The Relationship between Microstructure and Fracture Behavior of TiAl/Ti2AlNb SPDB Joint with High Temperature Titanium Alloy Interlayers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure and Elements Diffusion of the TiAl/Ti2AlNb SPDB Joint
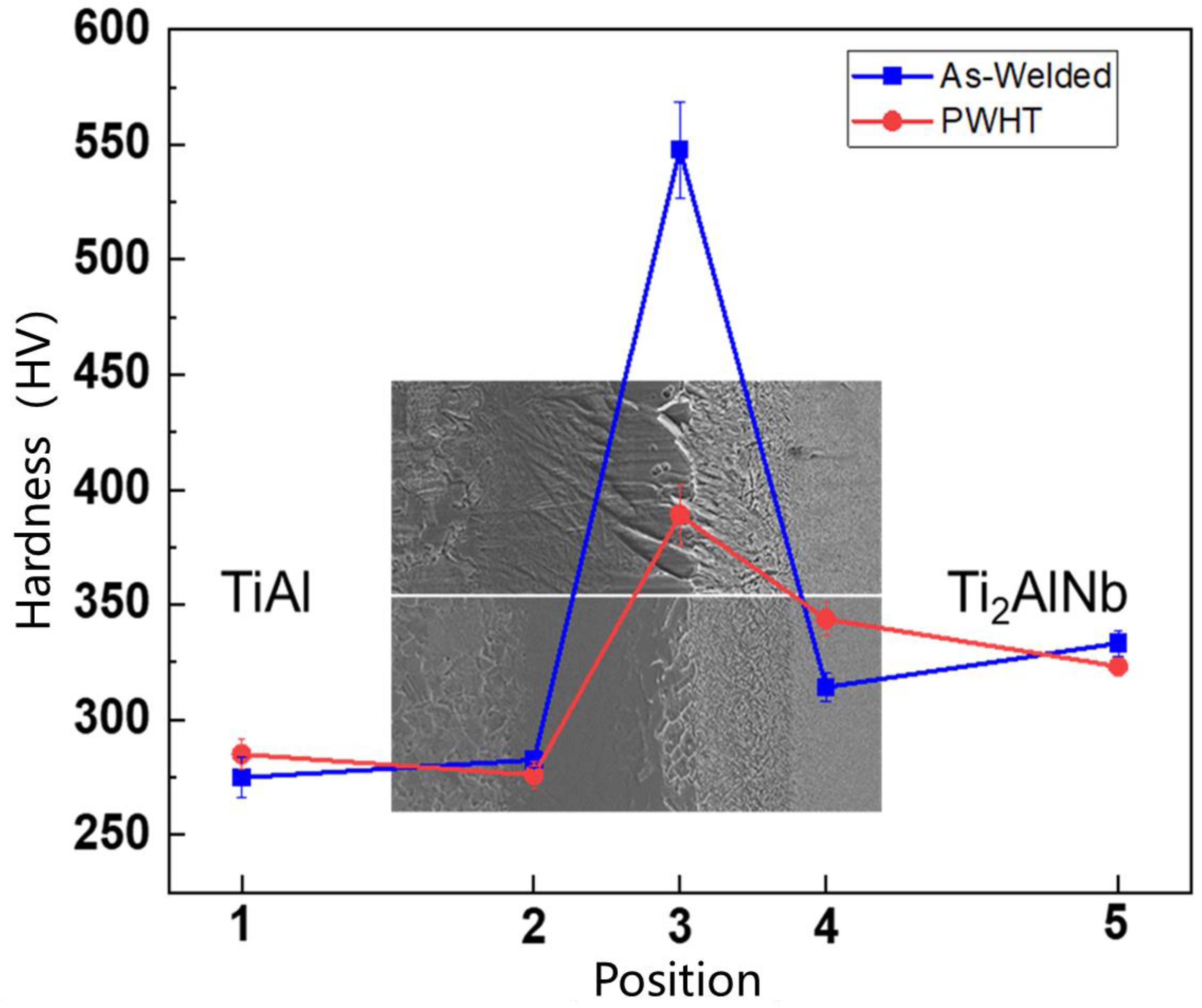
3.2. Microhardness of the TiAl/Ti2AlNb SPDB Joint
3.3. Tensile Tests of the TiAl/Ti2AlNb SPDB Joint
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The TiAl/Ti2AlNb joint at higher cooling rates exhibits several distinct regions, from TiAl to Ti2AlNb side: TiAl BM → DP and NG → α2-phase matrix with needle-like α-phase → bulk α2-phase → needle-like α-phase → metastable β-phase → Ti2AlNb BM. After heat treatment at 800 °C for 24 h, the density and size of the needle-like α phase in region 3 increased slightly, and a large number of fine O phases are precipitated from the metastable β phase matrix after heat treatment;
- (2)
- The microhardness of the joint is in the shape of a mountain peak. The maximum microhardness at the interface is above 500 HV, and after heat treatment, it is significantly reduced to 400 HV. Heat treatment has a certain effect on the Ti2AlNb side near the interface and the microhardness of this region increases after heat treatment;
- (3)
- The fracture of the joint occurred at the interface with brittle fracture. At room temperature tensile test conditions, the crack that formed in the joint penetrated the entire bulk α2 phase, appearing as cleavage fracture. The crack propagated along near the interface of TiAl with an intergranular fracture and Ti2AlNb with a quasi-cleavage fracture and crossed the joint with the tensile test conditions at 650 °C and 750 °C.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simões, S.; Viana, F.; Vieira, M.F. Joining Technology of γ-TiAl Alloys, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzogbewu, T.C.; du Preez, W.B. Additive Manufacturing of Ti-Based Intermetallic Alloys: A Review and Conceptualization of a Next-Generation Machine. Materials 2021, 14, 4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Wang, M.; Du, Y.; Li, J. Size-Dependent Structural Properties of a High-Nb TiAl Alloy Powder. Materials 2020, 13, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, S.; He, A.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, H. Investigation on the microstructure evolution and dynamic recrystallization mechanisms of TiAl alloy at elevated temperature. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 968–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Li, J.S.; Xue, X.Y.; Tang, B.; Kou, H.C.; Bouzy, E. Superplastic deformation mechanisms of high Nb containing TiAl alloy with (α2+γ) microstructure. Intermetallics 2016, 75, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.D.; Qi, Z.X.; Chen, G. Increasing high-temperature fatigue resistance of polysynthetic twinned TiAl single crystal by plastic strain delocalization. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 93, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmut, C.; Heinrich, K. Processing and applications of intermetallic γ-TiAl-based alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2000, 9, 551–570. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Cuiuri, D.; Li, H.J.; Pan, Z.X.; Shen, C. The effect of postproduction heat treatment on γ-TiAl alloys produced by the GTAW-based additive manufacturing process. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 657, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xue, S.H. Effect of Ag on the properties of solders and brazing filler metals. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiue, R.K.; Wu, S.K.; Chen, S.Y. Infrared brazing of TiAl intermetallic using pure silver. Intermetallics 2004, 12, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiue, R.K.; Wu, S.K.; Chen, S.Y. Infrared brazing of TiAl intermetallic using BAg-8 braze alloy. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 1991–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, W.; Sekulic, D.P.; He, P. Reactive wetting of AgCuTi filler metal on the TiAl-based alloy substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 259, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.K.; Lee, J.G. Mechanical and corrosion properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy joints brazed with a low-melting-point 62.7Zr-11.0Ti-13.2Cu-9.8Ni-3.3Be amorphous filler metal. Mater. Charact. 2013, 81, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Qi, J.L.; Song, X.G.; Feng, J.C. Welding and joining of titanium aluminides. Materials 2014, 7, 4930–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, X.Q.; Yang, Z.W.; Wang, D.P.; Liu, X.G.; Liu, Y.C. Diffusion bonding of Ti2AlNb alloy using pure Ti foil as an interlayer. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 756, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, W.; Feng, Z.X.; Sun, J.; Li, X.Q. Microstructure and shear strength of γ-TiAl/GH536 joints brazed with Ti-Zr-Cu-Ni-Fe-Co-Mo filler alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2020, 30, 2134–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Xiong, J.T.; Du, Y.J.; Wang, Y.; Shi, J.M.; Li, J.L. Effects of pure Ti or Zr powder on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti6Al4V and Ti2AlNb joints brazed with TiZrCuNi. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 788, 139602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Dai, X.Y.; Liu, J.Q.; Si, X.Q.; Feng, J.C. Relationship between microstructure and mechanical properties of TiAl/Ti2AlNb joint brazed using Ti-27Co eutectic filler metal. Mater. Des. 2017, 121, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.Y.; Ren, H.S.; Shang, Y.L.; Xiong, H.P.; Zhang, K.; Zheng, J.H.; Liu, D.; Lin, J.G.; Jiang, J. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of Ti2AlNb/TiAl brazed joint using newly-developed Ti-Ni-Nb-Zr filler alloy. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2020, 30, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; Liu, B.; He, Y. Diffusion bonding of Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W alloy by spark plasma sintering. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 230, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Hu, K.; Hu, D.W.; Han, C.; Tong, Y.; Yang, X.; Wei, F.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Diffusion bonding between TZM alloy and WRe alloy by spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 764, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.M.; Cao, L.; Xie, Y.H.; Zhou, Y.; Luoa, Y.F.; Mudia, K.Q.; Gaoa, H.Y.; Wanga, J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb alloy joints produced by transient liquid phase bonding using spark plasma sintering. Mater. Charact. 2019, 147, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.J.; Yu, L.P.; Liu, H.X.; He, Y.H.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Q.K. Diffusion welding of powder metallurgy high speed steel by spark plasma sintering. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2020, 275, 116383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetsui, T. Application of TiAl in a Turbocharger for Passenger Vehicles. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2001, 3, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanatusgu, N.; Sato, T.; Naruo, Y.; Kashiwagi, T.; Mizutani, T.; Monji, T.; Hanabe, K. Development study on ATREX engine. Acta Astronaut. 1997, 41, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.W.; Kong, J. A high-strength vacuum-brazed TiAl/Ni joint at room temperature and high temperature with an amorphous foil Zr-Al-Ni-Co filler metal. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 44, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhu, X.X.; Chen, H.Z.; Zhang, L.X. Brazing of TiAl and Ti2AlNb alloys using high-entropy braze fillers. Mater. Charact. 2022, 186, 111814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.J.; Ren, X.Y.; Shang, Y.L.; Xiong, H.P.; Jiang, J. Develop a novel high-strength vacuum brazing technique for γ-TiAl intermetallic. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2021, 4, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimiduk, D.M. Gamma titanium aluminide alloys-an assessment within the competition of aerospace structural materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 263, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.X.; Chen, C.H.; He, J.C.; Hou, J.B.; Chai, L.; Lv, Y.L. Spark plasma diffusion bonding of TiAl/Ti2AlNb with Ti as interlayer. Materials 2020, 13, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, F.; Xu, J.; Ma, X.; Liang, X. Precipitation Behavior of O Phase during Continuous Cooling of Ti-22Al-25Nb Alloy. Metals 2022, 12, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, H.; Liu, Y. Influence of cooling rates on microstructure and tensile properties of a heat treated Ti2AlNb-based alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 817, 141345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, J.; Zhang, T.; Tao, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Microstructure and Properties of a Ti3Al Linear Friction Welding Joint. Materials 2019, 12, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaszyca, K.; Schmidt, M.; Chmielewski, M.; Pietrzak, K.; Zybala, R. Joining of thermoelectric materials with metallic electrode using Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) technique. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 10277–10282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göken, M.; Kempf, M.; Nix, W.D. Hardness and modulus of the lamellar microstructure in PST-TiAl studied by nanoindentations and AFM. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathabathe, M.N.; Bolokang, A.S.; Govender, G.; Siyasiya, C.W.; Mostert, R.J. Deformation and fracture behaviour of the γ-TiAl based intermetallic alloys. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2021, 121, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ding, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, R.; Guo, J.; Fu, H. Variations of microstructure and tensile property of γ-TiAl alloys with 0–0.5 at% C additives. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 700, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Wu, Q.; Bi, K.; Xu, T.; Kong, F. Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of a Novel β-Solidifying TiAl Alloy. Materials 2019, 12, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mphahlele, M.R.; Olevsky, E.A.; Olubambi, P.A. Spark Plasma Sintering of Near Net Shape Titanium Aluminide: A Review. In Spark Plasma Sintering; Cao, G., Estournès, C., Garay, J., Orrù, R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Chapter 12; pp. 281–299. ISBN 9780128177440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.C.; Shan, D.B.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.A.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Nutt, S. Effects of extrusion deformation on microstructure, mechanical properties and hot workability of β containing TiAl alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 571, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Wei, Y.; Feng, G.; Deng, D. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Vacuum Diffusion Bonded Ti2AlNb/Ti/TC4 Joint. Crystals 2021, 11, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, K.; Sardana, N. Mechanical Properties of the Ti2AlNb Intermetallic: A Review. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2021, 74, 1839–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, H.; Mayer, S. Design, Processing, Microstructure, Properties and Applications of Advanced Intermetallic TiAl Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2013, 15, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Tang, B.; Chen, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Kou, H.; Li, J. Precipitation Behavior of Orthorhombic Phase in Ti-22Al-25Nb Alloy during Slow Cooling Aging Treatment and Its Effect on Tensile Properties. Metals 2020, 10, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Kim, J.-W.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, S.E.; Park, Y.-H. Effect of Microstructure Control on the Mechanical Properties of Hot Worked TiAl Alloy. Korean J. Met. Mater. 2020, 58, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Ti | Al | Nb | Cr | O | N | H | C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiAl | Bal. | 31.75 | 4.75 | 2.61 | 0.036 | 0.005 | 0.0005 | 0.041 |
| Ti2AlNb | Bal. | 10.90 | 43.6 | - | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.01 | - |
| Testing Temperature (°C) | Average Tensile Strength (Mpa) | Average Elongation |
|---|---|---|
| RT | 453.0 ± 51.0 | 1.76 ± 1.34 |
| 650 | 541.33 ± 4.67 | 3.0 ± 1.0 |
| 750 | 471.33 ± 9.33 | 3.33 ± 0.17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, M.; Tian, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, B.; He, J. The Relationship between Microstructure and Fracture Behavior of TiAl/Ti2AlNb SPDB Joint with High Temperature Titanium Alloy Interlayers. Materials 2022, 15, 4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144849
Liao M, Tian H, Zhao L, Zhang B, He J. The Relationship between Microstructure and Fracture Behavior of TiAl/Ti2AlNb SPDB Joint with High Temperature Titanium Alloy Interlayers. Materials. 2022; 15(14):4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144849
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Minxing, Hao Tian, Lei Zhao, Boxian Zhang, and Jianchao He. 2022. "The Relationship between Microstructure and Fracture Behavior of TiAl/Ti2AlNb SPDB Joint with High Temperature Titanium Alloy Interlayers" Materials 15, no. 14: 4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144849
APA StyleLiao, M., Tian, H., Zhao, L., Zhang, B., & He, J. (2022). The Relationship between Microstructure and Fracture Behavior of TiAl/Ti2AlNb SPDB Joint with High Temperature Titanium Alloy Interlayers. Materials, 15(14), 4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144849





