The Designation Degree of Tool Wear after Machining of the Surface Layer of Duplex Stainless Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
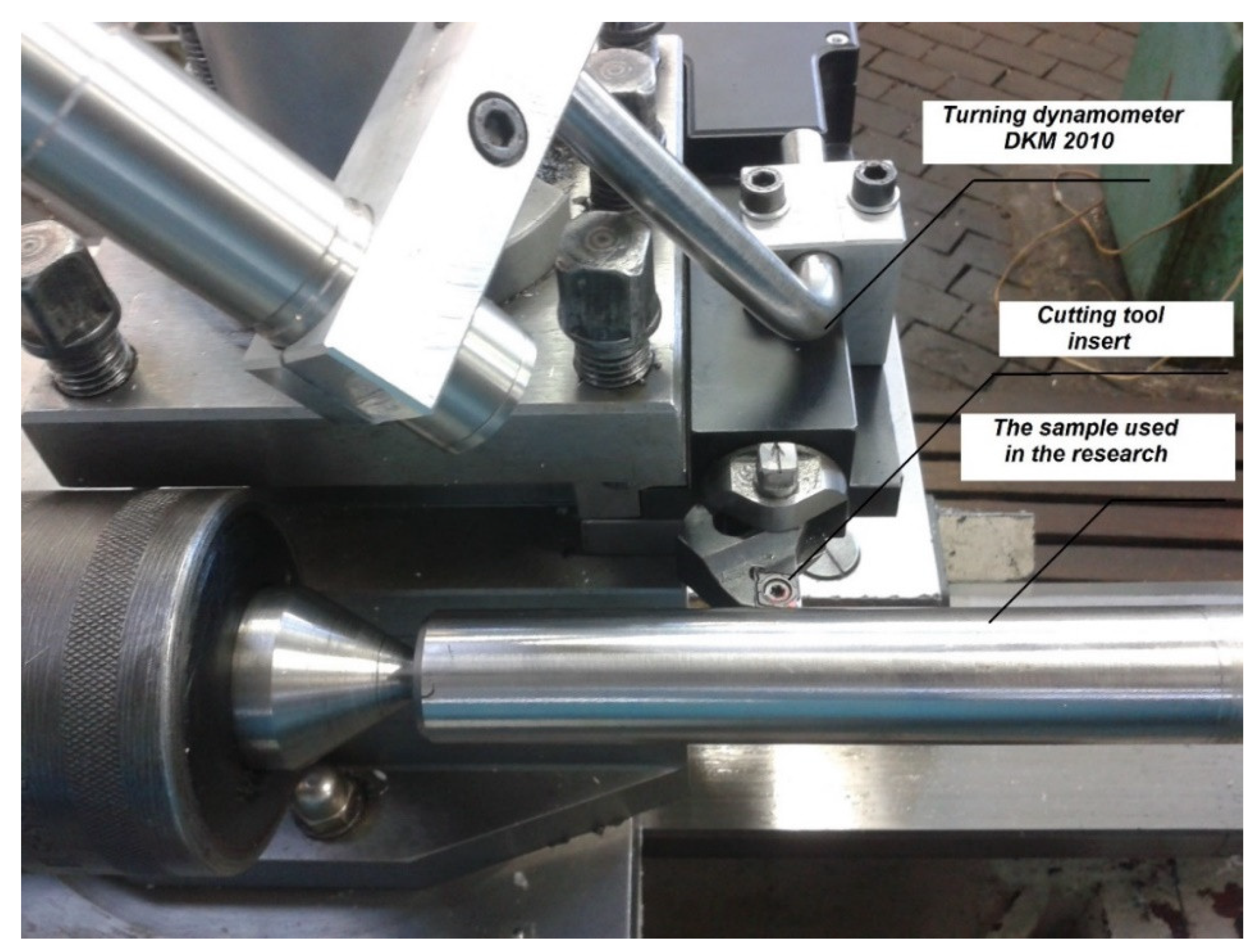
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
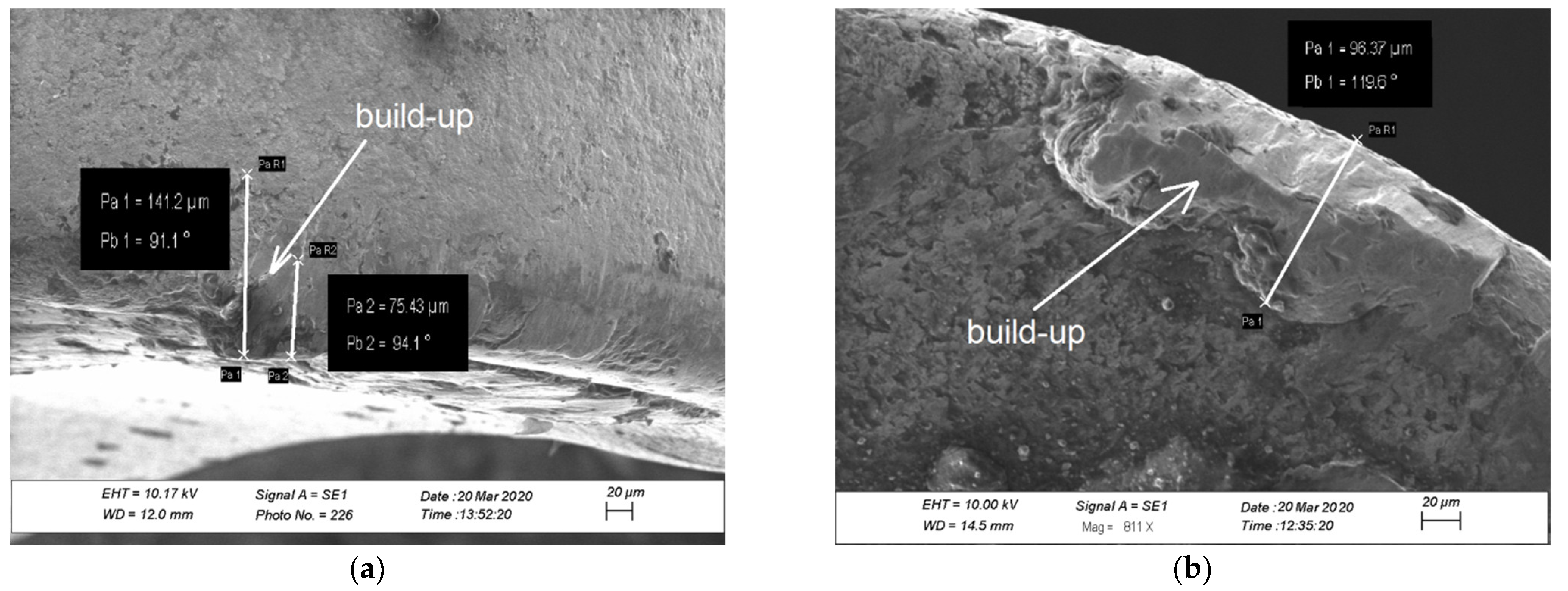
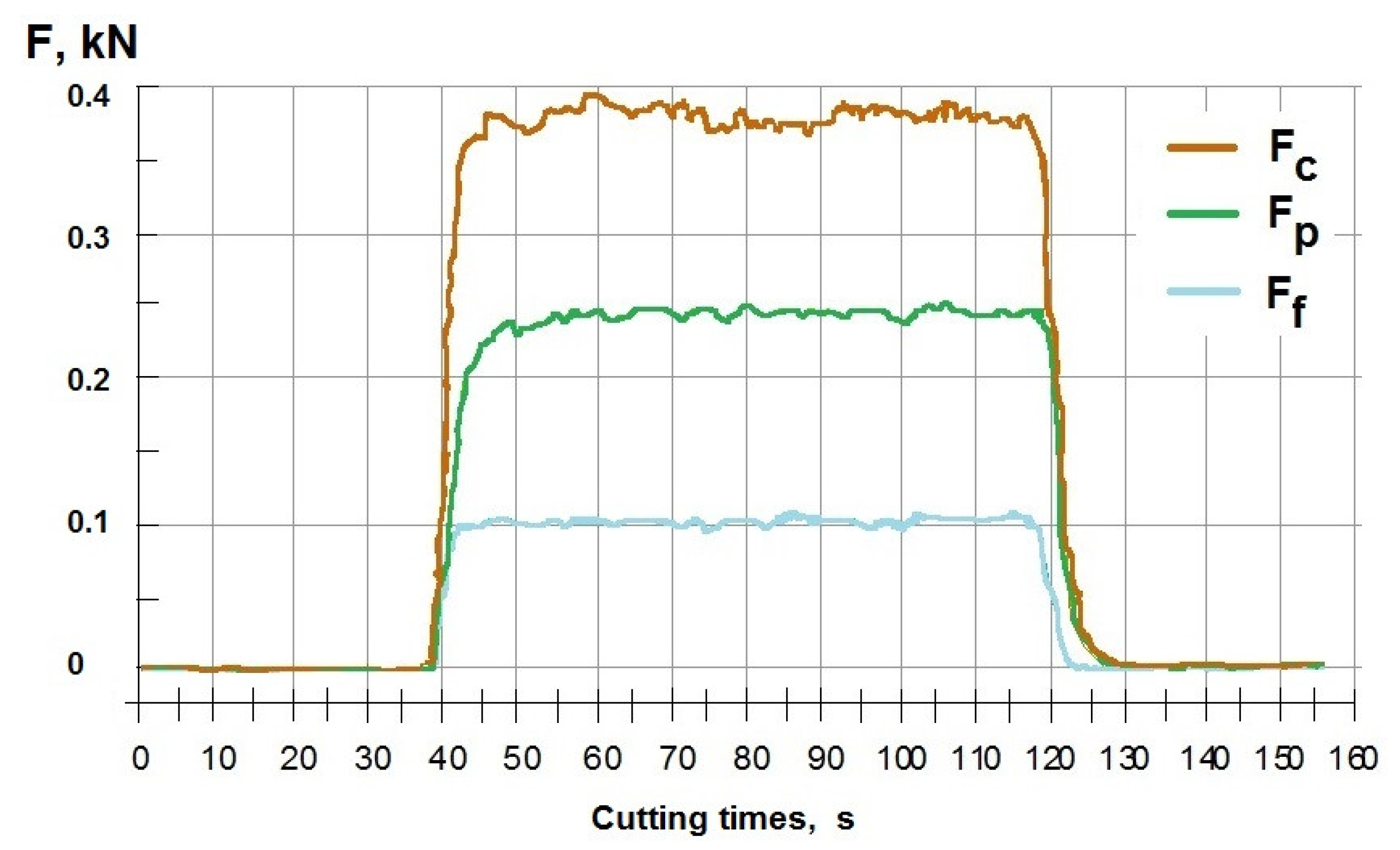
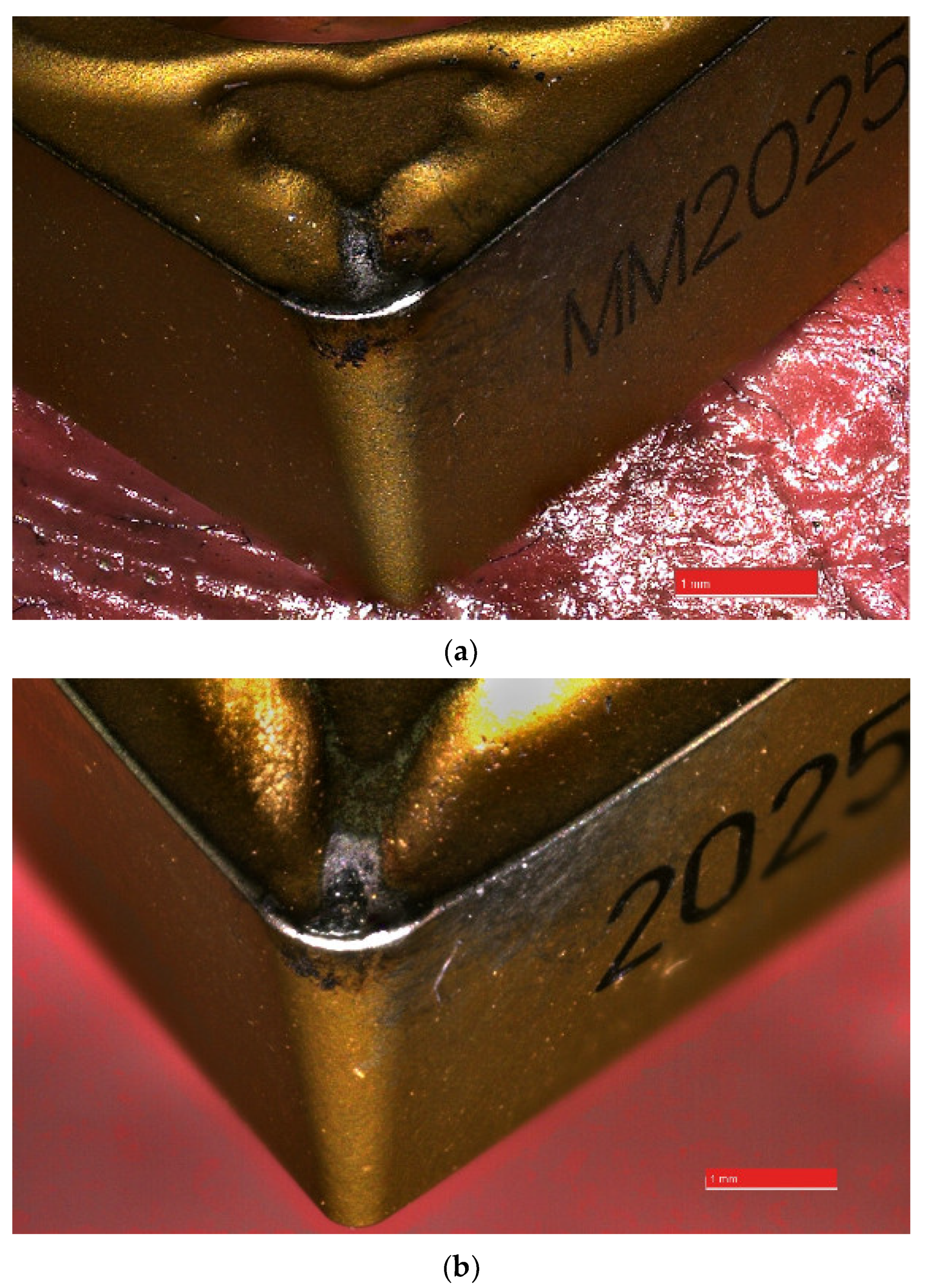
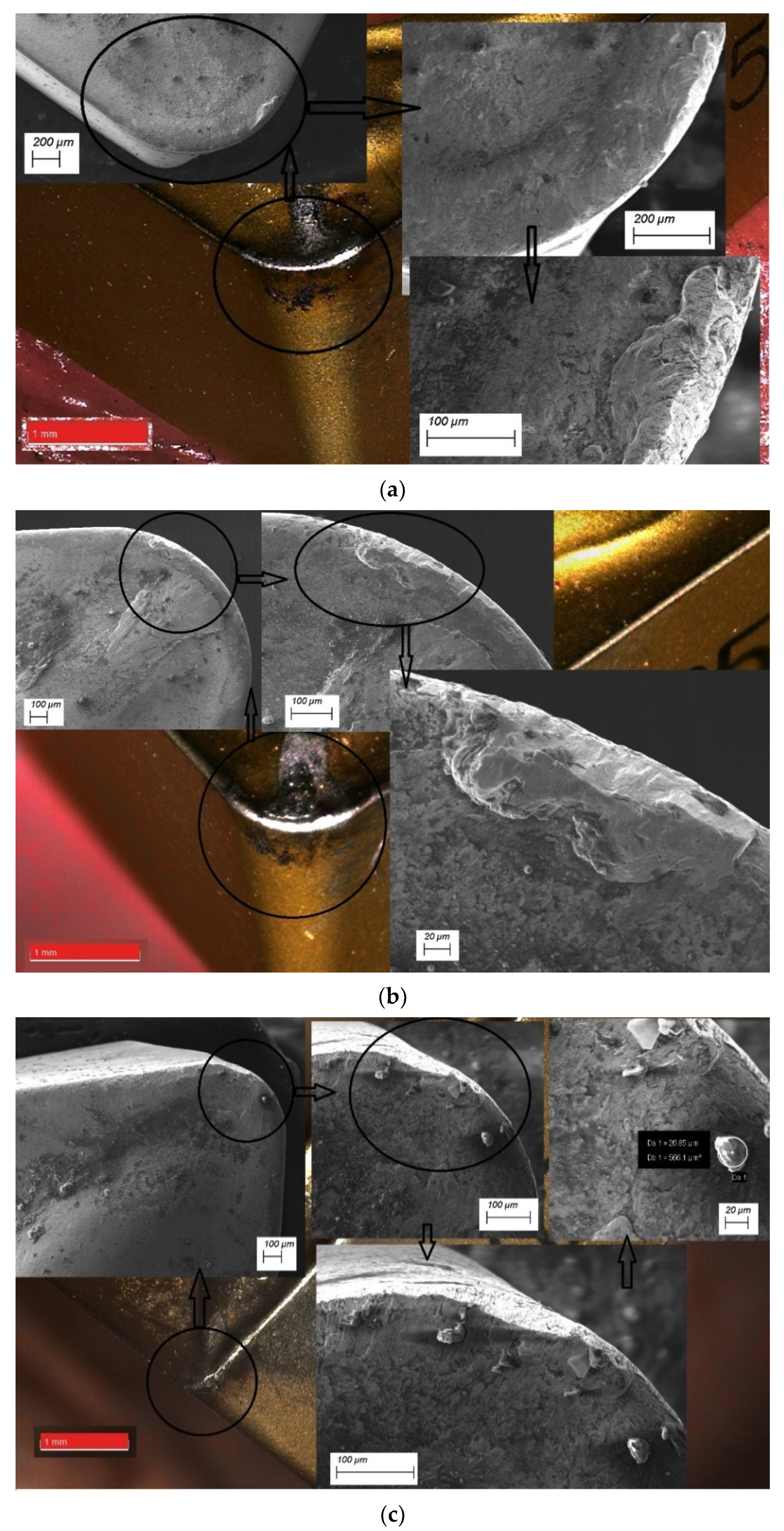
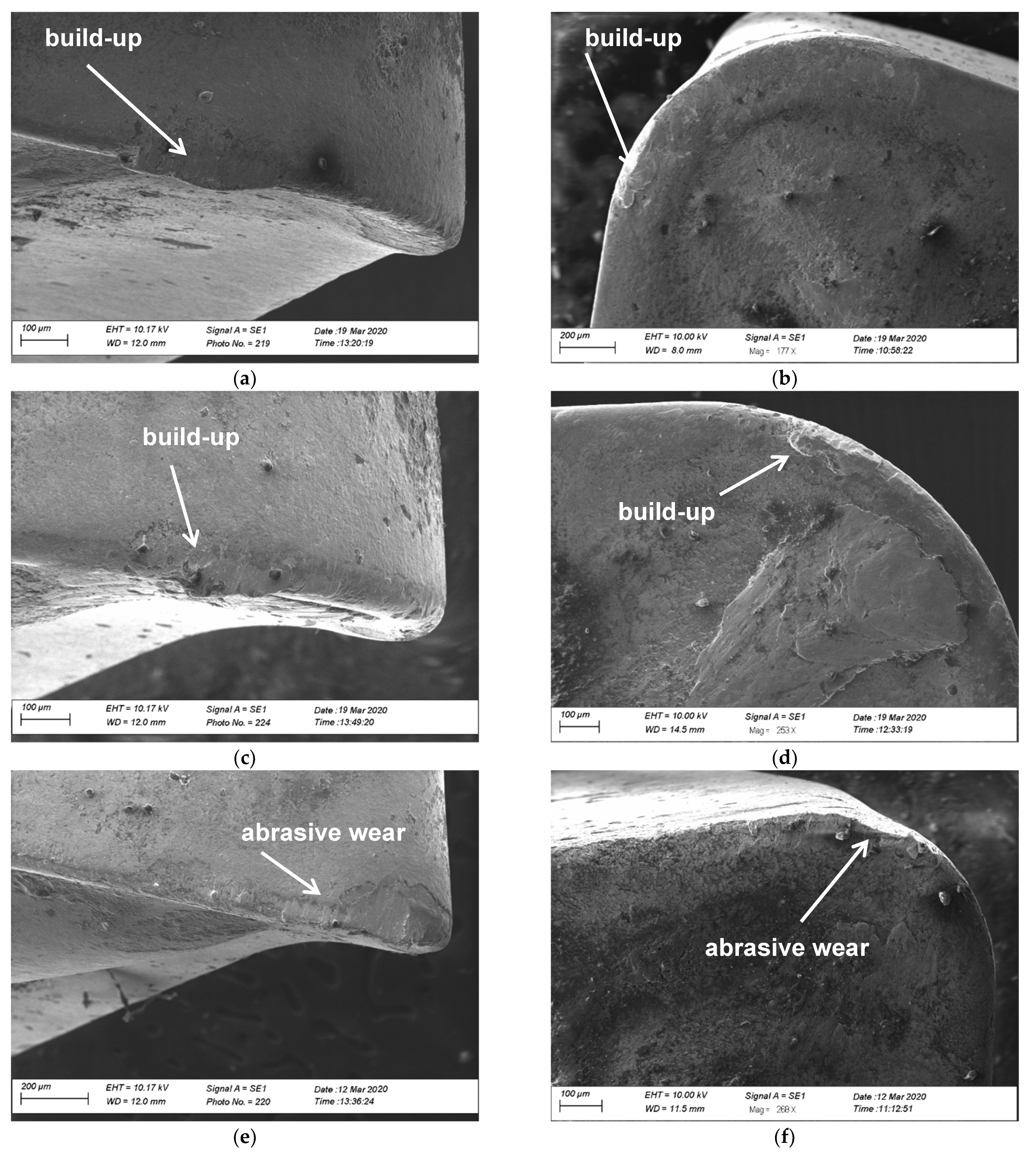
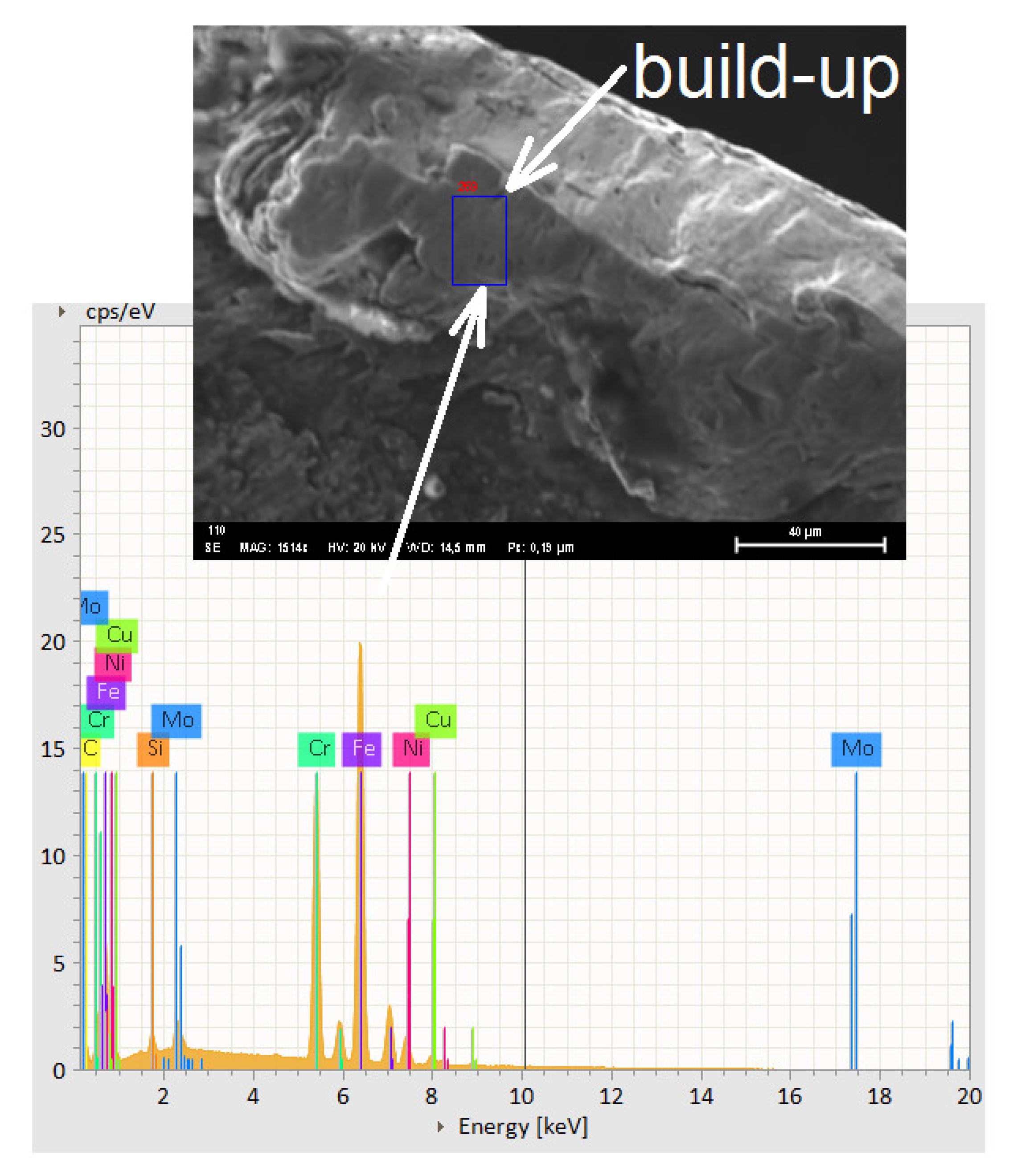
3. Results of Experimental Investigation
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscope |
| EDS | spectrometer analyzer |
| DSS | duplex stainless steel |
| LSC | length of spiral cutting, (m) |
| VB | flank wear, (mm) |
| KB | rake face wear, (mm) |
| Dm | diameter of the workpiece, (mm) |
| lm | length of the cutting materials, (mm) |
| f | feed rate, (mm/rev) |
| ap | depth of cut, (mm) |
| vc | cutting speed, (m/min) |
References
- Armas, A.; Moreuil, S.D. Duplex Stainless Steels; ISTE Ltd.: London, UK; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Burakowski, T.; Wierzchoń, T. Surface Engineering of Metals: Principles, Equipment, Technologies. In Materials Science and Technology; CRC Press LLC.: London, UK; New York, NY, USA; Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Charles, J. Duplex stainless steels, a review after DSS’07 held in Grado. Rev. Metall. 2008, 105, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamarra, J.R.; Diniz, A.E. Taper turning of super duplex stainless steel: Tool life, tool wear and workpiece surface roughness. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Królczyk, G.M.; Niesłony, P.; Legutko, S. Determination of tool life and research wear during duplex stainless steel turning. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2015, 15, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Królczyk, G.M.; Niesłony, P.; Legutko, S.; Hloch, S.; Samardzic, I. Investigation of selected surface integrity features of duplex stainless steel (DSS) after turning. Metalurgija 2015, 54, 91–94. Available online: https://hrcak.srce.hr/126702 (accessed on 29 September 2021). [CrossRef]
- Nowacki, J. Duplex Stainless Steel and Its Weldability; WNT: Warsaw, Poland, 2009. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Paro, J.; Hanninen, H.; Kauppinen, V. Tool wear and machinability of HIPed P/M and conventional cast duplex stainless steels. Wear 2001, 249, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paro, J.; Hanninen, H.; Kauppinen, V. Tool wear and machinability of X5 CrMnN 18 18 stainless steels. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2001, 119, 14–20. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924013601008779 (accessed on 27 September 2021). [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, X.; Yu, H.; Jiang, L. Novel Cu-bearing economic al 21Cr duplex stainless steels. Mater. Des. 2013, 46, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starosta, R.; Dyl, T. Surface Engineering; Gdynia Maritime University: Gdynia, Poland, 2008. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Stradomski, G. The Analysis of AISI A3 Type Ferritic—Austenitic Cast Steel Crystallization Mechanism. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2017, 17, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stradomski, G. The Impact of the Morphology of the Sigma Phase on Shape Properties of Steel and Cast Steel Duplex; Czestochowa University of Technology: Czestochowa, Poland, 2016. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Tools for Metal Cutting, Turning Tools, Turning Inserts and Grades for Stainless Steel; CoroTurn®107 Grade 2025; Sandvik Coromant. 2021. Available online: http://www.sandvik.coromant.com/en-us/products/pages/tools.aspx (accessed on 11 September 2021).
- Dyl, T.; Starosta, R. Finishing of Nickel Matrix Composite Coatings. Preprints 2019, 2019110374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Gao, W.; Yan, B.; Chen, T. Study on the Design and Cutting Performance of a Revolving Cycloid Milling Cutter. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzierwa, A. Influence of surface preparation on surface topography and tribological behaviours. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2017, 17, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzierwa, A.; Markopoulos, A.P. Influence of Ball-Burnishing Process on Surface Topography Parameters and Tribological Properties of Hardened Steel. Machines 2019, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, N.; Airao, J.; Gupta, M.K.; Song, Q.; Liu, Z.; Mia, M.; Maruda, R.; Królczyk, G.M. Optimization of Power Consumption Associated with Surface Roughness in Ultrasonic Assisted Turning of Nimonic-90 Using Hybrid Particle Swarm-Simplex Method. Materials 2019, 12, 3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, V.F.C.; Silva, F.J.G.; Lopes, H.; Casais, R.C.B.; Baptista, A.; Pinto, G.; Alexandre, R. Wear Behavior and Machining Performance of TiAlSiN-Coated Tools Obtained by dc MS and HiPIMS: A Comparative Study. Materials 2021, 14, 5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarıkaya, M.; Gupta, M.K.; Tomaz, I.; Pimenov, D.; Kuntoğlu, M.; Khanna, N.; Yıldırım, Ç.V.; Królczyk, G.M. A state-of-the-art review on tool wear and surface integrity characteristics in machining of superalloys. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 624–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, S.; Królczyk, G.M.; Maruda, R.W. Advances in Hard–to–Cut Materials: Manufacturing, Properties, Process Mechanics and Evaluation of Surface Integrity. Materials 2020, 13, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subhash, N.; Sambedana, S.; Raj, P.N.; Jagadeesha, T. Experimental Study on Tool Wear and Optimization of Process Parameters Using ANN-GA in Turning of Super-Duplex Stainless Steel Under Dry and Wet Conditions. In Advances in Manufacturing Technology. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Hiremath, S., Shanmugam, N., Bapu, B., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsi, P.K.; Kotha, R.S.; Routhu, T.; Pandey, S.; Dwivedy, M. Machinability evaluation of coated carbide inserts in turning of super-duplex stainless steel. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, L.G.; Madeira, D.S.; Ricomini, T.E.P.A.; Miranda, R.A.; Brito, T.G.; Paiva, E.J. Optimization of machining parameters using response surface methodology with desirability function in turning duplex stainless steel UNS S32760. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 117, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaguru, J.; Arunachalam, N. A comprehensive investigation on the effect of flood and MQL coolant on the machinability and stress corrosion cracking of super duplex stainless steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 276, 116417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, R.; Raina, A.; Haq, M.I.U.; Mir, M.J.; Gulzar, O.; Wani, M.F. Synergism of TiO2 and Graphene as Nano-Additives in Bio-Based Cutting Fluid—An Experimental Investigation. Tribol. Trans. 2021, 64, 350–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| C | Cr | Ni | Mo | Mn | Si | N | S | P |
| [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] |
| 24.0 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 0.24 | |||||
| 0.03 | 26.0 | 8.0 | 5.0 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 0.32 | 0.020 | 0.035 |
| Rp0.2 | Rm min. | Rm max. | A5 min. | HV max. | E | ρ | λ | cw |
| [MPa] | [MPa] | [MPa] | [%] | [-] | [GPa] | [kg/m3] | [J/m·s·K] | [J/kg·K] |
| 550 | 795 | 1000 | 15 | 310 | 200 | 7800 | 14.2 | 460 |
| No Cutting Insert | Insert Shape | Insert Type | Insert Grade | Nose Radius [mm] | Flank Angle [°] | Rake Angle [°] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC1 | CC09T3 | CCMT09T308-MM | 2025 | 0.8 | 7 | 7 |
| CC2 | CCMT09T308-UM | 6 | ||||
| CC3 | CCMT09T304-UM | 0.4 |
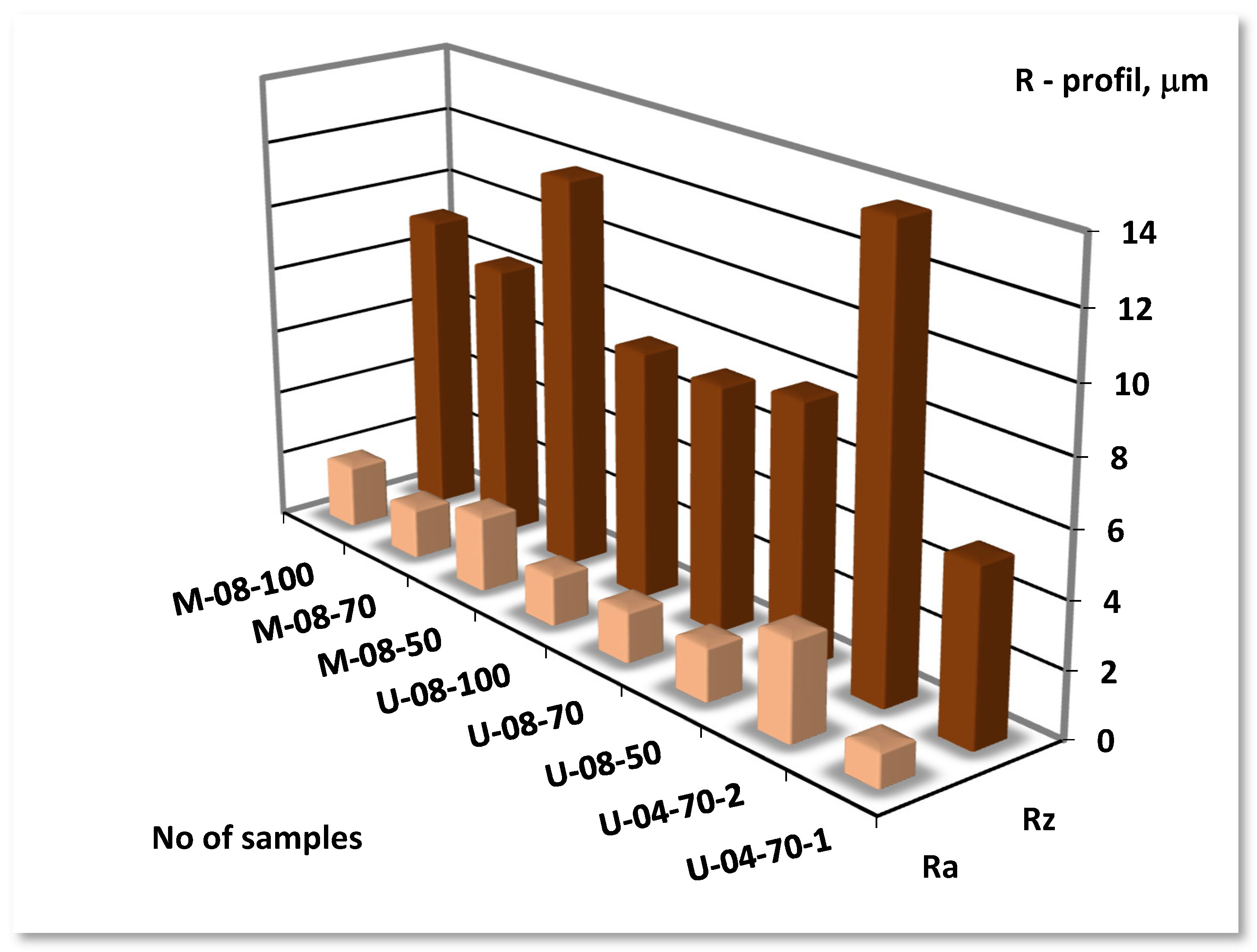
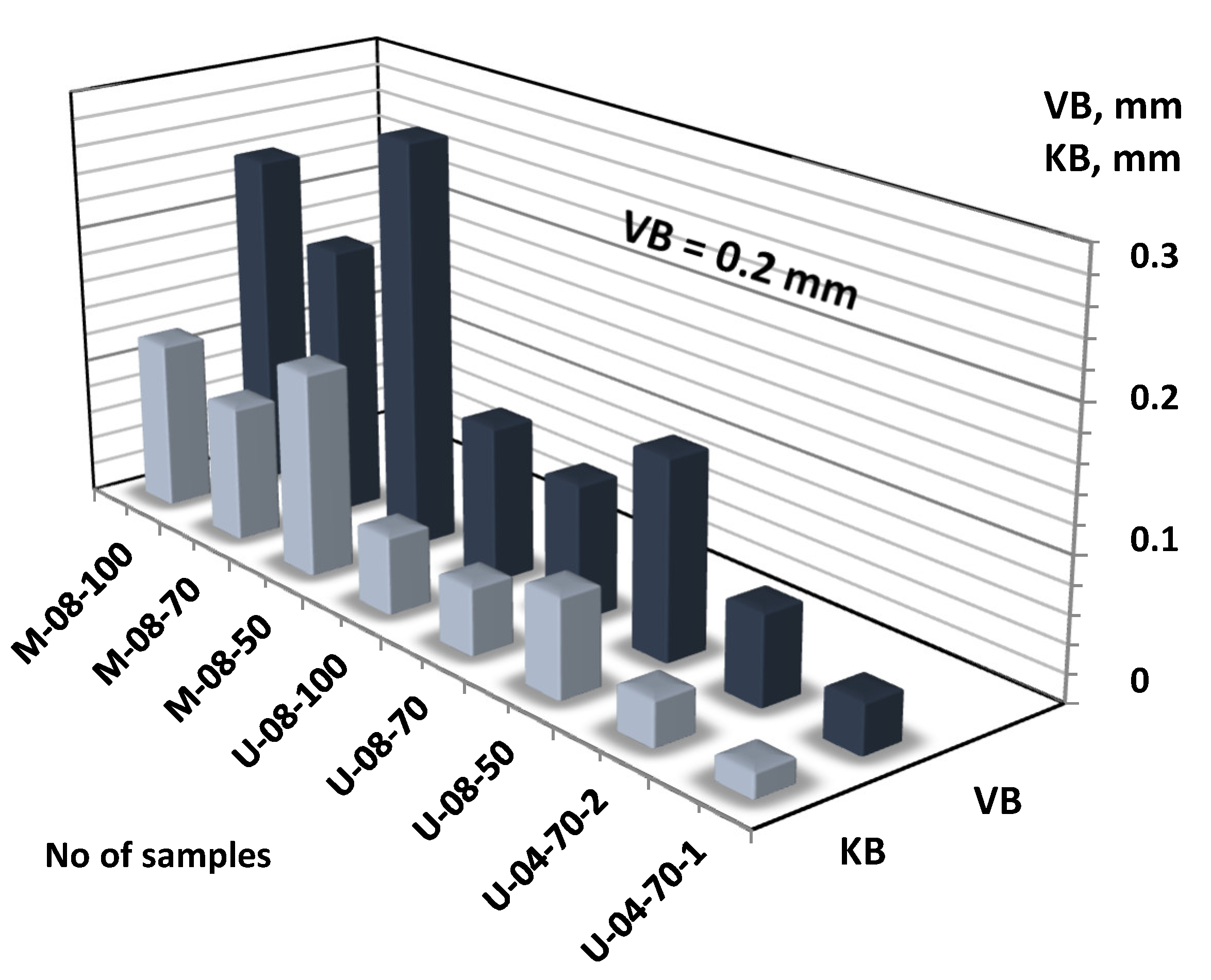
| No | No | Insert | f | vc | VB | KB | Rz | Ra | KRa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inserts | Samples | Type | [mm/rev] | [m/min] | [mm] | [mm] | [μm] | [μm] | [-] |
| CC1 | M-08-100 | CCMT09T308-MM | 0.2 | 100 | 0.242 | 0.121 | 9.21 | 1.91 | 1.71 |
| M-08-70 | 70 | 0.194 | 0.098 | 8.43 | 1.65 | 2.14 | |||
| M-08-50 | 50 | 0.292 | 0.147 | 11.95 | 2.31 | 1.43 | |||
| CC2 | U-08-100 | CCMT09T308-UM | 0.2 | 100 | 0.112 | 0.056 | 7.58 | 1.52 | 2.16 |
| U-08-70 | 70 | 0.097 | 0.048 | 7.48 | 1.55 | 2.13 | |||
| U-08-50 | 50 | 0.141 | 0.071 | 7.97 | 1.63 | 2.02 | |||
| CC3 | U-04-70-2 | CCMT09T304-UM | 0.2 | 70 | 0.064 | 0.032 | 13.86 | 3.03 | 1.09 |
| U-04-70-1 | 0.1 | 70 | 0.036 | 0.018 | 5.35 | 1.05 | 3.21 |
| C | Cr | Ni | Mo | Mn | Si | N | S | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] |
| 0.03 | 23.4 | 5.8 | 2.8 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.02 | 0.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dyl, T. The Designation Degree of Tool Wear after Machining of the Surface Layer of Duplex Stainless Steel. Materials 2021, 14, 6425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216425
Dyl T. The Designation Degree of Tool Wear after Machining of the Surface Layer of Duplex Stainless Steel. Materials. 2021; 14(21):6425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216425
Chicago/Turabian StyleDyl, Tomasz. 2021. "The Designation Degree of Tool Wear after Machining of the Surface Layer of Duplex Stainless Steel" Materials 14, no. 21: 6425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216425
APA StyleDyl, T. (2021). The Designation Degree of Tool Wear after Machining of the Surface Layer of Duplex Stainless Steel. Materials, 14(21), 6425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216425






