Water-Soluble Copper Ink for the Inkjet Fabrication of Flexible Electronic Components
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis Procedure
- (1)
- Copper formate Cu (OOCH)2 was prepared by adding 5 mL of 85% formic acid to 10 g of copper hydrocarbonate.
- (2)
- Ammonia complex of copper formate [Cu(NH3)2](OOCH)2 was prepared by dissolving 1 g of copper formate Cu(OOCH)2 in 2 mL of 25% aqueous ammonia solution.
- (3)
- Dimethylamine complex of copper formate [Cu(C2H6NH)2](OOCH)2 was prepared by dissolving 1 g of copper formate Cu(OOCH)2 in 2 mL of 33% aqueous solution of dimethylamine.
2.2. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
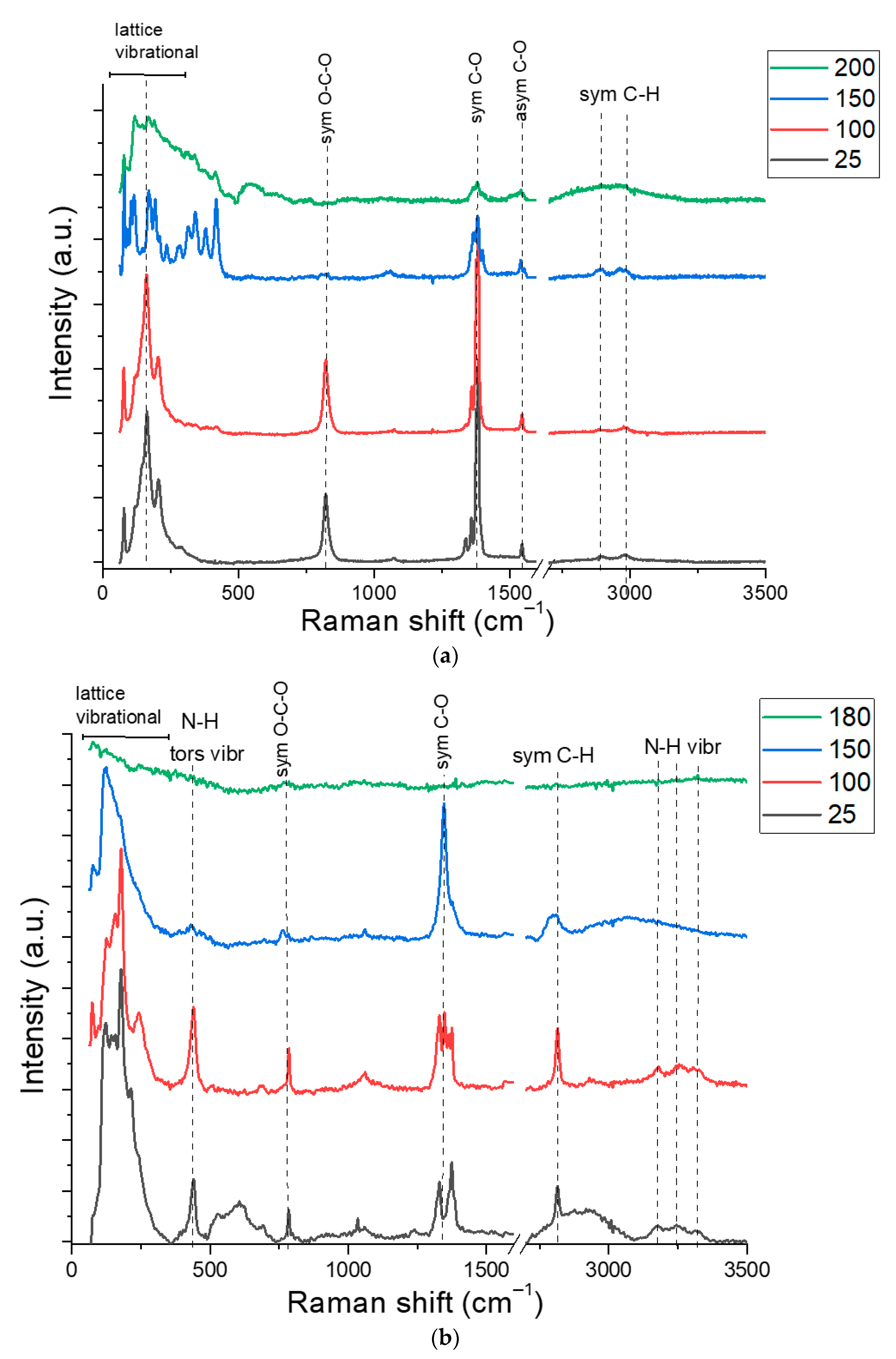
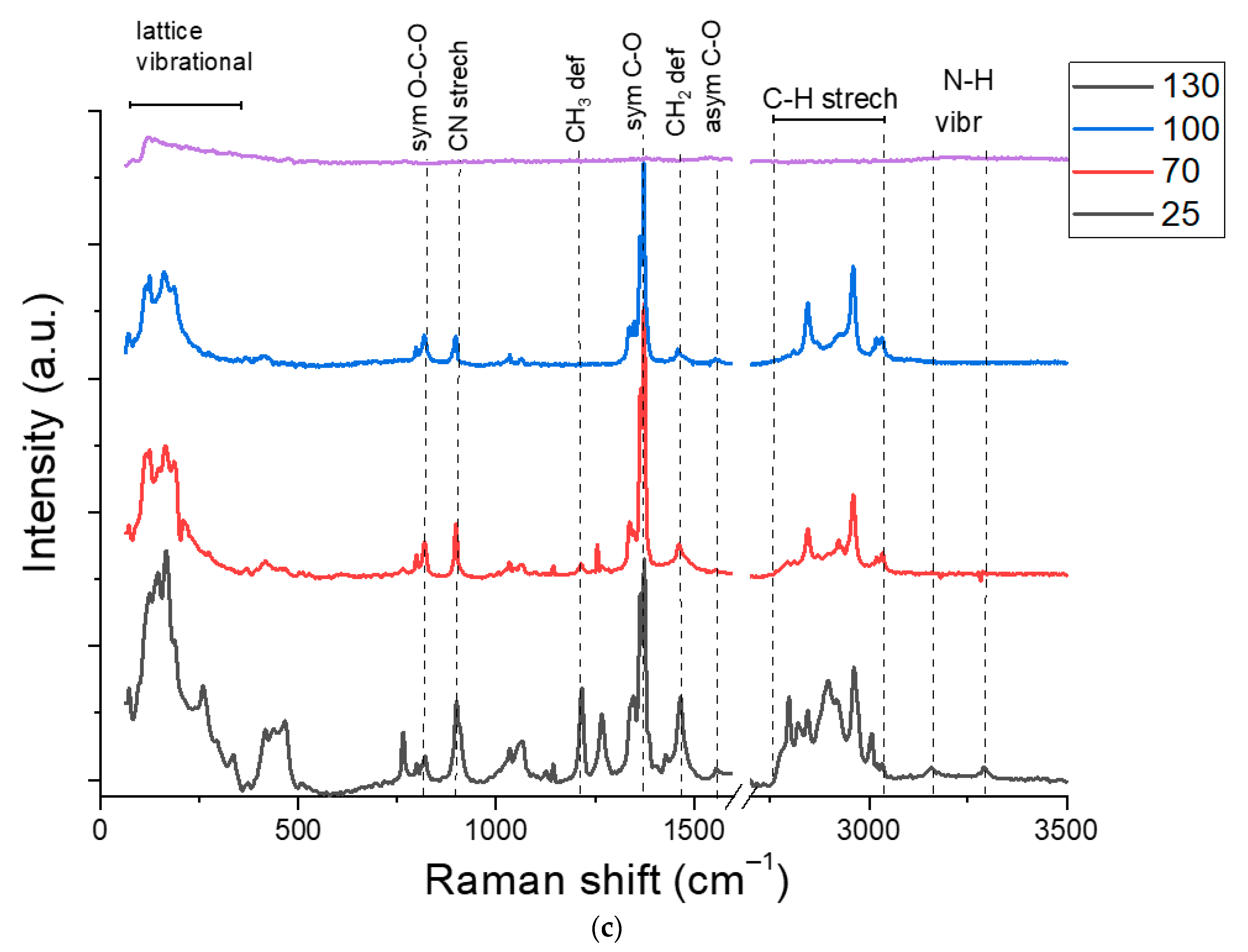
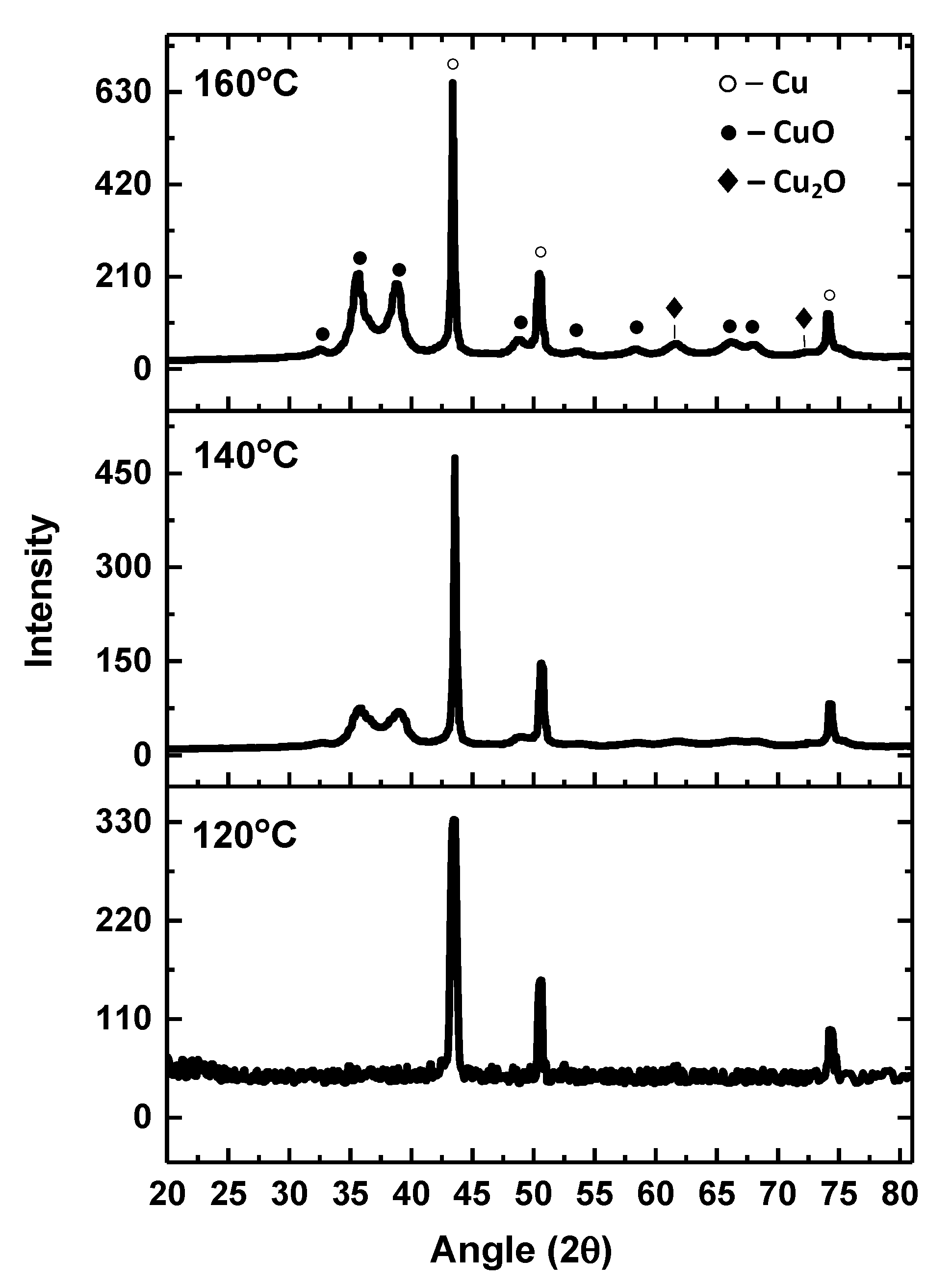
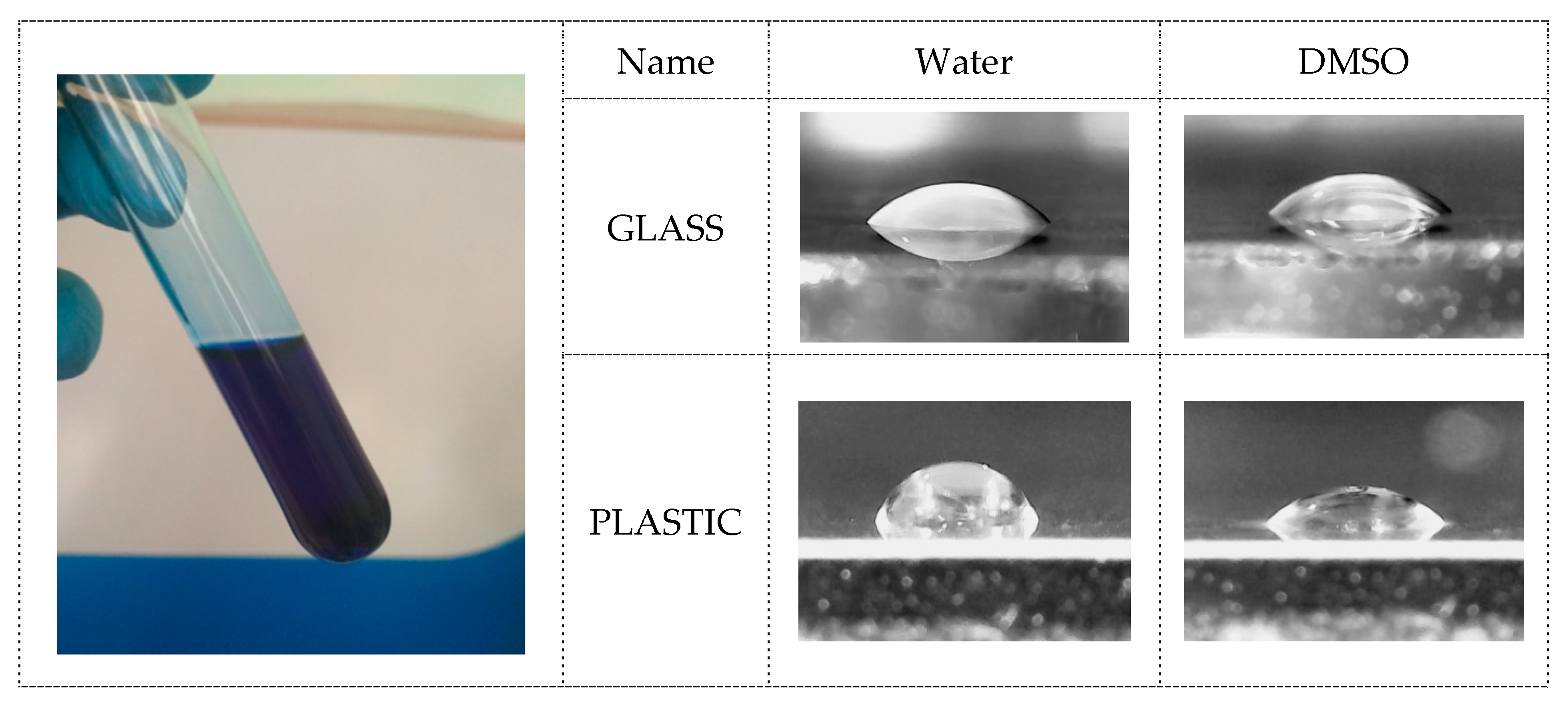
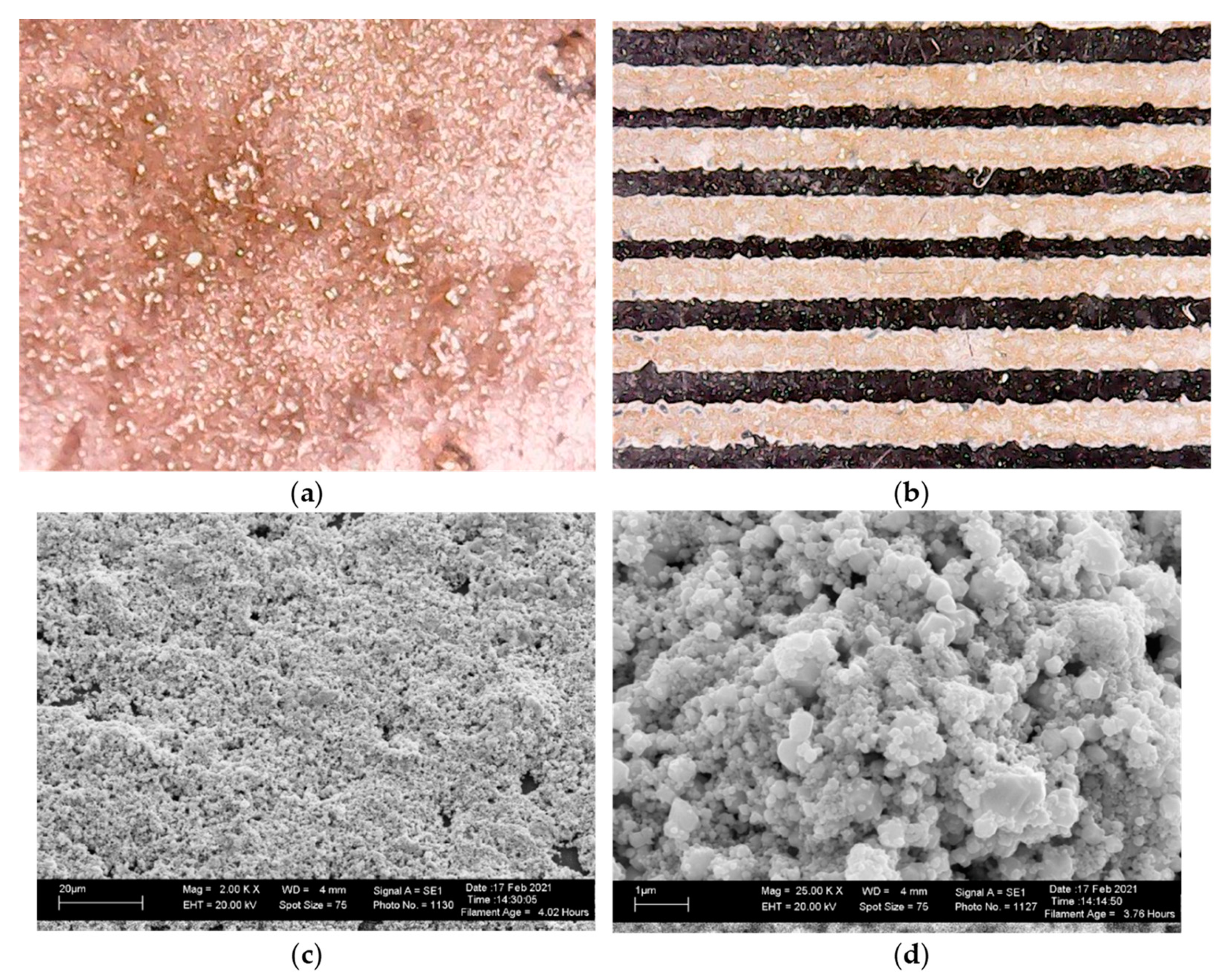
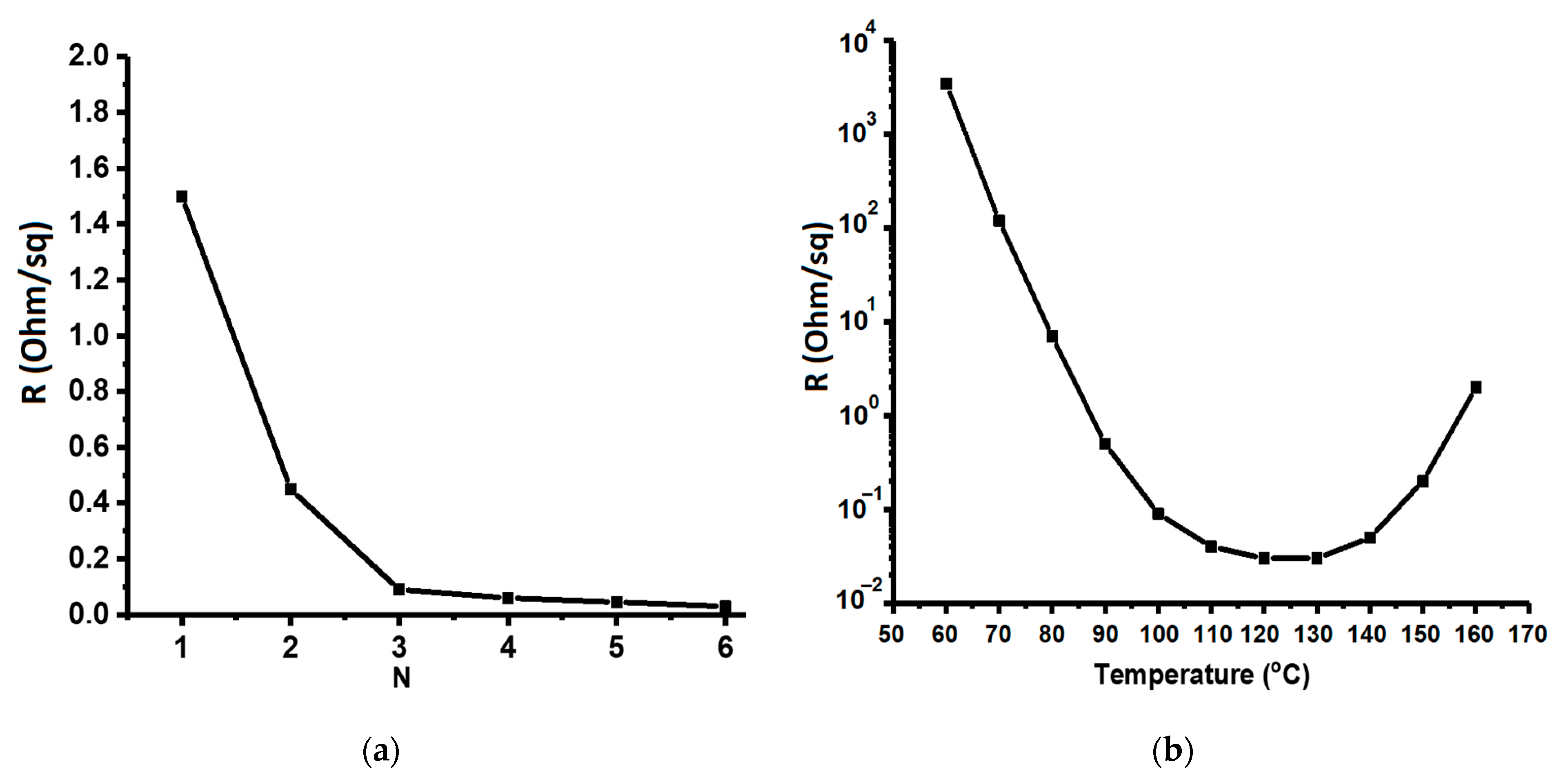
3.1. Copper-Inks Characterizations
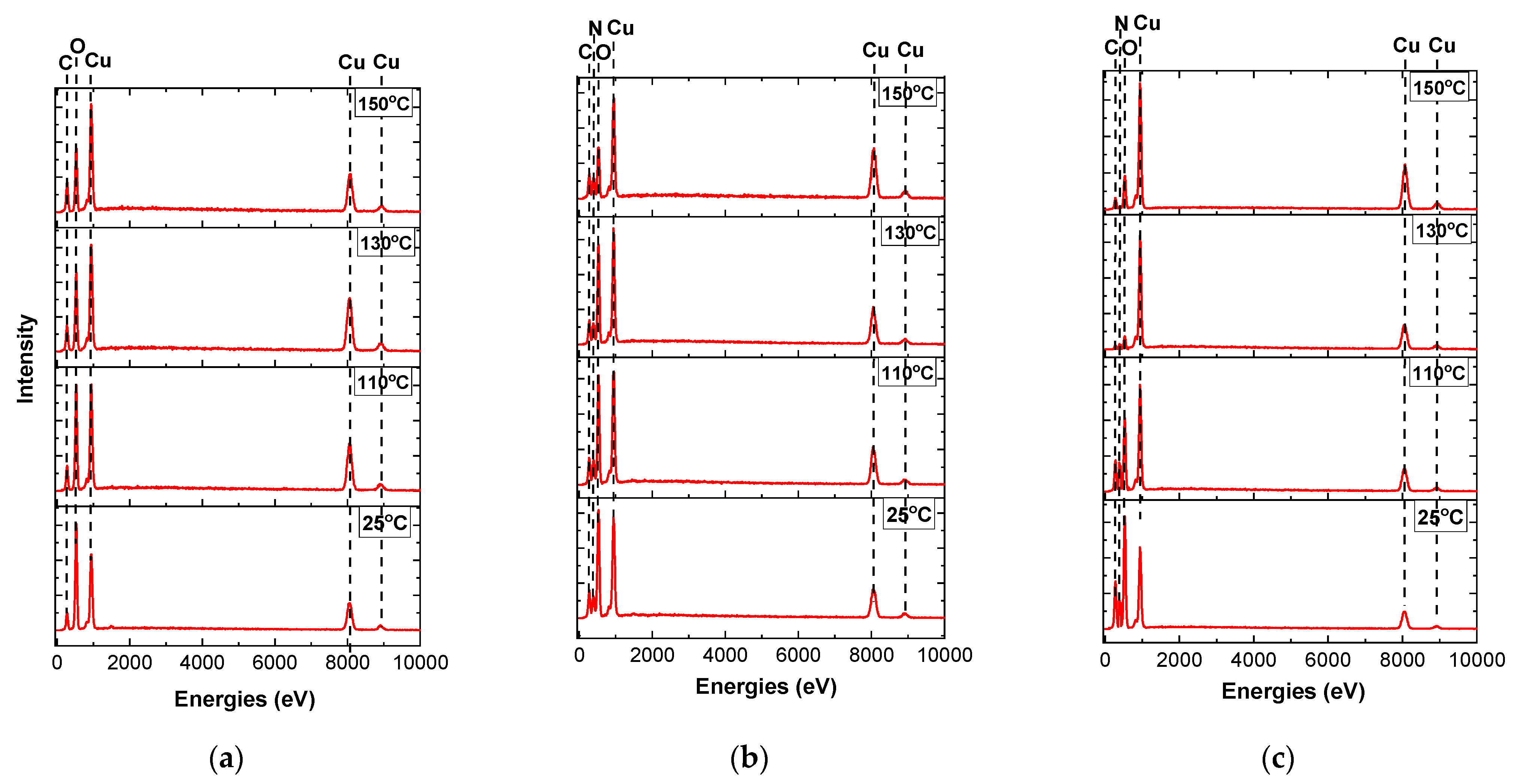
3.2. Realization of Copper Films on Flexible Substrates
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suganuma, K. Introduction to Printed Electronics; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Berggren, M.; Nilsson, D.; Robinson, N.D. Organic materials for printed electronics. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelaer, J.; Smith, P.J.; Mager, D.; Soltman, D.; Volkman, S.K.; Subramanian, V.; Korvink, J.G.; Schubert, U.S. Printed electronics: The challenges involved in printing devices, interconnects, and contacts based on inorganic materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 8446–8453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyshny, A.; Magdassi, S. Conductive Nanomaterials for Printed Electronics. Small 2014, 10, 3515–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-W.; Kang, H.-W.; Hsiao, S.-Y.; Yang, P.-F.; Chiang, K.-M.; Lin, H.-W. Efficient and Uniform Planar-Type Perovskite Solar Cells by Simple Sequential Vacuum Deposition. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6647–6652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraji, S.; Ani, F.N. The development supercapacitor from activated carbon by electroless plating—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-B.; Bae, C.-W.; Duy, L.T.; Sohn, I.-Y.; Kim, D.-I.; Song, Y.-J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, N.-E. Mogul-Patterned Elastomeric Substrate for Stretchable Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3069–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Ahn, B.Y.; Adams, J.J.; Duoss, E.B.; Bernhard, J.T.; Lewis, J.A. Pen-on-Paper Flexible Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3426–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, K.; Sekine, T.; Kumaki, D.; Tokito, S. Profile Control of Inkjet Printed Silver Electrodes and Their Application to Organic Transistors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 3916–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minari, T.; Kanehara, Y.; Liu, C.; Sakamoto, K.; Yasuda, T.; Yaguchi, A.; Tsukada, S.; Kashizaki, K.; Kanehara, M. Room-Temperature Printing of Organic Thin-Film Transistors with π-Junction Gold Nanoparticles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4886–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Someya, T. Recent progress in the development of printed thin-film transistors and circuits with high-resolution printing technology. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1602736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z. Printed Electronics: Materials, Technologies and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kamyshny, A.; Magdassi, S. Conductive nanomaterials for 2D and 3D printed flexible electronics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 48, 1712–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grouchko, M.; Kamyshny, A.; Mihailescu, C.F.; Anghel, D.F.; Magdassi, S. Conductive inks with a Built-In mechanism that enables sintering at room temperature. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3354–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.; Jiu, J.; Li, C.-F.; Chen, C.; Hu, D.; Goya, Y.; Wang, Y.; Koga, H.; et al. Highly reliable and highly conductive submicron Cu particle patterns fabricated by low temperature heat-welding and subsequent flash light sinter-reinforcement. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pischiutta, M.; Fondriest, M.; Demurtas, M.; Magnoni, F.; Di Toron, G.; Rovelli, A. Structural control on the directional amplification of seismic noise (campo imperatore, central Italy). Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 2017, 471, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-G.; Terashi, Y.; Purwanto, A.; Okuyama, K. Synthesis and film deposition of Ni nanoparticles for base metal electrode applications. Colloids Surf. A Phys. Eng. Asp. 2009, 337, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.K.; Kim, D.; Jeong, S.; Moon, J.; Kim, J.S. Direct writing of copper conductive patterns by ink-jet printing. Thin Solid Film 2007, 515, 7706–7711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdassi, S.; Grouchko, M.; Kamyshny, A. Copper Nanoparticles for Printed Electronics: Routes towards Achieving Oxidation Stability. Materials 2010, 3, 4626–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokita, Y.; Kanzaki, M.; Sugiyama, T.; Arakawa, R.; Kawasaki, H. High-Concentration Synthesis of Sub-10-nm Copper Nanoparticles for Application to Conductive Nanoinks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 19382–19389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Sun, Q.; Li, L.; Jiu, J.; Liu, X.-Y.; Kanehara, M.; Minari, T.; Suganuma, K. The rise of conductive copper inks: Challenges and perspectives. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 18, 100451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Woo, K.; Kim, D.; Lim, S.; Kim, J.S.; Shin, H.; Xia, Y.; Moon, J. Controlling the Thickness of the Surface Oxide Layer on Cu Nanoparticles for the Fabrication of Conductive Structures by Ink-Jet Printing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawande, M.B.; Goswami, A.; Felpin, F.-X.; Asefa, T.; Huang, X.; Silva, R.; Zou, X.; Zboril, R.; Varma, R.S. Cu and Cu-Based Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications in Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3722–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkata, A.K.; Rao, V.K.R.; Karthik, P.; Singh, S.P. Copper conductive inks: Synthesis and utilization in flexible electronics. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 63985–64030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanov, N.S.; Asvarov, A.S.; Chiolerio, A.; Rabadanov, K. Peroxy-Titanium Complex-based inks for low temperature compliant anatase thin films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 498, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavachari, K.; Trucks, G.W. Highly correlated systems. Excitation energies of first row transition metals Sc–Cu. J. Chem. Phys. 1989, 91, 1062–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiberg, K.B. Basis set effects on calculated geometries: 6-311++G** vs. aug-cc-pVDZ. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1342–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, A.; Dreyer, J.; Wang, F.; Akola, J.; Larrucea, J. Density functional study of Cu2+-phenylalanine complex under micro-solvation environment. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2013, 45, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, B.; Ramanujam, P. Raman and infrared spectra of copper formate tetrahydrate. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Spectrosc. 1972, 28, 2227–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, A.; Hyams, I.; Steele, D. The vibrational spectra of compounds containing the dimethylamino grouping. J. Mol. Spectrosc. 1965, 16, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

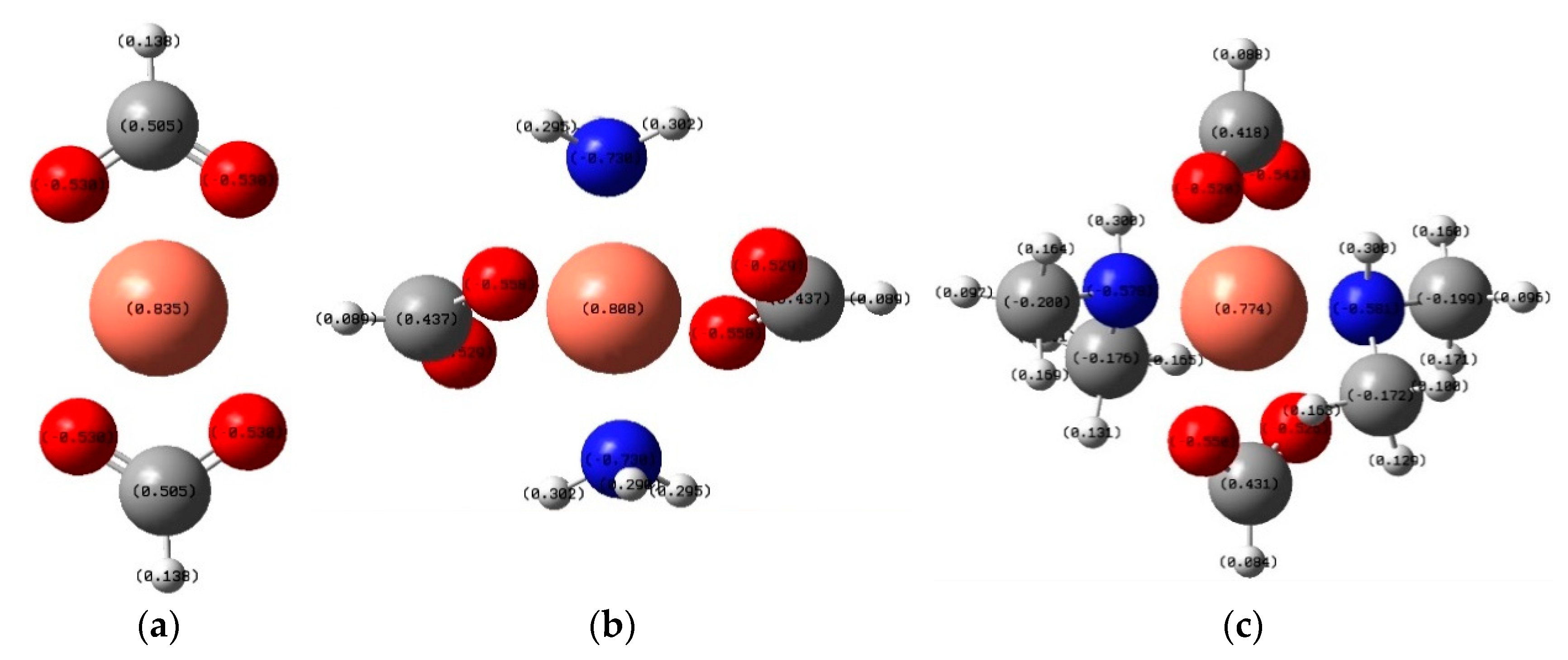
| Concurrent Reactions | ΔrH°, H | ΔrG°, H |
|---|---|---|
| Cu2+ + 2NH3 + 2H2O = Cu(OH)2 + 2NH4+ | −0.547 | −0.516 |
| Cu2+ + 2(CH3)2NH + 2H2O = Cu(OH)2 + 2(CH3)2NH2+ | −0.604 | −0.574 |
| Cu2+ + 2NH3 + 2H2O = [Cu(H2O)2(NH3)2]2+ | −0.537 | −0.483 |
| Cu2+ + 2(CH3)2NH + 2H2O = [Cu(H2O)2((CH3)2NH)2]2+ | −0.565 | −0.503 |
| Cu2+ + 2NH3 + 2NH4+ + 2OH− = Cu(NH3)42+ + 2H2O | −1.168 | −1.116 |
| Cu2+ + 2(CH3)2NH + 2(CH3)2NH2+ + 2OH− = Cu((CH3)2NH)42+ + 2H2O | −1.245 | −1.179 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shabanov, N.S.; Rabadanov, K.S.; Suleymanov, S.I.; Amirov, A.M.; Isaev, A.B.; Sobola, D.S.; Murliev, E.K.; Asvarova, G.A. Water-Soluble Copper Ink for the Inkjet Fabrication of Flexible Electronic Components. Materials 2021, 14, 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092218
Shabanov NS, Rabadanov KS, Suleymanov SI, Amirov AM, Isaev AB, Sobola DS, Murliev EK, Asvarova GA. Water-Soluble Copper Ink for the Inkjet Fabrication of Flexible Electronic Components. Materials. 2021; 14(9):2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092218
Chicago/Turabian StyleShabanov, Nabi S., Kamil Sh. Rabadanov, Sagim I. Suleymanov, Akhmed M. Amirov, Abdulgalim B. Isaev, Dinara S. Sobola, Eldar K. Murliev, and Gulnara A. Asvarova. 2021. "Water-Soluble Copper Ink for the Inkjet Fabrication of Flexible Electronic Components" Materials 14, no. 9: 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092218
APA StyleShabanov, N. S., Rabadanov, K. S., Suleymanov, S. I., Amirov, A. M., Isaev, A. B., Sobola, D. S., Murliev, E. K., & Asvarova, G. A. (2021). Water-Soluble Copper Ink for the Inkjet Fabrication of Flexible Electronic Components. Materials, 14(9), 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092218








