Animal-Protein-Based and Synthetic-Based Foamed Mixture Lightweight Soil Doped with Bauxite Tailings: Macro and Microscopic Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mix Proportion
2.3. Specimen Preparation and Curing
2.4. Test Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Foaming Agent Performance Test
3.1.1. Foaming Agent General Performance
3.1.2. Foam Stability
3.2. Microanalysis
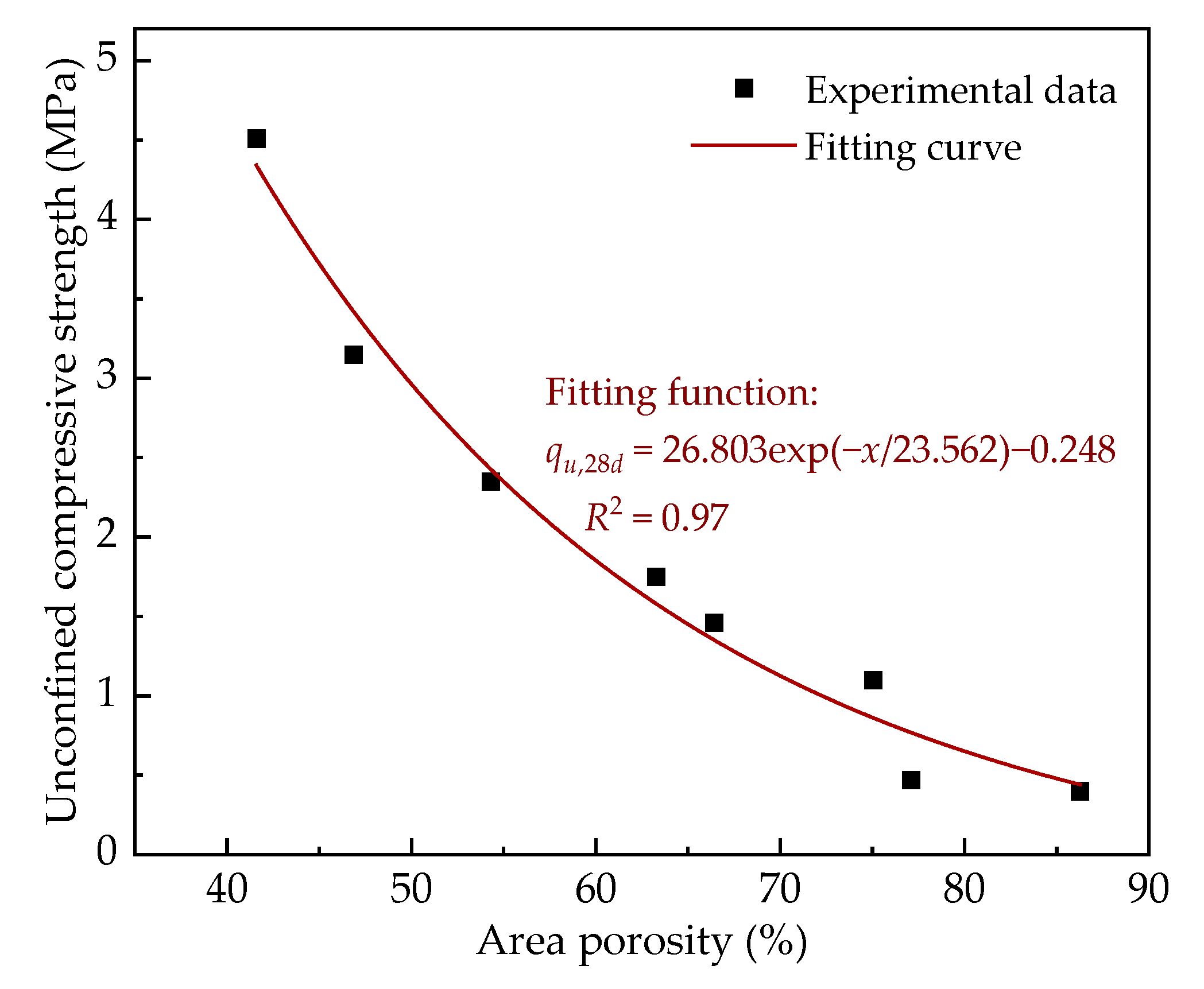
3.2.1. Pore Structure
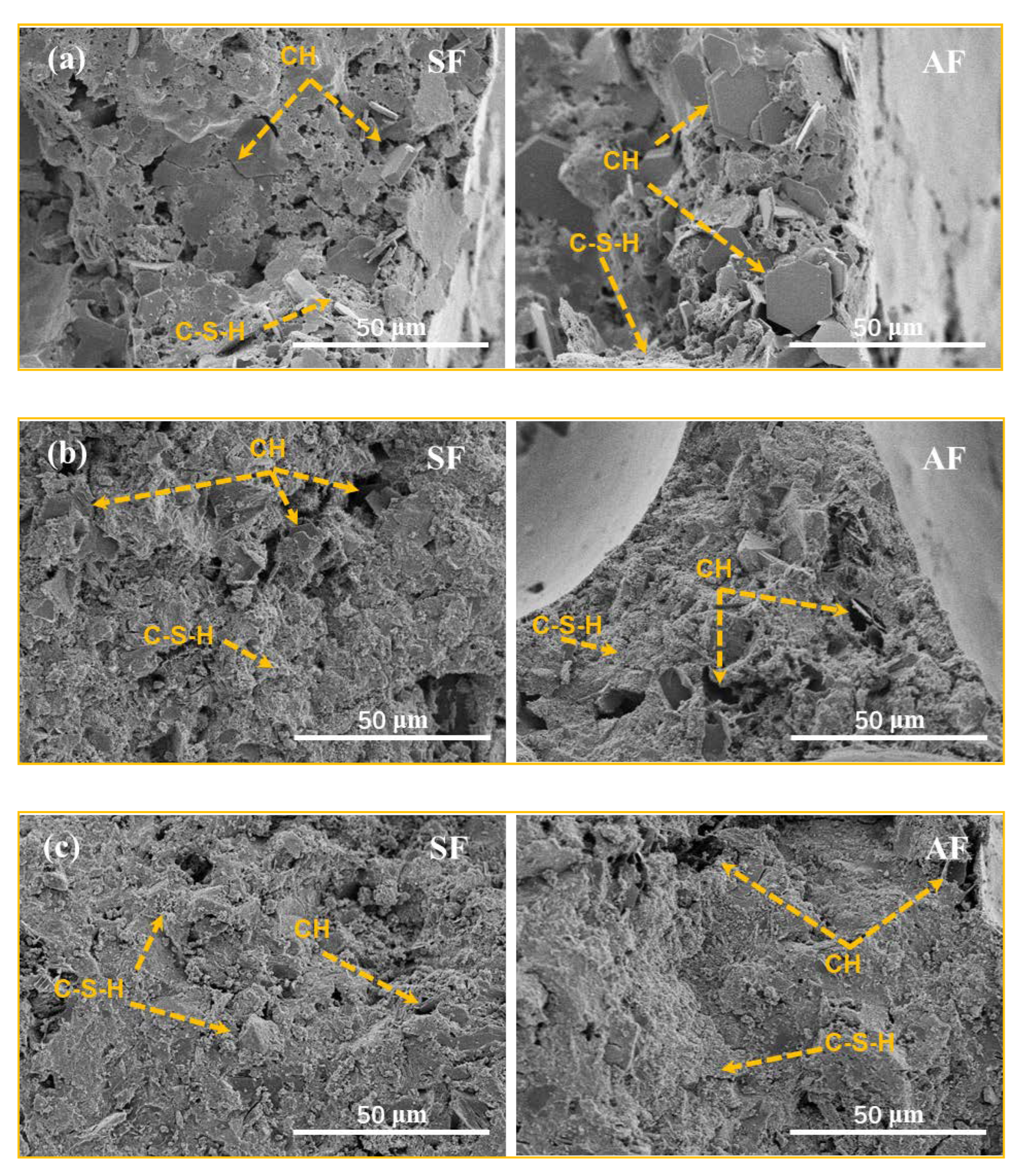
3.2.2. Skeletal Structure
3.3. Macro Performance Analysis
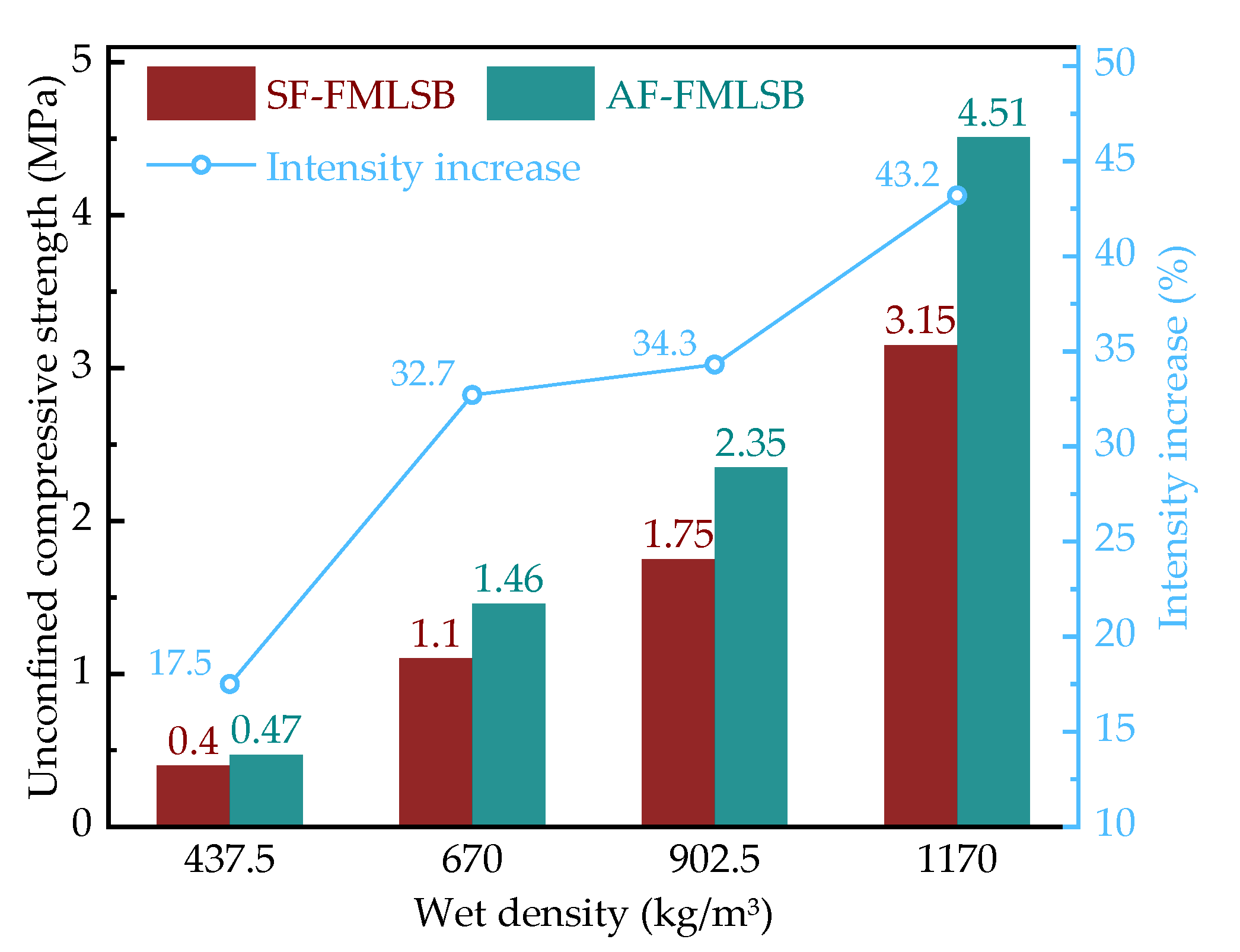
3.3.1. Uniaxial Compressive Performance
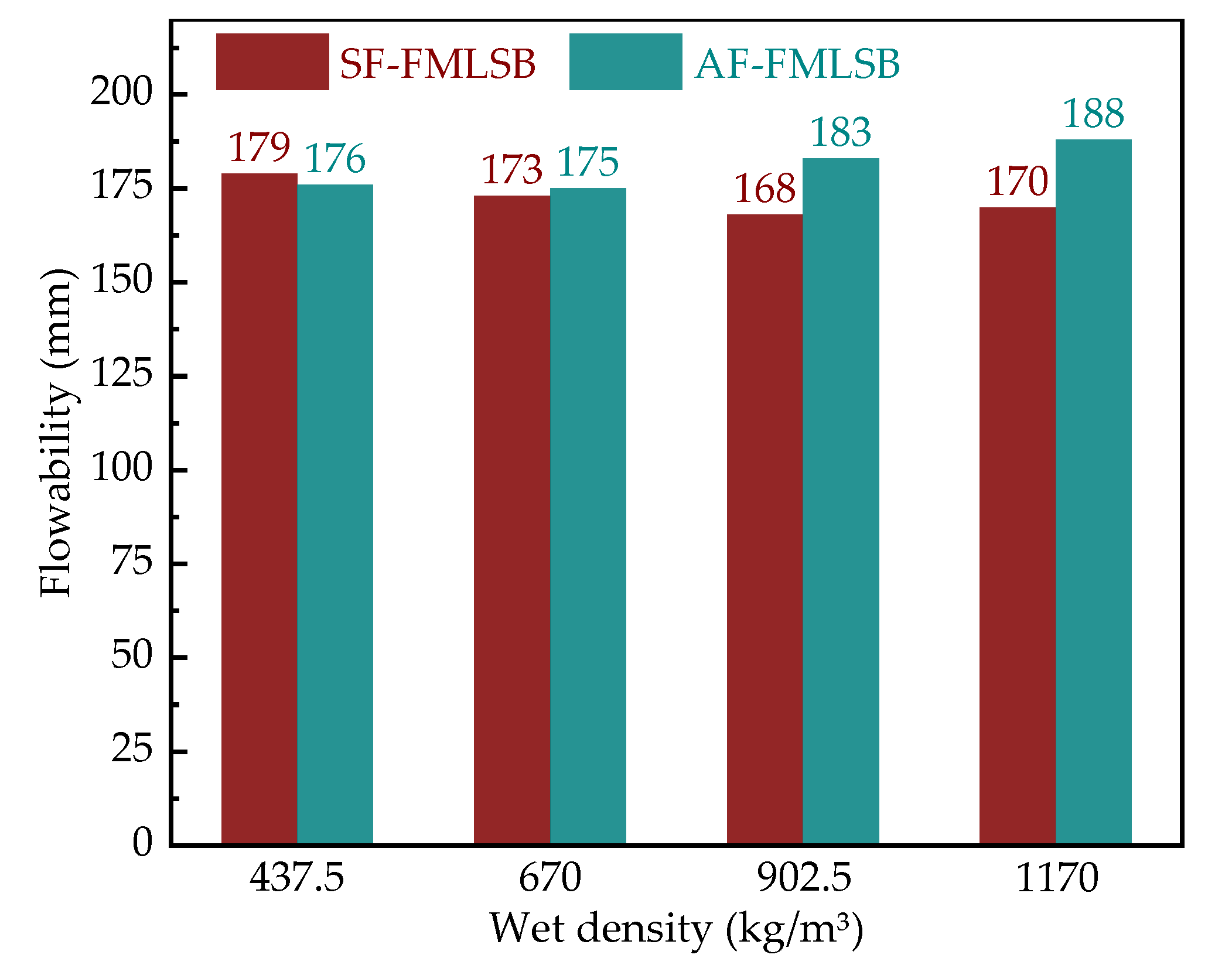
3.3.2. Flowability
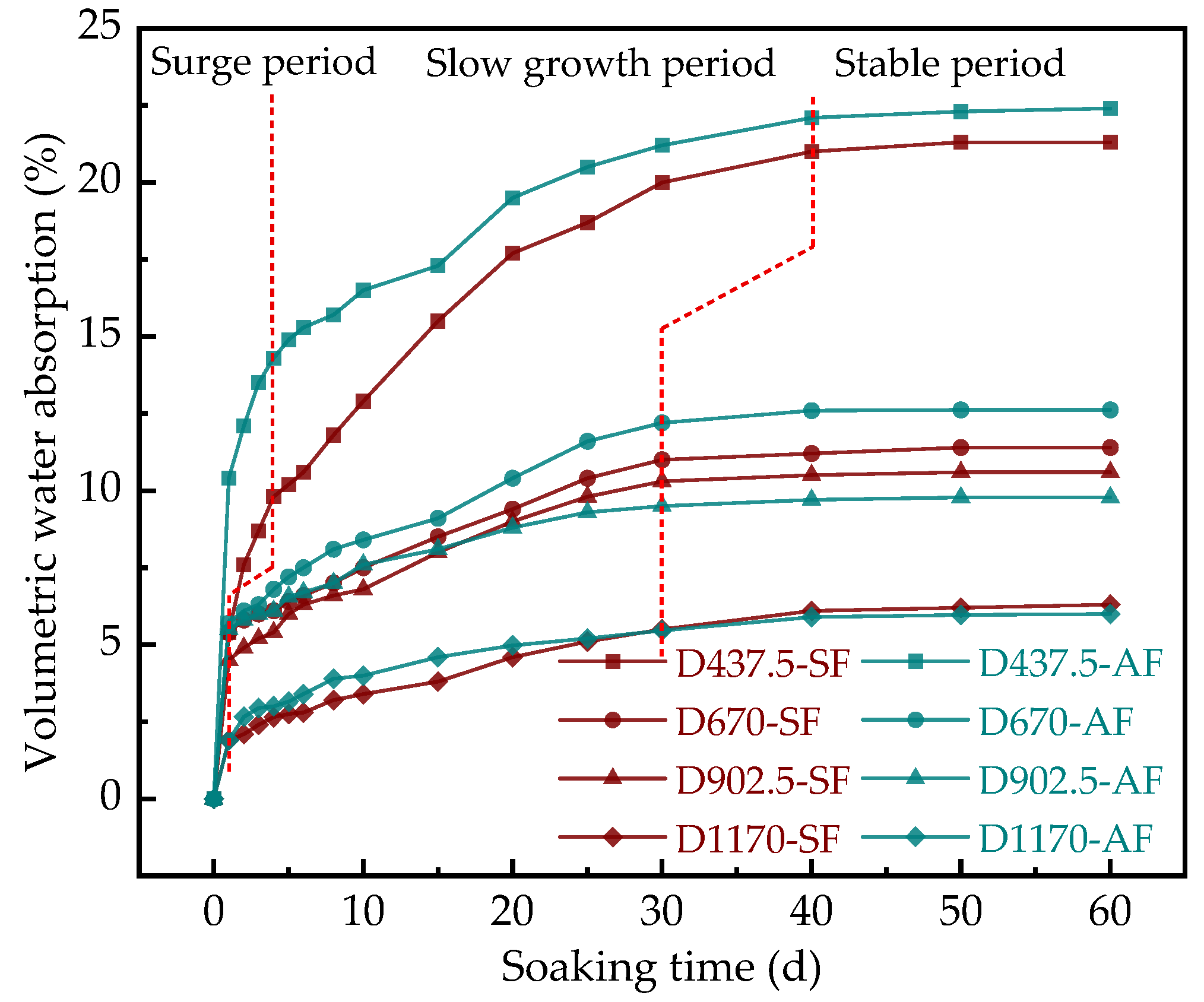
3.3.3. Volume of Water Absorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hulimka, J.; Krzywoń, R.; Jędrzejewska, A. Laboratory tests of foamed concrete slabs reinforced with composite grid. Procedia Eng. 2017, 193, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabha, P.; Palani, G.S.; Lakshmanan, N.; Senthil, R. Behaviour of steel-foam concrete composite panel under in-plane lateral load. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2017, 139, 437–448. [Google Scholar]
- Ramamurthy, K.; Nambiar, K.K.; Ranjani, G.I.S. A classification of studies on properties of foam concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Fang, Z.; Lin, B. Preparation and optimization of ultra-light and thermal insulative aerogel foam concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 205, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Huang, J.; Su, Q. Experimental and numerical analyses of lightweight foamed concrete as filler for widening embankment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 250, 118897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Peng, Y.; Mo, P.; Jiang, J. Study on the Physical Mechanical and Hydraulic Properties of Foamed Mixture Lightweight Soil Mixed with Bauxite Tailings. Mater. Rep. 2020, 34 (Suppl. S1), 241–245. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Jiang, J.; Ou, X.; Qin, J. Investigating the Properties of Foamed Mixture Lightweight Soil Mixed with Bauxite Tailings as Filler. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 2019, 6295348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Ou, X.; Chen, X.; Lin, X.; Shen, X. Utilization of discarded bauxite tailings into eco-friendly foamed mixture lightweight soil. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 333, 130167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.X.; Zhou, F.S.; Evelina, L.; Liu, J.-L.; Zhou, Y. A review on the industrial solid waste application in pelletizing additives: Composition, mechanism and process characteristics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 423, 127056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, B.; Wen, R.; Wu, P. Analysis of foamed concrete pore structure of railway roadbed based on X-ray computed tomography. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 273, 121773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.-Y.; Lehmann, C.; Abd Elrahman, M.; Dietmar, S. Pore Characteristics and Their Effects on the Material Properties of Foamed Concrete Evaluated Using Micro-CT Images and Numerical Approaches. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzielová, E.; Pach, L.; Palou, M. Effect of activated foaming agent on the foamed concrete properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xu, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, G.; Yu, J. Effect of foaming agent on properties and microstructure of foamed cement banking. New Build. Mater. 2015, 42, 50–53. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Falliano, D.; De Domenico, D.; Ricciardi, G.; Gugliandolo, E. Experimental investigation on the compressive strength of foamed concrete: Effect of curing conditions, cement type, foaming agent and dry density. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 165, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panesar, D.K. Cellular concrete properties and the effect of synthetic and protein foaming agents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 44, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Jeong, J.Y.; Hwang, E.H.; Shin, S.-C. Properties of Foamed Concrete According to Types and Concentrations of Foam Agent. J. Korea Concr. Inst. 2012, 24, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, G. Effects of foaming agent type on the workability, drying shrinkage, frost resistance and pore distribution of foamed concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Gao, Q.; Song, X.; Bu, X.; He, J. Effect of foaming agent on physical and mechanical properties of alkali-activated slag foamed concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 226, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, M.; Tantray, M. Comparative study on the performance of protein and synthetic-based foaming agents used in foamed concrete. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 14, e00524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Gu, H. Influence of Bubble Preparation Factors on Properties of Foamed Mixture Soil Using River Sludge. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2017, 34, 137–141,149. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y. Effect of nano-alumina modified foaming agents on properties of foamed concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 267, 121045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, W.; Du, Y.; Miao, C.; Liu, J.; Zhao, G.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y. Application of organic- and nanoparticle-modified foams in foamed concrete: Reinforcement and stabilization mechanisms. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 106, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Li, J.; Lu, Z.; Niu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Li, T. Effect of nanoparticles on foaming agent and the foamed concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 227, 116698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, M.; Song, X. Progress of foaming agent in foamed concrete. Concrete 2012, 9, 57–58,62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- CJJ/T 177-2012; Technical Specification for Foamed Mixture Lightweight Soil Filling Engineering. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Ou, X.; Wu, H.; Zhou, D.; Qin, W. Development and Application of the Environmental Generator in Geotechnical Engineering. J. Hunon Univ. Nat. Sci. 2008, 35, 74–78. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Du, J.; Gao, Y.; Ma, W. Performance evaluation indexes of foaming agent. J. Southeast Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2020, 50, 651–657. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Rong, H.; Liu, Z. Foam Characteristics of Biological Based Foaming Agent and Its Effect on Properties of Foam Concrete. J. Build. Mater. 2020, 23, 589–595. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G. Influence of Preparation Parameters on Working Performance and Mechanical Behavior of Foamed Concrete. Railw. Eng. 2017, 2017, 56–60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
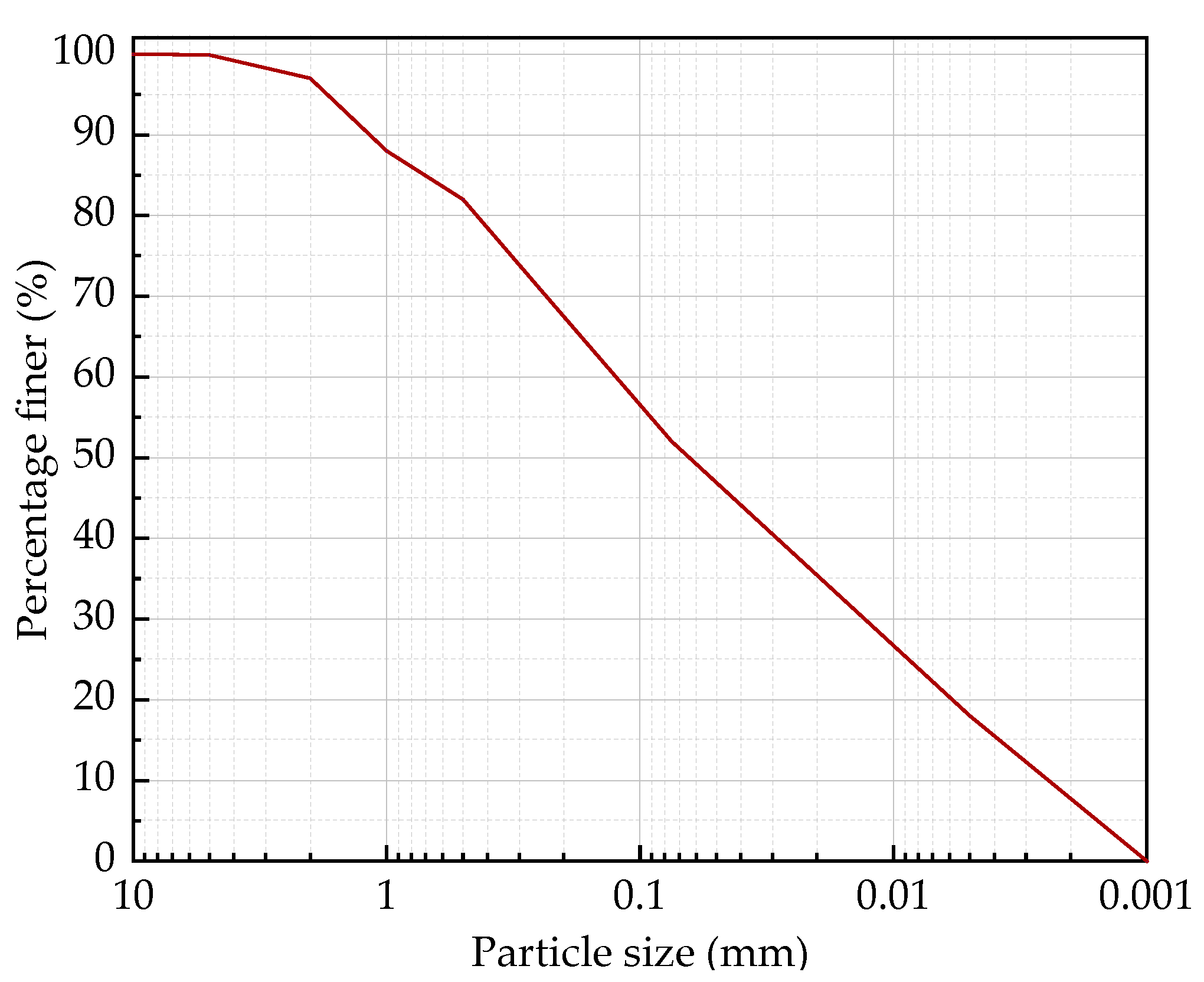
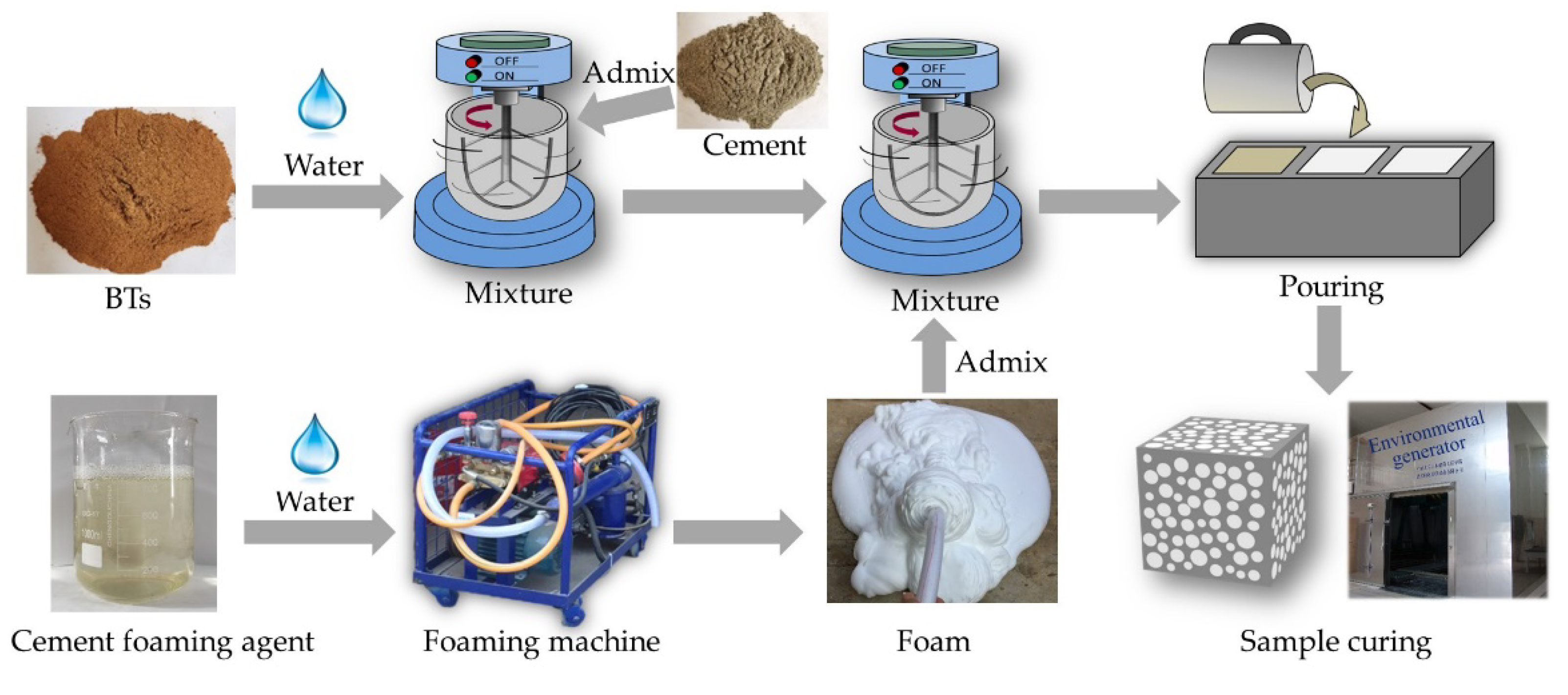
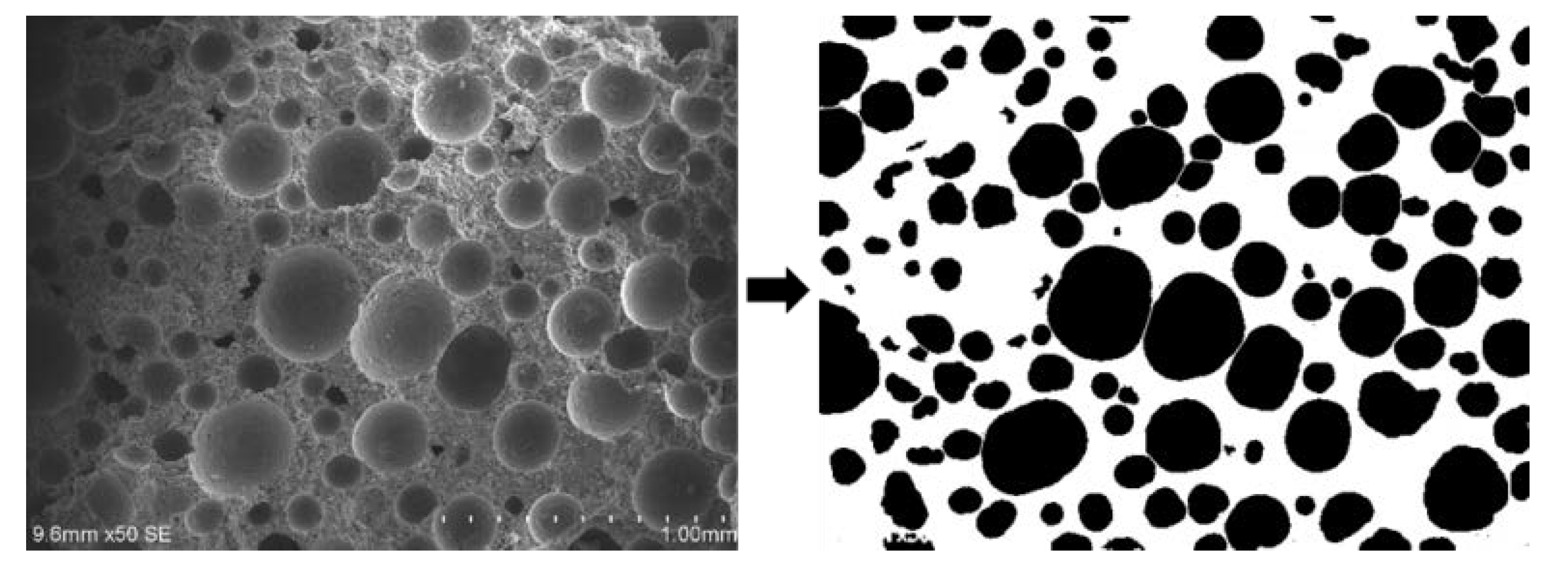
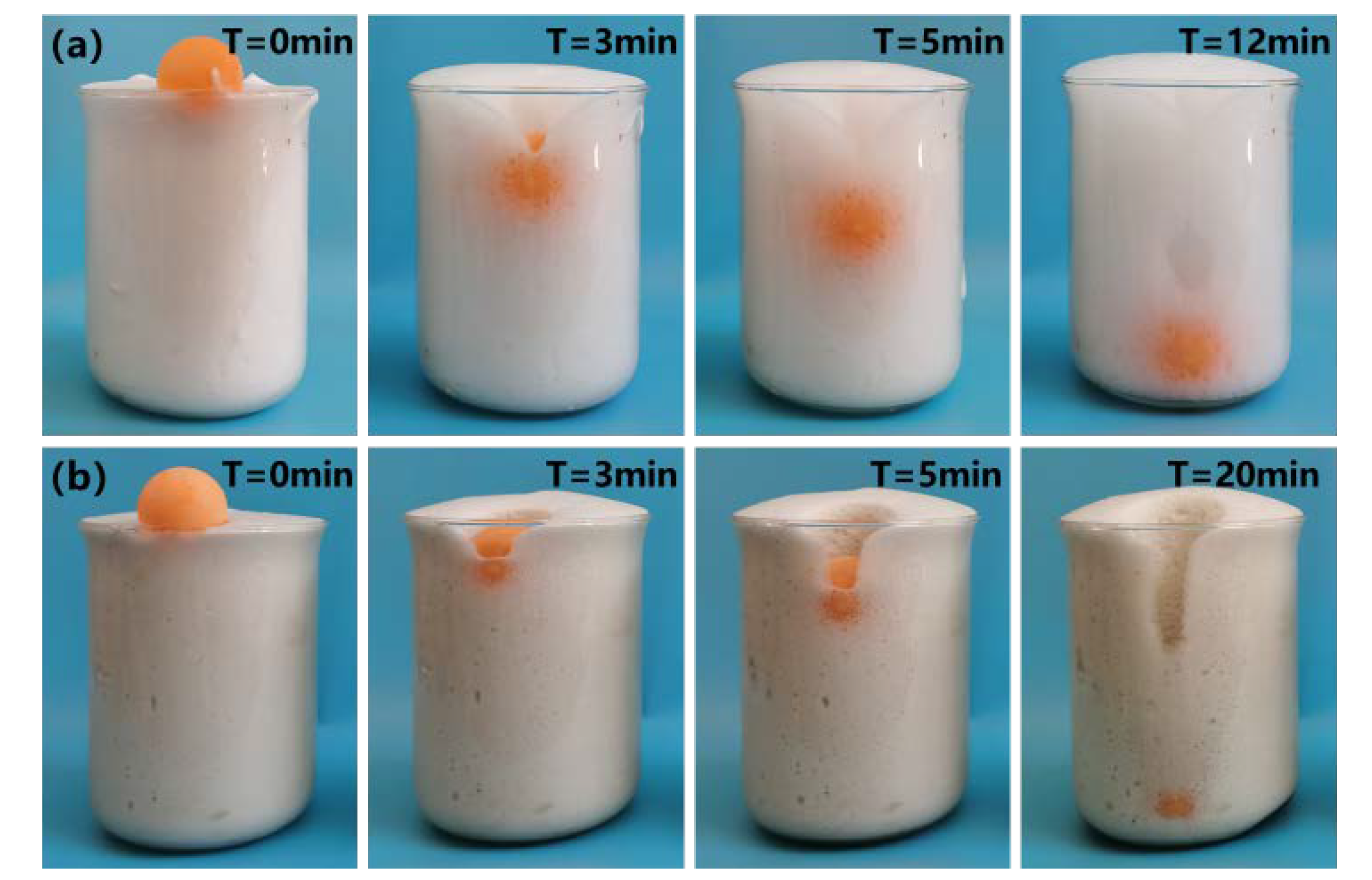
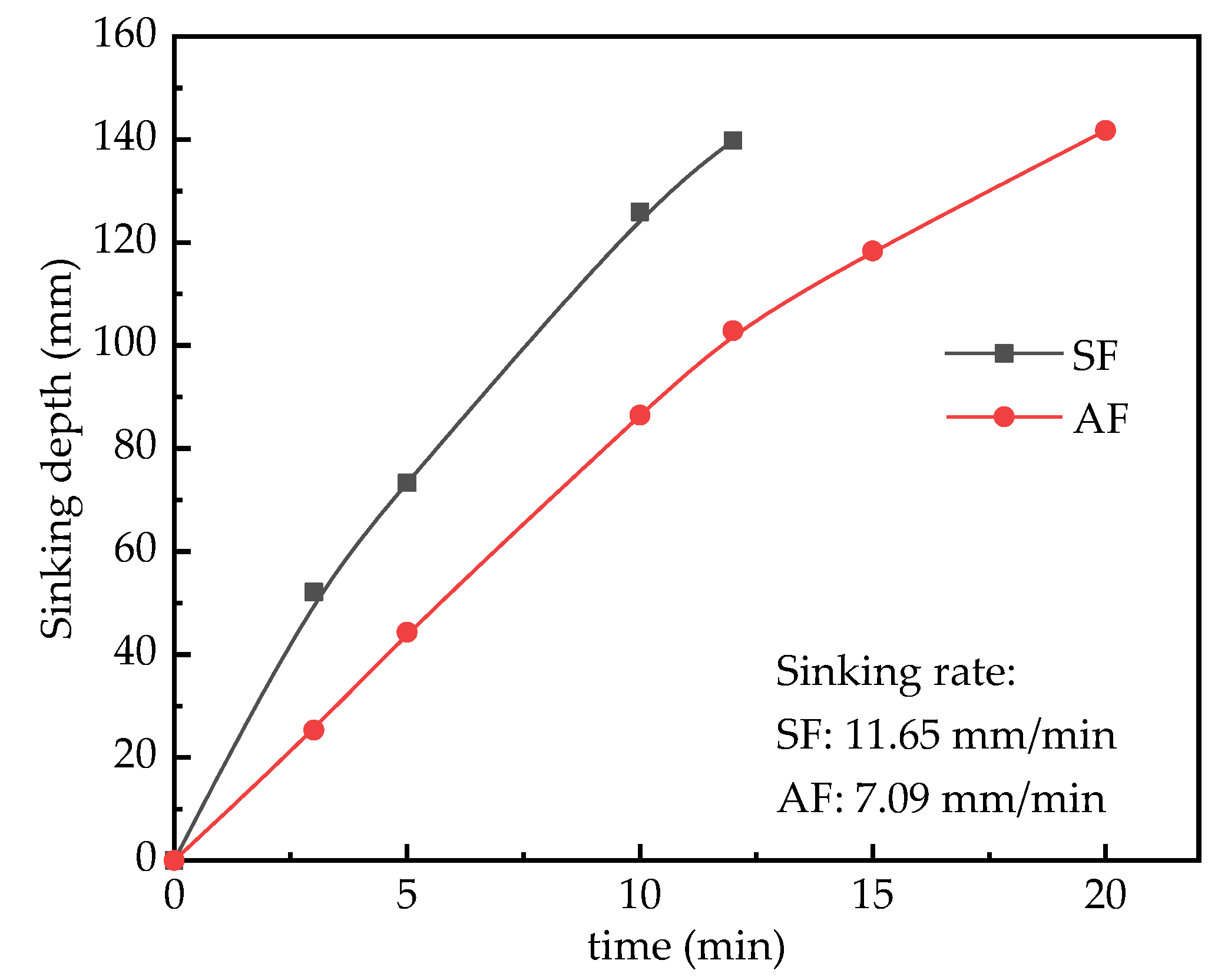
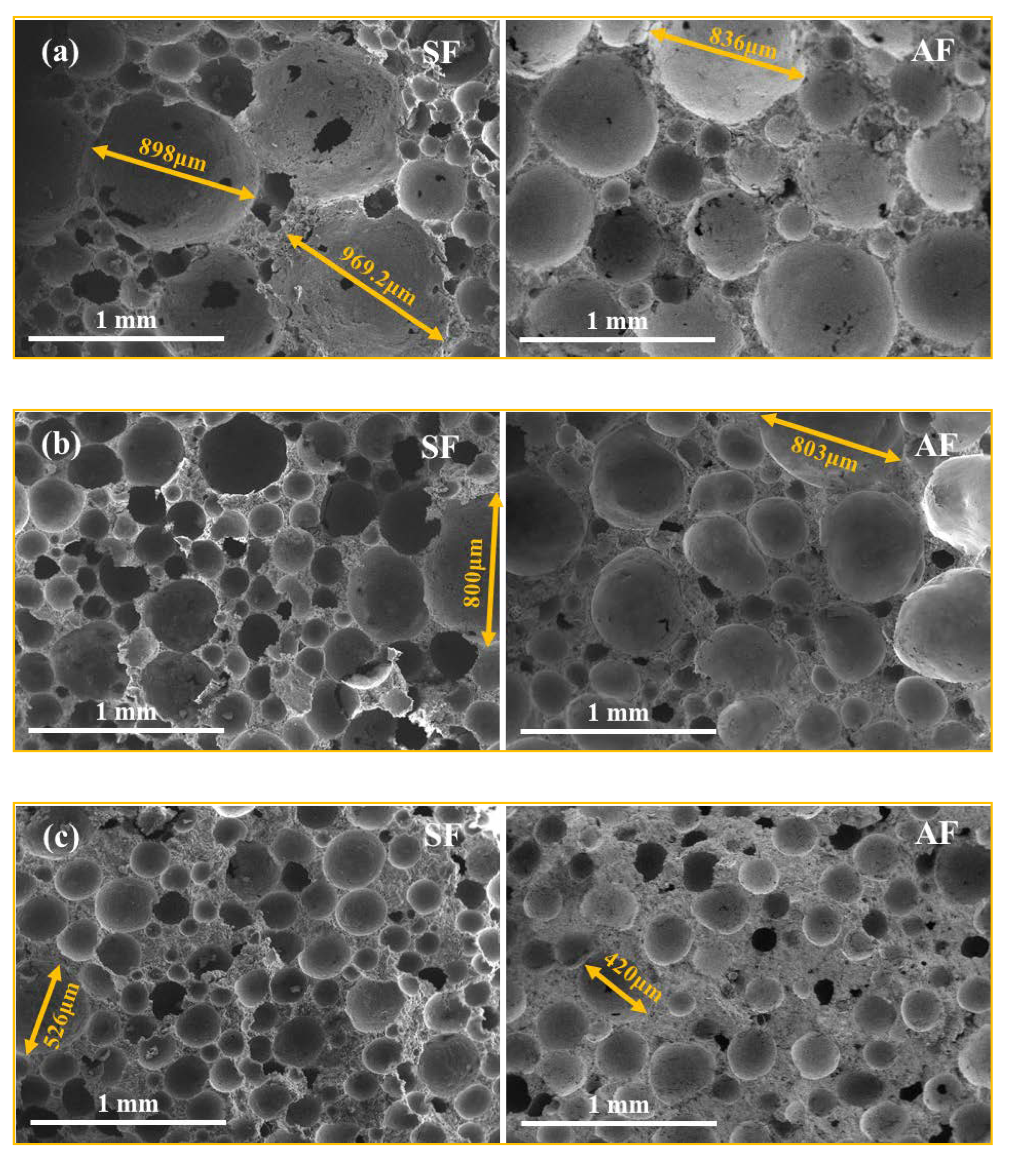
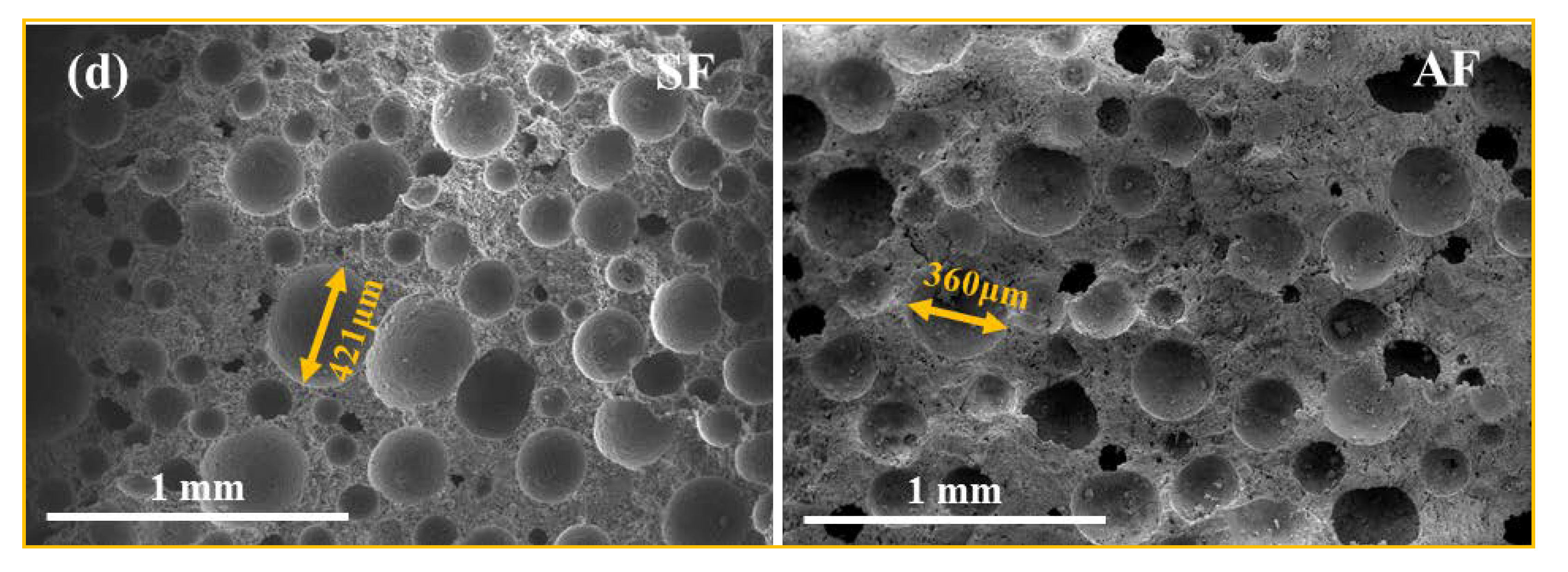
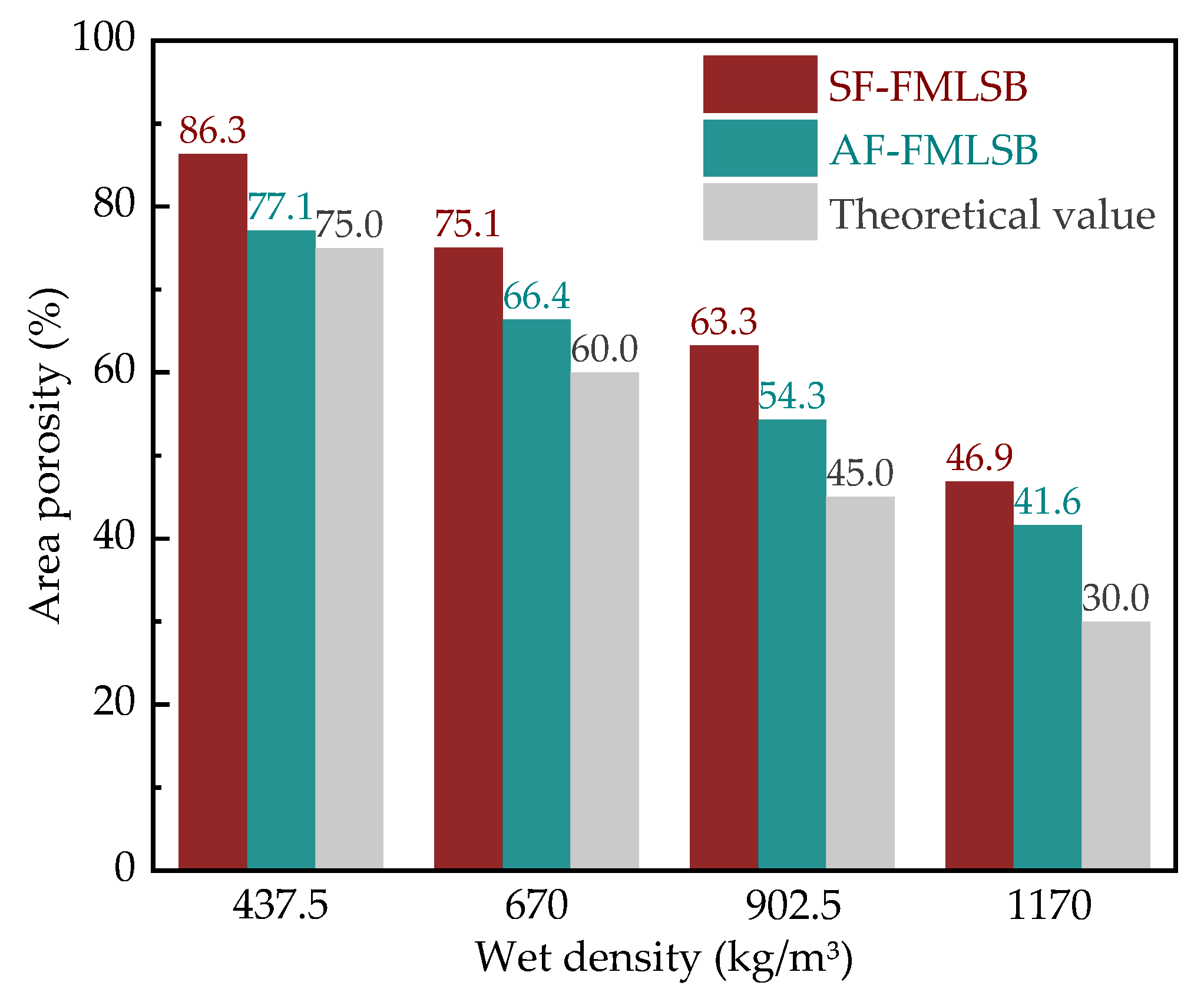

| Specific Gravity of Solid Particles | Liquid Limit (%) | Plastic Limit (%) | Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Void Ratio | Chemical Composition/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | CaO | TiO2 | K2O | |||||
| 2.76 | 70.43 | 31.96 | 1.58 | 0.96 | 38.10 | 28.32 | 14.93 | 0.32 | 1.70 | 0.78 |
| Foaming Agent Type | pH Value | Dilution Ratios | Foam Multiple | Water Secretion (mL/h) | Sink Distance (mm/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF | 7.5 | 1:40 | >40 | 16 | < 10 |
| AF | 7.0 | 1:30 | >40 | 12 | < 10 |
| Designed Wet Density | Cement (kg/m3) | BTs (kg/m3) | Foam Content (L/m3) | Water/Solid Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D437.5 | 200 | 50 | 750 | 0.6 |
| D670 | 300 | 100 | 600 | 0.6 |
| D902.5 | 400 | 150 | 450 | 0.6 |
| D1170 | 500 | 200 | 300 | 0.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ou, X.; Mo, P.; Lyu, Z.; Luo, J.; Jiang, J.; Bai, L.; Huang, Z. Animal-Protein-Based and Synthetic-Based Foamed Mixture Lightweight Soil Doped with Bauxite Tailings: Macro and Microscopic Properties. Materials 2022, 15, 6377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15186377
Ou X, Mo P, Lyu Z, Luo J, Jiang J, Bai L, Huang Z. Animal-Protein-Based and Synthetic-Based Foamed Mixture Lightweight Soil Doped with Bauxite Tailings: Macro and Microscopic Properties. Materials. 2022; 15(18):6377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15186377
Chicago/Turabian StyleOu, Xiaoduo, Peng Mo, Zhengfan Lyu, Junhui Luo, Jie Jiang, Lu Bai, and Zhongzheng Huang. 2022. "Animal-Protein-Based and Synthetic-Based Foamed Mixture Lightweight Soil Doped with Bauxite Tailings: Macro and Microscopic Properties" Materials 15, no. 18: 6377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15186377
APA StyleOu, X., Mo, P., Lyu, Z., Luo, J., Jiang, J., Bai, L., & Huang, Z. (2022). Animal-Protein-Based and Synthetic-Based Foamed Mixture Lightweight Soil Doped with Bauxite Tailings: Macro and Microscopic Properties. Materials, 15(18), 6377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15186377





