Design of High Volume CFBC Fly Ash Based Calcium Sulphoaluminate Type Binder in Mixtures with Ordinary Portland Cement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
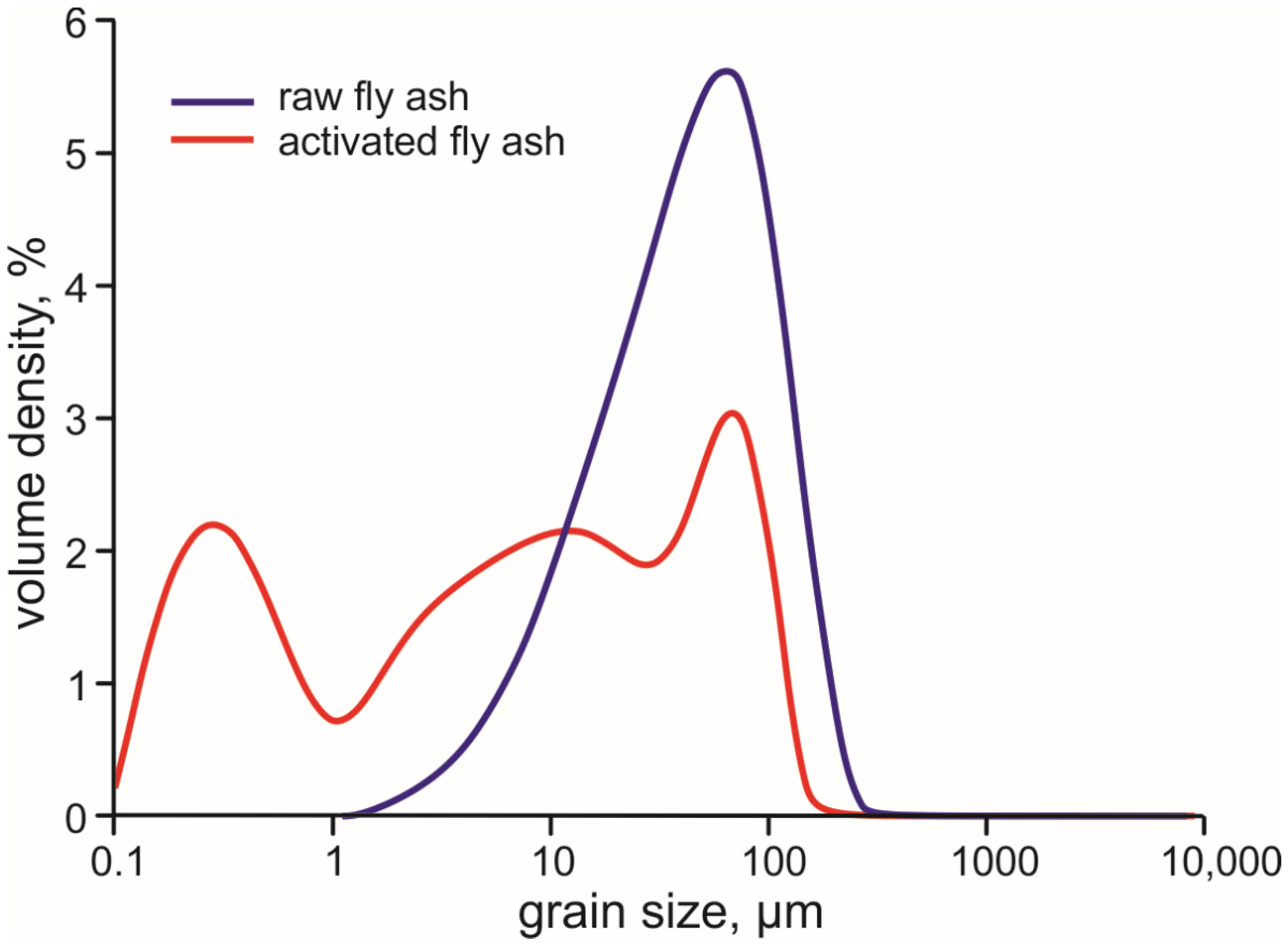
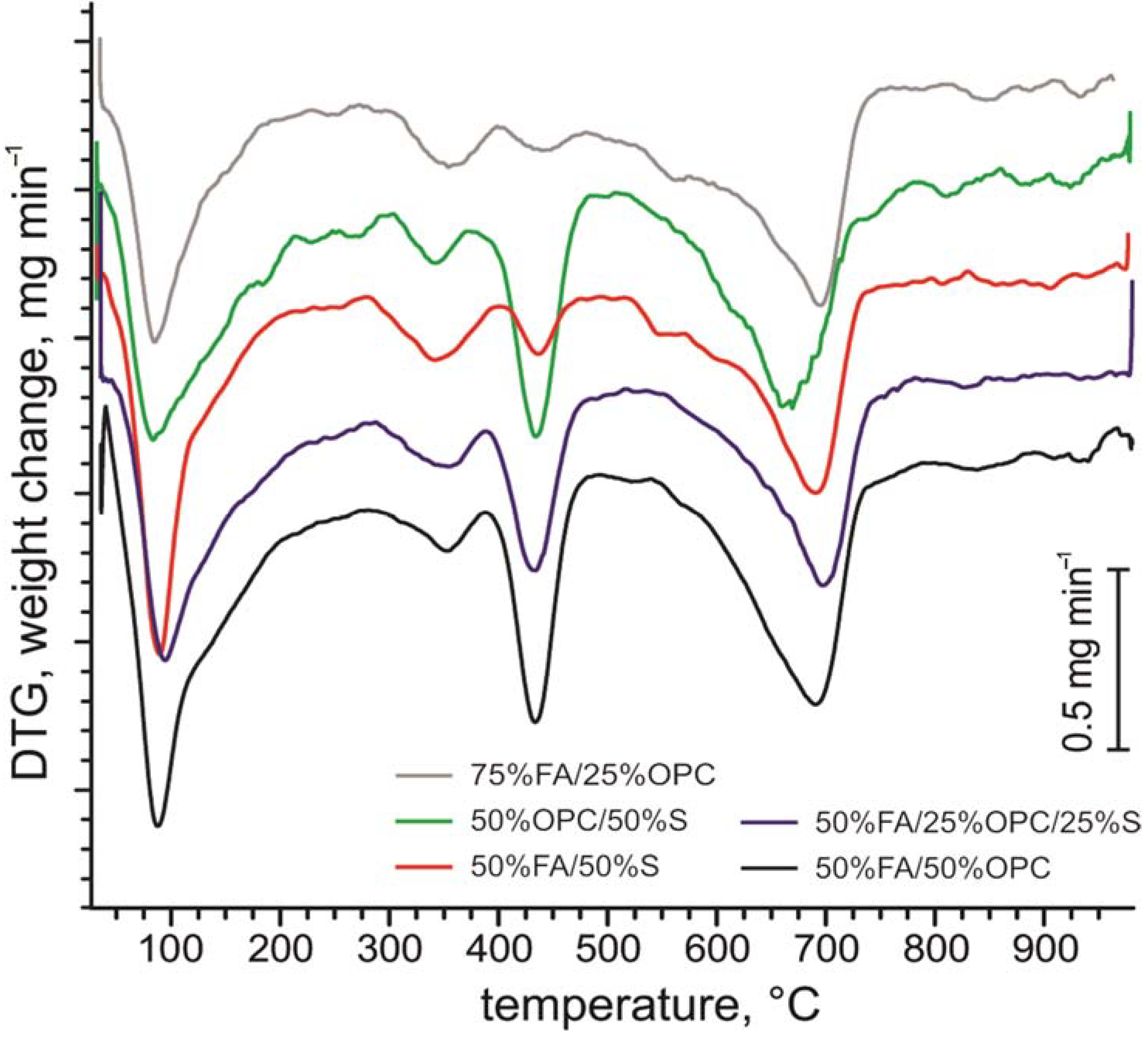
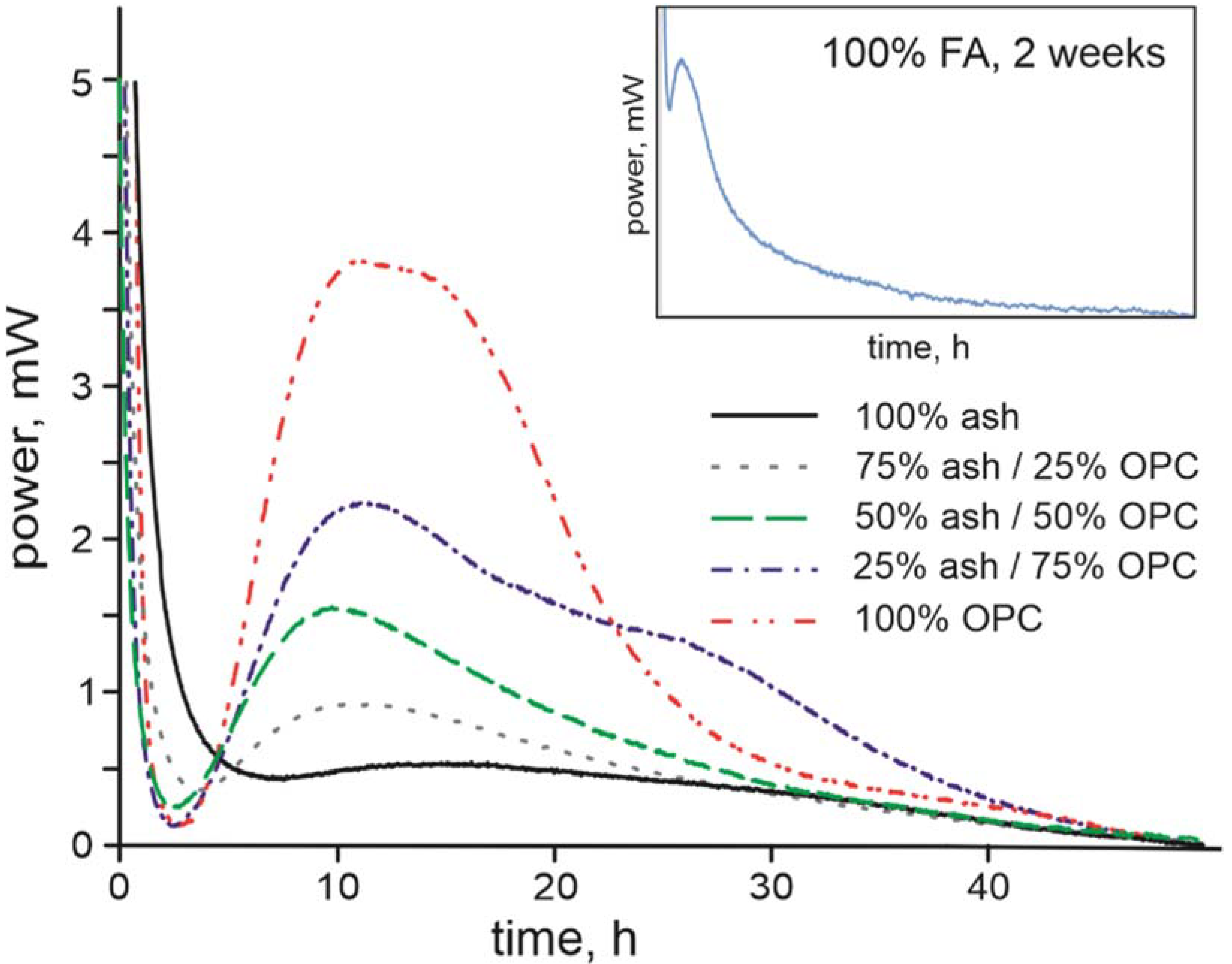
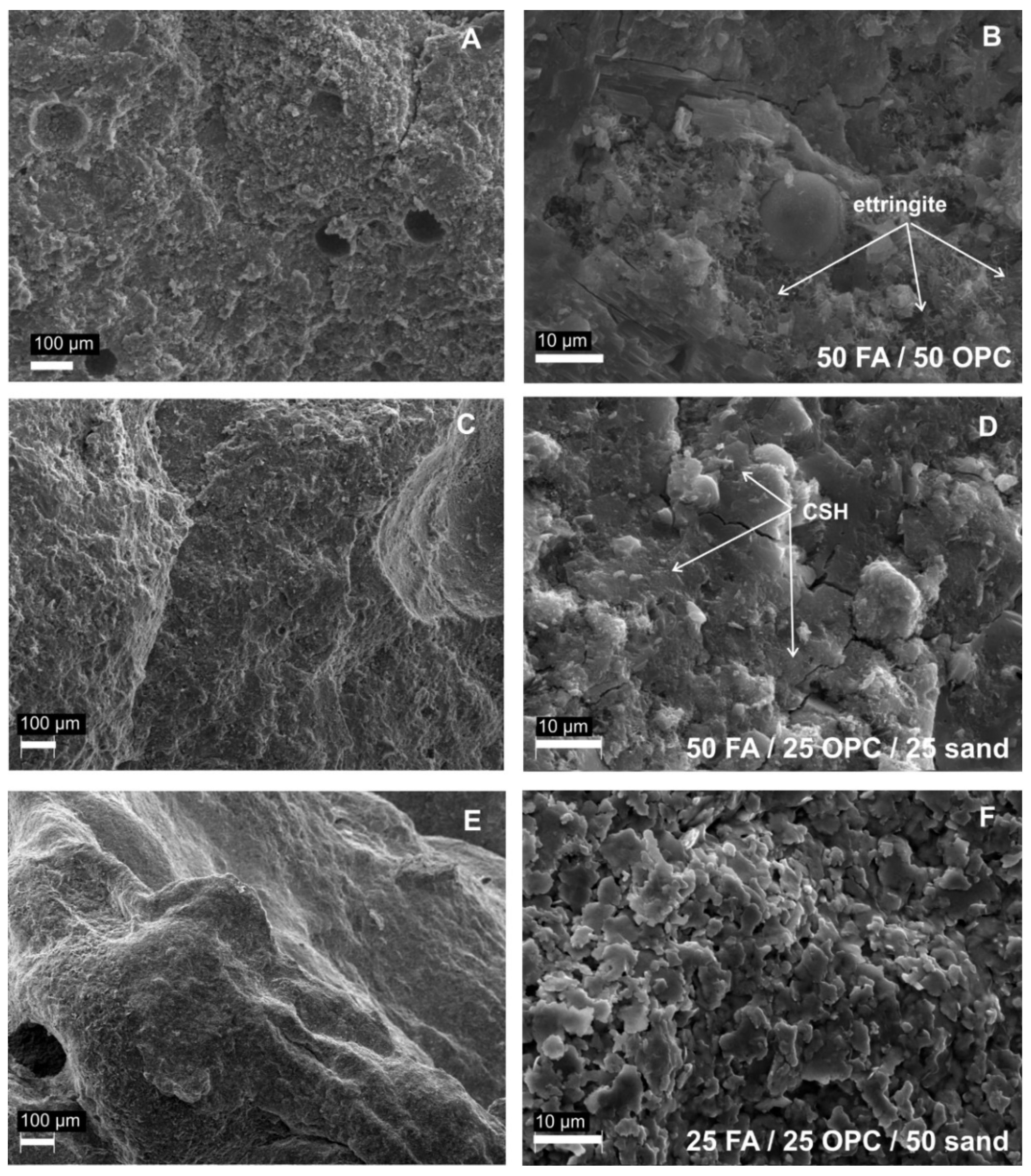
3.1. Composition of the Raw Ash and Hydration Products
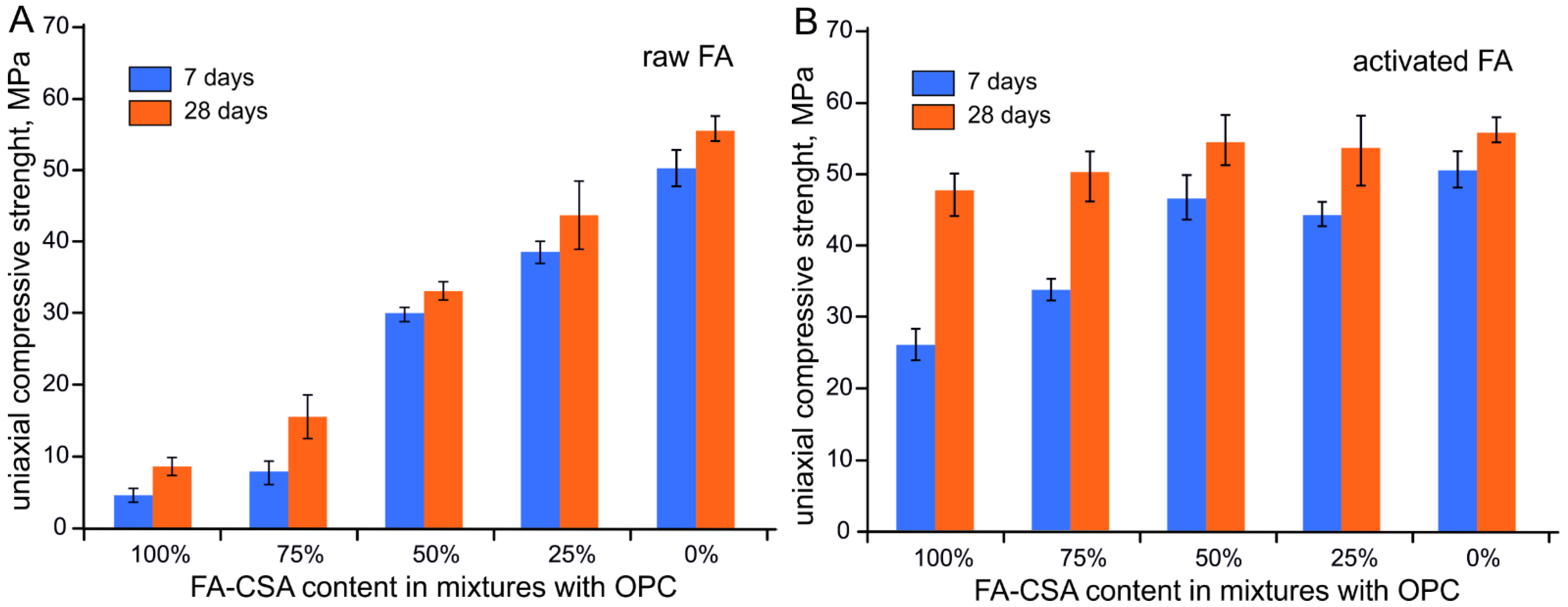
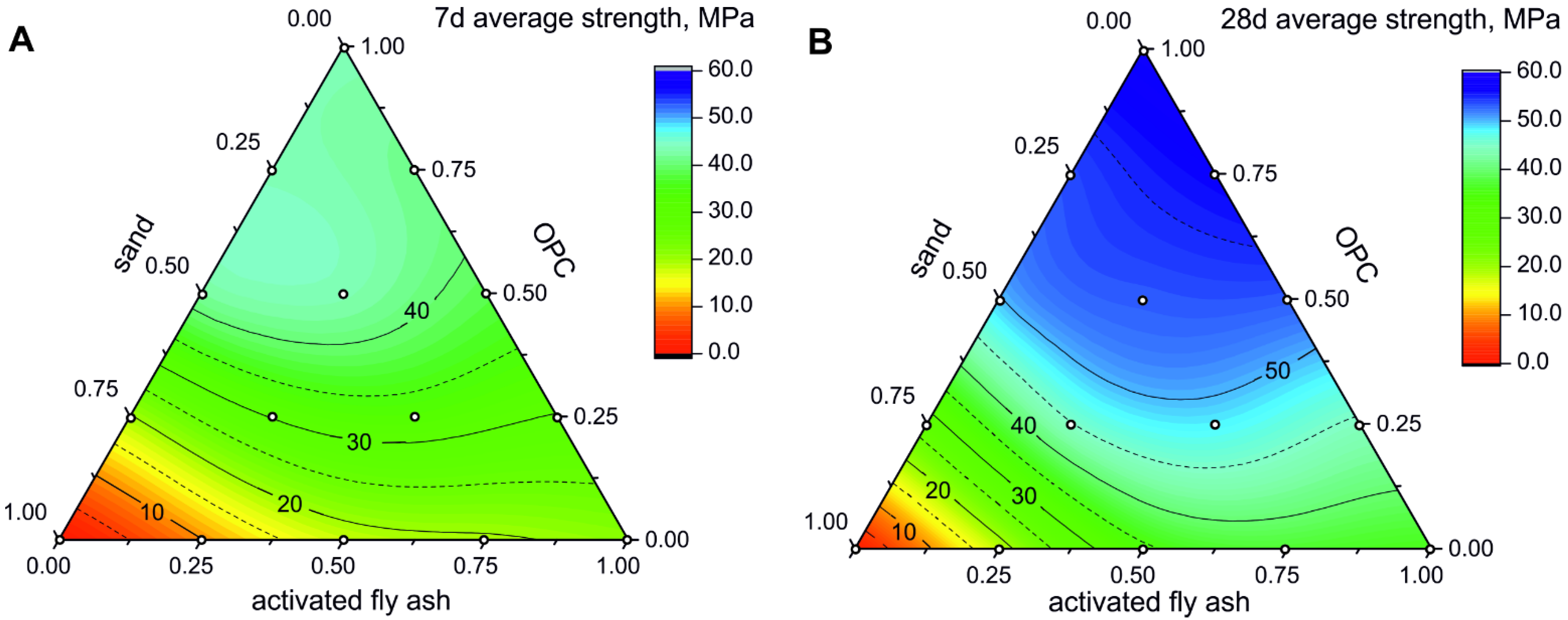
3.2. Compressive Strength of FA-CSA, OPC and Sand Mixtures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gartner, E.M.; Hirao, H. A review of alternative approaches to the reduction of CO2 emissions associated with the man-ufacture of the binder phase in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanein, T.; Galvez-Martos, J.-L.; Bannerman, M. Carbon footprint of calcium sulfoaluminate clinker production. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 2278–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glasser, F.; Zhang, L. High-performance cement matrices based on calcium sulfoaluminate–belite compositions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 1881–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juenger, M.; Winnefeld, F.; Provis, J.; Ideker, J. Advances in alternative cementitious binders. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juenger, M.C.; Snellings, R.; Bernal, S.A. Supplementary cementitious materials: New sources, characterization, and performance insights. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 122, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaunsali, P.; Mondal, P. Influence of Calcium Sulfoaluminate (CSA) Cement Content on Expansion and Hydration Behavior of Various Ordinary Portland Cement-CSA Blends. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 98, 2617–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargis, C.W.; Telesca, A.; Monteiro, P.J.M. Calcium sulfoaluminate (Ye’elimite) hydration in the presence of gypsum, calcite, and vaterite. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 65, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Haha, M.; Winnefeld, F.; Pisch, A. Advances in understanding ye’elimite-rich cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pera, J.; Ambroise, J. Use of Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement to Improve Strength of Mortars at Low Temperature; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2008; pp. 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péra, J.; Ambroise, J. New applications of calcium sulfoaluminate cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Shafei, B.; Liu, Z.; Phares, B.M. Early-age performance of longitudinal bridge joints made with shrink-age-compensating cement concrete. Eng. Struct. 2019, 197, 109391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooni, J.; Robert, D.; Giustozzi, F.; Setunge, S.; Xie, Y.; Xia, J. Performance evaluation of calcium sulfoaluminate as an alternative stabilizer for treatment of weaker subgrades. Transp. Geotech. 2020, 27, 100462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooni, J.; Robert, D.; Giustozzi, F.; Setunge, S.; Xie, Y.; Xia, J. Novel use of calcium sulfoaluminate (CSA) cement for treating problematic soils. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 120433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.H.; Winnefeld, F.; Tschopp, E.; Müller, C.J.; Lothenbach, B. Influence of fly ash on the hydration of calcium sulfoaluminate cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 95, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnefeld, F.; Lothenbach, B. Hydration of calcium sulfoaluminate cements - Experimental findings and thermody-namic modelling. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, A.; Marroccoli, M.; Pace, M.L.; Tomasulo, M.; Valenti, G.L.; Monteiro, P.J.M. A hydration study of various calcium sulfoaluminate cements. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 53, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žibret, G.; Teran, K.; Žibret, L.; Šter, K.; Dolenec, S. Building of the Al-Containing Secondary Raw Materials Registry for the Production of Low CO2 Mineral Binders in South-Eastern European Region. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, T.; Bulck, A.V.D.; Onisei, S.; Sivakumar, P.P.; Pontikes, Y. Boosting the use of bauxite residue (red mud) in cement—Production of an Fe-rich calciumsulfoaluminate-ferrite clinker and characterisation of the hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 145, 106463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Qian, J.S.; Huang, Y.B.; Yang, D.Y. Synthesis of belite sulfoaluminate-ternesite cements with phosphogypsum. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 63, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.A.; Juenger, M.C. Incorporation of coal combustion residuals into calcium sulfoaluminate-belite cement clinkers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, A.; Matschei, T.; Marroccoli, M. Study of Eco-Friendly Belite-Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cements Obtained from Special Wastes. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julphunthong, P.; Joyklad, P. Utilization of Several Industrial Wastes as Raw Material for Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement. Materials 2019, 12, 3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rungchet, A.; Chindaprasirt, P.; Wansom, S.; Pimraksa, K. Hydrothermal synthesis of calcium sulfoaluminate–belite cement from industrial waste materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 115, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, A.; Marroccoli, M.; Tomasulo, M.; Valenti, G.L.; Dieter, H.; Montagnaro, F. Low-CO2 Cements from Fluidized Bed Process Wastes and Other Industrial By-Products. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2016, 188, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paaver, P.; Paiste, P.; Liira, M.; Kirsimäe, K. Mechanical Activation of the Ca-Rich Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion Fly Ash: Development of an Alternative Binder System. Minerals 2021, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.J. Fluidized-Bed Combustion of Alternative Solid Fuels—Status, Successes and Problems of the Technology. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1995, 21, 239–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.J.; Berry, E.; Blondin, J.; Bulewicz, E.; Burwell, S. Advanced ash management technologies for CFBC ash. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, N.T.; Chang, T.-P.; Chen, C.-T. Hydration Process and Compressive Strength of Slag-CFBC Fly Ash Materials without Portland Cement. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 04014213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.K.; Jeon, S.M.; Lee, B.Y.; Kim, H.K. Use of circulating fluidized bed combustion bottom ash as a secondary ac-tivator in high-volume slag cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 234, 117240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, S.; Kim, H.; Jang, J.G. Properties of high-volume slag cement mortar incorporating circulating fluidized bed combustion fly ash and bottom ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 289, 123150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giergiczny, Z. Fly ash and slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinicki, M.A.; Jóźwiak-Niedźwiedzka, D.; Dąbrowski, M. The Influence of Fluidized Bed Combustion Fly Ash on the Phase Composition and Microstructure of Cement Paste. Materials 2019, 12, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leben, K.; Mõtlep, R.; Paaver, P.; Konist, A.; Pihu, T.; Paiste, P.; Heinmaa, I.; Nurk, G.; Anthony, E.J.; Kirsimäe, K. Long-term mineral transformation of Ca-rich oil shale ash waste. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 658, 1404–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pihu, T.; Arro, H.; Prikk, A.; Rootamm, R.; Konist, A.; Kirsimäe, K.; Liira, M.; Mõtlep, R. Oil shale CFBC ash cementation properties in ash fields. Fuel 2012, 93, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uibu, M.; Somelar, P.; Raado, L.M.; Irha, N.; Hain, T.; Koroljova, A.; Kuusik, R. Oil shale ash based backfilling concrete—Strength development, mineral transformations and leachability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 102, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raado, L.-M.; Hain, T.; Liisma, E.; Kuusik, R. Composition and Properties of Oil Shale Ash Concrete. Oil Shale 2014, 31, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paaver, P.; Paiste, P.; Kirsimäe, K. Geopolymeric Potential of the Estonian Oil Shale Solid Residues: Petroter Solid Heat Carrier Retorting Ash. Oil Shale 2016, 33, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paaver, P.; Paiste, P.; Mõtlep, R.; Kirsimäe, K. Self-Cementing Properties and Alkali Activation Of Enefit280 Solid Heat Carrier Retorting Ash. Oil Shale 2017, 34, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiste, P.; Liira, M.; Heinmaa, I.; Vahur, S.; Kirsimäe, K. Alkali activated construction materials: Assessing the alterna-tive use for oil shale processing solid wastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 122, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiste, P.; Külaviir, M.; Paaver, P.; Heinmaa, I.; Vahur, S.; Kirsimäe, K. Beneficiation of Oil Shale Processing Waste: Secondary Binder Phases in Alkali Activated Composites. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 10, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paaver, P.; Paiste, P.; Liira, M.; Kirsimäe, K. Alkali Activation of Estonian Ca-Rich Oil Shale Ashes: A Synthesis. Oil Shale 2019, 36, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usta, M.C.; Yoruk, C.R.; Hain, T.; Paaver, P.; Snellings, R.; Rozov, E.; Gregor, A.; Kuusik, R.; Trikkel, A.; Uibu, M. Evaluation of New Applications of Oil Shale Ashes in Building Materials. Minerals 2020, 10, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bityukova, L.; Mõtlep, R.; Kirsimäe, K. Composition of Oil Shale Ashes from Pulverized Firing and Circulating Flu-idized-Bed Boiler in Narva Thermal Power Plants, Estonia. Oil Shale 2010, 27, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuusik, R.; Uibu, M.; Kirsimäe, K.; Mõtlep, R.; Meriste, T. Open-Air Deposition of Estonian Oil Shale Ash: Formation, State of Art, Problems and Prospects for the Abatement of Environmental Impact. Oil Shale 2012, 29, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, H.F.W. Cement Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Thomas Telford Ltd.: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Liira, M.; Kirsimae, K.; Kuusik, R.; Motlep, R. Transformation of calcareous oil-shale circulating fluidized-bed com-bustion boiler ashes under wet conditions. Fuel 2009, 88, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mõtlep, R.; Kirsimäe, K.; Talviste, P.; Puura, E.; Jürgenson, J. Mineral composition of Estonian oil shale semi-coke sediments. Oil Shale 2007, 24, 405–422. [Google Scholar]
- Sedman, A.; Talviste, P.; Kirsimäe, K. The Study of Hydration and Carbonation Reactions and Corresponding Changes in the Physical Properties of Co-Deposited Oil Shale Ash and Semicoke Wastes in a Small-Scale Field Experi-ment. Oil Shale 2012, 29, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talviste, P.; Sedman, A.; Mõtlep, R.; Kirsimäe, K. Self-cementing properties of oil shale solid heat carrier retorting residue. Waste Manag. Res. 2013, 31, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo, G.; Telesca, A.; Valenti, G.L.; Montagnaro, F. Role of ettringite in the reuse of hydrated fly ash from fluid-ized-bed combustion as a sulfur sorbent: A hydration study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 4054–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, D.; Mingshu, T. Formation and expansion of ettringite crystals. Cem. Concr. Res. 1994, 24, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.K. Effect of Lime on Hydration of Pastes Containing Gypsum and Calcium Aluminates or Calcium Sul-foaluminate. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1973, 56, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.; Bulewicz, E.M.; Dudek, K.; Kozak, A. The long term behaviour of CFBC ash–water systems. Waste Manag. 2002, 22, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.L.; Snellings, R.; Lothenbach, B. A Practical Guide to Microstructural Analysis of Cementitious Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Ye, G. Dehydration kinetics of Portland cement paste at high temperature. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 110, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alarcon-Ruiz, L.; Platret, G.; Massieu, E.; Ehrlacher, A. The use of thermal analysis in assessing the effect of temperature on a cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemczak, B.; Batog, M.; Giergiczny, Z.; Żmij, A. Complex Effect of Concrete Composition on the Thermo-Mechanical Behaviour of Mass Concrete. Materials 2018, 11, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Batog, M.; Giergiczny, Z. Influence of mass concrete constituents on its properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 146, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supit, S.; Shaikh, F.; Sarker, P. Effect of ultrafine fly ash on mechanical properties of high volume fly ash mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 51, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwankwo, C.O.; Bamigboye, G.O.; Davies, I.E.E.; Michaels, T.A. High volume Portland cement replacement: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 120445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, F.U.A.; Supit, S.W.M.; Sarker, P.K. A study on the effect of nano silica on compressive strength of high volume fly ash mortars and concretes. Mater. Des. 2014, 60, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellmann, F.; Stark, J. Activation of blast furnace slag by a new method. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.L.; John, V.M.; Gartner, E.M. Eco-efficient cements: Potential economically viable solutions for a low-CO2 cement-based materials industry. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 114, 2–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giergiczny, Z. Effect of fly ash from different sources on the properties of hardened cement composites. Silic. Ind. 2005, 70, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Marjanović, N.; Komljenovic, M.; Baščarević, Z.; Nikolic, V. Improving reactivity of fly ash and properties of ensuing geopolymers through mechanical activation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 57, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| SiO2 | Al2O3 | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | MnO | CaO | MgO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | SO3 | LOI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FA | 35.1 | 8.5 | 0.4 | 3.9 | 0.1 | 29.9 | 5.1 | 0.1 | 4.3 | 0.1 | 6.8 | 4.9 |
| OPC | 20.6 | 4.9 | 0.2 | 2.1 | 0.1 | 63.4 | 4.0 | 0.2 | 1.7 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 1.7 |
| Sand | 89.6 | 3.6 | 0.05 | 0.5 | 0.04 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 1.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 3.2 |
| Mixture No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| content, wt.% | FA | 100 | 75 | 50 | 25 | 0 | 75 | 50 | 25 | 0 | 50 | 25 | 0 | 25 | 0 |
| OPC | 0 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 0 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 0 | 25 | 50 | 0 | 25 | |
| sand | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 75 | 75 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paaver, P.; Järvik, O.; Kirsimäe, K. Design of High Volume CFBC Fly Ash Based Calcium Sulphoaluminate Type Binder in Mixtures with Ordinary Portland Cement. Materials 2021, 14, 5798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195798
Paaver P, Järvik O, Kirsimäe K. Design of High Volume CFBC Fly Ash Based Calcium Sulphoaluminate Type Binder in Mixtures with Ordinary Portland Cement. Materials. 2021; 14(19):5798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195798
Chicago/Turabian StylePaaver, Peeter, Oliver Järvik, and Kalle Kirsimäe. 2021. "Design of High Volume CFBC Fly Ash Based Calcium Sulphoaluminate Type Binder in Mixtures with Ordinary Portland Cement" Materials 14, no. 19: 5798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195798
APA StylePaaver, P., Järvik, O., & Kirsimäe, K. (2021). Design of High Volume CFBC Fly Ash Based Calcium Sulphoaluminate Type Binder in Mixtures with Ordinary Portland Cement. Materials, 14(19), 5798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195798





