Sensitivity Analysis of Reinforced Aluminum Based Metal Matrix Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
2.1. Chemical Compositions of MMCs
2.2. Mixing and Compaction of Powders
2.3. Sintering
3. Experimental Results
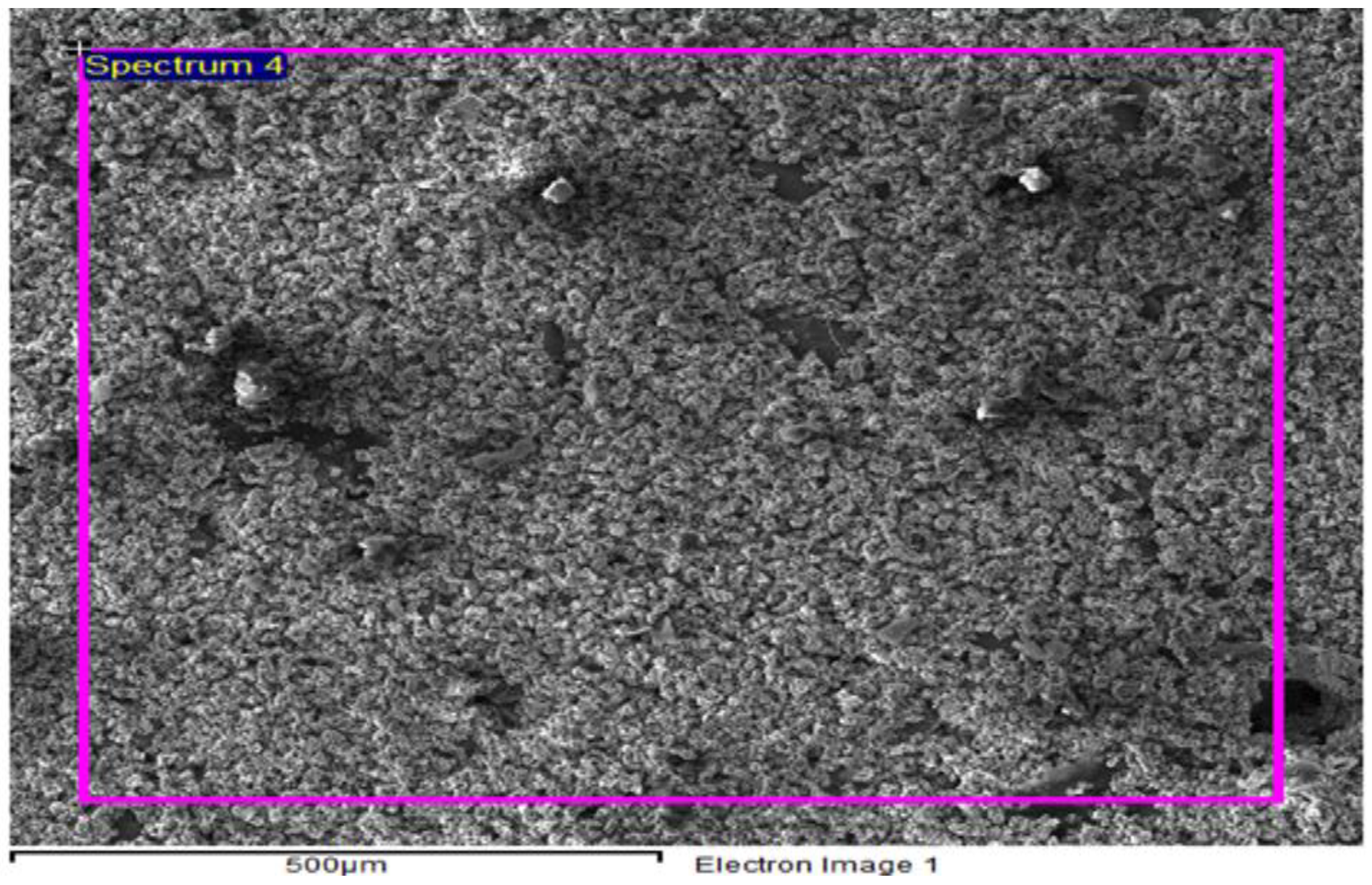
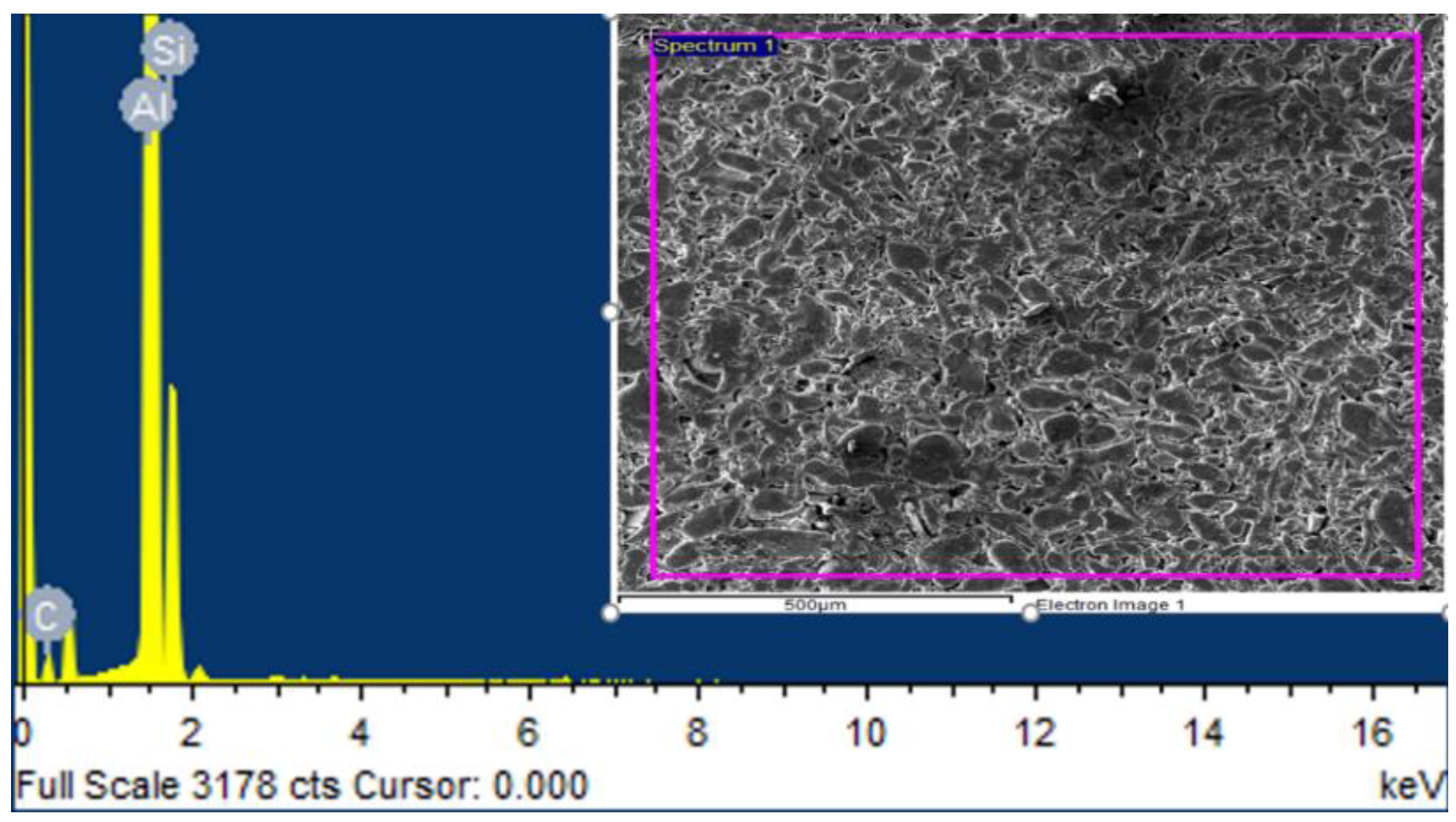
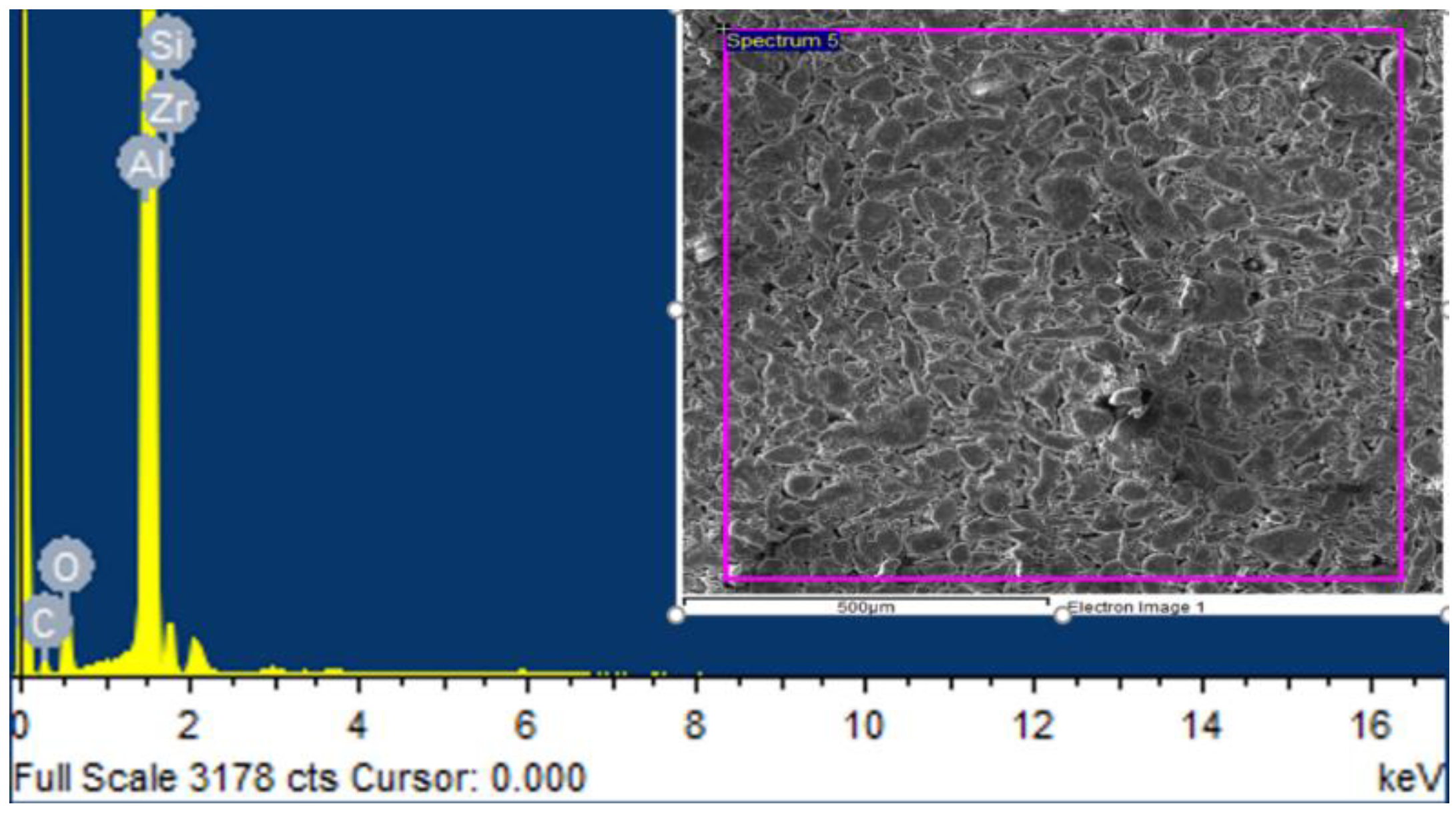
3.1. EDS Analysis of Samples
3.2. Density and Porosity
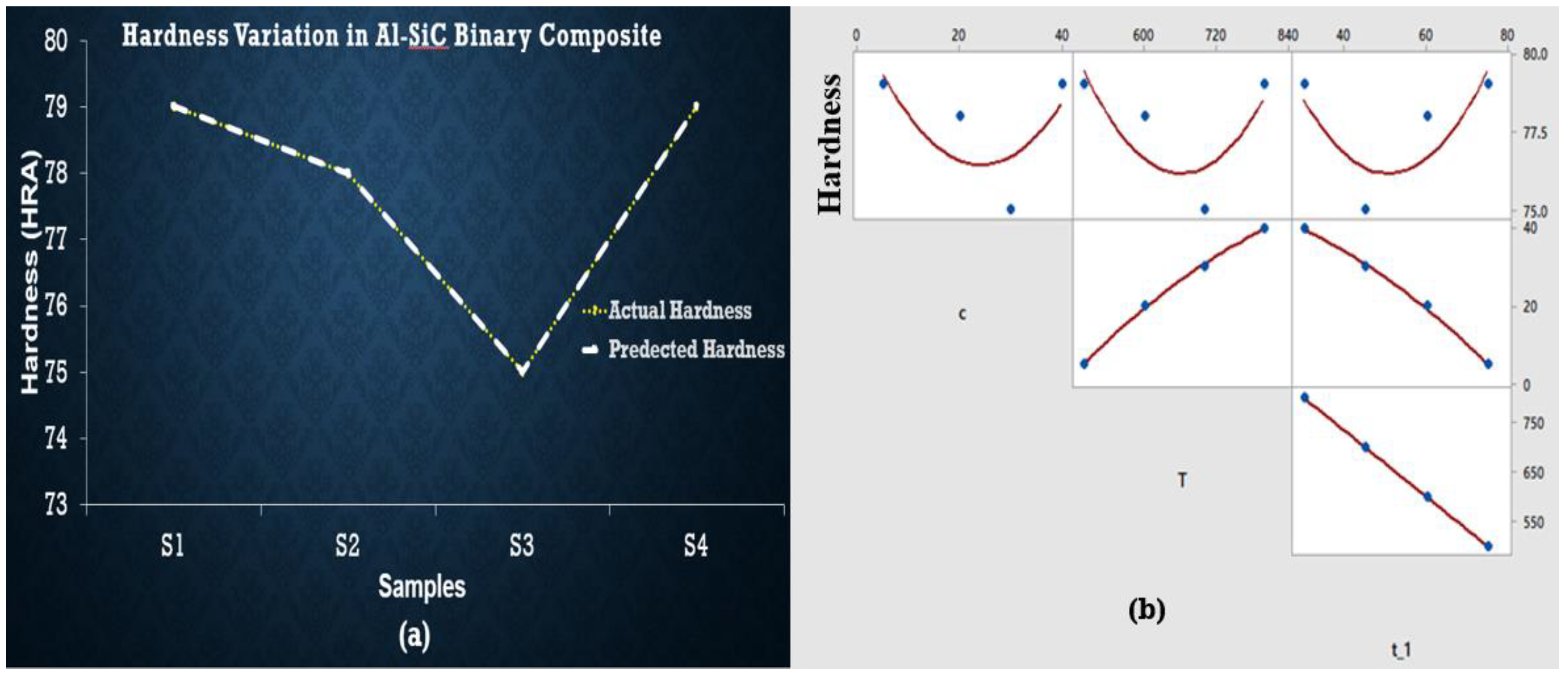
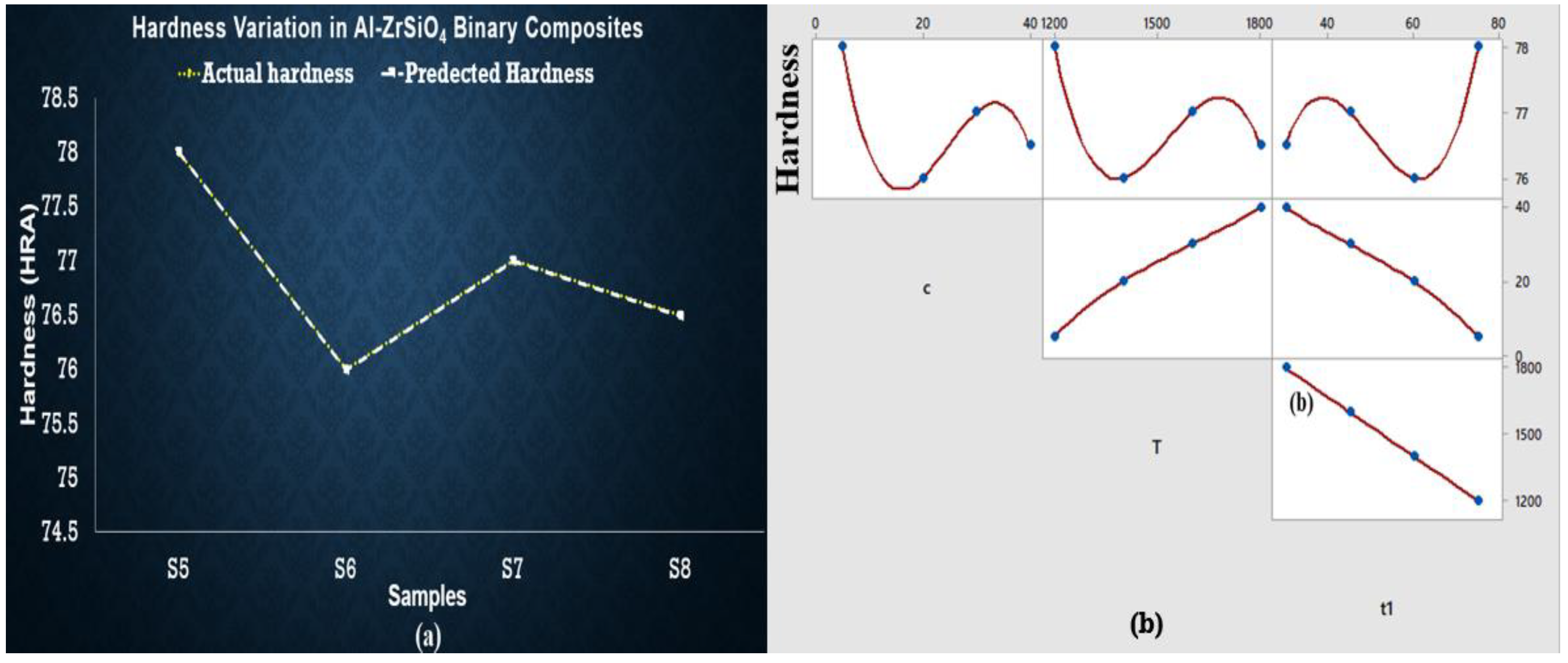
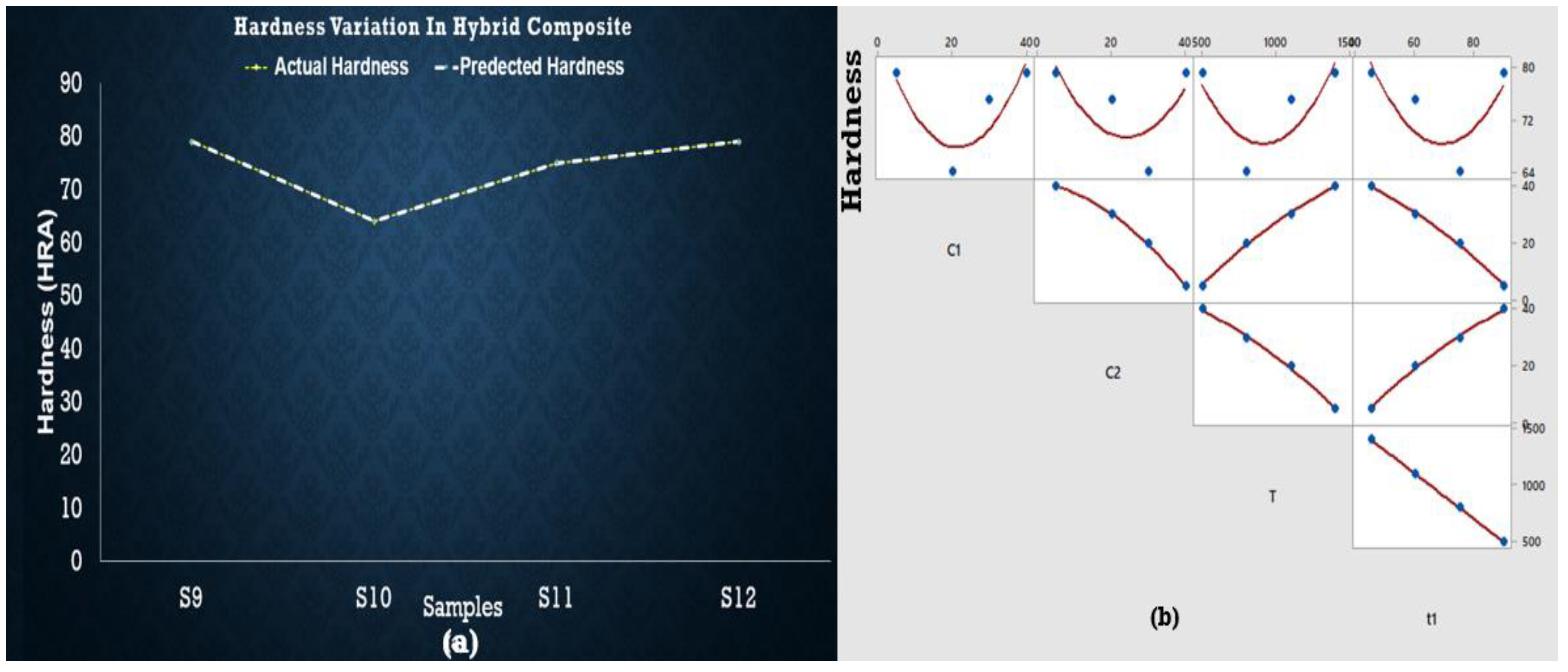
3.3. Hardness of Sintered Samples
3.4. Regression Analysis for Hardness of Sintered Samples
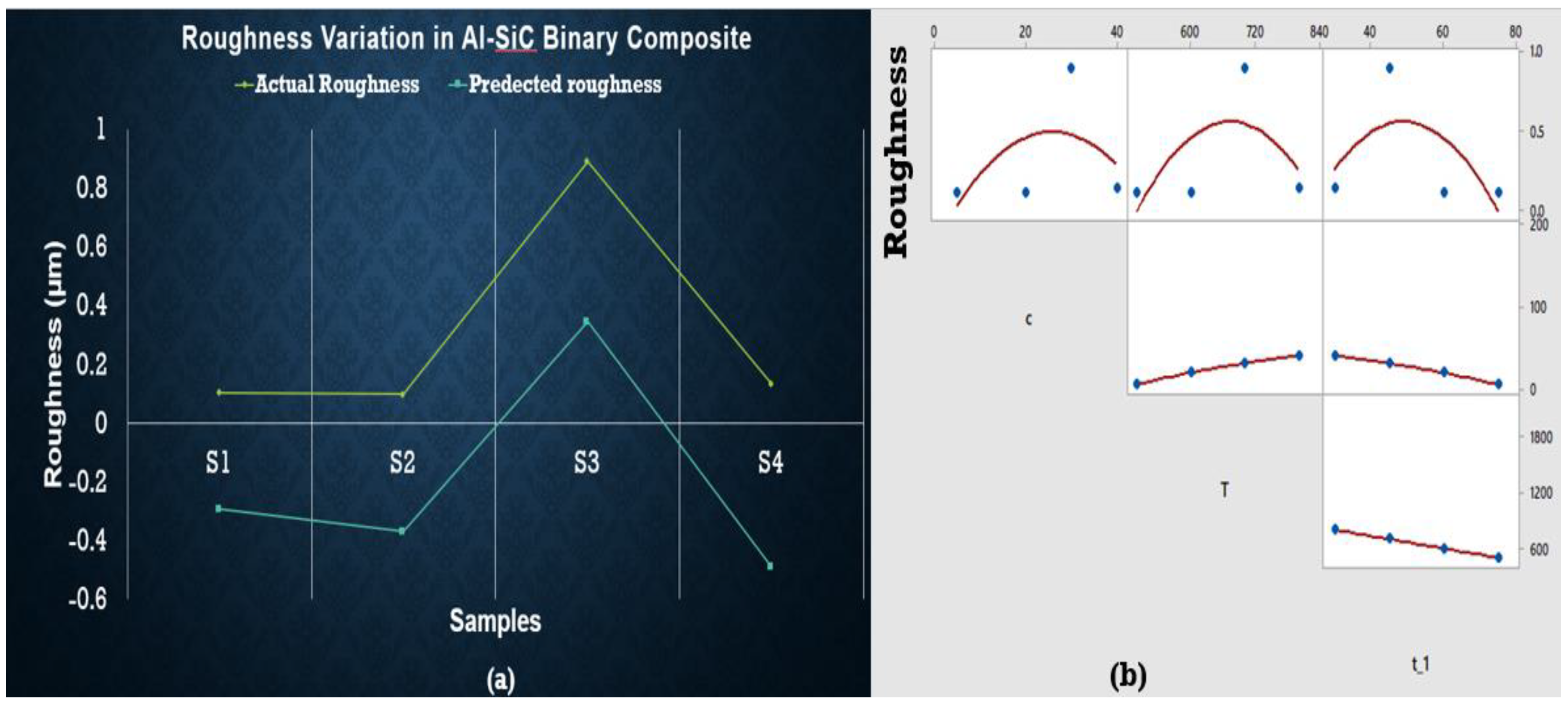
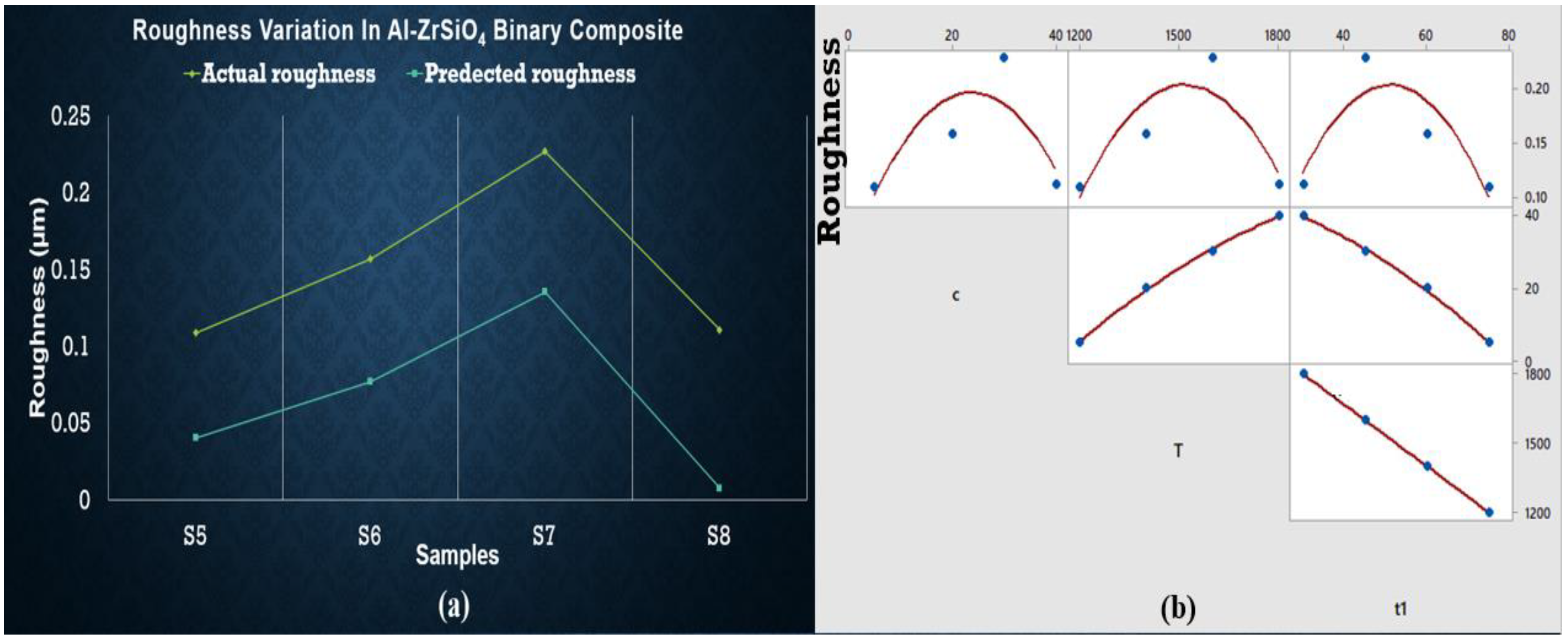
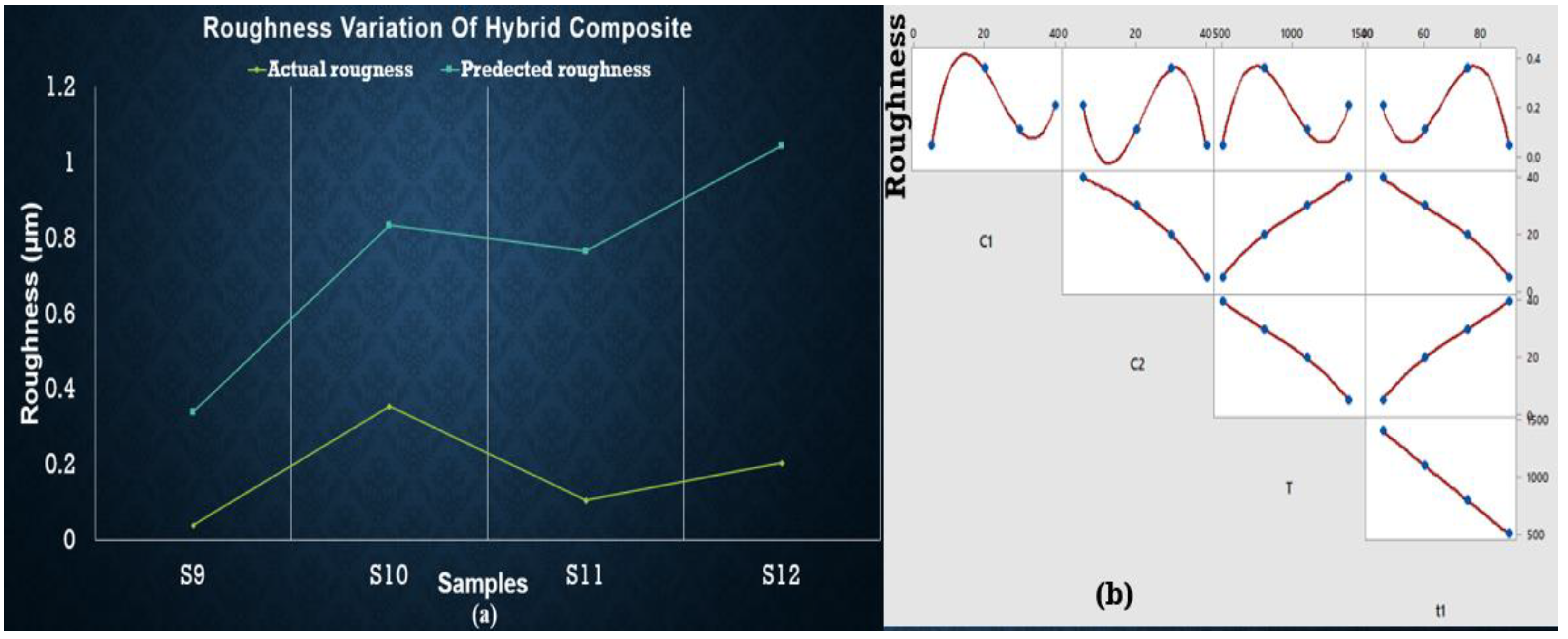
3.5. Roughness of Sintered Samples
3.6. Regression Analysis for Roughness of Sintered Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- EDS analysis validate the presence of SiC and ZrSiO4 in the fabricated composites, as the distribution of reinforced particles in the aluminum matrix is estimated from elemental analysis.
- It is concluded from the current study that the hardness of aluminum is enhanced the most with the addition of maximum wt % of SiC, i.e., wt % 40 at elevated temperature in the case of binary and hybrid MMCs.
- Enhancement of roughness is low in the case of less wt % of SiC but higher wt % of ZrSiO4.
- It has also been observed that the intercept values are higher in the case of hardness and roughness of Al-SiC binary samples. However, for hybrid samples, some parameters other than after composition, temperature, and time are also responsible for this behavior, which must be studied in further detail.
- It is concluded from the current study that the sintering time did not impart significant hardness and roughness in all the materials that were studied.
- Future studies may focus on investigating machining parameters adopted for the non-conventional machining of these samples. Effects of machining on the hardness and surface roughness of these samples and their parametric comparison before and after machining must be an exciting area to explore.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vani, V.V.; Chak, S.K. The Effect of Process Parameters in Aluminum Metal Matrix Composites with Powder Metallurgy. Manuf. Rev. 2018, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, S.; Mani, N.; Balaji, S.; Abhijith, M.; Surendaran, K. Mechanical Behaviour of Aluminium Hybrid Metal Matrix Composites–a Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 16, 1020–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.; Singh, B.; Saxena, K.K. Manufacturing Techniques for Metal Matrix Composites (MMC): An Overview. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 6, 441–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoi, N.K.; Singh, H.; Pratap, S. Developments in the Aluminum Metal Matrix Composites Reinforced by Micro/Nano Particles–a Review. J. Compos. Mater. 2020, 54, 813–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbulov, I.N.; Dobránszky, J. Producing Metal Matrix Syntactic Foams by Pressure Infiltration. Period. Polytechnica. Eng. Mech. Eng. 2008, 52, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaptay, G. The Threshold Pressure of Infiltration into Fibrous Preforms Normal to the Fibers’ Axes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Orbulov, I.N.; Németh, Á.; Dobránszky, J. Infiltration Characteristics of Carbon Fiber Reinforced MMCs. Mater. Sci. Forum 2008, 659, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cordovilla, C.; Louis, E.; Narciso, J. Pressure Infiltration of Packed Ceramic Particulates by Liquid Metals. Acta Mater. 1999, 47, 4461–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszczyńska-Malik, K.N.; Kamieniak, J. AZ91 Magnesium Matrix Foam Composites with Fly Ash Cenospheres Fabricated by Negative Pressure Infiltration Technique. Mater. Charact. 2017, 128, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, G.; Nutt, S.R. Synthesis of Syntactic Steel Foam Using Mechanical Pressure Infiltration. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 535, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkowski, L.B.; Liu, K.C.; Chattopadhyay, A. From Ordered to Disordered: The Effect of Microstructure on Composite Mechanical Performance. CMC 2013, 34, 161–193. [Google Scholar]
- Composite Production by Pressure Infiltration|Scientific.Net. Available online: https://www.scientific.net/msf.589.137 (accessed on 28 April 2022).
- Orbulov, I.N.; Németh, Á.; Dobránszky, J. Composite Production by Pressure Infiltration. Mater. Sci. Forum 2008, 589, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, X. Ultrasonic-Assisted Fabrication of Metal Matrix Nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 3211–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Eskandarany, M.S. Mechanical Solid State Mixing for Synthesizing of SiCp/Al Nanocomposites. J. Alloys Compd. 1998, 279, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Vichare, O.; Debnath, K.; Paswan, M. Fabrication Methods of Metal Matrix Composites (MMCs). Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 6840–6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magabe, R.; Sharma, N.; Gupta, K.; Davim, J.P. Modeling and Optimization of Wire-EDM Parameters for Machining of Ni 55.8 Ti Shape Memory Alloy Using Hybrid Approach of Taguchi and NSGA-II. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 102, 1703–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bains, P.S.; Sidhu, S.S.; Payal, H.S. Fabrication and Machining of Metal Matrix Composites: A Review. Mater. Manuf. Processes 2016, 31, 553–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torralba, J.D.; Da Costa, C.E.; Velasco, F. P/M Aluminum Matrix Composites: An Overview. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 133, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, R.S.; Purohit, R.; Soni, V.K.; Das, S. Characterization of Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Aluminium Alloy-SiC Composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.V.; Rohatgi, P.K. Tribological Properties of Al Alloy Particle Composites. JOM 1987, 39, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.; Jamwal, A.; Kumar, D.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Hussain, C.M.; Gupta, P. Advance Research Progresses in Aluminium Matrix Composites: Manufacturing & Applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 4924–4939. [Google Scholar]
- Ramnath, B.V.; Elanchezhian, C.; Annamalai, R.; Aravind, S.; Atreya, T.S.A.; Vignesh, V.; Subramanian, C. Aluminium Metal Matrix Composites—A Review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Pirkle, F.L.; Podmeyer, D.A. Zircon: Origin and Uses. AIME Trans. 1992, 292, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Sadasivuni, K.K.; Ponnamma, D.; Ko, H.-U.; Kim, H.C.; Zhai, L.; Kim, J. Flexible NO2 Sensors from Renewable Cellulose Nanocrystals/Iron Oxide Composites. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 233, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kady, O.; Fathy, A. Effect of SiC Particle Size on the Physical and Mechanical Properties of Extruded Al Matrix Nanocomposites. Mater. Des. 2014, 54, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Qiu, F.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Q. Manufacture of Nano-Sized Particle-Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites: A Review. Acta Metall. Sin. 2014, 27, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, B.; Routray, S.R.; Panda, R.R.; Singh, S. A Critical Review on Hybrid Aluminum Metal Matrix Composite. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 1706, p. 012195. [Google Scholar]
- Totten, G.E.; MacKenzie, D.S. Handbook of Aluminum: Volume 2: Alloy Production and Materials Manufacturing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.H.; Al Rashed, H.M. Characterization of Silicon Carbide Reinforced Aluminum Matrix Composites. Procedia Eng. 2014, 90, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdizadeh, H.; Ashuri, M.; Moghadam, P.T.; Nouribahadory, A.; Baharvandi, H.R. Improvement in Physical and Mechanical Properties of Aluminum/Zircon Composites Fabricated by Powder Metallurgy Method. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4417–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Singh, D.; Kalsi, N.S.; Sharma, S.; Mia, M.; Singh, J.; Rahman, M.A.; Khan, A.M.; Rao, K.V. Investigation on the Mechanical, Tribological, Morphological and Machinability Behavior of Stir-Casted Al/SiC/Mo Reinforced MMCs. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 930–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanavel, V.; Ravichandran, M. Experimental Investigation on Mechanical Properties of AA7075-AlN Composites. Mater. Test. 2019, 61, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Behera, R.; Datta, A.; Majumdar, G.; Oraon, B.; Sutradhar, G. Experimental Investigation on the Effect of Reinforcement Particles on the Forgeability and the Mechanical Properties of Aluminum Metal Matrix Composites. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2010, 1, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Singh, J.; Jawalkar, C.S.; Belokar, R.M. Analysis of Mechanical Properties of AMC Fabricated by Vacuum Stir Casting Process. Silicon 2020, 12, 2433–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, M. Production and Mechanical Properties of Al2O3 Particle-Reinforced 2024 Aluminium Alloy Composites. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2005, 161, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, O.; Buytoz, S. Abrasive Wear of Al2O3-Reinforced Aluminium-Based MMCs. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 2381–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, A.; Güneş, A.; Salur, E.; Şahin, Ö.S.; Karadağ, H.B.; Akdemir, A. Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Composites Produced by Recycling Metal Chips. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2018, 25, 1070–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On Porosity Formation in Metal Matrix Composites Made with Dual-Scale Fiber Reinforcements Using Pressure Infiltration Process|SpringerLink. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11661-015-2792-9 (accessed on 19 May 2022).
- Patel, M.; Sahu, S.K.; Singh, M.K. Fabrication and Investigation of Mechanical Properties of SiC Particulate Reinforced AA5052 Metal Matrix Composite. J. Mod. Mater. 2020, 7, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.K.; Mahant, D.; Upadhyay, G. Manufacturing of Metal Matrix Composites: A State of Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirala, A.; Soren, S.; Kumar, N.; Dwivedi, V.K.; Kaushal, D.R. A Comprehensive Review on Stir Cast Al-SiC Composite. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 21, 1610–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaraswamy, H.S.; Vishnu, P.; Bharath, V.; Rao, T.K. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Sintered Al 2024 Hybrid MMCs. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1455, 012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Type | SiC (37–45 µm) (wt %) | ZrSiO4 (<50 nm) (wt %) | SiC + ZrSiO4 (wt %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-SiC | Binary | 5 | - | - |
| 20 | - | - | ||
| 30 | - | - | ||
| 40 | - | - | ||
| Al-ZrSiO4 | Binary | - | 5 | - |
| - | 20 | - | ||
| - | 30 | - | ||
| - | 40 | - | ||
| Al-SiC-ZrSiO4 | Hybrid | 5 | 40 | 5 + 40 |
| 20 | 30 | 20 + 30 | ||
| 30 | 20 | 30 + 20 | ||
| 40 | 5 | 40 + 5 |
| Sample | Type | Sample | SiC (37–45 µm) (wt %) | ZrSiO4 (<50 nm) (wt %) | SiC + ZrSiO4 (wt %) | Sintering Temperature (°C) | Sintering Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-SiC | Binary | S1 | 5 | - | - | 500 | 60 |
| S2 | 20 | - | - | 700 | 45 | ||
| S3 | 30 | - | - | 900 | 30 | ||
| S4 | 40 | - | - | 1100 | 15 | ||
| Al-ZrSiO4 | Binary | S5 | - | 5 | - | 500 | 60 |
| S6 | - | 20 | - | 700 | 45 | ||
| S7 | - | 30 | - | 900 | 30 | ||
| S8 | - | 40 | - | 1100 | 15 | ||
| Al-SiC-ZrSiO4 | Hybrid | S9 | 5 | 40 | 5 + 40 | 500 | 60 |
| S10 | 20 | 30 | 20 + 30 | 700 | 45 | ||
| S11 | 30 | 20 | 30 + 20 | 900 | 30 | ||
| S12 | 40 | 5 | 40 + 5 | 1100 | 15 |
| Sample | Type | Sample | Mean Hardness (HRA) ± Std | Roughness (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-SiC | Binary | S1 | 79.0 ± 3.6 | 0.104 |
| S2 | 78.0 ± 3.3 | 0.099 | ||
| S3 | 75.0 ± 4.1 | 0.89 | ||
| S4 | 79.0 ± 3.6 | 0.132 | ||
| Al-ZrSiO4 | Binary | S5 | 78.0 ± 3.3 | 0.109 |
| S6 | 76.0 ± 4.2 | 0.157 | ||
| S7 | 77.0 ± 3.5 | 0.227 | ||
| S8 | 77.0 ± 3.5 | 0.111 | ||
| Al-SiC-ZrSiO4 | Hybrid | S9 | 79.0 ± 3.6 | 0.039 |
| S10 | 64.0 ± 2.5 | 0.354 | ||
| S11 | 75.0 ± 4.1 | 0.105 | ||
| S12 | 79.0 ± 3.6 | 0.204 |
| Elements | Weight% | Atomic% |
|---|---|---|
| Al | 75.3 | 61.7 |
| Si | 6.8 | 5.3 |
| C | 17.9 | 33.0 |
| Elements | Weight% | Atomic% |
|---|---|---|
| Al | 71.7 | 61.6 |
| Si | 2.5 | 2.0 |
| C | 9.8 | 19.0 |
| O | 11.2 | 16.3 |
| Zr | 4.8 | 1.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gillani, F.; Khan, M.Z.; Shah, O.R. Sensitivity Analysis of Reinforced Aluminum Based Metal Matrix Composites. Materials 2022, 15, 4225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15124225
Gillani F, Khan MZ, Shah OR. Sensitivity Analysis of Reinforced Aluminum Based Metal Matrix Composites. Materials. 2022; 15(12):4225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15124225
Chicago/Turabian StyleGillani, Fouzia, Muhammad Zubair Khan, and Owaisur Rahman Shah. 2022. "Sensitivity Analysis of Reinforced Aluminum Based Metal Matrix Composites" Materials 15, no. 12: 4225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15124225
APA StyleGillani, F., Khan, M. Z., & Shah, O. R. (2022). Sensitivity Analysis of Reinforced Aluminum Based Metal Matrix Composites. Materials, 15(12), 4225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15124225






