Co-Existence of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Manganese Oxide Nanorods as Decoration of Hollow Carbon Spheres for Boosting Electrochemical Performance of Li-Ion Battery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
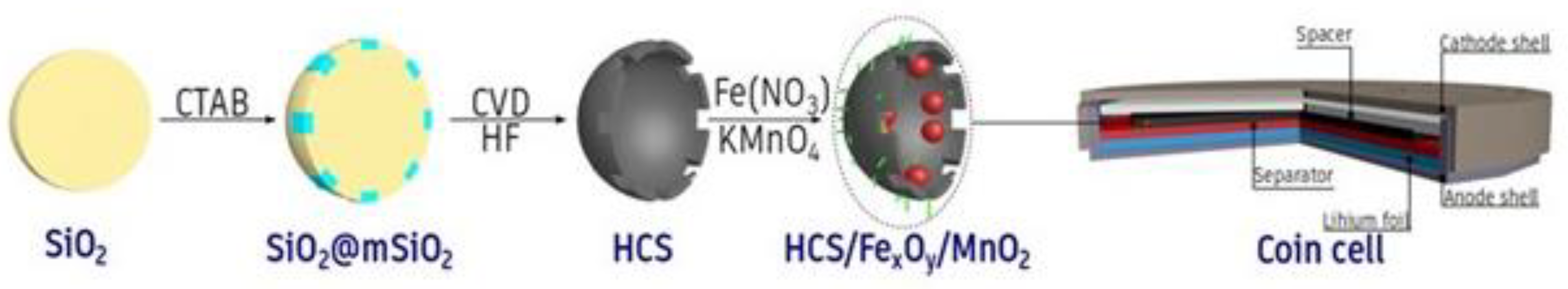
2. Experimental
2.1. Synthesis of Mesoporous Core/Shell Structured Silica Spheres (SiO2@mSiO2 Spheres)
2.2. Synthesis of Hollow Carbon Spheres (HCS)
2.3. Functionalization of HCS with Metal Oxides (FexOy/MnO2/HCS)
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Electrochemical Measurements
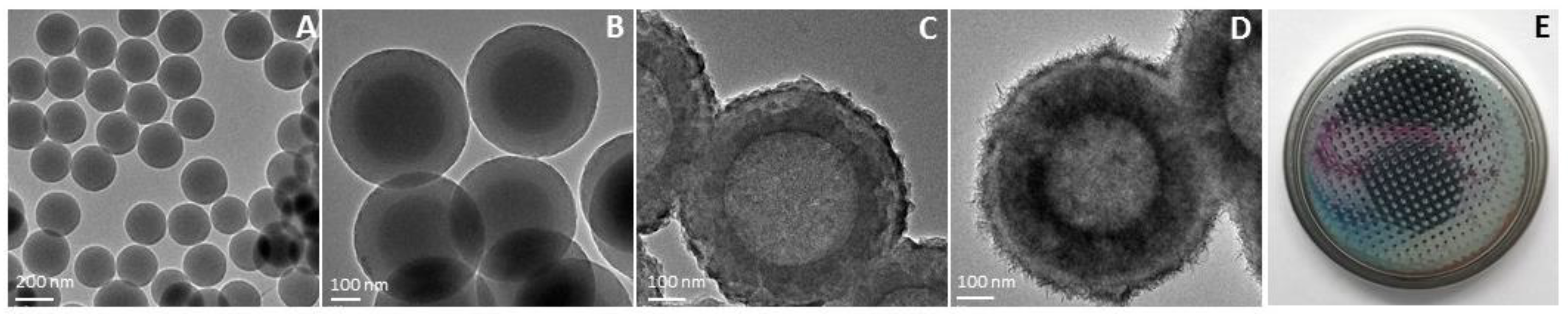
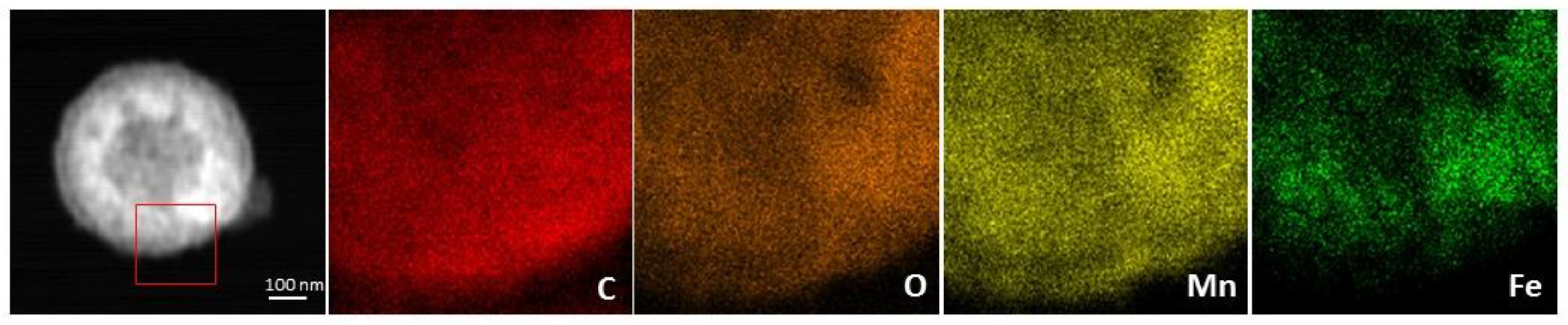
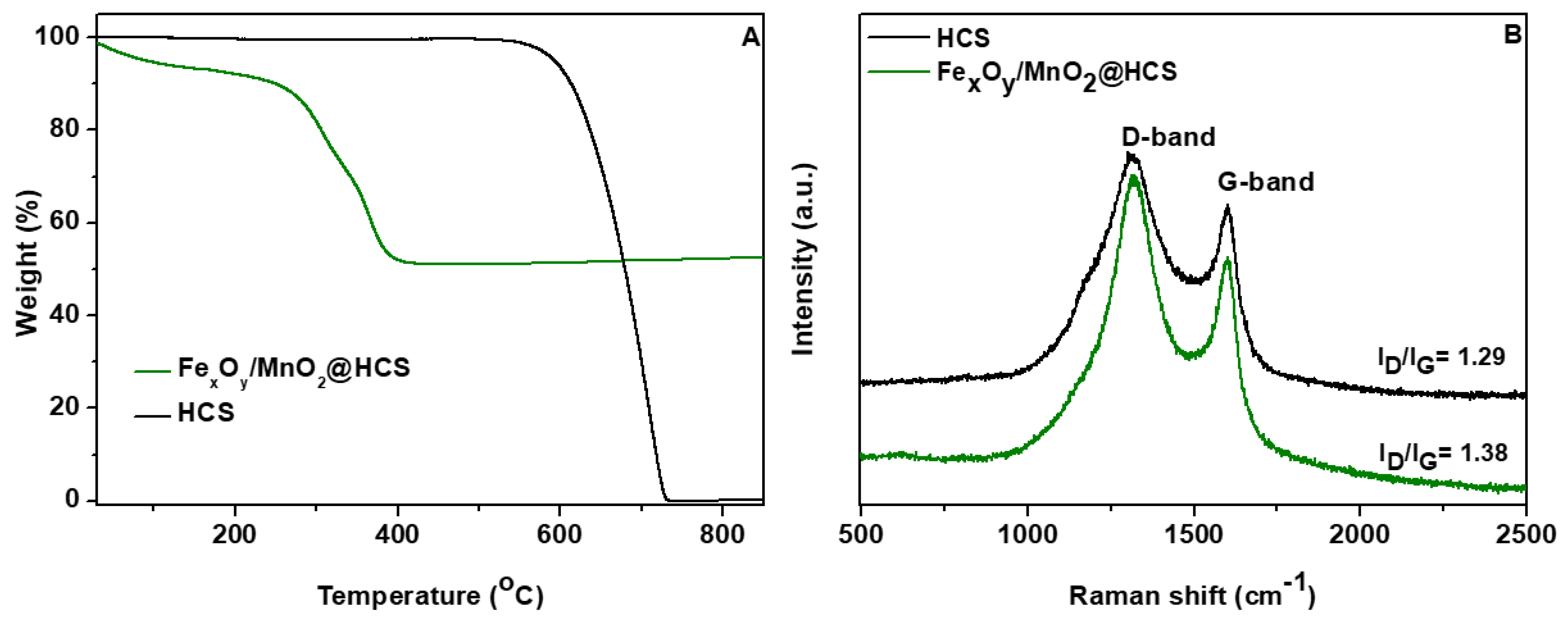
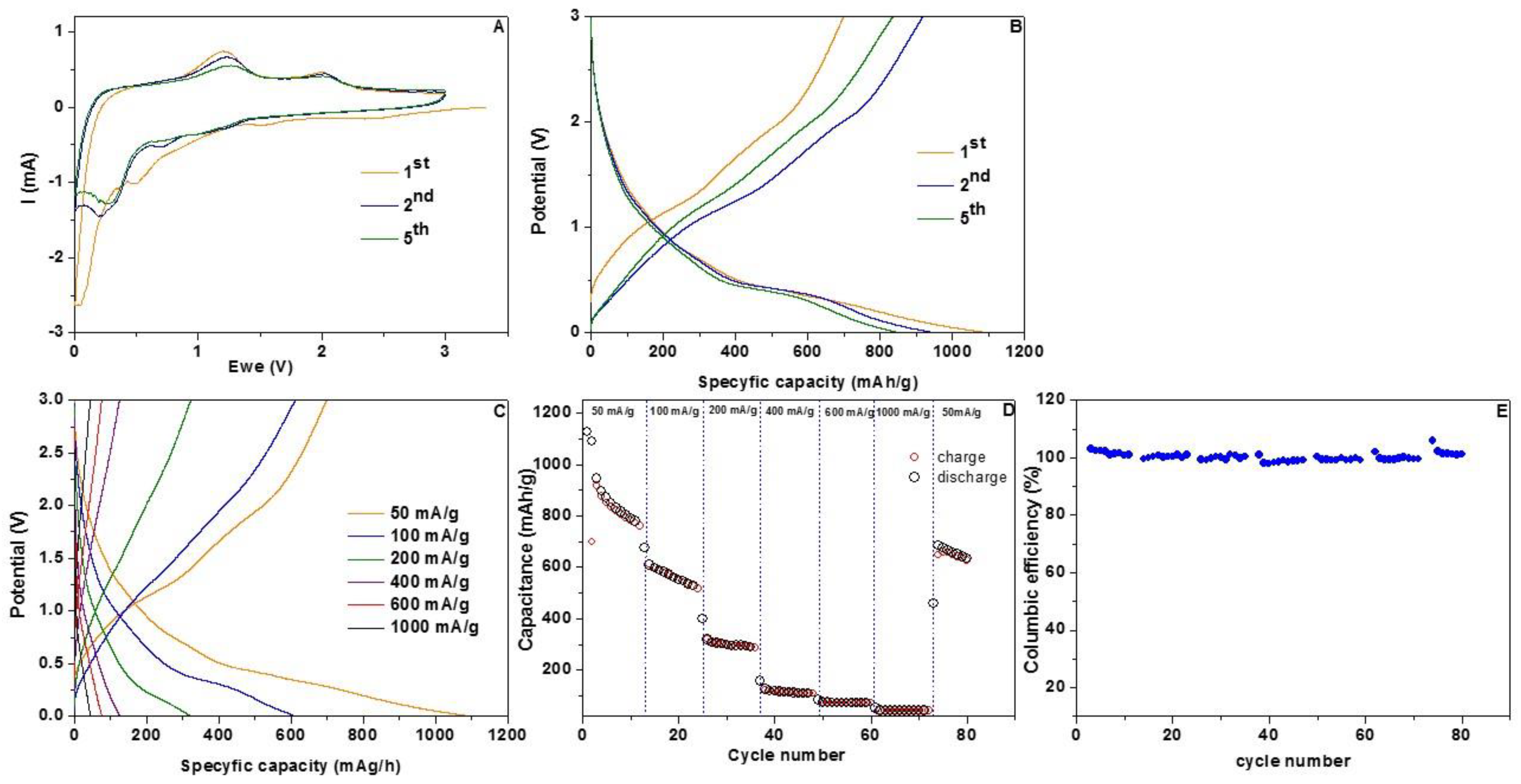
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amjad, S.; Rudramoorthy, R.; Neelakrishnan, S.; Varman, K.S.R.; Arjunan, T.; Shaik, A. Evaluation of energy requirements for all-electric range of plug-in hybrid electric two-wheeler. Energy 2011, 36, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, Z.; Lv, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, T.; Yang, T. Nano-sized Fe3O4/carbon as anode material for lithium ion battery. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 148, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Ceder, G. Battery materials for ultrafast charging and discharging. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 458, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, A.R.; Lyness, C.; Panchmatia, P.M.; Islam, M.S.; Bruce, P.G. The lithium intercalation process in the low-voltage lithium battery anode Li1+xV1−xO2. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaskhedikar, N.A.; Maier, J. Lithium Storage in Carbon Nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2664–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, X.; Ju, Z.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; Bai, Z.; Dou, S.; Yu, G. Thickness-independent scalable high-performance Li-S batteries with high areal sulfur loading via electron-enriched carbon framework. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Kong, L.; Li, Y.; Fu, H.; Sun, L.; Feng, Y.; Feng, W. Fluorinated graphene nanoribbons from unzipped single-walled carbon nanotubes for ultrahigh energy density lithium-fluorinated carbon batteries. Sci. China Mater. 2021, 64, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, I.A.; McKinnon, W.R.; Dahn, J.R. On the Aggregation of Tin in SnO Composite Glasses Caused by the Reversible Reaction with Lithium. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1999, 146, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, S.; Baudrin, E.; Touboul, M.; Tarascon, J.M. Synthesis and electrochemical properties vs. Li of amorphous/crystallized indium vanadates, Molecular crystals and liquid crystals science and technology. Sect. A Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1998, 311, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yao, K.; Zhang, G.; Gong, J.; Mijowska, E.; Kierzek, K.; Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Tang, T. Controllable Synthesis of 3D Hollow-Carbon-Spheres/Graphene-Flake Hybrid Nanostructures from Polymer Nanocomposite by Self-Assembly and Feasibility for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2015, 32, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.M.; Wu, X.L.; Hu, J.S.; Guo, Y.G.; Wan, L.J. Carbon Coated Fe3O4 Nanospindles as a Superior Anode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 3941–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kierzek, K.; Wilgosz, K.; Machnikowski, J.; Gong, J.; Feng, J.; Tang, T.; Kalenczuk, R.J.; Chen, H.; Chu, P.K.; et al. New easy way preparation of core/shell structured SnO2@carbon spheres and application for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2012, 216, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Huang, L.; Cai, J.S.; Zheng, X.M.; Sun, S.G. Structure and electrochemical performance of nanostructured Fe3O4/carbon nanotube composites as anodes for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 1140–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Ye, J.; Qian, H.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, M.; Dong, Q. Hollow carbon sphere with open pore encapsulated MnO2 nanosheets as high-performance anode materials for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 260, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poizot, P.; Laruelle, S.; Grugeon, S.; Dupont, L.; Tarascon, J.-M. Nano-sized transition-metal oxides as negative-electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 407, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Pharr, M.; Vlassak, J.J.; Suo, Z. Fracture of electrodes in lithium-ion batteries caused by fast charging. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 073517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etacheri, V.; Wang, C.; O’Connell, M.J.; Chan, C.K.; Pol, V.G. Porous carbon sphere anodes for enhanced lithium-ion storage. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 9861–9868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zou, Q.; Xia, Y. CoO-loaded graphitable carbon hollow spheres as anode materials for lithium-ion battery. J. Power Sources 2008, 177, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, J.H.; Yu, J.-S. Hierarchical Nanostructured Carbons with Meso-Macroporosity: Design, Characterization, and Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kierzek, K.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, H.; Tang, T.; Wojtoniszak, M.; Kalenczuk, R.J.; Chu, P.K.; Borowiak-Palen, E. Synthesis, Growth Mechanism, and Electrochemical Properties of Hollow Mesoporous Carbon Spheres with Controlled Diameter. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 17717–17724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalubarme, R.S.; Cho, M.-S.; Yun, K.-S.; Kim, T.-S.; Park, C.-J. Catalytic characteristics of MnO2 nanostructures for the O2 reduction process. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 395402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Karthikeyan, S.; Jayamoorthy, K. Effect of bulk and nano-Fe2O3 particles on peanutplant leaves studied by Fourier transform infraredspectral studies. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruíz-Baltazar, A.; Esparza, R.; Rosas, G.; Pérez, R. Effect of the Surfactant on the Growth and Oxidation of Iron Nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenelska, K.; Ottmann, A.; Schneider, P.; Thauer, E.; Klingeler, R.; Mijowska, E. Hollow carbon sphere/metal oxide nanocomposites anodes for lithium-ion batteries. Energy 2016, 103, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dresselhaus, M.; Jorio, A.; Saito, R. Characterizing Graphene, Graphite, and Carbon Nanotubes by Raman Spectroscopy. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 2010, 1, 89–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Zhou, J.; Xia, R.; Chu, Y.; Huang, J. Preparation of Advanced CuO Nanowires/Functionalized Graphene Composite Anode Material for Lithium Ion Batteries. Materials 2017, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, K.; Liu, H.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, L. FeMnO3: A high-performance Li-ion battery anode Material. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11414–11417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Wu, S.; Zhao, N.; Shi, C.; Liu, E.; Li, J. Carbon-Encapsulated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles as a High-Rate Lithium Ion Battery Anode Material. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 4459–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, D.-W.; Li, F.; Zhang, L.; Li, N.; Wu, Z.-S.; Wen, L.; Lu, G.Q.; Cheng, H.-M. Graphene-Wrapped Fe3O4 Anode Material with Improved Reversible Capacity and Cyclic Stability for Lithium Ion Batteries. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 5306–5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ng, K.Y.S.; Deng, D. Porous Olive-Like Carbon Decorated Fe3O4 Based Additive-Free Electrode for Highly Reversible Lithium Storage. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Huang, R.; Mu, D.; Wu, B.; Chen, S. New Synthesis of a Foamlike Fe3O4/C Composite via a Self-Expanding Process and Its Electrochemical Performance as Anode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 12, 19254–19264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Xu, L.; Yan, M.; Han, C.; He, L.; Hercule, K.M.; Niu, C.; Yuan, Z.; Xu, W.; Qu, L.; et al. Manganese Oxide/Carbon Yolk–Shell Nanorod Anodes for High Capacity Lithium Batteries. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.N.; Park, S.B.; Choi, S.H.; Kang, Y.C. One-pot synthesis of manganese oxide-carbon composite microspheres with three dimensional channels for Li-ion batteries. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, X.; Chen, L.; Ju, Z.; Xu, H.; Yang, J.; Qian, Y. Controlled Growth of Porous α-Fe2O3 Branches on β-MnO2 Nanorods for Excellent Performance in Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 4049–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Xu, S.; Fang, M.; Zhao, X.; Shang, Y. Electrochemical properties of MnO2 nanorods as anode materials for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 142, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhao, T. Freestanding graphene/MnO2 cathodes for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 201, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, Z.; Su, Y.; Ruan, H.; Hu, R.; Zhang, L. In Situ Synthesis of MnO2/Porous Graphitic Carbon Composites as High-Capacity Anode Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 392, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | SBET (m2/g) | VTOTAL (cm3/g) | Average Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HCS | 571 | 0.20 | 5.53 |
| FexOy/MnO2/HCS | 177 | 0.06 | 4.97 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wenelska, K.; Trukawka, M.; Kukulka, W.; Chen, X.; Mijowska, E. Co-Existence of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Manganese Oxide Nanorods as Decoration of Hollow Carbon Spheres for Boosting Electrochemical Performance of Li-Ion Battery. Materials 2021, 14, 6902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226902
Wenelska K, Trukawka M, Kukulka W, Chen X, Mijowska E. Co-Existence of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Manganese Oxide Nanorods as Decoration of Hollow Carbon Spheres for Boosting Electrochemical Performance of Li-Ion Battery. Materials. 2021; 14(22):6902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226902
Chicago/Turabian StyleWenelska, Karolina, Martyna Trukawka, Wojciech Kukulka, Xuecheng Chen, and Ewa Mijowska. 2021. "Co-Existence of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Manganese Oxide Nanorods as Decoration of Hollow Carbon Spheres for Boosting Electrochemical Performance of Li-Ion Battery" Materials 14, no. 22: 6902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226902
APA StyleWenelska, K., Trukawka, M., Kukulka, W., Chen, X., & Mijowska, E. (2021). Co-Existence of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Manganese Oxide Nanorods as Decoration of Hollow Carbon Spheres for Boosting Electrochemical Performance of Li-Ion Battery. Materials, 14(22), 6902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226902







