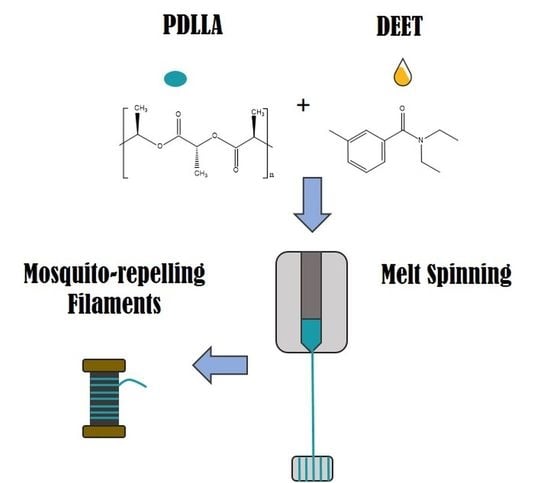
Melt-Spun Poly(D,L-lactic acid) Monofilaments Containing N,N-Diethyl-3-methylbenzamide as Mosquito Repellent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
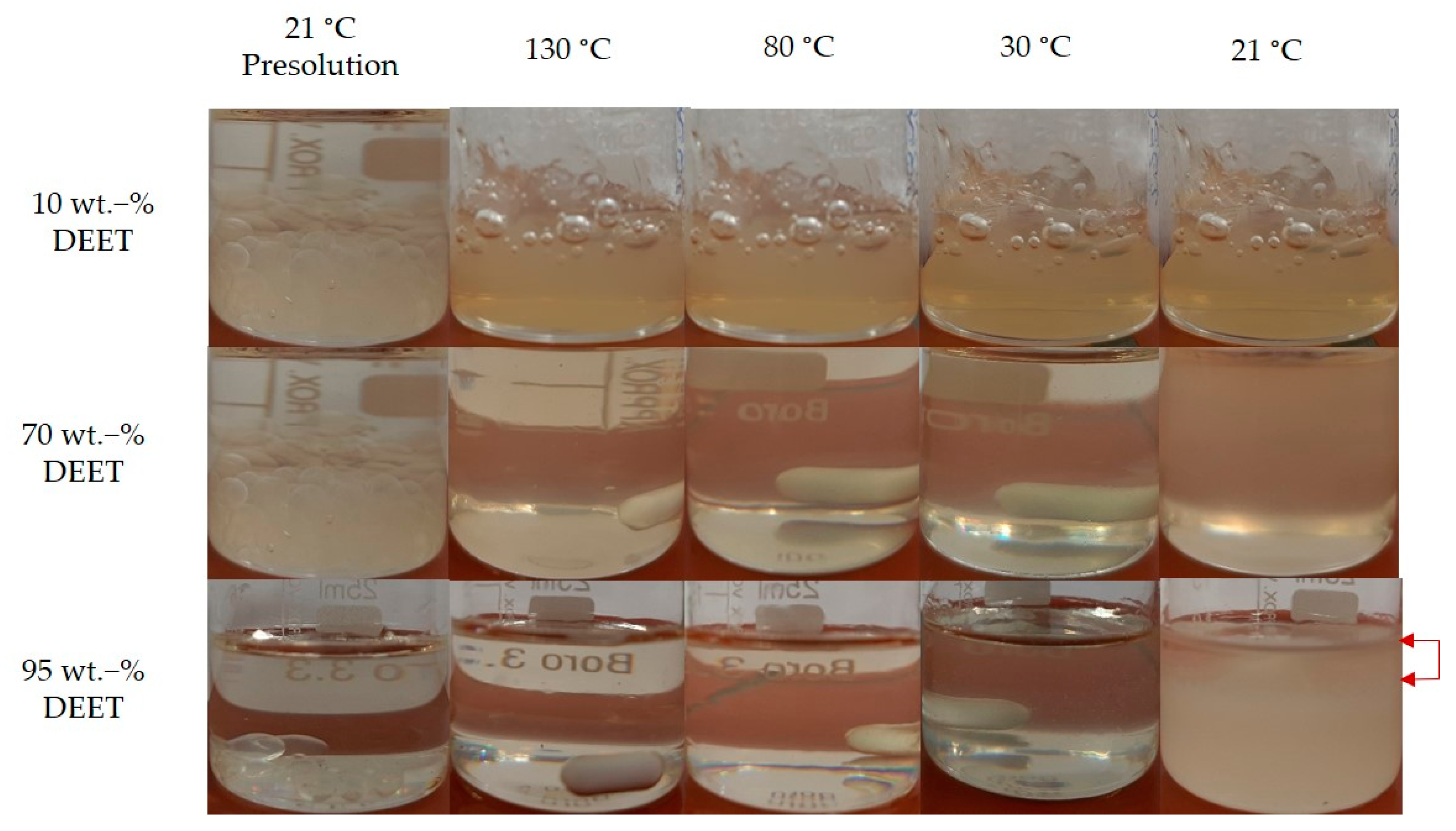
2.2. Preparation of DEET-PDLLA Solutions/Compounds
2.3. Monofilament Spinning
2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
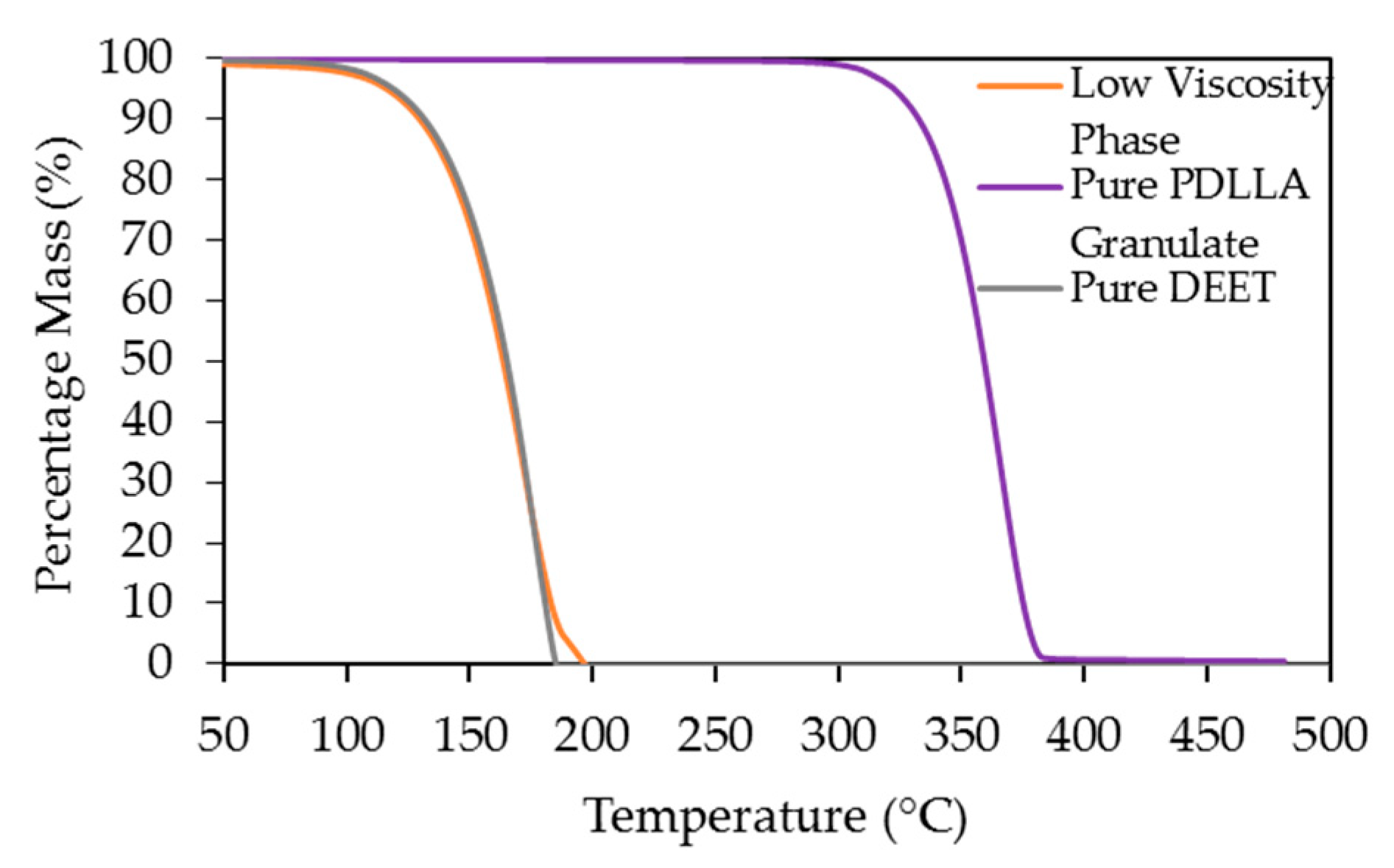
2.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.6. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.8. Tensile Tests
3. Results
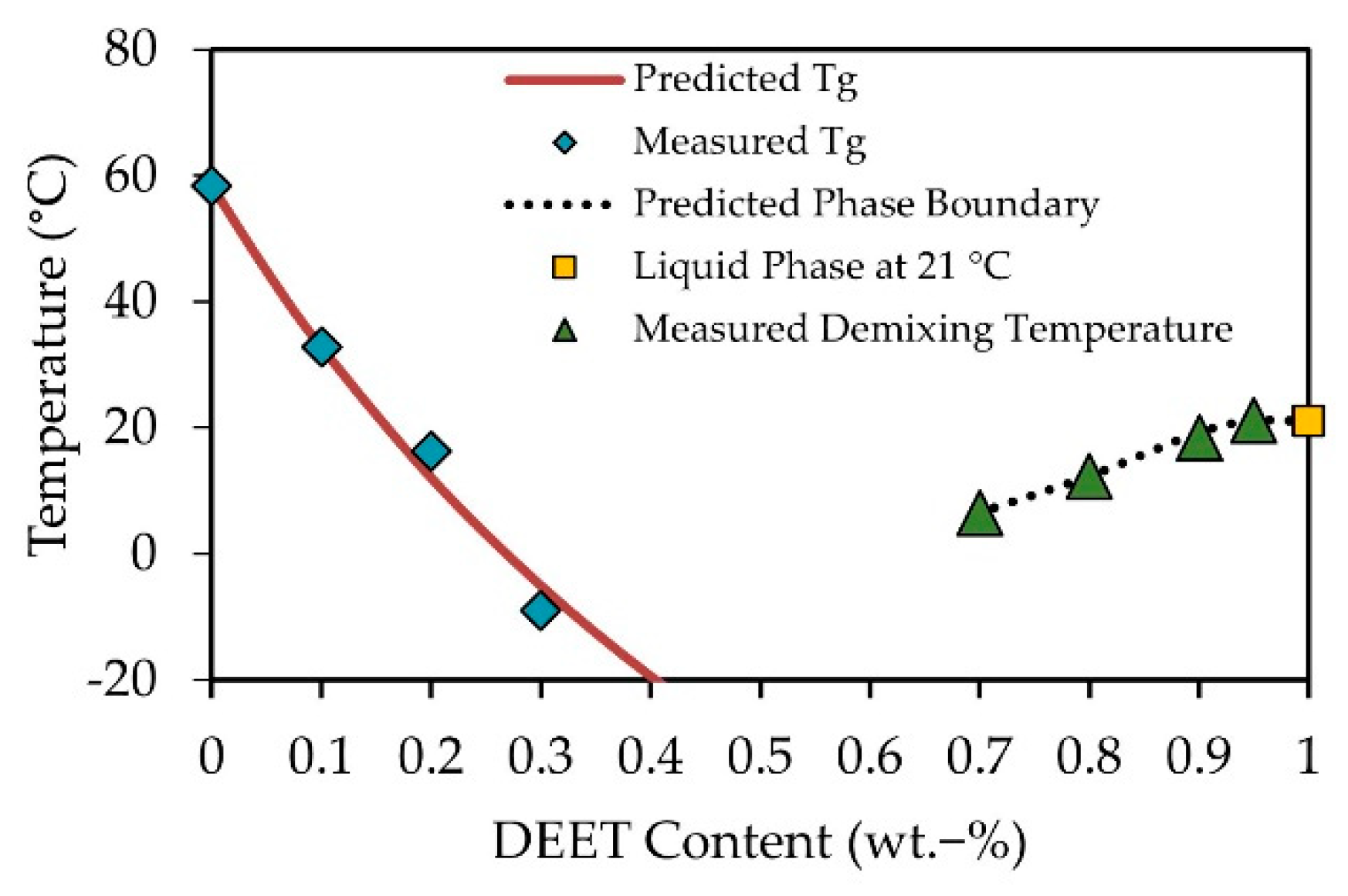
3.1. DEET-PLA Phase Behaviour
3.2. Spinnability of PDLLA Monofilaments with Varying DEET Content
3.3. Semicrystalline Morphology
3.4. DEET Content and Distribution
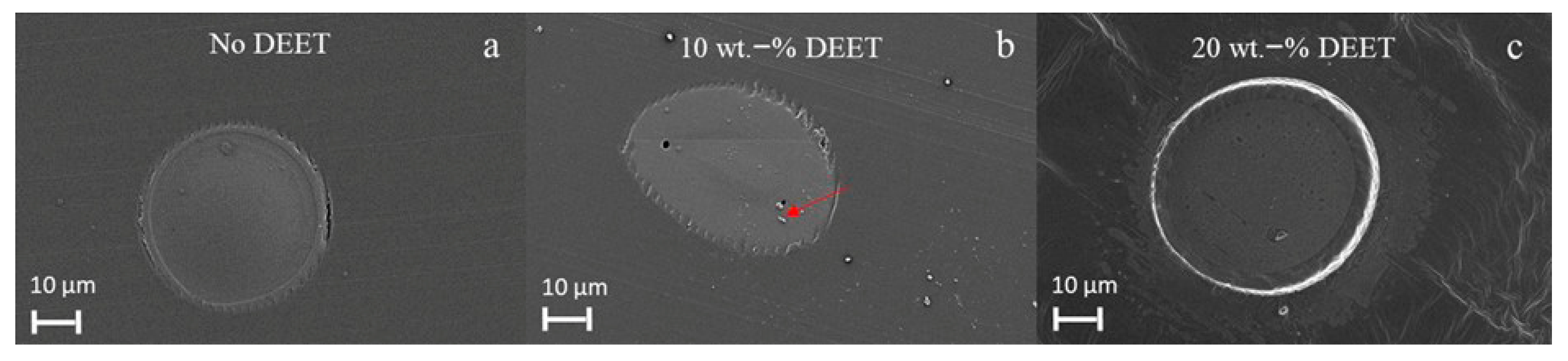
3.5. Filament Morphology and Size
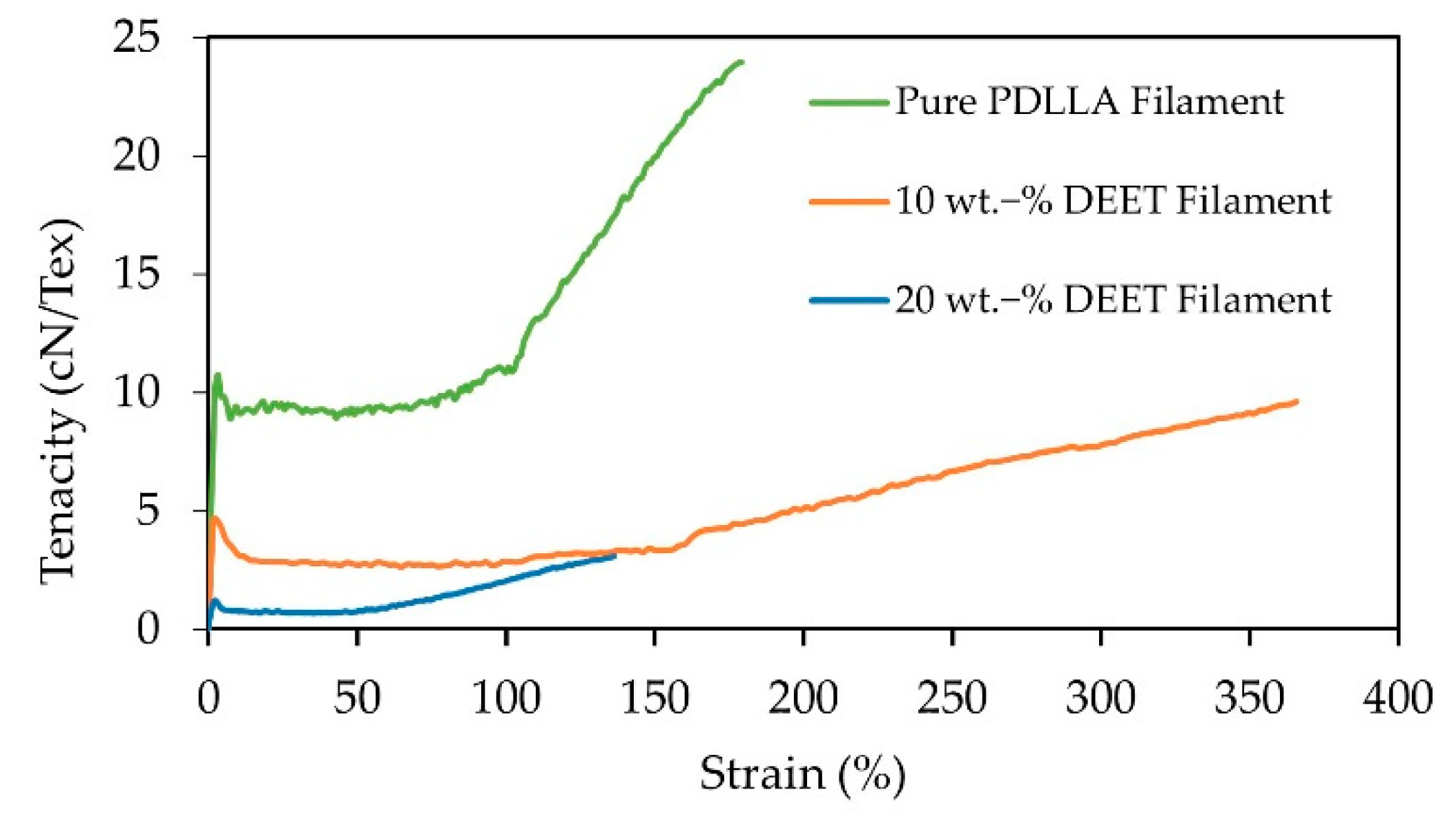
3.6. Filament Mechanical Integrity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Malaria Report 2019; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Sibanda, M.; Focke, W.; Braack, L.; Leuteritz, A.; Brünig, H.; Tran, N.H.A.; Trümper, W. Bicomponent fibres for controlled release of volatile mosquito repellents. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braack, L.E.O.; Coetzee, M.; Hunt, R.H.; Biggs, H.; Cornel, A.; Gericke, A. Biting pattern and host-seeking behaviour of Anopheles arabiensis (Diptera: Culicidae) in northeastern South Africa. J. Med. Entomol. 1994, 31, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braack, L.; Hunt, R.; Koekemoer, L.L.; Gericke, A.; Munhenga, G.; Haddow, A.D.; Coetzee, M. Biting behaviour of African malaria vectors: 1. where do the main vector species bite on the human body? Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debboun, M.; Frances, S.; Strickman, D. Insect Repellents, Principles, Methods, and Uses; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2007; p. 465. [Google Scholar]
- Costantini, C.; Badolo, A.; Ilboudo-Sanogo, E. Field evaluation of the efficacy and persistence of insect repellents DEET, IR3535, and KBR 3023 against Anopheles gambiae complex and other Afrotropical vector mosquitoes. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 98, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, T.W.; Robert, L.L.; Copeland, R.A.; Githeko, A.K.; Wirtz, R.A.; Githure, J.I.; Klein, T.A. Field evaluation of arthropod repellents, deet and a piperidine compound, AI3-37220, against Anopheles funestus and Anopheles arabiensis in western Kenya. J. Am. Mosq. Control. Assoc. 1996, 12, 172–176. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, Q.D.; Vu, M.N.; Hebert, A.A. Insect Repellents: An Updated Review for the Clinician. J. Am. Acad. Derm. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, E.M.; Judge, B.S.; Jones, J.S. Bug off! Severe toxicity following inhalational exposure to N, N-diethyl-meta-toluamide (DEET). Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 37, 1395.e3–1395.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Africa Review Report on Waste Management; United Nations Economic and Social Council: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2009.
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M. Processing technologies for poly (lactic acid). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 820–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnik, E. Compostable Polymer Materials: Definitions, Structures, and Methods of Preparation. In Handbook of Biopolymers and Biodegradable Plastics-Properties, Processing and Applications; Ebnesajjad, S., Ed.; Elsevier: Norwich, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 171–211. [Google Scholar]
- Avérous, L. Synthesis, Properties, Environmental and Biomedical Applications of Polylactic Acid. In Handbook of Biopolymers and Biodegradable Plastics-Properties, Processing and Applications; Ebnesajjad, S., Ed.; Elsevier: Norwich, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 171–188. [Google Scholar]
- Massardier-Nageotte, V.; Pestre, C.; Cruard-Pradet, T.; Bayard, R. Aerobic and anaerobic biodegradability of polymer films and physico-chemical characterization. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, V.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Perspective on polylactic acid (PLA) based sustainable materials for durable applications: Focus on toughness and heat resistance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2899–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, M.S.; Nassar, S.H.; Mashaly, H.; Mahmoud, S.; Maamoun, D.; Khattab, T.A. Polymerization products of lactic acid as synthetic thickening agents for textile printing. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1203, 127421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhvi, M.S.; Zinjarde, S.S.; Gokhale, D.V. Polylactic acid: Synthesis and biomedical applications. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 1612–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeidlou, S.; Huneault, M.A.; Li, H.; Park, C.B. Poly (lactic acid) crystallization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1657–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Ikada, Y. Crystallization from the melt of poly (lactide)s with different optical purities and their blends. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1996, 197, 3483–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androsch, R.; Di Lorenzo, M.L.; Schick, C. Crystal nucleation in random l/d-lactide copolymers. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 75, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urayama, H.; Moon, S.I.; Kimura, Y. Microstructure and Thermal Properties of Polylactides with Different L- and D-Unit Sequences: Importance of the Helical Nature of the L-Sequenced Segments. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2003, 288, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, M.L.; Longo, A. N,N-Diethyl-3-methylbenzamide (DEET): A mosquito repellent as functional plasticizer for poly(l-lactic acid). Thermochim. Acta 2019, 677, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungkapreecha, C.; Iqbal, N.; Focke, W.W.; Androsch, R. Crystallization of poly(l-lactic acid) in solution with the mosquito-repellent N,N-Diethyl-3-methylbenzamide. Polym. Cryst. 2019, 2, 10029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonadies, I.; Longo, A.; Androsch, R.; Jehnichen, D.; Göbel, M.; Di Lorenzo, M.L. Biodegradable electrospun PLLA fibers containing the mosquito-repellent DEET. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 113, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungkapreecha, C.; Focke, W.W.; Androsch, R. Competition between Liquid-liquid De-mixing, Crystallization, and Glass Transition in Solutions of PLA of Different Stereochemistry and DEET. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 38, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungkapreecha, C.; Iqbal, N.; Gohn, A.M.; Focke, W.W.; Androsch, R. Phase behavior of the polymer/drug system PLA/DEET. Polymer 2017, 126, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Schick, C.; Androsch, R. Full-composition-range glass transition behavior of the polymer/solvent system poly (lactic acid) / ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate (PLA/IR3535®). Polymer 2020, 209, 123058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungkapreecha, C.; Beily, M.J.; Kressler, J.; Focke, W.W.; Androsch, R. Phase behavior of the polymer/drug system PLA/DEET: Effect of PLA molar mass on subambient liquid-liquid phase separation. Thermochim. Acta 2018, 660, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bair, H.E. Thermal Analysis of Additives in Polymers. In Thermal Characterization of Polymeric Materials; Turi, E.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1981; pp. 845–909. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, S.F.; Pathak, J.; Wunderlich, B. Study of phase separation in blends of polystyrene and poly(α-methylstyrene) in the glass transition region using quantitative thermal analysis. Macromolecules 1982, 15, 1278–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, R.R.; Wardman, R.H. Introduction. In Chemistry of Textile Fibres; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Stoclet, G.; Seguela, R.; Lefebvre, J.M.; Rochas, C. New Insights on the Strain-Induced Mesophase of Poly (d,l-lactide): In Situ WAXS and DSC Study of the Thermo-Mechanical Stability. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 7228–7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, F.K.; Wan, Y. Melt Spinning. In Introduction to Nanofiber Materials; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, I.M.; Coates, P.D.; Dumoulin, M.M. Spinning Technology. In Solid Phase Processing of Polymers; Hanser Publishers: Munich, Germany, 2000; pp. 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Takasaki, M.; Ito, H.; Kikutani, T. Structure Development of Polylactides with Various d-Lactide Contents in the High-Speed Melt Spinning Process. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2003, 42, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tashiro, K.; Tsuji, H.; Domb, A.J. Disorder-to-Order Phase Transition and Multiple Melting Behavior of Poly(l-lactide) Investigated by Simultaneous Measurements of WAXD and DSC. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 1352–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasanasuk, K.; Tashiro, K. Crystal structure and disorder in Poly (l-lactic acid) δ form (α′ form) and the phase transition mechanism to the ordered α form. Polymer 2011, 52, 6097–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Tashiro, K. Phase Transition Mechanism of Poly (l-lactic acid) among the α, δ, and β Forms on the Basis of the Reinvestigated Crystal Structure of the β Form. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 3285–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuniwa, M.; Sakamo, K.; Ono, Y.; Kawahara, W. Melting behavior of poly (l-lactic acid): X-ray and DSC analyses of the melting process. Polymer 2008, 49, 1943–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androsch, R.; Schick, C.; Di Lorenzo, M.L. Melting of Conformationally Disordered Crystals (α′-Phase) of Poly (l-lactic acid). Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2014, 215, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Kai, W.; Zhu, B.; Dong, T.; Inoue, Y. Polymorphous Crystallization and Multiple Melting Behavior of Poly (l-lactide): Molecular Weight Dependence. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 6898–6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righetti, M.C.; Gazzano, M.; Di Lorenzo, M.L.; Androsch, R. Enthalpy of melting of α′- and α-crystals of poly (l-lactic acid). Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 70, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

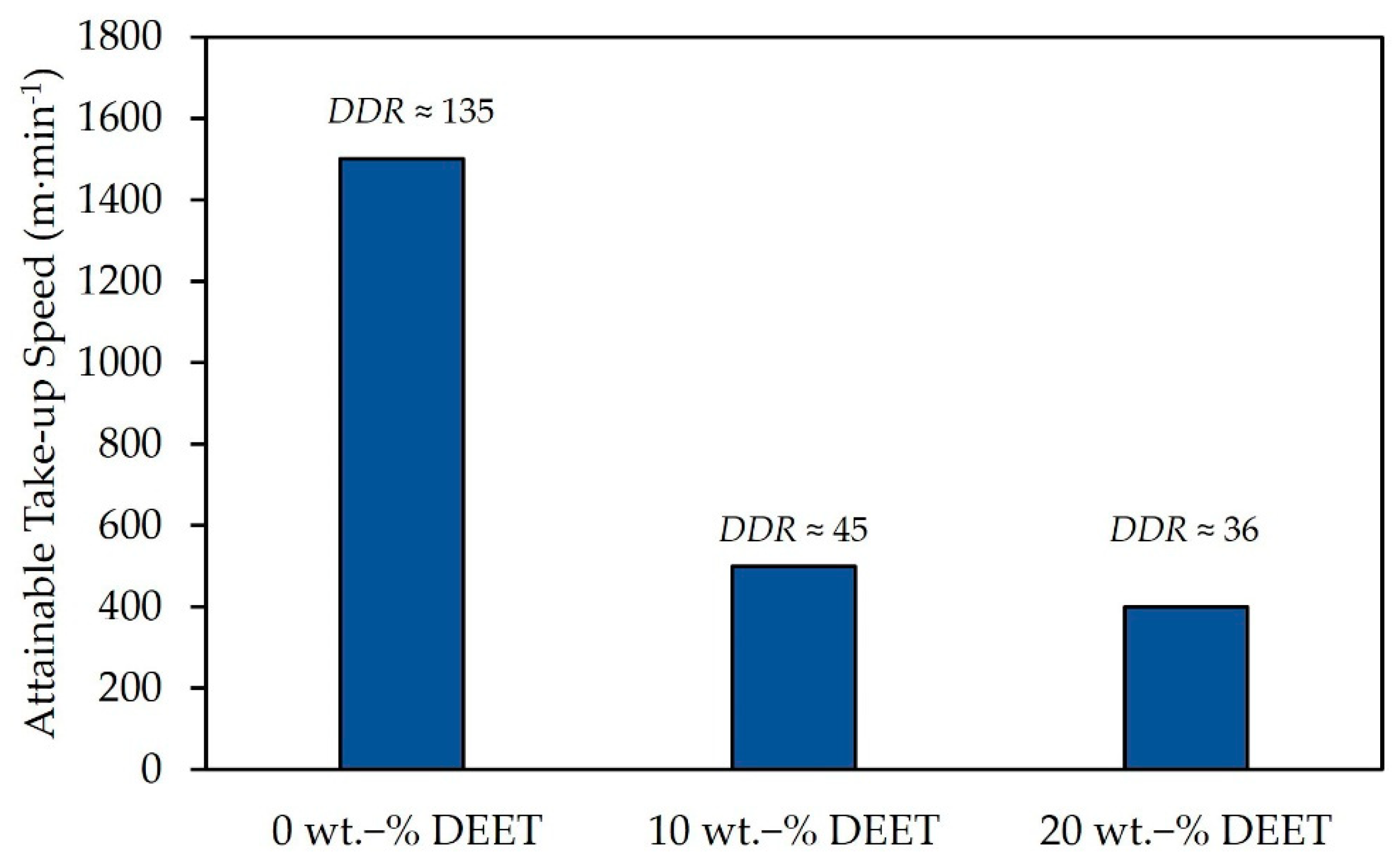
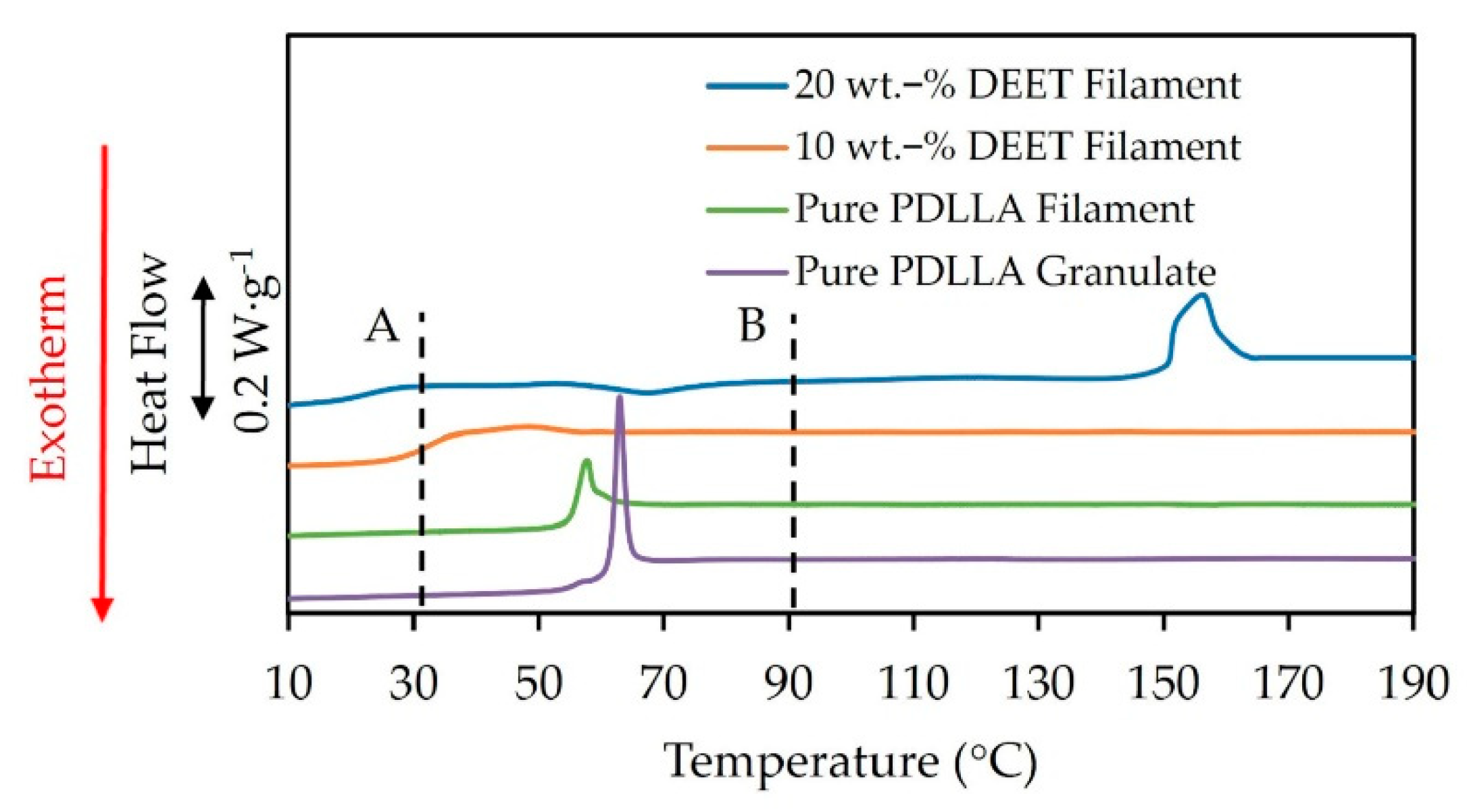
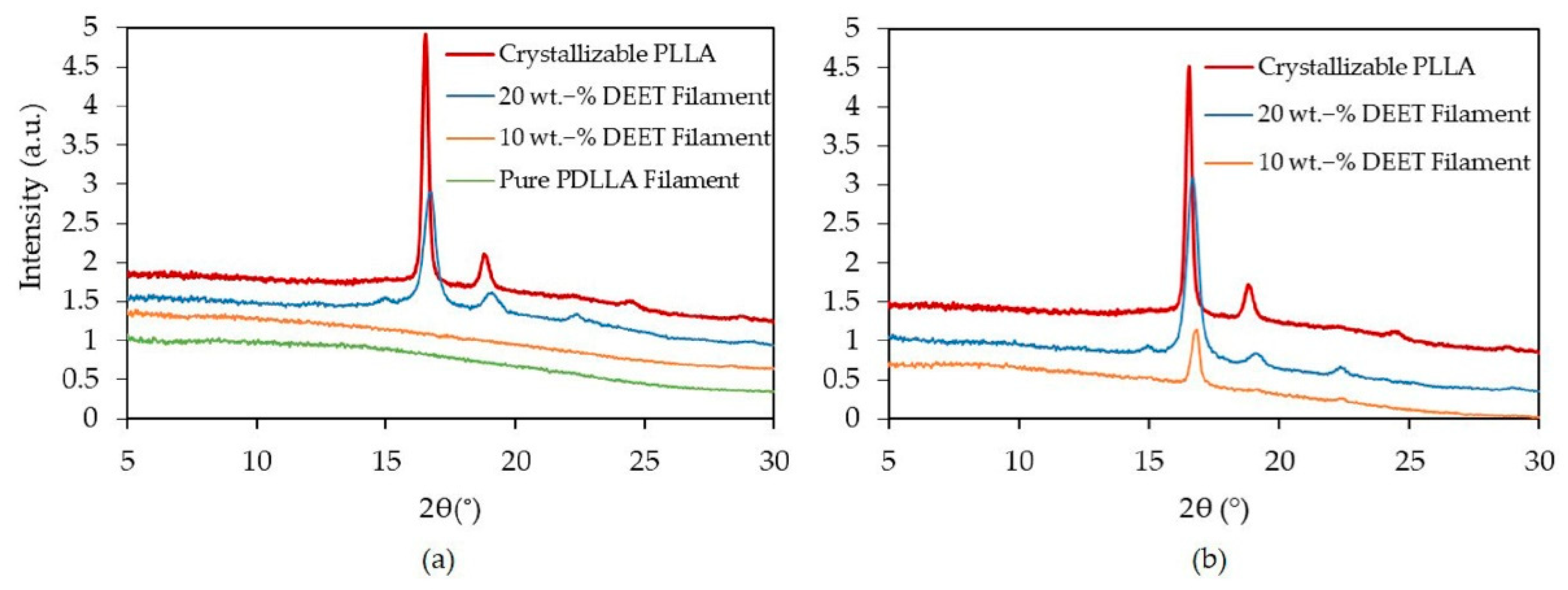
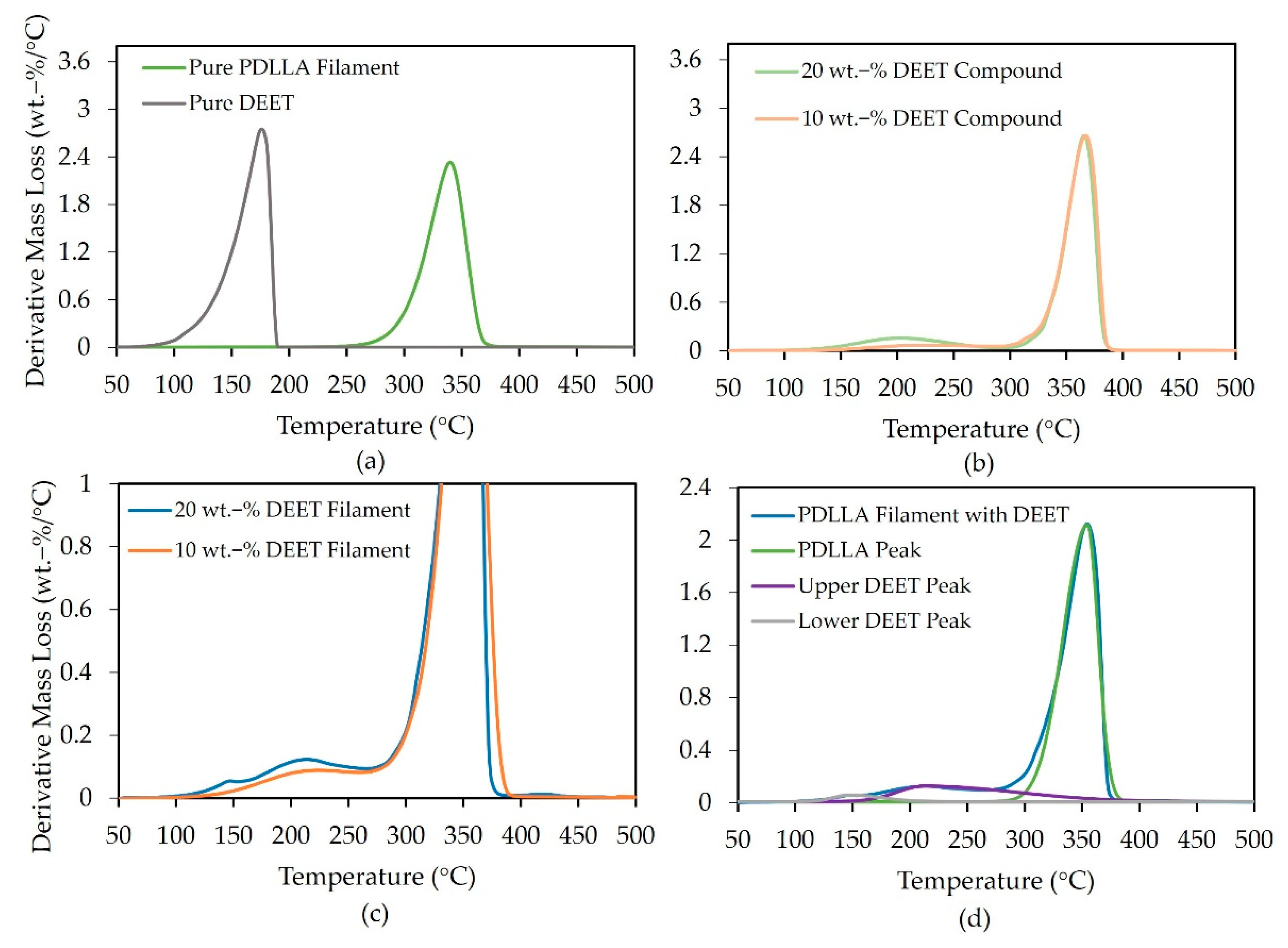
| XD (%) | Mw (kDa) | Mn (kDa) | D (-) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11.3 | 147.0 | 46.8 | 3.15 |
| Pure PDLLA Granulate | Pure Spun PDLLA | Spun PDLLA with 10 wt.-% DEET | Spun PDLLA with 20 wt.-% DEET | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tg onset (°C) | 53.6 ± 0.6 | 55.1 ± 3.9 | 27.4 ± 1.6 | 18.5 ± 0.1 |
| CC peak (°C) | - | - | - | 67.5 ± 0.1 |
| Melting peak (°C) | - | - | - | 156.4 ± 0.5 |
| ΔHm (J/g) | - | - | - | 11.4 ± 0.1 |
| ΔHcc (J/g) | - | - | - | 2.3 ± 0.4 |
| Description | PDLLA with 10 wt.-% DEET | PDLLA with 20 wt.-% DEET |
|---|---|---|
| Experimental DEET content | 12.8 | 17.8 |
| Theoretical DEET content | 10.0 | 20.0 |
| Property | PDLLA with 0 wt.‑% DEET | PDLLA with 10 wt.‑% DEET | PDLLA with 20 wt.‑% DEET |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ø (μm) | 30.7 ±0.8 | 38.9 ± 2.8 | 49.0 ± 7.5 |
| F (dTex) | 6.3 | 12.7 | 26.3 |
| Tensile Property | PDLLA with 0 wt.‑% DEET | PDLLA with 10 wt.‑% DEET | PDLLA with 20 wt.‑% DEET |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elastic modulus (cN/Tex) | 628.5 +/− 53.2 | 368.8 +/− 9.1 | 129.8 +/− 29.2 |
| Ultimate strength (cN/Tex) | 24.7 +/− 0.6 | 9.3 +/− 0.3 | 3.6 +/− 0.7 |
| Elongation at break (%) | 181.6 +/− 8.9 | 376.0 +/− 13.2 | 148.1 +/− 20.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira, I.; Brünig, H.; Focke, W.; Boldt, R.; Androsch, R.; Leuteritz, A. Melt-Spun Poly(D,L-lactic acid) Monofilaments Containing N,N-Diethyl-3-methylbenzamide as Mosquito Repellent. Materials 2021, 14, 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14030638
Ferreira I, Brünig H, Focke W, Boldt R, Androsch R, Leuteritz A. Melt-Spun Poly(D,L-lactic acid) Monofilaments Containing N,N-Diethyl-3-methylbenzamide as Mosquito Repellent. Materials. 2021; 14(3):638. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14030638
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira, Ignatius, Harald Brünig, Walter Focke, Regine Boldt, René Androsch, and Andreas Leuteritz. 2021. "Melt-Spun Poly(D,L-lactic acid) Monofilaments Containing N,N-Diethyl-3-methylbenzamide as Mosquito Repellent" Materials 14, no. 3: 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14030638
APA StyleFerreira, I., Brünig, H., Focke, W., Boldt, R., Androsch, R., & Leuteritz, A. (2021). Melt-Spun Poly(D,L-lactic acid) Monofilaments Containing N,N-Diethyl-3-methylbenzamide as Mosquito Repellent. Materials, 14(3), 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14030638