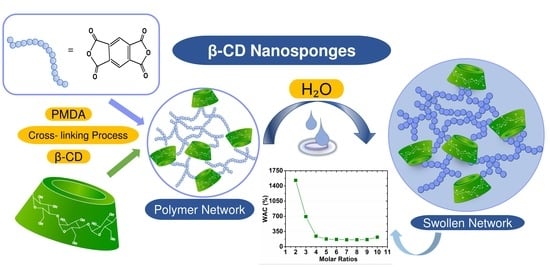
Effect of the Cross-Linking Density on the Swelling and Rheological Behavior of Ester-Bridged β-Cyclodextrin Nanosponges
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
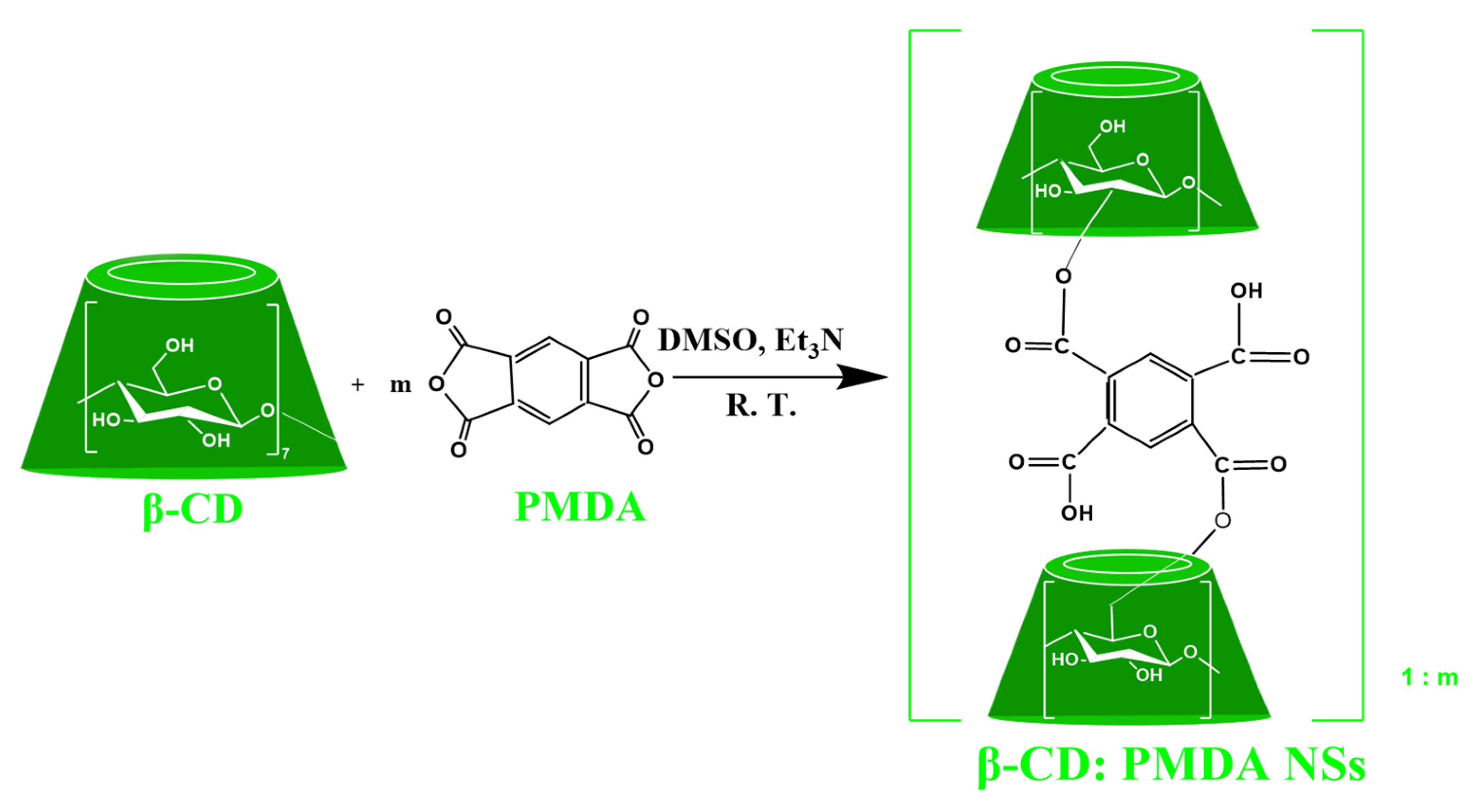
2.2.1. Synthesis of PMDA:β-CD NSs
2.2.2. Swelling Studies
2.2.3. Cross-Linking Density Determination Using Swelling Experiments
Flory–Rehner Theory
Rheological Measurements
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Synthesis of Ester-Bridged βCD-NSs Based on PMDA
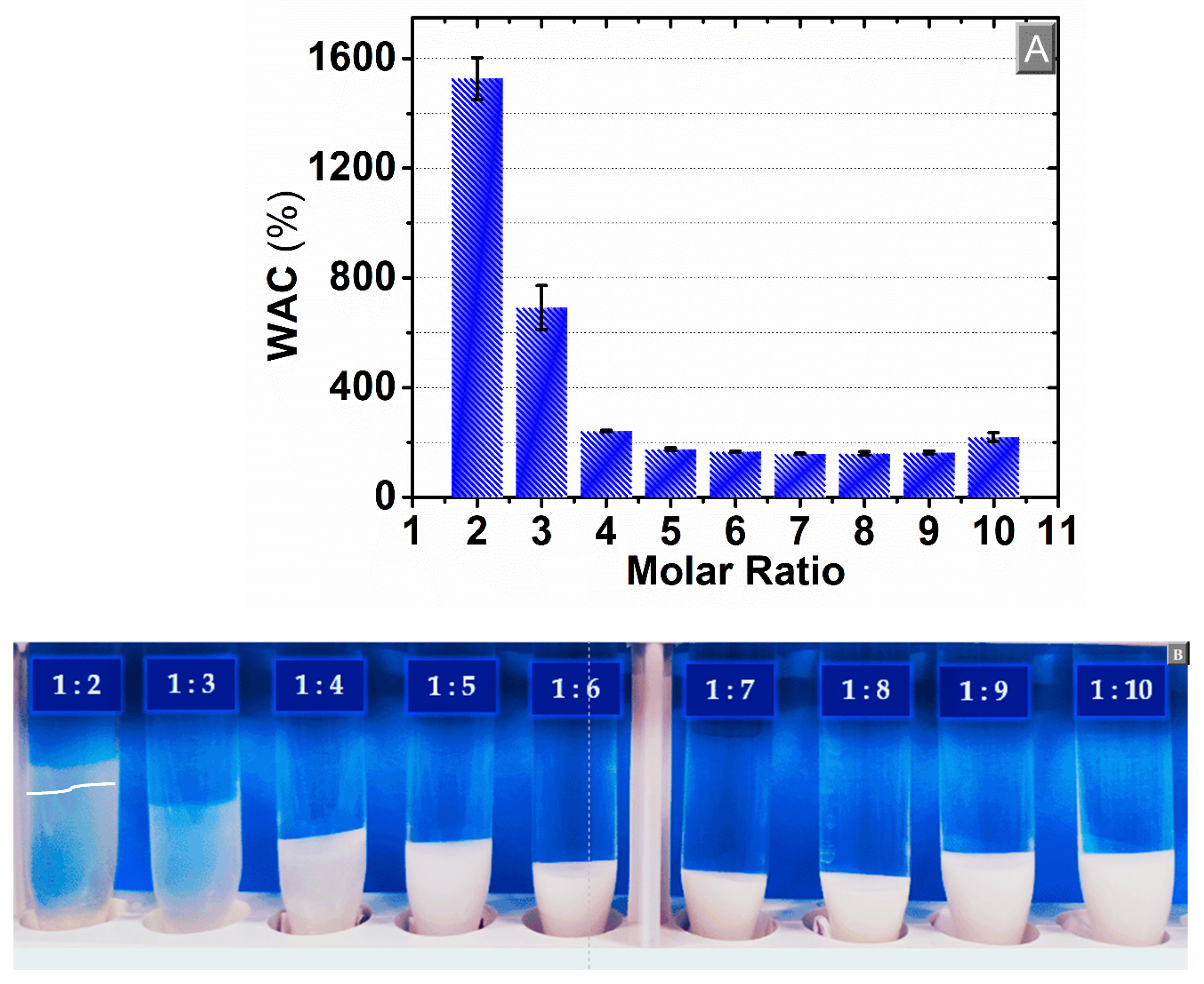
3.2. Water Absorption Capacity (WAC)
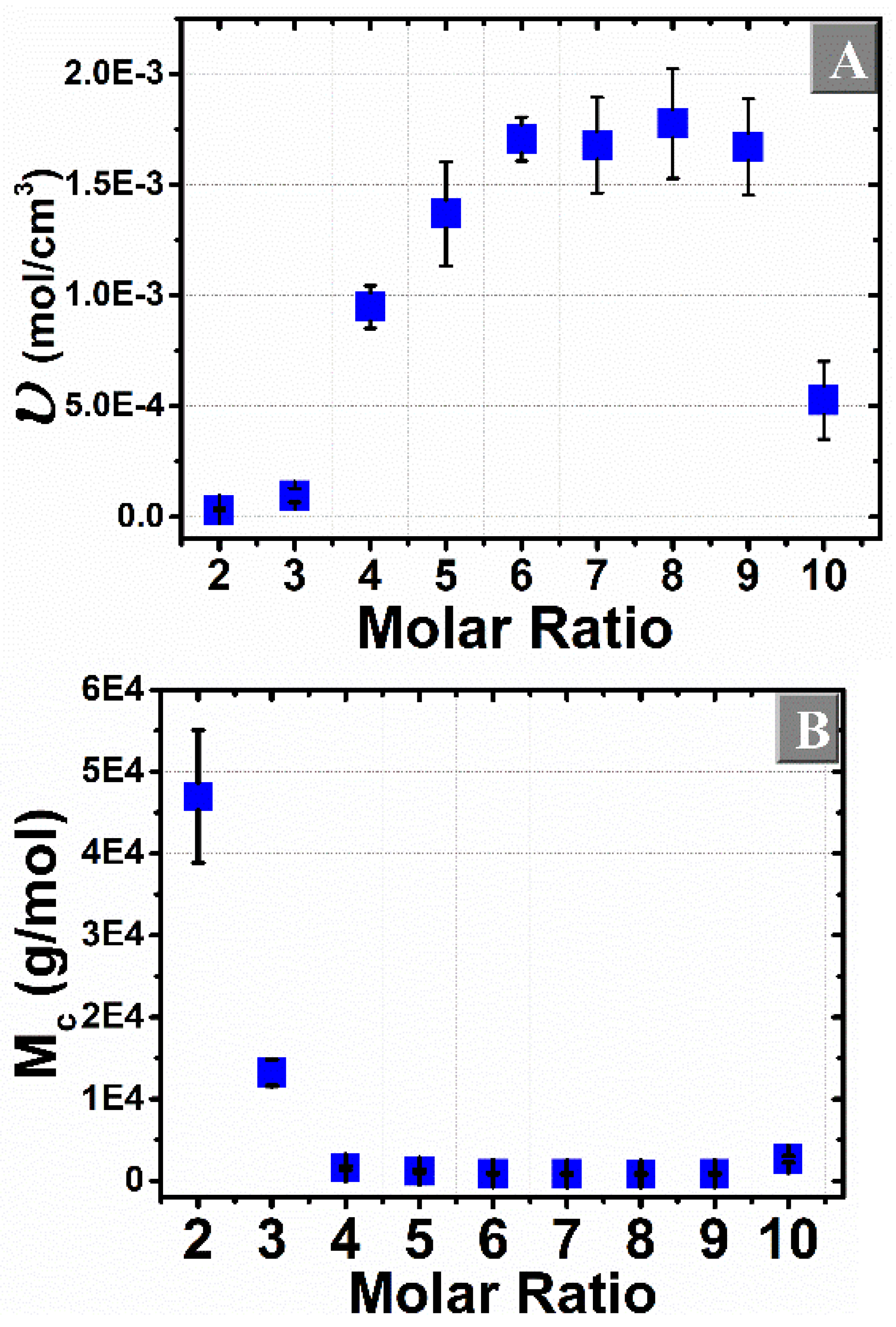
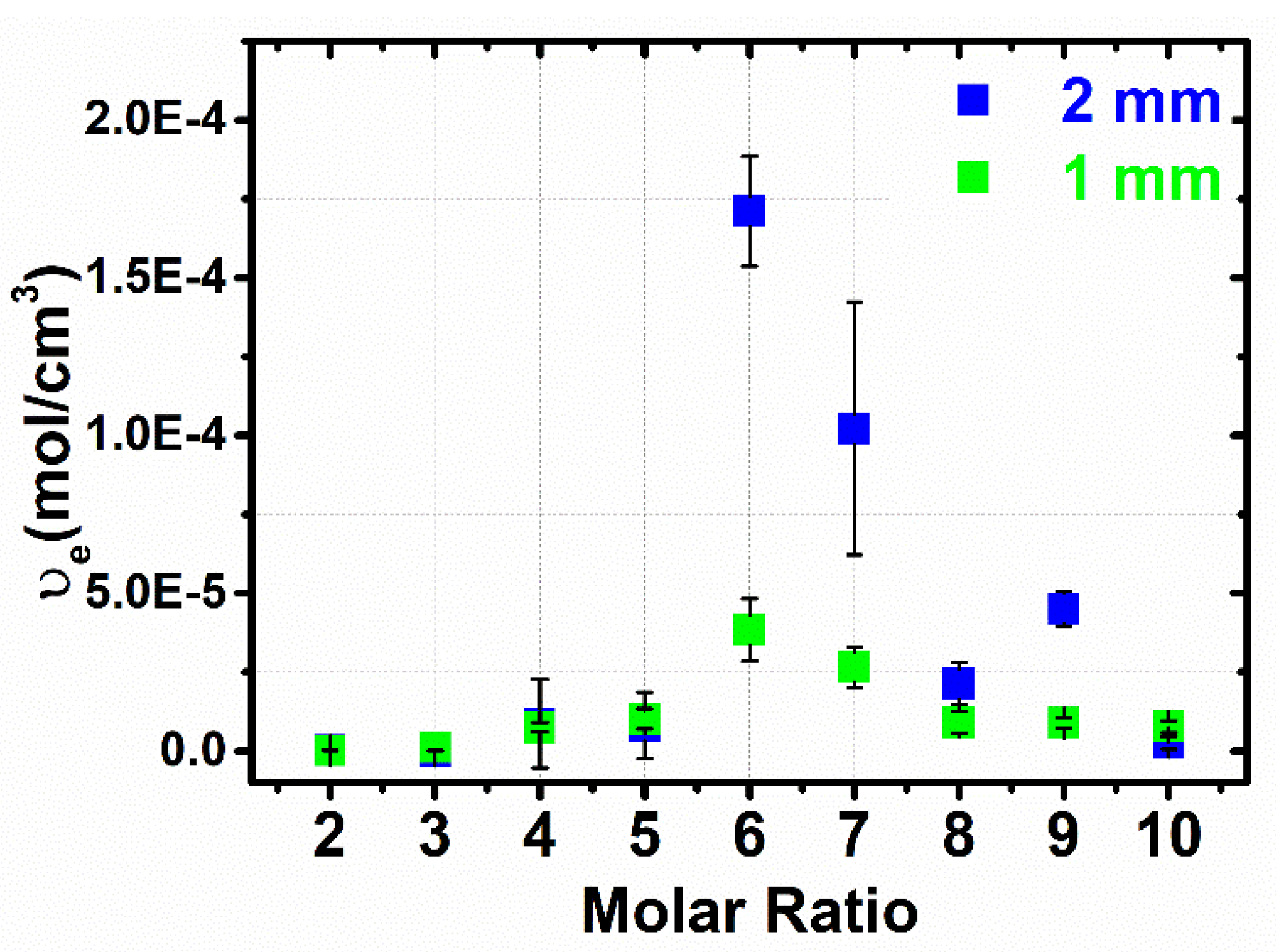
3.3. Flory–Rehner Theory
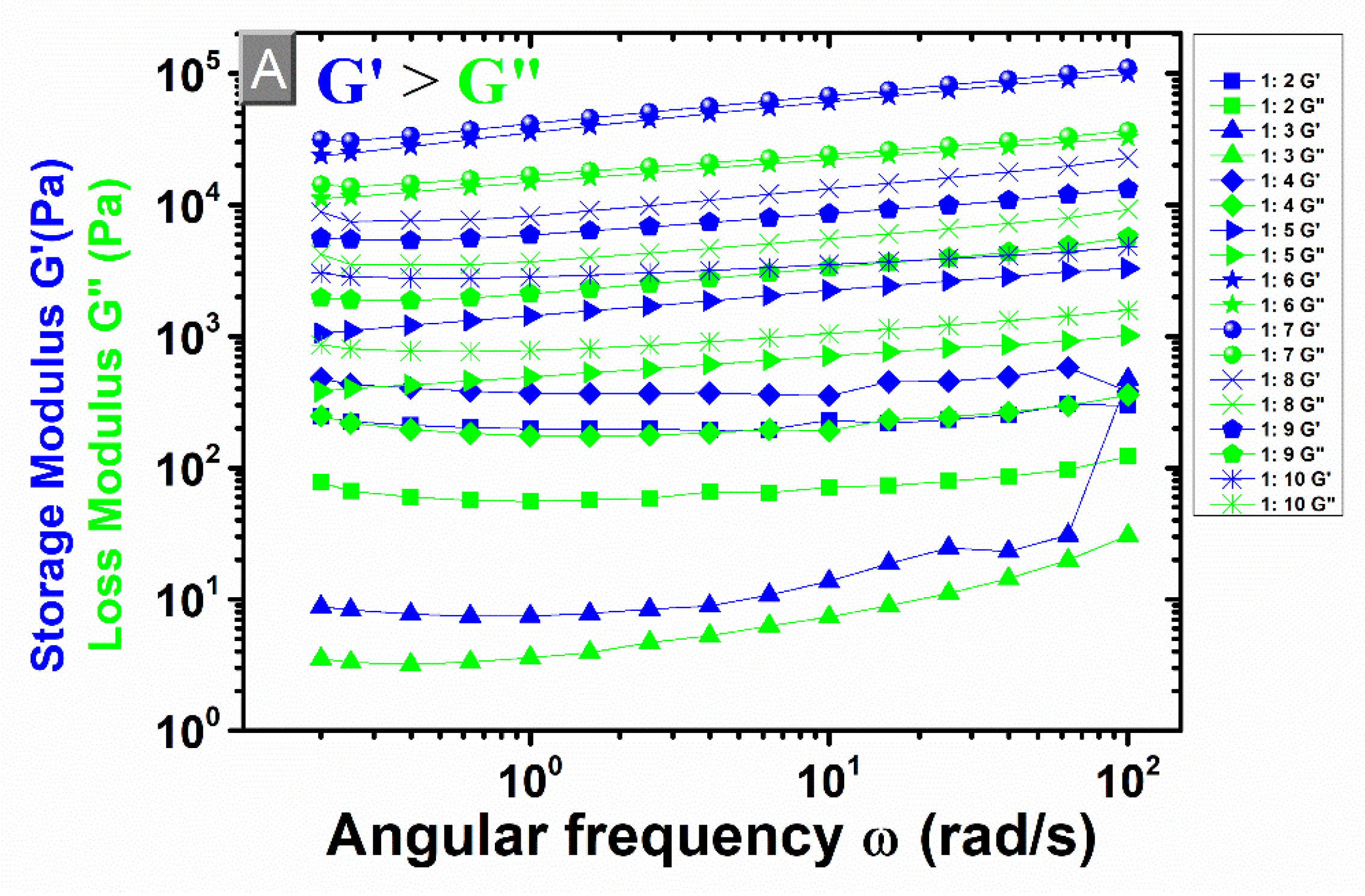
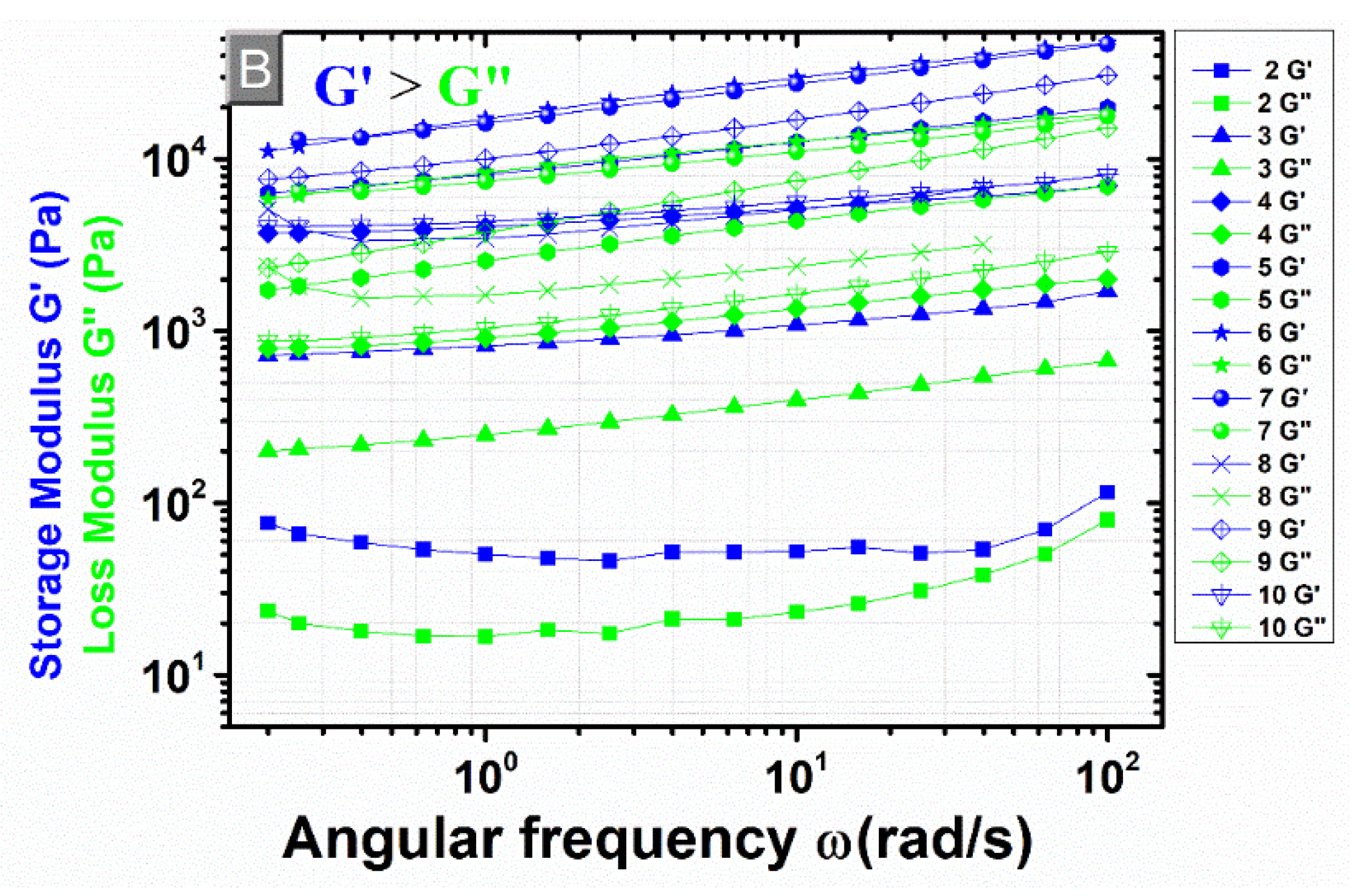
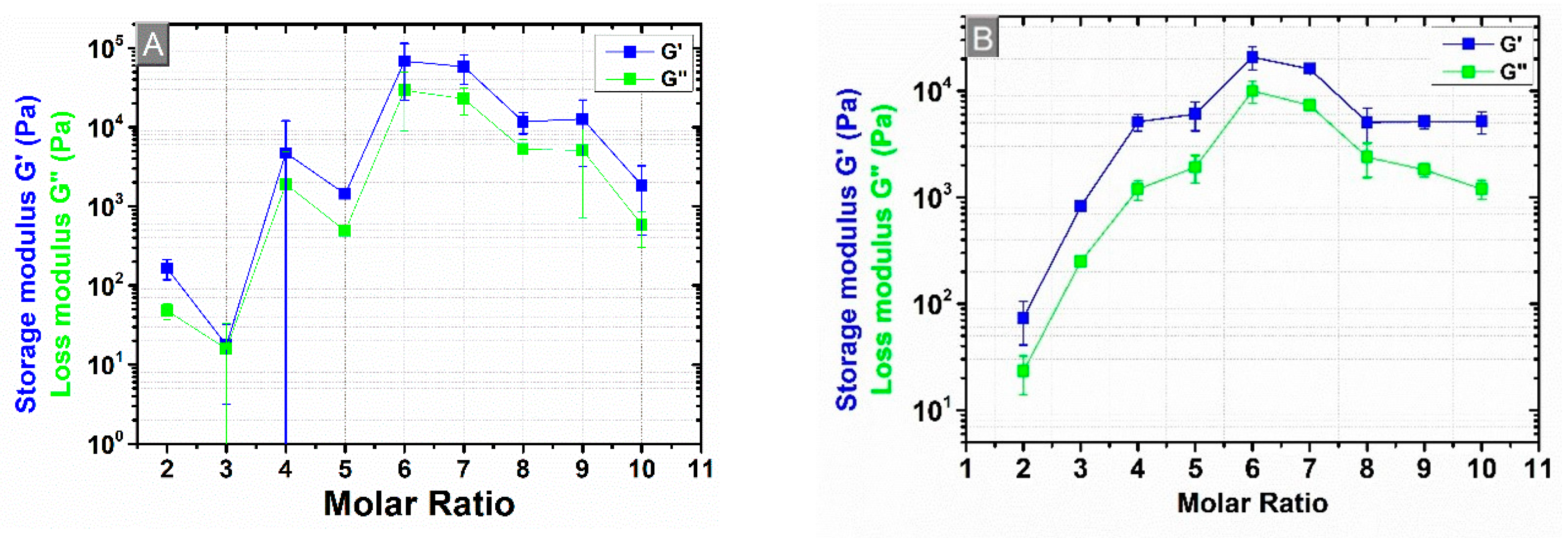
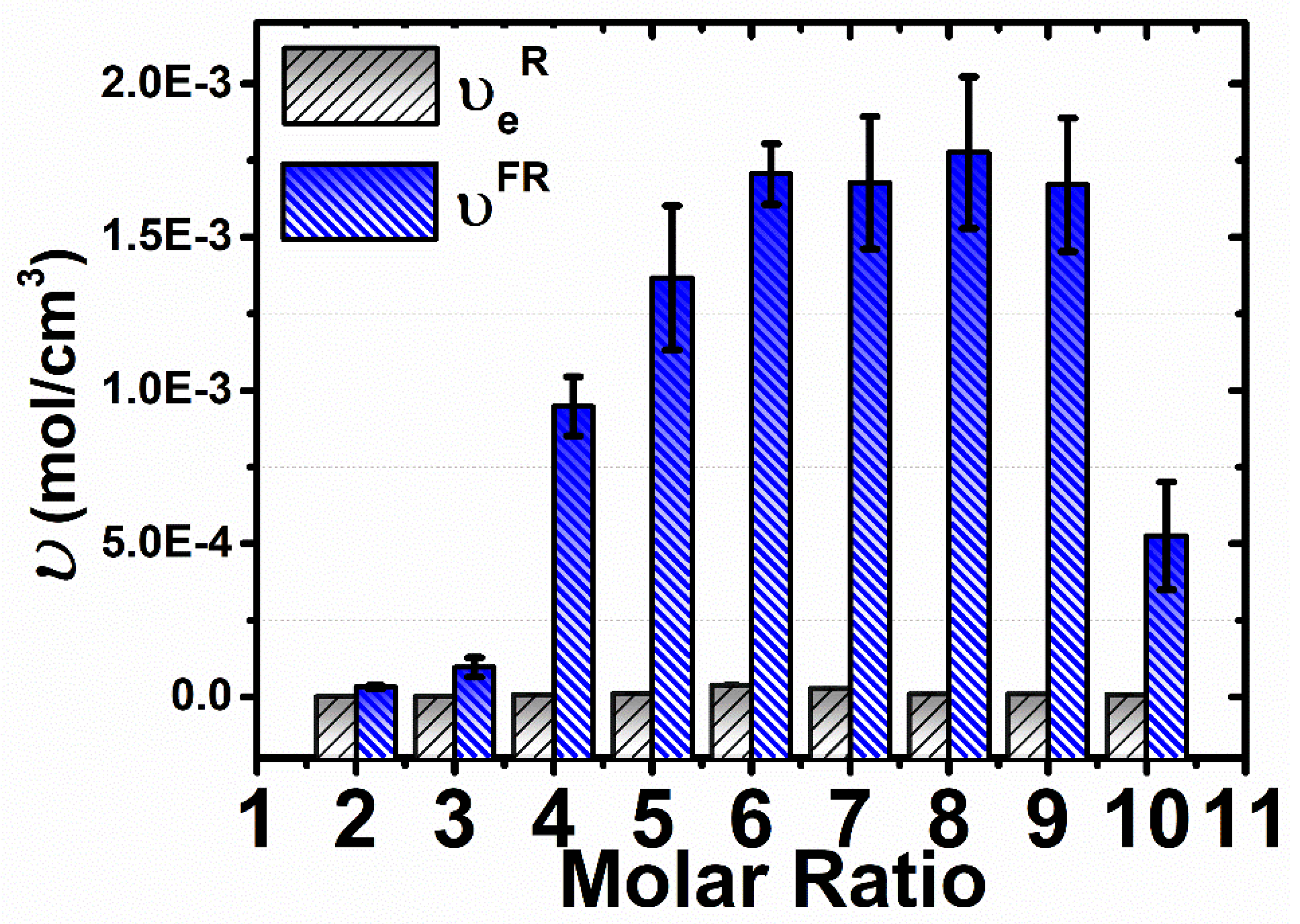
3.4. Rheological Measurements
3.5. Comparison of the Cross-Linking Density Determination Based on Two Different Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Derivation of Equilibrium Swelling Equation
References
- Salimi-Kenari, H.; Mollaie, F.; Dashtimoghadam, E.; Imani, M.; Nyström, B. Effects of chain length of the cross-linking agent on rheological and swelling characteristics of dextran hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennink, W.E.; Nostrum, C.F. Van Novel crosslinking methods to design hydrogels. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldera, F.; Tannous, M.; Cavalli, R.; Zanetti, M.; Trotta, F. Evolution of Cyclodextrin Nanosponges. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, V.A.; Veloso, T.C.; Leao, V.A. Hydrogels of cellulose acetate crosslinked with pyromellitic dianhydride-Part I: Synthesis and swelling kinetics. Artigo 2013, 36, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañeta, E.; Stewart, S.; Ervine, M.; Al-Kasasbeh, R.; Donnelly, F.R. Hydrogels for Hydrophobic Drug Delivery. Classification, Synthesis and Applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Lv, P.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liao, X.; Yang, B. Cyclodextrin-based delivery systems for cancer treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 96, 872–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, S.; Vavia, P.R.; Trotta, F.; Cavalli, R. Nanosponges encapsulating dexamethasone for ocular delivery: Formulation design, physicochemical characterization, safety and corneal permeability assessment. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mognetti, B.; Barberis, A.; Marino, S.; Berta, G.; De Francia, S.; Trotta, F.; Cavalli, R. In Vitro enhancement of anticancer activity of paclitaxel by a Cremophor free cyclodextrin-based nanosponge formulation. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2012, 74, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, M.; Castiglione, F.; Punta, C.; Melone, L.; Panzeri, W.; Rossi, B.; Trotta, F.; Mele, A. Anomalous diffusion of ibuprofen in cyclodextrin nanosponge hydrogels: An HRMAS NMR study. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 2715–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, F.; Cavalli, R. Characterization and Applications of New Hyper-Cross-Linked Cyclodextrins. Compos. Interfaces 2009, 16, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia Appleton, S.; Tannous, M.; Argenziano, M.; Muntoni, E.; Carolina Rosa, A.; Rossi, D.; Caldera, F.; Scomparin, A.; Trotta, F.; Cavalli, R. Nanosponges as protein delivery systems: Insulin, a case study. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 590, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Hreinsdóttir, D.; Másson, M. Evaluation of cyclodextrin solubilization of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 302, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins: Basic science and product development. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 1607–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewster, M.E.; Loftsson, T. Cyclodextrins as pharmaceutical solubilizers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 645–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saokham, P.; Muankaew, C.; Jansook, P.; Loftsson, T. Solubility of cyclodextrins and drug/cyclodextrin complexes. Molecules 2018, 23, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, E.M.M. Cyclodextrins and their uses: A review. Process. Biochem. 2004, 39, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, A. Cyclodextrins: Properties and Applications. In Starch—Chemistry and Technology, 3rd ed.; BeMiller, J., Whistler, R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; p. 900. ISBN 978-0-12-746275-2. [Google Scholar]
- Stella, V.J.; Rajewski, R.A. Cyclodextrins: Their Future in Drug Formulation and Delivery. Pharm. Res. 1997, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseau, J.; Menuel, S.; Rousseau, C.; Hapiot, F.; Monflier, E. Cyclodextrins as Porous Material for Catalysis; Organic Nanoreactors; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 15–42. ISBN 9780128018101. [Google Scholar]
- Hedges, A.R. Industrial applications of cyclodextrins. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 2035–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotta, F.; Dianzani, C.; Caldera, F.; Mognetti, B.; Cavalli, R. The application of nanosponges to cancer drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotta, F. Cyclodextrin Nanosponges and their Applications. In Cyclodextrins in Pharmaceutics, Cosmetics, and Biomedicine; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 323–342. [Google Scholar]
- Szejtli, J. Past, present, and future of cyclodextrin research. Pure Appl. Chem. 2004, 76, 1825–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.; Yang, Y. Citric acid cross-linking of starch films. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Bajaj, A.; Khole, I.; Munjapara, G.; Trotta, F. In Vitro and in vivo evaluation of β-cyclodextrin-based nanosponges of telmisartan. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2013, 77, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afinjuomo, F.; Barclay, T.G.; Song, Y.; Parikh, A.; Petrovsky, N.; Garg, S. Synthesis and characterization of a novel inulin hydrogel crosslinked with pyromellitic dianhydride. React. Funct. Polym. 2019, 134, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, B.; Caponi, S.; Castiglione, F.; Corezzi, S.; Fontana, A.; Giarola, M.; Mariotto, G.; Mele, A.; Petrillo, C.; Trotta, F.; et al. Networking Properties of Cyclodextrin-Based Cross-Linked Polymers Probed by Inelastic Light-Scattering Experiments. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 5323–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, S.; Shende, P.; Trotta, F. Diversity of β -cyclodextrin-based nanosponges for transformation of actives. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 565, 333–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shende, P.; Kulkarni, Y.A.; Gaud, R.S.; Deshmukh, K.; Cavalli, R.; Trotta, F.; Caldera, F. Acute and repeated dose toxicity studies of different β-cyclodextrin-based nanosponge formulations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 1856–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pushpalatha, R.; Selvamuthukumar, S.; Kilimozhi, D. Cyclodextrin nanosponge based hydrogel for the transdermal co-delivery of curcumin and resveratrol: Development, optimization, in vitro and ex vivo evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shende, P.K.; Trotta, F.; Gaud, R.S.; Deshmukh, K.; Cavalli, R.; Biasizzo, M. Influence of different techniques on formulation and comparative characterization of inclusion complexes of ASA with β-cyclodextrin and inclusion complexes of ASA with PMDA cross-linked β-cyclodextrin nanosponges. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2012, 74, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiancich, C.; Scutera, S.; Alotto, D.; Cambieri, I.; Fumagalli, M.; Casarin, S.; Rossi, S.; Trotta, F.; Stella, M.; Cavalli, R.; et al. Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges as a Nanotechnology Strategy for Imiquimod Delivery in Pathological Scarring Prevention and Treatment. J. Nanopharm. Drug Deliv. 2015, 2, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, E.M. Pharmaceutical Applications of Cyclodextrins. 1. Drug Solubilization and Stabilization. J. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 85, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibby, D.C.; Davies, N.M.; Tucker, I.G. Mechanisms by which cyclodextrins modify drug release from polymeric drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 197, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayiyana, Z.; Choonara, Y.; Makgotloe, A.; Toit, L.; Kumar, P.; Pillay, V. Ester-Based Hydrophilic Cyclodextrin Nanosponges for Topical Ocular Drug Delivery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 22, 6988–6997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crupi, V.; Fontana, A.; Giarola, M.; Majolino, D.; Mariotto, G.; Mele, A.; Melone, L.; Punta, C.; Rossi, B.; Venuti, V. Connection between the vibrational dynamics and the cross-linking properties in cyclodextrins-based polymers. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2013, 44, 1457–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesar Hernandez-Ortiz, J.; Vivaldo-lima, E. Crosslinking. In Handbook of Polymer Synthesis, Characterization and Processing, 1st ed.; Saldivar-Guerra, E., Vivaldo-Lima, E., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 187–204. [Google Scholar]
- Akalp, U.; Chu, S.; Skaalure, S.C.; Bryant, S.J.; Doostan, A.; Vernerey, F.J. Determination of the polymer-solvent interaction parameter for PEG hydrogels in water: Application of a self learning algorithm. Polymer 2015, 66, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krabicová, I.; Appleton, S.L.; Tannous, M.; Hoti, G.; Caldera, F.; Pedrazzo, A.R.; Cecone, C.; Cavalli, R.; Trotta, F. History of cyclodextrin nanosponges. Polymers 2020, 12, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ma, M. Nanosponges for water purification. Clean Prod. Process. 2000, 2, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecone, C.; Hoti, G.; Krabicova, I.; Appleton, S.L.; Caldera, F.; Bracco, P.; Zanetti, M.; Trotta, F. Sustainable synthesis of cyclodextrin-based polymers exploiting natural deep eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 5806–5814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrazzo, A.R.; Caldera, F.; Zanetti, M.; Appleton, S.L.; Dahkar, N.K.; Trotta, F. Mechanochemical green synthesis of hyper-crosslinked cyclodextrin polymers. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, A.; Castiglione, F.; Malpezzi, L.; Ganazzoli, F.; Raffaini, G.; Trotta, F.; Rossi, B.; Fontana, A.; Giunchi, G. HR MAS NMR, powder XRD and Raman spectroscopy study of inclusion phenomena in bCD nanosponges. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2011, 69, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglione, F.; Crupi, V.; Majolino, D.; Mele, A.; Rossi, B.; Trotta, F.; Venuti, V. Effect of Cross-Linking Properties on the Vibrational Dynamics of Cyclodextrins-Based Polymers: An Experimental–Numerical Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 7952–7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, B.; Paciaroni, A.; Venuti, V.; Fadda, G.C.; Melone, L.; Punta, C.; Crupi, V.; Majolino, D.; Mele, A. SANS investigation of water adsorption in tunable cyclodextrin-based polymeric hydrogels. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 6022–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanetti, M.; Anceschi, A.; Magnacca, G.; Spezzati, G.; Caldera, F.; Rosi, G.P.; Trotta, F. Micro porous carbon spheres from cyclodextrin nanosponges. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 235, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, F.; Tumiatti, W.; Vallero, R. Nanospugne a Base di Ciclodestrine Funzionalizzate con Gruppi Carbossilici: Sintesi e Utilizzo Nella Decontaminazione da Metalli Pesanti e da Composti Organici, Separazioni Cromatografiche e Veicolazione di Farmaci. Italian Patent No. MI2004A000614, 30 March 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, R.S.H.; Ashton, M.; Dodou, K. Effect of crosslinking agent concentration on the properties of unmedicated hydrogels. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, H.P.; Holden, H.W.; Barna, G. Rapid determination of crosslink densities and interaction parameters from swelling rate data. J. Polym. Sci., Part. C 1970, 30, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witono, J.R.; Noordergraaf, I.; Heeres, H.J.; Janssen, L.P.B.M.; Heeres, H. Water absorption, retention and the swelling characteristics of cassava starch grafted with polyacrylic acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Yuk, K.Y.; Huh, K.M. Polysaccharide-based superporous hydrogels with fast swelling and superabsorbent properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuburger, N.A.; Eichinger, B.E. Critical Experimental Test of the Flory-Rehner Theory of Swelling. Macromolecules 1988, 21, 3060–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Huang, Y.; Torres-Lugo, M.; Ward, J.H.; Zhang, J. Physicochemical Foundations and Structural Design of Hydrogels in Medicine and Biology. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 2, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flory, P.J. Principles of Polymer Chemistry; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1953; ISBN 0801401348. [Google Scholar]
- Chassé, W.; Lang, M.; Sommer, J.-U.; Saalwächter, K. Cross-Link Density Estimation of PDMS Networks with Precise Consideration of Networks Defects. Macromolecules 2011, 45, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Patchan, M.; Maranchi, J.; Elisseeff, J.; Trexler, M. Determination of Crosslinking Density of Hydrogels Prepared from Microcrystalline Cellulose. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 4537–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedo, C.; Caldera, F.; Poli, T.; Chiantore, O. Poly(vinylalcohol)-borate hydrogels with improved features for the cleaning of cultural heritage surfaces. Herit. Sci. 2015, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossard, F.; Aubry, T.; Gotzamanis, G.; Tsitsilianis, C. pH-Tunable rheological properties of a telechelic cationic polyelectrolyte reversible hydrogel. R. Soc. Chem. 2006, 2, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durairaj, R.; Wai Man, L.; Ekere, N.N.; Mallik, S. The effect of wall-slip formation on the rheological behaviour of lead-free solder pastes. Mater. Design 2010, 31, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, A.; Kirichek, A.; Chassagne, C. Effect of pre-shearing on the steady and dynamic rheological properties of mud sediments. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 116, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulicke, W.-M.; Aggour, Y.A.; Nottelmann, H.; Elsabee, M.Z. Swelling and Rheological Studies of Some Starch Hydrogels. Starch-Stärke 1989, 41, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-Y.; Yuan, L.-L. Advanced Polyimide Films. In Advanced Polyimide Materials, Synthesis, Characterization and Application; Elsevier, Inc.: London, UK, 2018; pp. 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Tokita, M. Structure and Frictional Properties of Colloid Gel. Polymers 2014, 6, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, Y.; Tokita, M. Real Space Structure of Opaque Gel. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 21, 5285–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, G.; Kijowska, K.; Witczak, M.; Kuterasiński, Ł.; Łukasiewicz, M. Synthesis and Effect of Structure on Swelling Properties of Hydrogels Based on High Methylated Pectin and Acrylic Polymers. Polymers 2019, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, V.K.; Kent, S.B.H.; Merrifield, R.B. Properties of Swollen Polymer Networks. Solvation and Swelling of Peptide-Containing Resins in Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 5463–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flory, P.J.; Rehner, J. Statistical Mechanics of Cross-Linked Polymer Networks II. Swelling. J. Chem. Phys. 1943, 11, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pó, R. Water-Absorbent Polymers: A Patent Survey. J. Macromol. Sci. 1994, 34, 607–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vlierberghe, S.; Graulus, G.; Samal, S.K.; Van Nieuwenhove, I.; Dubruel, P. Porous Hydrogel Biomedical foam Scaffolds for Tissue Repair; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 335–390. ISBN 9780857097033. [Google Scholar]
- Flory, P.J.; Rehner, J. Statistical Theory of Chain Configuration and Physical Properties of High Polymers. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 1943, 44, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentín, J.L.; Carretero-González, J.; Mora-Barrantes, I.; Chassé, W.; Saalwächter, K. Uncertainties in the determination of cross-link density by equilibrium swelling experiments in natural rubber. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 4717–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Pérez, M.; Maroto-Centeno, J.A.; Forcada, J.; Hidalgo-Alvarez, R. Gel swelling theories: The classical formalism and recent approaches. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 10536–10547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, E.; Kamphus, J.; Huyghe, J.M. The Importance of the Mixing Energy in Ionized Superabsorbent Polymer Swelling Models. Polymers 2020, 12, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urich, M.; Denton, A.R. Swelling, structure, and phase stability of compressible microgels. R. Soc. Chem. 2016, 12, 9086–9094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, E.; Huyghe, J.M. Chemically Responsive Hydrogel Deformation Mechanics: A Review. Molecules 2019, 24, 3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camponeschi, F.; Atrei, A.; Rocchigiani, G.; Mencuccini, L.; Uva, M.; Barbucci, R. New Formulations of Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels for Drug Release and Tissue Engineering. Gels 2015, 1, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqui, D.; De Cagna, M.; Barbucci, R. Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels: The Key Role of Water in Affecting Mechanical Properties. Polymers 2012, 4, 1517–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajighasem, A.; Kabiri, K. Cationic highly alcohol-swellable gels: Synthesis and characterization. J. Polym. Res. 2013, 20, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillet, A.M.; Wyatt, N.B.; Gloe, L.M. Polymer Gel Rheology and Adhesion. In Rheology; De Vicente, J., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; p. 338. ISBN 9789535101871. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, J.; Moreira, S.; Maia, J.; Gama, F.M. Characterization of dextrin-based hydrogels: Rheology, biocompatibility, and degradation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 93, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romania, F.; Corrieri, R.; Bragab, V.; Ciardelli, F. Monitoring the chemical crosslinking of propylene polymers through rheology. Polymer 2002, 43, 1115–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurz, J. Rheology of synovial fluids and substitute polymers. J. Macromol. Sci. Pure Appl. Chem. 1996, 33, 1249–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinaels, R.; Reddy, N.K.; Clasen, C. Quantifying the errors due to overfilling for Newtonian fluids in rotational rheometry. Rheol. Acta 2019, 58, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, F.; Ishida, M. Elastically Effective Chains in Transient Gels with Multiple Junctions. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 7571–7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulicke, W.M.; Nottelmann, H. Structure and Swelling of Some Synthetic, Semisynthetic and Biopolymer Hydrogels. Polym. Aqueous Media; Glas. J. Adv. Chem. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 2, 15–44. [Google Scholar]
- Sombatsompop, N. Practical Use of the Mooney-Rilvin Equation for Determination of Degree of Cross-linking of Swollen NR Vulcanisates. J. Sci. Soc. Thail. 1998, 24, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, L.A. Molecular Interpretations of Modulus and Swelling Relations in Natural Rubber Cross-Linked by Dicumyl Peroxide. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 1979, 84, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.G.; Richtering, W. Does Flory-Rehner theory quantitatively describe the swelling of thermoresposnive microgels? R. Soc. Chem. 2017, 13, 8271–8280. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, J.C.; Merrill, E.W. Poly (vinyl Alcohol) Hydrogels. Formation by Electron Beam Irradiation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1973, 17, 3779–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
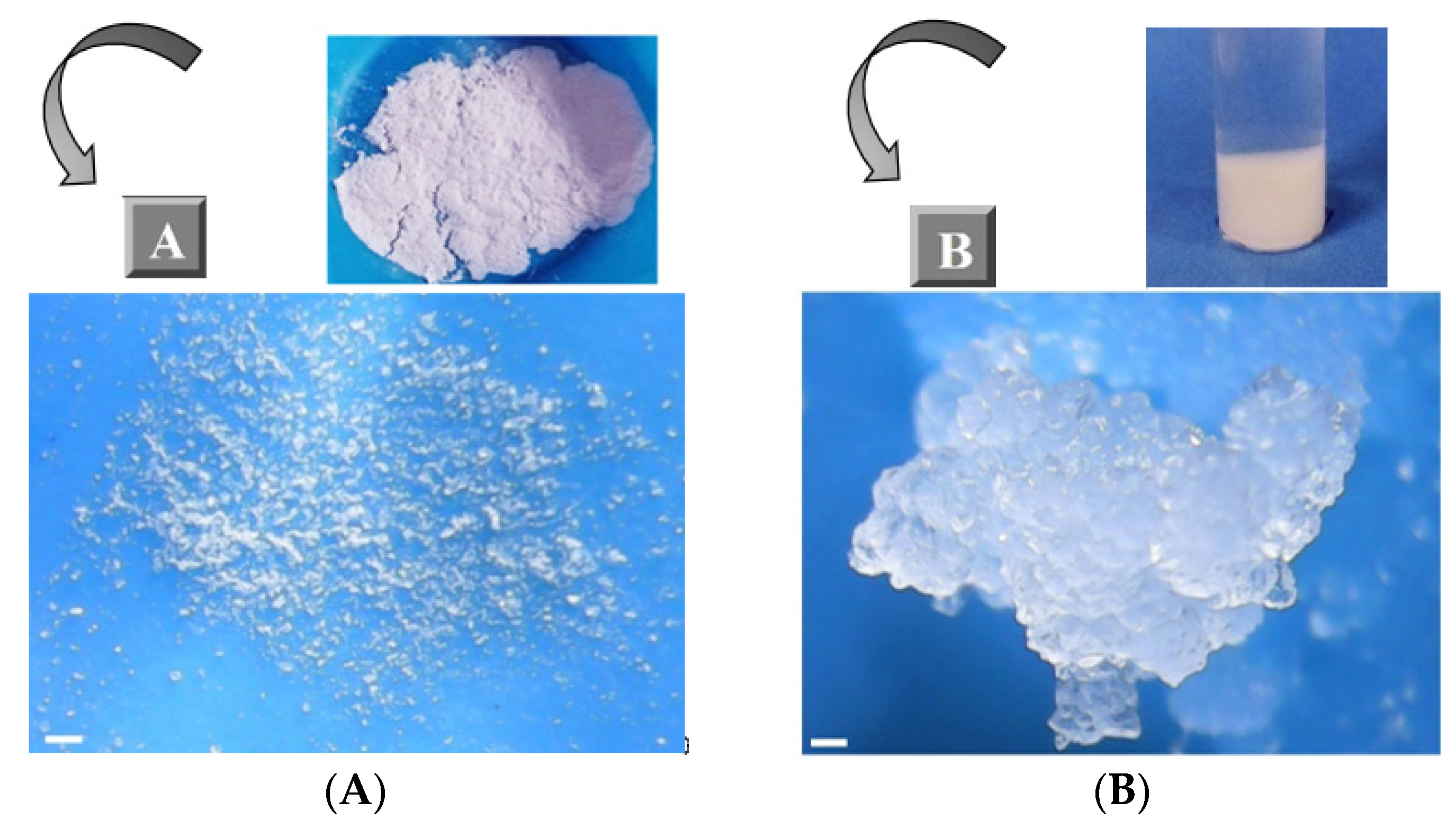

| Molar Ratios (β-CD:PMDA) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|
| 1:2 | 56% |
| 1:3 | 74% |
| 1:4 | >95% |
| 1:5 | >95% |
| 1:6 | >95% |
| 1:7 | >95% |
| 1:8 | >95% |
| 1:9 | >95% |
| 1:10 | 81% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoti, G.; Caldera, F.; Cecone, C.; Rubin Pedrazzo, A.; Anceschi, A.; Appleton, S.L.; Khazaei Monfared, Y.; Trotta, F. Effect of the Cross-Linking Density on the Swelling and Rheological Behavior of Ester-Bridged β-Cyclodextrin Nanosponges. Materials 2021, 14, 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14030478
Hoti G, Caldera F, Cecone C, Rubin Pedrazzo A, Anceschi A, Appleton SL, Khazaei Monfared Y, Trotta F. Effect of the Cross-Linking Density on the Swelling and Rheological Behavior of Ester-Bridged β-Cyclodextrin Nanosponges. Materials. 2021; 14(3):478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14030478
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoti, Gjylije, Fabrizio Caldera, Claudio Cecone, Alberto Rubin Pedrazzo, Anastasia Anceschi, Silvia Lucia Appleton, Yousef Khazaei Monfared, and Francesco Trotta. 2021. "Effect of the Cross-Linking Density on the Swelling and Rheological Behavior of Ester-Bridged β-Cyclodextrin Nanosponges" Materials 14, no. 3: 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14030478
APA StyleHoti, G., Caldera, F., Cecone, C., Rubin Pedrazzo, A., Anceschi, A., Appleton, S. L., Khazaei Monfared, Y., & Trotta, F. (2021). Effect of the Cross-Linking Density on the Swelling and Rheological Behavior of Ester-Bridged β-Cyclodextrin Nanosponges. Materials, 14(3), 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14030478