Chemical Distributions of Different Sodium Hydroxide Molarities on Fly Ash/Dolomite-Based Geopolymer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Solid Precursor
2.2. Alkaline Activator
3. Methodology
3.1. Preparation of Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) Solution
3.2. Sieving Process
3.3. Mixing Process
3.4. Curing Process
3.5. Compressive Strength Test
3.6. Water Absorption Analysis
3.7. Density Analysis
3.8. Porosity Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Compressive Strength Analysis
4.2. Density Analysis
4.3. Water Absorption Analysis
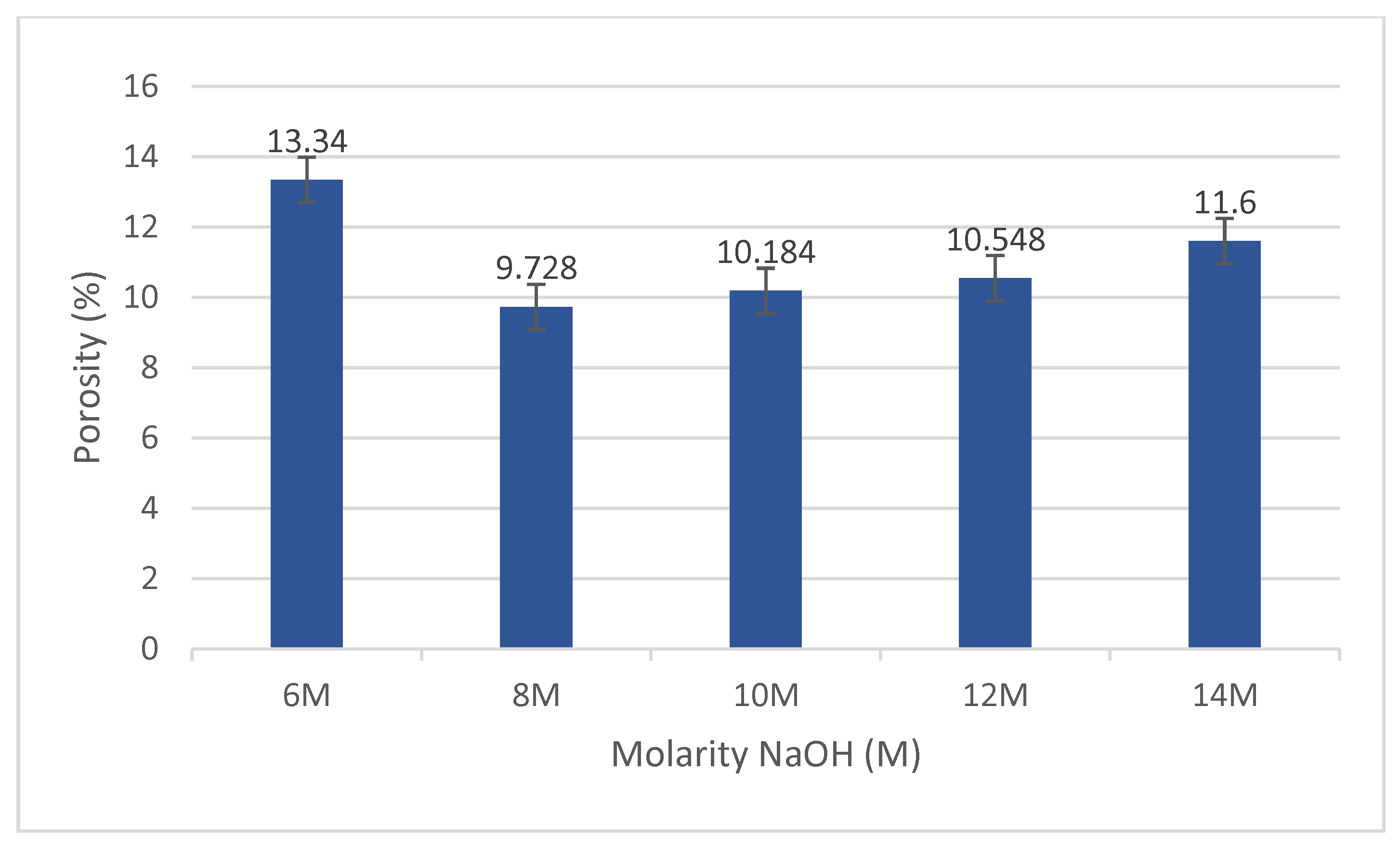
4.4. Porosity Analysis
4.5. Morphology Analysis
4.6. Elemental Distribution Analysis
4.7. Phase Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amran, Y.M.; Alyousef, R.; Alabduljabbar, H.; El-Zeadani, M. Clean production and properties of geopolymer concrete; A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 251, 119679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, M.F.A.A.; Muhamad, R.; Mo, K.H. Effect of Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag as Partial Replacement in Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Concrete. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 712, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, N.A.M.; Kamarudin, H.; Rafiza, R.A.; Meor, T.A.F.; Rosnita, M. Compressive Strength of Fly Ash Geopolymer Concrete by Varying Sodium Hydroxide Molarity and Aggregate to Binder Ratio. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 864, 012037. [Google Scholar]
- Almuwbber, O.; Haldenwang, R.; Mbasha, W.; Masalova, I. The influence of variation in cement characteristics on workability and strength of SCC with fly ash and slag additions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N. Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Binder: A Future Construction Material. Minerals 2018, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitarz, M.; Hager, I.; Choińska, M. Evolution of Mechanical Properties with Time of Fly-Ash-Based Geopolymer Mortars under the Effect of Granulated Ground Blast Furnace Slag Addition. Energies 2020, 13, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizat, E.A.; Bakri, A.M.; Liew, Y.M.; Heah, C.Y. Chemical composition and strength of dolomite geopolymer composites. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1885, 020192. [Google Scholar]
- Azimi, E.; Abdullah, M.; Ming, L.; Yong, H.; Hussin, K.; Aziz, I. Review of Dolomite as Precursor of Geopolymer Materials. MATEC Web Conf. 2016, 78, 01090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, B.; Tulliani, J.; Antonaci, P.; Palmero, P. Role of Natural Stone Wastes and Minerals in the Alkali Activation Process: A Review. Materials 2020, 13, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, M.N.; Al-Azzawi, M.; Yu, T. Effects of fly ash characteristics and alkaline activator components on compressive strength of fly ash-based geopolymer mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 175, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, E.M.; Ramamurthy, K. Influence of production on the strength, density and water absorption of aerated geopolymer paste and mortar using Class F fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C642-13; Standard Test Method for Density, Absorption, and Voids in Hardened Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- Hanjitsuwan, S.; Hunpratub, S.; Thongbai, P.; Maensiri, S.; Sata, V.; Chindaprasirt, P. Effects of NaOH concentrations on physical and electrical properties of high calcium fly ash geopolymer paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 45, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khale, D.; Chaudhary, R. Mechanism of geopolymerization and factors influencing its development: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 729–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somna, K.; Jaturapitakkul, C.; Kajitvicyanukul, P.; Cindaprasirt, P. NaOH-Activated Ground Fly Ash Geopolymer Cured at Ambient Temperature. Fuel 2011, 90, 2118–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangdaeng, S.; Sata, V.; Chindaprasirt, P. Effect of Sodium Hydroxide Concentration and Sodium Silicate to Sodium Hydroxide Ratio on Properties of Calcined Kaolin White Portland Cement Geopolymer. GEOMATE J. 2018, 14, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Aizat, E.A.; Abdullah, M.M.; Liew, Y.M.; Heah, C.Y. Dolomite/fly ash alkali activated geopolymer strengths with the influence of solid/liquid ratio. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 2030, 020274. [Google Scholar]
- Wazien, A.Z.W.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Razak, R.A.; Rozainy, M.A.Z.M.R.; Tahir, M.F.M. Strength and Density of Geopolymer Mortar Cured at Ambient Temperature for Use as Repair Material. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 133, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, W.M.; Hussin, K.; Abdullah, M.M.; Kadir, A.A.; Deraman, L.M. Effects of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution concentration on fly ash-based lightweight geopolymer. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1885, 020011. [Google Scholar]
- Jaya, N.A.; Yun-Ming, L.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Cheng-Yong, H.; Hussin, K. Effect of Sodium Hydroxide Molarity on Physical, Mechanical and Thermal Conductivity of Metakaolin Geopolymers. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 343, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.; Hussin, K.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Yahya, Z.; Sochacki, W.; Razak, R.A.; Błoch, K.; Fansuri, H. The Effects of Various Concentrations of NaOH on the Inter-Particle Gelation of a Fly Ash Geopolymer Aggregate. Materials 2021, 14, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivia, M.; Nikraz, H.R. Strength and Water Penetrability of Fly Ash Geopolymer Concrete. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2011, 6, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, M.M.; Kamarudin, H.; Bnhussain, M.; Nizar, I.K.; Rafiza, A.; Zarina, Y. The Relationship of NaOH Molarity, Na2SiO3/NaOH Ratio, Fly Ash/Alkaline Activator Ratio, and Curing Temperature to the Strength of Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 328, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseien, G.F.; Mirza, J.; Ismail, M.; Hussin, M.W.; Arrifin, M.A.; Hussein, A.A. The Effect of Sodium Hydroxide Molarity and Other Parameters on Water Absorption of Geopolymer Mortars. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, J.; Tan, X.; Chen, D. Relationship between Moisture Transportation, Efflorescence and Structure Degradation in Fly Ash/Slag Geopolymer. Materials 2020, 13, 5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Görhan, G.; Kürklü, G. The influence of the NaOH solution on the properties of the fly ash-based geopolymer mortar cured at different temperatures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 58, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patankar, S.V.; Ghugal, Y.M.; Jamkar, S.S. Effect of Concentration of Sodium Hydroxide and Degree of Heat Curing on Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Mortar. Indian J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 2014, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, L.; Perry, M.; Vlachakis, C.; Wu, Z.; Hamilton, A.; Mcalorum, J. Ambient cured fly ash geopolymer coatings for concrete. Materials 2019, 12, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwanjee, J.; Singh, D.N. A Review in Synthesis, Characterization and Industrial Applications of flyash zeolites. J. Mater. Educ. 2011, 33, 65–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ayeni, O.; Onwualu, A.P.; Boakye, E. Characterization and mechanical performance of metakaolin-based geopolymer for sustainable building applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 272, 121938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, N.H.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Pa, F.C.; Mohamad, H.; Ibrahim, W.M.A.W.; Chaiprapa, J. Influences of SiO2, Al2O3, CaO and MgO in phase transformation of sintered kaolin-ground granulated blast furnace slag geopolymer. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 14922–14932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Rattanasak, U. Characterization of the high-calcium fly ash geopolymer mortar with hot-weather curing systems for sustainable application. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 2317–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, S.A.; San Nicolas, R.; Myers, R.J.; Mejía de Gutiérrez, R.; Puertas, F.; van Deventer, J.S.J.; Provis, J.L. MgO content of slag controls phase evolution and structural changes induced by accelerated carbonation in alkali-activated binders. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 57, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kim, E.; Suraneni, P.; Struble, L. Quantitative Correlation between the Degree of Reaction and Compressive Strength of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymers. Materials 2020, 13, 5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, E.A.; Abdullah, M.M.A.; Vizureanu, P.; Salleh, M.A.A.M.; Sandu, A.V.; Chaiprapa, J.; Yoriya, S.; Hussin, K.; Aziz, I.H. Strength Development and Elemental Distribution of Dolomite/Fly Ash Geopolymer Composite under Elevated Temperature. Materials 2020, 13, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahedan, N.F.; Abdullah, M.M.A.; Mahmed, N.; Kusbiantoro, A.; Tammas-Williams, S.; Li, L.Y.; Aziz, I.H.; Vizureanu, P.; Wyslocki, J.J.; Bloch, K. Properties of a New Insulation Material Glass Bubble in Geo-Polymer Concrete. Materials 2021, 14, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizureanu, P.; Agop, M.A. Theoretical Approach of the Heat Transfer in Nanofluids. Mater. Trans. 2007, 48, 3021–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomayri, T. Effect of glass microfibre addition on the mechanical performances of fly ash-based geopolymer composites. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2017, 5, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alehyen, S.; Achouri, M.E.L.; Taibi, M. Characterization, microstructure and properties of fly ash-based geopolymer. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2017, 8, 1783–1796. [Google Scholar]











| Compound | Mass of Fly Ash Class C (wt.%) | Mass of Dolomite (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 30.70 | 2.19 |
| Al2O3 | 13.30 | 1.09 |
| MgO | 3.60 | 21.42 |
| CaO | 22.40 | 74.26 |
| Fe2 O3 | 23.92 | 0.22 |
| TiO2 | 0.94 | 0.06 |
| SO3 | 2.28 | 0.85 |
| Na2O | - | 1.26 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, W.M.W.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Ahmad, R.; Sandu, A.V.; Vizureanu, P.; Benjeddou, O.; Rahim, A.; Ibrahim, M.; Sauffi, A.S. Chemical Distributions of Different Sodium Hydroxide Molarities on Fly Ash/Dolomite-Based Geopolymer. Materials 2022, 15, 6163. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15176163
Ibrahim WMW, Abdullah MMAB, Ahmad R, Sandu AV, Vizureanu P, Benjeddou O, Rahim A, Ibrahim M, Sauffi AS. Chemical Distributions of Different Sodium Hydroxide Molarities on Fly Ash/Dolomite-Based Geopolymer. Materials. 2022; 15(17):6163. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15176163
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Wan Mastura Wan, Mohd Mustafa Al Bakri Abdullah, Romisuhani Ahmad, Andrei Victor Sandu, Petrica Vizureanu, Omrane Benjeddou, Afikah Rahim, Masdiyana Ibrahim, and Ahmad Syauqi Sauffi. 2022. "Chemical Distributions of Different Sodium Hydroxide Molarities on Fly Ash/Dolomite-Based Geopolymer" Materials 15, no. 17: 6163. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15176163
APA StyleIbrahim, W. M. W., Abdullah, M. M. A. B., Ahmad, R., Sandu, A. V., Vizureanu, P., Benjeddou, O., Rahim, A., Ibrahim, M., & Sauffi, A. S. (2022). Chemical Distributions of Different Sodium Hydroxide Molarities on Fly Ash/Dolomite-Based Geopolymer. Materials, 15(17), 6163. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15176163


_Low.png)







