The Unprecedented Role of 3D Printing Technology in Fighting the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
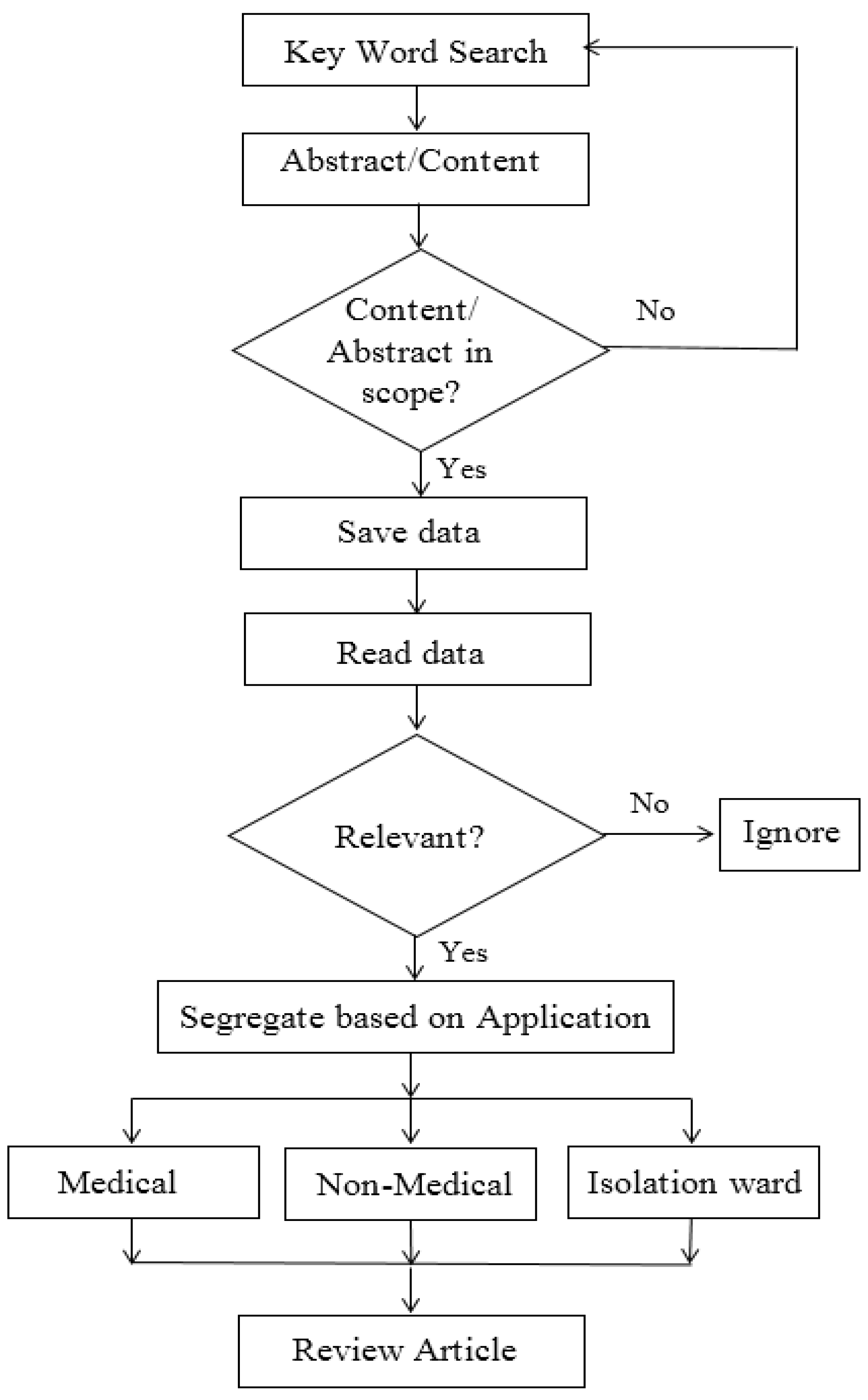
2. Methodology
3. COVID-19 and 3D Printing
4. AM/3D Printing in Medical Applications during COVID-19
4.1. AM/3D-Printed PPE
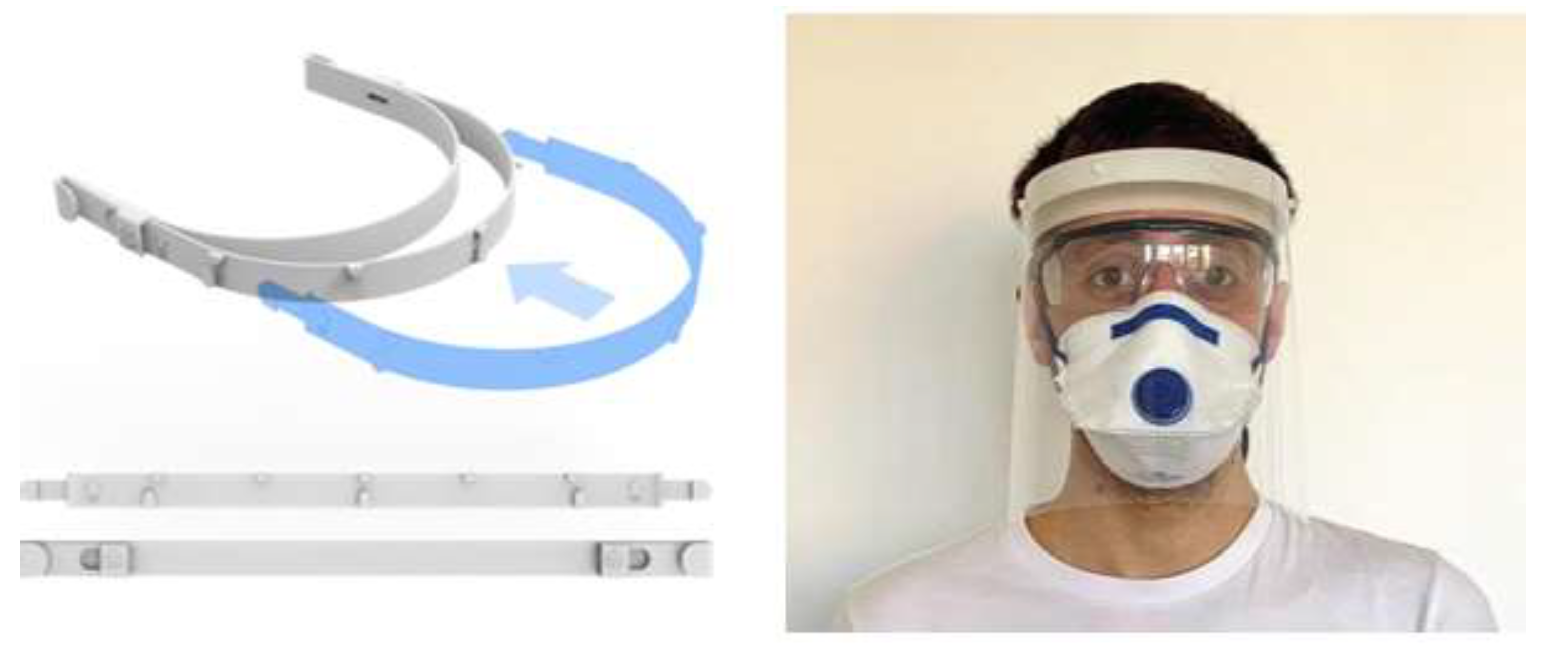
4.1.1. AM/3D-Printed Masks and Face Shields
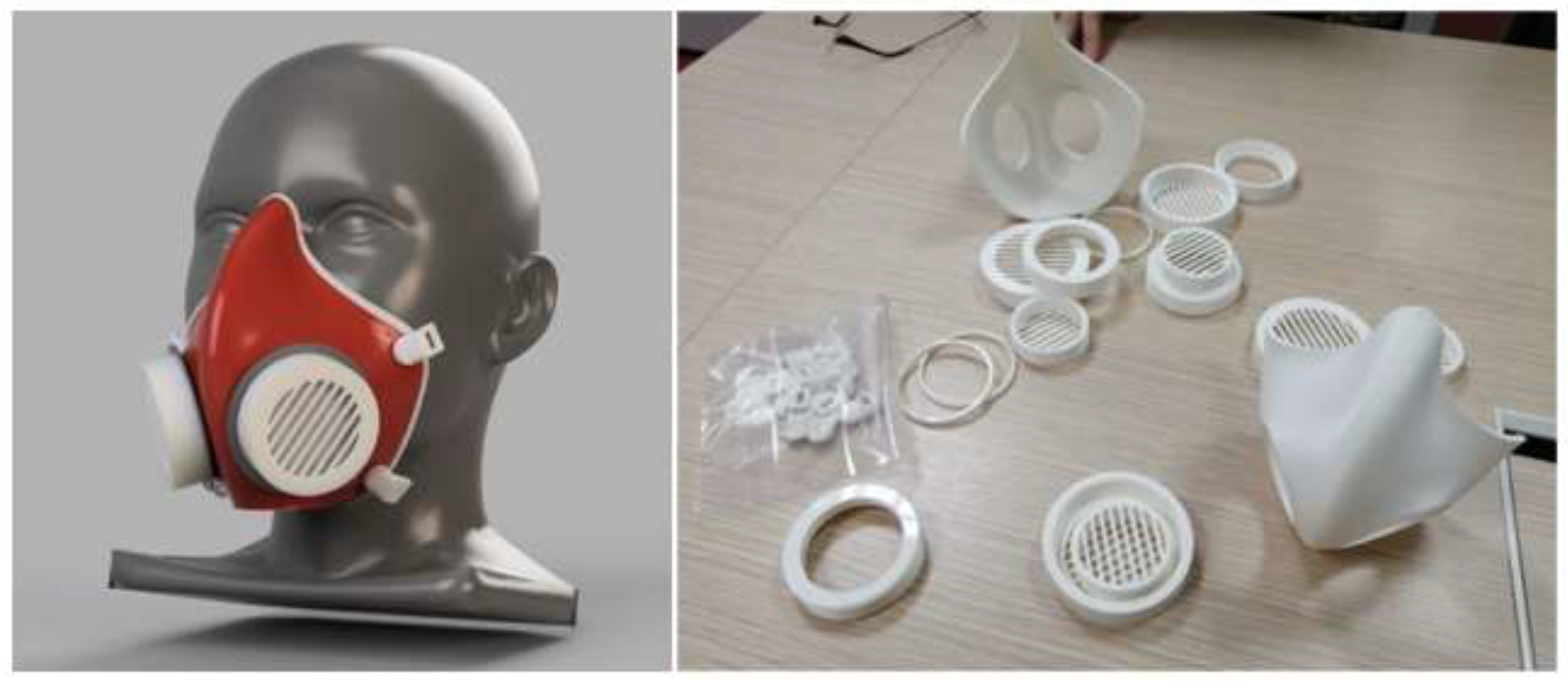
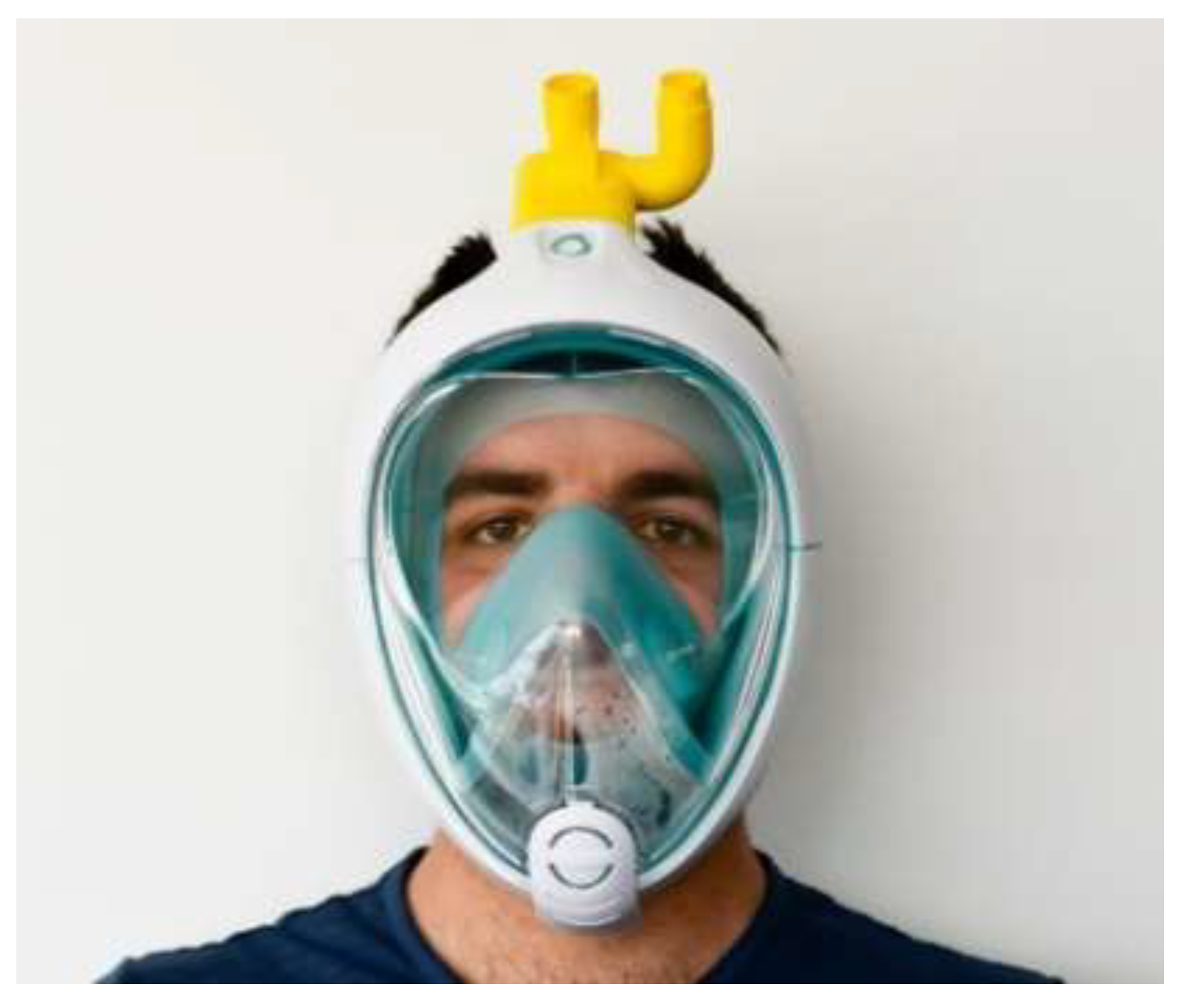
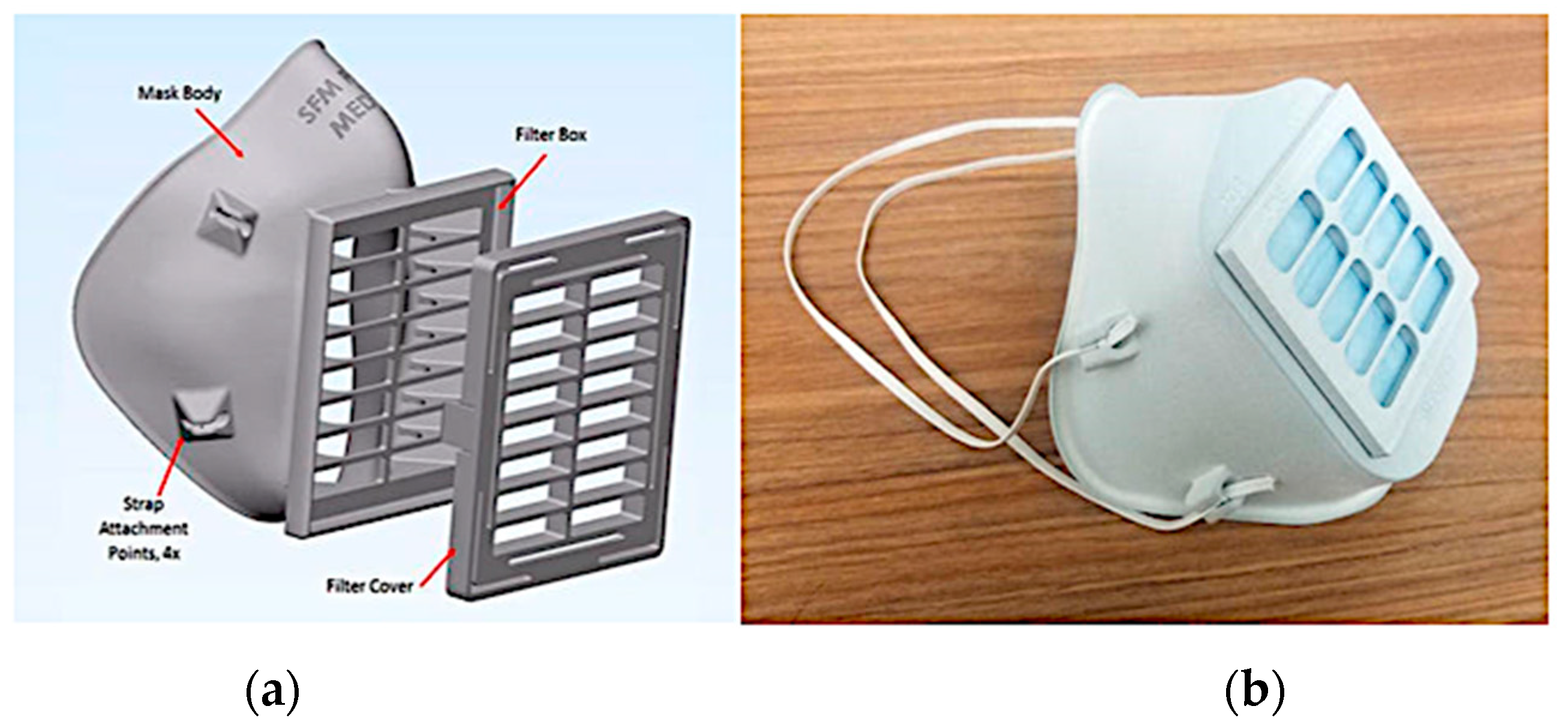
4.1.2. AM/3D-Printed Respirator
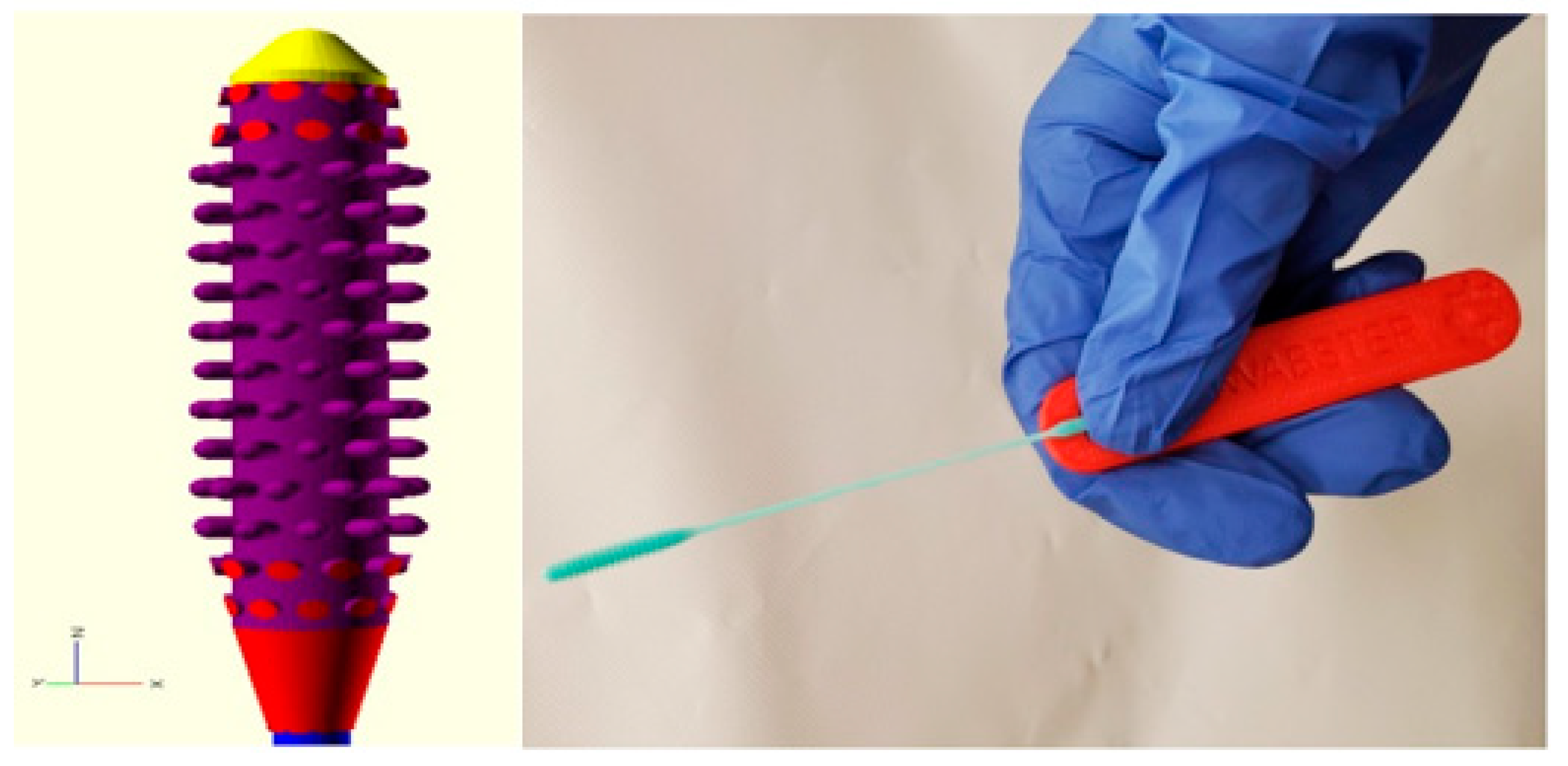
4.2. AM/3D-Printed Nasopharyngeal Swabs
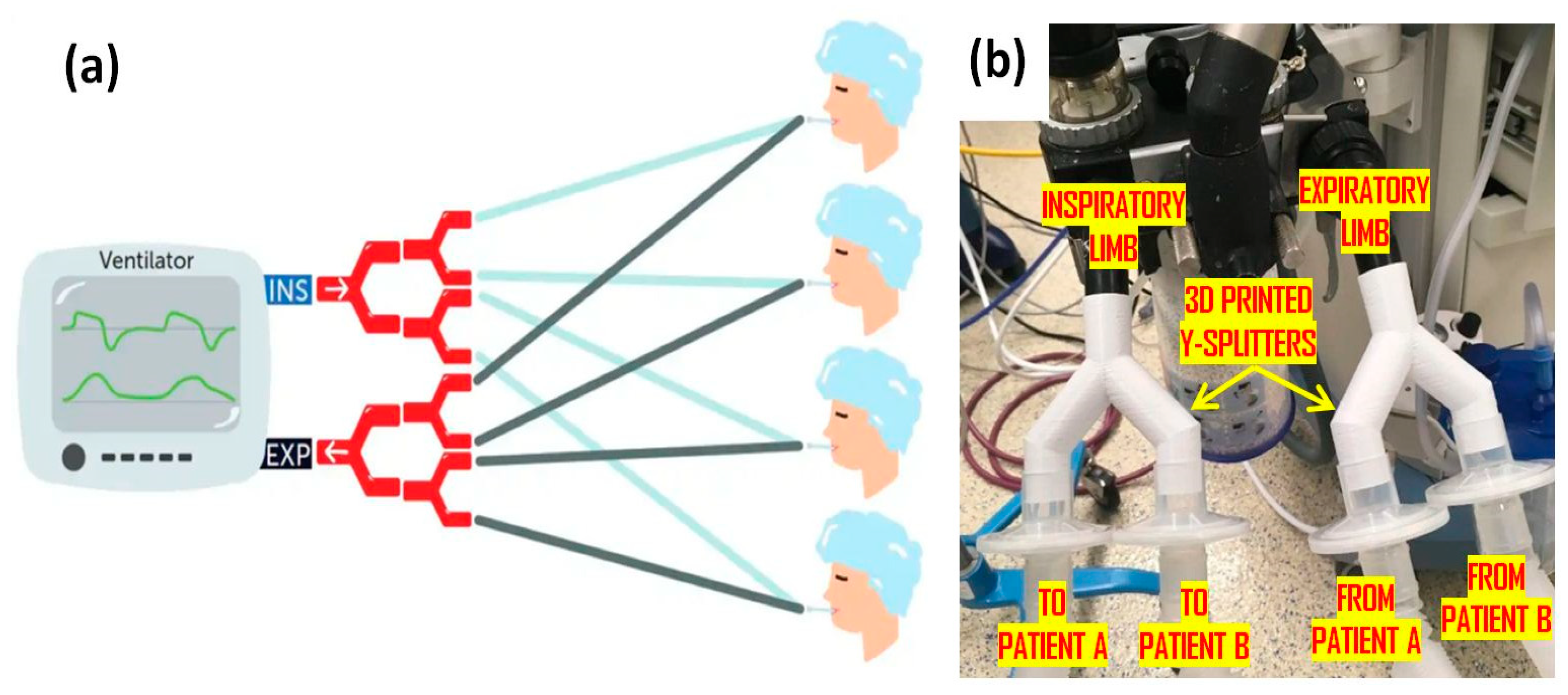
4.3. AM/3D-Printed Ventilators and Valves
5. AM/3D Printing in Non-Medical Applications of COVID-19
6. AM/3D Concrete Printing and COVID-19 Pandemic
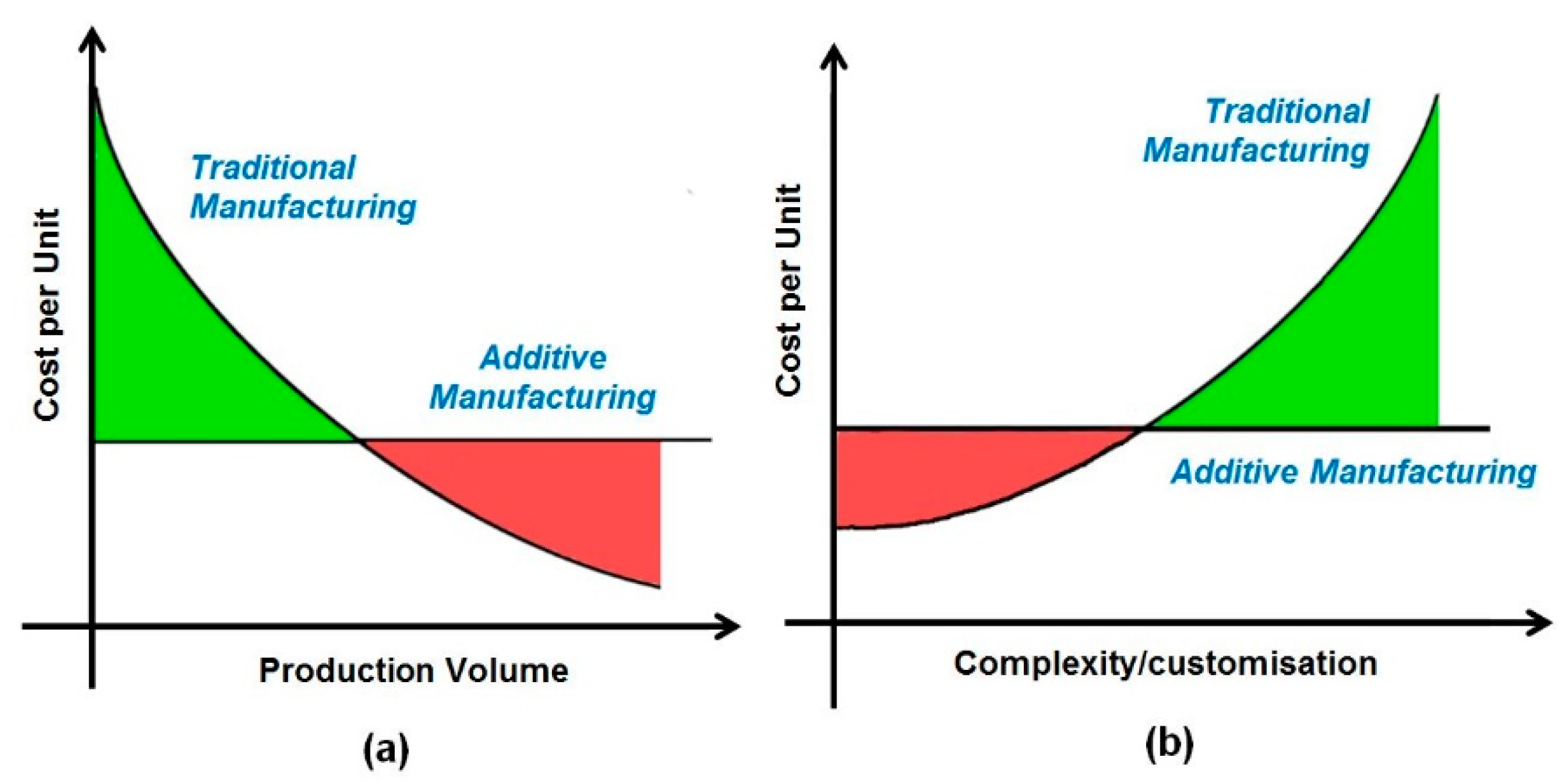
7. Traditional Manufacturing vs. 3D Printing
8. Use of AM Technology in India
9. Summary and Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Coronavirus. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 7 February 2021).
- Clipper, B. The Influence of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Technology: Adoption in Health Care. Nurse Lead. 2020, 18, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19—3 August 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-covid-19---3-august-2022 (accessed on 18 September 2022).
- Balacchi, C.; Brandi, N.; Ciccarese, F.; Coppola, F.; Lucidi, V.; Bartalena, L.; Parmeggiani, A.; Paccapelo, A.; Golfieri, R. Comparing the first and the second waves of COVID-19 in Italy: Differences in epidemiological features and CT findings using a semi-quantitative score. Emerg. Radiol. 2021, 28, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciapaglia, G.; Cot, C.; Sannino, F. Second wave COVID-19 pandemics in Europe: A temporal playbook. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, R.S.; Vergara, T.R.C. The COVID-19 second wave: A perspective to be explored. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 25, 101537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxminarayan, R.; Jameel, S.; Sarkar, S. India’s Battle against COVID-19: Progress and Challenges. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1343–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Gupta, P.K.; Srivastava, A. A review of modern technologies for tackling COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishack, S.; Lipner, S.R. Applications of 3D Printing Technology to Address COVID-19–Related Supply Shortages. Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, 771–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19—11 March 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020 (accessed on 7 February 2021).
- Vaishya, R.; Haleem, A.; Vaish, A.; Javaid, M. Emerging Technologies to Combat the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2020, 10, 409–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhouideg, S. Impact of 3D printed medical equipment on the management of the COVID19 pandemic. Int. J. Health Plan. Manag. 2020, 35, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economic and Operational Impacts of COVID-19 to Manufacturers|NAM. Available online: https://www.nam.org/coronasurvey/ (accessed on 7 February 2021).
- Antreas, K.; Piromalis, D. Employing a Low-Cost Desktop 3D Printer: Challenges, and How to Overcome Them by Tuning Key Process Parameters. Int. J. Mech. Appl. 2021, 10, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikkanna, N.; Krishnapillai, S.; Ramachandran, V. Static and dynamic flexural behaviour of printed polylactic acid with thermal annealing: Parametric optimisation and empirical modelling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 119, 1179–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikkanna, N.; Logakannan, K.P.; Krishnapillai, S.; Ramachandran, V. Quasi-static compression performance of material extrusion enabled re-entrant diamond auxetic metamaterial: Fabrication, tuning the geometrical parameters and fibre reinforcements. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 179, 109550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advincula, R.C.; Dizon, J.R.C.; Chen, Q.; Niu, I.; Chung, J.; Kilpatrick, L.; Newman, R. Additive manufacturing for COVID-19: Devices, materials, prospects, and challenges. MRS Commun. 2020, 10, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyouha, S.; Almazeedi, S.; Alghounaim, M.; Al-Mutawa, Y.; Alsabah, S. Polyester tipped 3-dimensionally printed swab that costs less than US$0.05 and can easily and rapidly be mass produced. BMJ Innov. 2020, 6, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choong, Y.Y.C.; Tan, H.W.; Patel, D.C.; Choong, W.T.N.; Chen, C.-H.; Low, H.Y.; Tan, M.J.; Patel, C.D.; Chua, C.K. The global rise of 3D printing during the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 637–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Chen, B.; Liang, Y.; Hu, L.; Jiang, G. 3D Printing Challenges in Enabling Rapid Response to Public Health Emergencies. Innovation 2020, 1, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombs, C. Will COVID-19 be the tipping point for the Intelligent Automation of work? A review of the debate and implications for research. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 55, 102182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, W.K.; Lorber, B.; Paudel, A. Can 3D printing of oral drugs help fight the current COVID-19 pandemic (and similar crisis in the future)? Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 899–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarfaoui, M.; Nachtane, M.; Goda, I.; Qureshi, Y.; Benyahia, H. 3D printing to support the shortage in personal protective equipment caused by COVID-19 pandemic. Materials 2020, 13, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, S.T.; Ballard, D.H. 3D Printed Face Shields: A Community Response to the COVID-19 Global Pandemic. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, 905–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attaran, M. 3D Printing Role in Filling the Critical Gap in the Medical Supply Chain during COVID-19 Pandemic. Am. J. Ind. Bus. Manag. 2020, 10, 988–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Noguerol, T.; Paulano-Godino, F.; Menias, C.O.; Luna, A. Lessons learned from COVID-19 and 3D printing. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 46, 659–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 8 Ways 3D Printing is Helping to Fight Coronavirus—ASME. Available online: https://www.asme.org/topics-resources/content/8-ways-3d-printing-is-helping-to-fight-coronavirus (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- 3D Printing in FDA’s Rapid Response to COVID-19|FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/emergency-preparedness-and-response/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19/3d-printing-fdas-rapid-response-covid-19 (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- Airbus to Produce 3D-Printed Hospital Visors in Fight against COVID-19—Company—Airbus. Available online: https://www.airbus.com/newsroom/press-releases/en/2020/04/airbus-to-produce-3dprinted-hospital-visors-in-fight-against-covid19.html (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- Ford Works With 3M, GE, UAW to Speed Production of Respirators for Healthcare Workers, Ventilators for Coronavirus Patients|Ford Media Center. Available online: https://media.ford.com/content/fordmedia/fna/us/en/news/2020/03/24/ford-3m-ge-uaw-respirators-ventilators.html (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- GM Adds Face Shields and Gowns to COVID-19 Personal Protection Equipment Production Push. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/edgarsten/2020/04/19/gm-adds-to-its-personal-protection-equipment-production/?sh=1773f638541d (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- Nagami Design 3D Prints Protective Masksto Help Fighting COVID-19. Available online: https://nagami.design/en/project/covid19-masks/ (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- COVID-19 and 3D Printing. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/stevebanker/2020/04/13/covid-19-and-3d-printing/?sh=642744733f7a (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- News-Yingchuang Building Technique (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. (WinSun). Available online: http://winsun3d.com/En/News/news_inner/id/566 (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- Tino, R.; Moore, R.; Antoline, S.; Ravi, P.; Wake, N.; Ionita, C.N.; Morris, J.M.; Decker, S.J.; Sheikh, A.; Rybicki, F.J.; et al. COVID-19 and the role of 3D printing in medicine. 3D Print. Med. 2020, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maracaja, L.; Blitz, D.; Maracaja, D.L.V.; Walker, C.A. How 3D Printing Can Prevent Spread of COVID-19 Among Healthcare Professionals During Times of Critical Shortage of Protective Personal Equipment. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesthesia 2020, 34, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.S. Ventilators by Lottery: The Least Unjust Form of Allocation in the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic. Chest 2020, 158, 890–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vordos, N.; Gkika, D.A.; Maliaris, G.; Tilkeridis, K.E.; Antoniou, A.; Bandekas, D.V.; Mitropoulos, A.C. How 3D printing and social media tackles the PPE shortage during COVID-19 pandemic. Saf. Sci. 2020, 130, 104870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Food and Drug Administration; Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH); Office of Product Evaluation and Quality (OPEQ). Enforcement Policy for Telethermographic Systems During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Public Health Emergency. In Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff; Food and Drug Administration: Rockville, MD, USA, 2020; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ford Partners with 3M, GE Healthcare to Make Respirators, Ventilators and Face Shields Amid Coronavirus Outbreak. Available online: https://www.detroitnews.com/story/business/autos/ford/2020/03/24/ford-partners-3-m-ge-healthcare-respirators-ventilators-face-shields/2905986001/ (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- People Are 3D Printing Personal Protective Equipment to Help Hospitals With Shortage: NPR. Available online: https://www.npr.org/local/305/2020/04/01/825217523/people-are-3-d-printing-personal-protective-equipment-to-help-hospitals-with-shortage (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- Provenzano, D.; Rao, Y.J.; Mitic, K.; Obaid, S.N.; Pierce, D.; Huckenpahler, J.; Berger, J.; Goyal, S.; Loew, M.H. Rapid Prototyping of Reusable 3D-Printed N95 Equivalent Respirators at the George Washington University. Preprints 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recommended Guidance for Extended Use and Limited Reuse of N95 Filtering Facepiece Respirators in Healthcare Settings|NIOSH|CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/hcwcontrols/recommendedguidanceextuse.html (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- Navarro, M.; Michiardi, A.; Castaño, O.; Planell, J.A. Biomaterials in orthopaedics. J. R. Soc. Interface 2008, 5, 1137–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- About GrabCAD—GrabCAD—Resources. Available online: https://resources.grabcad.com/company/ (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- Breathing Mask with Screw-In Filters (Version 2)|3D CAD Model Library|GrabCAD. Available online: https://grabcad.com/library/breathing-mask-with-screw-in-filters-version-2-1 (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- 3D System Company. Stopgap Face Mask (SFM)—Instructions for Use; Department of Health and Human Services (HHS): Washington, DC, USA, 2020; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Shokrani, A.; Loukaides, E.G.; Elias, E.; Lunt, A.J.G. Exploration of alternative supply chains and distributed manufacturing in response to COVID-19; a case study of medical face shields. Mater. Des. 2020, 192, 108749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, N.J.; Laffey, J.G. Challenges and solutions for addressing critical shortage of supply chain for personal and protective equipment (PPE) arising from Coronavirus disease (COVID19) pandemic—Case study from the Republic of Ireland. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, D.; Nguyen, N.; Roser, S.M.; Abramowicz, S. 3D Printing of Face Shields During COVID-19 Pandemic: A Technical Note. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 78, 1275–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armijo, P.R.; Markin, N.W.; Nguyen, S.; Ho, D.H.; Horseman, T.S.; Lisco, S.J.; Schiller, A.M. 3D printing of face shields to meet the immediate need for PPE in an anesthesiology department during the COVID-19 pandemic. Am. J. Infect. Control 2020, 49, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantaros, A.; Laskaris, N.; Piromalis, D.; Ganetsos, T. Manufacturing Zero-Waste COVID-19 Personal Protection Equipment: A Case Study of Utilizing 3D Printing While Employing Waste Material Recycling. Circ. Econ. Sustain. 2021, 1, 851–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 3D-Printed Protective Visor—3DVerkstan—Quick to Print, Easy to Assemble. Available online: https://3dverkstan.se/protective-visor/ (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- Prusa Face Shield—Cover|PrusaPrinters. Available online: https://www.prusaprinters.org/prints/27318-prusa-protective-face-shield-cover-rc1-wip#_ga=2.137673648.1814275440.1610550741-724956520.1610550741 (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- 3d Systems. Reusable 3D-Printed Face Shield Frame The Outcome (SLS); Future Medicine: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, M.M.; Richardson, E.S.; Hernandez, N.M.; Bobbert, D.W.; Gall, K.; Fearis, P. Helmet Modification to PPE With 3D Printing During the COVID-19 Pandemic at Duke University Medical Center: A Novel Technique. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, S23–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viera-Artiles, J.; Valdiande, J.J. 3D-printable headlight face shield adapter. Personal protective equipment in the COVID-19 era. Am. J. Otolaryngol.—Head Neck Med. Surg. 2020, 41, 102576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easy—COVID19 ENG|Isinnova. Available online: https://www.isinnova.it/easy-covid19-eng/ (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- Decker, S.J.; Goldstein, T.A.; Ford, J.M.; Teng, M.N.; Pugliese, R.S.; Berry, G.J.; Pettengill, M.; Silbert, S.; Hazelton, T.R.; Wilson, J.W.; et al. 3D Printed Alternative to the Standard Synthetic Flocked Nasopharyngeal Swabs Used for COVID-19 testing. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 73, e3027–e3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starosolski, Z.; Admane, P.; Dunn, J.; Kaziny, B.; Huisman, T.A.G.M.; Annapragada, A. Design of 3D-printed nasopharyngeal swabs for children is enabled by radiologic imaging. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 2345–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, I.; Bulterys, P.L.; Chang, M.; DeSimone, J.M.; Fralick, J.; Herring, M.; Kabaria, H.; Kong, C.S.; Larson, B.; Lu, O.; et al. The rapid deployment of a 3D printed ‘Latticed’ nasopharyngeal swab for COVID-19 testing made using digital light synthesis. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.; Bond, K.; Isles, N.; Chong, B.; Johnson, D.; Druce, J.; Hoang, T.; Ballard, S.A.; Hall, V.; Muhi, S.; et al. Pandemic printing: A novel 3D-printed swab for detecting SARS-CoV-2. Med. J. Aust. 2020, 213, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallup, N.; Pringle, A.M.; Oberloier, S.; Tanikella, N.G.; Pearce, J.M. Parametric nasopharyngeal swab for sampling COVID-19 and other respiratory viruses: Open source design, SLA 3-D printing and UV curing system. HardwareX 2020, 8, e00135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oland, G.; Garner, O.; de St Maurice, A. Prospective clinical validation of 3D printed nasopharyngeal swabs for diagnosis of COVID-19. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 99, 115257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 3D Printed COVID-19 Test Swabs|Formlabs. Available online: https://formlabs.com/asia/covid-19-response/covid-test-swabs/ (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- Lyengar, K.; Bahl, S.; Vaishya, R.; Vaish, A. Challenges and solutions in meeting up the urgent requirement of ventilators for COVID-19 patients. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 499–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neyman, G.; Irvin, C.B. A Single Ventilator for Multiple Simulated Patients to Meet Disaster Surge. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2006, 13, 1246–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ventsplitter.org—Free 3D Printable Ventilator Circuit Splitter. Available online: http://ventsplitter.org/ (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- Coronavirus: 3D Printers Save Hospital with Valves—BBC News. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-51911070 (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- Meet The Italian Engineers 3D-Printing Respirator Parts For Free To Help Keep Coronavirus Patients Alive. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/amyfeldman/2020/03/19/talking-with-the-italian-engineers-who-3d-printed-respirator-parts-for-hospitals-with-coronavirus-patients-for-free/?sh=277a072778f1 (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- 3D Printing of Medical Devices, Accessories, Components, and Parts during the COVID-19 Pandemic|FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-covid-19-and-medical-devices/3d-printing-medical-devices-accessories-components-and-parts-during-covid-19-pandemic (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Manekiya, M.; Donelli, M. Monitoring the COVID-19 diffusion by combining wearable biosensors and smartphones. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 2021, 100, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Additive manufacturing and coronavirus 3D Printing Media Network—The Pulse of the AM Industry. Available online: https://www.3dprintingmedia.network/category/industry-2/additive-manufacturing-and-coronavirus/ (accessed on 7 February 2021).
- François, P.M.; Bonnet, X.; Kosior, J.; Adam, J.; Khonsari, R.H. 3D-printed contact-free devices designed and dispatched against the COVID-19 pandemic: The 3D COVID initiative. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 122, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hands-Free Door Opener: Technical Information—Materialise. Available online: https://www.materialise.com/en/hands-free-door-opener/technical-information (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- Abuzairi, T.; Sumantri, N.I.; Irfan, A.; Mohamad, R.M. Infrared thermometer on the wall (iThermowall): An open source and 3-D print infrared thermometer for fever screening. HardwareX 2021, 9, e00168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjayan, J.G.; Nematollahi, B. 3D Concrete Printing for Construction Applications; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddika, A.; al Mamun, M.A.; Ferdous, W.; Saha, A.K.; Alyousef, R. 3D-printed concrete: Applications, performance, and challenges. J. Sustain. Cem. Mater. 2020, 9, 127–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhumayani, H.; Gomaa, M.; Soebarto, V.; Jabi, W. Environmental assessment of large-scale 3D printing in construction: A comparative study between cob and concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.; Aditya, S.D.; Adarsh, R.N.; Nandan, M.; Dharek, M.S.; Sreedhara, B.M.; Prashant, S.C.; Sreekeshava, K.S. Additive Manufacturing of Concrete: Challenges and opportunities. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 814, 012022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennai: 350 Sqft House Can Be Built in Week at Low Cost. Available online: https://www.deccanchronicle.com/nation/current-affairs/251018/chennai-350-sqft-house-can-be-built-in-week-at-low-cost.html (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- This Startup Will Build Your House in Three Weeks at Half the Cost—Times of India. Available online: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/companies/this-startup-will-build-your-house-in-three-weeks-at-half-the-cost/articleshow/79614197.cms (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- WinSun Deploys 3D Printed Isolation Wards for Coronavirus Medical Staff » 3D Printing Media Network—The Pulse of the AM Industry. Available online: https://www.3dprintingmedia.network/winsun-3d-printed-isolation-wards-coronavirus-medical-workers/ (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- Shang, G.; Sun, C. Effect of 3D Printing Technology on 3C Product Manufacturing. World J. Eng. Technol. 2020, 8, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, G.; Johnson, A.; Marques, J.; Franco, A. Three-dimensional(3D) printing in forensic science–An emerging technology in India. Ann. 3D Print. Med. 2021, 1, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Bhadariya, V.; Singh, J.; Gupta, P.; Sharma, K.; Rasane, P. Materials for Food Printing. In Food Printing: 3D Printing in Food Industry; Sandhu, K., Singh, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Kader, N.A.; Sujatha, G.; Raj, T.; Patil, S. 3D printing in dentistry. J. 3D Print. Med. 2018, 2, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KRaichurkar, K.; Lochan, R.; Jacob, M.; Asthana, S. The Use of a 3D Printing Model in Planning a Donor Hepatectomy for Living Donor Liver Transplantation: First in India. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2020, 11, 515–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnada, S.; Gorle, D.B.; Bose, R.S.C.; Kiai, M.S.; Devi, M.; Raju, C.V.; Baydogan, N.; Nanda, K.K.; Marken, F.; Sharma, R.K. Current Insight into 3D Printing in Solid-State Lithium-Ion Batteries: A Perspective. Batter. Supercaps 2022, 5, e202200223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Goyal, P. Design and Development of Textile Fabrics Using 3D Printing Technology. ECS Trans. 2022, 107, 19313–19323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, D.; Srinivas, D.; Panda, B.; Sitharam, T.G. Processing of Cementitious Materials for 3D Concrete Printing. In Industry 4.0 and Advanced Manufacturing. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Chakrabarti, A., Suwas, S., Arora, M., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kumar, R.; Chohan, J.; Sharma, S.; Singh, J.; Ilyas, R.A.; Rangappa, S.M.; Siengchin, S.; Naresh, K.; Raghu, S.; et al. Investigation of copper reinforced Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene and Nylon 6 based thermoplastic polymer nanocomposite filaments for 3D printing of electronic components. High Perform. Polym. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




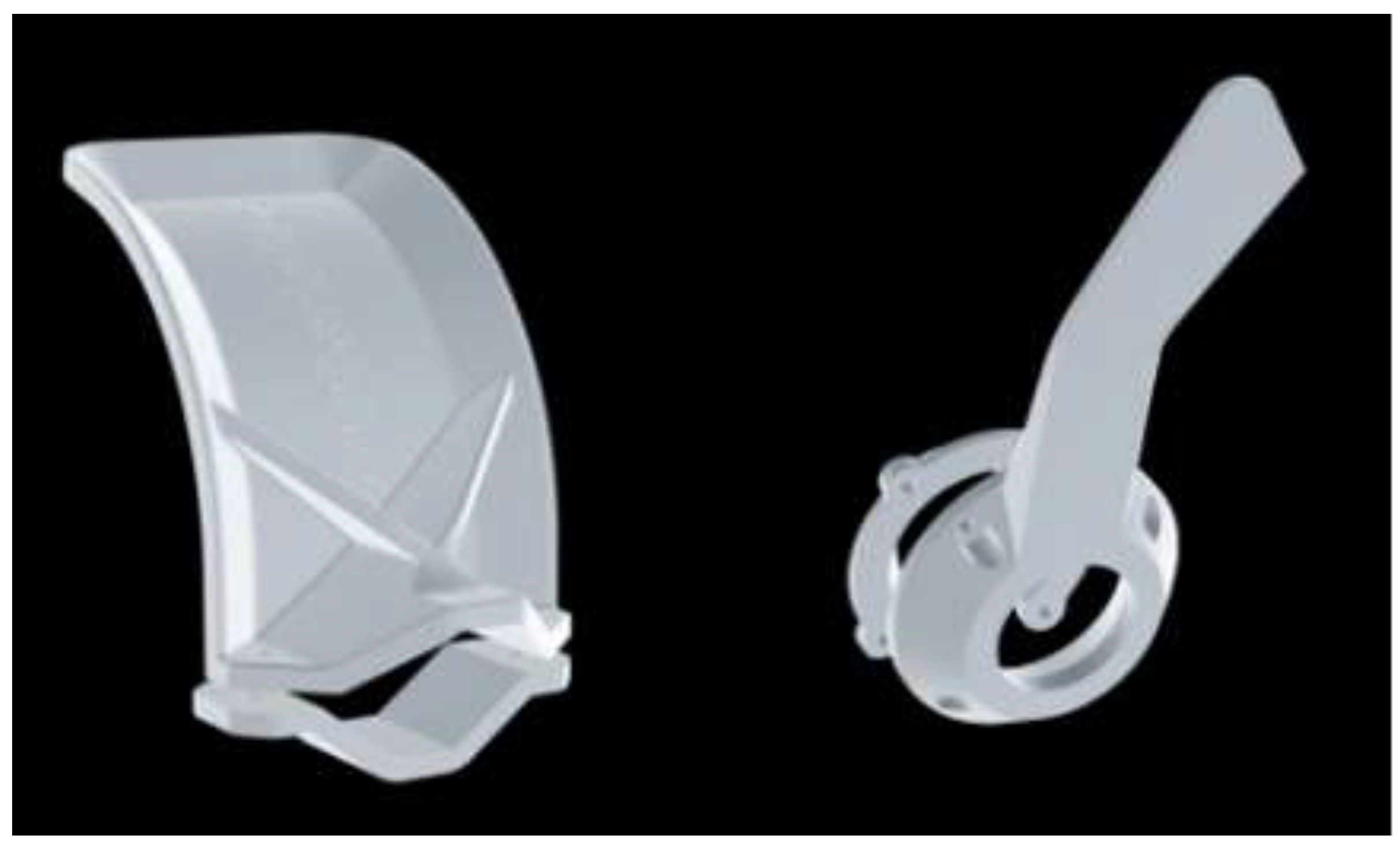
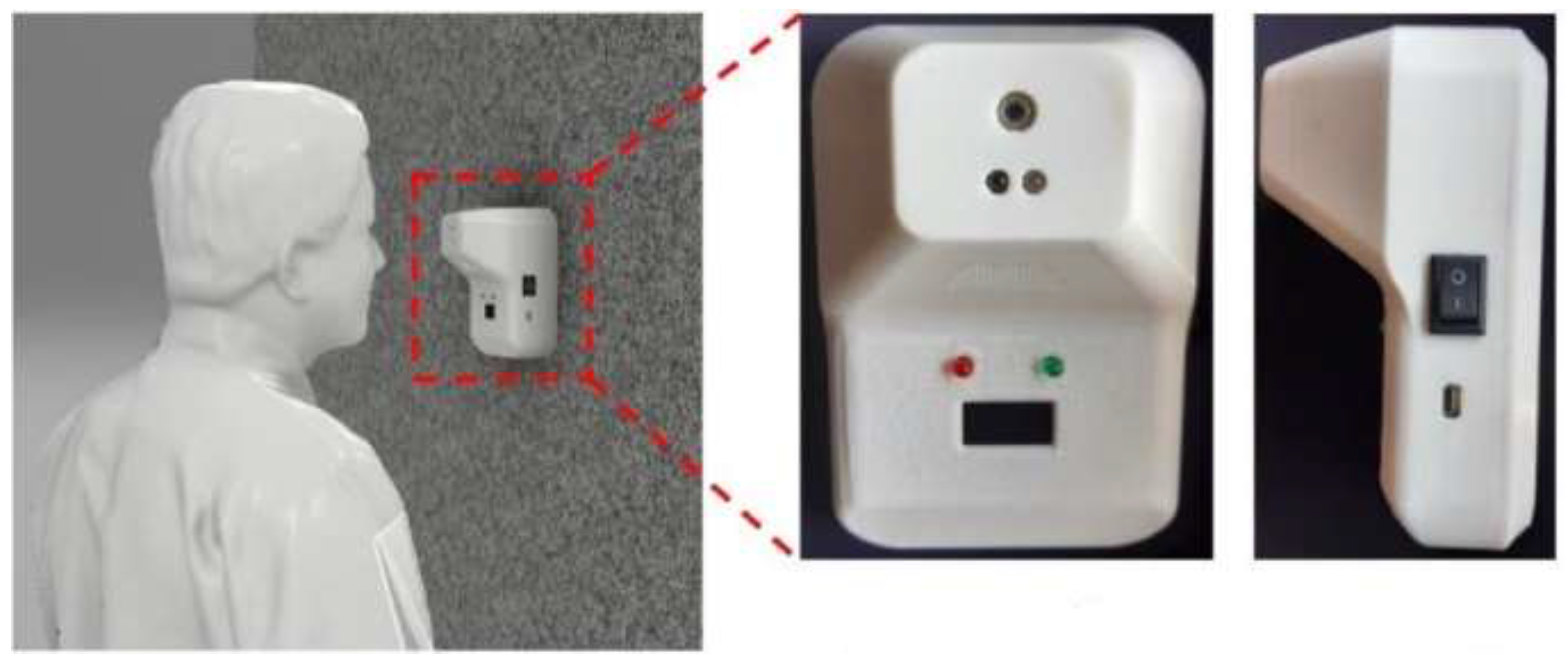
| Sl. No | Manufacturer/Organization | Domain | Products Manufactured | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Pandemic | During Pandemic | ||||
| 1 | Airbus | Aerospace | Aircraft components | Medical visors | [30] |
| 2 | Ford | Automotive | Automotive components | Respirators, ventilators, facemasks, and face shields. | [31] |
| 3 | General Motor | Automotive | Automotive components | Ventilators and their components | [32] |
| 4 | Nagami | Product Design | Furniture | Masks | [33] |
| 5 | Toyota | Automotive | Automotive components | Face shields and ventilators | [34] |
| 6 | Yingchuang Building Technique (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China | Construction | 3D printing architecture | Isolation wards and quarantine shelters | [35] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niranjan, Y.C.; Channabasavanna, S.G.; Krishnapillai, S.; Velmurugan, R.; Kannan, A.R.; G. Mohan, D.; Karganroudi, S.S. The Unprecedented Role of 3D Printing Technology in Fighting the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Comprehensive Review. Materials 2022, 15, 6827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196827
Niranjan YC, Channabasavanna SG, Krishnapillai S, Velmurugan R, Kannan AR, G. Mohan D, Karganroudi SS. The Unprecedented Role of 3D Printing Technology in Fighting the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Comprehensive Review. Materials. 2022; 15(19):6827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196827
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiranjan, Y. C., S. G. Channabasavanna, Shankar Krishnapillai, R. Velmurugan, A. Rajesh Kannan, Dhanesh G. Mohan, and Sasan Sattarpanah Karganroudi. 2022. "The Unprecedented Role of 3D Printing Technology in Fighting the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Comprehensive Review" Materials 15, no. 19: 6827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196827
APA StyleNiranjan, Y. C., Channabasavanna, S. G., Krishnapillai, S., Velmurugan, R., Kannan, A. R., G. Mohan, D., & Karganroudi, S. S. (2022). The Unprecedented Role of 3D Printing Technology in Fighting the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Comprehensive Review. Materials, 15(19), 6827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196827











