Experimental Study on the Optimization of Coal-Based Solid Waste Filling Slurry Ratio Based on the Response Surface Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Response Surface Function Method Optimization Theory
2.1. Response Surface Theory
2.2. Satisfaction Function Multi-Objective Optimization Method
3. Filling Material Proportioning Test
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Filling Materials
3.2. Proportioning Test Design
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Response Surface Function Fitting
4.2. Influence of Single Factors of Response Surface Parameters on the Strength of the Filled Body
4.3. Effect of Response Surface Parameter Interactions on the Strength of the Filler
5. Multi-Objective Optimization of Filling Slurry Ratio
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, N. Shaft failure characteristics and the control effects of backfill body compression ratio at ultra-contiguous coal seams mining. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Zhang, J.; Duan, H. Reutilization of gangue wastes in underground backfilling mining: Overburden aquifer protection. Chemosphere 2021, 264 Pt 1, 128400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.P.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, G.F.; Ren, H.W.; Liu, J.Z.; Ge, S.R.; Zhou, H.W.; Wu, G.; Ren, S.H. New Concept of Coal Revolution and Development Concept of Coal Science and Technology. J. China Coal Soc. 2018, 43, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, W.; Zhang, D.; Cui, Z.C. Environmental implications of mitigating overburden failure and subsidences using paste-like backfill mining: A case study. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2015, 29, 521–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.G.; Xu, J.L.; Wang, J.C. Re-discussion on the scientific mining of coal. J. Coal Sci. 2018, 43, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.S.; Ning, J.G.; Tan, Y.L.; Xu, Q.; Fan, D.Y. Coordinated supporting method of gob-side entry retaining in coal mines and a case study with hard roof. Geomech. Eng. 2018, 15, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Yin, D.; Cao, F.; Liu, Y.; Ren, K. An overview of integrated surface subsidence-reducing technology in mining areas of China. Nat. Hazards 2016, 81, 1129–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Ju, F.; Li, M.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, Q. Coal mine gangue sorting and in-situ filling mining method. J. China Coal Soc. 2020, 45, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Fall, M.; Benzaazoua, M.; Saa, E.G. Mix proportioning of underground cemented tailings backfill. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2008, 23, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.G.; Qiao, D.P.; Guo, Z.L.; Xie, J.C.; Huang, F.; Wang, J.X. Experimental study on mix proportion and strength of waste rock aeolian sand cemented body based on rsm-bbd. J. China Coal Soc. 2018, 43, 694–703. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Yang, X.B.; Wen, Z.J.; Chen, D.X.; He, J.Y. RSM-BBD-Based RSM-BBD-Based Mixed Aggregate Filling Filler-Slurry Ratio Optimization. J. Hunan Univ. 2019, 46, 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.Q.; Gao, Q.; Chen, D.X.; Wang, Y.D.; He, J.Y. Development of cemented powder cementitious materials and strength test of cemented fillings. J. Hohai Univ. 2017, 45, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.Q.; Yin, S.H.; Cao, Y.; Dai, C.Q. Analysis of strength growth law of mixed aggregate cemented backfill based on RSM-BBD. Mater. Rev. 2020, 34, 14063–14069. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.F.; Li, K.Q.; Han, B.; Li, H.Y.; Zhao, J.T. Strength development and optimization analysis of mixed aggregate backfill based on response surface methodology-satisfaction criterion. J. Cent. South Univ. 2022, 53, 620–630. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.L.; Wang, F.G.; Li, G.C.; Liu, G.L.; Wang, J.; Qi, Z.J. Optimization of composite filling slurry ratio and influence mechanism of microstructure based on response surface methodology. J. Compos. Mater. 2021, 38, 2724–2736. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.C.; Fourie, A.; Chen, Q. Neural network and particle swarm optimization for predicting the unconfined compressive strength of cemented paste backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 159, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yao, Y.; Wang, L. Effect of shrinkage reducing agent on volume stability of cement stone and its mechanism. J. Silic. 2010, 38, 478–485. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, S.H.; Shao, Y.J.; Wu, A.X. Expansion and strength properties of cemented backfill using sulphidic mill tailings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 165, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.X.; Du, C.F.; Song, W.D. Strength sensitivity and failure mechanism of full tailings cemented backfill. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing 2014, 36, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, G.H.; Zhang, J.X.; Li, M. Prediction of compression and deformation behaviours of gangue backfill materials under multi-factor coupling effects for strata control and pollution reduction. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 36528–36540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derringer, G.C.; Suich, R.R. Simultaneous Optimization of Several Response Variable. J. Qual. Technol. 1980, 12, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.S.; Li, L.; Yao, M.L. An Investigation of the Uniaxial Compressive Strength of a Cemented Hydraulic Backfill Made of Alluvial Sand. Minerals 2017, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, S.; Song, W.D. Effect of Filling Interval Time on Long-Term Mechanical Strength of Layered Cemented Tailing Backfill. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 9507852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, S.; Yilmaz, E.; Yin, Z. CT scanning of internal crack mechanism and strength behavior of cement-fiber-tailings matrix composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 116, 103865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.S.; Zhang, Q.L.; Qi, C.C. Recycling phosphogypsum and construction demolition waste for cemented paste backfill and its environmental impact. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 186, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Huang, Y.L.; Qiao, M. Effects of Water Soaked Height on the Deformation and Crushing Characteristics of Loose Gangue Backfill Material in Solid Backfill Coal Mining. Processes 2018, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, Y. Ground control in mining steeply dipping coal seams by backfilling with waste rock. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2018, 118, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Kang, T.H.; Kang, J.T. Hydration dynamic process and hydration mechanism of fly ash paste filling material. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2018, 37, 4384–4394. [Google Scholar]

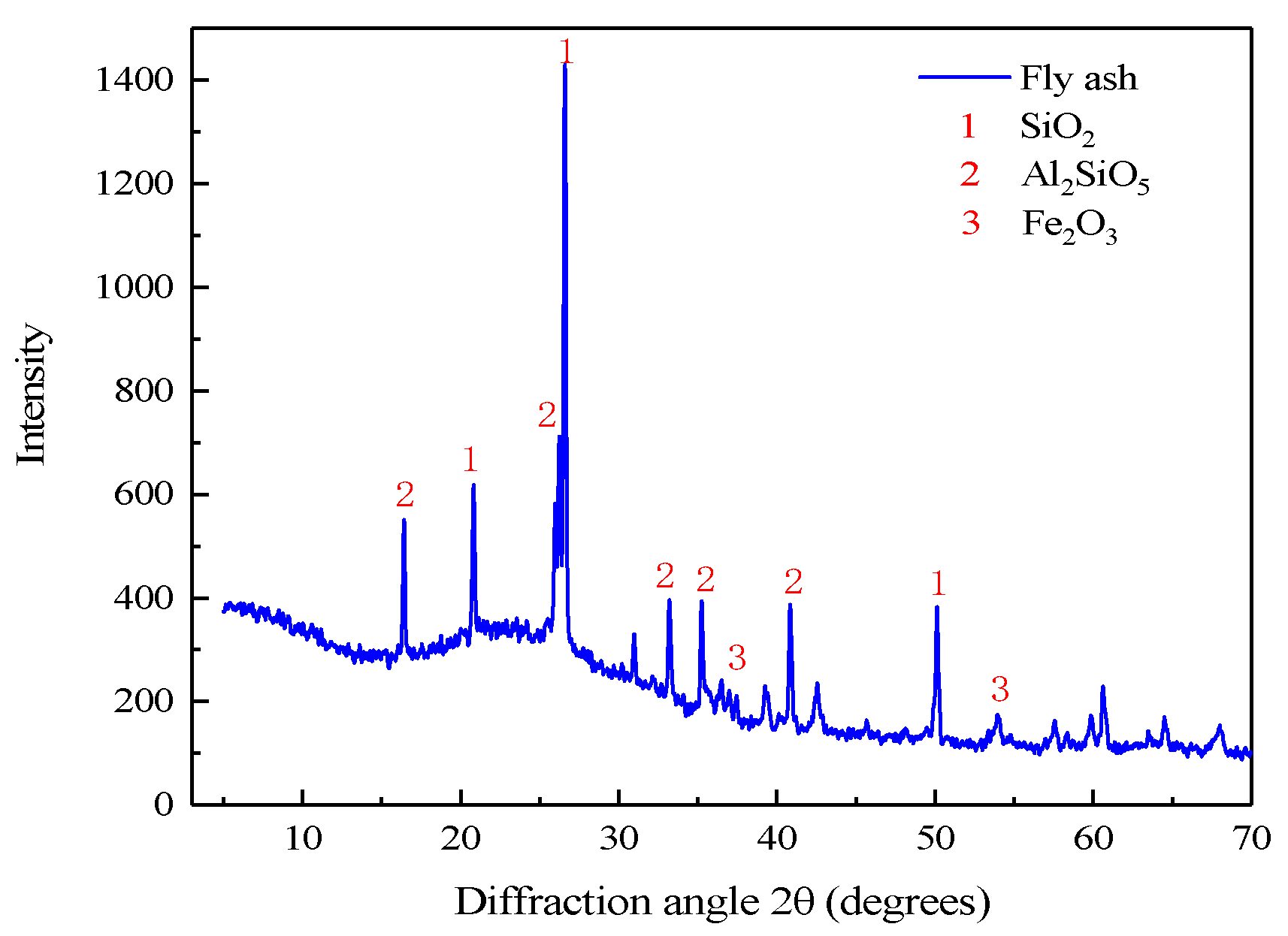
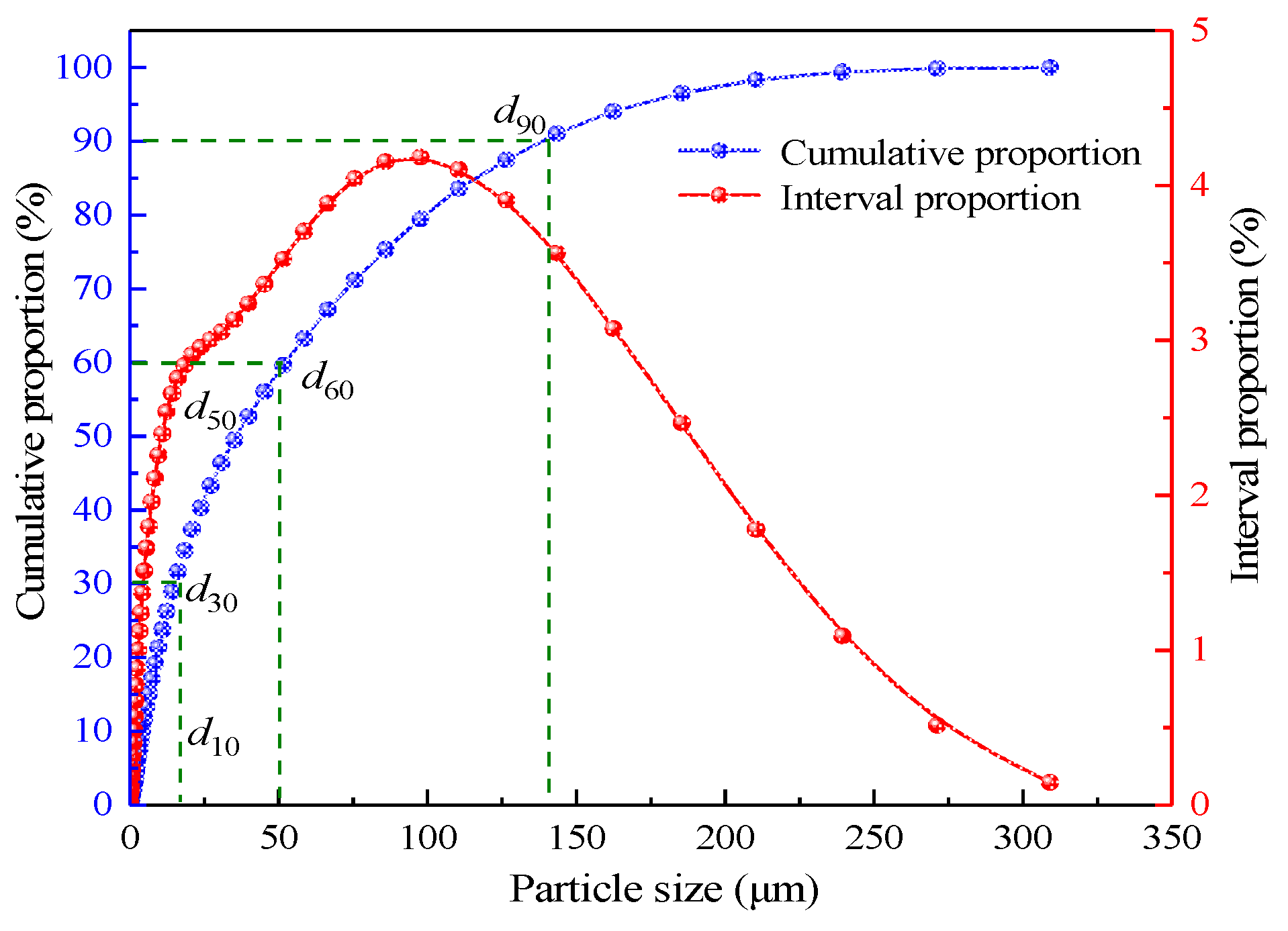


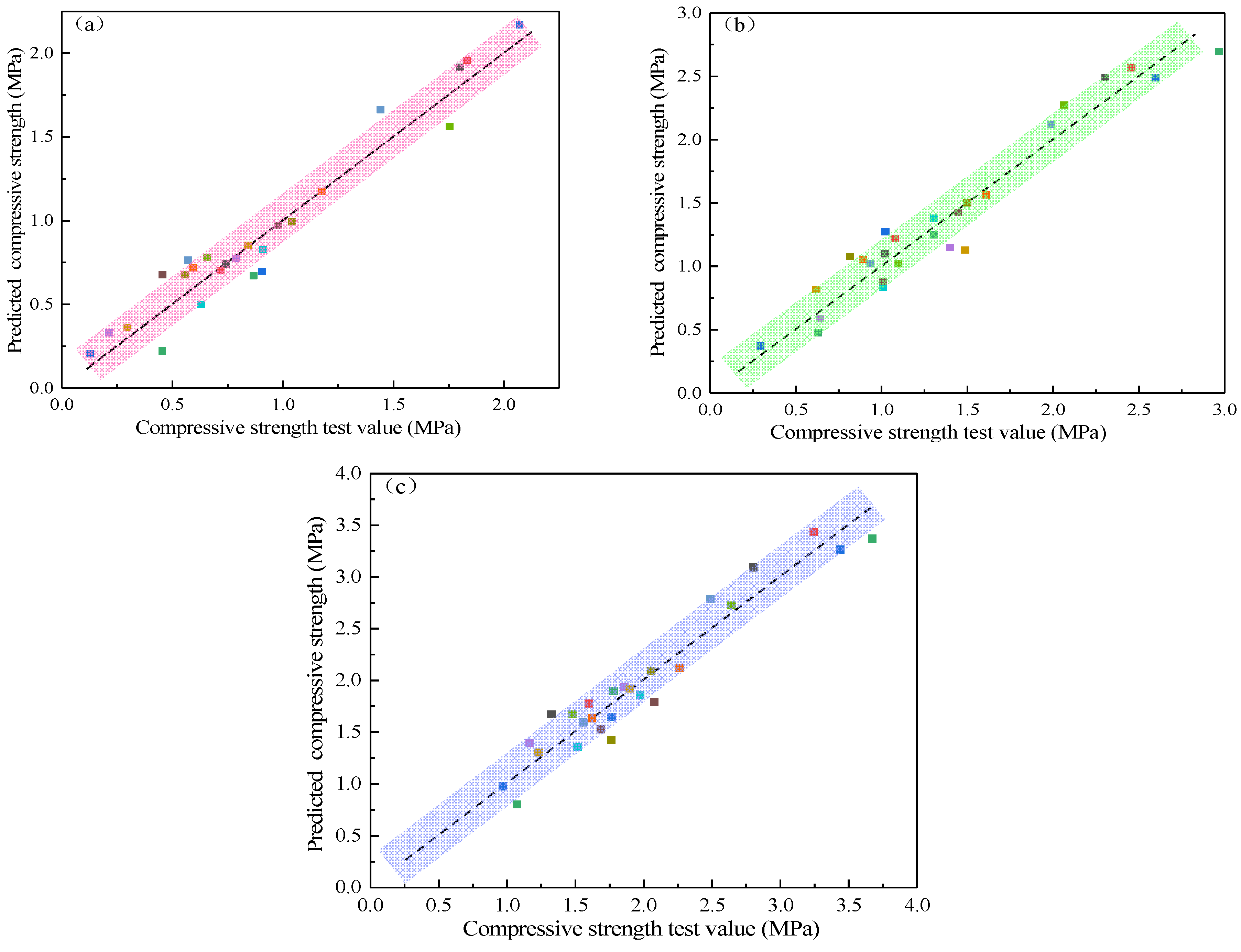

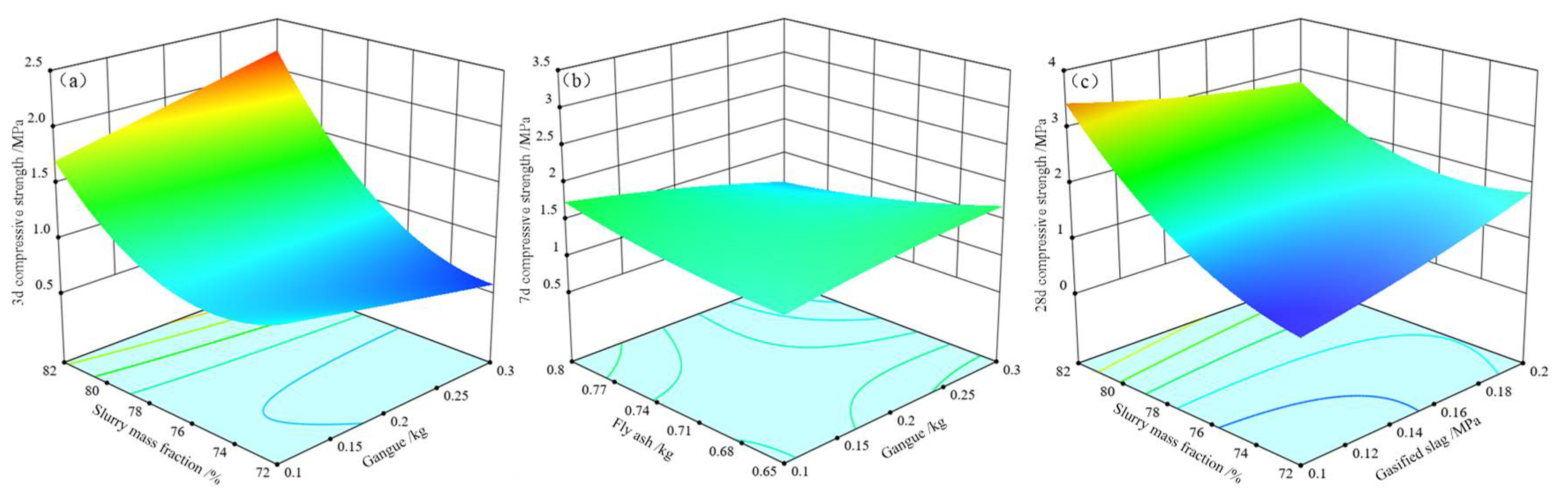
| Grain size (mm) | 0–5 | 5–10 | 10–15 | >15 |
| Percentage (%) | 24.8 | 32.7 | 28.3 | 14.2 |
| Factors | Variables | Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coal gangue | 0.1 kg | 0.2 kg | 0.3 kg | |
| Fly ash | 0.65 kg | 0.73 kg | 0.8 kg | |
| Gasification slag | 0.1 kg | 0.15 kg | 0.2 kg | |
| Mass fraction | 72% | 77% | 82% | |
| Number | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.15 | 82 | 1.97 | 3.18 | 4.38 |
| 2 | 0.2 | 0.65 | 0.15 | 82 | 1.96 | 2.74 | 3.52 |
| 3 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 77 | 1.13 | 1.23 | 1.89 |
| 4 | 0.1 | 0.73 | 0.15 | 82 | 1.88 | 2.21 | 2.61 |
| 5 | 0.1 | 0.65 | 0.15 | 77 | 0.94 | 1.58 | 1.65 |
| 6 | 0.2 | 0.73 | 0.15 | 77 | 0.86 | 1.53 | 1.77 |
| 7 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 0.15 | 77 | 0.54 | 0.90 | 1.13 |
| 8 | 0.1 | 0.73 | 0.2 | 77 | 0.80 | 1.33 | 1.50 |
| 9 | 0.1 | 0.73 | 0.1 | 77 | 0.88 | 1.50 | 1.52 |
| 10 | 0.2 | 0.65 | 0.1 | 77 | 0.97 | 1.63 | 1.66 |
| 11 | 0.2 | 0.73 | 0.2 | 82 | 1.63 | 2.14 | 2.48 |
| 12 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.15 | 77 | 1.25 | 1.77 | 1.68 |
| 13 | 0.3 | 0.73 | 0.2 | 77 | 1.12 | 1.65 | 2.06 |
| 14 | 0.2 | 0.73 | 0.15 | 77 | 0.86 | 1.23 | 1.60 |
| 15 | 0.2 | 0.73 | 0.15 | 77 | 0.84 | 1.16 | 1.24 |
| 16 | 0.3 | 0.65 | 0.15 | 77 | 1.41 | 1.70 | 2.02 |
| 17 | 0.1 | 0.73 | 0.15 | 72 | 1.03 | 1.20 | 1.41 |
| 18 | 0.3 | 0.73 | 0.15 | 82 | 2.38 | 2.40 | 2.78 |
| 19 | 0.3 | 0.73 | 0.15 | 72 | 0.50 | 0.53 | 0.96 |
| 20 | 0.2 | 0.73 | 0.15 | 77 | 1.15 | 1.32 | 1.46 |
| 21 | 0.2 | 0.65 | 0.2 | 77 | 1.30 | 1.25 | 2.19 |
| 22 | 0.2 | 0.73 | 0.1 | 72 | 0.80 | 0.91 | 1.03 |
| 23 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 77 | 1.08 | 1.15 | 1.59 |
| 24 | 0.2 | 0.73 | 0.15 | 77 | 1.01 | 1.16 | 1.48 |
| 25 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.15 | 72 | 0.56 | 0.92 | 1.19 |
| 26 | 0.3 | 0.73 | 0.1 | 77 | 1.00 | 1.26 | 1.75 |
| 27 | 0.2 | 0.73 | 0.2 | 72 | 1.17 | 1.23 | 1.94 |
| 28 | 0.2 | 0.65 | 0.15 | 72 | 0.90 | 1.08 | 1.31 |
| 29 | 0.2 | 0.73 | 0.1 | 82 | 2.18 | 2.82 | 4.25 |
| Variation Source | Square and | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Models | 5.91 | 8.94 | 12.72 | 0.4222 | 0.6387 | 0.9087 | 15.82 | 11.20 | 9.86 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| 0.0024 | 0.1008 | 0.0002 | 0.0024 | 0.1008 | 0.0002 | 0.0903 | 1.77 | 0.0023 | 0.7683 | 0.2050 | 0.9627 | |
| 0.0602 | 0.0520 | 0.0752 | 0.0602 | 0.0520 | 0.0752 | 2.26 | 0.9116 | 0.8163 | 0.1553 | 0.3559 | 0.3816 | |
| 0.0048 | 0.0019 | 0.1045 | 0.0048 | 0.0019 | 0.1045 | 0.1799 | 0.0329 | 1.13 | 0.6779 | 0.8587 | 0.3048 | |
| 4.01 | 7.11 | 9.26 | 4.01 | 7.11 | 9.26 | 150.43 | 124.71 | 100.48 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| 0.2916 | 0.2450 | 0.2970 | 0.2916 | 0.2450 | 0.2970 | 10.93 | 4.29 | 3.22 | 0.0052 | 0.0472 | 0.0942 | |
| 0.0100 | 0.0784 | 0.0342 | 0.0100 | 0.0784 | 0.0342 | 0.3748 | 1.37 | 0.3715 | 0.5502 | 0.2607 | 0.5520 | |
| 0.2162 | 0.1640 | 0.1190 | 0.2162 | 0.1640 | 0.1190 | 8.10 | 2.88 | 1.29 | 0.0129 | 0.1121 | 0.2748 | |
| 0.0196 | 0.0529 | 0.0042 | 0.0196 | 0.0529 | 0.0042 | 0.7346 | 0.9272 | 0.0459 | 0.4058 | 0.3519 | 0.8335 | |
| 0.0306 | 0.1024 | 0.0506 | 0.0306 | 0.1024 | 0.0506 | 1.15 | 1.79 | 0.5495 | 0.3021 | 0.2017 | 0.4708 | |
| 0.2116 | 0.1260 | 0.7056 | 0.2116 | 0.1260 | 0.7056 | 7.93 | 2.21 | 7.66 | 0.0137 | 0.1594 | 0.0151 | |
| 0.0001 | 0.0147 | 0.1038 | 0.0001 | 0.0147 | 0.1038 | 0.0041 | 0.2574 | 1.13 | 0.9501 | 0.6198 | 0.3065 | |
| 0.0173 | 0.0401 | 0.2429 | 0.0173 | 0.0401 | 0.2429 | 0.6469 | 0.7036 | 2.64 | 0.4347 | 0.4157 | 0.1268 | |
| 0.0133 | 0.0429 | 0.0413 | 0.0133 | 0.0429 | 0.0413 | 0.4996 | 0.7521 | 0.4478 | 0.4913 | 0.4004 | 0.5143 | |
| 1.01 | 0.6954 | 1.62 | 1.01 | 0.6954 | 1.62 | 38.00 | 12.19 | 17.58 | <0.0001 | 0.0036 | 0.0009 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Z.; Yang, K.; He, X.; Zhang, J.; Hu, G. Experimental Study on the Optimization of Coal-Based Solid Waste Filling Slurry Ratio Based on the Response Surface Method. Materials 2022, 15, 5318. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155318
Wei Z, Yang K, He X, Zhang J, Hu G. Experimental Study on the Optimization of Coal-Based Solid Waste Filling Slurry Ratio Based on the Response Surface Method. Materials. 2022; 15(15):5318. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155318
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Zhen, Ke Yang, Xiang He, Jiqiang Zhang, and Guangcheng Hu. 2022. "Experimental Study on the Optimization of Coal-Based Solid Waste Filling Slurry Ratio Based on the Response Surface Method" Materials 15, no. 15: 5318. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155318
APA StyleWei, Z., Yang, K., He, X., Zhang, J., & Hu, G. (2022). Experimental Study on the Optimization of Coal-Based Solid Waste Filling Slurry Ratio Based on the Response Surface Method. Materials, 15(15), 5318. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155318






