Pyridine Derivatives—A New Class of Compounds That Are Toxic to E. coli K12, R2–R4 Strains
Abstract
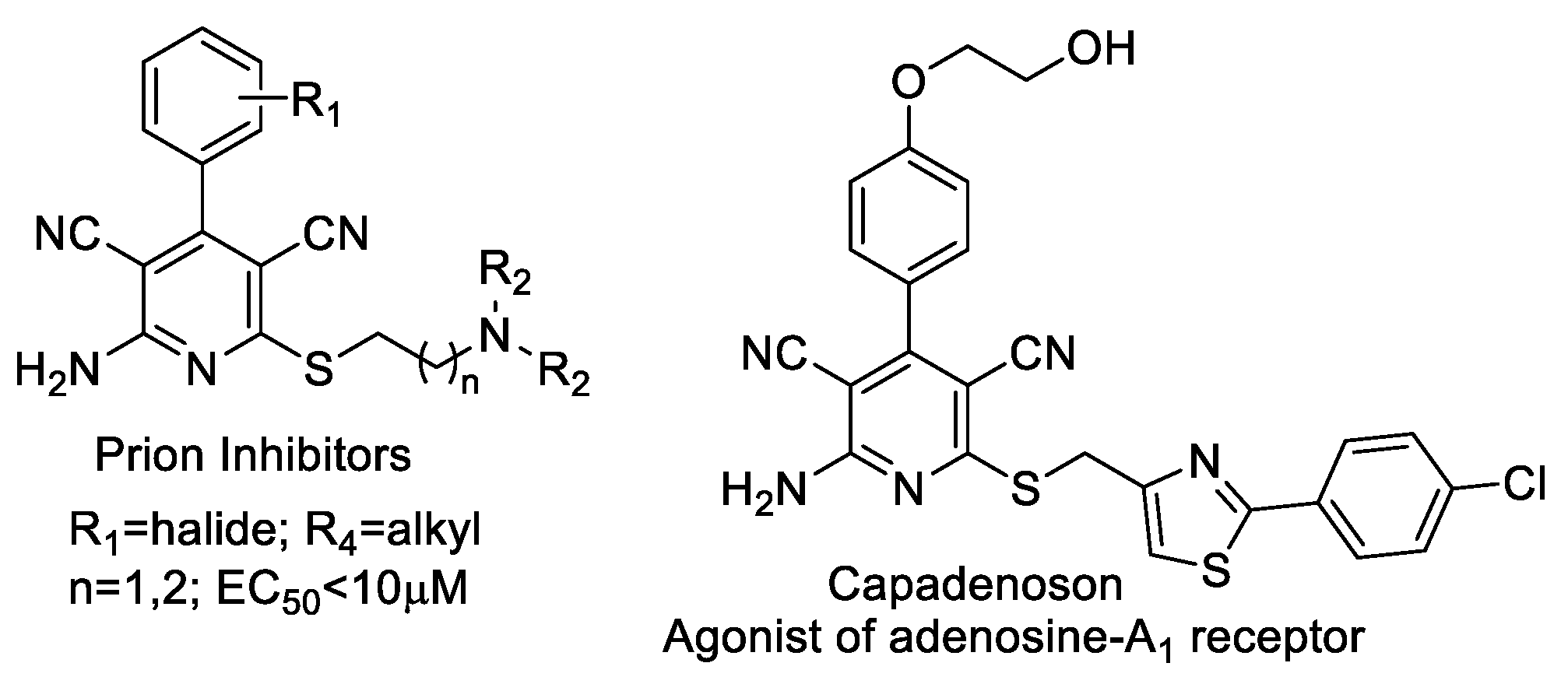
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
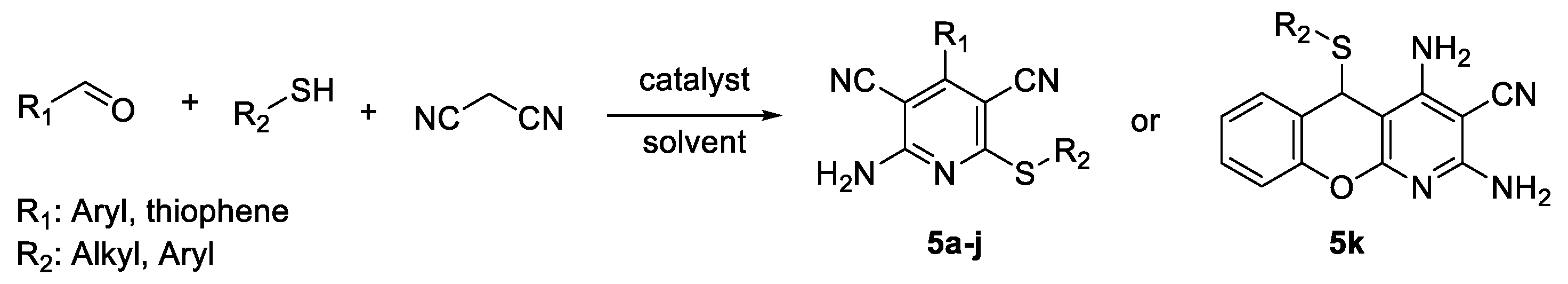
2.1. General Methods of Synthesis Pyridine Derivatives
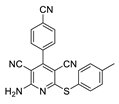
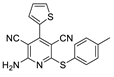
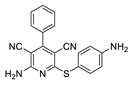
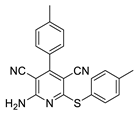
2.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 2-Amino-4-aryl-3,5-dicyano-6-phenyl Thiopyridines (5a–k)


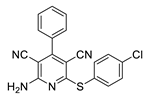


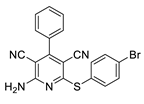
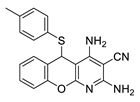
2.3. Microorganisms and Media
3. Results
3.1. Chemistry
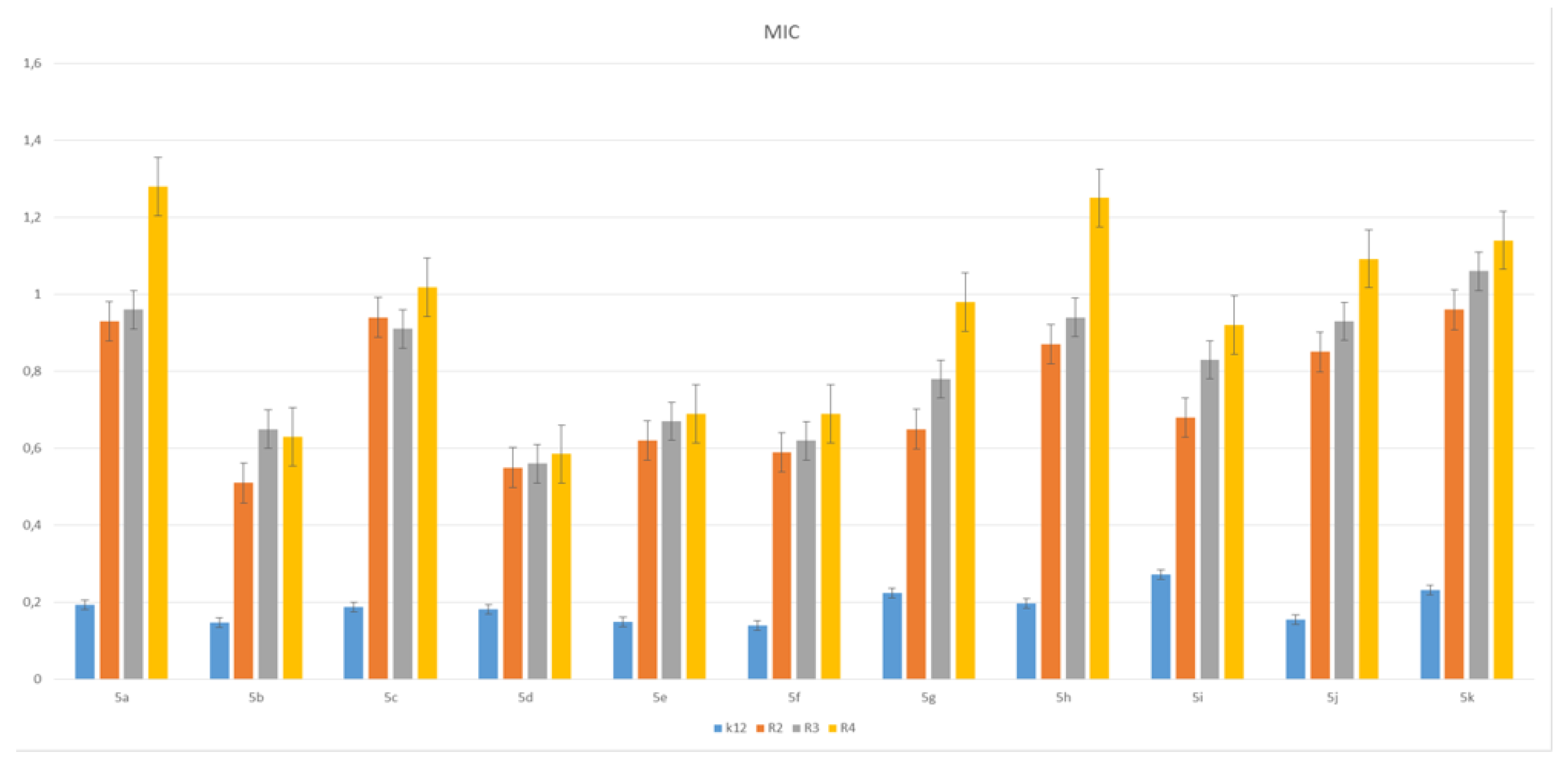
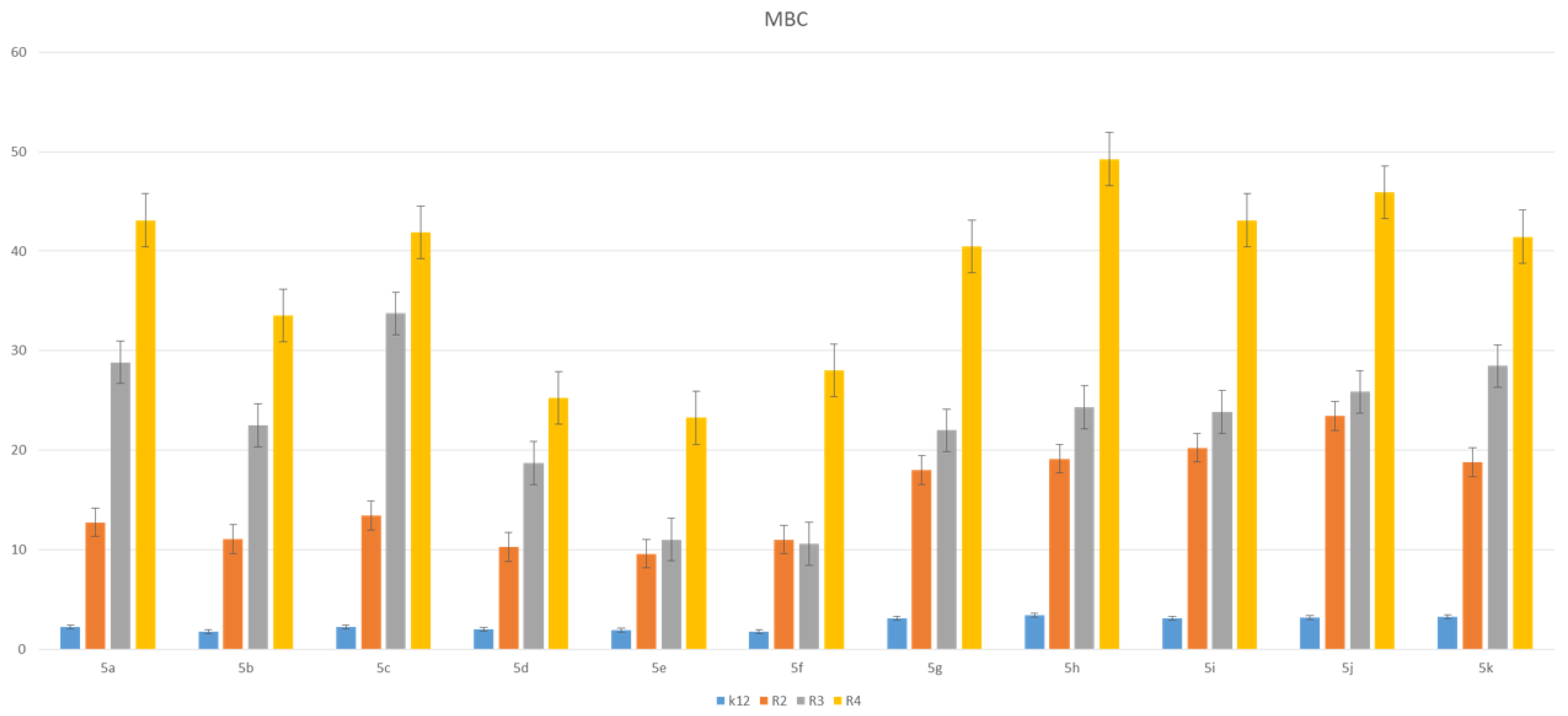
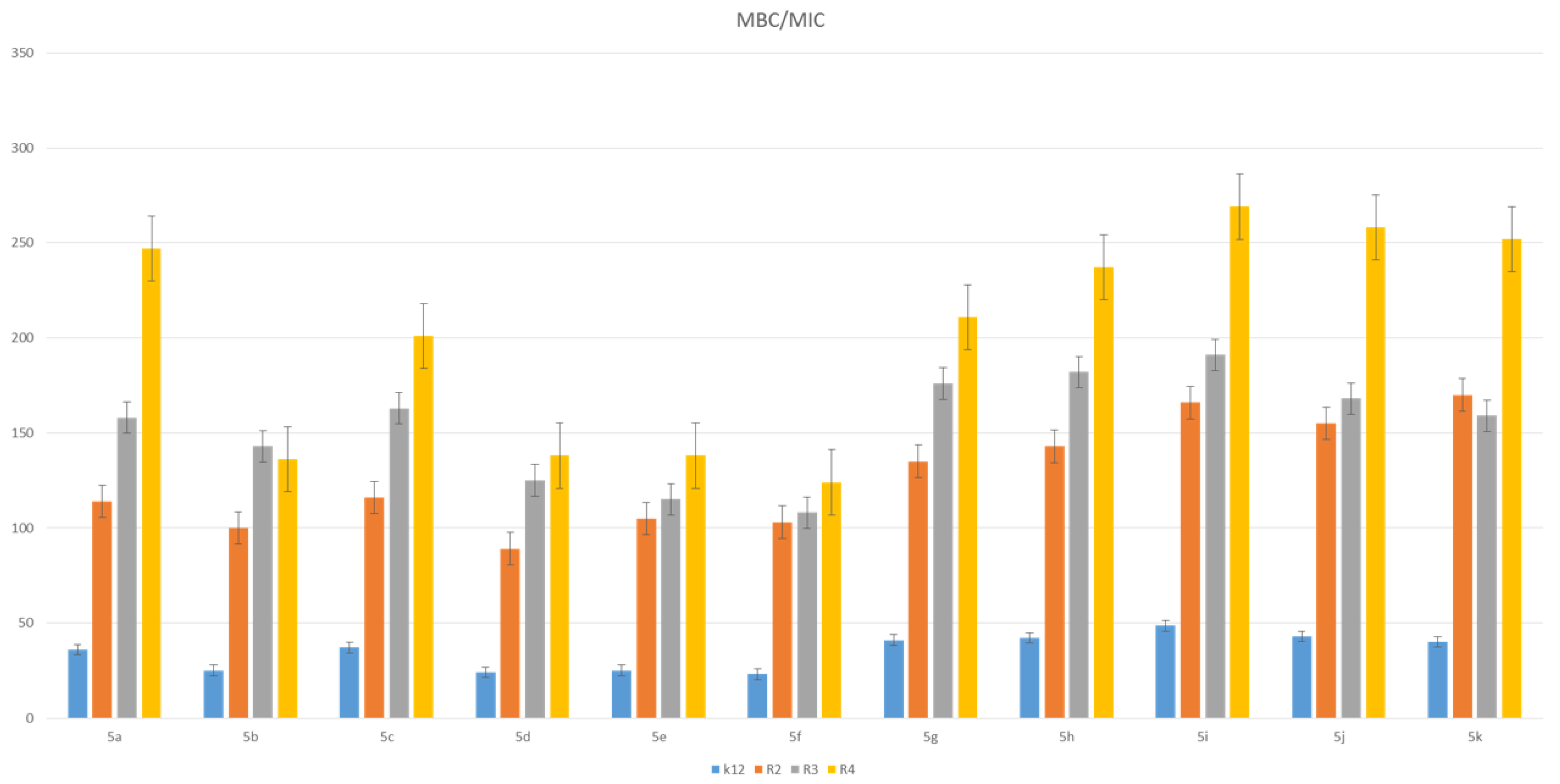
3.2. Toxicity of Piryidine Derivatives
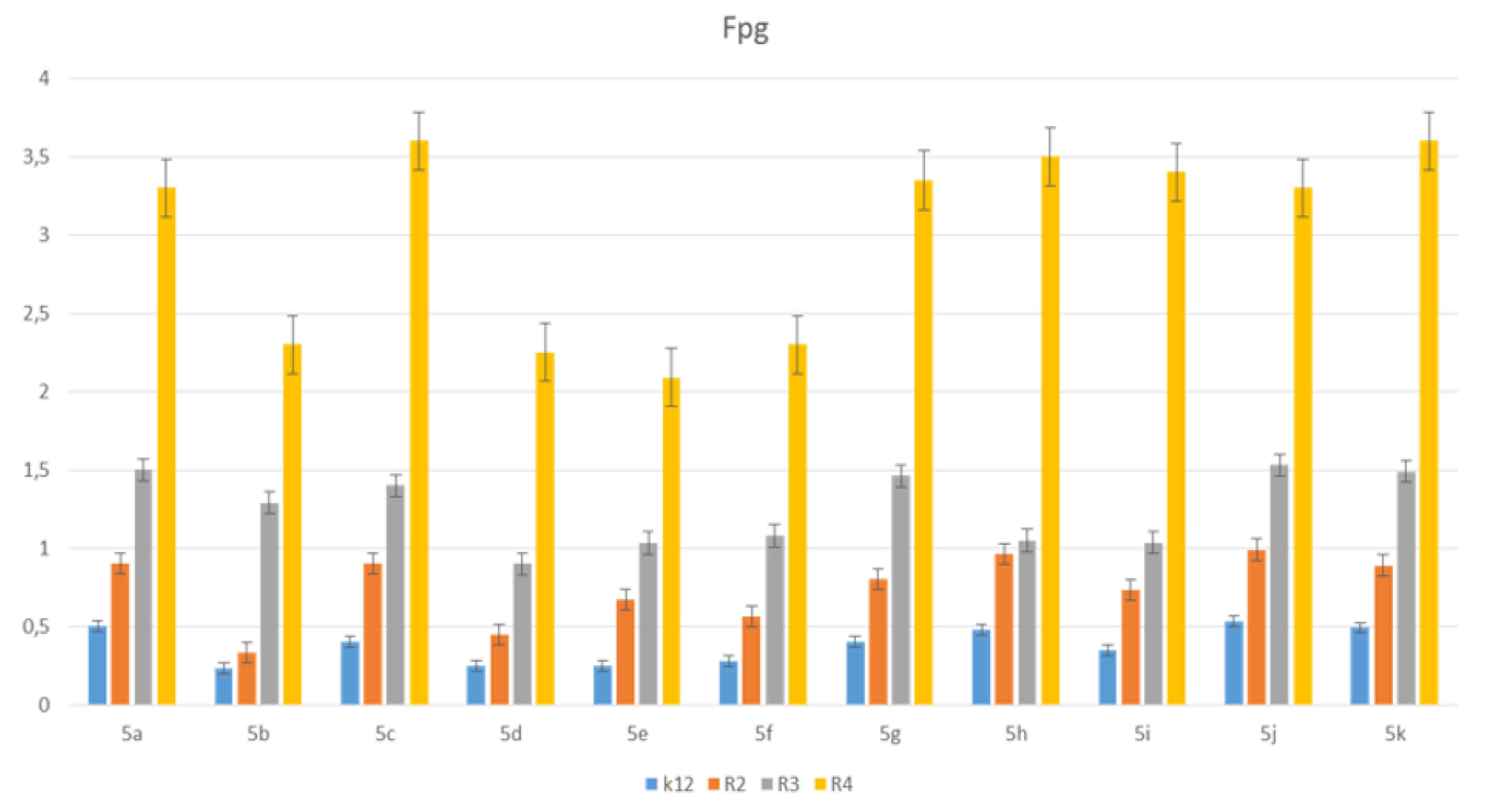
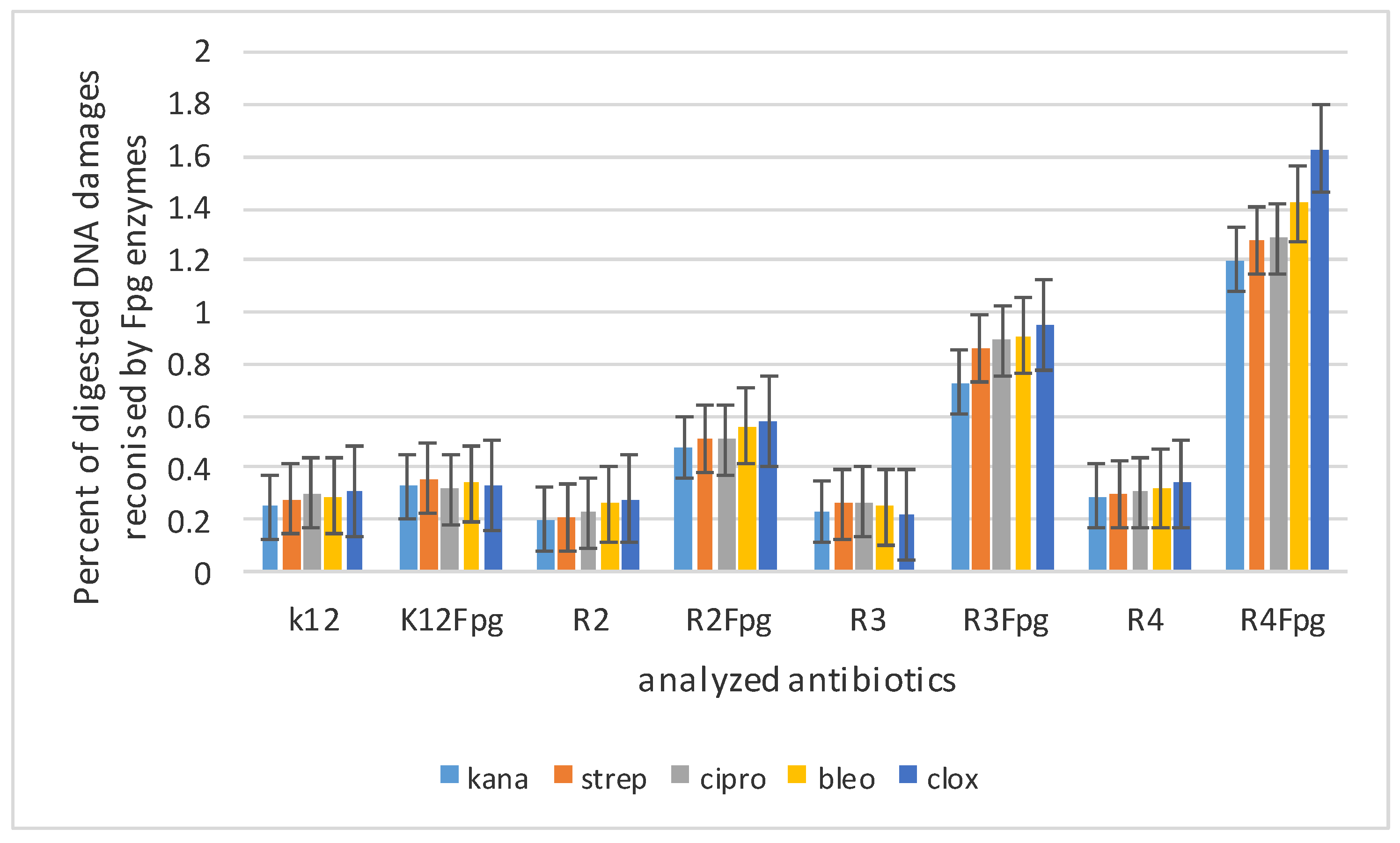
3.3. Modification of Plasmid DNA Isolated from E. coli R2–R4 Strains with Tested Pirydine Derivatives
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- May, B.C.H.; Zorn, J.A.; Witkop, J.; Sherrill, J.; Wallace, A.C.; Legname, G.; Prusiner, S.B.; Cohen, F.E. Structure−Activity Relationship Study of Prion Inhibition by 2-Aminopyridine-3,5-dicarbonitrile-Based Compounds: Parallel Synthesis, Bioactivity, and in Vitro Pharmacokinetics. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrier, V.; Wallace, A.C.; Kaneko, K.; Safar, J.; Prusiner, S.B.; Cohen, F.E. Mimicking Dominant Negative Inhibition of Prion Replication through Structure-Based Drug Design. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6073–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meibom, D.; Albrecht-Küpper, B.; Diedrichs, N.; Hübsch, W.; Kast, R.; Krämer, T.; Krenz, U.; Lerchen, H.-G.; Mittendorf, J.; Nell, P.G.; et al. Neladenoson Bialanate Hydrochloride: A Prodrug of a Partial Adenosine A1Receptor Agonist for the Chronic Treatment of Heart Diseases. Chem. Med. Chem. 2017, 12, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beukers, M.W.; Chang, L.C.W.; Künzel, J.K.V.F.D.; Mulder-Krieger, T.; Spanjersberg, R.F.; Brussee, A.J.; Ijzerman, A.P. New, Non-Adenosine, High-Potency Agonists for the Human Adenosine A2BReceptor with an Improved Selectivity Profile Compared to the Reference AgonistN-Ethylcarboxamidoadenosine. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 3707–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadilla, R.; Turnbull, P. Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators in Drug Discovery: Medicinal Chemistry and Therapeutic Potential. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2006, 6, 245–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, G. A review of non-nucleoside anti-hepatitis B virus agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 75, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, T.R.K.; Mutter, R.; Heal, W.; Guo, K.; Gillet, V.J.; Pratt, S.; Chen, B. Library Design, Synthesis, and Screening: Pyridine Dicarbonitriles as Potential Prion Disease Therapeutics. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Mutter, R.; Heal, W.; Reddy, T.R.; Cope, H.; Pratt, S.; Thompson, M.J.; Chen, B. Synthesis and evaluation of a focused library of pyridine dicarbonitriles against prion disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhu, L.; Yao, D.; Chen, L.; Fu, L.; Ouyang, L. Recent progress in potential anti-hepatitis B virus agents: Structural and pharmacological perspectives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 147, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamaghani, M.; Tabatabaeian, K.; Bayat, M.; Nia, R.H.; Rassa, M. Regioselective Synthesis and Antibacterial Evaluation of a New Class of Substituted Pyrazolo[3,4-b] Pyridines. J. Chem. Res. 2013, 37, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.R.; Hegde, S.; Reinhard, E.; Gomez, L.; Vernier, W.F.; Lee, L.; Liu, S.; Sambandam, A.; Snider, P.A.; Masih, L. Aminocyanopyridine inhibitors of mitogen activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 (MK-2). Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Qiu, Y.; Li, X.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Woods, M.; Kraft, P.; Lundeen, S.G.; Sui, Z. Discovery and structure–activity relationships of a novel series of benzopyran-based KATP openers for urge urinary incontinence. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, A.; Marco-Contelles, J.; Soriano, E.; Álvarez-Pérez, M.; Chioua, M.; Romero, A.; González-Lafuente, L.; Gandía, L.; Roda, J.M.; López, M.G.; et al. Multipotent drugs with cholinergic and neuroprotective properties for the treatment of Alzheimer and neuronal vascular diseases. I. Synthesis, biological assessment, and molecular modeling of simple and readily available 2-aminopyridine-, and 2-chloropyridine-3,5-dicarbonitriles. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 5861–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evdokimov, N.M.; Kireev, A.S.; Yakovenko, A.A.; Antipin, M.Y.; Magedov, I.V.; Kornienko, A. One-Step Synthesis of Heterocyclic Privileged Medicinal Scaffolds by a Multicomponent Reaction of Malononitrile with Aldehydes and Thiols. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 3443–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantam, M.L.; Mahendar, K.; Bhargava, S.K. One-pot, three-component synthesis of highly substituted pyridines and 1,4-dihydropyridines by using nanocrystalline magnesium oxide. J. Chem. Sci. 2010, 122, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.N.S.A.S.K.; Singh, S.K. Microwave-assisted, one-pot multicomponent synthesis of highly substituted pyridines of medicinal utility using KF/alumina. ARKIVOC 2009, 2009, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamgain, R.; Singh, R.; Rawat, D.S. DBU-catalyzed three-component one-pot synthesis of highly functionalized pyridines in aqueous ethanol. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2009, 46, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Choudhury, L.H.; Pal, S.; Parvin, T. A simple and efficient method for the facile access of highly functionalized pyridines and their fluorescence property studies. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 12305–12314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, P.V.; Shingate, B.B.; Shingare, M.S. Aqueous Suspension of Basic Alumina: An Efficient Catalytic System for the Synthesis of Poly Functionalized Pyridines. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, 32, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koszelewski, D.; Brodzka, A.; Madej, A.; Trzepizur, D.; Ostaszewski, R. Evaluation of gem-Diacetates as Alternative Reagents for Enzymatic Regio- and Stereoselective Acylation of Alcohols. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 6331–6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madej, A.; Koszelewski, D.; Paprocki, D.; Brodzka, A.; Ostaszewski, R. The amine as carbonyl precursor in the chemoenzymatic synthesis of Passerini adducts in aqueous medium. Catal. Commun. 2020, 145, 106118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paprocki, D.; Koszelewski, D.; Madej, A.; Brodzka, A.; Walde, P.; Ostaszewski, R. Evaluation of Biodegradable Glucose Based Surfactants as a Promoting Medium for the Synthesis of Peptidomimetics with the Coumarin Scaffold. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 9607–9614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paprocki, D.; Madej, A.; Koszelewski, D.; Brodzka, A.; Ostaszewski, R. Multicomponent Reactions Accelerated by Aqueous Micelles. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, A.S.; Kharat, A.S.; Bhosle, M.R.; Mane, R.A. A convenient Baker yeast accelerated, one-pot synthesis of pentasubstituted thiopyridines. Synth. Commun. 2017, 47, 1777–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kęciek, A.; Paprocki, D.; Koszelewski, D.; Ostaszewski, R. Evaluation of alcohols as substrates for the synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones under environmentally friendly conditions. Catal. Commun. 2020, 135, 105887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaorska, E.; Gawryś-Kopczyńska, M.; Ostaszewski, R.; Ufnal, M.; Koszelewski, D. Evaluation of thionolactones as a new type of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) donors for a blood pressure regulation. Bioorganic Chem. 2021, 108, 104650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truppo, M.D. Biocatalysis in the Pharmaceutical Industry: The Need for Speed. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedee, B.P.; Soni, S.; Sharma, M.; Bhaumik, J.; Laha, J.K.; Banerjee, U.C. Promiscuity of Lipase-Catalyzed Reactions for Organic Synthesis: A Recent Update. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 2441–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koszelewski, D.; Ostaszewski, R. Biocatalytic Promiscuity of Lipases in Carbon-Phosphorus Bond Formation. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 2554–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koszelewski, D.; Ostaszewski, R. Enzyme Promiscuity as a Remedy for the Common Problems with Knoevenagel Condensation. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2019, 25, 10156–10164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, D.C.M.; Gaggero, N. Albumin as a promiscuous biocatalyst in organic synthesis. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 10588–10598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei-Ghomi, J.; Ghasemzadeh, M.A. CuI nanoparticles: A highly active and easily recyclable catalyst for the synthesis of 2-amino-3,5-dicyano-6-sulfanyl pyridines. J. Sulfur Chem. 2012, 34, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Ghosh, R. K2CO3-Mediated, One-Pot, Multicomponent Synthesis of Medicinally Potent Pyridine and Chromeno[2,3-b]pyridine Scaffolds. Synth. Commun. 2012, 42, 2229–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottawar, S.S.; Siddiqui, S.A.; Bhusare, S.R. Scandium triflate-catalyzed one-pot multi-component synthesis of 2-amino-6-thiopyridine-3,5-dicarbonitriles. Heterocycl. Commun. 2012, 18, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei-Ghomi, J.; Shahbazi-Alavi, H.; Heidari-Baghbahadorani, E. SnO nanoparticles as an efficient catalyst for the one-pot synthesis of chromeno[2,3-b]pyridines and 2-amino-3,5-dicyano-6-sulfanyl pyridines. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 50668–50677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimmaiah, M.; Li, P.; Regati, S.; Chen, B.; Zhao, J.C.-G. Multi-component synthesis of 2-amino-6-(alkylthio)pyridine-3,5-dicarbonitriles using Zn(II) and Cd(II) metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) under solvent-free conditions. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 4870–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allahi, A.; Akhlaghinia, B. WEB (water extract of banana): An efficient natural base for one-pot multi-component synthesis of 2-amino-3,5-dicarbonitrile-6-thio-pyridines. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elements 2020, 196, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, F.; Mohammadpoor-Baltork, I.; Khosropour, A.R.; Moghadam, M.; Tangestaninejad, S.; Mirkhani, V. Propylphosphonium hydrogen carbonate ionic liquid supported on nano-silica as a reusable catalyst for the efficient multicomponent synthesis of fully substituted pyridines and bis-pyridines. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 39978–39991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei-Ghomi, J.; Tavazo, M.; Vakili, M.R.; Shahbazi-Alavi, H. Chitosan functionalized by citric acid: An efficient catalyst for one-pot synthesis of 2,4-diamino-5H-[1]benzopyrano[2,3-b]pyridine-3-carbonitriles 5-(arylthio) or 5-[(arylmethyl)thio] substituted. J. Sulfur Chem. 2017, 38, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, P.; Madej, A.; Paprocki, D.; Szymczak, M.; Ostaszewski, R. Coumarin Derivatives as New Toxic Compounds to Selected K12, R1–R4 E. coli Strains. Materials 2020, 13, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, P.; Trzepizur, D.; Szymczak, M.; Skiba, G.; Kramkowski, K.; Ostaszewski, R. 1,2-Diarylethanols—A New Class of Compounds That Are Toxic to E. coli K12, R2–R4 Strains. Materials 2021, 14, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczyk, P.; Madej, A.; Szymczak, M.; Ostaszewski, R. α-Amidoamids as New Replacements of Antibiotics—Research on the Chosen K12, R2–R4 E. coli Strains. Materials 2020, 13, 5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, P.; Borkowski, A.; Czerwonka, G.; Cłapa, T.; Cieśla, J.; Misiewicz, A.; Borowiec, M.; Szala, M. The microbial toxicity of quaternary ammonium ionic liquids is dependent on the type of lipopolysaccharide. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 266, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkowski, A.; Kowalczyk, P.; Czerwonka, G.; Cieśla, J.; Cłapa, T.; Misiewicz, A.; Szala, M.; Drabik, M. Interaction of quaternary ammonium ionic liquids with bacterial membranes–Studies with Escherichia coli R1–R4-type lipopolysaccharides. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 246, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, P.; Gawdzik, B.; Trzepizur, D.; Szymczak, M.; Skiba, G.; Raj, S.; Kramkowski, K.; Lizut, R.; Ostaszewski, R. δ-Lactones—A New Class of Compounds That Are Toxic to E. coli K12 and R2–R4 Strains. Materials 2021, 14, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, K.; Heinrichs, D.E.; Frirdich, E.; Ziebell, K.; Johnson, R.P.; Whitfield, C. Distribution of Core Oligosaccharide Types in Lipopolysaccharides from Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, A.; Kaszowska, M.; Jachymek, W.; Lugowski, C.; Lukasiewicz, J. Lipopolysaccharide-linked Enterobacterial Common Antigen (ECALPS) Occurs in Rough Strains of Escherichia coli R1, R2, and R4. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prost, M.E.; Prost, R. Basic parameters of evaluation of the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy. OphthaTherapy 2017, 4, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, R.S.; Silva, F.L.; Silva, J.F.; Morais, P.B.; Braga, D.T.; Rosa, C.A.; Corrêa, A., Jr. Biological control of Penicillium italicum, P. digitatum and P. expansum by the predacious yeast Saccharomycopsis schoenii on oranges. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2008, 39, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wink, D.A.; Laval, J. The Fpg protein, a DNA repair enzyme, is inhibited by the biomediator nitric oxide in vitro and in vivo. Carcinogenesis 1994, 15, 2125–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, P.; Jantzen, K.; Løhr, M.; Andersen, M.H.G.; Jensen, D.M.; Roursgaard, M.; Danielsen, P.H.; Jensen, A.; Loft, S. Searching for assay controls for the Fpg- and hOGG1-modified comet assay. Mutagenesis 2017, 33, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, W.; Tong, C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhou, H.; Wang, W. A cascade amplification platform assisted with DNAzyme for activity analysis, kinetic study and effector screening of Fpg in vitro. Analyst 2019, 144, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoci, V.; Cucu, D.; Zbancioc, G.; Moldoveanu, C.; Mangalagiu, V.; Amariucai-Mantu, D.; Aricu, A.; Mangalagiu, V. Bis-(imidazole/benzimidazole)-pyridine derivatives: Synthesis, structure and antimycobacterial activity. Futur. Med. Chem. 2020, 12, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eryılmaz, S.; Çelikoğlu, E.T.; Idil, Ö.; Inkaya, E.; Kozak, Z.; Mısır, E.; Gül, M. Derivatives of pyridine and thiazole hybrid: Synthesis, DFT, biological evaluation via antimicrobial and DNA cleavage activity. Bioorganic Chem. 2019, 95, 103476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Dong, Y.; Lei, K.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, M. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of amide-pyridine derivatives as novel dual-target (SE, CYP51) antifungal inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 2427–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Entry | Catalyst | T (°C) | Solvent | Yield [%] e |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | None | 40 | cyclohexane | 4 |
| 2 | Porcine pancreas lipase (PPL) | 40 | cyclohexane | 31 |
| 3 | Porcine pancreas lipase (PPL) | 40 | H2O | 49 |
| 4 | Porcine pancreas lipase (PPL) | 40 | EtOH | 83 |
| 5 | Porcine pancreas lipase (PPL) | 40 | MeCN | 52 |
| 6 | Porcine pancreas lipase (PPL) | 40 | DMF | 24 |
| 7 | Porcine pancreas lipase (PPL) | 40 | DMSO | 33 |
| 8 | Porcine pancreas lipase (PPL) | 50 | EtOH | 75 |
| 9 | Porcine pancreas lipase (PPL) b | 40 | EtOH | 80 |
| 10 | Pseudomonas fluorescens lipase (PFL) | 40 | cyclohexane | 11 |
| 11 | Candida rugosa lipase (CRL) | 40 | cyclohexane | 16 |
| 12 | Candida cylindracea lipase (CCL) | 40 | cyclohexane | 18 |
| 13 | Novozym 435 | 40 | cyclohexane | 4 |
| 14 | Bovine serum albumin (BSA) | 40 | cyclohexane | 8 |
| 15 | Pig liver acetone powder (PLAP) c | 40 | cyclohexane | 14 |
| 16 | Denatured PPL d | 40 | cyclohexane | 6 |
| Entry | Compound | R1 | R2 | Yield [%] b | Mp (°C) c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5a | 4-CNC6H4 | 4-MeC6H4 | 83 | 275 |
| 2 | 5b | thiophene | 4-MeC6H4 | 78 | 197 |
| 3 | 5c | Ph | 4-NH2C6H4 | 53 | 223 |
| 4 | 5d | Ph | 4-MeC6H4 | 89 | 249 |
| 5 | 5e | Ph | n-C6H13 | 76 | 148 |
| 6 | 5f | 4-MeC6H4 | 4-MeC6H4 | 91 | 223–224 |
| 7 | 5g | Ph | 4-ClC6H4 | 89 | 247 |
| 8 | 5h | 4-MeOC6H4 | 4-MeC6H4 | 82 | 230–231 |
| 9 | 5i | 4-NO2C6H4 | 4-MeC6H4 | 88 | 298 |
| 10 | 5j | Ph | 4-BrC6H4 | 74 | 255–257 |
| 11 | 5k | 2-OHC6H4 | 4-MeC6H4 | 79 | 224 |
| No of Samples | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | Type of Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K12 | *** | * | ** | * | * | * | ** | *** | * | ** | ** | MIC |
| R2 | *** | * | ** | * | * | * | ** | *** | * | *** | ** | MIC |
| R3 | *** | * | ** | * | * | * | ** | *** | * | ** | ** | MIC |
| R4 | *** | * | ** | * | * | * | ** | *** | * | ** | ** | MIC |
| K12 | *** | * | ** | * | * | * | ** | ** | * | ** | *** | MBC |
| R2 | ** | * | ** | * | * | * | ** | ** | * | ** | *** | MBC |
| R3 | ** | * | ** | * | * | * | ** | ** | * | ** | *** | MBC |
| R4 | ** | * | ** | * | * | * | ** | ** | * | ** | *** | MBC |
| K12 | * | * | ** | * | * | * | * | * | * | ** | * | MBC/MIC |
| R2 | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | ** | * | MBC/MIC |
| R3 | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | ** | * | MBC/MIC |
| R4 | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | ** | * | MBC/MIC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koszelewski, D.; Ostaszewski, R.; Śmigielski, P.; Hrunyk, A.; Kramkowski, K.; Laskowski, Ł.; Laskowska, M.; Lizut, R.; Szymczak, M.; Michalski, J.; et al. Pyridine Derivatives—A New Class of Compounds That Are Toxic to E. coli K12, R2–R4 Strains. Materials 2021, 14, 5401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185401
Koszelewski D, Ostaszewski R, Śmigielski P, Hrunyk A, Kramkowski K, Laskowski Ł, Laskowska M, Lizut R, Szymczak M, Michalski J, et al. Pyridine Derivatives—A New Class of Compounds That Are Toxic to E. coli K12, R2–R4 Strains. Materials. 2021; 14(18):5401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185401
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoszelewski, Dominik, Ryszard Ostaszewski, Paweł Śmigielski, Anastasiia Hrunyk, Karol Kramkowski, Łukasz Laskowski, Magdalena Laskowska, Rafał Lizut, Mateusz Szymczak, Jacek Michalski, and et al. 2021. "Pyridine Derivatives—A New Class of Compounds That Are Toxic to E. coli K12, R2–R4 Strains" Materials 14, no. 18: 5401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185401
APA StyleKoszelewski, D., Ostaszewski, R., Śmigielski, P., Hrunyk, A., Kramkowski, K., Laskowski, Ł., Laskowska, M., Lizut, R., Szymczak, M., Michalski, J., Gawin, K., & Kowalczyk, P. (2021). Pyridine Derivatives—A New Class of Compounds That Are Toxic to E. coli K12, R2–R4 Strains. Materials, 14(18), 5401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185401








