Investigation of the TeO2/GeO2 Ratio on the Spectroscopic Properties of Eu3+-Doped Oxide Glasses for Optical Fiber Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
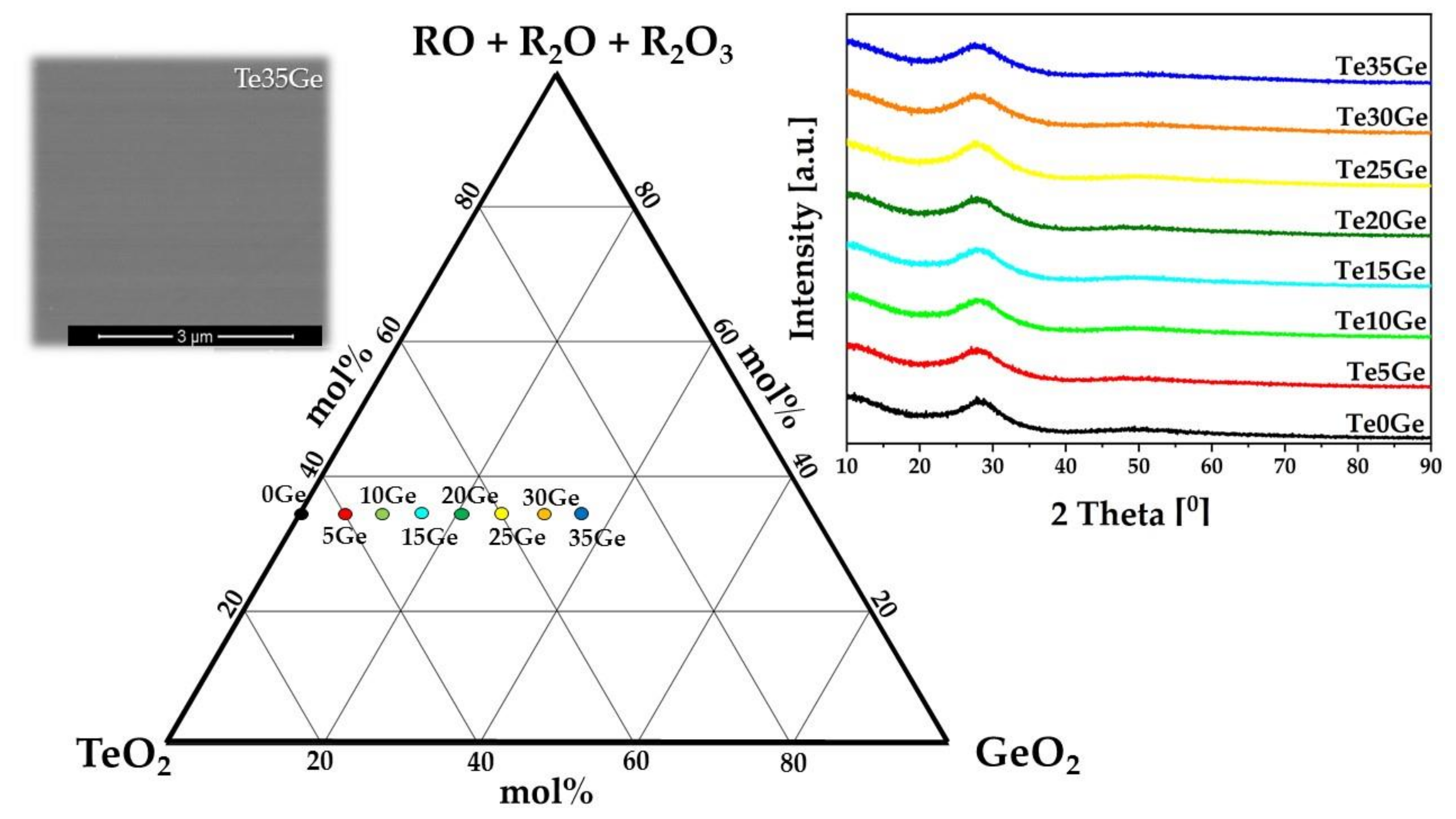
3.1. Glass Forming Ability (GFA)
3.2. Thermal Properties and Refractive Indexes
DSC Curves of Glasses
3.3. Structural Studies
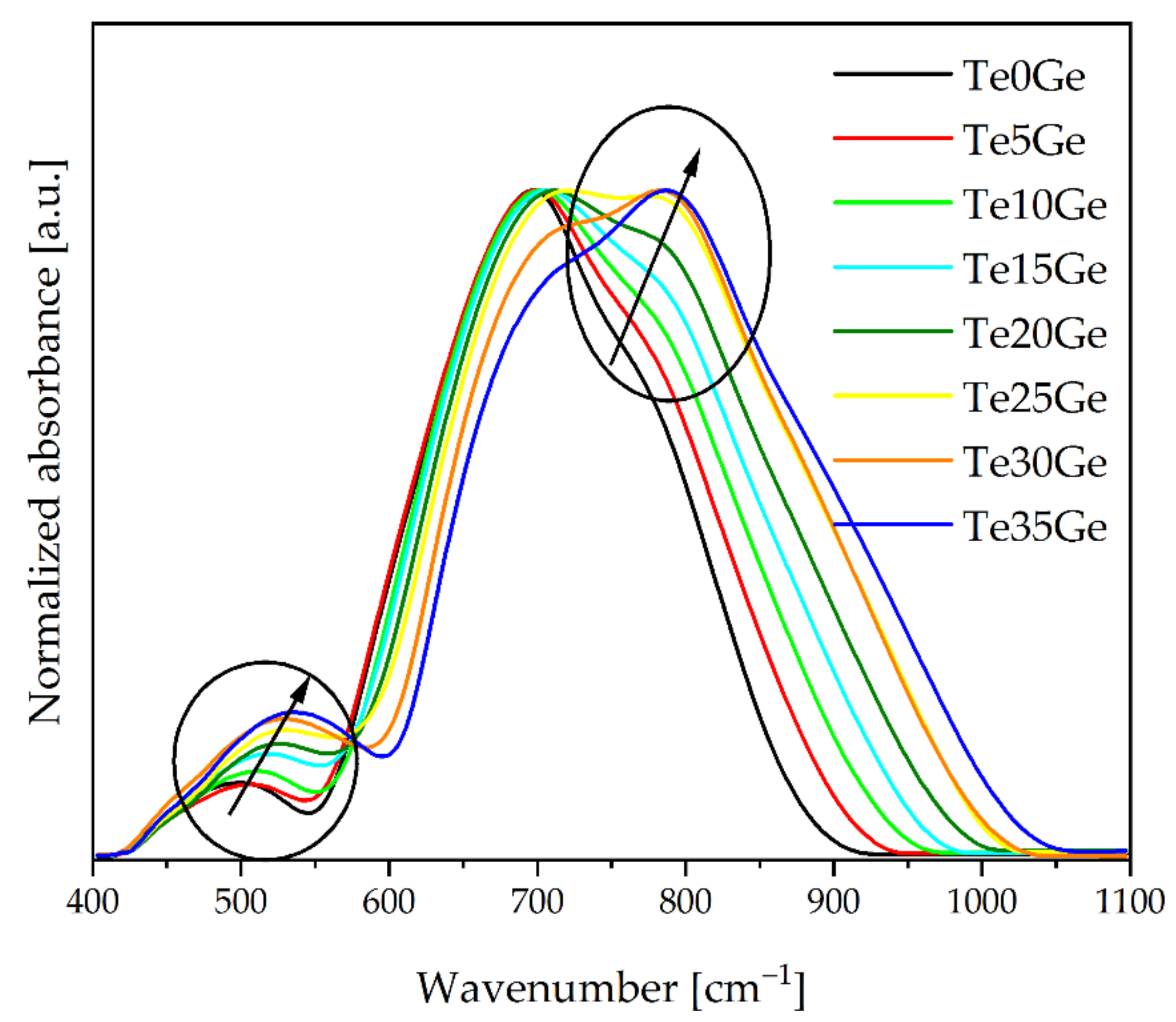
3.3.1. MIR Spectra
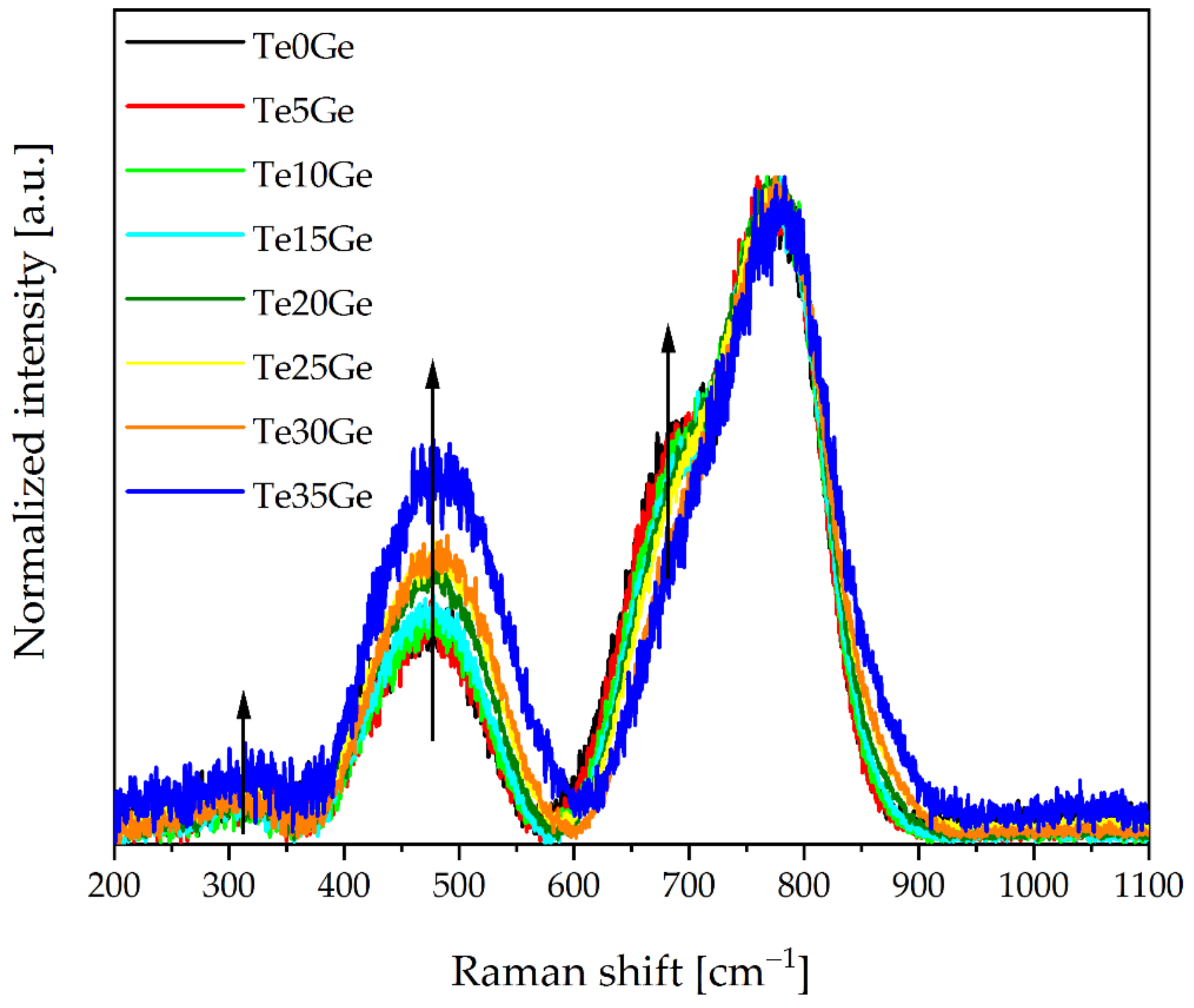
3.3.2. Raman Spectra
3.4. Optical Studies
3.4.1. Refractive Index
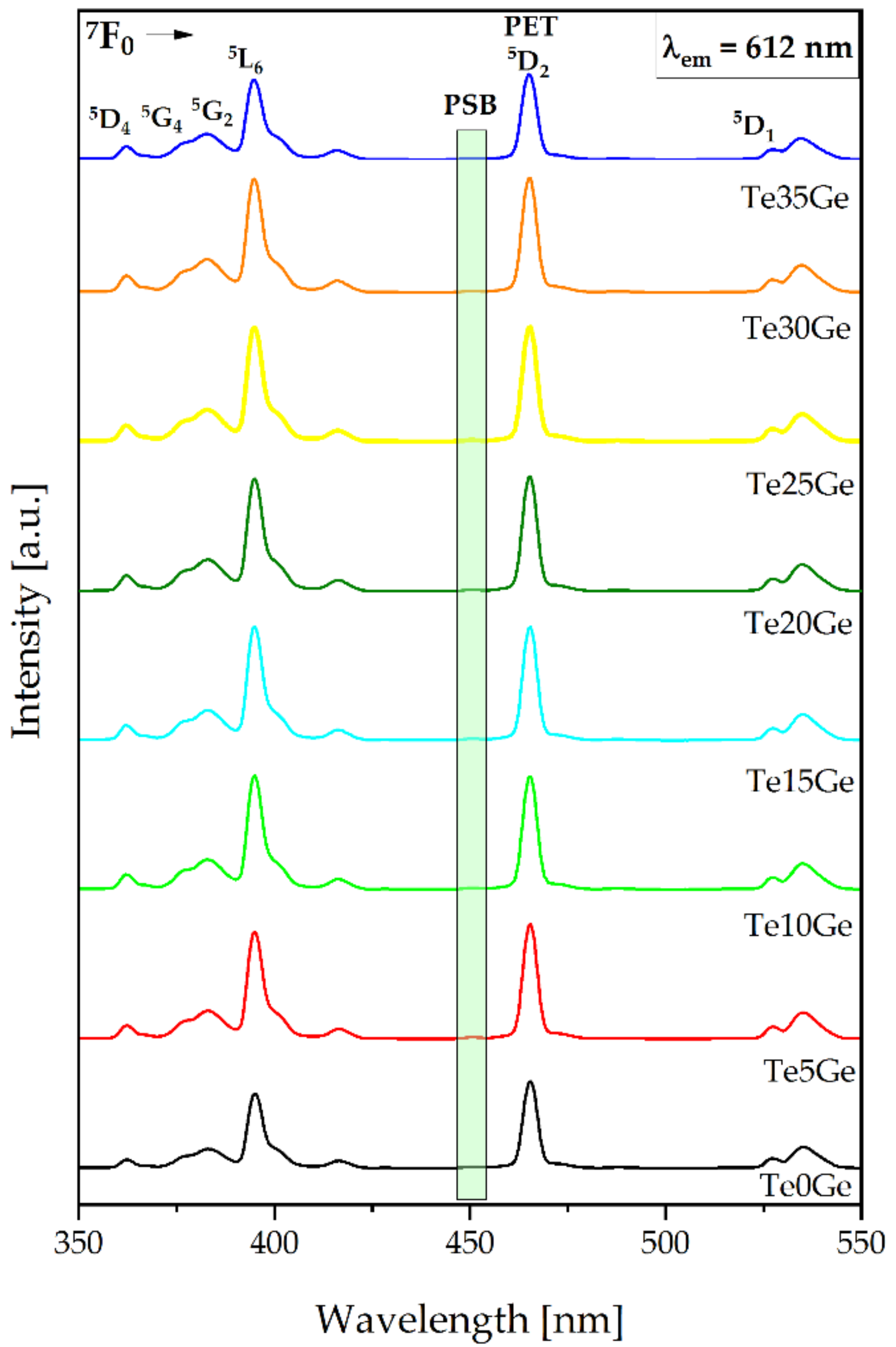
3.4.2. Excitation Spectra and Phonon Sideband Analysis
3.4.3. Emission Spectra Analysis
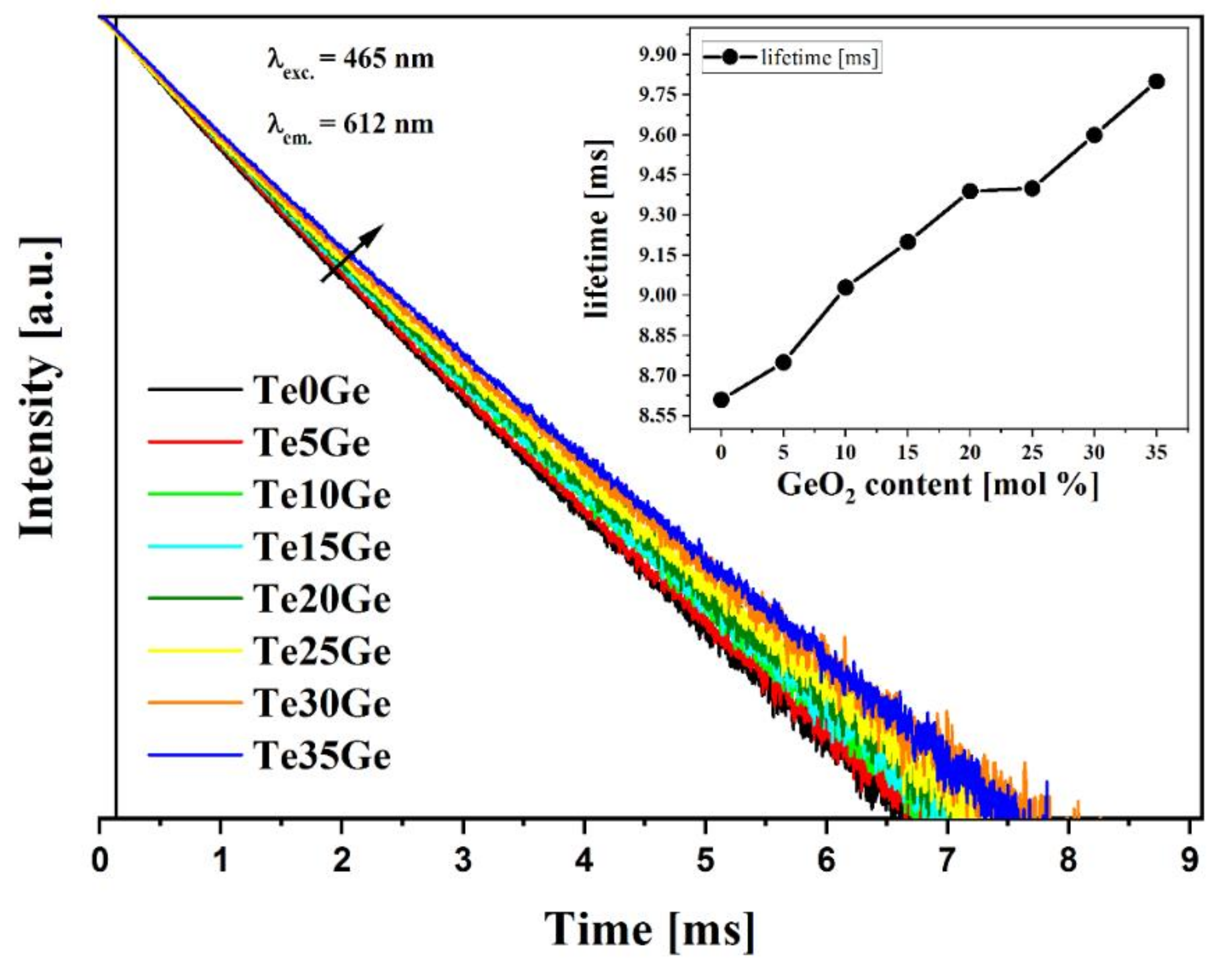
3.4.4. Luminescence Decay Analysis
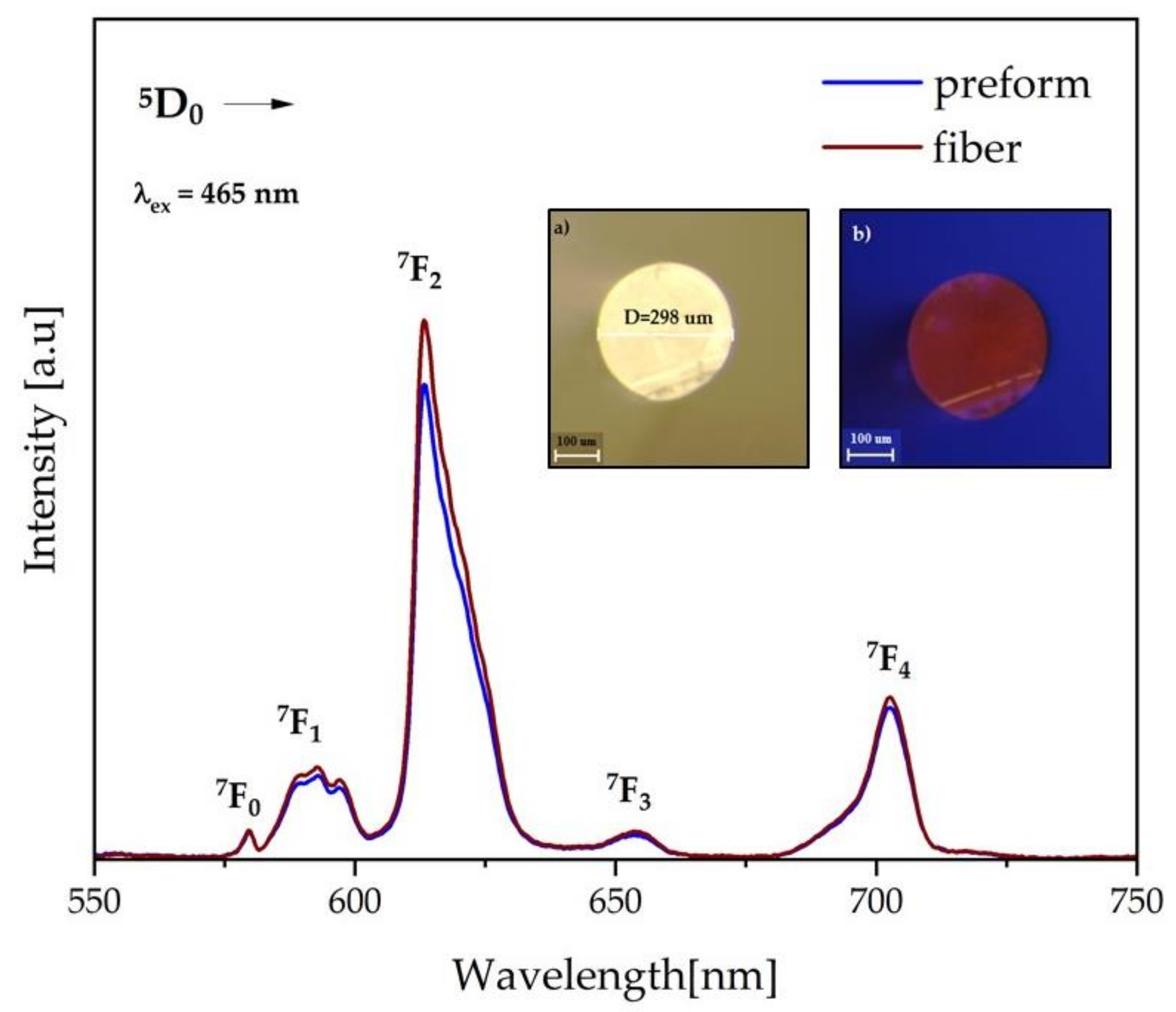
3.5. Optical Fiber
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Song, Y.; Zhang, H. Recent developments in mid-infrared fiber lasers: Status and challenges. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 132, 106497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordu, M.; Basu, S.N. Recent progress in germanium-core optical fibers for mid-infrared optics. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 111, 103507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, C.; Li, Z.; Ping, Y.; Miao, X.; Zhang, C. Up-Conversion and 2 μm Mid-Infrared Emission Effective Enhancements in Ho3+/Yb3+ Co-Doped Tellurite Glass; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 242, p. 167262. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Jia, S.; Wang, L.; Ning, Y.; Peng, H.; Farrell, G.; Wang, S.; Wang, R. 3.5 μm emission in Er3+ doped fluoroindate glasses under 635 nm laser excitation. J. Lumin. 2021, 237, 118200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Sun, M.; Ren, H.; Lin, H.; Feng, X.; Yang, Z. Dy3+-doped Ga2S3-Sb2S3-La2S3 chalcogenide glass for mid-infrared fiber laser medium. J. Lumin. 2021, 237, 118169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Zhang, C.; Fu, W.; Li, G.; Xia, J.; Ping, Y. Broadband mid-infrared 2.0 μm and 4.1 μm emission in Ho3+/Yb3+ co-doped tellurite-germanate glasses. J. Lumin. 2020, 217, 116769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongisto, M.; Veber, A.; Petit, Y.; Cardinal, T.; Danto, S.; Jubera, V.; Petit, L. Radiation-Induced Defects and Effects in Germanate and Tellurite Glasses. Materials 2020, 13, 3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, L.; Li, C.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y. Enhanced 2.7 µm mid-infrared emission in Er3+/Ho3+ co-doped tellurite glass. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 138, 106913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mallawany, R. Tellurite Glass Smart Materials; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, R.; Wang, P.; Li, S.; Ma, Y. 2.86 μm emission and fluorescence enhancement through controlled precipitation of ZnTe nanocrystals in DyF3 doped multicomponent tellurite oxyfluoride glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2021, 564, 120842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, G.J.; Devaraja, C.; Eraiah, B.; Dahshan, A.; Nazrin, S. Structural, thermal and spectroscopic studies of Europium trioxide doped lead boro-tellurite glasses. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 871, 159585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Tian, Y.; Li, B.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S. Effect of introduction of TiO2 and GeO2 oxides on thermal stability and 2 μm luminescence properties of tellurite glasses. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 16411–16416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sołtys, M.; Górny, A.; Zur, L.; Ferrari, M.; Righini, G.C.; Pisarski, W.; Pisarska, J. White light emission through energy transfer processes in barium gallo-germanate glasses co-doped with Dy3+-Ln3+ (Ln =Ce, Tm). Opt. Mater. 2019, 87, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Tang, G.; Yang, Q.; Chen, X.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Z. Highly Tm3+ doped germanate glass and its single mode fiber for 2.0 μm laser. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kochanowicz, J.; Zmojda, J.; Miluski, P.; Baranowska, A.; Leich, M.; Dorosz, D. Tm3+/Ho3+ co-doped germanate glass and double-clad optical fiber for broadband emission and lasing above 2 µm. Opt. Mater. Express 2019, 9, 1450–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, C.; Zhang, C.; Miao, X.; Li, Z.; Ping, Y. Effective enhancement on mid-infrared fluorescence emission of Ho3+/Yb3+ doped tellurite glass introduced Ag nanoparticles. Opt. Mater. 2021, 115, 111025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, T.M.; Falci, R.F.; Silva, I.L.; Anjos, V.; Bell, M.J.; Silva, M.A. Erbium 1.55 μm luminescence enhancement due to copper nanoparticles plasmonic activity in tellurite glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 224, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.M.; Kassab, L.R.P.; da Silva, D.M.; de Araujo, C.B. Tm3+ doped Bi2O3-GeO2 glasses with silver nanoparticles for optical amplifiers in the short-wave-infrared-region. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 772, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassab, L.R.P.; Kumada, D.K.; da Silva, D.M.; Garcia, J.A.M. Enhanced infrared-to-visible frequency upconversion in Yb3+/Er3+ codoped Bi2O3–GeO2 glasses with embedded silver nanoparticles. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 498, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Xiao, P. Compositional effects of Na2O, GeO2, and Bi2O3 on 1.8µm spectroscopic properties of Tm3+ doped zinc tellurite glasses. J. Lumin. 2018, 196, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalaiah, B. GeO2 activated tellurite tungstate glass: A new candidate for solid state lasers and fiber devices. J. Non-Crystalline Solids 2018, 502, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, C.; Feng, Y.; Sun, L.; Ni, Y.; Xu, Z. Effects of GeO2 on the thermal stability and optical properties of Er3+/Yb3+-codoped oxyfluoride tellurite glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 126, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Cai, M.; Lu, Y.; Wang, N.; Huang, F.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J. Preparation and investigation of Tm3+/Ho3+ co-doped germanate-tellurite glass as promising materials for ultrashort pulse laser. Opt. Mater. 2017, 67, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Cai, M.; Cao, R.; Qian, S.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J. Er3+ doped germanate–tellurite glass for mid-infrared 2.7 μm fiber laser material. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2016, 171, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Bai, X.; Zhou, H. Preparation of Ho3+/Tm3+ Co-doped Lanthanum Tungsten Germanium Tellurite Glass Fiber and Its Laser Performance for 2.0 μm. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manzani, D.; Ledemi, Y.; Skripachev, I.; Messaddeq, Y.; Ribeiro, S.; De Oliveira, R.E.P.; De Matos, C.J.S. Yb3+, Tm3+ and Ho3+ triply-doped tellurite core-cladding optical fiber for white light generation. Opt. Mater. Express 2011, 1, 1515–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alvarez-Ramos, M.; Carrillo-Torres, R.C.; Sánchez-Zeferino, R.; Caldiño, U.; Alvarado-Rivera, J. Co-emission and energy transfer of Sm3+ and/or Eu3+ activated zinc-germanate- tellurite glass as a potential tunable orange to reddish-orange phosphor. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2019, 521, 119462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xia, Y.; Shen, X.; Wei, W. Effects of GeO2 concentration on the absorption and fluorescence behaviors of Yb3+ in tellurite glasses. J. Lumin. 2018, 198, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghribi, N.; Dutreilh-Colas, M.; Duclère, J.-R.; Gouraud, F.; Chotard, T.; Karray, R.; Kabadou, A.; Thomas, P. Structural, mechanical and optical investigations in the TeO2-rich part of the TeO2–GeO2–ZnO ternary glass system. Solid State Sci. 2015, 40, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marczewska, A.; Środa, M. Spectroscopic and thermal study of a new glass from TeO2-Ga2O3-GeO2 system. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1164, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Z. Spectroscopic properties of GeO2- and Nb2O5-modified tellurite glasses doped with Er3+. J. Alloy. Compd. 2008, 461, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesniak, M.; Zmojda, J.; Kochanowicz, M.; Miluski, P.; Baranowska, A.; Mach, G.; Kuwik, M.; Pisarska, J.; Pisarski, W.A.; Dorosz, D. Spectroscopic Properties of Erbium-Doped Oxyfluoride Phospho-Tellurite Glass and Transparent Glass-Ceramic Containing BaF2 Nanocrystals. Materials 2019, 12, 3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rammah, Y.; El-Agawany, F.; Abu El Soad, A.; Yousef, E.S.S.; El-Mesady, I. Ionizing radiation attenuation competences of gallium germanate-tellurite glasses utilizing MCNP5 simulation code and Phy-X/PSD program. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 22766–22773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Lu, Y.; Cao, R.; Tian, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J. 2 μm emission properties and hydroxy groups quenching of Tm3+ in germanate-tellurite glass. Opt. Mater. 2016, 57, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Cai, M.; Cao, R.; Tian, Y.; Huang, F.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J. Enhanced effect of Er3+ ions on 2.0 and 2.85 μm emission of Ho3+/Yb3+ doped germanate-tellurite glass. Opt. Mater. 2016, 60, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Tian, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, F.; Jing, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S. 2μm fluorescence of Ho3+:5I7→5I8 transition sensitized by Er3+ in tellurite germanate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2015, 49, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaky, K.M.; Sayyed, M.; Mhareb, M.; Abdalsalam, A.H.; Mahmoud, K.; Baki, S.; Mahdi, M. Physical, structural, optical and gamma radiation attenuation properties of germanate-tellurite glasses for shielding applications. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2020, 545, 120250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalin, S.; Edukondalu, A.; Samee, M.A.; Ahmmad, S.K.; Taqiullah, S.M.; Rahman, S. Non-linear optical properties of Bi2O3-TeO2-B2O3-GeO2 glasses. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2269, 030102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Khanna, A. Photoluminescence and thermal properties of trivalent ion-doped lanthanum tellurite anti-glass and glass composite samples. J. Lumin. 2020, 225, 117375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Li, J.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, L. Regulation of Y2O3 on glass stability of Ga2O3-rich oxyfluoride glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2021, 558, 120653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, V.; Komatsu, T. Average single bond strength and optical basicity of Na2O-GeO2 glasses. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 117, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimitrov, V.; Komatsu, T.; Tasheva, T. Group optical basicity and single bond strength of oxide glasses. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2018, 53, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Elkholy, H.; Othman, H.; Hager, I.; Ibrahim, M.; de Ligny, D. Thermal and optical properties of binary magnesium tellurite glasses and their link to the glass structure. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 823, 153781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polosan, S. Structure and low field magnetic properties in phosphate-tellurite glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2019, 524, 119651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Khanna, A.; Fabian, M.; Krishna, P.S.R.; Shinde, A.B. Structure of lead tellurite glasses and its relationship with stress-optic properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 2019, 110, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Khanna, A.; González-Barriuso, M.; González, F.; Chen, B. Short-range structure and thermal properties of alumino-tellurite glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2017, 470, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marple, M.A.; Jesuit, M.; Hung, I.; Gan, Z.; Feller, S.; Sen, S. Structure of TeO2 glass: Results from 2D 125Te NMR spectroscopy. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2019, 513, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroleva, O.N.; Shtenberg, M.; Ivanova, T.N. The structure of potassium germanate glasses as revealed by Raman and IR spectroscopy. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2019, 510, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradtmüller, H.; Rodrigues, A.C.M.; Eckert, H. Network former mixing (NFM) effects in alkali germanotellurite glasses. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 873, 159835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, B.; Hynek, D.; Kaizer, S.; Feller, S.; Martin, S.W. Composition dependence of the short range order structures in 0.2Na2O + 0.8[xBO3/2 + (1-x)GeO2] mixed glass formers. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 500, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabadel, J.-C.; Armand, P.; Lippens, P.-E.; Cachau-Herreillat, D.; Philippot, E. Mössbauer and XANES of TeO2–BaO–TiO2 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1999, 244, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todoroki, S.; Hirao, K.; Soga, N. A study of the local structure around Eu3+ ions in oxide glasses using Mössbauer spectroscopy. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B: Beam Interactions Mater. Atoms 1993, 76, 76–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Khanna, A.; Dippel, A.C.; Gutowski, O. Structure of bismuth tellurite and bismuth niobium tellurite glasses and Bi2Te4O11 anti-glass by high energy X-ray diffraction. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 13237–13251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barney, E.R.; Laorodphan, N.; Mohd-Noor, F.; Holland, D.; Kemp, T.; Iuga, D.; DuPree, R. Toward a Structural Model for the Aluminum Tellurite Glass System. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 20516–20529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Hu, L. Statistical structure analysis of GeO2 modified Yb3+: Phosphate glasses based on Raman and FTIR study. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 698, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaszczak, K.; Jelonek, W.; Adamczyk, A. Infrared studies of glasses in the Li2O–B2O3–GeO2(SiO2) systems. J. Mol. Struct. 1999, 511, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, S.; Culea, E.; Rada, M.; Pascuta, P.; Măties, V. Structural and electronic properties of tellurite glasses. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 3235–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, S.; Culea, E.; Rada, M. Towards understanding of the germanate anomaly in europium–lead–germanate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2010, 356, 1277–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticha, H.; Schwarz, J.; Tichy, L. Raman spectra and optical band gap in some PbO-ZnO-TeO2 glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 237, 121834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Torres, R.C.; Saavedra-Rodriguez, G.; Alvarado-Rivera, J.; Caldino, U. Tunable emission and energy transfer in TeO2-GeO2-ZnO and TeO2-GeO2-MgCl2 glasses activated with Eu3+/Dy3+ for solid state lighting applications. J. Lumin. 2019, 212, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terny, C.; De la Rubia, M.; Alonso, R.; DE Frutos, J.; Frechero, M. Structure and electrical behavior relationship of a magnesium–tellurite glass using Raman and impedance spectroscopy. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2015, 411, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroleva, O.N.; Shtenberg, M.V.; Zainullina, R.T.; Lebedeva, S.M.; Nevolina, L. Vibrational spectroscopy and density of K2O–B2O3–GeO2 glasses with variable B/Ge ratio. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 12676–12684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcik, N.A.; Tagiara, N.S.; Ali, S.; Gornicka, K.; Segawa, H.; Klimczuk, T. Structure and magnetic properties of BeO-Fe2O3-Al2O3-TeO2 glass-ceramic composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 5214–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroleva, O.N.; Osipov, A.A. In situ Raman spectroscopy of K2O-GeO2 melts. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2020, 531, 119850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardelean, I.; Lupsor, S.; Rusu, R. Infrared and Raman spectroscopic investigations of xMnO (100−x)[As2O3 TeO2] glass system. Phys. B: Condens. Matter 2010, 405, 2259–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Shao, C.; Kang, S.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; He, D.; Chen, W.; Hu, L. Relationship investigation of structure and properties of Nd3+: Ga2O3-Al2O3-PbO-CaO via Raman, infrared, NMR and EPR spectroscopy. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 499, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, V.; Komatsu, T. Classification of Simple Oxides: A Polarizability Approach. J. Solid State Chem. 2002, 163, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, N.; Jali, V.M.; Patil, S.D. Structure And Optical Properties Of TeO2-GeO2 Glasses. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2016, 4, 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, S.; Hakeem, D.A.; Su, S.; Wen, H.; Song, W. Optical properties of V, Eu doped sodium borosilicate glass. Optik 2021, 229, 166225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachari, D.; Moorthy, L.R.; Jayasankar, C. Phonon sideband spectrum and vibrational analysis of Eu3+-doped niobium oxyfluorosilicate glass. J. Lumin. 2013, 143, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshvaran, K.; Veeran, P.K.; Marimuthu, K. Structural and optical studies on Eu3+ doped boro-tellurite glasses. Solid State Sci. 2013, 17, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodaraiah, S.; Prasad, V.R.; Lakshmi, R.V.; Ratnakaram, Y. Luminescence behaviour and phonon sideband analysis of europium doped Bi2O3 based phosphate glasses for red emitting device applications. Opt. Mater. 2019, 92, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, M.; Rajasekhara Reddy, G.; Sushma, N.J.; Devarajulu, G.; Deva Prasad Raju, B. Phonon sideband analysis, structural and spectroscopic properties of Eu3+ ions embedded SiO2–B2O3–CaF2–NaF–Na2O glasses. Opt. Mater. 2020, 107, 110038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthanthirakumar, P.; Arunkumar, S.; Marimuthu, K. Investigations on the spectroscopic properties and local structure of Eu3+ ions in zinc telluro-fluoroborate glasses for red laser applications. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 760, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasler, C.; Hauser, A.; Olchowka, J.; Hagemann, H. Energy transfer between different Eu2+ ions in the white phosphor Ba7F12Cl2:Eu2+. J. Lumin. 2021, 233, 117866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, P.; Jang, K.H.; Seo, H.J.; Jayasankar, C.K. Optical and site-selective spectral studies of Eu3+-doped zinc oxyfluorotellurite glass. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 053522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajna, M.; Gopi, S.; Prakashan, V.; Sanu, M.; Joseph, C.; Biju, P.; Unnikrishnan, N. Spectroscopic investigations and phonon side band analysis of Eu3+ -doped multicomponent tellurite glasses. Opt. Mater. 2017, 70, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.T.; Dung, P.T.; Quang, V.X. Energy Transfer Process of Eu3+ Ions Doped in Tellurite Glass. J. Electron. Mater. 2016, 45, 2569–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Brocklesby, W.S.; Lincoln, J.R.; Townsend, J.E.; Payne, D.N. Local structures of rare-earth ions in glasses: The ‘crystal-chemistry’ approach. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1993, 163, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlik, N.; Szpikowska-Sroka, B.; Pietrasik, E.; Goryczka, T.; Dulski, M.; Swinarew, A.S.; Zubko, M.; Lelątko, J.; Pisarski, W.A. Reddish-orange Eu3+-doped sol-gel emitters based on LaF3 nanocrystal–Synthesis, structural and photoluminescence investigations. Opt. Mater. 2019, 89, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarska, J.; Pisarski, W.A.; Lisiecki, R.; Ryba-Romanowski, W. Phonon Sideband Analysis and Near-Infrared Emission in Heavy Metal Oxide Glasses. Materials 2020, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anashkina, E.A. Laser Sources Based on Rare-Earth Ion Doped Tellurite Glass Fibers and Microspheres. Fibers 2020, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, S.; Culea, E. FTIR spectroscopic and DFT theoretical study on structure of europium–phosphate–tellurate glasses and glass ceramics. J. Mol. Struct. 2009, 929, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, V.J.M. Elements: High field strength, In Encyclopedia of Earth Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Alderman, O.L.G.; Hannon, A.C.; Feller, S.; Beanland, R.; Holland, D. The Germanate Anomaly in Alkaline Earth Germanate Glasses. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 9462–9479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





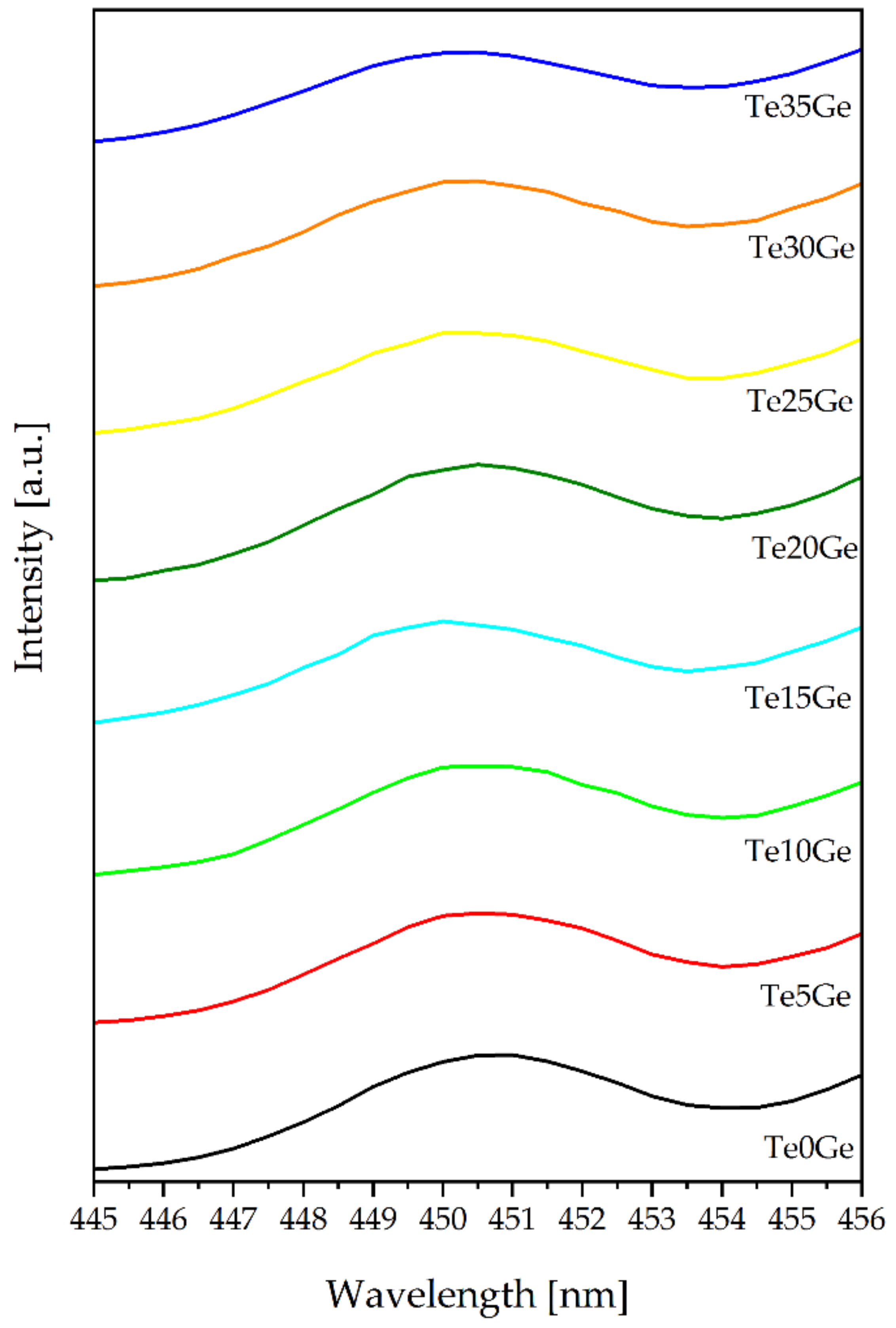
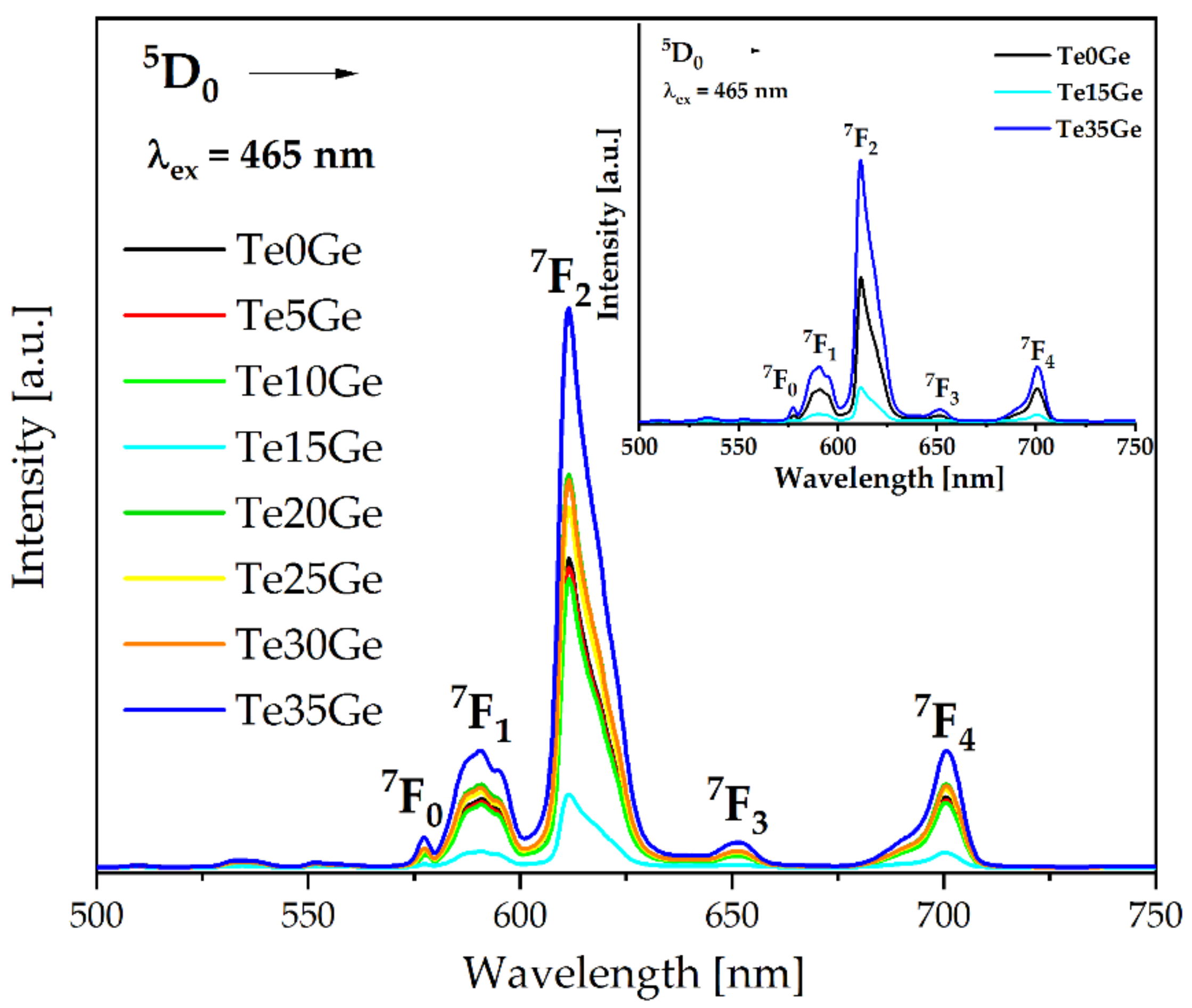
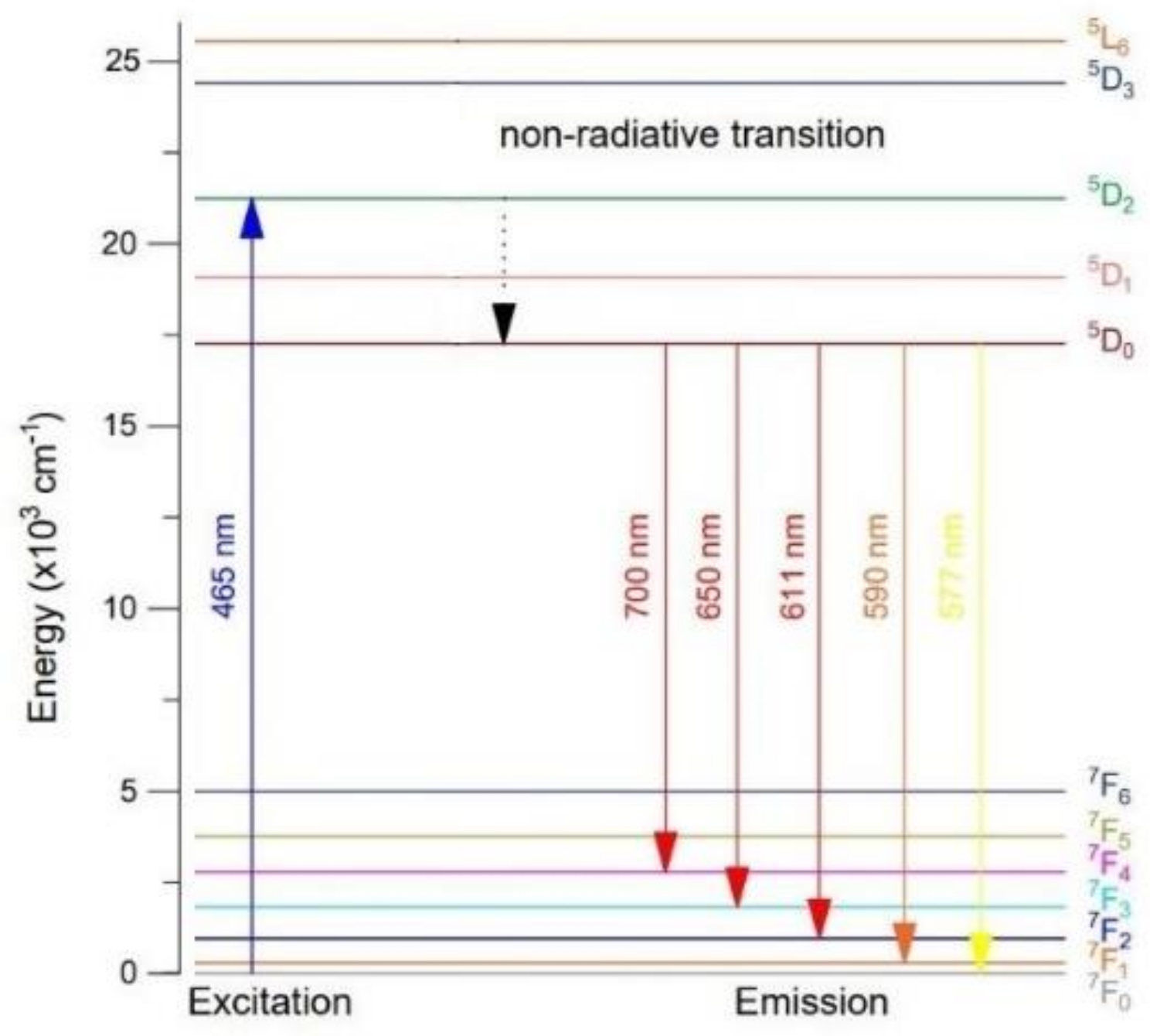
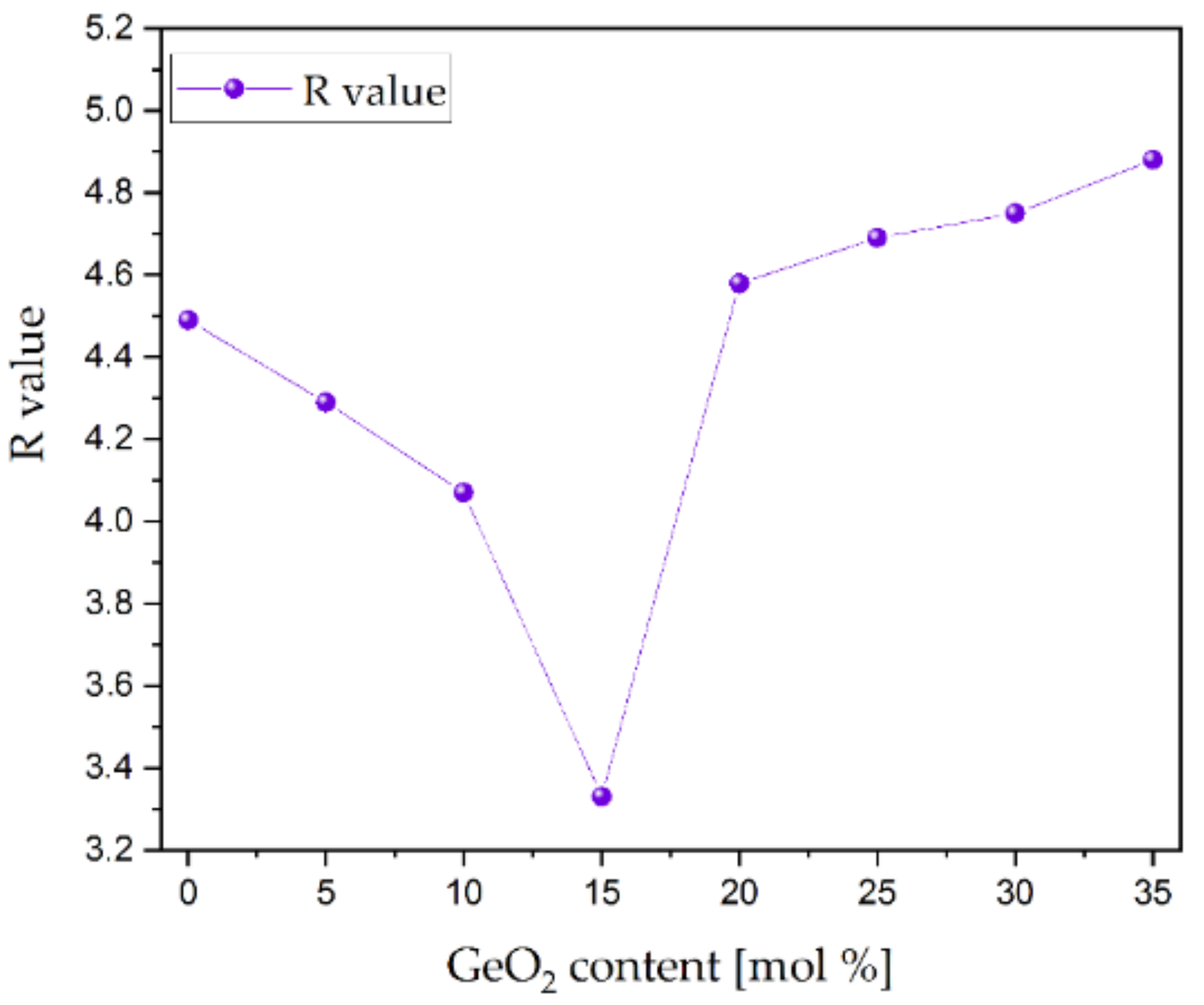
| Glass | Tg (±1 °C) | Tx (±1 °C) |
|---|---|---|
| Te0Ge | 356 | - |
| Te5Ge | 361 | - |
| Te10Ge | 368 | - |
| Te15Ge | 375 | - |
| Te20Ge | 380 | 618 |
| Te25Ge | 395 | 625 |
| Te30Ge | 410 | 620 |
| Te35Ge | 420 | 630 |
| Positionof the Component Bands [cm−1] | Assignment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass | |||||
| Te0Ge | Te15Ge | Te35Ge | Te0Ge | Te15Ge | Te35Ge |
| - | 454 | 479 | bending vibrations of Te–O–X, (X = Te, Ge, Ga) | ||
| 500 | 512 | 532 | |||
| - | - | 571 | Stretching vibration of the Ge(IV)-O-Ge(IV) | ||
| 615 | - | - | stretching vibrations of [TeO4]tbp units with bridging oxygen | ||
| 681 | 687 | 673 | vibrations of trigonally coordinated tellurium ions [TeO3]tp/[TeO3+1] | ||
| 760 | 799 | 783 | symmetrical stretching vibrations of [TeO3]tp/[TeO3+1] units with NBO | ||
| 886 | 912 | asymmetrical stretching vibrations of the Ge-O-Ge connecting [GeO4] tetrahedra | |||
| Position of Component Band [cm−1] | Assignment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass | |||||
| Te0Ge | Te15Ge | Te35Ge | Te0Ge | Te15Ge | Te35Ge |
| 305 | 305 | 310 | bending vibrations of the Te-O-X bridges, where X = Te, Ga, Ge | ||
| 429 | 459 | 443 | symmetric stretching vibrations of Te-O-Te bridges formed by corner-sharing of [TeO4]tbp, [TeO3+1]tp polyhedra, and [TeO3] units; symmetric stretching vibrations of Ge-O-Ge in 4-membered GeO4 rings; bending vibration of the Ga-O-Ga bond | ||
| 486 | 511 | 502 | bending vibrations of the Te-O-Te bridges in [TeO4]tbp and [TeO3]tp units; symmetric stretching vibrations of Ge-O-Ge in 3-membered GeO4 rings; bending vibration of the Ga-O-Ga bond | ||
| 682 | 671 | 697 | asymmetrical stretching vibrations of Te–O–Te between [TeO4]tbp units, and [TeO3+1] units; stretching vibration of O–Ga–O | ||
| 756 | 731 | - | stretching vibrations of the [TeO3+1] units and TeO32− trigonal pyramids (tp’s) with three terminal oxygen atoms; symmetrical stretching vibrations of the Ge-O− of Ge(1) unit; stretching vibration of O–Ga–O | ||
| 798 | 785 | 782 | stretching vibrations of Te-O− in [TeO3]tp and [TeO3+1] units; vibrations of the continuous [TeO4]tbp network;antisymmetric stretching vibrations of Ge-O− in Ge(2) units; stretching vibration of O–Ga–O | ||
| - | - | 873 | symmetrical stretching vibrations of Ge-O− in Ge(3) units; stretching vibration of O–Ga–O | ||
| Glass | PSB | PET | PSB-PET [cm−1] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Te0Ge | 450.77 nm (22.184 cm−1) | 465.44 nm (21.485 cm−1) | 699 |
| Te5Ge | 450.53 nm (22.196 cm−1) | 465.50 nm (21.482 cm−1) | 714 |
| Te10Ge | 450.51 nm (22.197 cm−1) | 465.22 nm (21.495 cm−1) | 702 |
| Te15Ge | 449.95 nm (22.224 cm−1) | 464.93 nm (21.508 cm−1) | 716 |
| Te20Ge | 450.45 nm (22.200 cm−1) | 465.22 nm (21.495 cm−1) | 705 |
| Te25Ge | 450.02 nm (22.221 cm−1) | 465.22 nm (21.495 cm−1) | 726 |
| Te30Ge | 450.39 nm (22.202 cm−1) | 465.93 nm (21.462 cm−1) | 746 |
| Te35Ge | 450.26 nm (22.209 cm−1) | 465.98 nm (21.460 cm−1) | 749 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lesniak, M.; Zeid, J.; Starzyk, B.; Kochanowicz, M.; Kuwik, M.; Zmojda, J.; Miluski, P.; Baranowska, A.; Dorosz, J.; Pisarski, W.; et al. Investigation of the TeO2/GeO2 Ratio on the Spectroscopic Properties of Eu3+-Doped Oxide Glasses for Optical Fiber Application. Materials 2022, 15, 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15010117
Lesniak M, Zeid J, Starzyk B, Kochanowicz M, Kuwik M, Zmojda J, Miluski P, Baranowska A, Dorosz J, Pisarski W, et al. Investigation of the TeO2/GeO2 Ratio on the Spectroscopic Properties of Eu3+-Doped Oxide Glasses for Optical Fiber Application. Materials. 2022; 15(1):117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15010117
Chicago/Turabian StyleLesniak, Magdalena, Jakub Zeid, Bartłomiej Starzyk, Marcin Kochanowicz, Marta Kuwik, Jacek Zmojda, Piotr Miluski, Agata Baranowska, Jan Dorosz, Wojciech Pisarski, and et al. 2022. "Investigation of the TeO2/GeO2 Ratio on the Spectroscopic Properties of Eu3+-Doped Oxide Glasses for Optical Fiber Application" Materials 15, no. 1: 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15010117
APA StyleLesniak, M., Zeid, J., Starzyk, B., Kochanowicz, M., Kuwik, M., Zmojda, J., Miluski, P., Baranowska, A., Dorosz, J., Pisarski, W., Pisarska, J., & Dorosz, D. (2022). Investigation of the TeO2/GeO2 Ratio on the Spectroscopic Properties of Eu3+-Doped Oxide Glasses for Optical Fiber Application. Materials, 15(1), 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15010117






