Assessment of the Effect of Structural Modification of Ibuprofen on the Penetration of Ibuprofen from Pentravan® (Semisolid) Formulation Using Human Skin and a Transdermal Diffusion Test Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Ibuprofen and Its Derivatives
2.3. Production of Pharmaceutical Creams
2.4. In Vitro Penetration Studies through Human Skin and a Transdermal Diffusion Test Model
2.5. In Vitro Membranes Accumulation
2.6. HPLC Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
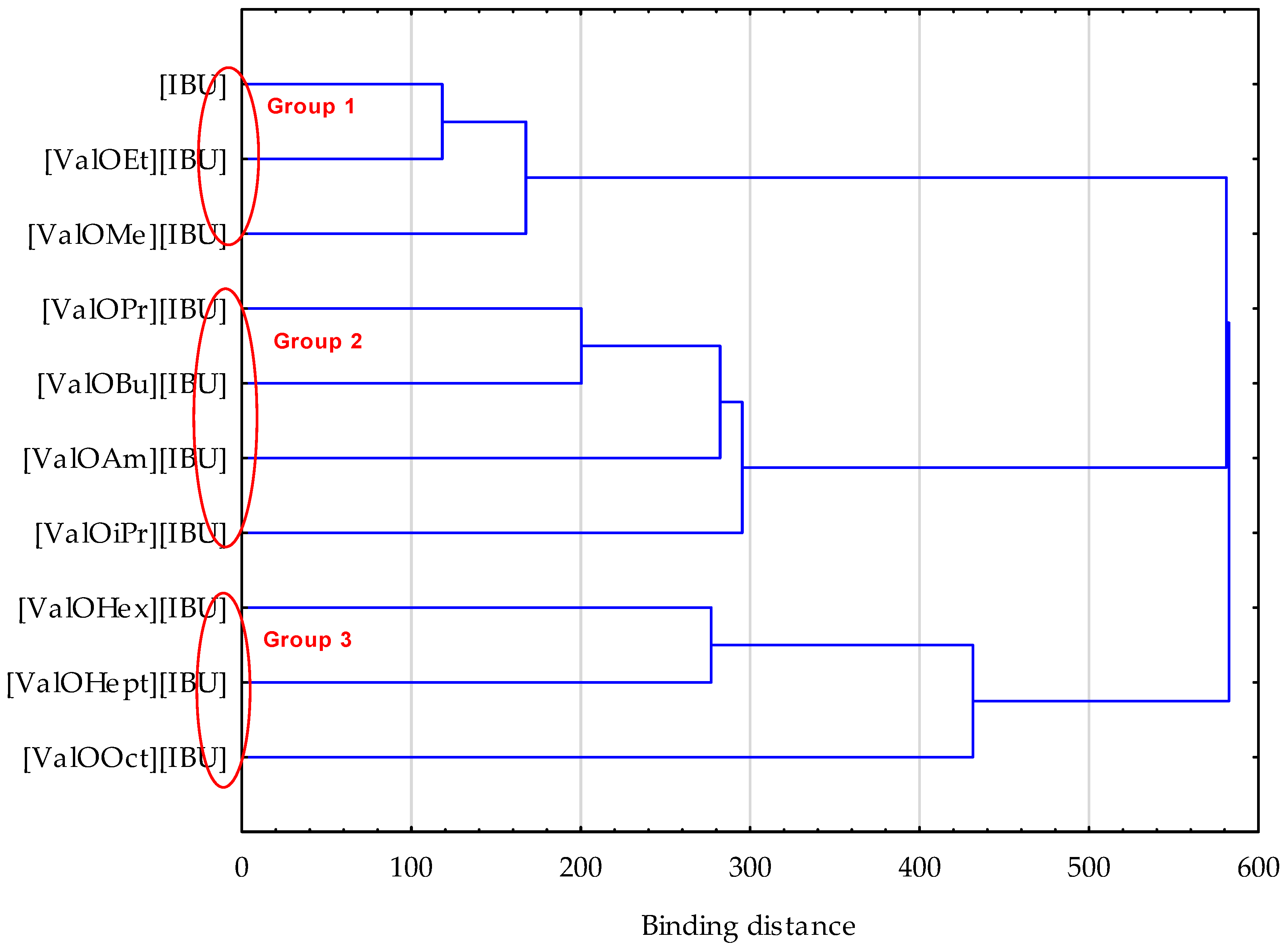
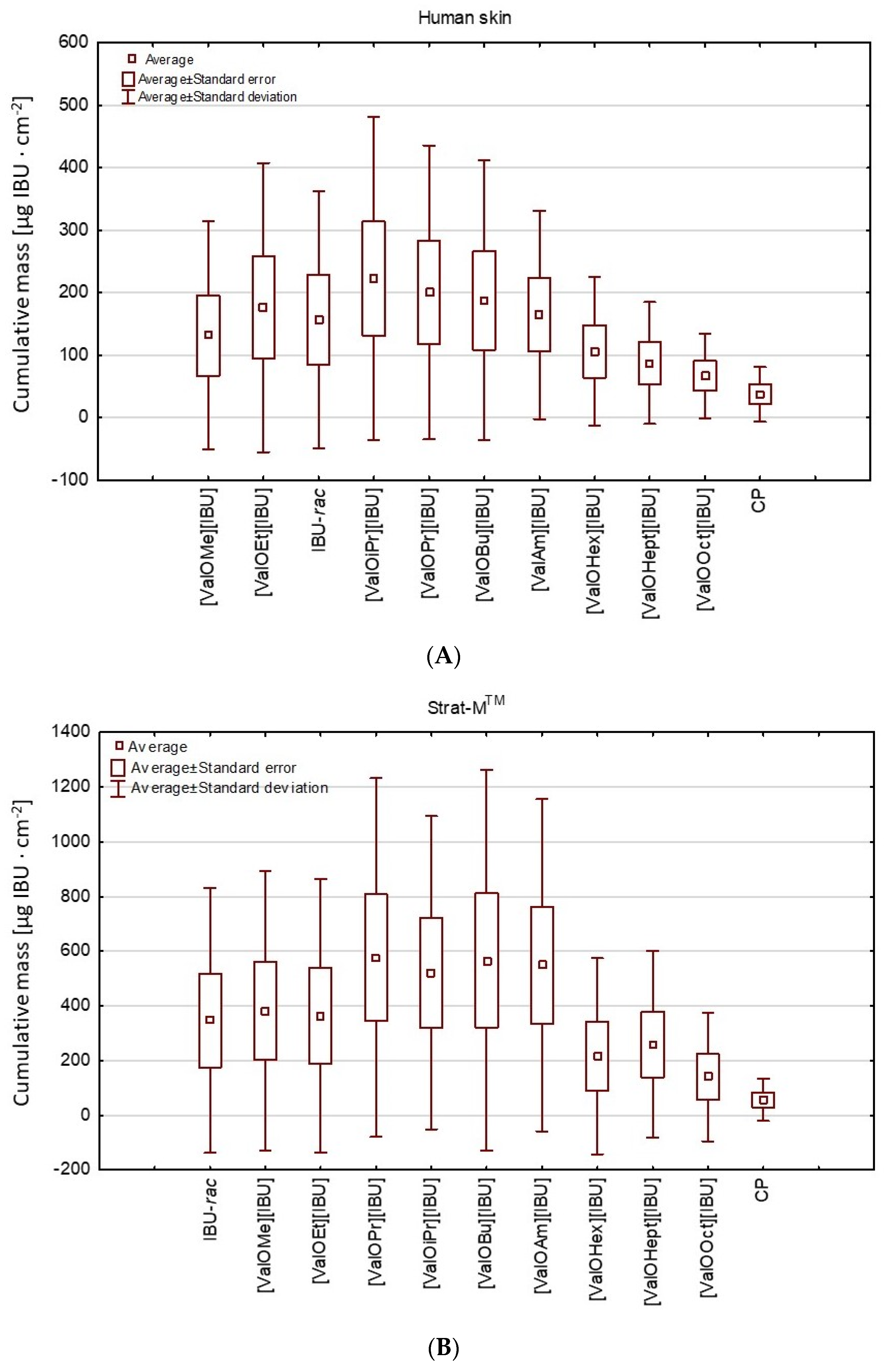
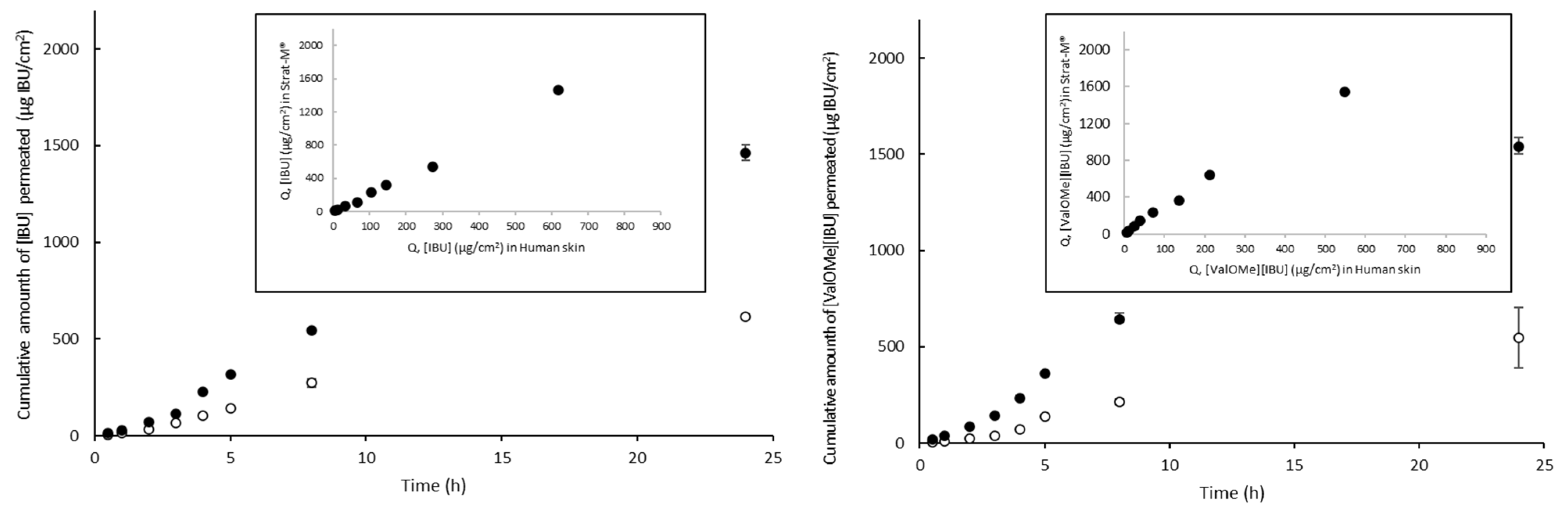
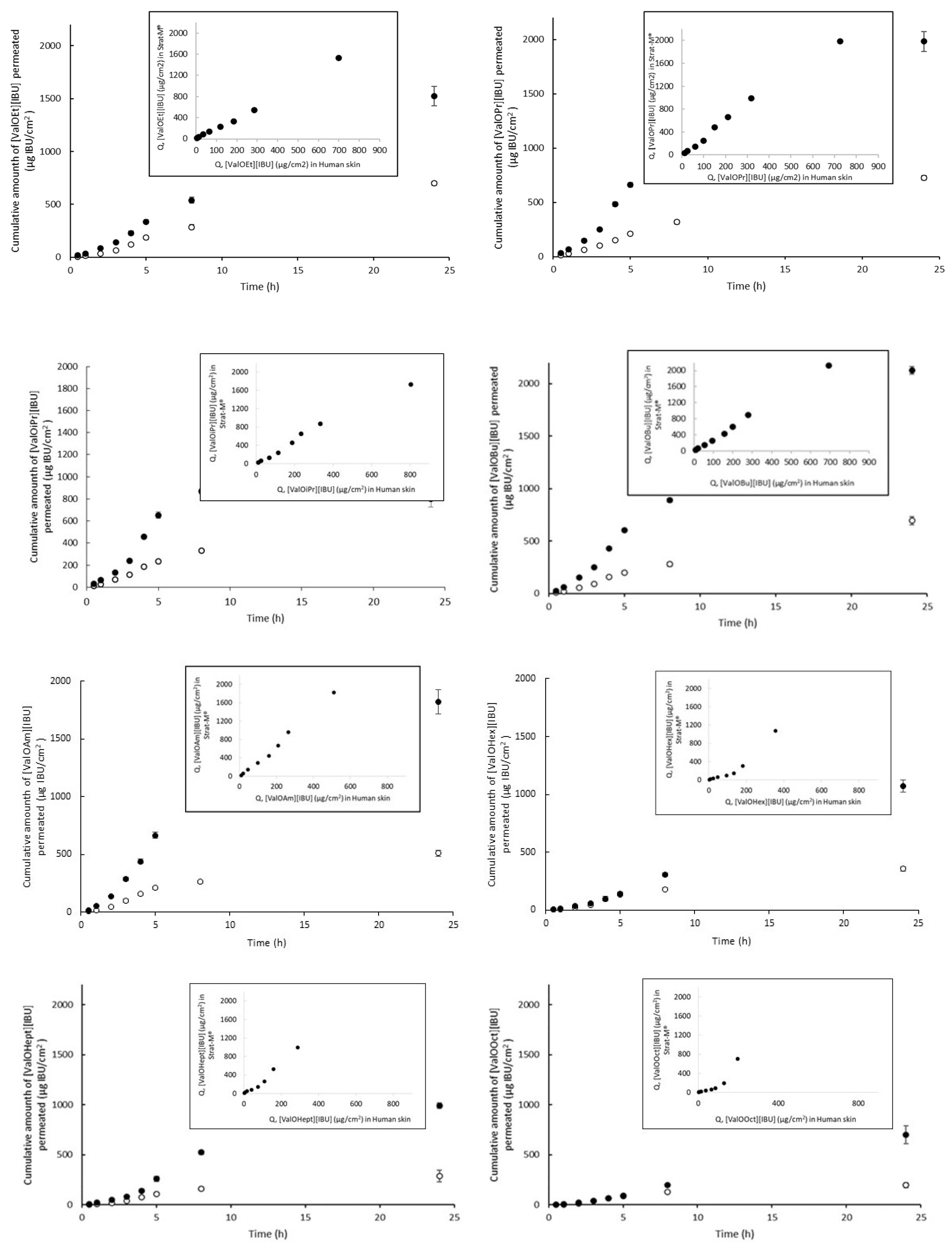
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolla, P.K.; Clark, B.A.; Juluri, A.; Cheruvu, H.S.; Renukuntla, J. Evaluation of Formulation Parameters on Permeation of Ibuprofen from Topical Formulations Using Strat-M® Membrane. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Janus, E.; Ossowicz, P.; Klebeko, J.; Nowak, A.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, Ł.; Klimowicz, A. Enhancement of Ibuprofen Solubility and Skin Permeation by Conjugation with l-Valine Alkyl Esters. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 7570–7584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawana, M.; Miyamoto, M.; Ohno, Y.; Kihara, A. Comparative Profiling and Comprehensive Quantification of Stratum Corneum Ceramides in Humans and Mice by LC/MS/MS. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Quan, P.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Fang, L. Novel Chemical Permeation Enhancers for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pham, Q.D.; Björklund, S.; Engblom, J.; Topgaard, D.; Sparr, E. Chemical Penetration Enhancers in Stratum Corneum—Relation between Molecular Effects and Barrier Function. J. Control. Release 2016, 232, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolla, P.K.; Meraz, C.A.; Rodriguez, V.A.; Deaguero, I.; Singh, M.; Yellepeddi, V.K.; Renukuntla, J. Clotrimazole Loaded Ufosomes for Topical Delivery: Formulation Development and In-Vitro Studies. Molecules 2019, 24, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrer, V.; Alonso, C.; Pont, M.; Zanuy, M.; Córdoba, M.; Espinosa, S.; Barba, C.; Oliver, M.A.; Martí, M.; Coderch, L. Effect of Propylene Glycol on the Skin Penetration of Drugs. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2020, 312, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, D.W.; Musakhanian, J. Skin Penetration and Permeation Properties of Transcutol®—Neat or Diluted Mixtures. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 3512–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitzanti, G.; Rosa, A.; Nieddu, M.; Valenti, D.; Pireddu, R.; Lai, F.; Cardia, M.C.; Fadda, A.M.; Sinico, C. Transcutol® P Containing SLNs for Improving 8-Methoxypsoralen Skin Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopečná, M.; Macháček, M.; Nováčková, A.; Paraskevopoulos, G.; Roh, J.; Vávrová, K. Esters of Terpene Alcohols as Highly Potent, Reversible, and Low Toxic Skin Penetration Enhancers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aqil, M.; Ahad, A.; Sultana, Y.; Ali, A. Status of Terpenes as Skin Penetration Enhancers. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapra, B.; Jain, S.; Tiwary, A.K. Percutaneous Permeation Enhancement by Terpenes: Mechanistic View. AAPS J. 2008, 10, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haq, A.; Michniak-Kohn, B. Effects of Solvents and Penetration Enhancers on Transdermal Delivery of Thymoquinone: Permeability and Skin Deposition Study. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1943–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luzuriaga, M.A.; Berry, D.R.; Reagan, J.C.; Smaldone, R.A.; Gassensmith, J.J. Biodegradable 3D Printed Polymer Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Li, W.; Zhou, X.; Yang, F.; Qian, Z. Microneedles-Based Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems: A Review. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 13, 1581–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.-H.; Lee, J.; Son, D.U.; Kang, D.H.; Park, M.J.; Cho, K.W.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.-H.; Ko, J.; Jang, M.-H.; et al. Facilitated Transdermal Drug Delivery Using Nanocarriers-Embedded Electroconductive Hydrogel Coupled with Reverse Electrodialysis-Driven Iontophoresis. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 4523–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Song, W.; Liu, J. Influencing Factors and Drug Application of Iontophoresis in Transdermal Drug Delivery: An Overview of Recent Progress. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, H.; Lim, G.-S.; Kim, N.; Kim, D.; Kim, Y.-C. Enhanced Transdermal Drug Delivery by Sonophoresis and Simultaneous Application of Sonophoresis and Iontophoresis. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegre-Sánchez, A.; Jiménez-Gómez, N.; Boixeda, P. Laser-Assisted Drug Delivery. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas Engl. Ed. 2018, 109, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossowicz, P.; Klebeko, J.; Janus, E.; Nowak, A.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, Ł.; Klimowicz, A. The Effect of Alcohols as Vehicles on the Percutaneous Absorption and Skin Retention of Ibuprofen Modified with l-Valine Alkyl Esters. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 41727–41740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdon, F.; Lecoeur, M.; Leconte, L.; Ultré, V.; Kouach, M.; Odou, P.; Vaccher, C.; Foulon, C. Evaluation of Pentravan ®, Pentravan ® Plus, Phytobase ®, Lipovan ® and Pluronic Lecithin Organogel for the Transdermal Administration of Antiemetic Drugs to Treat Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting at the Hospital. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, S.; Hattori, G.; Sakai, S.; Kamiya, N. Highly Efficient and Low Toxic Skin Penetrants Composed of Amino Acid Ionic Liquids. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 87753–87755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarveiya, V.; Templeton, J.F.; Benson, H.A.E. Ion-Pairs of Ibuprofen: Increased Membrane Diffusion. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 56, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polonini, H.C.; Soldati, P.P.; Oliveira, M.A.L.d.; Brandão, M.A.F.; Chaves, M.d.G.M.; Raposo, N.R.B. Transdermal formulations containing human sexual steroids: Development and validation of methods and in vitro drug release. Quím. Nova 2014, 37, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntsche, J.; Bunjes, H.; Fahr, A.; Pappinen, S.; Rönkkö, S.; Suhonen, M.; Urtti, A. Interaction of Lipid Nanoparticles with Human Epidermis and an Organotypic Cell Culture Model. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 354, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, C. Treatment of Refractory Endometriosis-Related Pain with Vaginal Gestrinone in Pentravan Associated with Pinus Pinaster Extract and Resveratrol: A Preliminary Study. Gynecol. Obstet. 2014, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hadgraft, J.; Whitefield, M.; Rosher, P.H. Skin Penetration of Topical Formulations of Ibuprofen 5%: An in Vitro Comparative Study. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2003, 16, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, M.M.; Kuntsche, J.; Fahr, A. Skin Penetration Enhancement by a Microneedle Device (Dermaroller®) in Vitro: Dependency on Needle Size and Applied Formulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 36, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.J.; Ward, R.J.; Heylings, J.R. Multi-Species Assessment of Electrical Resistance as a Skin Integrity Marker for in Vitro Percutaneous Absorption Studies. Toxicol. In Vitro 2004, 18, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klebeko, J.; Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P.; Nowak, A.; Janus, E.; Duchnik, W.; Adamiak-Giera, U.; Kucharski, Ł.; Prowans, P.; Petriczko, J.; Czapla, N.; et al. Permeability of Ibuprofen in the Form of Free Acid and Salts of l-Valine Alkyl Esters from a Hydrogel Formulation through Strat-MTM Membrane and Human Skin. Materials 2021, 14, 6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonini, H.C.; Soldati, P.P.; de Almeida, P.A.; da Silva, C.G.A.; Collins, C.H.; de Oliveira, M.A.L.; de Oliveira Ferreira, A.; Raposo, N.R.B.; Brandão, M.A.F. Permeation Profiles of Resveratrol Cream Delivered through Porcine Vaginal Mucosa: Evaluation of Different HPLC Stationary Phases. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 1002, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenkers, B.P.; Lippold, B.C. Skin Penetration of Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs out of a Lipophilic Vehicle: Influence of the Viable Epidermis. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 88, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chang, X.; Du, D.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Yang, X. Microemulsion-Based Hydrogel Formulation of Ibuprofen for Topical Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 315, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intarakumhaeng, R.; Li, S.K. Effects of Solvent on Percutaneous Absorption of Nonvolatile Lipophilic Solute. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 476, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, A.; Goodyear, B.; Ameen, D.; Joshi, V.; Michniak-Kohn, B. Strat-M® Synthetic Membrane: Permeability Comparison to Human Cadaver Skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 547, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, T.; Kadhum, W.R.; Kanai, S.; Todo, H.; Oshizaka, T.; Sugibayashi, K. Prediction of Skin Permeation by Chemical Compounds Using the Artificial Membrane, Strat-MTM. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 67, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon, A.; Amaro, M.I.; Healy, A.M.; Cabral, L.M.; de Sousa, V.P. Comparative Evaluation of Rivastigmine Permeation from a Transdermal System in the Franz Cell Using Synthetic Membranes and Pig Ear Skin with in Vivo-in Vitro Correlation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 512, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, L.; Singh, K.; Paul, S.; Singh, S.; Singh, S.; Jain, S.K. A Mechanistic Study to Determine the Structural Similarities Between Artificial Membrane Strat-MTM and Biological Membranes and Its Application to Carry Out Skin Permeation Study of Amphotericin B Nanoformulations. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 1606–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadzovska, D.; Riviere, J.E. Assessing Vehicle Effects on Skin Absorption Using Artificial Membrane Assays. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, F.J.; Asano, N.; See, G.L.; Itakura, S.; Todo, H.; Sugibayashi, K. Usefulness of Artificial Membrane, Strat-M®, in the Assessment of Drug Permeation from Complex Vehicles in Finite Dose Conditions. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atta-ur-Rahman, W.; Caldwell, G.; Iqbal Choudhary, M.; Yan, Z. (Eds.) Frontiers in Drug Design & Discovery; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2012; Volume 4, ISBN 978-1-60805-202-8. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, H. Transdermal Drug Delivery: Penetration Enhancement Techniques. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, D.I.J.; McCarron, P.A.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Innovative Strategies for Enhancing Topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery. Open Drug Deliv. J. 2007, 1, 36–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Compound | Acronym | Structural Formula | Molar Weight [g∙mol−1] | Solubility in Water | log P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [IBU] | 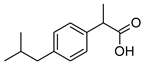 | 206.28 | 0.076 ± 0.001 [2] | 2.415 ± 0.001 [2] |
| 2 | [ValOMe][IBU] | 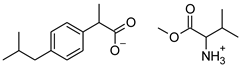 | 337.45 | 3.833 ± 0.005 [20] | 0.840 ± 0.006 |
| 3 | [ValOEt][IBU] | 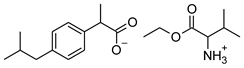 | 351.48 | 5.542 ± 0.007 [2] | 0.992 ± 0.00 [2] |
| 4 | [ValOiPr][IBU] |  | 365.51 | 3.468 ± 0.007 [2] | 1.249 ± 0.005 [2] |
| 5 | [ValOPr][IBU] | 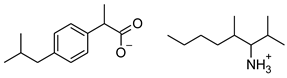 | 365.51 | 4.221 ± 0.033 [2] | 1.154 ± 0.004 [2] |
| 6 | [ValOBu][IBU] | 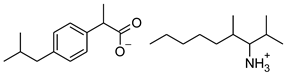 | 379.53 | 3.125 ± 0.007 [2] | 1.520 ± 0.004 [2] |
| 7 | [ValOAm][IBU] | 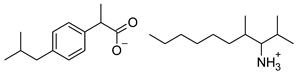 | 393.56 | 1.798 ± 0.019 [2] | 1.750 ± 0.003 [2] |
| 8 | [ValOHex][IBU] | 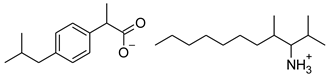 | 407.59 | 1.058 ± 0.002 [2] | 1.750 ± 0.003 [2] |
| 9 | [ValOHept][IBU] | 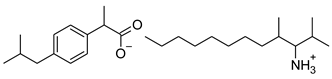 | 421.61 | 0.533 ± 0.001 [20] | 2.003 ± 0.001 |
| 10 | [ValOOct][IBU] | 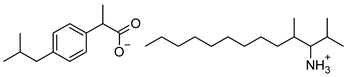 | 435.64 | 0.300 ± 0.004 [20] | 2.117 ± 0.004 |
| Compound | The Molar Mass of the Compound, g∙mol−1 | Pharmaceutical Vehicle, g | Compound, g | Ethanol, g | TOTAL, g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [IBU] | 206.284 | 0.8501 | 0.0500 | 0.1000 | 1.0001 |
| [ValOMe][IBU] | 337.458 | 0.8502 | 0.0820 | 0.1000 | 1.0322 |
| [ValOEt][IBU] | 351.485 | 0.8500 | 0.0857 | 0.1000 | 1.0357 |
| [ValOiPr][IBU] | 365.512 | 0.8504 | 0.0890 | 0.1000 | 1.0394 |
| [ValOPr][IBU] | 365.512 | 0.8500 | 0.0896 | 0.1000 | 1.0396 |
| [ValOBu][IBU] | 379.539 | 0.8501 | 0.0920 | 0.1000 | 1.0421 |
| [ValOAm][IBU] | 393.565 | 0.8502 | 0.0954 | 0.1000 | 1.0456 |
| [ValOHex][IBU] | 405.576 | 0.8500 | 0.0982 | 0.1000 | 1.0482 |
| [ValOHept][IBU] | 421.619 | 0.8504 | 0.1020 | 0.1000 | 1.0524 |
| [ValOOct][IBU] | 435.646 | 0.8503 | 0.1060 | 0.1000 | 1.0563 |
| Compound | Human Skin | Strat-M® |
|---|---|---|
| Cumulative Mass (μg IBU∙cm−2) | Cumulative Mass (μg IBU∙cm−2) | |
| [IBU] | 617.263 ± 13.986 b | 1463.510 ± 39.201 b |
| [ValOMe][IBU] | 547.900 ± 57.800 b | 1540.787 ± 45.741 b |
| [ValOEt][IBU] | 698.429 ± 17.291 b,* | 1524.711 ± 91.932 b |
| [ValOiPr][IBU] | 725.308 ± 19.788 b,* | 1982.469 ± 92.275 b,* |
| [ValOPr][IBU] | 803.349 ± 39.183 b,* | 1732.188 ± 89.107 b,* |
| [ValOBu][IBU] | 693.593 ± 37.451 b,* | 2126.476 ± 37.451 b,* |
| [ValOAm][IBU] | 510.010 ± 27.905 b | 1822.126 ± 75.816 b,* |
| [ValOHex][IBU] | 342.336 ± 20.442 b | 1072.816 ± 53.024 b |
| [ValOHept][IBU] | 287.633 ± 18.271 b | 991.647 ± 27.137 b |
| [ValOOct][IBU] | 195.635 ± 24.639 b | 701.425 ± 88.702 b |
| Commercial product (CP) | ||
| Cumulative mass (μg IBU∙cm−2) | Cumulative mass (μg IBU∙cm−2) | |
| Ibuprofen | 125.656 ± 7.827 a | 234.500 ± 6.703 a |
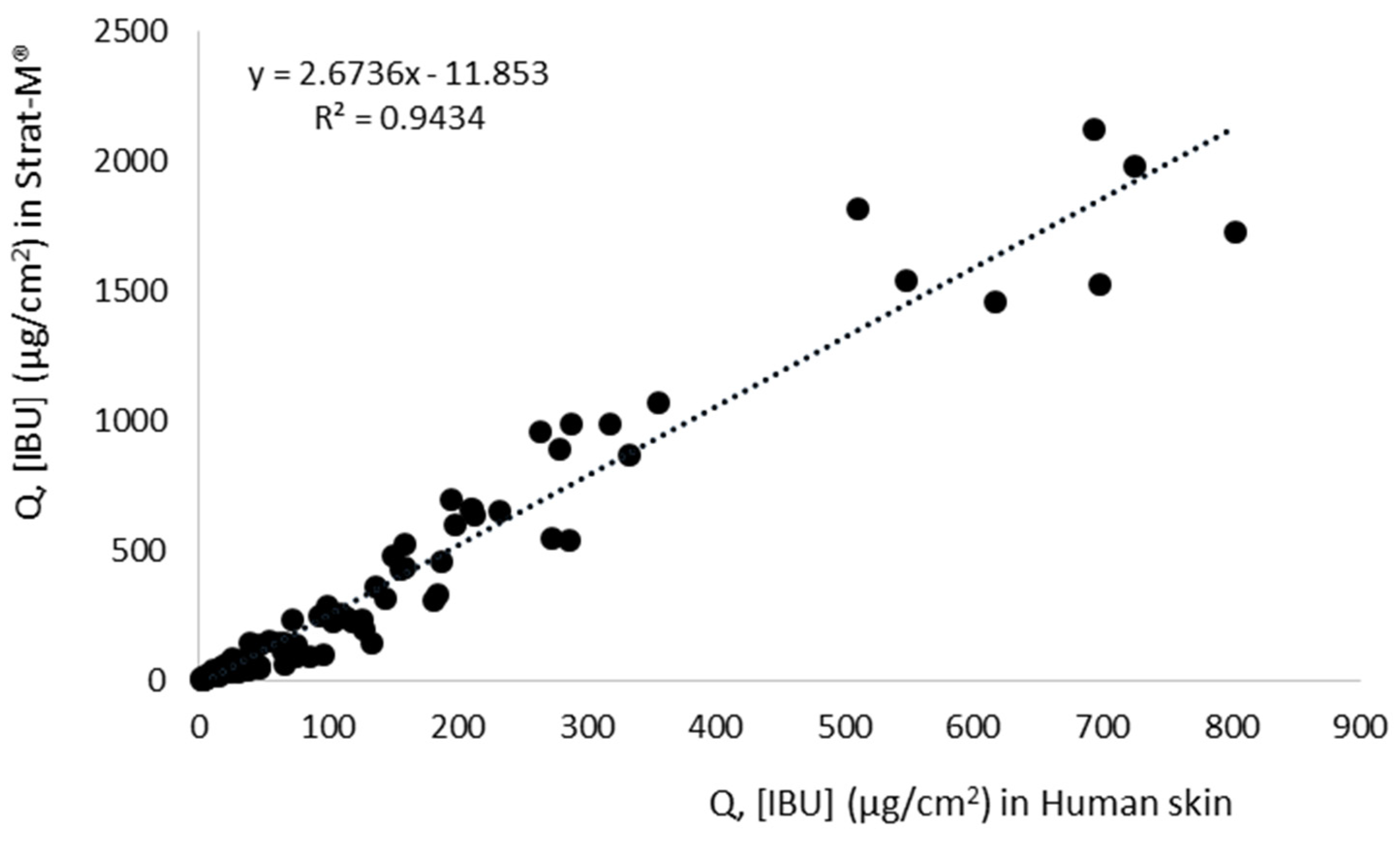
| Compound | Human Skin | Strat-M® | Permeation Ratio (JStrat-M®/JSkin) | r2 (QStrat-M® vs. QSkin) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jss, μg∙cm–2∙h–1 | KP·103, cm∙h–1 | LT, h | Jss, μg∙cm–2∙h–1 | KP·103, cm∙h–1 | LT, h | |||
| [IBU] | 36.98 ± 1.45 b | 0.74 ± 0.03 bc | 1.17 ± 0.01 d | 163.45 ± 12.13 e | 3.26 ± 0.24 d | 1.55 ± 0.04 c | 4.42 e | 0.995 c |
| [ValOMe][IBU] | 36.37 ± 0.35 b | 0.72 ± 0.01 b | 1.81 ± 0.09 g | 82.38 ± 5.30 cd | 1.65 ± 0.11 c | 1.06 ± 0.05 ab | 2.27 b | 0.998 c |
| [ValOEt][IBU] | 43.23 ± 5.52 c | 0.86 ± 0.11 c | 1.20 ± 0.04 d | 77.66 ± 4.98 c | 1.54 ± 0.10 c | 0.97 ± 0.06 a | 1.79 ab | 0.995 c |
| [ValOiPr][IBU] | 43.71 ± 3.46 c | 0.87 ± 0.0 c | 0.55 ± 0.02 a | 177.23 ± 4.97 f | 3.54 ± 0.10 d | 1.33 ± 0.05 bc | 4.05 d | 0.993 c |
| [ValOPr][IBU] | 56.56 ± 2.74 d | 1.12 ± 0.01 d | 0.83 ± 0.12 b | 205.81 ± 12.78 g | 4.09 ± 0.25 e | 1.82 ± 0.02 d | 3.64 cd | 0.986 c |
| [ValOBu][IBU] | 49.73 ± 5.23 cd | 0.99 ± 0.01 d | 0.98 ± 0.01 c | 153.29 ± 9.75 e | 3.10 ± 0.20 d | 1.17 ± 0.02 ab | 3.07 c | 0.999 c |
| [ValOAm][IBU] | 55.10 ± 2.95 d | 1.09 ± 0.01 d | 1.17 ± 0.14 d | 172.48 ± 1.73 f | 3.42 ± 0.03 d | 1.28 ± 0.10 bc | 3.13 c | 0.986 c |
| [ValOHex][IBU] | 43.65 ± 3.42 c | 0.87 ± 0.01 c | 1.89 ± 0.01 g | 50.23 ± 1.50 b | 0.99 ± 0.03 b | 2.00 ± 0.32 de | 1.15 a | 0.912 b |
| [ValOHept][IBU] | 32.47 ± 4.89 b | 0.65 ± 0.01 b | 1.55 ± 0.09 f | 93.98 ± 2.83 d | 1.88 ± 0.06 c | 2.22 ± 0.17 e | 2.89 bc | 0.977 c |
| [ValOOct][IBU] | 23.80 ± 1.83 a | 0.47 ± 0.01 a | 1.35 ± 0.03 e | 31.96 ± 1.10 a | 0.64 ± 0.02 a | 1.95 ± 0.18 d | 1.34 a | 0.816 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P.; Nowak, A.; Klebeko, J.; Janus, E.; Duchnik, W.; Adamiak-Giera, U.; Kucharski, Ł.; Prowans, P.; Petriczko, J.; Czapla, N.; et al. Assessment of the Effect of Structural Modification of Ibuprofen on the Penetration of Ibuprofen from Pentravan® (Semisolid) Formulation Using Human Skin and a Transdermal Diffusion Test Model. Materials 2021, 14, 6808. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226808
Ossowicz-Rupniewska P, Nowak A, Klebeko J, Janus E, Duchnik W, Adamiak-Giera U, Kucharski Ł, Prowans P, Petriczko J, Czapla N, et al. Assessment of the Effect of Structural Modification of Ibuprofen on the Penetration of Ibuprofen from Pentravan® (Semisolid) Formulation Using Human Skin and a Transdermal Diffusion Test Model. Materials. 2021; 14(22):6808. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226808
Chicago/Turabian StyleOssowicz-Rupniewska, Paula, Anna Nowak, Joanna Klebeko, Ewa Janus, Wiktoria Duchnik, Urszula Adamiak-Giera, Łukasz Kucharski, Piotr Prowans, Jan Petriczko, Norbert Czapla, and et al. 2021. "Assessment of the Effect of Structural Modification of Ibuprofen on the Penetration of Ibuprofen from Pentravan® (Semisolid) Formulation Using Human Skin and a Transdermal Diffusion Test Model" Materials 14, no. 22: 6808. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226808
APA StyleOssowicz-Rupniewska, P., Nowak, A., Klebeko, J., Janus, E., Duchnik, W., Adamiak-Giera, U., Kucharski, Ł., Prowans, P., Petriczko, J., Czapla, N., Bargiel, P., Markowska, M., & Klimowicz, A. (2021). Assessment of the Effect of Structural Modification of Ibuprofen on the Penetration of Ibuprofen from Pentravan® (Semisolid) Formulation Using Human Skin and a Transdermal Diffusion Test Model. Materials, 14(22), 6808. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226808









