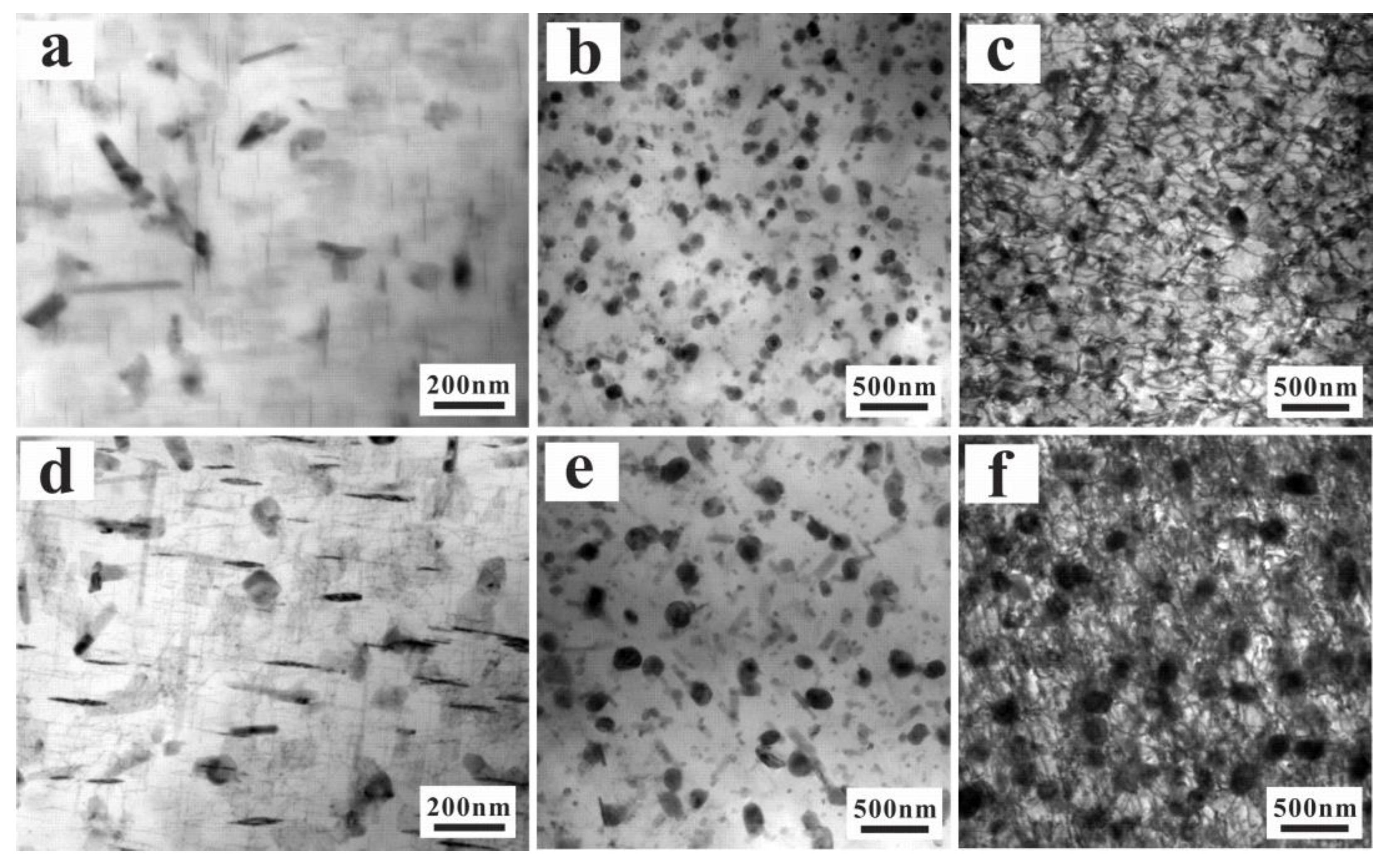
3.1. Micro-Structure
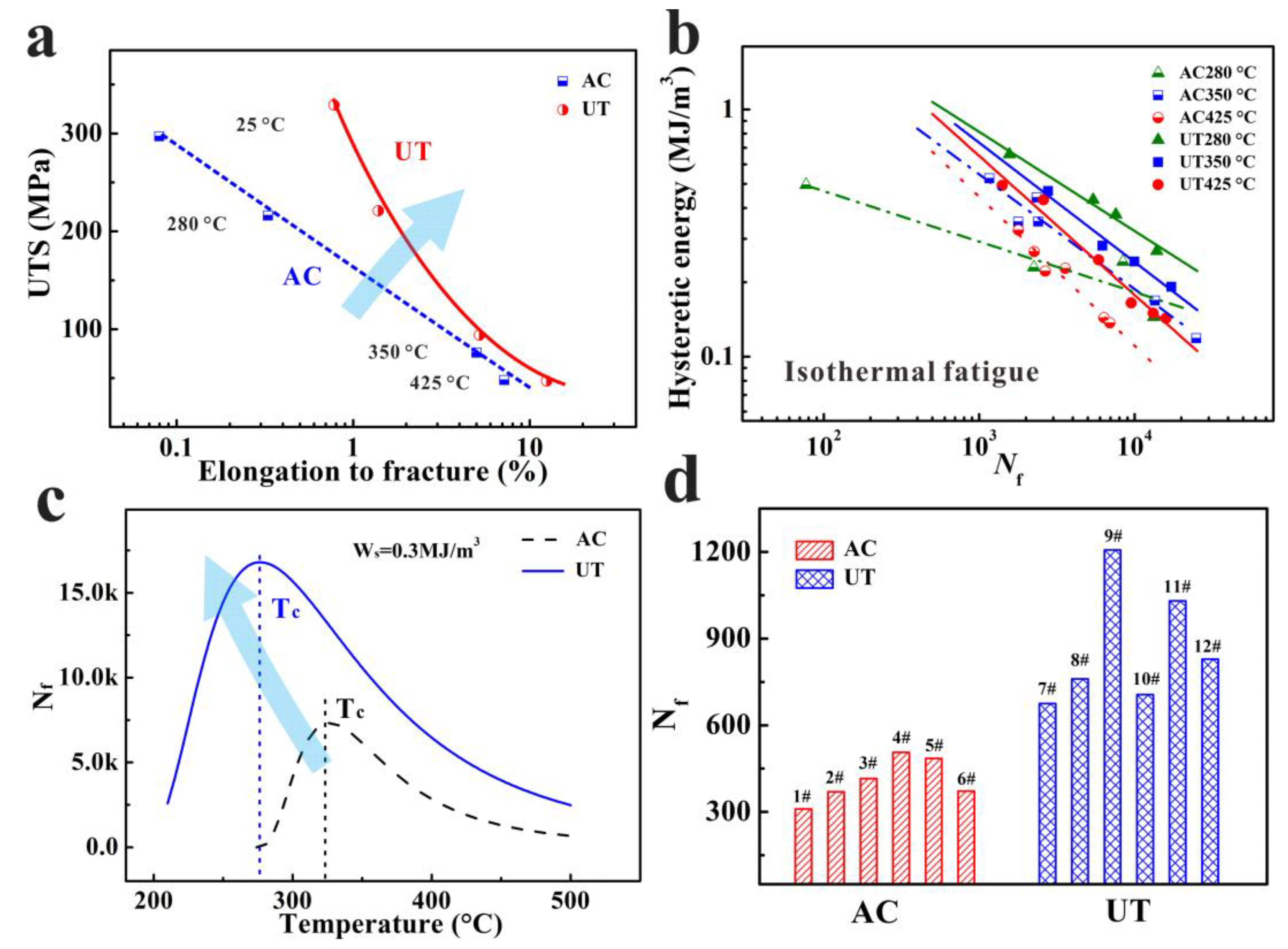
3.2. Tensile and Isothermal Low-Cycle Fatigue Properties
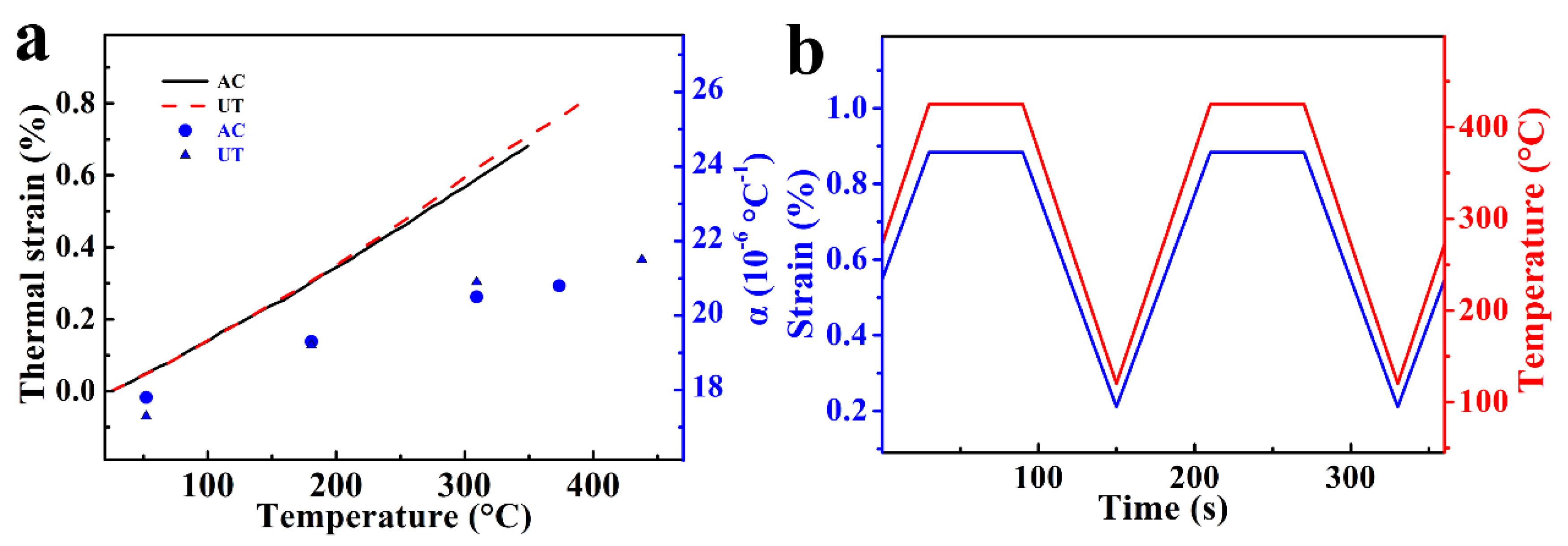
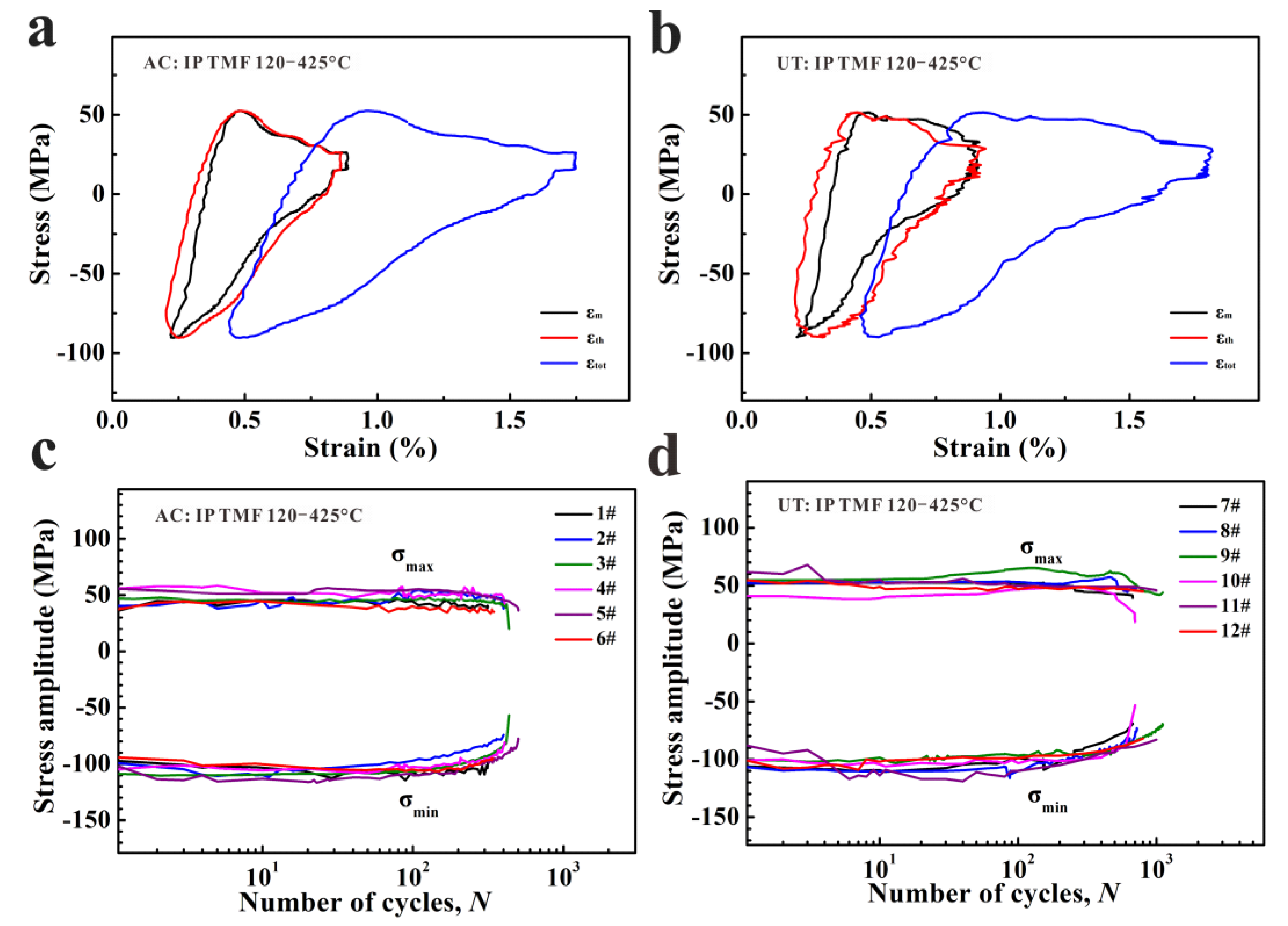
3.3. Thermo-Mechanical Fatigue Behaviors
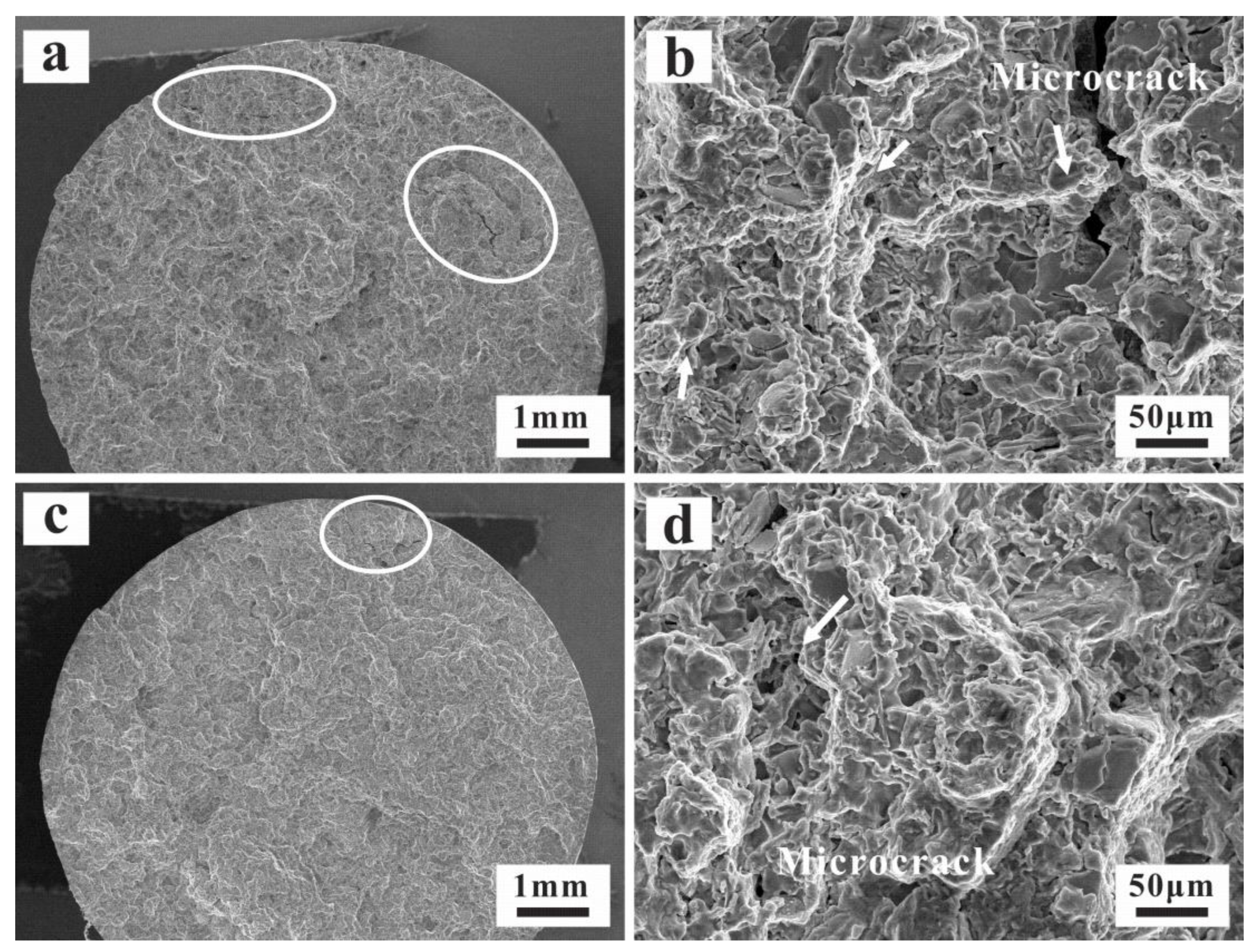
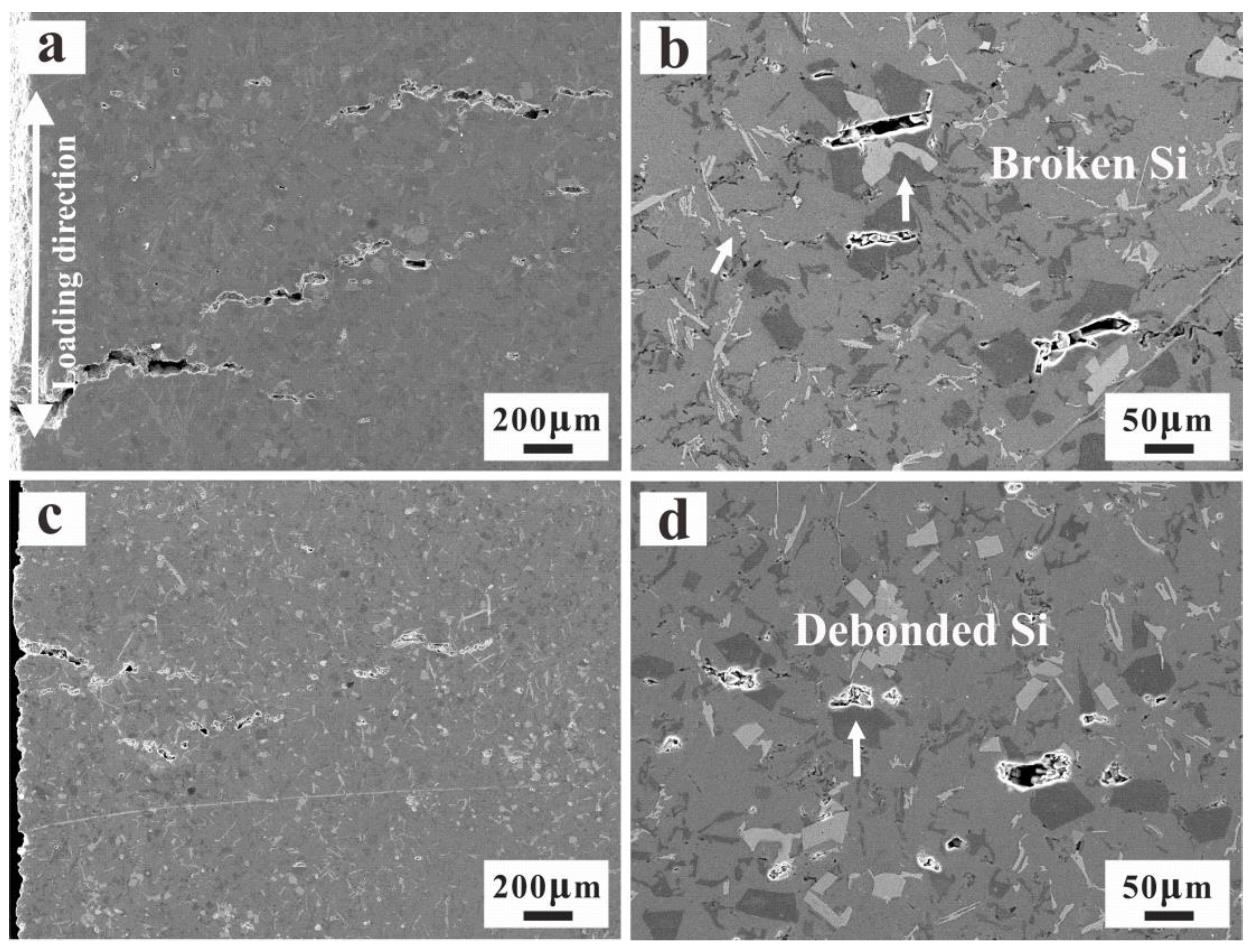
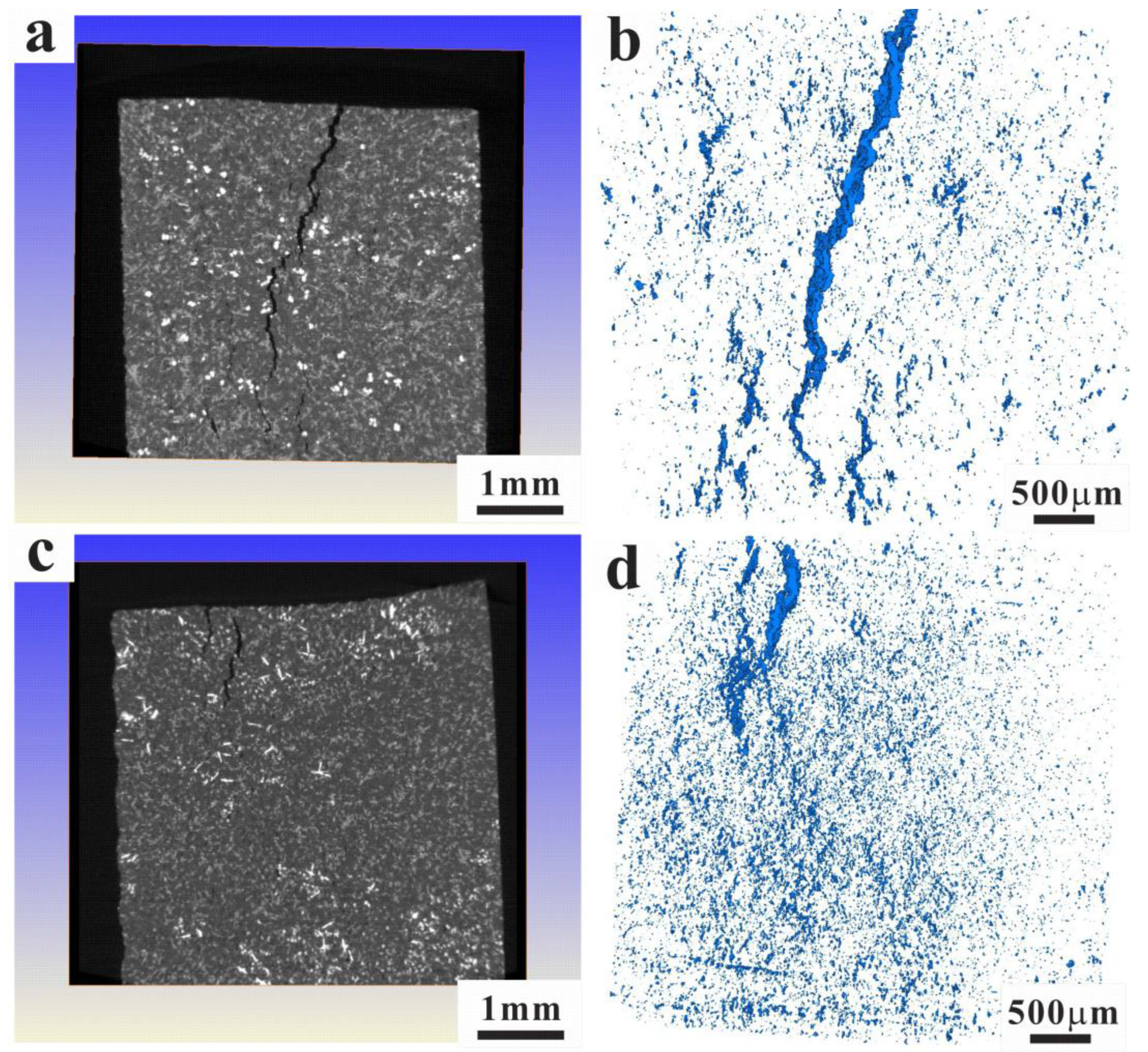
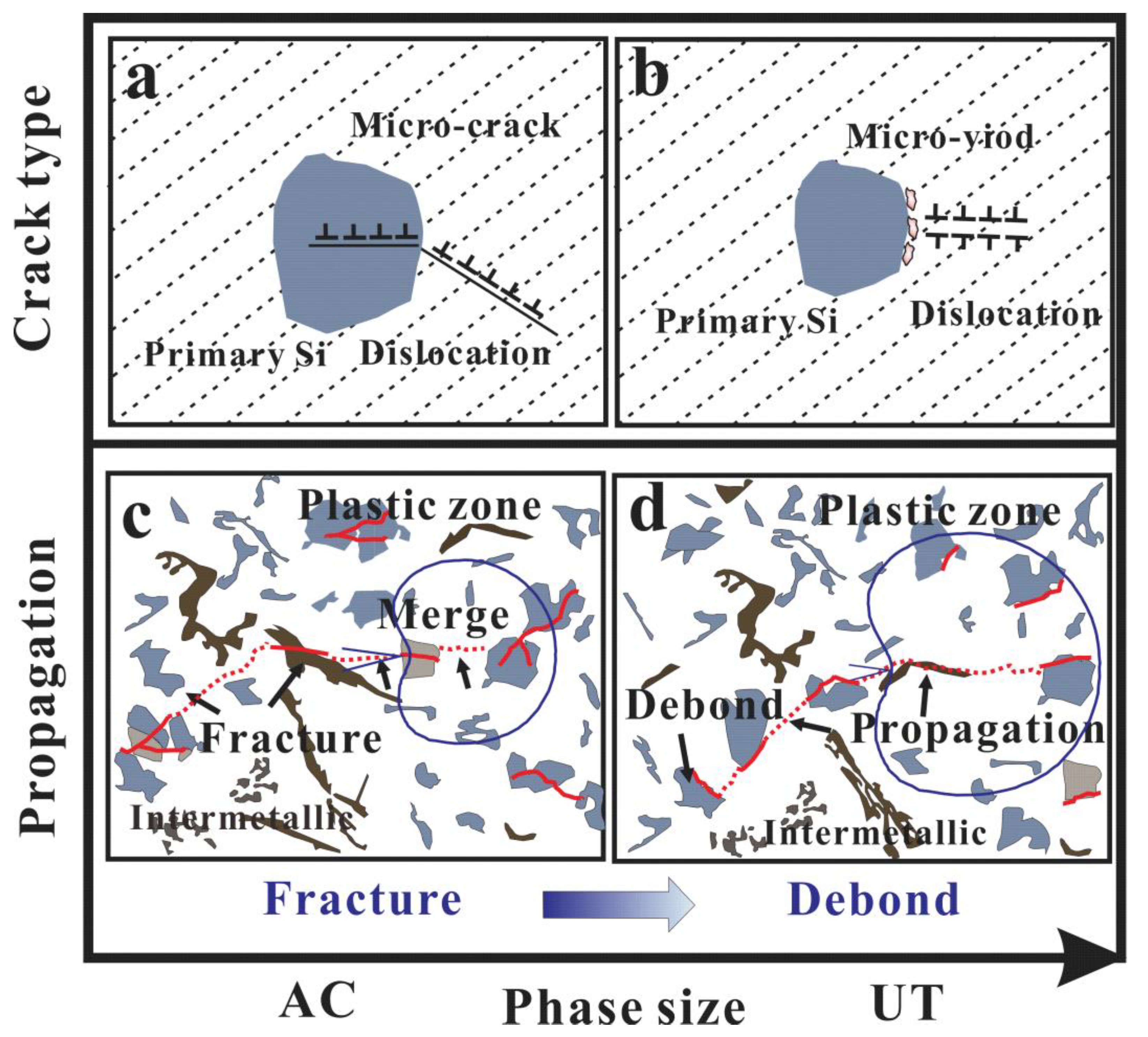
3.4. Thermo-Mechanical Fatigue Damage Mechanism
4. Conclusions
- The grain size, primary Si, and intermetallic compound are reduced significantly in the UT alloy. The tensile, isothermal low-cycle fatigue and TMF resistance are significantly improved due to the amelioration of the micro-structures. The UT alloy (805 ± 253 cycles) has about twice the TMF life of the AC alloy (403 ± 98 cycles);
- As a result of pilling-up of dislocations, the competitive effects of the critical strain/stress for fatigue crack nucleation can be found: one is primary Si fracture for the AC alloy with limited critical strain/stress for fatigue crack nucleation at fractured Si particles, and the other is primary Si debonding for the UT alloy with increasing critical fracture strain/stress. The micro-cracks are perpendicular to the loading direction for both alloys;
- After the crack initiation, the fractured or debonded primary phases provide the favorable conditions for further development of main cracks along pre-existing damage. The close-packed primary Si and intermetallic particles are the major cause of limited critical stress or strain for fatigue crack initiation for the AC alloy. The finer structures of the UT alloy have a positive impact on the TMF resistance. Reduced volume fractions of highly interconnected rigid phases can lead to the deformation reversibility and homogeneity for the UT alloy. The damage behaviors change from concentrated damage near then main crack to rather dispersed damage with fractured or debonded Si.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fischer, C.; Schweizer, C. Experimental investigation of the damage characteristics of two cast aluminium alloys: Part I–Temperature dependent low cycle and thermomechanical fatigue behavior. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 152, 106359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, M.; Barry, W.; Guy, J.; Ford, P.; Douglas, E.; Mark, T.; Nigel, Y. Development of a Structurally Optimized Heavy Duty Diesel Cylinder Head Design Capable of 250 Bar Peak Cylinder Pressure Operation. Sae Int. J. Engines 2011, 4, 2736–2755. [Google Scholar]
- Pierce, D.; Haynes, A.; Hughes, J.; Graves, R.; Maziasz, P.; Muralidharan, G.; Shyam, A.; Wang, B.; England, R.; Daniel, C. High temperature materials for heavy duty diesel engines: Historical and future trends. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 103, 109–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Pang, J.C.; Liu, H.Q.; Li, S.X.; Zhang, M.X.; Zhang, Z.F. Effect of constraint factor on the thermo-mechanical fatigue behavior of an Al-Si eutectic alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 783, 139279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Ye, B.; Zuo, L.; Qi, R.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Huang, R.; Ding, W.; Yao, J.; Wang, C. Effects of Zr, Ti and Sc additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-0.4Cu-0.14Si-0.05Mg-0.2Fe alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Q.; Pang, J.C.; Wang, M.; Li, S.X.; Zhang, Z.F. Effect of temperature on the mechanical properties of Al–Si–Cu–Mg–Ni–Ce alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 824, 141762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, G.; Kumaran, S.; Rao, T.S. Effect of graphite and transition elements (Cu, Ni) on high temperature tensile behaviour of Al-Si Alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 128, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, X. Quantitative comparison of three Ni-containing phases to the elevated-temperature properties of Al-Si piston alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 7132–7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, K.; Li, Y.; Zhao, D.; Liu, X. Evolution of nickel-rich phases in Al-Si-Cu-Ni-Mg piston alloys with different Cu additions. Mater. Des. 2012, 33, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Ye, B.; Zuo, L.; Qi, R.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Huang, R.; Ding, W. Effects of Ni content on low cycle fatigue and mechanical properties of Al-12Si-0.9Cu-0.8Mg- x Ni at 350 °C. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 706, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugelnig, K.; Germann, H.; Steffens, T.; Wilde, F.; Requena, G. Damage mechanisms and evolution during thermomechanical fatigue of cast near eutectic Al-Si piston alloys. In Proceedings of the Euromat 2017, Thessaloniki, Greece, 17–22 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Floweday, G.; Petrov, S.; Tait, R.B.; Press, J. Thermo-mechanical fatigue damage and failure of modern high performance diesel pistons. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2011, 18, 1664–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Pang, J.C.; Liu, H.Q.; Li, S.X.; Zhang, Z.F. Property optimization of low-cycle fatigue in Al-Si piston alloy at elevated temperatures by ultrasonic melt treatment. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 4556–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Pang, J.C.; Liu, H.Q.; Li, S.X.; Zhang, Z.F. Influence of microstructures on the tensile and low-cycle fatigue damage behaviors of cast Al12Si4Cu3NiMg alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 759, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.-G.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, J.-M.; Cho, Y.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Yoon, W.-H. Improved mechanical properties of near-eutectic Al-Si piston alloy through ultrasonic melt treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 669, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.-G.; Lee, J.-M.; Cho, Y.-H.; Yoon, W.-H. Combined effects of ultrasonic melt treatment, Si addition and solution treatment on the microstructure and tensile properties of multicomponent Al Si alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S. Correlation of materials property and performance with internal structures evolvement revealed by laboratory X-ray tomography. Materials 2018, 11, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, S. Application of high resolution transmission x-ray tomography in material science. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2013, 49, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.X.; Pang, J.C.; Qiu, Y.; Li, S.X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.F. Thermo-mechanical fatigue property and life prediction of vermicular graphite iron. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 698, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidani, M.; Larouche, D. Application of cast Al-Si alloys in internal combustion engine components. Int. Mater. Rev. 2014, 59, 132–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minichmayr, R.; Riedler, M.; Winter, G.; Leitner, H.; Eichlseder, W. Thermo-mechanical fatigue life assessment of aluminium components using the damage rate model of Sehitoglu. Int. J. Fatigue 2008, 30, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Pang, J.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z. Tensile strength evolution and damage mechanisms of Al-Si piston alloy at different temperatures. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Pang, J.C.; Li, S.X.; Zhang, Z.F. Low-cycle fatigue properties and life prediction of Al-Si piston alloy at elevated temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 704, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.F. Extremely-low-cycle fatigue behaviors of Cu and Cu-Al alloys: Damage mechanisms and life prediction. Acta Mater. 2015, 83, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Perez, M.; Poole, W.J.; Wells, M. Numerical integration of the Gibbs-Thomson equation for multicomponent systems. Scr. Mater. 2012, 66, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Gottstein, G.; Shvindlerman, L.S. Generalized Gibbs-Thomson equation for nanoparticles at grain boundaries. Acta Mater. 2017, 129, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M. Gibbs-Thomson effects in phase transformations. Scr. Mater. 2005, 52, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughrabi, H. Cyclic slip irreversibilities and the evolution of fatigue damage. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2009, 40, 431–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.B.; Houria, M.I.; Fathallah, R.; Sidhom, H. The effect of interacting defects on the HCF behavior of Al-Si-Mg aluminum alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 779, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.S. Roles of microstructure in fatigue crack initiation. Int. J. Fatigue 2010, 32, 1428–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangid, M.D. The physics of fatigue crack initiation. Int. J. Fatigue 2013, 57, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, T.; Löhe, D.; Luft, J.; Henne, I. Damage mechanisms of cast Al-Si-Mg alloys under superimposed thermal-mechanical fatigue and high-cycle fatigue loading. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 468–470, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Element | Si | Cu | Ni | Mg | Ti | Zn | Ce | Fe | V | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC (%) | 12.10 | 3.42 | 2.16 | 0.82 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.24 | 0.016 | Bal. |
| UT (%) | 11.81 | 3.52 | 2.26 | 0.85 | 0.20 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.26 | 0.017 | Bal. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Pang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z. Optimization of Thermo-Mechanical Fatigue Life for Eutectic Al–Si Alloy by the Ultrasonic Melt Treatment. Materials 2022, 15, 7113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207113
Wang M, Pang J, Liu X, Wang J, Liu Y, Li S, Zhang Z. Optimization of Thermo-Mechanical Fatigue Life for Eutectic Al–Si Alloy by the Ultrasonic Melt Treatment. Materials. 2022; 15(20):7113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207113
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Meng, Jianchao Pang, Xinfeng Liu, Jianqiu Wang, Yongquan Liu, Shouxin Li, and Zhefeng Zhang. 2022. "Optimization of Thermo-Mechanical Fatigue Life for Eutectic Al–Si Alloy by the Ultrasonic Melt Treatment" Materials 15, no. 20: 7113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207113
APA StyleWang, M., Pang, J., Liu, X., Wang, J., Liu, Y., Li, S., & Zhang, Z. (2022). Optimization of Thermo-Mechanical Fatigue Life for Eutectic Al–Si Alloy by the Ultrasonic Melt Treatment. Materials, 15(20), 7113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207113






